化工学报 ›› 2024, Vol. 75 ›› Issue (1): 120-137.DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20230845
收稿日期:2023-08-17
修回日期:2023-12-16
出版日期:2024-01-25
发布日期:2024-03-11
通讯作者:
巩雁军
作者简介:刘琦(1994—),男,博士研究生,LiuQ0330@163.com
基金资助:
Qi LIU( ), Zikang CHEN, Yu PIAO, Peng XIAO, Yafen GE, Yanjun GONG(
), Zikang CHEN, Yu PIAO, Peng XIAO, Yafen GE, Yanjun GONG( )
)
Received:2023-08-17
Revised:2023-12-16
Online:2024-01-25
Published:2024-03-11
Contact:
Yanjun GONG
摘要:
乙烯、丙烯等低碳烯烃是化学工业重要的基础原料。近年来,全球低碳烯烃的需求量持续增加,发展不同原料催化裂解增产低碳烯烃的技术仍将是主流方向。围绕催化裂解高效制备低碳烯烃工艺,阐述了分子筛催化剂制备及其催化裂解性能的研究进展,尤其是基于ZSM-5分子筛综述了催化裂解催化剂的研制及性能调控的研究进展,包括用于增产低碳烯烃的ZSM-5分子筛的高效合成及结构形貌控制,探讨了通过元素改性、多级孔结构制备对ZSM-5分子筛的织构性质、酸性质的调变,分析总结了其对原料转化率、低碳烯烃选择性和催化剂稳定性的影响,阐明了不同微观结构性质的ZSM-5分子筛催化剂上催化裂解增产低碳烯烃的构效关系,为精准调控ZSM-5分子筛的结构性质研究提供新思路,为设计烃类催化裂解制低碳烯烃工艺关键催化剂奠定基础。
中图分类号:
刘琦, 陈子康, 朴宇, 肖鹏, 葛亚粉, 巩雁军. 烃类催化裂解高选择性制低碳烯烃的分子筛催化剂[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(1): 120-137.
Qi LIU, Zikang CHEN, Yu PIAO, Peng XIAO, Yafen GE, Yanjun GONG. Zeolite catalysts for catalytic cracking of hydrocarbon to increase light olefins selectivity[J]. CIESC Journal, 2024, 75(1): 120-137.
| 分子筛 | 硅铝比 | 实验条件 | 转化率/% | 产物收率/% | 文献 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 低碳烯烃 | 乙烯 | 丙烯 | 丁烯 | |||||
| MCM-68 | 51 | 己烷, 550℃ | 45.0 | — | 12.0 | 50.0 | — | [ |
| 丝光沸石 | 45 | 己烷, 550℃ | 45.3 | — | 14.0 | 41.0 | — | [ |
| ZSM-5 | 45 | 己烷, 550℃ | 59.0 | — | 20.0 | 37.0 | — | [ |
| Beta | 41 | 己烷, 550℃ | 64.0 | — | 20.0 | 37.0 | — | [ |
| ZSM-5纳米片 | 54 | 正庚烷, 550℃ | 85.8 | — | — | 31.0 | — | [ |
| Y | 10.7 | 正辛烷, 460℃, 空速3.88 h-1 | 93.0 | — | — | — | — | [ |
| Beta | 40 | 十二烷, 550℃ | 98.0 | 49.7 | 7.8 | 25.5 | 16.4 | [ |
| ZSM-5(块状,500 nm) | 50 | 十二烷, 550℃ | 98.0 | 40.4 | 12.9 | 17.9 | 9.6 | [ |
| MCM-22 | 52 | 1-丁烯, 550℃, 空速5 h-1 | 83.0 | — | 12.0 | 29.5 | — | [ |
表1 不同分子筛催化剂的催化裂解性能
Table 1 The catalytic cracking performance of different zeolite catalysts
| 分子筛 | 硅铝比 | 实验条件 | 转化率/% | 产物收率/% | 文献 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 低碳烯烃 | 乙烯 | 丙烯 | 丁烯 | |||||
| MCM-68 | 51 | 己烷, 550℃ | 45.0 | — | 12.0 | 50.0 | — | [ |
| 丝光沸石 | 45 | 己烷, 550℃ | 45.3 | — | 14.0 | 41.0 | — | [ |
| ZSM-5 | 45 | 己烷, 550℃ | 59.0 | — | 20.0 | 37.0 | — | [ |
| Beta | 41 | 己烷, 550℃ | 64.0 | — | 20.0 | 37.0 | — | [ |
| ZSM-5纳米片 | 54 | 正庚烷, 550℃ | 85.8 | — | — | 31.0 | — | [ |
| Y | 10.7 | 正辛烷, 460℃, 空速3.88 h-1 | 93.0 | — | — | — | — | [ |
| Beta | 40 | 十二烷, 550℃ | 98.0 | 49.7 | 7.8 | 25.5 | 16.4 | [ |
| ZSM-5(块状,500 nm) | 50 | 十二烷, 550℃ | 98.0 | 40.4 | 12.9 | 17.9 | 9.6 | [ |
| MCM-22 | 52 | 1-丁烯, 550℃, 空速5 h-1 | 83.0 | — | 12.0 | 29.5 | — | [ |
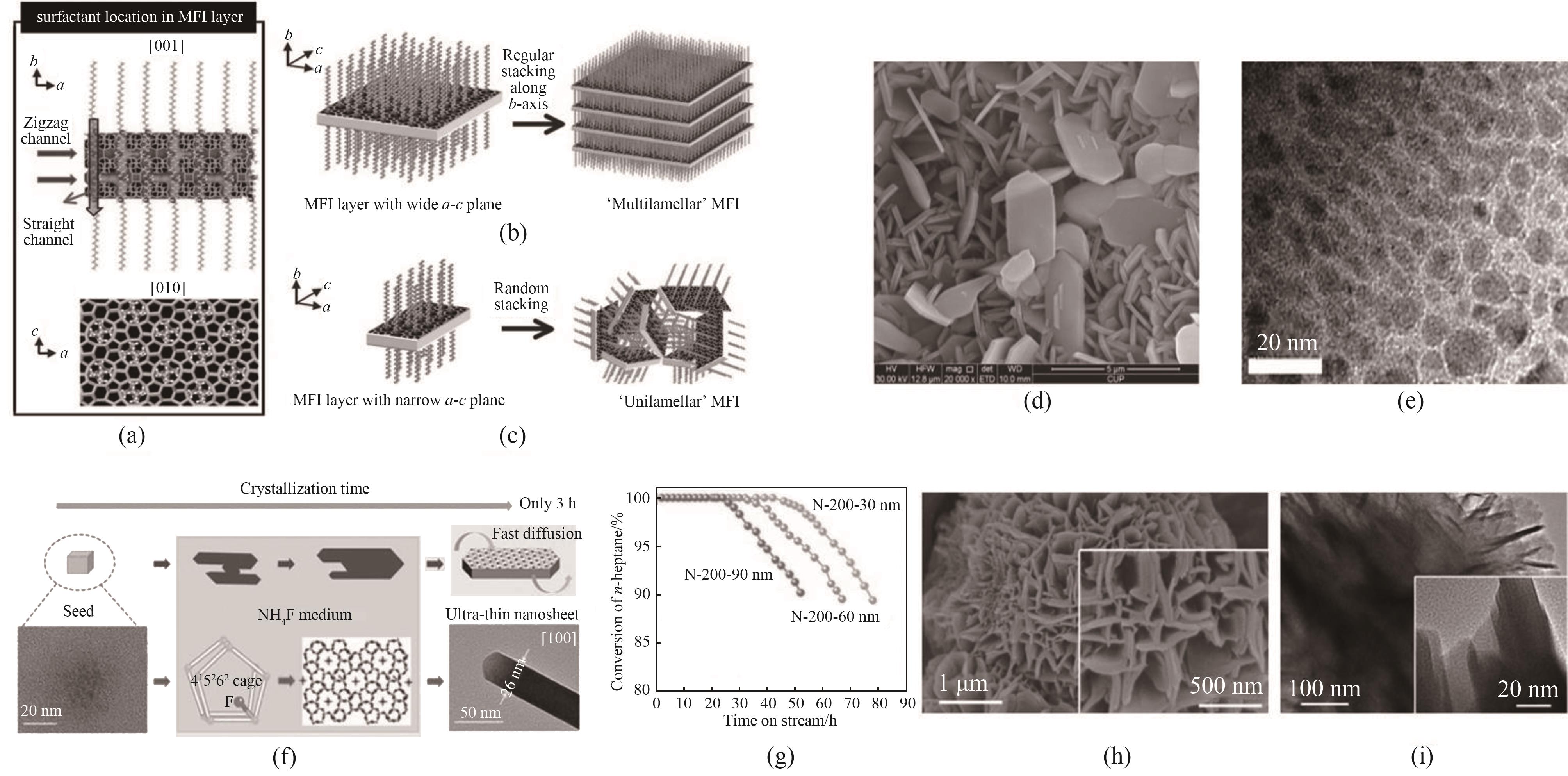
图2 (a)单MFI纳米片的结构模型;(b)MFI纳米片沿b轴形成多层堆叠;(c)单层结构的随机组合[57];(d), (e)本课题组合成的片状结构ZSM-5分子筛SEM图和HRTEM图[59];(f), (g)模板剂和F体系合成ZSM-5纳米片示意图及催化裂解性能[63];(h), (i)柱支撑HZSM-5纳米片的SEM图和HRTEM图[65]
Fig.2 (a) Structure model for the single MFI nanosheet; (b) Many MFI nanosheets form either multilamellar stacking along the b-axis; (c) A random assembly of unilamellar structure[57]; (d), (e) The SEM and HRTEM images of ZSM-5 zeolite with a sheet-like structure combined in our group[59]; (f), (g) Schematic diagram of the synthesis of ZSM-5 nanosheets using template and fluoride and their catalytic cracking performance[63]; (h), (i) SEM and HRTEM images of the pillared HZSM-5 nanosheet zeolite[65]
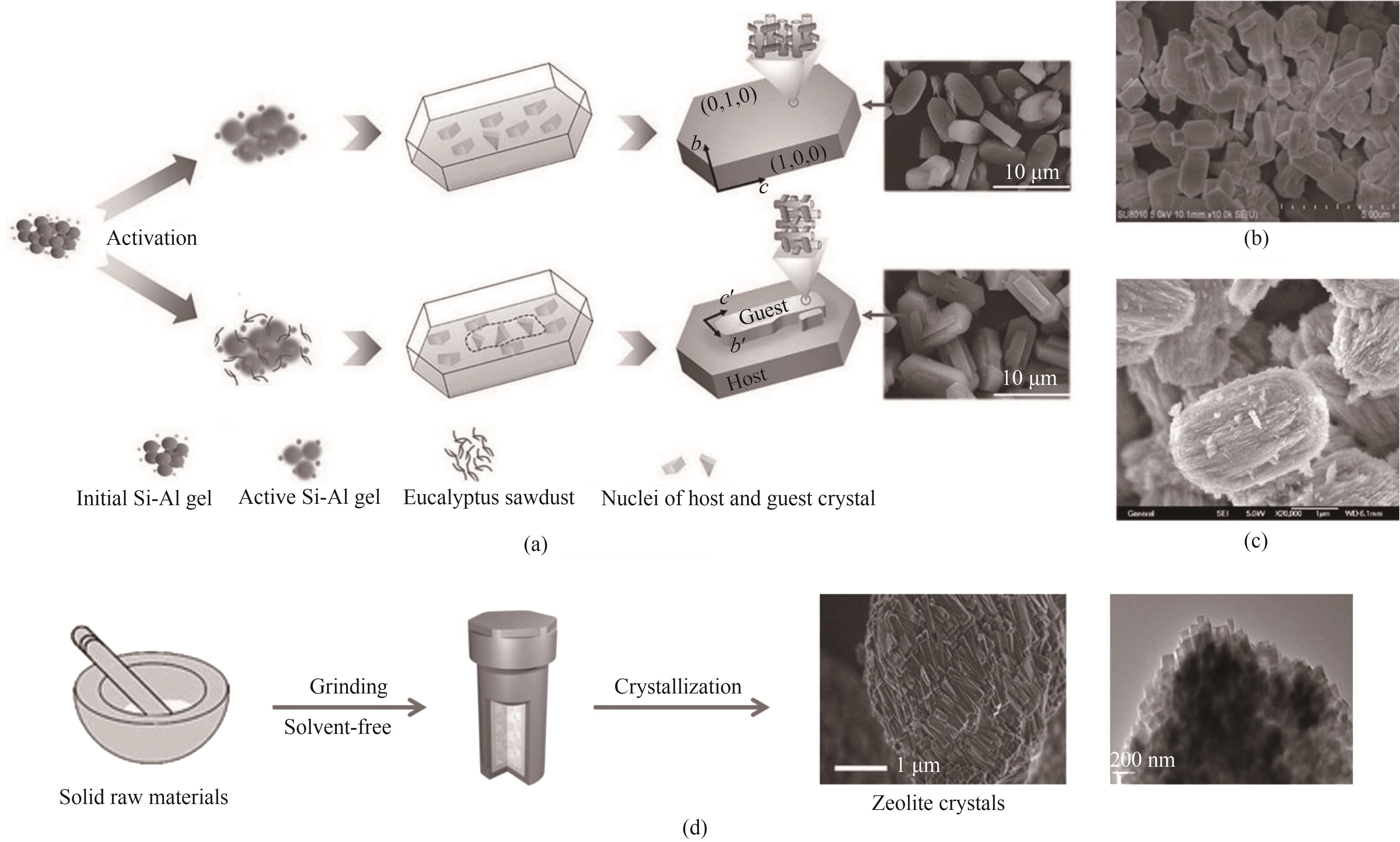
图3 在不同体系下合成分子筛示意图及分子筛形貌图:(a)~(c)无有机模板剂合成体系[68,71,74];(d)无溶剂合成体系[75,77]
Fig.3 Schematic for synthesizing zeolites in different systems and theirs morphology images: (a)—(c) organic-free synthesis system[68,71,74]; (d) solvent-free synthesis system[75,77]
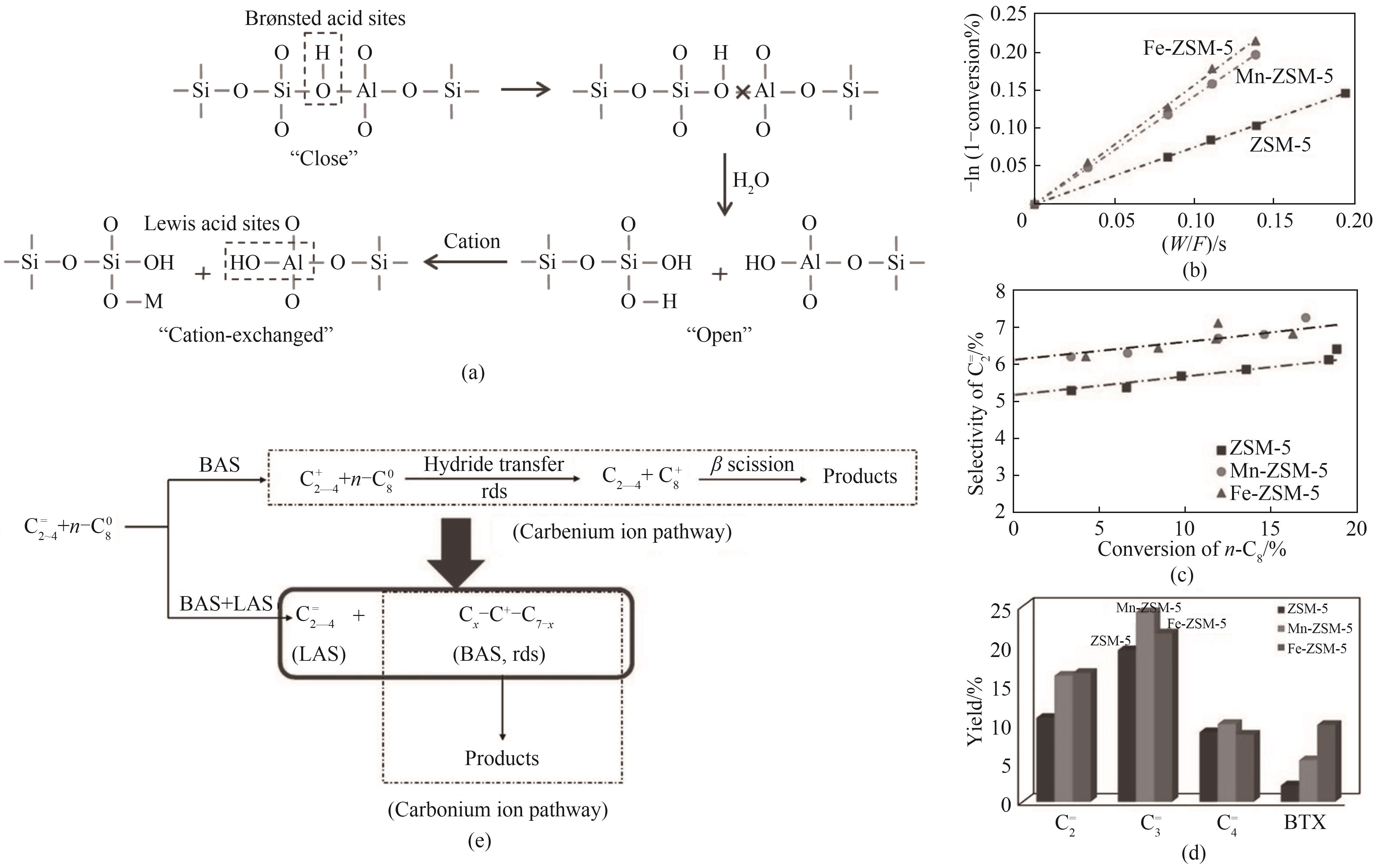
图4 (a)传统金属改性ZSM-5分子筛的机理图[83];(b)~(e)Fe、Mn改性ZSM-5分子筛的催化性能及裂解正辛烷反应网络[90]
Fig.4 (a) Schematic of possible mechanism for ZSM-5 modified by metal cations[83]; (b)—(e) Catalytic performance of Fe and Mn modified ZSM-5 and reaction network for cracking n-octane[90]
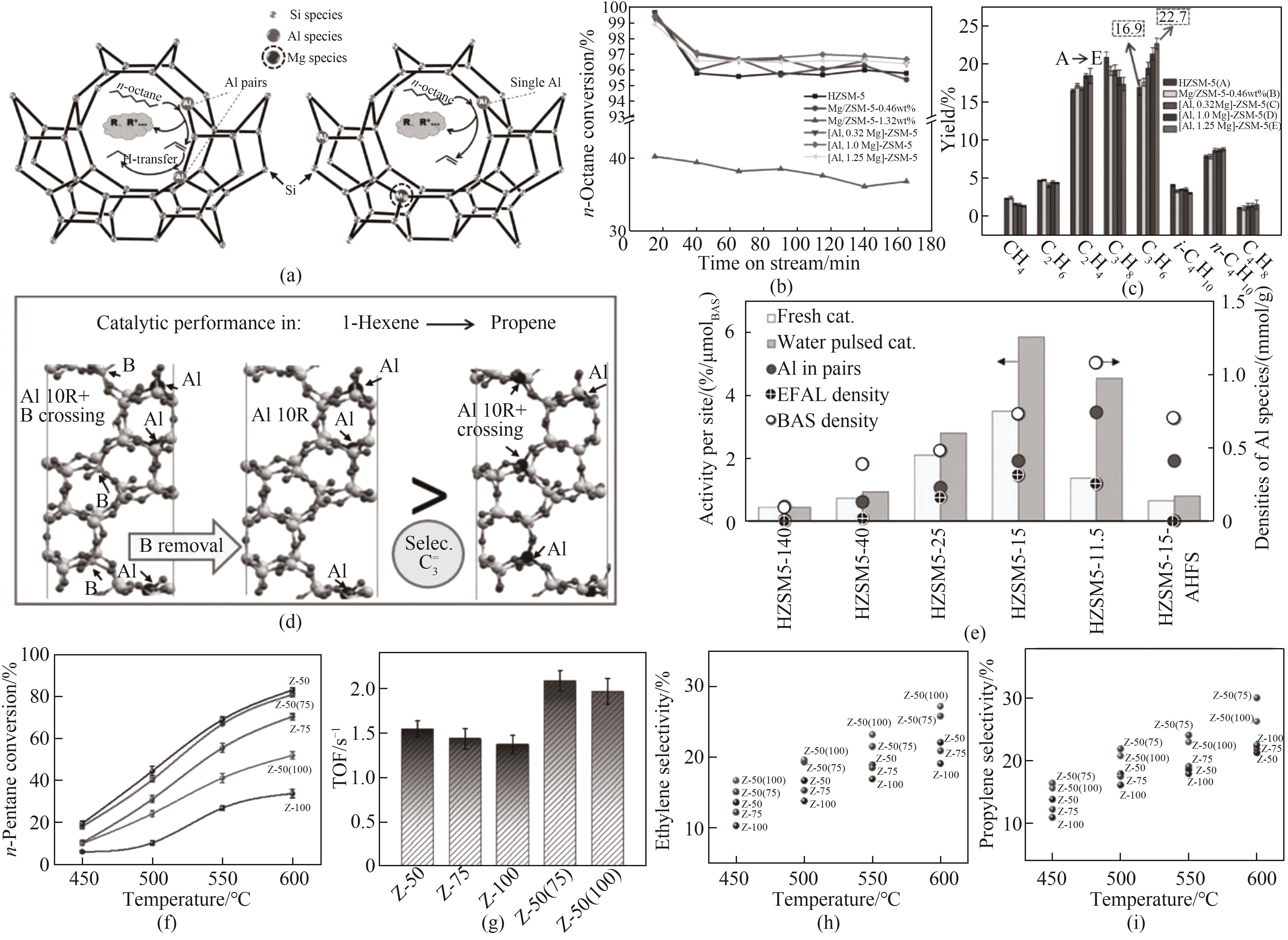
图5 (a)~(d)原位合成引入金属对分子筛Al分布的影响示意图及其催化性能[95-96];(e)EFAL和BAS密度与己烷裂解反应速率的关系[97];(f)~(i)ZSM-5分子筛Al物种的变化对催化裂解反应的影响[98]
