化工学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 76 ›› Issue (10): 5290-5299.DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20250356
收稿日期:2025-04-08
修回日期:2025-05-31
出版日期:2025-10-25
发布日期:2025-11-25
通讯作者:
刘泽贤,邢卫红
作者简介:韩霜(2001—),女,硕士研究生,hans@njtech.edu.cn
Shuang HAN( ), Qiuyue WANG, Ze-Xian LOW(
), Qiuyue WANG, Ze-Xian LOW( ), Zhaoxiang ZHONG, Weihong XING(
), Zhaoxiang ZHONG, Weihong XING( )
)
Received:2025-04-08
Revised:2025-05-31
Online:2025-10-25
Published:2025-11-25
Contact:
Ze-Xian LOW, Weihong XING
摘要:
医疗领域广泛使用抗生素治疗感染性疾病,然而其高极性、低挥发性的理化特性导致废水中大量药物残留,进而引发环境-生态-健康的风险级联效应,使得细菌具有耐药性的同时破坏水生生态系统。因此,高效处理废水中残存的抗生素十分必要。光催化与光芬顿技术是降解废水中残存抗生素的有效手段,然而现有光催化与光芬顿技术催化剂回收机制不完善、反应器光能利用效率低下,严重阻碍该技术从实验室向工业规模转化。为解决上述问题,本工作通过功能层原位设计,成功制备了PVDF/LFTCO (LaFe0.55Ti0.2Co0.25O3)催化膜,在光催化与类芬顿氧化协同耦合机制下,催化剂经由光致激发产生光生电子-空穴对,通过电荷分离和转移过程以及氧化还原循环反应,高效激活H2O2并生成活性自由基,PVDF/LFTCO催化膜在连续流装置中可稳定高效降解87.78%的盐酸四环素并在90 min内维持该性能。类光芬顿再生后,PVDF/LFTCO催化膜经过五次循环重复使用对盐酸四环素的降解率保持在73.50%,为构建高效废水处理膜提供了创新性解决方案。
中图分类号:
韩霜, 王秋月, 刘泽贤, 仲兆祥, 邢卫红. PVDF/LFTCO(LaFe0.55Ti0.2Co0.25O3)催化膜类光芬顿降解盐酸四环素[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(10): 5290-5299.
Shuang HAN, Qiuyue WANG, Ze-Xian LOW, Zhaoxiang ZHONG, Weihong XING. Fabrication of PVDF/LFTCO (LaFe0.55Ti0.2Co0.25O3) catalytic membrane for photo-Fenton-like degradation of tetracycline hydrochloride[J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(10): 5290-5299.
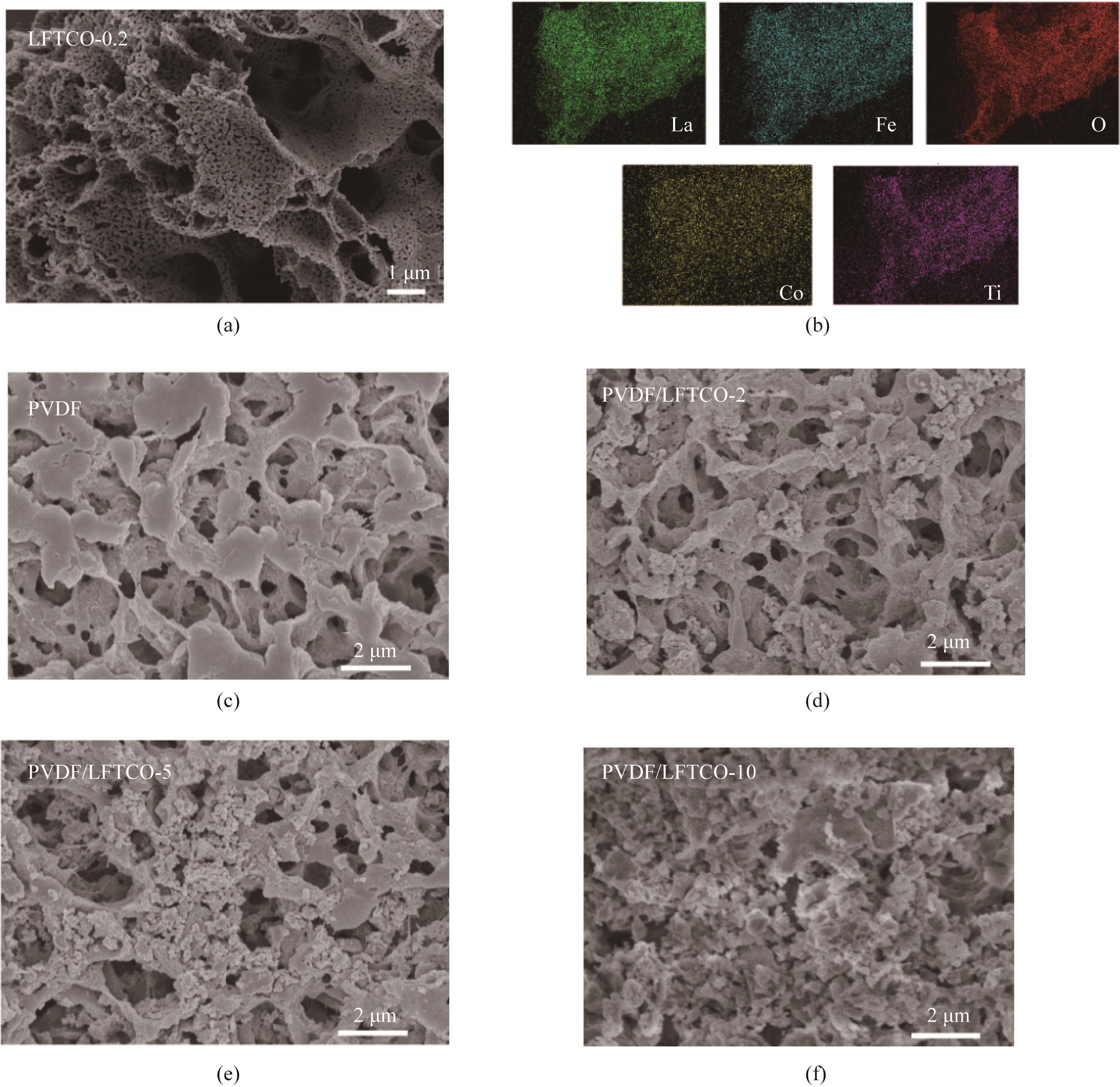
图3 LFTCO-0.2的SEM图像(a)和元素扫描图像(b);PVDF膜(c)和2、5和10 mg催化剂负载时PVDF/LFTCO催化膜的SEM图像[(d)~(f)]
Fig.3 SEM image (a) and EDX mapping (b) of LFTCO-0.2; SEM images of PVDF (c) and PVDF/LFTCO catalytic membranes with 2, 5, and 10 mg catalysts loads [(d)—(f)]
| 项目 | 检测结果 |
|---|---|
| 孔径 | 0.22 μm |
| 厚度 | 100~120 μm |
| 直径 | (50.00±0.30) mm |
| 水流速 | 8.22 ml/(cm2·min) |
| 泡点 | 300 MPa |
表1 PVDF商业膜的产品信息
Table 1 Product information of PVDF commercial membranes
| 项目 | 检测结果 |
|---|---|
| 孔径 | 0.22 μm |
| 厚度 | 100~120 μm |
| 直径 | (50.00±0.30) mm |
| 水流速 | 8.22 ml/(cm2·min) |
| 泡点 | 300 MPa |
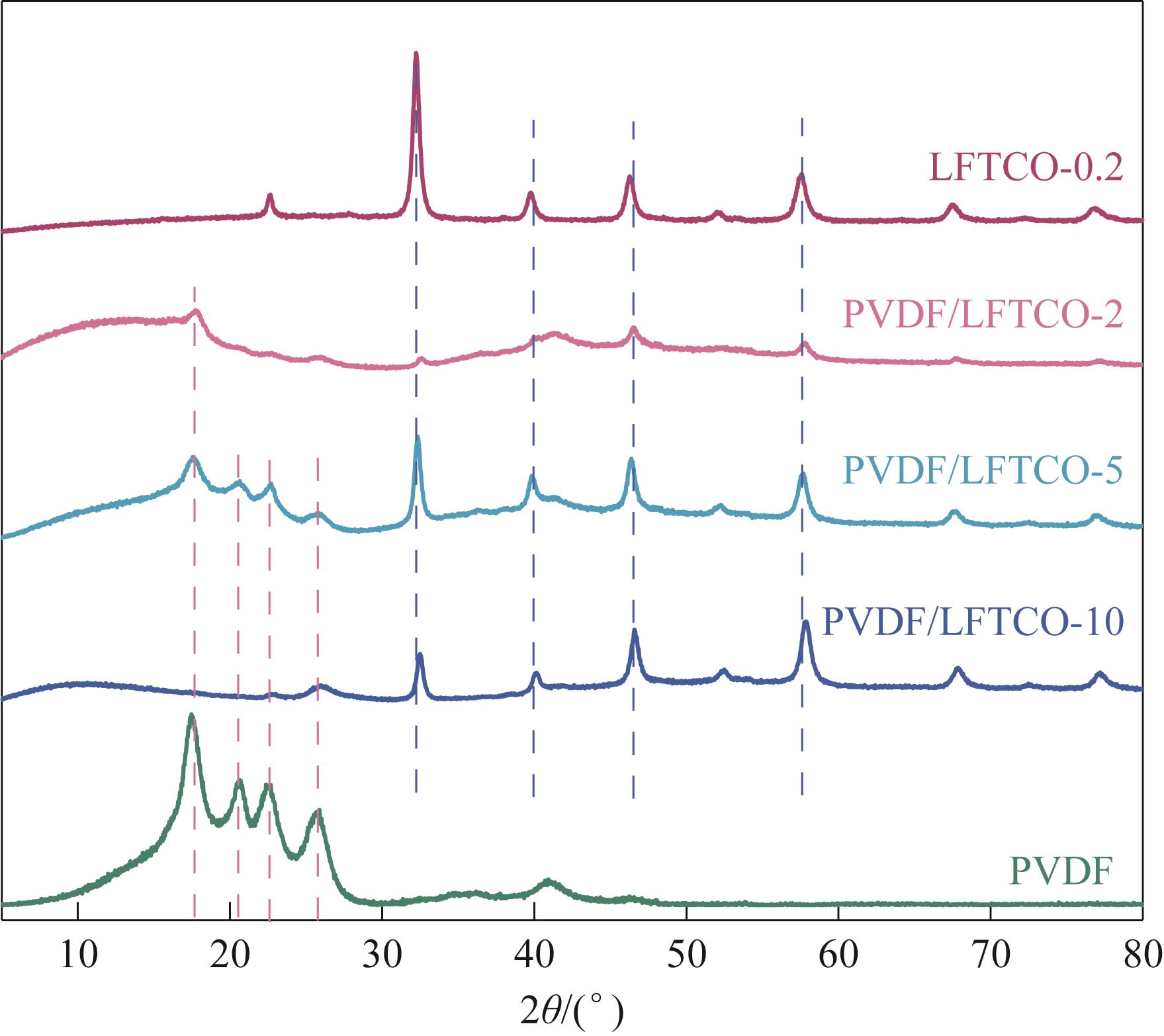
图4 LFTCO-0.2、PVDF、PVDF/LFTCO-2、PVDF/LFTCO-5和PVDF/LFTCO-10膜的XRD谱图
Fig.4 XRD patterns of LFTCO-0.2, PVDF, PVDF/LFTCO-2, PVDF/LFTCO-5, and PVDF/LFTCO-10 membranes
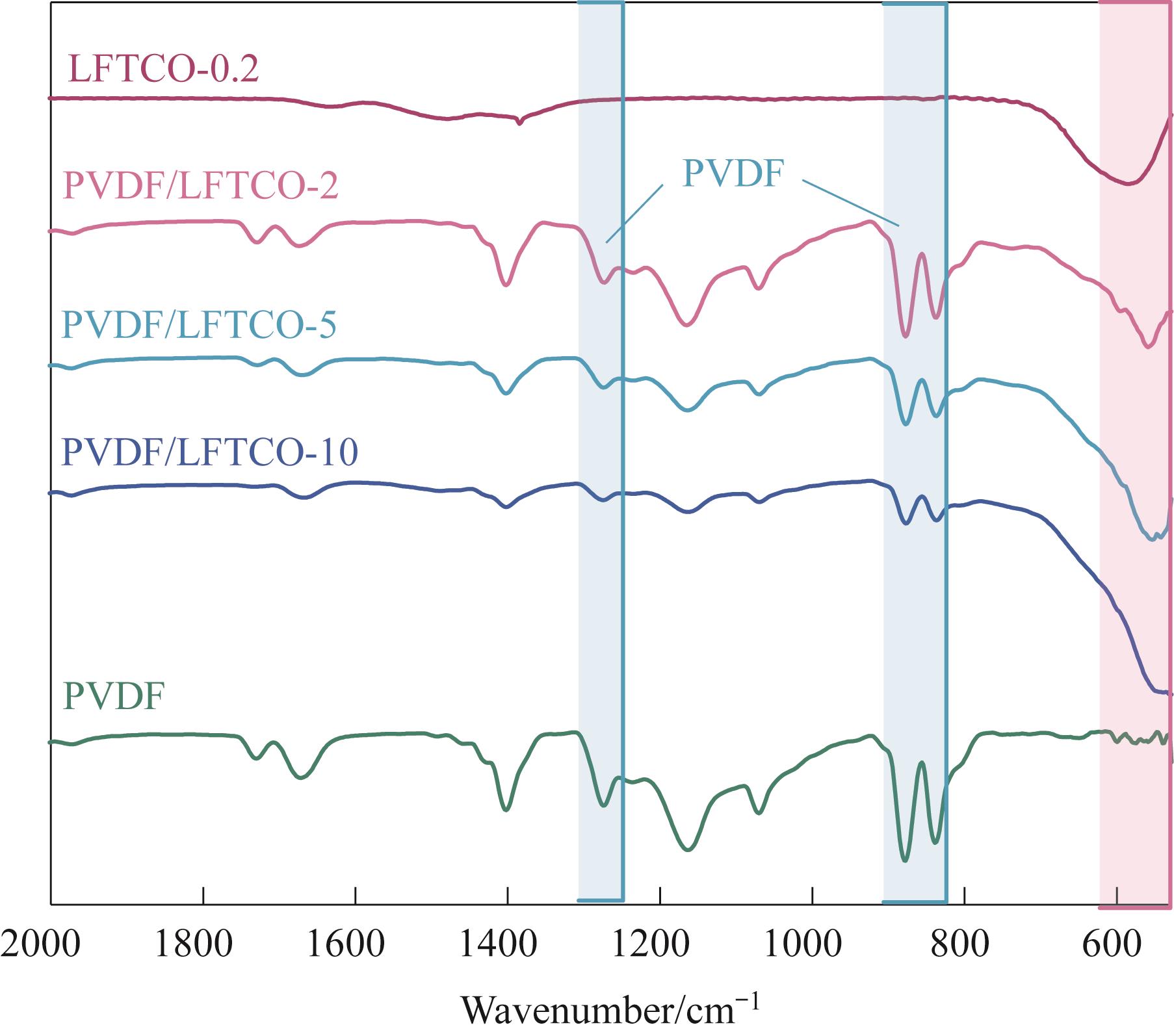
图5 LFTCO-0.2、PVDF、PVDF/LFTCO-2、PVDF/LFTCO-5和PVDF/LFTCO-10膜的FTIR谱图
Fig.5 FTIR spectra of LFTCO-0.2, PVDF, PVDF/LFTCO-2, PVDF/LFTCO-5, and PVDF/LFTCO-10 membranes
