化工学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 76 ›› Issue (10): 5475-5485.DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20250131
宋一博1( ), 杨顺宽1, 罗丽芬2, 潘发伍2, 高媛媛2, 李逸鑫1, 詹国武1(
), 杨顺宽1, 罗丽芬2, 潘发伍2, 高媛媛2, 李逸鑫1, 詹国武1( )
)
收稿日期:2025-02-13
修回日期:2025-05-10
出版日期:2025-10-25
发布日期:2025-11-25
通讯作者:
詹国武
作者简介:宋一博(1998—),女,博士研究生,1021792263@qq.com
基金资助:
Yibo SONG1( ), Shunkuan YANG1, Lifen LUO2, Fawu PAN2, Yuanyuan GAO2, Yixin LI1, Guowu ZHAN1(
), Shunkuan YANG1, Lifen LUO2, Fawu PAN2, Yuanyuan GAO2, Yixin LI1, Guowu ZHAN1( )
)
Received:2025-02-13
Revised:2025-05-10
Online:2025-10-25
Published:2025-11-25
Contact:
Guowu ZHAN
摘要:
生物质衍生的碳量子点(carbon quantum dots, CDs)具有优异的生物相容性和可再生特性,目前的合成方法具有步骤烦琐、经济性较低的缺点,不利于CDs的规模化生产。通过高温碳化和超声分散分离工艺,简便快速合成水仙基碳量子点(Nar-CDs)。以水仙球茎作为生物质前体材料,其20 L体系产率最高可达16.4%。通过紫外-可见光谱、荧光光谱、透射电子显微镜(TEM)等表征,证实纳米尺度的Nar-CDs成功制备。X射线衍射(XRD)和傅里叶变换红外光谱(FTIR)表明其因带有含氧官能团而具有水溶性,KMnO4和DPPH法实验的结果显示,Nar-CDs具有较强的还原能力和自由基清除能力。此外,通过细胞毒性测试和溶血试验验证Nar-CDs的优良生物相容性,对人脐静脉内皮细胞(HUVEC)几乎无毒性,并且没有引起明显的溶血作用。这些性能研究证明了Nar-CDs潜在的商业应用价值,为生物基CDs的进一步工业化生产和应用提供理论基础。
中图分类号:
宋一博, 杨顺宽, 罗丽芬, 潘发伍, 高媛媛, 李逸鑫, 詹国武. 规模化制备水仙基生物相容抗氧化碳量子点[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(10): 5475-5485.
Yibo SONG, Shunkuan YANG, Lifen LUO, Fawu PAN, Yuanyuan GAO, Yixin LI, Guowu ZHAN. Industrialization-scale synthesis of Narcissus-based carbon quantum dots with biocompatibility and antioxidant properties[J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(10): 5475-5485.
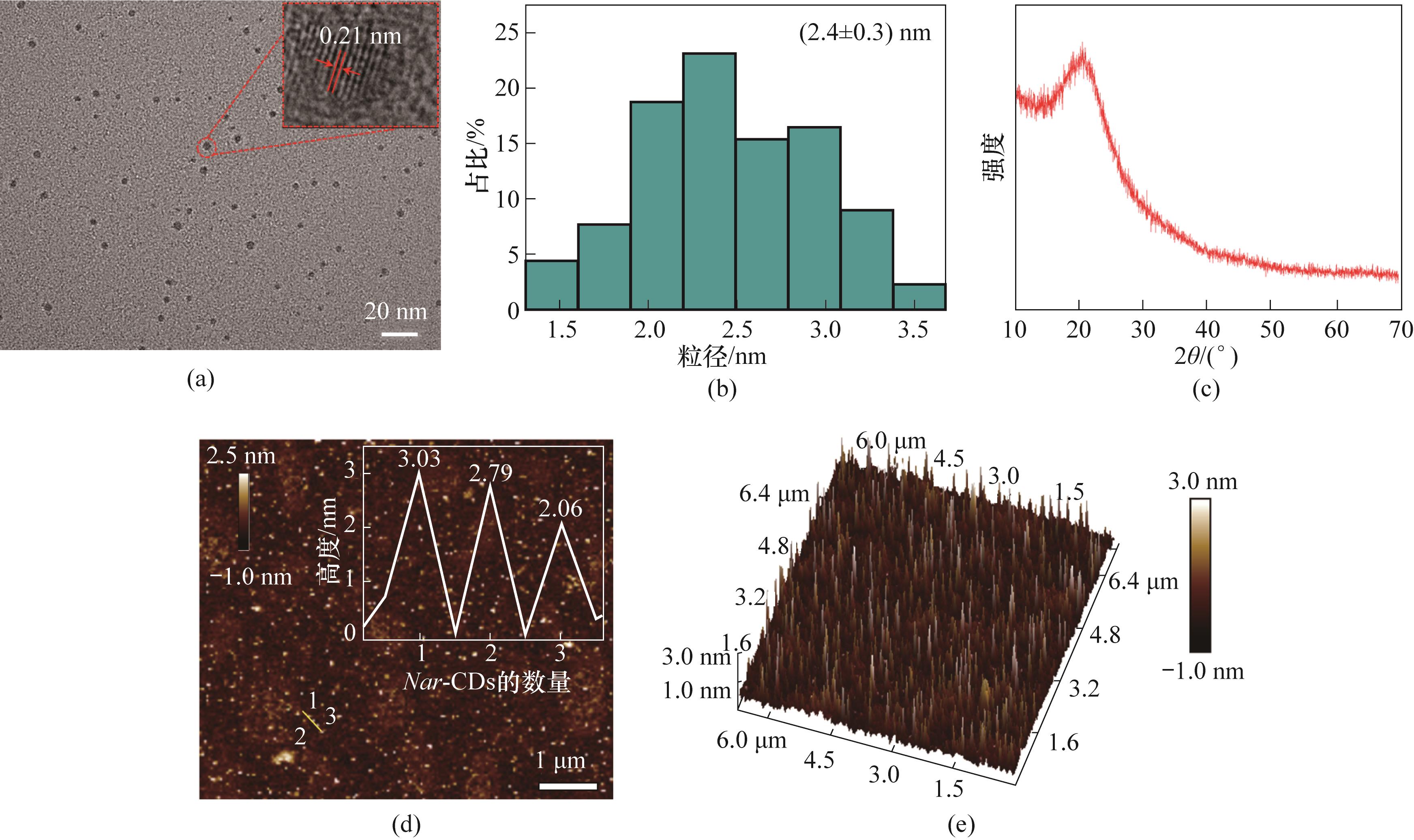
图2 Nar-CDs的(a)透射电镜图(插图为相应的HRTEM图像),(b)粒径分布,(c)X射线衍射谱图,(d)AFM图像和厚度分布和(e)三维AFM图像
Fig.2 (a) TEM image (the inset shows the corresponding HRTEM image), (b) particle size distribution, (c) XRD spectrum, (d) AFM image and thickness distribution of Nar-CDs and (e) 3D AFM image of Nar-CDs