Fig.5 (a)—(d) Schematic of the effect of introducing metals on the Al distribution of zeolites by in-situ synthesis and their catalytic performance[95-96]; (e) EFAL and BAS densities as a function of rate per site of the hexane cracking reaction[97]; (f)—(i) The effect of changes in Al species of ZSM-5 zeolites for catalytic cracking reaction[98]
| 催化剂 | 改性金属 及含量(质量分数) | ΔS比表面积/ (m2/g) | ΔS微孔表面积/ (m2/g) | ΔS外表面积/ (m2/g) | ΔV孔体积/ (cm3/g) | ΔV微孔体积/ (cm3/g) | ΔV介孔体积/ (cm3/g) | 文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1K/HZ-280 | K, 1% | -97.0 | — | — | -0.03 | — | — | [ |
| Ca-ZSM-5 | Ca, — | -78.0 | — | — | — | — | — | [ |
| ZSM-5-Cs | Cs, — | -50.0 | — | — | 0.00 | -0.02 | — | [ |
| 0.5Fe/H-ZSM-5 | Fe, 0.5% | -32.5 | -13.5 | -19.0 | -0.02 | -0.02 | 0.00 | [ |
| 0.5Cu/H-ZSM-5 | Cu, 0.5% | -13.3 | -7.7 | -5.6 | -0.01 | -0.01 | +0.01 | [ |
| 0.5Ni/H-ZSM-5 | Ni, 0.5% | -34.9 | -24.7 | -10.2 | -0.01 | -0.02 | 0.00 | [ |
| Au/ZSM-5-8.5 | Au, 0.5% | -47.0 | +10.0 | — | -0.03 | +0.01 | — | [ |
| 0.5%Au/ZSM-5 | Au, 0.5% | -14.8 | +6.1 | — | -0.01 | 0.00 | — | [ |
| 0.5%Au/2.0%La-ZSM-5 | Au, 0.5%; La, 2.0% | -32.9 | -4.6 | — | -0.02 | 0.00 | — | [ |
表2 不同金属改性ZSM-5分子筛的孔性质
Table 2 The pore properties of different metal modified ZSM-5 zeolites
| 催化剂 | 改性金属 及含量(质量分数) | ΔS比表面积/ (m2/g) | ΔS微孔表面积/ (m2/g) | ΔS外表面积/ (m2/g) | ΔV孔体积/ (cm3/g) | ΔV微孔体积/ (cm3/g) | ΔV介孔体积/ (cm3/g) | 文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1K/HZ-280 | K, 1% | -97.0 | — | — | -0.03 | — | — | [ |
| Ca-ZSM-5 | Ca, — | -78.0 | — | — | — | — | — | [ |
| ZSM-5-Cs | Cs, — | -50.0 | — | — | 0.00 | -0.02 | — | [ |
| 0.5Fe/H-ZSM-5 | Fe, 0.5% | -32.5 | -13.5 | -19.0 | -0.02 | -0.02 | 0.00 | [ |
| 0.5Cu/H-ZSM-5 | Cu, 0.5% | -13.3 | -7.7 | -5.6 | -0.01 | -0.01 | +0.01 | [ |
| 0.5Ni/H-ZSM-5 | Ni, 0.5% | -34.9 | -24.7 | -10.2 | -0.01 | -0.02 | 0.00 | [ |
| Au/ZSM-5-8.5 | Au, 0.5% | -47.0 | +10.0 | — | -0.03 | +0.01 | — | [ |
| 0.5%Au/ZSM-5 | Au, 0.5% | -14.8 | +6.1 | — | -0.01 | 0.00 | — | [ |
| 0.5%Au/2.0%La-ZSM-5 | Au, 0.5%; La, 2.0% | -32.9 | -4.6 | — | -0.02 | 0.00 | — | [ |
| 催化剂 | 改性金属及含量 (质量分数) | Δ总酸量/(mmol/g) | Δ弱酸量/(mmol/g) | Δ中强酸量/(mmol/g) | Δ强酸量/(mmol/g) | ΔB酸量/(mmol/g) | ΔL酸量/(mmol/g) | 文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1K/HZ-280 | K, 1% | — | -0.02 | — | — | — | — | [ |
| ZSM-5-Cs | Cs, — | -0.86 | — | — | — | — | — | [ |
| Gd/HZSM-5 | Gd, 7.54% | 0.00 | -0.01 | — | +0.01 | -0.17 | -0.01 | [ |
| 0.5Fe/H-ZSM-5 | Fe, 0.5% | -0.22 | -0.07 | -0.03 | -0.11 | — | — | [ |
| 0.5Cu/H-ZSM-5 | Cu, 0.5% | -0.16 | -0.04 | -0.04 | -0.07 | — | — | [ |
| 0.5Ni/H-ZSM-5 | Ni, 0.5% | -0.17 | -0.06 | +0.04 | -0.14 | — | — | [ |
| Zr-Z5 | Zr, — | -0.12 | -0.06 | — | -0.06 | -0.19 | +0.07 | [ |
| Ag-Z5 | Ag, — | -0.30 | -0.38 | — | +0.08 | -1.56 | +1.26 | [ |
| Au/ZSM-5-8.5 | Au, 0.5% | -0.02 | +0.01 | -0.02 | -0.01 | — | — | [ |
| 0.5%Au/ZSM-5 | Au, 0.5% | -0.02 | -0.01 | 0.00 | -0.01 | — | — | [ |
| 0.5%Au/2.0%La-ZSM-5 | Au, 0.5%; La, 2.0% | -0.05 | -0.01 | -0.02 | -0.02 | — | — | [ |
表3 不同金属改性ZSM-5分子筛的酸性质
Table 3 The acid properties of different metal modified ZSM-5 zeolites
| 催化剂 | 改性金属及含量 (质量分数) | Δ总酸量/(mmol/g) | Δ弱酸量/(mmol/g) | Δ中强酸量/(mmol/g) | Δ强酸量/(mmol/g) | ΔB酸量/(mmol/g) | ΔL酸量/(mmol/g) | 文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1K/HZ-280 | K, 1% | — | -0.02 | — | — | — | — | [ |
| ZSM-5-Cs | Cs, — | -0.86 | — | — | — | — | — | [ |
| Gd/HZSM-5 | Gd, 7.54% | 0.00 | -0.01 | — | +0.01 | -0.17 | -0.01 | [ |
| 0.5Fe/H-ZSM-5 | Fe, 0.5% | -0.22 | -0.07 | -0.03 | -0.11 | — | — | [ |
| 0.5Cu/H-ZSM-5 | Cu, 0.5% | -0.16 | -0.04 | -0.04 | -0.07 | — | — | [ |
| 0.5Ni/H-ZSM-5 | Ni, 0.5% | -0.17 | -0.06 | +0.04 | -0.14 | — | — | [ |
| Zr-Z5 | Zr, — | -0.12 | -0.06 | — | -0.06 | -0.19 | +0.07 | [ |
| Ag-Z5 | Ag, — | -0.30 | -0.38 | — | +0.08 | -1.56 | +1.26 | [ |
| Au/ZSM-5-8.5 | Au, 0.5% | -0.02 | +0.01 | -0.02 | -0.01 | — | — | [ |
| 0.5%Au/ZSM-5 | Au, 0.5% | -0.02 | -0.01 | 0.00 | -0.01 | — | — | [ |
| 0.5%Au/2.0%La-ZSM-5 | Au, 0.5%; La, 2.0% | -0.05 | -0.01 | -0.02 | -0.02 | — | — | [ |
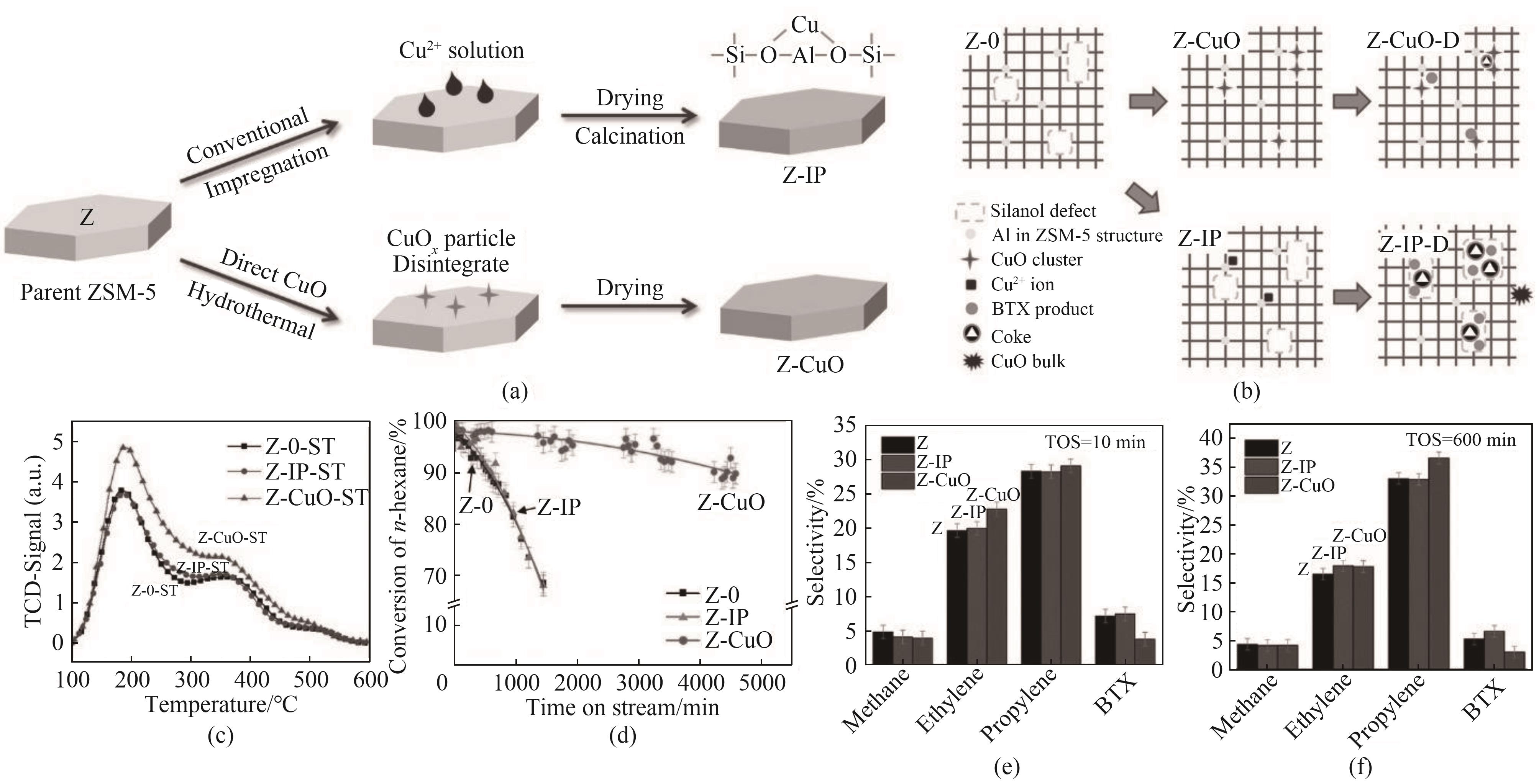
图7 (a)CuO x /ZSM-5复合催化剂的制备;(b)不同样品的微结构及失活行为;(c)不同样品的NH3-TPD曲线;(d)~(f)不同样品的催化裂解反应性能[108]