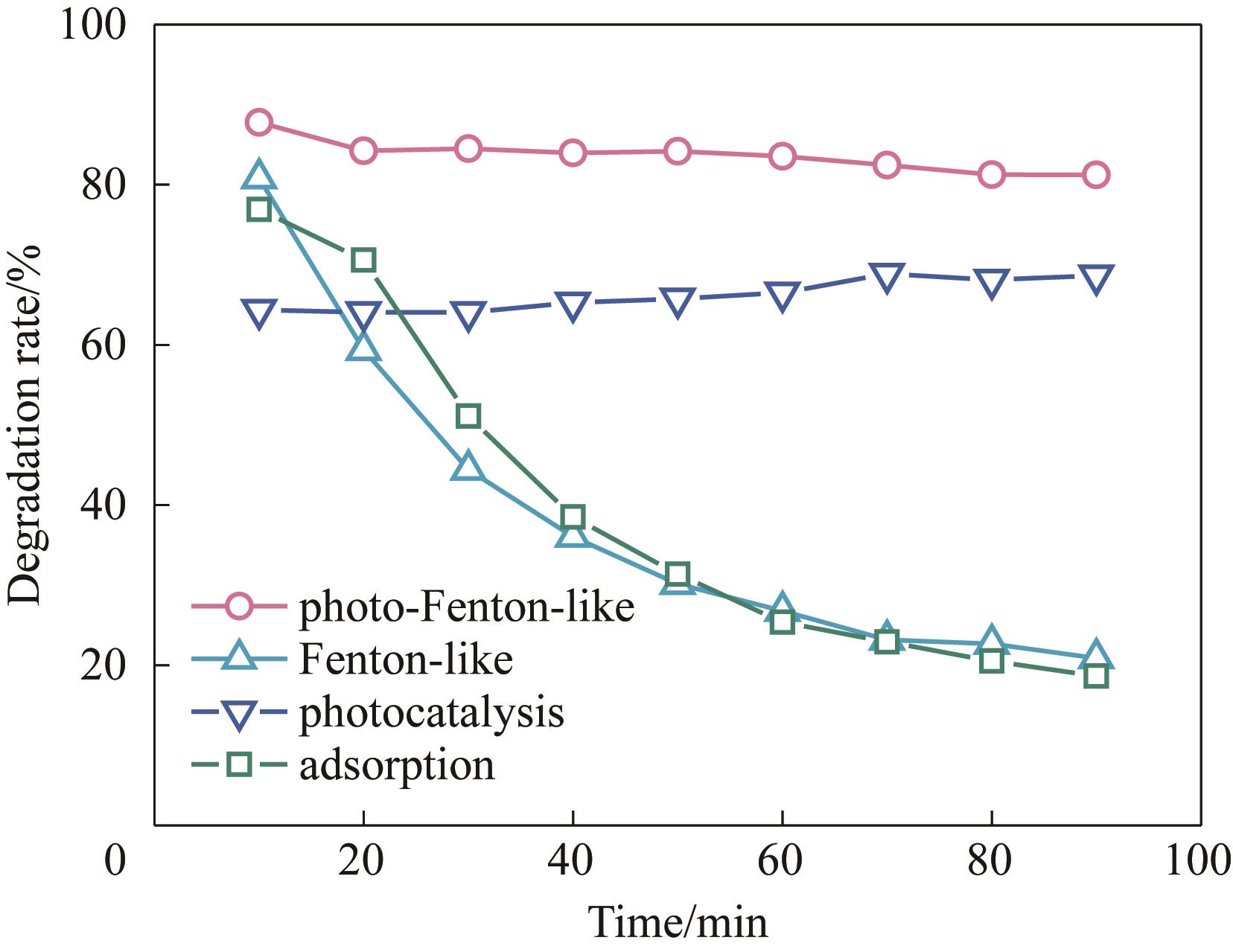
图6 PVDF/LFTCO膜在不同反应体系下的降解效果[实验条件:初始污染物浓度10 mg/L,催化剂负载量5 mg,H2O2浓度20 mmol/L,膜通量334.39 L/(m2·h),光照强度100 mW/cm2,不调节溶液pH,具体参数变化除外]
Fig.6 The degradation of PVDF/LFTCO membranes in different reaction systems [Experiment conditions: initial pollutant concentration 10 mg/L, catalyst load 5 mg, H2O2 concentration 20 mmol/L, membrane flux 334.39 L/(m2·h), light intensity 100 mW/cm2, natural pH except for the specific varied parameter]
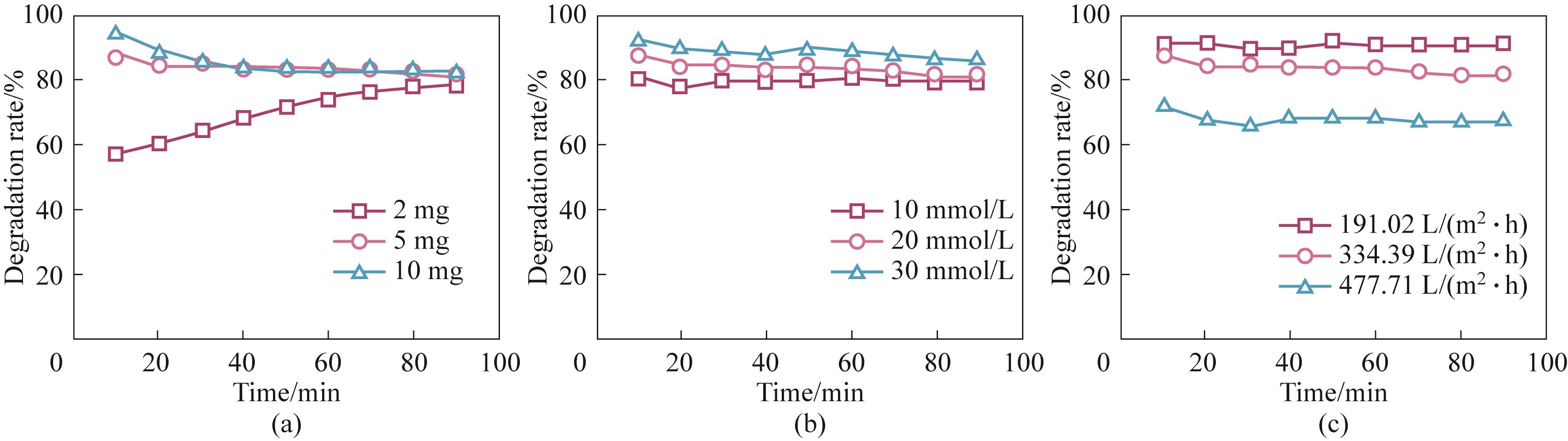
图7 催化剂负载量(a)、H2O2浓度(b)和膜通量(c)对TCH降解的影响[实验条件:初始污染物浓度10 mg/L,催化剂负载量5 mg,H2O2浓度20 mmol/L,膜通量334.39 L/(m2·h),光照强度100 mW/cm2,不调节溶液pH,具体参数变化除外]
Fig.7 Effects of catalyst load (a), H2O2 concentration (b) and feed flow rate (c) on TCH degradation [Experiment conditions: initial pollutant concentration 10 mg/L, catalyst load 5 mg, H2O2 concentration 20 mmol/L, membrane flux 334.39 L/(m2·h), light intensity 100 mW/cm2, natural pH except for the specific varied parameter]
| 催化剂 | 污染物 | 催化类型 | 通量/(L/(m2·h)) | 去除效果/% | 文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S,N双掺杂碳(SNC) | 四环素 | 过氧一硫酸盐 | 1726.65 | 91 | [ |
| Fe@NC | 2,4-二氯苯酚 | 过氧一硫酸盐 | 306 | 99.2 | [ |
| Cu-MOF-74 | 四环素 | 过氧一硫酸盐 | 274.6 | 69.8 | [ |
| CuFeS2 | 莫西沙星 | 过氧一硫酸盐 | 344.8 | 68.2 | [ |
| ZCO | 磷酸氯喹 | 过氧一硫酸盐 | 192 | 45.3 | [ |
| ZnIn2S4 | 盐酸四环素 | 光催化 | 84.06 | 90 | [ |
| Co@CNT-GO | 阿特拉津 | 过氧一硫酸盐 | 95.3 | 79 | [ |
| LFTCO | 盐酸四环素 | 光芬顿 | 334.39 | 87.78 | 本工作 |
表2 PVDF真空过滤负载催化膜对有机污染物的降解工作对比
Table 2 Comparison of organic contaminant degradation performance by PVDF vacuum filtration-supported catalytic membranes of previous researches
| 催化剂 | 污染物 | 催化类型 | 通量/(L/(m2·h)) | 去除效果/% | 文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S,N双掺杂碳(SNC) | 四环素 | 过氧一硫酸盐 | 1726.65 | 91 | [ |
| Fe@NC | 2,4-二氯苯酚 | 过氧一硫酸盐 | 306 | 99.2 | [ |
| Cu-MOF-74 | 四环素 | 过氧一硫酸盐 | 274.6 | 69.8 | [ |
| CuFeS2 | 莫西沙星 | 过氧一硫酸盐 | 344.8 | 68.2 | [ |
| ZCO | 磷酸氯喹 | 过氧一硫酸盐 | 192 | 45.3 | [ |
| ZnIn2S4 | 盐酸四环素 | 光催化 | 84.06 | 90 | [ |
| Co@CNT-GO | 阿特拉津 | 过氧一硫酸盐 | 95.3 | 79 | [ |
| LFTCO | 盐酸四环素 | 光芬顿 | 334.39 | 87.78 | 本工作 |
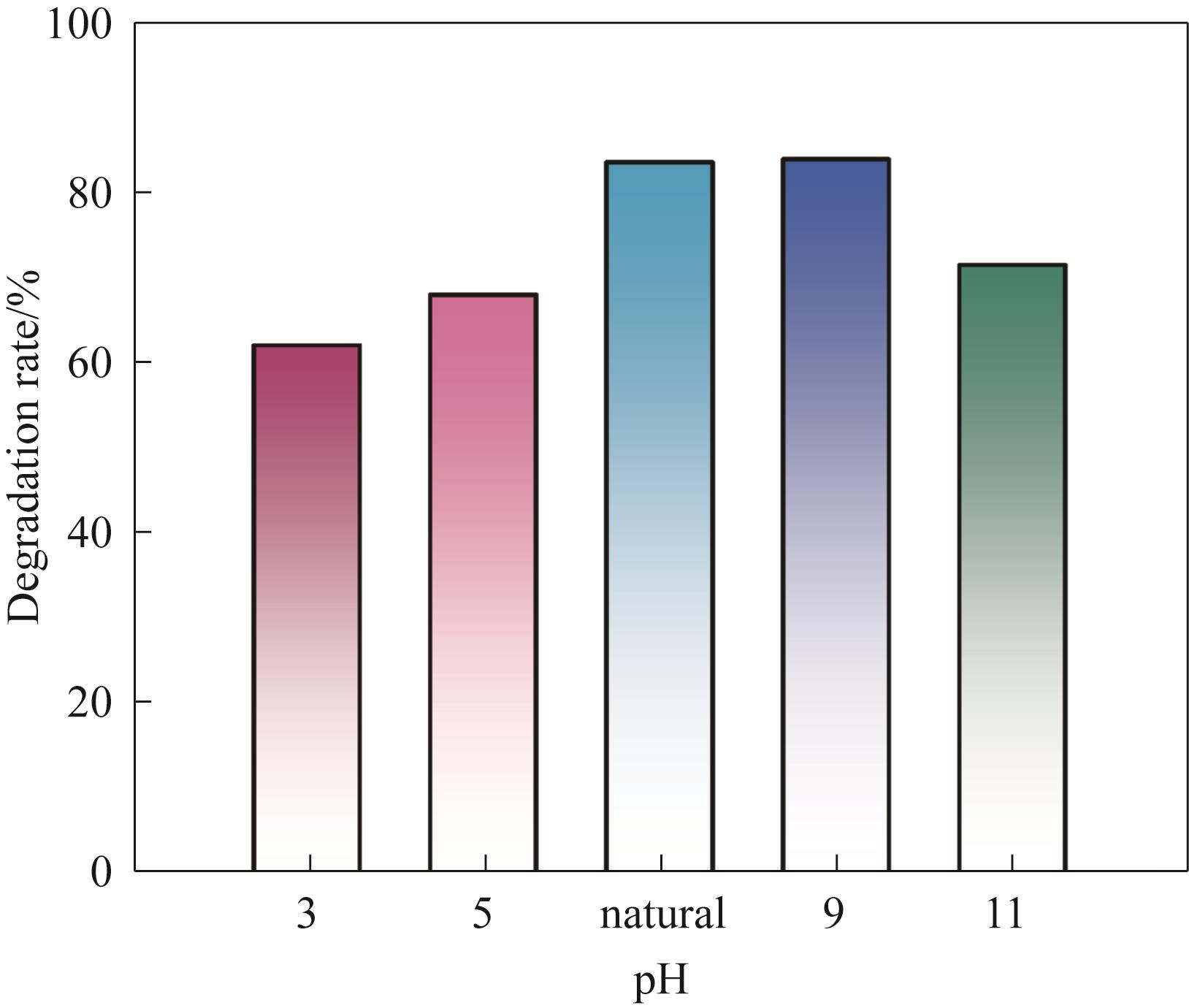
图8 不同pH条件下TCH的催化降解效果[实验条件:初始污染物浓度10 mg/L,催化剂负载量5 mg,H2O2浓度20 mmol/L,膜通量334.39 L/(m2·h),光照强度100 mW/cm2]
Fig.8 Catalytic degradation effect of TCH under different pH conditions [Experiment conditions: initial pollutant concentration 10 mg/L, catalyst load 5 mg, H2O2 concentration 20 mmol/L, membrane flux 334.39 L/(m2·h), light intensity 100 mW/cm2]
