化工学报 ›› 2020, Vol. 71 ›› Issue (8): 3699-3709.DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20191466
蒋滨繁1,2( ),夏德宏1,2(
),夏德宏1,2( ),安苛苛1,张培昆1,敖雯青3
),安苛苛1,张培昆1,敖雯青3
收稿日期:2019-12-03
修回日期:2020-05-14
出版日期:2020-08-05
发布日期:2020-08-05
通讯作者:
夏德宏
作者简介:蒋滨繁(1994—),女,博士研究生,基金资助:
Binfan JIANG1,2( ),Dehong XIA1,2(
),Dehong XIA1,2( ),Keke AN1,Peikun ZHANG1,Wenqing AO3
),Keke AN1,Peikun ZHANG1,Wenqing AO3
Received:2019-12-03
Revised:2020-05-14
Online:2020-08-05
Published:2020-08-05
Contact:
Dehong XIA
摘要:
白云石是一种广泛应用的冶金、建材和化工原料。针对白云石煅烧过程中CO2排放严重等问题,构建了基于CO2循环载热与资源化回收的白云石低碳煅烧竖窑新工艺。通过白云石(CaCO3·MgCO3)煅烧过程的Gibbs自由能变计算,发现提高煅烧温度(50~100 K)可有效克服CO2对反应的抑制作用;通过纯CO2环境中CaCO3分解过程的热重实验分析,验证了CO2循环煅烧白云石煅烧的可行性;通过化学反应动力学计算,解析了全CO2组分环境下CO2压力对CaCO3·MgCO3高温分解过程的影响,并发现提高CO2压力可促进气固传热,从而提升分解速率和改善矿料分解均匀性;对CO2循环煅烧工艺系统能-质平衡计算表明:该工艺理论能耗仅为140 kg/(t 煅白),且煅烧过程的CO2排放降低70%以上,环境效益显著。
中图分类号:
蒋滨繁, 夏德宏, 安苛苛, 张培昆, 敖雯青. 基于CO2循环的低碳高效白云石煅烧新工艺[J]. 化工学报, 2020, 71(8): 3699-3709.
Binfan JIANG, Dehong XIA, Keke AN, Peikun ZHANG, Wenqing AO. Efficient low-carbon dolomite calcination process based on CO2 looping and recovering[J]. CIESC Journal, 2020, 71(8): 3699-3709.

图2 CO2环境中碳酸盐分解模型
Fig.2 Kinetic model for carbonate decomposition with CO2 surrounding (from outside to inside: product layer, reacting layer and unreacted layer)
| Chemical | ΔG? (298 K) / (kJ/mol) | ΔH? (298 K) /(kJ/mol) | ΔS? (298 K) / (J/(mol K)) |
|---|---|---|---|
| CaCO3 | -1128.8 | -1206.9 | 92.9 |
| CaO | -604.2 | -635.1 | 39.7 |
| MgCO3 | -1012 | -1096 | 65.7 |
| MgO | -569.4 | -601.7 | 26.9 |
| CO2 | -394.4 | -393.5 | 213.6 |
表1 CaCO3·MgCO3分解热力学计算参数
Table 1 Calculation parameters for thermochemical analysis of CaCO3·MgCO3 decomposition
| Chemical | ΔG? (298 K) / (kJ/mol) | ΔH? (298 K) /(kJ/mol) | ΔS? (298 K) / (J/(mol K)) |
|---|---|---|---|
| CaCO3 | -1128.8 | -1206.9 | 92.9 |
| CaO | -604.2 | -635.1 | 39.7 |
| MgCO3 | -1012 | -1096 | 65.7 |
| MgO | -569.4 | -601.7 | 26.9 |
| CO2 | -394.4 | -393.5 | 213.6 |
| 参数 | 数值 |
|---|---|
| 2700 | |
| ρCaO/MgO/(kg/m3) | 3000 |
| 2 | |
| 1.16 | |
| λCaO/MgO /(W/(m·K) ) | 1.2 |
| 0.014 | |
| 0.8~1.3 | |
| 1.0~1.2 | |
| 5×10-5 | |
| Ts / K | 300 |
| Tg / K | 1600 |
| vg /(m/s) | 2 |
| r/m | 0.03 |
| Pr | 0.724 |