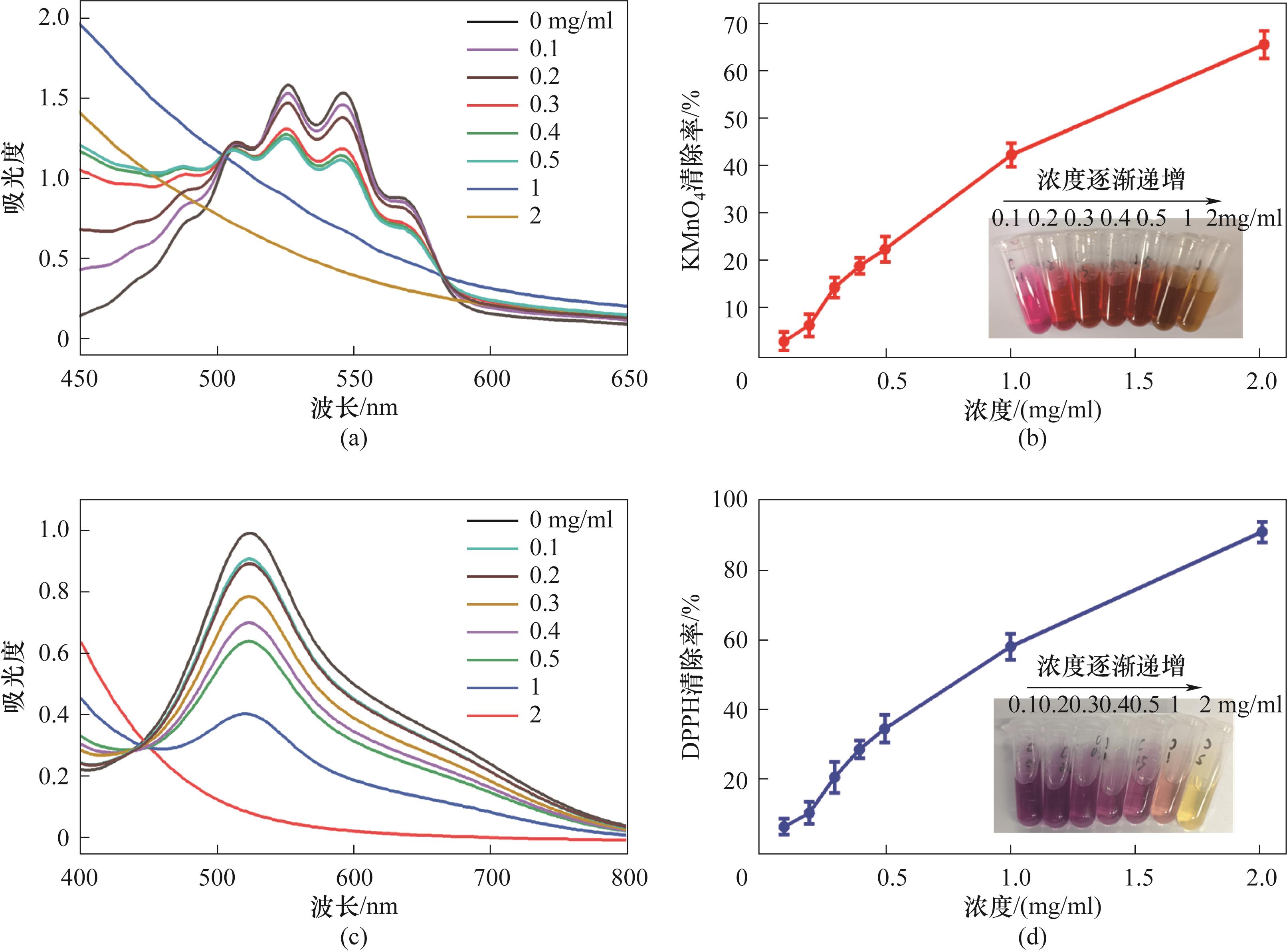
图5 KMnO4检测Nar-CDs(0~2 mg/ml)抗氧化性能:(a)紫外光谱,(b)KMnO4清除率(插图为反应后的样品图像);DPPH法检测Nar-CDs(0~2 mg/ml)抗氧化性能:(c)紫外光谱,(d)DPPH清除率(插图为反应后的样品图像)
Fig.5 Detection of antioxidant properties of Nar-CDs (0—2 mg/ml) by KMnO4 and DPPH: (a) UV-Vis absorption spectrum and (b) scavenging activity of KMnO4 (the illustration shows the image of the samples after the reaction); (c) UV-Vis absorption spectrum and (d) scavenging ability of DPPH (the illustration shows the image of the samples after the reaction)
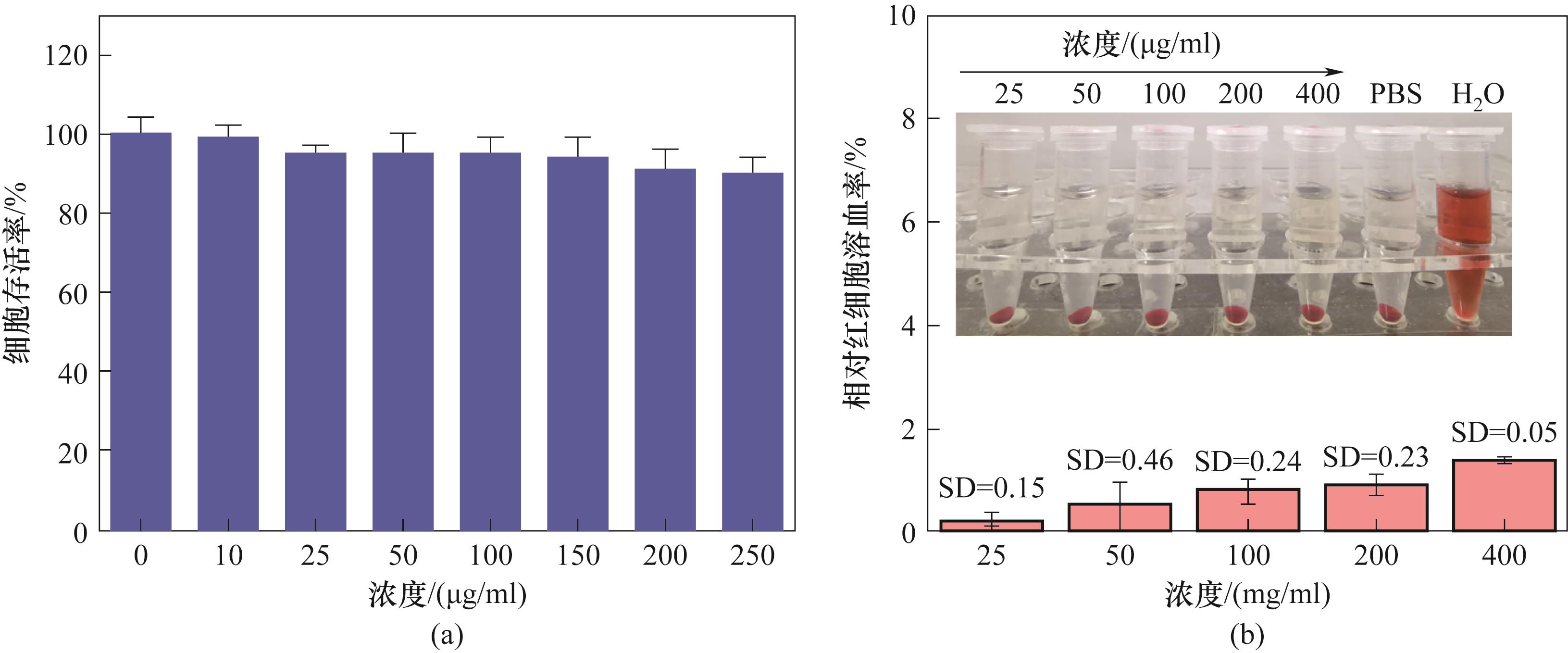
图6 (a)Nar-CDs对HUVEC细胞的细胞毒性;(b)小鼠红细胞经H2O(阳性对照)、PBS(阴性对照)和不同浓度的Nar-CDs溶液在37.0°C下处理2 h后的溶血率(插图为离心后的相应红细胞样品,SD值为标准差)
Fig.6 (a) The cytotoxicity of Nar-CDs on HUVEC cells; (b) the hemolysis rate of mouse red blood cells after being treated at 37.0°C for 2 h with H2O (positive control), PBS (negative control), and different concentrations of Nar-CDs solution (inset shows the corresponding centrifuged red blood cell samples, with SD representing the standard deviation)
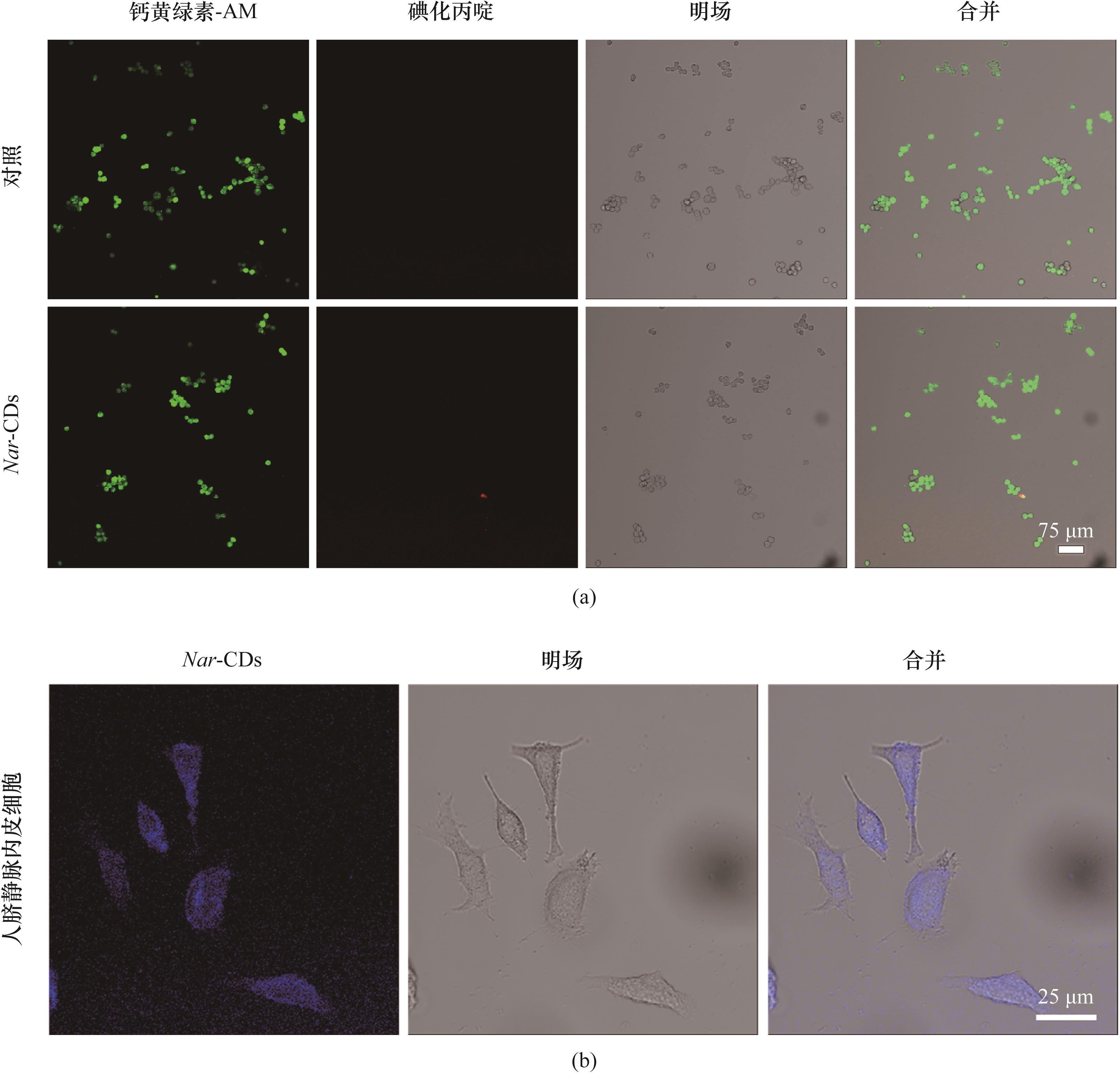
图7 (a)Nar-CDs处理后HUVEC细胞的活/死染色激光共聚焦图像;(b)HUVEC细胞孵育Nar-CDs后的激光共聚焦图像
Fig.7 (a) CLSM images of HUVEC cells stained with Calcein-AM and PI; (b) CLSM images of HUVEC cells incubated with Nar-CDs
| 序号 | 碳源 | 合成方法 | 合成条件 | CDs应用 | 合成产率/% | 文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 橙汁 | 水热处理 | 120℃,2.5 h | 生物成像 | <1 | [ |
| 2 | 鸡蛋 | 高温热解 | 250℃,2 h | 荧光印刷材料 | 5.9 | [ |
| 3 | 壳聚糖 | 水热处理 | 180℃,12 h | 生物成像 | 7.8 | [ |
| 4 | 咖啡 | 高温煅烧 | 300℃,2 h | 生物成像 | 12 | [ |
| 5 | 水仙球茎 | 高温煅烧 | 200℃,2 h | 抗氧化,细胞成像 | 16.4 | 本工作 |
表1 不同生物质碳源制备CDs的产率比较
Table 1 Comparison of yields of CDs prepared from different biomass carbon sources
| 序号 | 碳源 | 合成方法 | 合成条件 | CDs应用 | 合成产率/% | 文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 橙汁 | 水热处理 | 120℃,2.5 h | 生物成像 | <1 | [ |