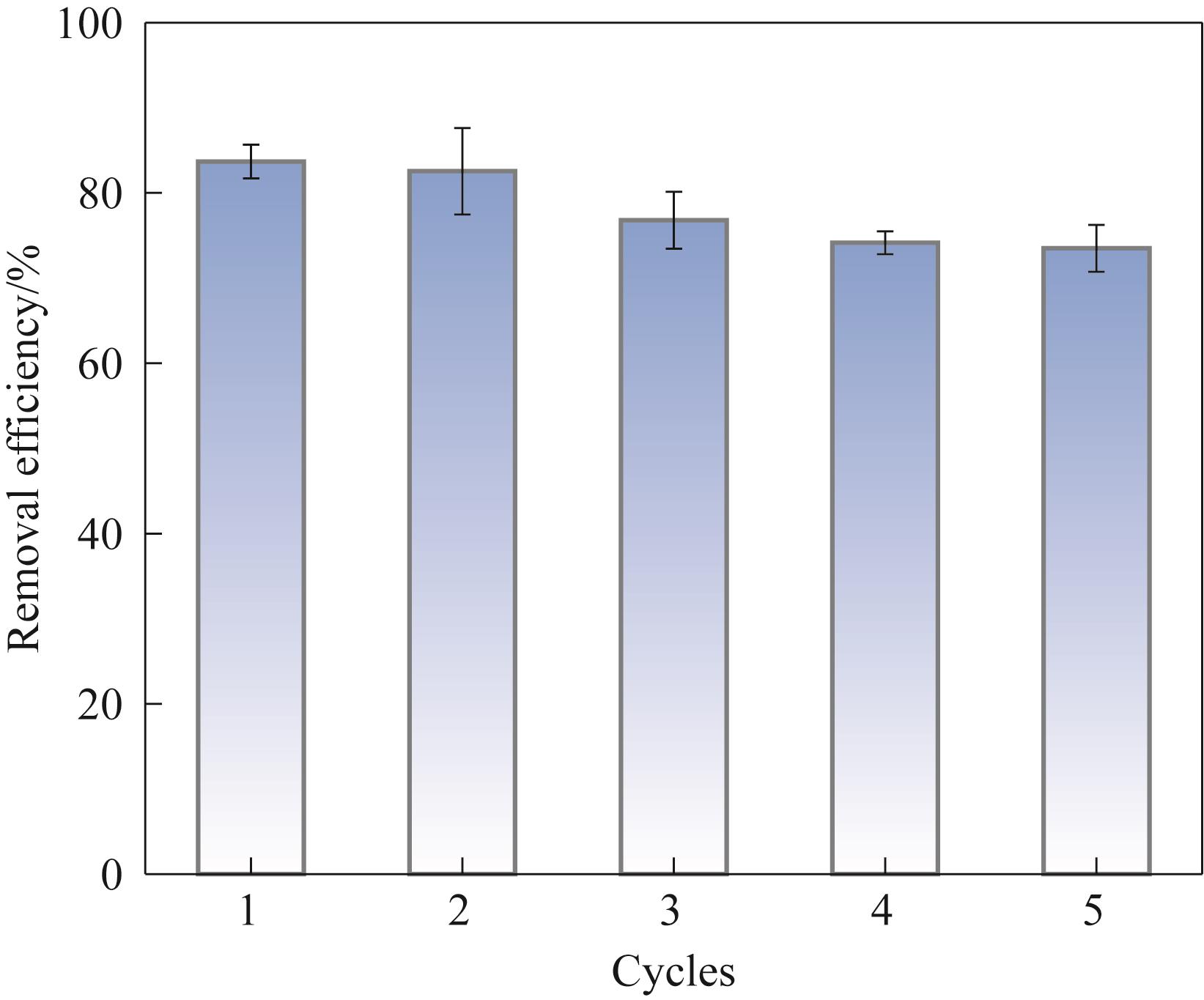
图9 PVDF/LFTCO膜循环催化降解性能[实验条件:初始污染物浓度10 mg/L,催化剂负载量5 mg,H2O2浓度20 mmol/L,膜通量334.39 L/(m2·h),光照强度100 mW/cm2]
Fig.9 Cyclic catalytic degradation performance of PVDF/LFTCO membrane [Experiment conditions: initial pollutant concentration 10 mg/L, catalyst load 5 mg, H2O2 concentration 20 mmol/L, membrane flux 334.39 L/(m2·h), light intensity 100 mW/cm2]
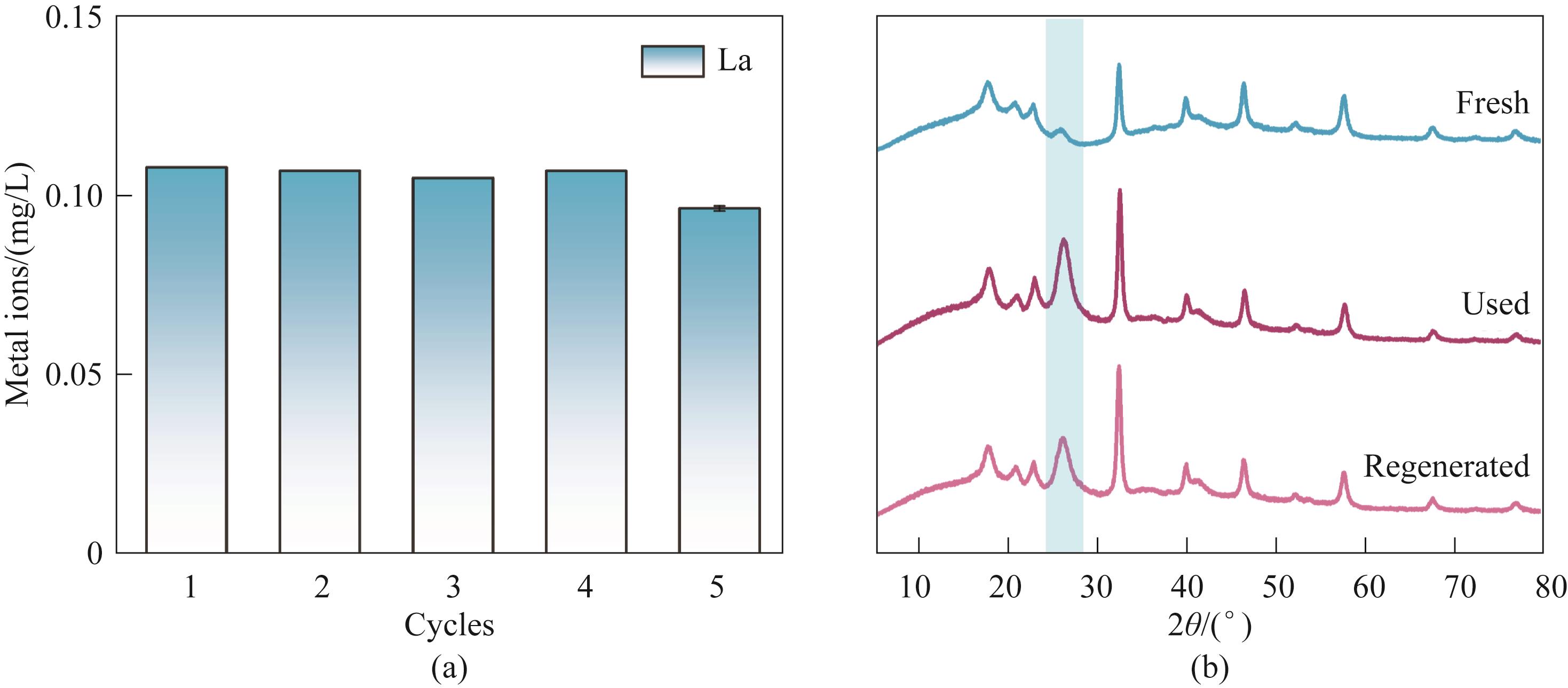
图10 PVDF/LFTCO催化膜的金属离子浸出情况(a);新鲜、催化后以及再生后PVDF/LFTCO催化膜的XRD谱图(b)
Fig.10 Metal ion leaching of PVDF/LFTCO catalytic membranes (a); XRD patterns of fresh, used and regenerated PVDF/LFTCO catalytic membranes (b)
| [1] | Miao S, Zhang Y Y, Li B C, et al. Antibiotic intermediates and antibiotics synergistically promote the development of multiple antibiotic resistance in antibiotic production wastewater[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2024, 479: 135601. |
| [2] | Segura Y, Martinez F, Melero J A. Effective pharmaceutical wastewater degradation by Fenton oxidation with zero-valent iron[J]. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 2013, 136: 64-69. |
| [3] | Hu Y R, Lei D D, Wu D, et al. Residual β-lactam antibiotics and ecotoxicity to Vibrio fischeri, Daphnia magna of pharmaceutical wastewater in the treatment process[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2022, 425: 127840. |
| [4] | Li J C, Zhao L, Feng M B, et al. Abiotic transformation and ecotoxicity change of sulfonamide antibiotics in environmental and water treatment processes: a critical review[J]. Water Research, 2021, 202: 117463. |
| [5] | Kumar M, Mazumder P, Mohapatra S, et al. A chronicle of SARS-CoV-2: seasonality, environmental fate, transport, inactivation, and antiviral drug resistance[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2021, 405: 124043. |
| [6] | Wang W J, Li G Y, An T C, et al. Photocatalytic hydrogen evolution and bacterial inactivation utilizing sonochemical-synthesized g-C3N4/red phosphorus hybrid nanosheets as a wide-spectral-responsive photocatalyst: the role of type Ⅰ band alignment[J]. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 2018, 238: 126-135. |
| [7] | Xia T C, Li Q, Zhao X Y, et al. Bismuth and chlorine dual-doped perovskite chloride as a phase-structure-stable and moisture-resistant solid electrolyte for chloride ion batteries[J]. Advanced Materials, 2024, 36(4): e2310565. |