Fig.7 (a) Schematic of the preparation process of the CuO x /ZSM-5 catalyst; (b) The microstructure and deactivation behavior of different samples; (c) The NH3-TPD profiles of different samples; (d)—(f) The catalytic performance of different samples[108]
| 1 | Meng X H, Gao J S, Li L, et al. Advances in catalytic pyrolysis of hydrocarbons[J]. Petroleum Science and Technology, 2004, 22(9/10): 1327-1341. |
| 2 | Sadrameli S M. Thermal/catalytic cracking of liquid hydrocarbons for the production of olefins: a state-of-the-art review (Ⅱ): Catalytic cracking review[J]. Fuel, 2016, 173: 285-297. |
| 3 | 王洪华, 孙丽媛, 邢隆飞, 等. ZSM-5分子筛上轻烃裂解性能: 晶粒尺寸的影响[J]. 化工学报, 2015, 66(10): 3940-3949. |
| Wang H H, Sun L Y, Xing L F, et al. Transformation of light hydrocarbons to olefins: effect of ZSM-5 zeolites crystal size[J]. CIESC Journal, 2015, 66(10): 3940-3949. | |
| 4 | 唐勖尧, 王拴紧, 肖敏, 等. 重质油催化裂解制轻烯烃技术及催化剂研究进展[J]. 当代化工, 2020, 49(4): 620-625. |
| Tang X Y, Wang S J, Xiao M, et al. Research progress in heavy oil catalytic pyrolysis technology for light olefins and its catalysts[J]. Contemporary Chemical Industry, 2020, 49(4): 620-625. | |
| 5 | Auepattana-Aumrung C, Suriye K, Jongsomjit B, et al. Inhibition effect of Na+ form in ZSM-5 zeolite on hydrogen transfer reaction via 1-butene cracking[J]. Catalysis Today, 2020, 358: 237-245. |
| 6 | Peng P, Gao X H, Yan Z F, et al. Diffusion and catalyst efficiency in hierarchical zeolite catalysts[J]. National Science Review, 2020, 7(11): 1726-1742. |
| 7 | Xie Z K, Liu Z C, Wang Y D, et al. Applied catalysis for sustainable development of chemical industry in China[J]. National Science Review, 2015, 2(2): 167-182. |
| 8 | Cnudde P, de Wispelaere K, van der Mynsbrugge J, et al. Effect of temperature and branching on the nature and stability of alkene cracking intermediates in H-ZSM-5[J]. Journal of Catalysis, 2017, 345: 53-69. |
| 9 | 张燕, 沈凯旭, 滕加伟. 烯烃催化裂解技术研究进展[J]. 化学反应工程与工艺, 2021, 37(2): 181-192. |
| Zhang Y, Shen K X, Teng J W. Review of the olefin catalytic cracking technology[J]. Chemical Reaction Engineering and Technology, 2021, 37(2): 181-192. | |
| 10 | Liu X L, Shi J, Yang G, et al. A diffusion anisotropy descriptor links morphology effects of H-ZSM-5 zeolites to their catalytic cracking performance[J]. Communications Chemistry, 2021, 4: 107. |
| 11 | Liu Y H, Zhang Q, Li J Y, et al. Protozeolite-seeded synthesis of single-crystalline hierarchical zeolites with facet-shaped mesopores and their catalytic application in methanol-to-propylene conversion[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2022, 61(34): e202205716. |
| 12 | Zhao D, Tian X X, Doronkin D E, et al. In situ formation of ZnO x species for efficient propane dehydrogenation[J]. Nature, 2021, 599: 234-238. |
| 13 | Shi J, Wang Y D, Yang W M, et al. Recent advances of pore system construction in zeolite-catalyzed chemical industry processes[J]. Chemical Society Reviews, 2015, 44(24): 8877-8903. |
| 14 | Bai Y E, Zhang G H, Liu D Y, et al. The advance in catalytic pyrolysis of naphtha technology using ZSM-5 as catalyst[J]. Applied Catalysis A: General, 2021, 628: 118399. |
| 15 | Rahimi N, Karimzadeh R. Catalytic cracking of hydrocarbons over modified ZSM-5 zeolites to produce light olefins: a review[J]. Applied Catalysis A: General, 2011, 398(1/2): 1-17. |
| 16 | Inagaki S, Takechi K, Kubota Y. Selective formation of propylene by hexane cracking over MCM-68 zeolite catalyst[J]. Chemical Communications, 2010, 46(15): 2662-2664. |
| 17 | Corma A, Planelles J, Sánchez-Marín J, et al. The role of different types of acid site in the cracking of alkanes on zeolite catalysts[J]. Journal of Catalysis, 1985, 93(1): 30-37. |
| 18 | Wielers A F H, Vaarkamp M, Post M F M. Relation between properties and performance of zeolites in paraffin cracking[J]. Journal of Catalysis, 1991, 127(1): 51-66. |
| 19 | Yamaguchi A, Jin D F, Ikeda T, et al. Deactivation of ZSM-5 zeolite during catalytic steam cracking of n-hexane[J]. Fuel Processing Technology, 2014, 126: 343-349. |
| 20 | Hou X, Zhao L, Diao Z H. Roles of alkenes and coke formation in the deactivation of ZSM-5 zeolites during n-pentane catalytic cracking[J]. Catalysis Letters, 2020, 150(9): 2716-2725. |