| 2 | 鸡蛋 | 高温热解 | 250℃,2 h | 荧光印刷材料 | 5.9 | [ |
| 3 | 壳聚糖 | 水热处理 | 180℃,12 h | 生物成像 | 7.8 | [ |
| 4 | 咖啡 | 高温煅烧 | 300℃,2 h | 生物成像 | 12 | [ |
| 5 | 水仙球茎 | 高温煅烧 | 200℃,2 h | 抗氧化,细胞成像 | 16.4 | 本工作 |
| [22] | Ding Z J, Cheng L J, Wei J M, et al. Synthesis of carbon dots fluorescent probe and its application in determination of rutin content[J]. Fine Chemicals, 2022, 39(4): 719-724, 733. |
| [23] | Li F F, Li D C, Liu D X, et al. Hydrophilic, upconverting, multicolor, lanthanide-doped NaGdF4 nanocrystals as potential multifunctional bioprobes[J]. Chemistry-A European Journal, 2012, 18(37): 11641-11646. |
| [24] | 田振, 许戈文, 黄毅萍, 等. 微波合成含氮掺杂碳量子点改性水性聚氨酯的制备与性能[J]. 化工进展, 2020, 39(10): 4127-4133. |
| Tian Z, Xu G W, Huang Y P, et al. Preparation and properties of microwave-synthesized nitrogen-doped carbon quantum dots modified waterborne polyurethane[J]. Chemical Industry and Engineering Progress, 2020, 39(10): 4127-4133. | |
| [25] | Sidorov A I, Lebedev V F, Kobranova A A, et al. Formation of carbon quantum dots and nanodiamonds in laser ablation of a carbon film[J]. Quantum Electronics, 2018, 48(1): 45. |
| [26] | Park S Y, Lee H U, Park E S, et al. Photoluminescent green carbon nanodots from food-waste-derived sources: large-scale synthesis, properties, and biomedical applications[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2014, 6(5): 3365-3370. |
| [27] | Jeong G, Park C H, Yi D C, et al. Green synthesis of carbon dots from spent coffee grounds via ball-milling: application in fluorescent chemosensors[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2023, 392: 136250. |
| [28] | 范金玥, 孔祥鑫, 李伟, 等. 水热炭化制备手性碳点及其应用[J]. 化学进展, 2023, 35(12): 1764-1782. |
