化工学报 ›› 2024, Vol. 75 ›› Issue (10): 3507-3517.DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20240494
收稿日期:2024-05-06
修回日期:2024-06-26
出版日期:2024-10-25
发布日期:2024-11-04
通讯作者:
吴晅
作者简介:吴晅(1976—),男,博士,教授,wxgif@163.com
基金资助:
Xuan WU( ), Xiaofeng LI, Hui DONG, Gaojin SUN, Xiaopei LIU, Zhengyang WANG
), Xiaofeng LI, Hui DONG, Gaojin SUN, Xiaopei LIU, Zhengyang WANG
Received:2024-05-06
Revised:2024-06-26
Online:2024-10-25
Published:2024-11-04
Contact:
Xuan WU
摘要:
利用高速摄像技术研究载颗粒气泡上升行为特性,引入颗粒黏附率定量表征气泡的颗粒黏附量,用聚甲基丙烯酸甲酯 (PMMA) 颗粒物料作为颗粒床层基本材料,观察在不同粒径和不同流量下气泡颗粒黏附率的变化过程,分析载颗粒的气泡形态、气泡尺寸、气泡垂直上升速度的变化规律,揭示了载颗粒气泡的上升行为特性。研究结果表明:颗粒粒径300 μm条件下流量增大会使气泡负载颗粒量减小,导致颗粒黏附率降低,但粒径的减小可以有效抵消流量增大对颗粒黏附率的影响;在较大粒径条件下,颗粒黏附率越大,气泡形态越稳定,气泡整体尺寸越小,气泡垂直上升速度越低;减小载颗粒粒径可以减弱流量对气泡的形态、尺寸和垂直上升速度的影响;颗粒黏附率近似的气泡,颗粒粒径的减小会增加异形气泡的产出。
中图分类号:
吴晅, 李晓峰, 董慧, 孙高瑾, 刘孝培, 王正阳. 颗粒黏附率对载颗粒气泡上升行为特性的实验研究[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(10): 3507-3517.
Xuan WU, Xiaofeng LI, Hui DONG, Gaojin SUN, Xiaopei LIU, Zhengyang WANG. Experimental study of characteristics of particle adhesion rate on rising behavior of particle-loaded bubbles[J]. CIESC Journal, 2024, 75(10): 3507-3517.
| 折射率 | 硬度 | 拉伸强度 | 断裂伸长率 | 弯曲强度 | 热变形稳定温度 | 玻璃化温度 | 透光率 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1.49 | 25~28 | 50~77 MPa | 2%~3% | 90~130 MPa | 96℃ | 104℃ | >92% |
表1 PMMA材料的物理特性
Table 1 Physical properties of PMMA materials
| 折射率 | 硬度 | 拉伸强度 | 断裂伸长率 | 弯曲强度 | 热变形稳定温度 | 玻璃化温度 | 透光率 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1.49 | 25~28 | 50~77 MPa | 2%~3% | 90~130 MPa | 96℃ | 104℃ | >92% |
| 气泡初始直径 | 密度 | 黏度 | 界面张力 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2~8 mm | 1.225 kg/m3 | 1.789×10-5 Pa∙s | 0.09 N/m |
表2 气相物理性质
Table 2 Physical properties of gas phase
| 气泡初始直径 | 密度 | 黏度 | 界面张力 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2~8 mm | 1.225 kg/m3 | 1.789×10-5 Pa∙s | 0.09 N/m |