| 21 | Javaid R, Urata K, Furukawa S, et al. Factors affecting coke formation on H-ZSM-5 in naphtha cracking[J]. Applied Catalysis A: General, 2015, 491: 100-105. |
| 22 | Urata K, Furukawa S, Komatsu T. Location of coke on H-ZSM-5 zeolite formed in the cracking of n-hexane[J]. Applied Catalysis A: General, 2014, 475: 335-340. |
| 23 | Nakasaka Y, Nishimura J I, Tago T, et al. Deactivation mechanism of MFI-type zeolites by coke formation during n-hexane cracking[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2015, 278: 159-165. |
| 24 | 胡思, 张卿, 巩雁军, 等. HZSM-5分子筛在甲醇制丙烯反应中的失活与再生[J]. 物理化学学报, 2016, 32(7): 1785-1794. |
| Hu S, Zhang Q, Gong Y J, et al. Deactivation and regeneration of HZSM-5 zeolite in methanol-to-propylene reaction[J]. Acta Physico-Chimica Sinica, 2016, 32(7): 1785-1794. | |
| 25 | Zabihpour A, Ahmadpour J, Yaripour F. Strategies to control reversible and irreversible deactivation of ZSM-5 zeolite during the conversion of methanol to propylene (MTP): a review[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2023, 273: 118639. |
| 26 | Guan L J, Liu M Y, Liu H H, et al. Regionally spatial framework Al distribution in MFI channels and its impact on the n-butane cracking reaction pathways[J]. Fuel, 2023, 353: 129230. |
| 27 | Song J H, Chen P L, Kim S H, et al. Catalytic cracking of n-hexane over MoO2 [J]. Journal of Molecular Catalysis A: Chemical, 2002, 184(1/2): 197-202. |
| 28 | Xu Q H, Gong Y J, Xu W J, et al. Synthesis of high-silica EU-1 zeolite in the presence of hexamethonium ions: a seeded approach for inhibiting ZSM-48[J]. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 2011, 358(1): 252-260. |
| 29 | Kosinov N, Wijpkema A S G, Uslamin E, et al. Confined carbon mediating dehydroaromatization of methane over Mo/ZSM-5[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2018, 57(4): 1016-1020. |
| 30 | Jin Z, Wang L, Zuidema E, et al. Hydrophobic zeolite modification for in situ peroxide formation in methane oxidation to methanol[J]. Science, 2020, 367(6474): 193-197. |
| 31 | Pop G, Ivanus G, Boteanu S, et al. Catalytic process for preparing olefins by hydrocarbon pyrolysis: US4172816[P]. 1979-10-30. |
| 32 | Wang S, Li Z K, Qin Z F, et al. Catalytic roles of the acid sites in different pore channels of H-ZSM-5 zeolite for methanol-to-olefins conversion[J]. Chinese Journal of Catalysis, 2021, 42(7): 1126-1136. |
| 33 | Xiao X, Zhang Y Y, Jiang G Y, et al. Simultaneous realization of high catalytic activity and stability for catalytic cracking of n-heptane on highly exposed (010) crystal planes of nanosheet ZSM-5 zeolite[J]. Chemical Communications, 2016, 52(65): 10068-10071. |
| 34 | 孙宇. ZSM-5分子筛微-介结构与酸性质调变及其反应性能[D]. 北京: 中国石油大学(北京), 2023. |
| Sun Y. Regulating ZSM-5 zeolite structural morphology and acid properties and its reactivity[D].Beijing: China University of Petroleum, 2023. | |
| 35 | Cui W H, Zhu D L, Tan J, et al. Synthesis of mesoporous high-silica zeolite Y and their catalytic cracking performance[J]. Chinese Journal of Catalysis, 2022, 43(7): 1945-1954. |
| 36 | 赵长斌, 周翔, 许昀, 等. 高丙烯低生焦催化裂解催化剂的工业应用[J]. 石油炼制与化工, 2022, 53(3): 37-40. |
| Zhao C B, Zhou X, Xu Y, et al. Commercial application of deep catalytic cracking catalyst for high propylene and low coke[J]. Petroleum Processing and Petrochemicals, 2022, 53(3): 37-40. | |
| 37 | Mavrovouniotis G M, Cheng W C, Peters A W. Role of hydrogen transfer in isobutene-isobutane selectivities[J]. ACS Symposium Series, 1994, 571: 16-23. |
| 38 | Al-Shafei E N, Albahar M Z, Aljishi M F, et al. Effect of zeolite structure and addition of steam on naphtha catalytic cracking to improve olefin production[J]. Fuel, 2022, 321: 124089. |
| 39 | Wang X Y, Ma Y, Wu Q M, et al. Zeolite nanosheets for catalysis[J]. Chemical Society Reviews, 2022, 51(7): 2431-2443. |
| 40 | Corma A, Martı́nez-Triguero J. The use of MCM-22 as a cracking zeolitic additive for FCC[J]. Journal of Catalysis, 1997, 165(1): 102-120. |
| 41 | Xu G L, Zhu X X, Niu X L, et al. One-pot synthesis of high silica MCM-22 zeolites and their performances in catalytic cracking of 1-butene to propene[J]. Microporous and Mesoporous Materials, 2009, 118(1/2/3): 44-51. |