表2 CaCO3·MgCO3传热与分解动力学计算参数
Table 2 Calculation parameters for kinetic analysis of CaCO3·MgCO3 decomposition
| 参数 | 数值 |
|---|---|
| 2700 | |
| ρCaO/MgO/(kg/m3) | 3000 |
| 2 | |
| 1.16 | |
| λCaO/MgO /(W/(m·K) ) | 1.2 |
| 0.014 | |
| 0.8~1.3 | |
| 1.0~1.2 | |
| 5×10-5 | |
| Ts / K | 300 |
| Tg / K | 1600 |
| vg /(m/s) | 2 |
| r/m | 0.03 |
| Pr | 0.724 |

图6 PCO2为 0.2 atm和1 atm时碳酸盐矿分解反应层厚度Dr随时间t的变化(橘色为产物层,高亮黄色为反应层,蓝色为未反应核)
Fig.6 Reaction layer thickness in carbonate ore at PCO2 = 0.2 atm and 1 atm (orange: product layer; yellow: reacting layer; blue: unreacted layer)
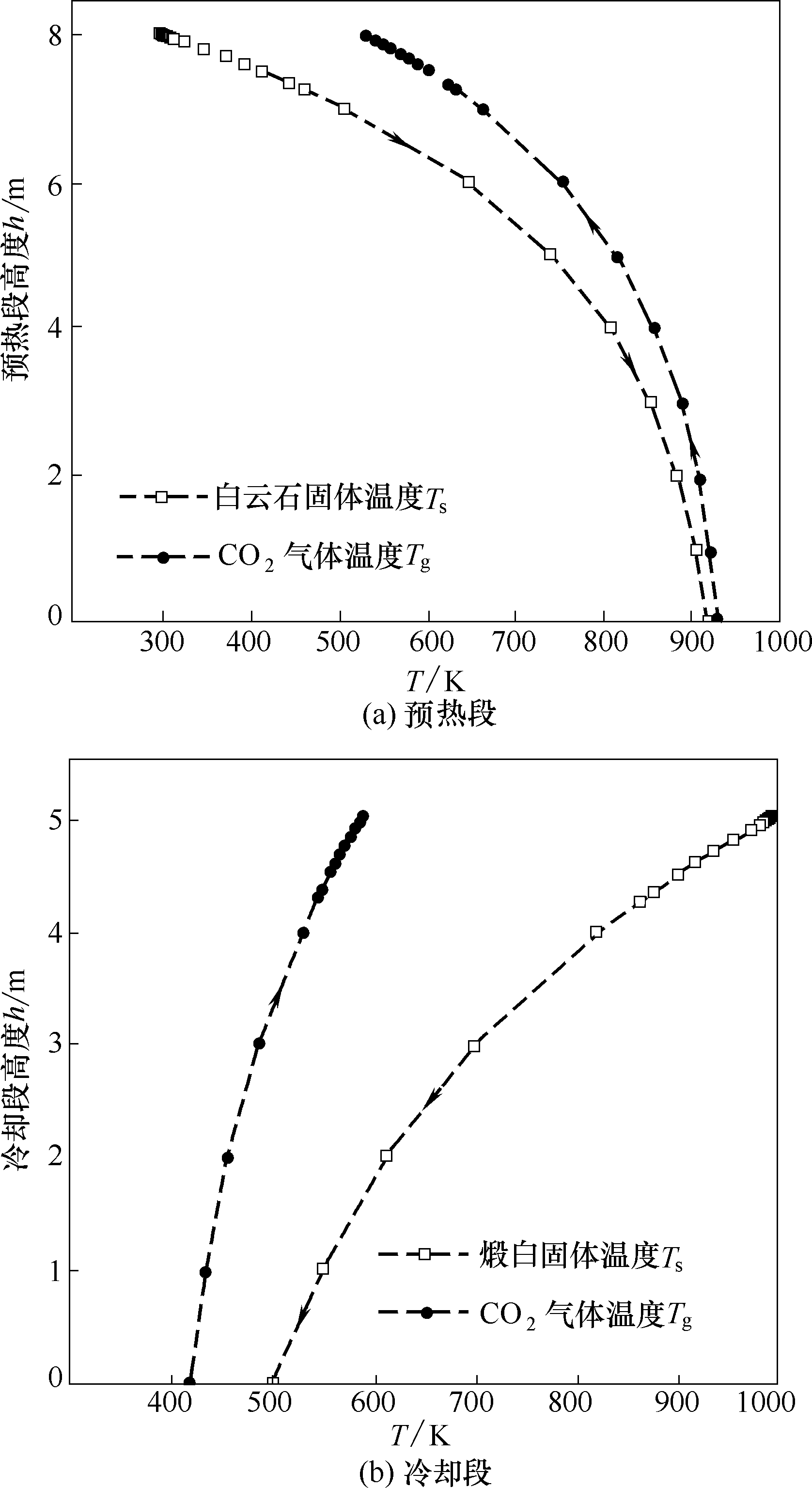
图8 预热段和冷却段内气固温度随高度的变化(预热段和冷却段均以CO2的入口为h = 0)
Fig.8 Temperature variations of gas and solid in preheating and cooling zone (h =0 is CO2 inlet of each zone)
| 区域 | 收入项 | 支出项 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 参数 | 值 | 参数 | 值 | |
| 预热段 | 白云石质量流量 qb /(kg/h) | 5000 | 白云石质量流量 qb/(kg/h) | 5000 |
| CO2质量流量 qc,3/(kg/h) | 18400 | CO2质量流量 qc,3/(kg/h) | 18400 | |
| 入口白云石温度 Tb,yin/K | 300 | 出口白云石温度 Tb,yout/K | 900~1000 | |
| 入口CO2温度 Tc,yin/K | 900~1000 | 出口CO2温度 Tc,yout /K | 500 | |
| 白云石显热上升 Qb/(kJ/s) | 750 | |||
| 煅烧段 | 白云石质量流量 qb /(kg/h) | 5000 | 煅白质量流量 qdb/(kg/h) | 2600 |
| CO2质量流量 qc,1 /(kg/h) | 16000 | CO2质量流量 qc,3/(kg/h) | 18400 | |
| 入口白云石温度 Tb,din /K | 900 | 出口煅白温度 Tb,dout /K | 900~1000 | |
| 入口CO2温度 Tc,din/K | 1400~1600 | 出口CO2温度 Tc,dout /K | 900~1000 | |
| 白云石反应热 Qb,r/(kJ/s) | 2050 | 白云石分解产生CO2qc,2 /(kg/h) | 2400 | |
| 冷却段 | 煅白质量流量 qdb/(kg/h) | 2600 | 煅白质量流量 qdb/(kg/h) | 2600 |
| CO2质量流量 qc,1/(kg/h) | 16000 | CO2质量流量 qc,2 /(kg/h) | 16000 | |
| 入口煅白温度 Tb,lin /K | 900~1000 | 出口煅白温度 Tb,lout /K | 500 | |
| 入口CO2温度 Tc,lin /K | 400 | 出口CO2温度 Tc,lout /K | 600 | |
| 蓄热式加热炉 | CO2质量流量 qc,1 /(kg/h) | 16000 | CO2质量流量 qc,1/(kg/h) | 16000 |
| 入口CO2温度 Tc,xin /K | 600 | 出口CO2温度 Tc,xout /K | 1400~1600 | |
| 燃料消耗/(kg ce/(t 煅白)) | 140 | 燃烧产生和排放的CO2 /(kg/h) | 980 | |
表3 稳定运行后CO2载热循环煅烧白云石(CaCO3·MgCO3)系统热平衡分析
Table 3 Thermal analysis of dolomite calcination system with CO2 looping and recovering (steady state)
| 区域 | 收入项 | 支出项 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 参数 | 值 | 参数 | 值 | |
| 预热段 | 白云石质量流量 qb /(kg/h) | 5000 | 白云石质量流量 qb/(kg/h) | 5000 |