| [8] | Simböeck J, Ghiasi M, Schöenebaum S, et al. Electronic parameters in cobalt-based perovskite-type oxides as descriptors for chemocatalytic reactions[J]. Nature Communications, 2020, 11(1): 652. |
| [9] | Cai R X, Dou J, Krzystowczyk E, et al. Chemical looping air separation with Sr0.8Ca0.2Fe0.9Co0.1O3- δ perovskite sorbent: packed bed modeling, verification, and optimization[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2022, 429: 132370. |
| [10] | Zheng W, Zhou X Y, Na Y Y, et al. Facile fabrication of regenerable spherical La0.8Ce0.2MnO3 pellet via wet-chemistry molding strategy for elemental mercury removal[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2024, 479: 147659. |
| [11] | Yang G, Liang Y J, Xiong Z R, et al. Molten salt-assisted synthesis of Ce4O7/Bi4MoO9 heterojunction photocatalysts for photo-Fenton degradation of tetracycline: enhanced mechanism, degradation pathway and products toxicity assessment[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2021, 425: 130689. |
| [12] | Sun Y, Li R, Chen X X, et al. A-site management prompts the dynamic reconstructed active phase of perovskite oxide OER catalysts[J]. Advanced Energy Materials, 2021, 11(12): 2003755. |
| [13] | Zhu Y P, Chen G, Zhong Y J, et al. A surface-modified antiperovskite as an electrocatalyst for water oxidation[J]. Nature Communications, 2018, 9(1): 2326. |
| [14] | Mathews I, Kantareddy S N R, Sun S J, et al. Self-powered sensors enabled by wide-bandgap perovskite indoor photovoltaic cells[J]. Advanced Functional Materials, 2019, 29(42): 1904072. |
| [15] | Wang J, Ren Y, Liu H, et al. Ultrathin 2D NbWO6 perovskite semiconductor based gas sensors with ultrahigh selectivity under low working temperature[J]. Advanced Materials, 2022, 34(2): e2104958. |
| [16] | Yu R X, Zhao J H, Zhao Z W, et al. Copper substituted zinc ferrite with abundant oxygen vacancies for enhanced ciprofloxacin degradation via peroxymonosulfate activation[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2020, 390: 121998. |
| [17] | Vadivel S, Maruthamani D, Habibi-Yangjeh A, et al. Facile synthesis of novel CaFe2O4/g-C3N4 nanocomposites for degradation of methylene blue under visible-light irradiation[J]. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 2016, 480: 126-136. |