| 粒径/μm | 流量/(ml/min) | 黏附率/% | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1号气泡 | 2号气泡 | 3号气泡 | 4号气泡 | 5号气泡 | ||
| 300 | 38 (A组) | 77.60 | 100.00 | 100.00 | 100.00 | 9.68 |
| 76 (B组) | 100.00 | 46.77 | 8.36 | 11.96 | 24.54 | |
| 114 (C组) | 55.23 | 20.57 | 14.76 | 51.31 | 6.18 | |
| 152 (D组) | 23.07 | 16.17 | 5.33 | 7.00 | 5.60 | |
| 190 (E组) | 19.45 | 16.34 | 13.16 | 9.69 | 14.03 | |
| 200 | 38 (A组) | 39.93 | 100.00 | 21.34 | 13.92 | 100.00 |
| 76 (B组) | 31.75 | 100.00 | 9.10 | 100.00 | 8.29 | |
| 114 (C组) | 22.05 | 20.34 | 28.42 | 33.91 | 100.00 | |
| 152 (D组) | 9.26 | 10.76 | 9.75 | 8.79 | 100.00 | |
| 190 (E组) | 26.49 | 100.00 | 100.00 | 11.83 | 13.50 | |
| 100 | 38 (A组) | 72.46 | 100.00 | 14.55 | 100.00 | 100.00 |
| 76 (B组) | 56.46 | 63.29 | 62.88 | 100.00 | 9.48 | |
| 114 (C组) | 1.18 | 78.05 | 100.00 | 18.33 | 100.00 | |
| 152 (D组) | 18.85 | 71.03 | 100.00 | 18.61 | 100.00 | |
| 190 (E组) | 43.43 | 72.27 | 100.00 | 47.87 | 13.92 | |
表3 颗粒黏附率统计数值
Table 3 Statistical values of particle adhesion rate
| 粒径/μm | 流量/(ml/min) | 黏附率/% | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1号气泡 | 2号气泡 | 3号气泡 | 4号气泡 | 5号气泡 | ||
| 300 | 38 (A组) | 77.60 | 100.00 | 100.00 | 100.00 | 9.68 |
| 76 (B组) | 100.00 | 46.77 | 8.36 | 11.96 | 24.54 | |
| 114 (C组) | 55.23 | 20.57 | 14.76 | 51.31 | 6.18 | |
| 152 (D组) | 23.07 | 16.17 | 5.33 | 7.00 | 5.60 | |
| 190 (E组) | 19.45 | 16.34 | 13.16 | 9.69 | 14.03 | |
| 200 | 38 (A组) | 39.93 | 100.00 | 21.34 | 13.92 | 100.00 |
| 76 (B组) | 31.75 | 100.00 | 9.10 | 100.00 | 8.29 | |
| 114 (C组) | 22.05 | 20.34 | 28.42 | 33.91 | 100.00 | |
| 152 (D组) | 9.26 | 10.76 | 9.75 | 8.79 | 100.00 | |
| 190 (E组) | 26.49 | 100.00 | 100.00 | 11.83 | 13.50 | |
| 100 | 38 (A组) | 72.46 | 100.00 | 14.55 | 100.00 | 100.00 |
| 76 (B组) | 56.46 | 63.29 | 62.88 | 100.00 | 9.48 | |
| 114 (C组) | 1.18 | 78.05 | 100.00 | 18.33 | 100.00 | |
| 152 (D组) | 18.85 | 71.03 | 100.00 | 18.61 | 100.00 | |