| CO2质量流量 qc,3/(kg/h) | 18400 | CO2质量流量 qc,3/(kg/h) | 18400 | |
| 入口白云石温度 Tb,yin/K | 300 | 出口白云石温度 Tb,yout/K | 900~1000 | |
| 入口CO2温度 Tc,yin/K | 900~1000 | 出口CO2温度 Tc,yout /K | 500 | |
| 白云石显热上升 Qb/(kJ/s) | 750 | |||
| 煅烧段 | 白云石质量流量 qb /(kg/h) | 5000 | 煅白质量流量 qdb/(kg/h) | 2600 |
| CO2质量流量 qc,1 /(kg/h) | 16000 | CO2质量流量 qc,3/(kg/h) | 18400 | |
| 入口白云石温度 Tb,din /K | 900 | 出口煅白温度 Tb,dout /K | 900~1000 | |
| 入口CO2温度 Tc,din/K | 1400~1600 | 出口CO2温度 Tc,dout /K | 900~1000 | |
| 白云石反应热 Qb,r/(kJ/s) | 2050 | 白云石分解产生CO2qc,2 /(kg/h) | 2400 | |
| 冷却段 | 煅白质量流量 qdb/(kg/h) | 2600 | 煅白质量流量 qdb/(kg/h) | 2600 |
| CO2质量流量 qc,1/(kg/h) | 16000 | CO2质量流量 qc,2 /(kg/h) | 16000 | |
| 入口煅白温度 Tb,lin /K | 900~1000 | 出口煅白温度 Tb,lout /K | 500 | |
| 入口CO2温度 Tc,lin /K | 400 | 出口CO2温度 Tc,lout /K | 600 | |
| 蓄热式加热炉 | CO2质量流量 qc,1 /(kg/h) | 16000 | CO2质量流量 qc,1/(kg/h) | 16000 |
| 入口CO2温度 Tc,xin /K | 600 | 出口CO2温度 Tc,xout /K | 1400~1600 | |
| 燃料消耗/(kg ce/(t 煅白)) | 140 | 燃烧产生和排放的CO2 /(kg/h) | 980 | |
| 1 | 狄跃忠, 王智慧, 王耀武, 等. 新法铝热炼镁还原渣提取高白氢氧化铝[J]. 化工学报, 2013, 64(3): 1106-1111. |
| Di Y Z, Wang Z H, Wang Y W, et al. Extract of high-whiteness aluminum hydroxide from residues of novel process of magnesium production by aluminothermic reduction[J]. CIESC Journal, 2013, 64(3): 1106-1111. | |
| 2 | 中国有色金属工业协会. 中国有色金属工业年鉴2018[M]. 北京: 中国有色金属协会, 2019. |
| China Nonferrous Metals Industry Association. The Yearbook of Nonferrous Metals Industry of China2018[M]. Beijing: China Nonferrous Metals Industry Association, 2018. | |
| 3 | Li R, Zhang S, Guo L, et al. Numerical study of magnesium (Mg) production by the Pidgeon process: impact of heat transfer on Mg reduction process[J]. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 2013, 59: 328-337. |
| 4 | 夏德宏, 余涛. 皮江法炼镁工艺用能状况诊断及节能措施[J]. 工业炉, 2005, 27(2): 32-35. |
| Xia D H, Yu T. Diagnosis on energy consumption and energy-saving measures for Pidgeons magnesium reduction process[J]. Industrial Furnace, 2005, 27(2): 32-35. | |
| 5 | Pidgeon L M, Alexander W A. Thermal production of magnesiums pilot plant studies on the retort ferrosilicon process[J]. Trans. Am. Inst. Min. Mater. Eng. , 1944, 159: 315-352. |
| 6 | Zang J, Ding W. The Pidgeon Process in China and Its Future[M]. Hryn J. New Orleans: Magnesium Technology, TMS (The Minerals, Metals & Materials Society), 2001: 7-10. |