| [18] | Dubey A, Keat C H, Shvartsman V V, et al. Mono-, di-, and tri-valent cation doped BiFe0.95Mn0.05O3 nanoparticles: ferroelectric photocatalysts[J]. Advanced Functional Materials, 2022, 32(43): 2207105. |
| [19] | Humayun M, Ullah H, Usman M, et al. Perovskite-type lanthanum ferrite based photocatalysts: preparation, properties, and applications[J]. Journal of Energy Chemistry, 2022, 66: 314-338. |
| [20] | Gabra S, Marek E J, Poulston S, et al. The use of strontium ferrite perovskite as an oxygen carrier in the chemical looping epoxidation of ethylene[J]. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 2021, 286: 119821. |
| [21] | Mehdizadeh P, Amiri O, Rashki S, et al. Effective removal of organic pollution by using sonochemical prepared LaFeO3 perovskite under visible light[J]. Ultrasonics Sonochemistry, 2020, 61: 104848. |
| [22] | Vijayaraghavan T, Bradha M, Babu P, et al. Influence of secondary oxide phases in enhancing the photocatalytic properties of alkaline earth elements doped LaFeO3 nanocomposites[J]. Journal of Physics and Chemistry of Solids, 2020, 140: 109377. |
| [23] | Chen X, Zhang M, Qin H W, et al. Synergy effect between adsorption and heterogeneous photo-Fenton-like catalysis on LaFeO3/lignin-biochar composites for high efficiency degradation of ofloxacin under visible light[J]. Separation and Purification Technology, 2022, 280: 119751. |
| [24] | Yi M, Xia Q, Tan J L, et al. Catalytic-separation technology for highly efficient removal of emerging pollutants, desalination, and antimicrobials: a new strategy for complex wastewater treatment[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2024, 493: 152568. |
| [25] | Li Y B, He Y, Zhuang J, et al. Dual defense against membrane fouling for efficient and sustainable oil/water separation on a novel super-hydrophilic/underwater superoleophobic and catalytic nanofibrous membrane[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2024, 497: 154489. |
| [26] | Zhang H L, Zheng Y L, Zhou H W, et al. Nanocellulose-intercalated MXene NF membrane with enhanced swelling resistance for highly efficient antibiotics separation[J]. Separation and Purification Technology, 2023, 305: 122425. |
| [27] | Kumar M, Sreedhar N, Thomas N, et al. Polydopamine-coated graphene oxide nanosheets embedded in sulfonated poly(ether sulfone) hybrid UF membranes with superior antifouling properties for water treatment[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2022, 433: 133526. |