| 190 (E组) | 43.43 | 72.27 | 100.00 | 47.87 | 13.92 | |
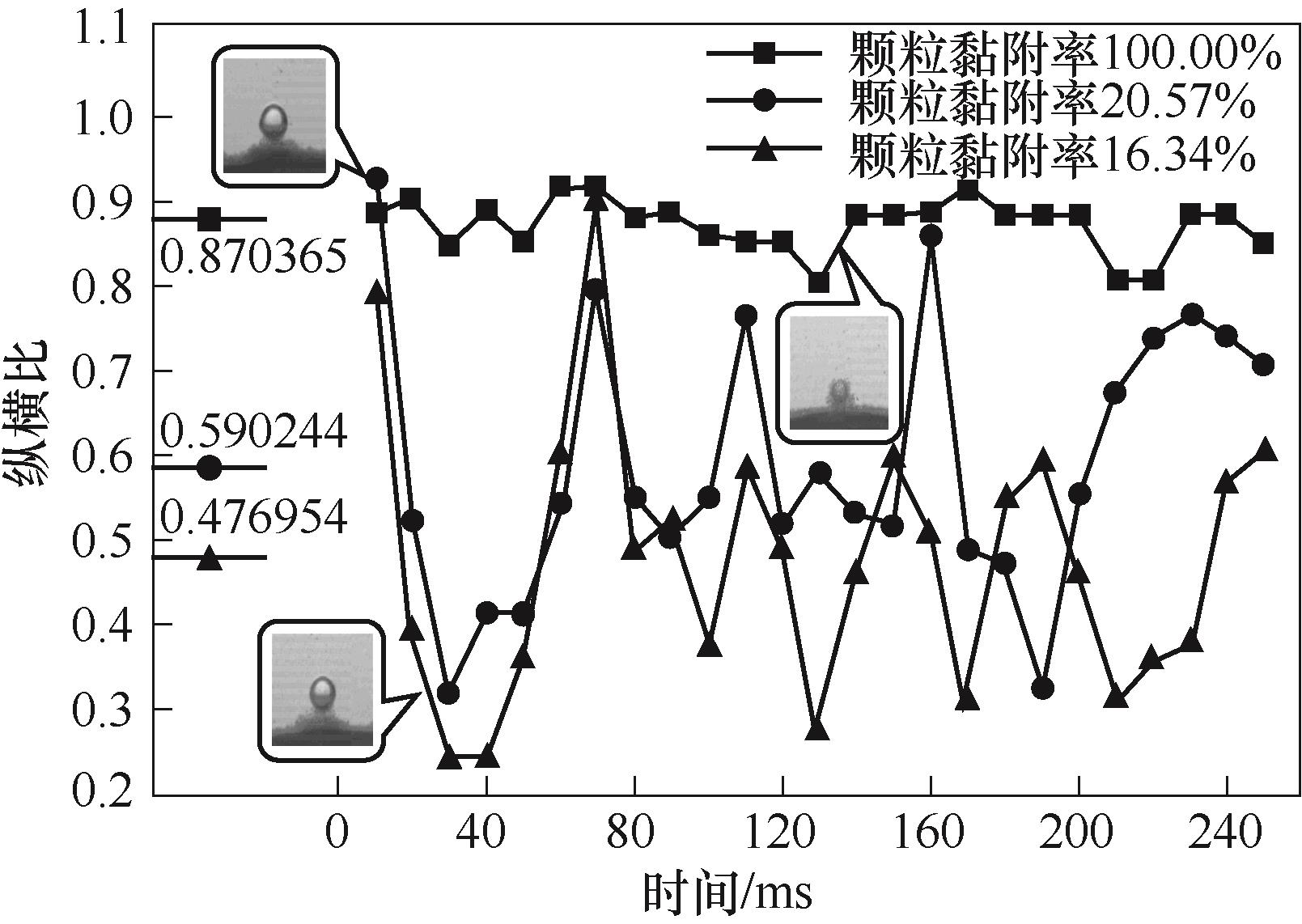
图7 粒径300 μm,颗粒黏附率分别为100.00%、20.57%、16.34% (2号气泡) 的纵横比变化
Fig.7 Aspect ratio changes for a particle size of 300 μm with adhesion rates of 100.00%, 20.57% and 16.34% (bubble 2)
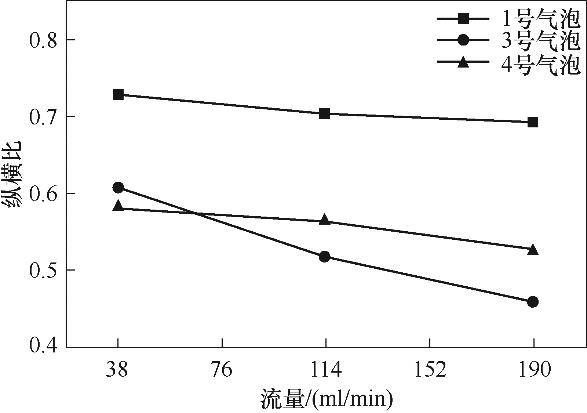
图8 粒径300 μm,颗粒黏附率递减的1、3、4号气泡的纵横比平均值变化
Fig.8 Mean aspect ratio changes of bubbles 1, 3 and 4 with decreasing particle adhesion rates for particle size of 300 μm
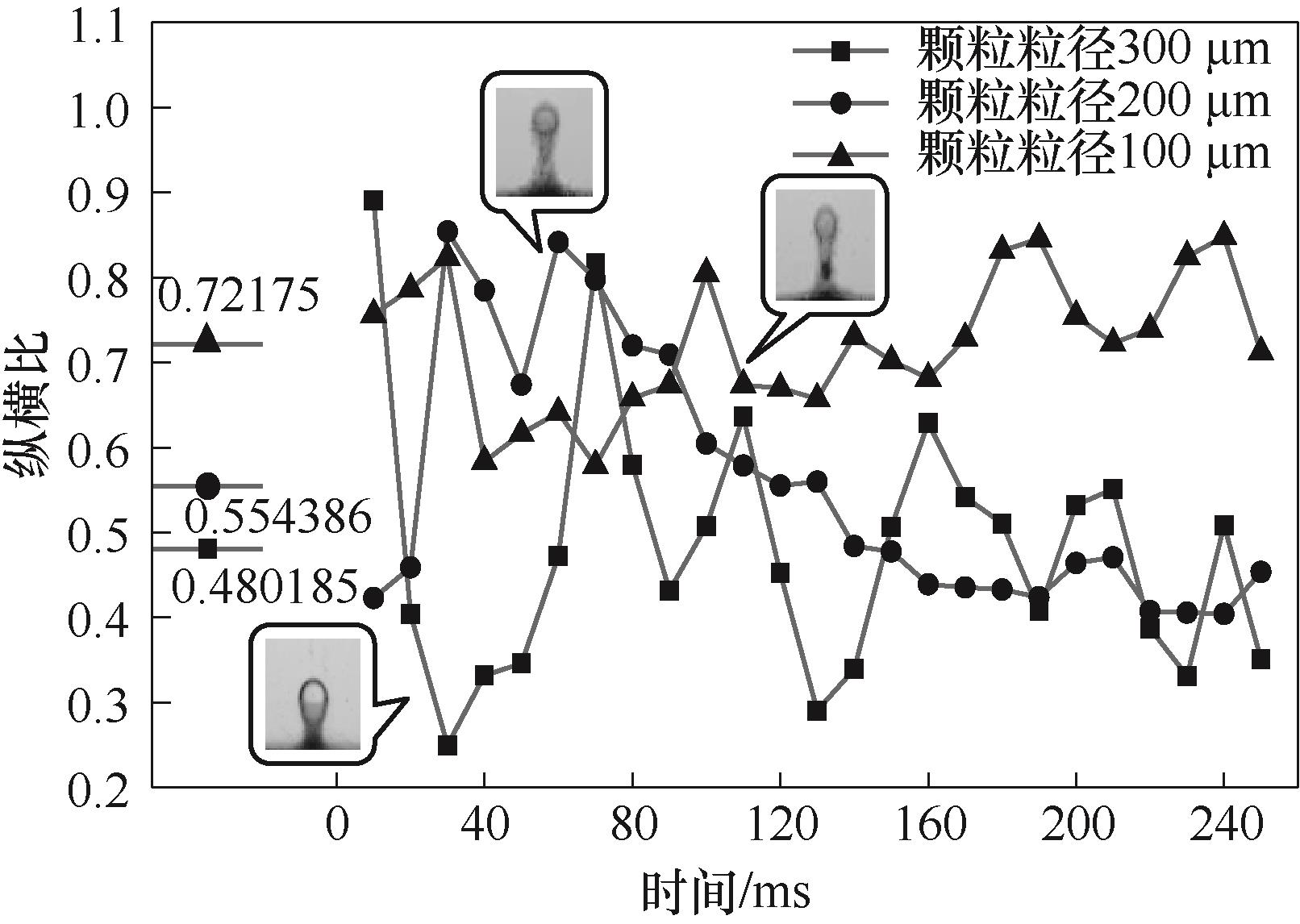
图10 3种粒径下颗粒黏附率分别为14.03%、13.50%、13.92% (5号气泡) 的纵横比变化
Fig.10 Aspect ratio changes in adhesion of 14.03%, 13.50% and 13.92% (bubble 5) for three particle sizes
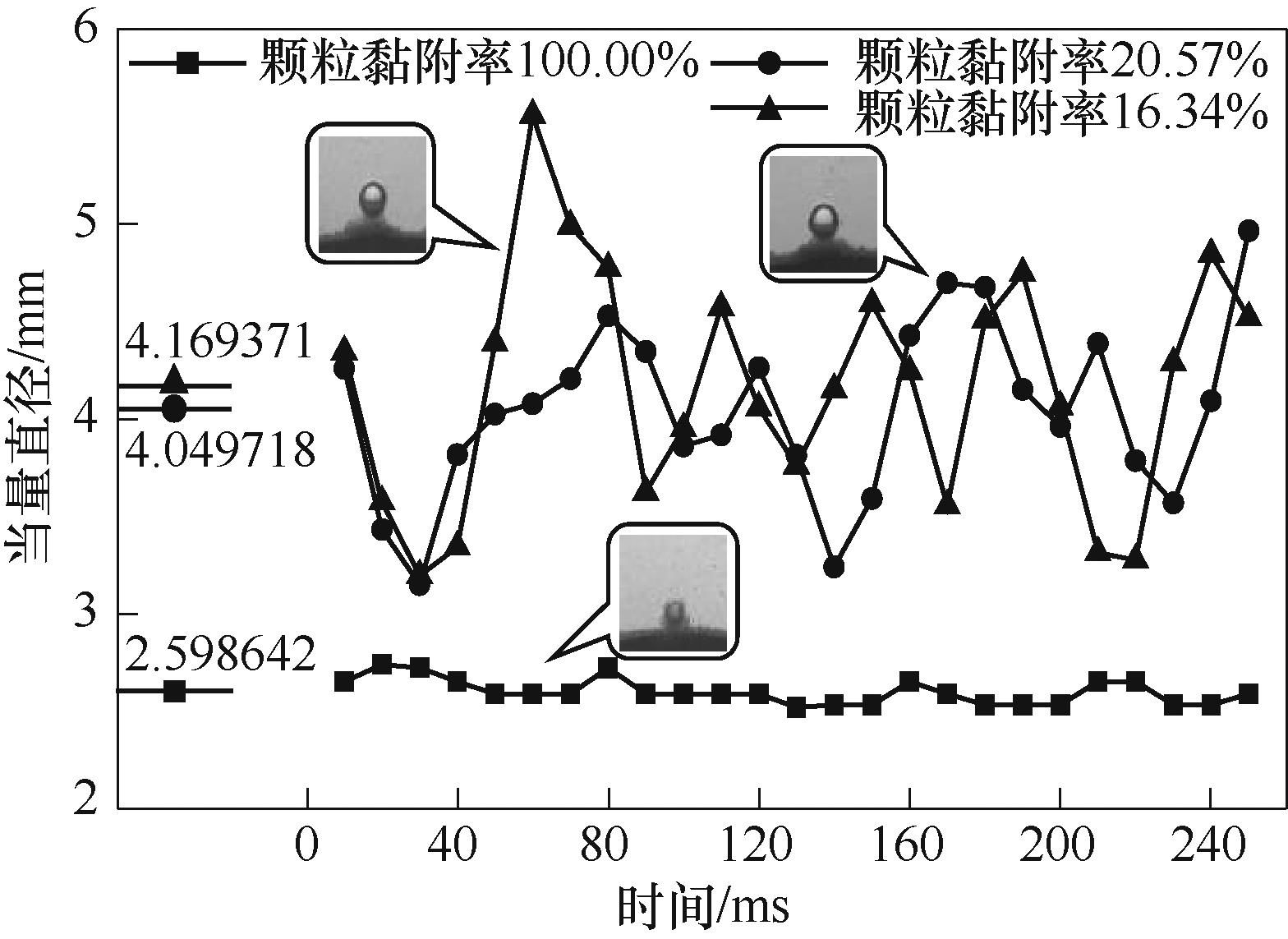
图11 粒径 300 μm,颗粒黏附率分别为100.00%、20.57%、16.34% (2号气泡)的当量直径变化
Fig.11 Equivalent diameter changes for a particle size of 300 μm with adhesion rates of 100.00%, 20.57% and 16.34% (bubble 2)
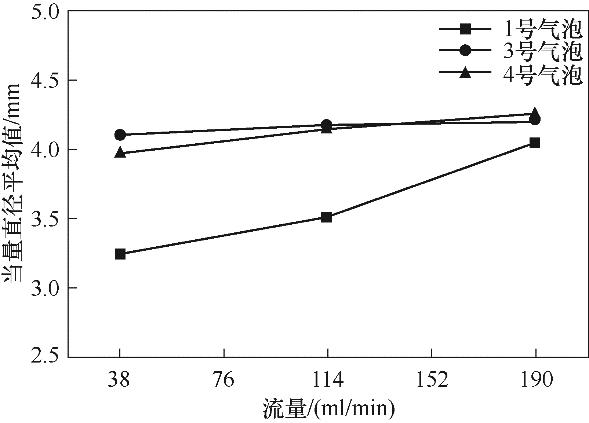
图12 粒径 300 μm,颗粒黏附率递减的1、3、4号气泡的当量直径平均值变化
Fig.12 Mean equivalent diameter changes of bubbles 1, 3 and 4 with decreasing particle adhesion rates for a particle size of 300 μm
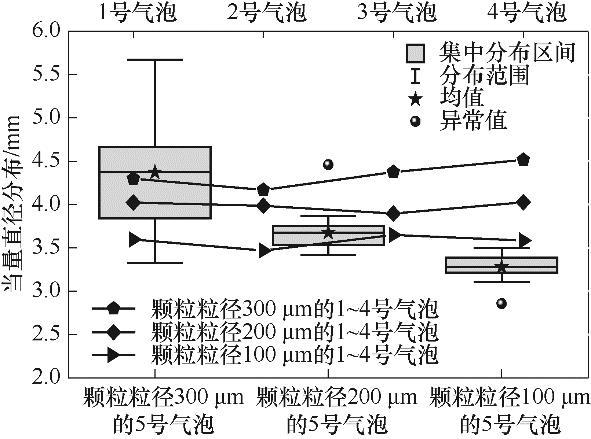
图14 3种粒径条件下颗粒黏附率分别为14.03%、13.50%、13.92% (5号气泡) 的当量直径分布
Fig.14 Equivalent diameter distributions of particle adhesion of 14.03%, 13.50% and 13.92% (bubble 5) for three particle sizes
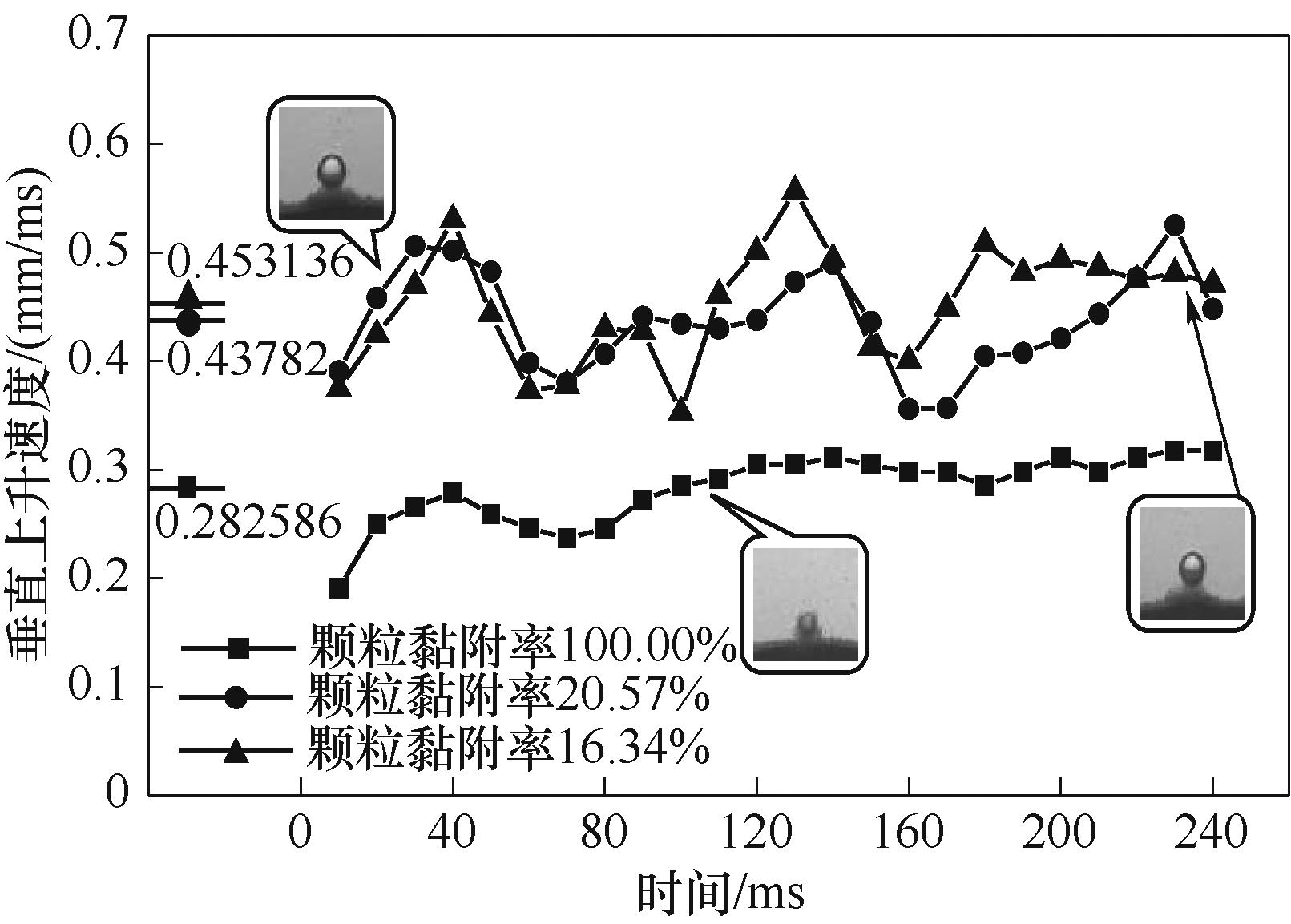
图15 粒径300 μm,颗粒黏附率分别为100.00%、20.57%、16.34%(2号气泡)的垂直上升速度变化
Fig.15 Vertical ascent speed changes for a particle size of 300 μm with adhesion rates of 100.00%, 20.57% and 16.34%
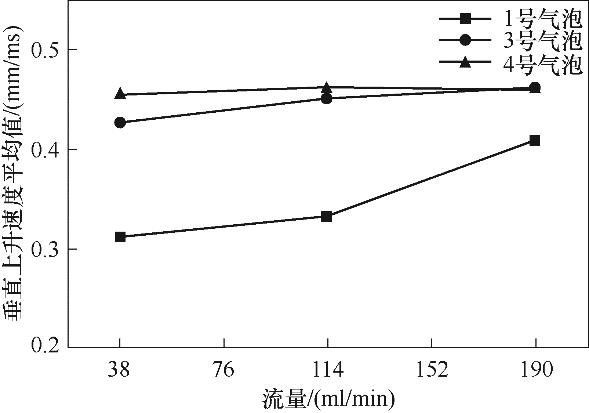
图16 粒径 300 μm,颗粒黏附率递减的1、3、4号气泡的垂直上升速度平均值变化
Fig.16 Mean vertical ascent speed changes of bubbles 1, 3 and 4 with decreasing particle adhesion rates for a particle size of 300 μm
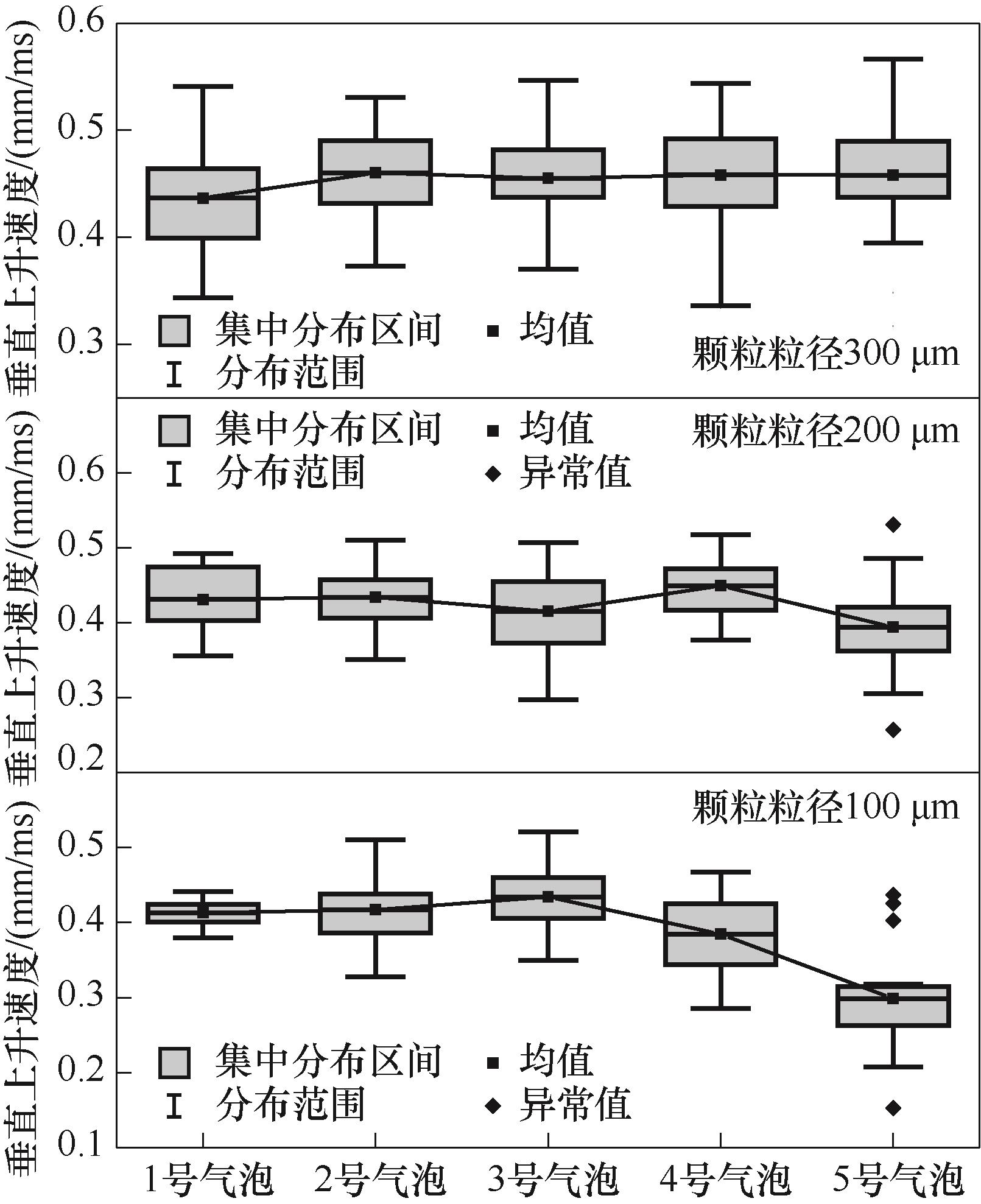
图18 3种粒径条件下颗粒黏附率分别为14.03%、13.50%、13.92% (5号气泡) 的垂直上升速度分布
Fig.18 Vertical upward velocity distributions of particle adhesion of 14.03%, 13.50% and 13.92% (bubble 5) for three particle sizes