| 7 | Peters G P, Marland G, Quéré C L, et al. Rapid growth in CO2 emissions after the 2008—2009 global financial crisis[J]. Nature Climate Change, 2010, 2: 2-4. |
| 8 | Wang W, Wang S, Ma X, et al. Recent advances in catalytic hydrogenation of carbon dioxide[J]. Chemical Society Reviews, 2011, 40(7): 3703. |
| 9 | Brown R.Magnesium in the 21st century[J]. Adv. Mater. Processes, 2009, 167(1): 31-33. |
| 10 | Halmann M, Frei A, Steinfeld A. Magnesium production by the Pidgeon process involving dolomite calcination and MgO silicothermic reduction: thermodynamic and environmental analyses[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2008, 47: 2146-2154. |
| 11 | Maitra S, Choudhury A, Das H S, et al. Effect of compaction on the kinetics of thermal decomposition of dolomite under non-isothermal condition[J]. Journal of Materials Science, 2005, 18(40): 4749-4751. |
| 12 | 陈文仲, 王春华, 刘宝玉, 等. 回转窑供风管参数对窑内热工状况的影响[J]. 化工学报, 2011, 62(11): 3109-3114. |
| Chen W Z, Wang C H, Liu B Y, et al. Influences of air pipe parameters on thermal working conditions in carbon rotary kilns[J]. CIESC Journal, 2011, 62(11): 3109-3114. | |
| 13 | 张志霄, 池涌, 李水清, 等. 回转窑传热模型与数值模拟[J]. 化学工程, 2003, 31(4): 27-31. |
| Zhang Z X, Chi Y, Li S Q, et al. Axial heat-transfer model and numerical simulation for rotary kiln[J]. Chemical Engineering (China), 2003, 31(4): 27-31. | |
| 14 | 徐祥斌, 罗序燕, 曹慧君, 等. 硅热法炼镁白云石煅烧节能技术研究及最新进展[J]. 轻金属, 2010, 9: 55-59. |
| Xu X B, Luo X Y, Cao H J, et al. The research and the latest evolution of saving energy in the dolomite calcination of silicon thermal process[J]. Light Metals, 2010, 9: 55-59. | |
| 15 | 殷谦, 杜文静, 纪兴林, 等. 一种回转窑余热回收用集热器的实验研究及其结构优化[J]. 化工学报, 2016, 67(7): 2740-2747. |
| Yin Q, Du W J, Ji X L, et al. Experimental measurement and structure optimization of heat recovery exchangers on rotary kilns[J]. CIESC Journal, 2016, 67(7): 2740-2747. | |
| 16 | Yin Q, Du W J, Ji X L, et al. Optimization design and economic analyses of heat recovery exchangers on rotary kilns[J]. Applied Energy, 2016, 180: 743-756. |
| 17 | Söğüt Z, Oktay Z, Karakoç H. Mathematical modeling of heat recovery from a rotary kiln[J]. Applied Thermal Engineering, 2010, 30(8): 817-825. |
