• •
收稿日期:2025-11-04
修回日期:2025-12-17
出版日期:2026-01-13
通讯作者:
郭超
作者简介:罗凯(2002—),男,硕士研究生,cekailuo@stu.cdut.edu.cn。
基金资助:
Kai LUO1( ), Chao GUO1(
), Chao GUO1( ), Wei HOU1, Ge HE2
), Wei HOU1, Ge HE2
Received:2025-11-04
Revised:2025-12-17
Online:2026-01-13
Contact:
Chao GUO
摘要:
丙烯/丙烷作为近沸难分离物系,现有精馏技术存在高能耗和高设备投资等问题。离子液体可忽略的挥发特性及强作用力属性,使得其在分离近沸物系方面得到了广泛研究。因此,本研究通过多尺度模拟,分析了离子液体强化丙烯/丙烷的微观机制及工艺性能。研究提出了一种基于MATLAB平台的计算机辅助离子液体设计与工艺并行优化的集成策略,采用基团贡献法和生成测试的求解策略进行离子液体设计。基于多粒子并行的粒子群优化方法对多种进料工况和多种离子液体工艺进行并行优化。结果表明,[MMIM][TFA]强化丙烯/丙烷分离的机理是离子液体与丙烯间的π-π、C-H···π和π···H···O相互作用,离子液体与丙烯的静电作用力强于与丙烷的静电作用力,从而显著提高了丙烯/丙烷的选择性。与热泵精馏及ACN水溶液萃取精馏相比,[MMIM][TFA]萃取精馏节能工艺的年总成本分别降低了38.26%~45.45%和24.04%~40.07%。
中图分类号:
罗凯, 郭超, 侯微, 贺革. 丙烯/丙烷分离的离子液体设计与工艺并行优化[J]. 化工学报, DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20251221.
Kai LUO, Chao GUO, Wei HOU, Ge HE. Design of ionic liquids and process parallel optimization for separation of propylene/propane[J]. CIESC Journal, DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20251221.
| 排名 | 离子液体 | MW(g/mol) | S | Tm (K) | η(cp) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1CH3, 1[MIM][TFA] | 210.2 | 3.1 | 271.7 | 16.6 |
| 2 | 1CH3, 1CH2, 1[MIM][TFA] | 224.2 | 3.0 | 267.9 | 19.1 |
| 3 | 1CH3, 3CH2, 1[MIM][TFA] | 252.2 | 2.8 | 264.2 | 21.9 |
| 4 | 1CH3, 1[MIM][SCN] | 155.2 | 2.5 | 304.8 | 14.8 |
| 5 | 1CH3, 3CH2, 1[MIM][TfO] | 288.3 | 2.4 | 322.4 | 34.8 |
| 6 | 1CH3, 1CH2, 1[MIM][SCN] | 169.2 | 2.1 | 301.0 | 17.0 |
表1 离子液体设计结果及热力学和物性数据
Table 1 Design results of ionic liquids and their thermodynamic properties
| 排名 | 离子液体 | MW(g/mol) | S | Tm (K) | η(cp) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1CH3, 1[MIM][TFA] | 210.2 | 3.1 | 271.7 | 16.6 |
| 2 | 1CH3, 1CH2, 1[MIM][TFA] | 224.2 | 3.0 | 267.9 | 19.1 |
| 3 | 1CH3, 3CH2, 1[MIM][TFA] | 252.2 | 2.8 | 264.2 | 21.9 |
| 4 | 1CH3, 1[MIM][SCN] | 155.2 | 2.5 | 304.8 | 14.8 |
| 5 | 1CH3, 3CH2, 1[MIM][TfO] | 288.3 | 2.4 | 322.4 | 34.8 |
| 6 | 1CH3, 1CH2, 1[MIM][SCN] | 169.2 | 2.1 | 301.0 | 17.0 |
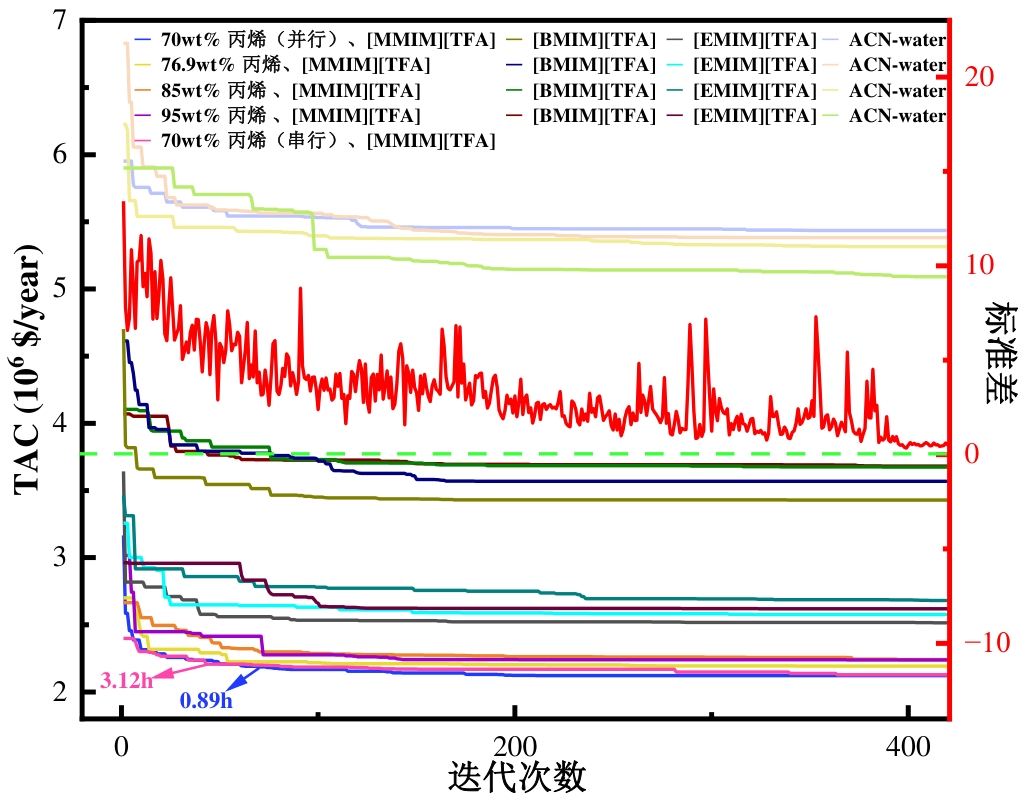
图5 不同丙烯进料的[MMIM][TFA]、[EMIM][TFA]、[BMIM][TFA]和ACN水溶液萃取精馏工艺的动态收敛特性