| 1 | 曾金兰. 浮选原理在固体废物处理中的应用[J]. 中国资源综合利用, 2017, 35(10): 40-42. |
| Zeng J L. Application of flotation principle in solid waste treatment[J]. China Resources Comprehensive Utilization, 2017, 35(10): 40-42. | |
| 2 | 胡天佑, 唐瑾, 陈志莉. 石油工业含油废水处理进展[J]. 水处理技术, 2021, 47(6): 12-17. |
| Hu T Y, Tang J, Chen Z L. Progress of oily wastewater treatment in petroleum industry[J]. Technology of Water Treatment, 2021, 47(6): 12-17. | |
| 3 | 周梁源, 湛含辉. 石油工业含油废水处理工艺应用研究[J]. 黑龙江环境通报, 2022, 35(1): 72-73. |
| Zhou L Y, Zhan H H. Study on application of oily wastewater treatment process in petroleum industry[J]. Heilongjiang Environmental Journal, 2022, 35(1): 72-73. | |
| 4 | 王凯玥, 马永丽, 李琛, 等. 气液固微型流化床的气液传质系数[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(8): 3529-3540. |
| Wang K Y, Ma Y L, Li C, et al. Gas-liquid mass transfer coefficients in the gas-liquid-solid micro-fluidized beds[J]. CIESC Journal, 2022, 73(8): 3529-3540. | |
| 5 | 王永磊, 刘威, 田立平, 等. 气浮工艺中微纳米气泡应用特性与检测技术研究[J]. 工业水处理, 2020, 40(4): 18-23. |
| Wang Y L, Liu W, Tian L P, et al. Research progress on micro-nano bubble characteristics detection method and its application in air floatation process[J]. Industrial Water Treatment, 2020, 40(4): 18-23. | |
| 6 | Rajapakse N, Zargar M, Sen T, et al. Effects of influent physicochemical characteristics on air dissolution, bubble size and rise velocity in dissolved air flotation: a review[J]. Separation and Purification Technology, 2022, 289: 120772. |
| 7 | Li Y J, Liu M Y, Li X N. Single bubble behavior in gas-liquid-solid mini-fluidized beds[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2016, 286: 497-507. |
| 8 | 李美, 蒋昊, 刘志龙, 等. 浮选颗粒与气泡间动态作用过程研究进展[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2022, 32(6): 1796-1809. |
| Li M, Jiang H, Liu Z L, et al. Research progress of dynamic interaction process between flotation particles and bubbles[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2022, 32(6): 1796-1809. | |