| 18 | Luo Q, Li P, Cai L, et al. A thermoelectric waste-heat-recovery system for portland cement rotary kilns[J]. Journal of Electronic Materials, 2015, 44(6): 1750-1762. |
| 19 | Senegačnik A, Oman J, Širok B. Analysis of calcination parameters and the temperature profile in an annular shaft kiln (Ⅰ): Theoretical survey[J]. Applied Thermal Engineering, 2007, 27(8/9): 1467-1472. |
| 20 | Senegačnik A, Oman J, Širok B. Annular shaft kiln for lime burning with kiln gas recirculation[J]. Applied Thermal Engineering, 2008, 28(7): 785-792. |
| 21 | Zuideveld P L, Berg P J V D. Design of lime shaft kilns[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 1971, 26(6): 875-883. |
| 22 | Gutiérreza A, Cogollos M J B, Vandecasteeleb C. Energy and exergy assessments of a lime shaft kiln[J]. Applied Thermal Engineering, 2013, 51(1/2): 273-280. |
| 23 | Piringer H. Lime shaft kilns[J]. Energy Procedia, 2017, 120: 75-95. |
| 24 | Krause B, Liedmann B, Wiese J, et al. 3D-DEM-CFD simulation of heat and mass transfer, gas combustion and calcination in an intermittent operating lime shaft kiln[J]. International Journal of Thermal Sciences, 2017, 117: 121-135. |
| 25 | 任玲, 夏德宏, 赵恒, 镁冶金白云石煅烧振荡式均匀加热U型窑的开发[J]. 中国有色冶金, 2010, 41(2): 51-55. |
| Ren L, Xia D H, Zhao H. Development of U-shaped calcining kiln with oscillating and uniform heating for dolomite calcination in magnesium metallurgy[J]. China Nonferrous Metallurgy, 2010, 41(2): 51-55. | |
| 26 | Sasaki K, Qiu X, Hosomomi Y, et al. Effect of natural dolomite calcination temperature on sorption of borate onto calcined products[J]. Microporous and Mesoporous Materials, 2013, 171: 1-8. |
| 27 | Knndsen M. The laws of molecular and viscous flow of gases through tribes[J]. Annual Physics, 1909, 28: 75 |
| 28 | Jiang B, Xia D, Yu B, et al. An environment-friendly process for limestone calcination with CO2 looping and recovery[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2019, 240: 118147. |
| 29 | Darroudi T, Searcy A W. Effect of carbon dioxide pressure on the rate of decomposition of calcite (CaCO3)[J]. Journal of Physical Chemistry, 2013, 85: 124-131. |