| 42 | Meloni D, Martin D, Guisnet M. Acidic and catalytic properties of H-MCM-22 zeolites[J]. Applied Catalysis A: General, 2001, 215(1/2): 67-79. |
| 43 | Song Y, Liu S L, Wang Q X, et al. Coke burning behavior of a catalyst of ZSM-5/ZSM-11 co-crystallized zeolite in the alkylation of benzene with FCC off-gas to ethylbenzene[J]. Fuel Processing Technology, 2006, 87(4): 297-302. |
| 44 | Chen H L, Shen B J, Pan H F. In situ formation of ZSM-5 in NaY gel and characterization of ZSM-5/Y composite zeolite[J]. Chemistry Letters, 2003, 32(8): 726-727. |
| 45 | 巩雁军, 张亚飞, 孙丽媛, 等. 一种EU-1/ZSM-48共生分子筛及其制备和应用: 105000571A[P]. 2015-10-28. |
| Gong Y J, Zhang Y F, Sun L Y, et al. An EU-1/ZSM-48 intergrowth zeolite and its preparation and application: 105000571A[P]. 2015-10-28. | |
| 46 | Ryoo R, Park I S, Jun S, et al. Synthesis of ordered and disordered silicas with uniform pores on the border between micropore and mesopore regions using short double-chain surfactants[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2001, 123(8): 1650-1657. |
| 47 | Sun M H, Gao S S, Hu Z Y, et al. Boosting molecular diffusion following the generalized Murray's Law by constructing hierarchical zeolites for maximized catalytic activity[J]. National Science Review, 2022, 9(12): nwac236. |
| 48 | Li W L, Ma T, Zhang Y F, et al. Facile control of inter-crystalline porosity in the synthesis of size-controlled mesoporous MFI zeolites via in situ conversion of silica gel into zeolite nanocrystals for catalytic cracking[J]. CrystEngComm, 2015, 17(30): 5680-5689. |
| 49 | 王务刚, 张少龙, 张兰兰, 等. 系列硅铝比纳米薄层ZSM-5分子筛的合成和表征[J]. 物理化学学报, 2013, 29(9): 2035-2040. |
| Wang W G, Zhang S L, Zhang L L, et al. Synthesis and characterization of nanosheet ZSM-5 zeolites with different SiO2/Al2O3 molar ratios[J]. Acta Physico-Chimica Sinica, 2013, 29(9): 2035-2040. | |
| 50 | Wang J, Shan J W, Tian Y J, et al. Catalytic cracking of n-heptane over Fe modified HZSM-5 nanosheet to produce light olefins[J]. Fuel, 2021, 306: 121725. |
| 51 | Lin L F, Qiu C F, Zhuo Z X, et al. Acid strength controlled reaction pathways for the catalytic cracking of 1-butene to propene over ZSM-5[J]. Journal of Catalysis, 2014, 309: 136-145. |
| 52 | Zhou J, Teng J W, Ren L P, et al. Full-crystalline hierarchical monolithic ZSM-5 zeolites as superiorly active and long-lived practical catalysts in methanol-to-hydrocarbons reaction[J]. Journal of Catalysis, 2016, 340: 166-176. |
| 53 | Xu H, Wu P. New progress in zeolite synthesis and catalysis[J]. National Science Review, 2022, 9(9): nwac045. |
| 54 | Ma T, Zhang L M, Song Y, et al. A comparative synthesis of ZSM-5 with ethanol or TPABr template: distinction of Brønsted/Lewis acidity ratio and its impact on n-hexane cracking[J]. Catalysis Science & Technology, 2018, 8(7): 1923-1935. |
| 55 | Zhu J L, Yan S Y, Qian Y, et al. Fabrication of fluffy-ball like ZSM-5 zeolite and its application in hexane catalytic cracking[J]. Microporous and Mesoporous Materials, 2023, 351: 112465. |
| 56 | Pérez-Ramírez J, Christensen C H, Egeblad K, et al. Hierarchical zeolites: enhanced utilisation of microporous crystals in catalysis by advances in materials design[J]. Chemical Society Reviews, 2008, 37(11): 2530-2542. |
| 57 | Choi M, Na K, Kim J, et al. Stable single-unit-cell nanosheets of zeolite MFI as active and long-lived catalysts[J]. Nature, 2009, 461: 246-249. |
| 58 | Zhang X Y, Liu D X, Xu D D, et al. Synthesis of self-pillared zeolite nanosheets by repetitive branching[J]. Science, 2012, 336(6089): 1684-1687. |
| 59 | Zhang L L, Song Y, Li G D, et al. F-Assisted synthesis of a hierarchical ZSM-5 zeolite for methanol to propylene reaction: a b-oriented thinner dimensional morphology[J]. RSC Advances, 2015, 5(75): 61354-61363. |
| 60 | Hao J, Cheng D G, Chen F Q, et al. n-Heptane catalytic cracking on ZSM-5 zeolite nanosheets: effect of nanosheet thickness[J]. Microporous and Mesoporous Materials, 2021, 310: 110647. |