| Fan J Y, Kong X X, Li W, et al. Preparation and applications of chiral carbon dots prepared via hydrothermal carbonization method[J]. Progress in Chemistry, 2023, 35(12): 1764-1782. | |
| [29] | Kim D, Jo G, Chae Y J, et al. Bioinspired Camellia japonica carbon dots with high near-infrared absorbance for efficient photothermal cancer therapy[J]. Nanoscale, 2021, 13(34): 14426-14434. |
| [30] | Li J T, Fu W J, Zhang X Y, et al. Green preparation of ginger-derived carbon dots accelerates wound healing[J]. Carbon, 2023, 208: 208-215. |
| [31] | Hua X W, Bao Y W, Wu F G. Fluorescent carbon quantum dots with intrinsic nucleolus-targeting capability for nucleolus imaging and enhanced cytosolic and nuclear drug delivery[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2018, 10(13): 10664-10677. |
| [1] | Alivisatos A P. Semiconductor clusters, nanocrystals, and quantum dots[J]. Science, 1996, 271(5251): 933-937. |
| [2] | Xu X Y, Ray R, Gu Y L, et al. Electrophoretic analysis and purification of fluorescent single-walled carbon nanotube fragments[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2004, 126(40): 12736-12737. |
| [3] | Xu G Y, Bao X, Chen J Q, et al. In vivo tumor photoacoustic imaging and photothermal therapy based on supra-(carbon nanodots)[J]. Advanced Healthcare Materials, 2019, 8(2): 1800995. |
| [4] | 刘清浩, 何艳飞, 梁丽娜, 等. 基于氮掺杂碳量子点的荧光微球制备和Fe3+检测[J]. 化工进展, 2018, 37(10): 3936-3942. |
| Liu Q H, He Y F, Liang L N, et al. Preparation of fluorescent microspheres and their detection of Fe3+ based on nitrogen doped carbon quantum dots[J]. Chemical Industry and Engineering Progress, 2018, 37(10): 3936-3942. | |
| [5] | Xin Q, Liu Q, Geng L L, et al. Chiral nanoparticle as a new efficient antimicrobial nanoagent[J]. Advanced Healthcare Materials, 2017, 6(4): 1601011. |