| 9 | 张迎霜, 杨雅斌, 蒋鸿儒, 等. 环境诱导表面重构调控PVC和PET塑料的可浮性[J]. 中国环境科学, 2022, 42(2): 761-769. |
| Zhang Y S, Yang Y B, Jiang H R, et al. Regulating PVC and PET floatability based on surface reconstruction induced by environments[J]. China Environmental Science, 2022, 42(2): 761-769. | |
| 10 | 朱兆亮, 曹相生, 孟雪征, 等. 气浮净水工艺述评[J]. 环境科学与技术, 2008, 31(8): 55-58. |
| Zhu Z L, Cao X S, Meng X Z, et al. Review on air flotation technology for water and wastewater treatment[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2008, 31(8): 55-58. | |
| 11 | 石孝刚, 赵国静, 吴迎亚, 等. 挡板鼓泡床内气泡特性的CFD模拟分析[J]. 石油学报(石油加工), 2020, 36(1): 113-120. |
| Shi X G, Zhao G J, Wu Y Y, et al. CFD simulation of bubbles behavior in baffled bubbling fluidized bed[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica (Petroleum Processing Section), 2020, 36(1): 113-120. | |
| 12 | 郭士元. 复极性颗粒床电解槽处理有机废水改进研究[D]. 大连: 大连理工大学, 2006. |
| Guo S Y. Improvement of the treatment of organic wastewater by bipolar granulated bed cell[D]. Dalian: Dalian University of Technology, 2006. | |
| 13 | 魏楠, 吴晅, 薄宇轩, 等. 气泡在颗粒床层表面的生成脱离行为[J]. 化工进展, 2021, 40(2): 678-687. |
| Wei N, Wu X, Bo Y X, et al. Bubble formation and detachment behaviors on surface layer of packed particles[J]. Chemical Industry and Engineering Progress, 2021, 40(2): 678-687. | |
| 14 | Yoon R H, Mao L Q. Application of extended DLVO theory. Ⅳ Derivation of flotation rate equation from first principles[J]. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 1996, 181(2): 613-626. |
| 15 | Xia W C, Ma G X, Bu X N, et al. Effect of particle shape on bubble-particle attachment angle and flotation behavior of glass beads and fragments[J]. Powder Technology, 2018, 338: 168-172. |
| 16 | 胡晨辉, 王亦飞, 包泽彬, 等. 蒸发热水塔内固体颗粒对气泡运动的影响[J]. 化工学报, 2019, 70(1): 39-48. |