| 61 | Seo Y, Cho K, Jung Y, et al. Characterization of the surface acidity of MFI zeolite nanosheets by 31P NMR of adsorbed phosphine oxides and catalytic cracking of decalin[J]. ACS Catalysis, 2013, 3(4): 713-720. |
| 62 | Tian Y J, Qiu Y, Hou X, et al. Catalytic cracking of JP-10 over HZSM-5 nanosheets[J]. Energy & Fuels, 2017, 31(11): 11987-11994. |
| 63 | Zhang J X, Ren L M, Zhou A J, et al. Tailored synthesis of ZSM-5 nanosheets with controllable b-axis thickness and aspect ratio: strategy and growth mechanism[J]. Chemistry of Materials, 2022, 34(7): 3217-3226. |
| 64 | Zhu J L, Yan S Y, Xu G H, et al. Fabrication of sheet-like HZSM-5 zeolites with various SiO2/Al2O3 and process optimization in hexane catalytic cracking[J]. Journal of Solid State Chemistry, 2023, 318: 123772. |
| 65 | Tian Y J, Zhang B F, Liang H R, et al. Synthesis and performance of pillared HZSM-5 nanosheet zeolites for n-decane catalytic cracking to produce light olefins[J]. Applied Catalysis A: General, 2019, 572: 24-33. |
| 66 | Hao J, Xu S M, Cheng D G, et al. Synthesis of nanosheet epitaxial growth ZSM-5 zeolite with increased diffusivity and its catalytic cracking performance[J]. Catalysis Science & Technology, 2022, 12(12): 3912-3920. |
| 67 | Nakhaei Pour A, Mohammadi A. Kinetic study of the crystallization of ZSM-5 under organic template-free conditions[J]. Inorganic and Nano-Metal Chemistry, 2023, 53(1): 33-38. |
| 68 | Li F W, Wang X F, Gu H S, et al. Catalytic co-cracking of biomass and waste plastics with sawdust mediated ZSM-5 synthesized via activating gel process[J]. Fuel, 2023, 332: 126141. |
| 69 | Meng X J, Xiao F S. Green routes for synthesis of zeolites[J]. Chemical Reviews, 2014, 114(2): 1521-1543. |
| 70 | Shestakova D O, Babina K A, Sladkovskiy D A, et al. Seed-assisted synthesis of hierarchical zeolite ZSM-5 in the absence of organic templates[J]. Materials Chemistry and Physics, 2022, 288: 126432. |
| 71 | 唐贺. 晶种辅助合成ZSM-5分子筛及其应用性能[D]. 北京: 中国石油大学(北京), 2022. |
| Tang H. Seed-assisted synthesis of ZSM-5 zeolite and its application performance[D].Beijing: China University of Petroleum, 2022. | |
| 72 | Pan H H, Pan Q X, Zhao Y S, et al. A green and efficient synthesis of ZSM-5 using NaY as seed with mother liquid recycling and in the absence of organic template[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2010, 49(16): 7294-7302. |
| 73 | Pour A N, Mohammadi A. Effect of ZSM-5 zeolite porosity on catalytic cracking of n-heptane[J]. New Journal of Chemistry, 2022, 46(32): 15585-15595. |
| 74 | Zhang H Y, Wang L, Zhang D L, et al. Mesoporous and Al-rich MFI crystals assembled with aligned nanorods in the absence of organic templates[J]. Microporous and Mesoporous Materials, 2016, 233: 133-139. |
| 75 | Wu Q M, Meng X J, Gao X H, et al. Solvent-free synthesis of zeolites: mechanism and utility[J]. Accounts of Chemical Research, 2018, 51(6): 1396-1403. |
| 76 | Luo W, Yang X Y, Wang Z R, et al. Synthesis of ZSM-5 aggregates made of zeolite nanocrystals through a simple solvent-free method[J]. Microporous and Mesoporous Materials, 2017, 243: 112-118. |
| 77 | Gu Y, Wang X H, Qin Z X, et al. Intra-crystalline mesoporous ZSM-5 zeolite by grinding synthesis method[J]. Microporous and Mesoporous Materials, 2020, 306: 110437. |
| 78 | Qian M, Lei H W, Zhao Y F, et al. Lignin-mediated preparation of hierarchical ZSM-5 catalysts and their effects in the catalytic co-pyrolysis of softwood biomass and low-density polyethylene mixtures[J]. ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering, 2021, 9(37): 12602-12613. |
| 79 | Zhu T T, Liang H R, Zhang B F, et al. Controllably tailoring external surface sites of nanosheet HZSM-5 for maximizing light olefins in catalytic cracking of n-decane[J]. Chinese Journal of Chemical Engineering, 2021, 38: 276-285. |
| 80 | Zhang X X, Cheng D G, Chen F Q, et al. The role of external acidity of hierarchical ZSM-5 zeolites in n-heptane catalytic cracking[J]. ChemCatChem, 2018, 10(12): 2655-2663. |
| 81 | Epelde E, Gayubo A G, Olazar M, et al. Modified HZSM-5 zeolites for intensifying propylene production in the transformation of 1-butene[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2014, 251: 80-91. |