| [6] | Yang Z, Li Z H, Xu M H, et al. Controllable synthesis of fluorescent carbon dots and their detection application as nanoprobes[J]. Nano-Micro Letters, 2013, 5(4): 247-259. |
| [7] | Li H T, Dr X H, Prof Z K, et al. Water-soluble fluorescent carbon quantum dots and photocatalyst design[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2010, 49(26): 4430-4434. |
| [8] | Oza G, Oza K, Pandey S, et al. A green route towards highly photoluminescent and cytocompatible carbon dot synthesis and its separation using sucrose density gradient centrifugation[J]. Journal of Fluorescence, 2015, 25(1): 9-14. |
| [9] | Bankoti K, Rameshbabu A P, Datta S, et al. Onion derived carbon nanodots for live cell imaging and accelerated skin wound healing[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry. B, 2017, 5(32): 6579-6592. |
| [10] | Gao S Y, Wang X, Xu N, et al. From coconut petiole residues to fluorescent carbon dots via a green hydrothermal method for Fe3+ detection[J]. Cellulose, 2021, 28(3): 1647-1661. |
| [11] | Dong C, Xu M S, Wang S N, et al. Fluorescent carbon dots with excellent moisture retention capability for moisturizing lipstick[J]. Journal of Nanobiotechnology, 2021, 19(1): 299. |
| [32] | Xue S S, Li P F, Sun L, et al. The formation process and mechanism of carbon dots prepared from aromatic compounds as precursors: a review[J]. Small, 2023, 19(31): 2206180. |
| [33] | Yuan S, Luo Y P, Jiang Y X, et al. Poria Cocos-derived carbon dots for cellular imaging, free radical scavenging and pH sensing[J]. Diamond and Related Materials, 2023, 137: 110121. |
| [34] | 陈卫, 谷彩花, 叶兆伟, 等. 大别山艾叶多糖提取工艺优化及其吸湿保湿、抗氧化性能研究[J]. 化学试剂, 2024, 46(2): 67-73. |