| [28] | Pan Y P, Shi Z Z, Li J, et al. Graphene oxide laminates intercalated with Prussian blue nanocube as a photo-Fenton self-cleaning membrane for enhanced water purification[J]. Journal of Membrane Science, 2023, 672: 121465. |
| [29] | Zheng H A, Li M Y, Jiang S Y, et al. MIL-88A/carbon quantum dots nanomaterials promote the photo-Fenton reaction to enhance the fouling resistance of PVDF membrane[J]. Journal of Membrane Science, 2023, 684: 121855. |
| [30] | Gao Y X, Yan S M, He Y, et al. A photo-Fenton self-cleaning membrane based on NH2-MIL-88B (Fe) and graphene oxide to improve dye removal performance[J]. Journal of Membrane Science, 2021, 626: 119192. |
| [31] | Chen C X, Wang S M, Han F, et al. Synergy of rapid adsorption and photo-Fenton-like degradation in CoFe-MOF/TiO2/PVDF composite membrane for efficient removal of antibiotics from water[J]. Separation and Purification Technology, 2024, 333: 125942. |
| [32] | Zheng H A, Xiao C Z, Jiang S Y, et al. Fabrication of PVDF membrane loaded with ultra-thin g-C3N4/FeOCl nanomaterials and study on catalytic and antifouling properties[J]. Separation and Purification Technology, 2024, 331: 125641. |
| [33] | Chen C C, Xie M, Kong L S, et al. Mn3O4 nanodots loaded g-C3N4 nanosheets for catalytic membrane degradation of organic contaminants[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2020, 390: 122146. |
| [34] | Zhong Q, Shi G G, Sun Q, et al. Robust PVA-GO-TiO2 composite membrane for efficient separation oil-in-water emulsions with stable high flux[J]. Journal of Membrane Science, 2021, 640: 119836. |
| [35] | Zhou M, Ma X, Ji C Y, et al. Chelating adsorption-engaged anionic dye removal and Fenton-driven regeneration in ferromagnetic Ti/Co-LaFeO3 perovskite[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2024, 479: 147600. |
| [36] | Gao B R, Dou M M, Wang J, et al. Effect of carbon nitride synthesized by different modification strategies on the performance of carbon nitride/PVDF photocatalytic composite membranes[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2022, 422: 126877. |
| [37] | Lin H B, Fang Q L, Wang W, et al. Prussian blue/PVDF catalytic membrane with exceptional and stable Fenton oxidation performance for organic pollutants removal[J]. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 2020, 273: 119047. |
| [38] | Cao Z, Zhao Y P, Zhou Z H, et al. Efficiency LaFeO3 and BiOI heterojunction for the enhanced photo-Fenton degradation of tetracycline hydrochloride[J]. Applied Surface Science, 2022, 590: 153081. |