| 82 | Wakui K, Satoh K, Sawada G, et al. Cracking of n-butane over alkaline earth-containing HZSM-5 catalysts[J]. Catalysis Letters, 2002, 84(3): 259-264. |
| 83 | Ji Y J, Yang H H, Yan W. Effect of alkali metal cations modification on the acid/basic properties and catalytic activity of ZSM-5 in cracking of supercritical n-dodecane[J]. Fuel, 2019, 243: 155-161. |
| 84 | Wang X N, Zhao Z, Xu C M, et al. Effects of light rare earth on acidity and catalytic performance of HZSM-5 zeolite for catalytic cracking of butane to light olefins[J]. Journal of Rare Earths, 2007, 25(3): 321-328. |
| 85 | Tynjälä P, Pakkanen T T. Acidic properties of ZSM-5 zeolite modified with Ba2+, Al3+ and La3+ ion-exchange[J]. Journal of Molecular Catalysis A: Chemical, 1996, 110(2): 153-161. |
| 86 | 李延锋. 镧改性ZSM-5分子筛的结构、水热稳定性及其催化性能的理论研究[D]. 北京: 北京化工大学, 2011. |
| Li Y F. Theoretical study on the structure, hydrothermal stability and catalytic performance of La-modified ZSM-5 zeolite[D].Beijing: Beijing University of Chemical Technology, 2011. | |
| 87 | Auepattana-aumrung C, Praserthdam S, Wannakao S, et al. Observation of reduction on alkane products in butene cracking over ZSM-5 modified with Fe, Cu, and Ni catalysts[J]. Fuel, 2021, 291: 120265. |
| 88 | Li X F, Shen B J, Xu C M. Interaction of titanium and iron oxide with ZSM-5 to tune the catalytic cracking of hydrocarbons[J]. Applied Catalysis A: General, 2010, 375(2): 222-229. |
| 89 | Hou X, Qiu Y, Yuan E X, et al. Promotion on light olefins production through modulating the reaction pathways for n-pentane catalytic cracking over ZSM-5 based catalysts[J]. Applied Catalysis A: General, 2017, 543: 51-60. |
| 90 | Wang L X, Peng B, Zheng A G, et al. Mechanistic origin of transition metal modification on ZSM-5 zeolite for the ethylene yield enhancement from the primary products of n-octane cracking[J]. Journal of Catalysis, 2022, 416: 387-397. |
| 91 | Fu X P, Guo L W, Wang W W, et al. Direct identification of active surface species for the water-gas shift reaction on a gold-ceria catalyst[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2019, 141(11): 4613-4623. |
| 92 | Qi C X, Wang Y X, Ding X T, et al. Catalytic cracking of light diesel over Au/ZSM-5 catalyst for increasing propylene production[J]. Chinese Journal of Catalysis, 2016, 37(10): 1747-1754. |
| 93 | Zhang M, Liu Q, Long H A, et al. Insights into Au nanoparticle size and chemical state of Au/ZSM-5 catalyst for catalytic cracking of n-octane to increase propylene production[J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2021, 125(29): 16013-16023. |
| 94 | Liu Q, Zhang M, Sun L B, et al. The performance of catalytic conversion of ZSM-5 comodified with gold and lanthanum for increasing propylene production[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2019, 58(32): 14695-14704. |
| 95 | Chen K, Wu X Q, Zhao J Y, et al. Organic-free modulation of the framework Al distribution in ZSM-5 zeolite by magnesium participated synthesis and its impact on the catalytic cracking reaction of alkanes[J]. Journal of Catalysis, 2022, 413: 735-750. |
| 96 | Li C G, Vidal-Moya A, Miguel P J, et al. Selective introduction of acid sites in different confined positions in ZSM-5 and its catalytic implications[J]. ACS Catalysis, 2018, 8(8): 7688-7697. |
| 97 | Pham T N, Nguyen V, Nguyen-Phu H, et al. Influence of Brønsted acid site proximity on alkane cracking in MFI zeolites[J]. ACS Catalysis, 2023, 13(2): 1359-1370. |
| 98 | He X Y, Tian Y J, Guo L H, et al. Fabrication of extra-framework Al in ZSM-5 to enhance light olefins production in catalytic cracking of n-pentane[J]. Journal of Analytical and Applied Pyrolysis, 2022, 165: 105550. |
| 99 | Blasco T, Corma A, Martínez-Triguero J. Hydrothermal stabilization of ZSM-5 catalytic-cracking additives by phosphorus addition[J]. Journal of Catalysis, 2006, 237(2): 267-277. |
| 100 | Lv J, Hua Z L, Ge T G, et al. Phosphorus modified hierarchically structured ZSM-5 zeolites for enhanced hydrothermal stability and intensified propylene production from 1-butene cracking[J]. Microporous and Mesoporous Materials, 2017, 247: 31-37. |