| 30 | Borgwardt R H. Sintering of nascent calciumoxide[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 1989, 44: 53-63. |
| 31 | Barin I. Thermochemical Data of Pure Substances [M]. 3rd ed. Weinheim (VCH): Verlagsgesellschaft mbH, 2008. |
| [1] | 程成, 段钟弟, 孙浩然, 胡海涛, 薛鸿祥. 表面微结构对析晶沉积特性影响的格子Boltzmann模拟[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(S1): 74-86. |
| [2] | 宋瑞涛, 王派, 王云鹏, 李敏霞, 党超镔, 陈振国, 童欢, 周佳琦. 二氧化碳直接蒸发冰场排管内流动沸腾换热数值模拟分析[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(S1): 96-103. |
| [3] | 张义飞, 刘舫辰, 张双星, 杜文静. 超临界二氧化碳用印刷电路板式换热器性能分析[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(S1): 183-190. |
| [4] | 吴雷, 刘姣, 李长聪, 周军, 叶干, 刘田田, 朱瑞玉, 张秋利, 宋永辉. 低阶粉煤催化微波热解制备含碳纳米管的高附加值改性兰炭末[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(9): 3956-3967. |
| [5] | 程业品, 胡达清, 徐奕莎, 刘华彦, 卢晗锋, 崔国凯. 离子液体基低共熔溶剂在转化CO2中的应用[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(9): 3640-3653. |
| [6] | 盛冰纯, 于建国, 林森. 铝基锂吸附剂分离高钠型地下卤水锂资源过程研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(8): 3375-3385. |
| [7] | 杨菲菲, 赵世熙, 周维, 倪中海. Sn掺杂的In2O3催化CO2选择性加氢制甲醇[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(8): 3366-3374. |
| [8] | 洪瑞, 袁宝强, 杜文静. 垂直上升管内超临界二氧化碳传热恶化机理分析[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(8): 3309-3319. |
| [9] | 张曼铮, 肖猛, 闫沛伟, 苗政, 徐进良, 纪献兵. 危废焚烧处理耦合有机朗肯循环系统工质筛选与热力学优化[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(8): 3502-3512. |
| [10] | 汪林正, 陆俞冰, 张睿智, 罗永浩. 基于分子动力学模拟的VOCs热氧化特性分析[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(8): 3242-3255. |
| [11] | 张蒙蒙, 颜冬, 沈永峰, 李文翠. 电解液类型对双离子电池阴阳离子储存行为的影响[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(7): 3116-3126. |
| [12] | 张琦钰, 高利军, 苏宇航, 马晓博, 王翊丞, 张亚婷, 胡超. 碳基催化材料在电化学还原二氧化碳中的研究进展[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(7): 2753-2772. |
| [13] | 毛磊, 刘冠章, 袁航, 张光亚. 可捕集CO2的纳米碳酸酐酶粒子的高效制备及性能研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(6): 2589-2598. |
| [14] | 张媛媛, 曲江源, 苏欣欣, 杨静, 张锴. 循环流化床燃煤机组SNCR脱硝过程气液传质和反应特性[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(6): 2404-2415. |
| [15] | 杨峥豪, 何臻, 常玉龙, 靳紫恒, 江霞. 生物质快速热解下行式流化床反应器研究进展[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(6): 2249-2263. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备 11010102001995号
京公网安备 11010102001995号