| Chen W, Gu C H, Ye Z W, et al. Study on extraction optimization of artemisia argyi polysaccharide in Dabie Mountain and its moisture-absorption-retention and antioxidant properties[J]. Chemical Reagents, 2024, 46(2): 67-73. | |
| [35] | 党艳艳, 郭禹熙, 曹文静, 等. 葡萄籽多酚类物质的盐析萃取[J]. 化工学报, 2014, 65(8): 3048-3053. |
| Dang Y Y, Guo Y X, Cao W J, et al. Salting-out extraction of phenolics from grape(Vitis vinifera) seed[J]. CIESC Journal, 2014, 65(8): 3048-3053. | |
| [36] | Sahu S, Behera B, Maiti T K, et al. Simple one-step synthesis of highly luminescent carbon dots from orange juice: application as excellent bio-imaging agents[J]. Chemical Communications, 2012, 48(70): 8835-8837. |
| [37] | Wang J, Wang D C, Chen P S. Amphiphilic egg-derived carbon dots: rapid plasma fabrication, pyrolysis process, and multicolor printing patterns[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2012, 51(37): 9297-9301. |
| [38] | Yang Y H, Cui J H, Zheng M T, et al. One-step synthesis of amino-functionalized fluorescent carbon nanoparticles by hydrothermal carbonization of chitosan[J]. Chemical Communications, 2012, 48(3): 380-382. |
| [39] | Hsu P C, Shih Z Y, Lee C H, et al. Synthesis and analytical applications of photoluminescent carbon nanodots[J]. Green Chemistry, 2012, 14(4): 917-920. |
| [12] | Qureshi W A, Vivekanandan B, Jayaprasath J A, et al. Antimicrobial activity and characterization of pomegranate peel-based carbon dots[J]. Journal of Nanomaterials, 2021, 2021(1): 9096838. |
| [13] | Zhao S J, Lan M H, Zhu X Y, et al. Green synthesis of bifunctional fluorescent carbon dots from garlic for cellular imaging and free radical scavenging[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2015, 7(31): 17054-17060. |
| [14] | Roshni V, Misra S, Santra M K, et al. One pot green synthesis of C-dots from groundnuts and its application as Cr(Ⅵ) sensor and in vitro bioimaging agent[J]. Journal of Photochemistry and Photobiology A: Chemistry, 2019, 373: 28-36. |