| [39] | Xie A T, Cui J Y, Yang J, et al. Graphene oxide/Fe(Ⅲ)-based metal-organic framework membrane for enhanced water purification based on synergistic separation and photo-Fenton processes[J]. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 2020, 264: 118548. |
| [40] | Wang Z W, Liu W J, Jin H B, et al. Layered double hydroxide helps LaFeO3 photocatalyst activate peroxymonosulfate to efficiently degrade dyes[J]. Separation and Purification Technology, 2024, 341: 126832. |
| [41] | Yi H, Huang D L, Qin L, et al. Selective prepared carbon nanomaterials for advanced photocatalytic application in environmental pollutant treatment and hydrogen production[J]. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 2018, 239: 408-424. |
| [42] | Gong X B, Xie J L, Pan X F, et al. S, N co-doped carbon material functionalized catalytic membrane for efficient peroxymonosulfate activation and continuous refractory pollutants flow-treatment[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2023, 282: 119353. |
| [43] | Ma T G, Ren H J, Liu M J, et al. Nanoconfined catalytic membrane assembled by nitrogen-doped carbon encapsulating Fe-based nanoparticles for rapid removal of 2, 4-dichlorophenol in wastewater by peroxymonosulfate activation[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2024, 466: 133523. |
| [44] | Zheng H A, Zhou Y, Wang D R, et al. Surface-functionalized PVDF membranes by facile synthetic Cu-MOF-74 for enhanced contaminant degradation and antifouling performance[J]. Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 2022, 651: 129640. |
| [45] | Zhang D Y, Li K F, Fang L, et al. CuFeS2/MXene-modified polyvinylidene fluoride membrane for antibiotics removal through peroxymonosulfate activation[J]. Water, 2024, 16(11): 1504. |
| [46] | Xu S T, Feng K, Zhang X, et al. Spinel-based zinc-doped Co3O4 (ZCO) catalytic membrane for efficient peroxymonosulfate activation and chloroquine phosphate degradation: an atom doping strategy[J]. Environmental Research, 2025, 275: 121408. |
| [47] | Gao B, Chen W P, Liu J D, et al. Continuous removal of tetracycline in a photocatalytic membrane reactor (PMR) with ZnIn2S4 as adsorption and photocatalytic coating layer on PVDF membrane[J]. Journal of Photochemistry and Photobiology A: Chemistry, 2018, 364: 732-739. |