| Hu C H, Wang Y F, Bao Z B, et al. Effect of solid particles in evaporative hot water tower on bubble movement[J]. CIESC Journal, 2019, 70(1): 39-48. | |
| 17 | 苏巧玲, 王军锋, 张伟, 等. 低电导率工质中气泡的极化运动实验研究[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(9): 3861-3869. |
| Su Q L, Wang J F, Zhang W, et al. Experimental study on polarization motion characteristics of bubbles in a low conductivity working medium[J]. CIESC Journal, 2022, 73(9): 3861-3869. | |
| 18 | 朱恂, 谢建, 王宏, 等. 微小通道内液体扰流微孔逸出气泡串的迁移行为[J]. 化工学报, 2014, 65(10): 3805-3810. |
| Zhu X, Xie J, Wang H, et al. Migration behavior of bubble cluster emerging from micro-orifice with liquid cross flow in mini-channel[J]. CIESC Journal, 2014, 65(10): 3805-3810. | |
| 19 | 周宸, 林文博, 王勇军, 等. 黏性流体中气泡上升运动行为的实验研究[J]. 浙江理工大学学报(自然科学版), 2021, 45(6): 780-785. |
| Zhou C, Lin W B, Wang Y J, et al. Experimental study on the upward motion of bubbles in viscous fluids[J]. Journal of Zhejiang Sci-Tech University (Natural Sciences Edition), 2021, 45(6): 780-785. | |
| 20 | 申耀宗, 张巧荣, 赵凯, 等. 氧煤燃烧熔分炉熔池内射流行为规律的物理模拟[J]. 中国有色冶金, 2022, 51(3): 22-29, 42. |
| Shen Y Z, Zhang Q R, Zhao K, et al. Physical simulation of jet behavior rule in bath of oxygen coal combustion smelting-separation furnace[J]. China Nonferrous Metallurgy, 2022, 51(3): 22-29, 42. | |
| 21 | 李维仲, 张晓红, 董波, 等. 单气泡沿倾斜绝热表面运动特性的LBM方法研究[J]. 化工学报, 2013, 64(11): 3940-3948. |
| Li W Z, Zhang X H, Dong B, et al. Lattice Boltzmann simulation of moving characteristics of a single bubble rising along inclined adiabatic surface[J]. CIESC Journal, 2013, 64(11): 3940-3948. | |
| 22 | 赵莎. 微藻悬浮液中CO2气泡的动力学行为及固碳特性研究[D]. 重庆: 重庆大学, 2015. |
| Zhao S. CO2 bubble dynamic behaviors and carbon fixation in microalgae suspension[D]. Chongqing: Chongqing University, 2015. | |
| 23 | 金涌, 俞芷青, 张礼, 等. 采用激光示踪法观测流化床中气泡对固体颗粒运动的影响[J]. 化工学报, 1981, 32(1): 21-28. |
| Jin Y, Yu Z Q, Zhang L, et al. A study of particle movement in a gas-fluidized bed[J]. Journal of Chemical Industry and Engineering (China), 1981, 32(1): 21-28. | |