| [15] | Shan F S, Fu L J, Chen X Y, et al. Waste-to-wealth: functional biomass carbon dots based on bee pollen waste and application[J]. Chinese Chemical Letters, 2022, 33(6): 2942-2948. |
| [16] | He Y, Chen X J, Wang P L, et al. One-step green synthesis of carbon dots derived from Plumeria alba flowers for sensing and bioimaging[J]. New Journal of Chemistry, 2023, 47(18): 8877-8884. |
| [17] | Zhou J J, Sheng Z H, Han H Y, et al. Facile synthesis of fluorescent carbon dots using watermelon peel as a carbon source[J]. Materials Letters, 2012, 66(1): 222-224. |
| [18] | Das B, Pal P, Dadhich P, et al. In vivo cell tracking, reactive oxygen species scavenging, and antioxidative gene down regulation by long-term exposure of biomass-derived carbon dots[J]. ACS Biomaterials Science & Engineering, 2019, 5(1): 346-356. |
| [19] | Wang D, Zhu L, McCleese C, et al. Fluorescent carbon dots from milk by microwave cooking[J]. RSC Advances, 2016, 6(47): 41516-41521. |
| [20] | Das B, Dadhich P, Pal P, et al. Carbon nanodots from date molasses: new nanolights for the in vitro scavenging of reactive oxygen species[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry B, 2014, 2(39): 6839-6847. |
| [21] | Wang L, Wang Y L, Xu T, et al. Gram-scale synthesis of single-crystalline graphene quantum dots with superior optical properties[J]. Nature Communications, 2014, 5: 5357. |
| [22] | 丁志杰, 程禄军, 魏居孟, 等. 碳点荧光探针的合成及其对芦丁含量的检测[J]. 精细化工, 2022, 39(4): 719-724, 733. |
| [1] | 李泽权, 蔡天宇, 刘家骏, 陈奇志, 肖沛文, 徐小飞, 赵双良. 木质素基絮凝剂的合成与应用[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(9): 4709-4722. |
| [2] | 王三一, 黄文来. 电化学合成氨流程建模与优化[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(9): 4474-4486. |