| [48] | Liu T, He Y L, He M R, et al. Nanoconfined catalytic membranes assembled by cobalt-loaded carbon nanotubes and graphene oxide for highly efficient water decontamination[J]. Journal of Membrane Science, 2024, 707: 123002. |
| [49] | Shan Z L, Ma F, You S J, et al. Enhanced visible light photo-Fenton catalysis by lanthanum-doping BiFeO3 for norfloxacin degradation[J]. Environmental Research, 2023, 216: 114588. |
| [1] | 王三龙, 王跃霖, 曹宇. 基于相异质结的高效无机钙钛矿太阳能电池的性能研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(3): 1346-1352. |
| [2] | 薛潇, 商敏静, 苏远海. 微反应器内药物连续流合成的研究进展[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(4): 1439-1454. |
| [3] | 马浩天, 荆体瑞, 刘程程, 玉散·吐拉甫, 张喆, 王一迪, 王庆宏, 陈春茂, 徐春明. Sr改性LaFeO3用于甲烷化学链重整的还原性能与动力学研究[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(12): 4532-4546. |
| [4] | 吴云, 龚海峰. 疏水改性羰基铁负载TiO2光催化降解石油烃污染物[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(12): 4555-4562. |
| [5] | 马烨玮, 孙艳娜, 高栋, 王海彬, 姚善泾, 林东强. 模型辅助的单抗连续捕获工艺分析和过程优化[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(11): 4274-4285. |
| [6] | 范孝雄, 郝丽芳, 范垂钢, 李松庚. LaMnO3/生物炭催化剂低温NH3-SCR催化脱硝性能研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(9): 3821-3830. |
| [7] | 傅予, 刘兴翀, 王瀚雨, 李海敏, 倪亚飞, 邹文静, 雷月, 彭永姗. F3EACl修饰层对钙钛矿太阳能电池性能提升的研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(8): 3554-3563. |
| [8] | 杨小芹, 刘馨雨, 杨玉寒, 叶彦, 贾琼, 杨浩男, 秦志宏. 煤基泡沫炭复合F-TiO2光催化降解苯酚[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(12): 4914-4925. |
| [9] | 杨柳青, 赵子瑞, 张军社, 魏进家. 钡含量对(La0.5Sr0.5)1-x Ba x Fe0.6Co0.4O3化学链甲烷干重整性能的影响[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(10): 4286-4301. |
| [10] | 张婉晨, 陈晓阳, 吕秋秋, 钟秦, 朱腾龙. Co掺杂SrTi0.3Fe0.7O3-δ 阳极SOFC在化工副产气燃料下的性能及稳定性[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(9): 4079-4086. |
| [11] | 艾承燚, 乔金硕, 王振华, 孙旺, 孙克宁. 原位析出纳米合金的PrBaFe2O6-δ 基阳极构筑及其在固体碳燃料电池中的应用研究[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(8): 3708-3719. |
| [12] | 徐珂, 史国强, 薛冬峰. 无机杂化钙钛矿团簇材料:介尺度钙钛矿材料发光性质研究[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(6): 2748-2756. |
| [13] | 李文怀, 周嵬. 高氧离子电导钙钛矿的影响因素分析和设计策略[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(4): 1455-1471. |
| [14] | 董晓珊, 李健, 颜蓓蓓, 陈冠益. 钙钛矿催化剂在生物质热化学利用领域的研究进展[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(2): 504-520. |
| [15] | 娄锋炎, 尹佳滨, 段笑南, 王祁宁, 艾宁, 张吉松. 连续微反应加氢技术在脱保护反应中的应用[J]. 化工学报, 2021, 72(2): 761-771. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备 11010102001995号
京公网安备 11010102001995号