| 24 | 孙皓楠. 起泡剂作用下负载颗粒的单气泡运动特性实验研究[D]. 徐州: 中国矿业大学, 2021. |
| Sun H N. Experimental study on motion characteristic of single particle-loaded bubble in surfactant solution[D]. Xuzhou: China University of Mining and Technology, 2021. | |
| 25 | 粟文兵. 载颗粒气泡运动特性研究与曳力模型修正[D]. 徐州: 中国矿业大学, 2020. |
| Su W B. The motion characteristic study and drag model correction of the particle-laden bubbles[D]. Xuzhou: China University of Mining and Technology, 2020. | |
| 26 | Ireland P M, Jameson G J. Collision of a rising bubble-particle aggregate with a gas-liquid interface[J]. International Journal of Mineral Processing, 2014, 130: 1-7. |
| 27 | Wang P P, Cilliers J J, Neethling S J, et al. The behavior of rising bubbles covered by particles[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2019, 365: 111-120. |
| 28 | Hoque M M, Peng Z B, Evans G, et al. Influence of bubble surface loading on particle-laden bubble rising dynamics in a fluid flow system[J]. Minerals Engineering, 2023, 195: 108043. |
| 29 | Yang H C, Xing Y W, Sun L J, et al. Kinetics of bubble-particle attachment and detachment at a single-bubble scale[J]. Powder Technology, 2020, 370: 251-258. |
| 30 | Wang A, Hoque M M, Moreno-Atanasio R, et al. Effect of bubble surface loading on bubble rise velocity[J]. Minerals Engineering, 2021, 174: 107252. |
| 31 | 王超, 孙春宝, 寇珏. 浮选过程中颗粒-气泡黏附作用机理及研究进展[J]. 工程科学学报, 2018, 40(12): 1423-1433. |
| Wang C, Sun C B, Kou J. Mechanism and research progress of the bubble-particle attachment in flotation[J]. Chinese Journal of Engineering, 2018, 40(12): 1423-1433. | |
| 32 | 赵亮. 颗粒-气泡脱附界面行为和力学行为研究[D]. 北京: 中国矿业大学, 2021. |
| Zhao L. The study of interface behaviors and force behaviors during particle-bubble detachment[D]. Beijing: China University of Mining & Technology, 2021. |
| [1] | 罗欣怡, 徐强, 佘永璐, 聂腾飞, 郭烈锦. 光电分解水制氢气泡动力学特性及其传质机理研究[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(9): 3083-3093. |