| [3] | 徐佳琪, 张文君, 余燕萍, 苏宝根, 任其龙, 杨启炜. 热等离子体重整炼厂气制合成气过程数值模拟与实验研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(9): 4462-4473. |
| [4] | 彭梦圆, 李家明, 沙敏, 张丁. 季铵盐氟碳表面活性剂复配体系的性能研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(8): 4177-4184. |
| [5] | 周运桃, 崔丽凤, 张杰, 于富红, 李新刚, 田野. Ga2O3调控CuCeO催化CO2加氢制甲醇的研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(8): 4042-4051. |
| [6] | 巢欣旖, 陈文尧, 张晶, 钱刚, 周兴贵, 段学志. 甲醇和乙酸甲酯一步法制丙酸甲酯催化剂的可控制备与性能调控[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(8): 4030-4041. |
| [7] | 王御风, 罗小雪, 范鸿亮, 吴白婧, 李存璞, 魏子栋. 耦合电解水制氢的绿色有机电合成——电极界面调控策略综述[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(8): 3753-3771. |
| [8] | 郭铮铮, 赵一丹, 王辅强, 裴璐, 靳彦岭, 任芳, 任鹏刚. 异质结构MoS2/RGO/NiFe2O4复合材料的构筑及电磁波吸收性能研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(7): 3719-3732. |
| [9] | 乔亮, 李尚, 刘新亮, 王明, 张沛, 侯影飞. 三元共聚物稠油降黏剂的合成及分子模拟研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(7): 3686-3695. |
| [10] | 刘沁雯, 叶恒冰, 张逸伟, 朱法华, 钟文琪. 煤与禽类粪便混合燃料的加压富氧燃烧特性研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(7): 3487-3497. |
| [11] | 陆昕晟, 郭晓镭, 王世丞, 陆海峰, 刘海峰. 秸秆类生物质的粉碎特性研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(7): 3539-3551. |
| [12] | 吴天灏, 叶霆威, 林延, 黄振. 生物质化学链气化原位补氢制H2/CO可控合成气[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(7): 3498-3508. |
| [13] | 姬海燕, 刘家印, 吴海军, 何璟琳, 靳紫恒, 魏钿航, 江霞. 低温等离子体在生物质气化制氢中的应用研究进展[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(6): 2419-2433. |
| [14] | 郭乃胜, 朱小波, 王双, 陈平, 褚召阳, 王志臣. 聚氨酯改性沥青高低温性能及影响因素的研究进展[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(6): 2505-2523. |
| [15] | 梁碧麟, 余倩, 贾思琦, 李芳, 李其明. Ni-MOF-74金属有机框架膜的结构调变及气体分离性能研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(6): 2714-2721. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备 11010102001995号
京公网安备 11010102001995号