| 101 | Degnan T F, Chitnis G K, Schipper P H. History of ZSM-5 fluid catalytic cracking additive development at Mobil[J]. Microporous and Mesoporous Materials, 2000, 35/36: 245-252. |
| 102 | Zhao Y, Liu J X, Xiong G, et al. Enhancing hydrothermal stability of nano-sized HZSM-5 zeolite by phosphorus modification for olefin catalytic cracking of full-range FCC gasoline[J]. Chinese Journal of Catalysis, 2017, 38(1): 138-145. |
| 103 | Xue N H, Chen X K, Nie L, et al. Understanding the enhancement of catalytic performance for olefin cracking: hydrothermally stable acids in P/HZSM-5[J]. Journal of Catalysis, 2007, 248(1): 20-28. |
| 104 | Li J W, Li T, Ma H F, et al. Effect of impregnating Fe into P-modified HZSM-5 in the coupling cracking of butene and pentene[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2015, 54(6): 1796-1805. |
| 105 | Li J W, Ma H F, Sun Q W, et al. Effect of iron and phosphorus on HZSM-5 in catalytic cracking of 1-butene[J]. Fuel Processing Technology, 2015, 134: 32-38. |
| 106 | Li J W, Li T, Ma H F, et al. Effect of nickel on phosphorus modified HZSM-5 in catalytic cracking of butene and pentene[J]. Fuel Processing Technology, 2017, 159: 31-37. |
| 107 | Ravandi R, Khoshbin R, Karimzadeh R. Synthesis of free template ZSM-5 catalyst from rice husk ash and co-modified with lanthanum and phosphorous for catalytic cracking of naphtha[J]. Journal of Porous Materials, 2018, 25(2): 451-461. |
| 108 | Zhang L M, Gong Y J, Zhai Y L, et al. Creation of CuO x /ZSM-5 zeolite complex: healing defect sites and boosting acidic stability and catalytic activity[J]. Catalysis Science & Technology, 2020, 10(15): 4981-4989. |
| 109 | 商世明. 金属改性调控ZSM-5分子筛酸性和微结构及其催化裂解性能[D]. 北京: 中国石油大学(北京), 2021. |
| Shang S M. Metal modification of ZSM-5 zeolite regulating its acidity and microstructure for hexane catalytic cracking[D].Beijing: China University of Petroleum, 2021. | |
| 110 | 杨正康. ZSM-5分子筛的金属改性及其对烃类裂解性能的影响[D]. 北京: 中国石油大学(北京), 2022. |
| Yang Z K. Metal modification of ZSM-5 zeolite and its effect on hydrocarbon cracking performance[D].Beijing: China University of Petroleum, 2022. |
| [1] | 孟祥军, 花莹曦, 张长金, 张弛, 杨林睿, 杨若昔, 刘鉴漪, 许春建. 6N电子级氘气的制备与纯化技术研究[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(1): 377-390. |
| [2] | 张强, 王宪飞, 王凯, 骆广生, 路忠凯. 非金属催化剂在环氧化物和环状酸酐共聚中的研究进展[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(1): 60-73. |
| [3] | 王欣雨, 王永涛, 姚加, 李浩然. 电子顺磁共振技术在化工基础研究中的应用进展[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(1): 74-82. |
| [4] | 咸国义, 陈立芳, 漆志文. 基于DFT的环己酮肟液相贝克曼重排机理研究[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(1): 302-311. |
| [5] | 王雪杰, 崔国庆, 王文涵, 杨扬, 王淙恺, 姜桂元, 徐春明. 电内加热Pt/NPC催化剂高效催化甲基环己烷脱氢反应研究[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(1): 292-301. |
| [6] | 张家琳, 徐大为, 高越, 李新刚. 泡沫镍负载CeO2改性CuO催化剂的碳烟燃烧性能研究[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(1): 312-321. |
| [7] | 李艺彤, 郭航, 陈浩, 叶芳. 催化剂非均匀分布的质子交换膜燃料电池操作条件研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(9): 3831-3840. |
| [8] | 范孝雄, 郝丽芳, 范垂钢, 李松庚. LaMnO3/生物炭催化剂低温NH3-SCR催化脱硝性能研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(9): 3821-3830. |
| [9] | 杨学金, 杨金涛, 宁平, 王访, 宋晓双, 贾丽娟, 冯嘉予. 剧毒气体PH3的干法净化技术研究进展[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(9): 3742-3755. |
| [10] | 吴雷, 刘姣, 李长聪, 周军, 叶干, 刘田田, 朱瑞玉, 张秋利, 宋永辉. 低阶粉煤催化微波热解制备含碳纳米管的高附加值改性兰炭末[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(9): 3956-3967. |
| [11] | 程业品, 胡达清, 徐奕莎, 刘华彦, 卢晗锋, 崔国凯. 离子液体基低共熔溶剂在转化CO2中的应用[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(9): 3640-3653. |
| [12] | 陈杰, 林永胜, 肖恺, 杨臣, 邱挺. 胆碱基碱性离子液体催化合成仲丁醇性能研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(9): 3716-3730. |
| [13] | 杨菲菲, 赵世熙, 周维, 倪中海. Sn掺杂的In2O3催化CO2选择性加氢制甲醇[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(8): 3366-3374. |
| [14] | 李凯旋, 谭伟, 张曼玉, 徐志豪, 王旭裕, 纪红兵. 富含零价钴活性位点的钴氮碳/活性炭设计及甲醛催化氧化应用研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(8): 3342-3352. |
| [15] | 杨欣, 彭啸, 薛凯茹, 苏梦威, 吴燕. 分子印迹-TiO2光电催化降解增溶PHE废水性能研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(8): 3564-3571. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备 11010102001995号
京公网安备 11010102001995号