| [2] | 唐昊, 胡定华, 李强, 张轩畅, 韩俊杰. 抗加速度双切线弧流道内气泡动力学行为数值与可视化研究[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(9): 3074-3082. |
| [3] | 王皓宇, 杨杨, 荆文婕, 杨斌, 唐雨, 刘毅. 不同旋流器作用下气液螺旋环状流动特性研究[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(8): 2744-2755. |
| [4] | 赵亮, 李雨桥, 张德, 沈胜强. 螺旋喷嘴内外流场特性的实验研究[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(8): 2777-2786. |
| [5] | 罗正航, 李敬宇, 陈伟雄, 种道彤, 严俊杰. 摇摆运动下低流率蒸汽冷凝换热特性和气泡受力数值模拟[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(8): 2800-2811. |
| [6] | 曲玖哲, 杨鹏, 杨绪飞, 张伟, 宇波, 孙东亮, 王晓东. 硅基微柱簇阵列微通道流动沸腾实验研究[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(8): 2840-2851. |
| [7] | 李彦熹, 王晔春, 谢向东, 王进芝, 王江, 周煜, 潘盈秀, 丁文涛, 郭烈锦. 蜗壳式多通道气液旋流分离器结构优化及分离特性研究[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(8): 2875-2885. |
| [8] | 吕方明, 包志铭, 王博文, 焦魁. 气体扩散层侵入流道对燃料电池水管理影响研究[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(8): 2929-2938. |
| [9] | 赵赫, 费滢洁, 朱春英, 付涛涛, 马友光. 高黏体系中纳米颗粒稳定气泡的形变及破裂行为[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(6): 2180-2189. |
| [10] | 李新泽, 张双星, 杨洪海, 杜文静. 基于电池冷却用新型脉动热管性能的实验研究[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(6): 2222-2232. |
| [11] | 师毓辉, 邢继远, 姜雪晗, 叶爽, 黄伟光. 基于PBM的离心式叶轮内气泡破碎合并数值模拟[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(5): 1816-1829. |
| [12] | 关朝阳, 黄国庆, 张一喃, 陈宏霞, 杜小泽. 泡沫铜导离气泡强化流动沸腾换热实验研究[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(5): 1765-1776. |
| [13] | 汪威, 白旭, 赵翔, 马学良, 林纬, 喻九阳. 基于响应面法的气浮旋流分离条件优化[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(5): 1929-1938. |
| [14] | 王娟, 李秀明, 邵炜涛, 丁续, 霍莹, 付连超, 白云宇, 李迪. 多孔板鼓泡塔流动与传质特性数值模拟[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(3): 801-814. |
| [15] | 陈思睿, 毕景良, 王雷, 李元媛, 陆规. 气液两相流流型特征无监督提取的卷积自编码器:机理及应用[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(3): 847-857. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备 11010102001995号
京公网安备 11010102001995号