Fig.5 Dynamic convergence characteristics of the [MMIM][TFA], [EMIM][TFA], [BMIM][TFA] and ACN-water-based extractive distillation process at different propylene feedstock
| 变量 | 单位 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NT | - | 54 | 65 | 56 | 56 | 52 | 58 | 60 | 57 | 61 | 60 | 48 | 52 |
| NE | - | 3 | 4 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 4 | 3 | 3 | 4 | 3 | 4 |
| NF | - | 13 | 19 | 18 | 22 | 17 | 17 | 19 | 23 | 17 | 18 | 16 | 21 |
| S | kmol/h | 394.04 | 432.12 | 476.93 | 478.73 | 427.93 | 434.36 | 446.12 | 453.57 | 386.01 | 376.58 | 457.18 | 410.56 |
| D | kg/h | 7677.6 | 5885.73 | 3788.39 | 1194.12 | 7678.27 | 5884.01 | 3786.01 | 1194.31 | 7677.95 | 5886.28 | 3787.47 | 1193.81 |
| RR | - | 4.8 | 6.27 | 9.59 | 27.99 | 4.86 | 4.66 | 11 | 33.28 | 5.05 | 6.37 | 10.27 | 29.74 |
| T | ℃ | 64.4 | 64.32 | 66.46 | 69.78 | 74.6 | 78.32 | 74.33 | 74.5 | 102.15 | 103.33 | 101.45 | 103.18 |
| P | MPa | 0.619 | 0.661 | 0.539 | 0.476 | 0.532 | 0.466 | 0.526 | 0.535 | 0.495 | 0.337 | 0.394 | 0.297 |
| X | - | 0.9816 | 0.9799 | 0.9860 | 0.9894 | 0.9748 | 0.9815 | 0.9748 | 0.9745 | 0.9718 | 0.9818 | 0.9782 | 0.9841 |
表2 离子液体萃取精馏工艺参数优化结果
Table 2 Optimization results of ionic liquids extractive distillation process parameters
| 变量 | 单位 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NT | - | 54 | 65 | 56 | 56 | 52 | 58 | 60 | 57 | 61 | 60 | 48 | 52 |
| NE | - | 3 | 4 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 4 | 3 | 3 | 4 | 3 | 4 |
| NF | - | 13 | 19 | 18 | 22 | 17 | 17 | 19 | 23 | 17 | 18 | 16 | 21 |
| S | kmol/h | 394.04 | 432.12 | 476.93 | 478.73 | 427.93 | 434.36 | 446.12 | 453.57 | 386.01 | 376.58 | 457.18 | 410.56 |
| D | kg/h | 7677.6 | 5885.73 | 3788.39 | 1194.12 | 7678.27 | 5884.01 | 3786.01 | 1194.31 | 7677.95 | 5886.28 | 3787.47 | 1193.81 |
| RR | - | 4.8 | 6.27 | 9.59 | 27.99 | 4.86 | 4.66 | 11 | 33.28 | 5.05 | 6.37 | 10.27 | 29.74 |
| T | ℃ | 64.4 | 64.32 | 66.46 | 69.78 | 74.6 | 78.32 | 74.33 | 74.5 | 102.15 | 103.33 | 101.45 | 103.18 |
| P | MPa | 0.619 | 0.661 | 0.539 | 0.476 | 0.532 | 0.466 | 0.526 | 0.535 | 0.495 | 0.337 | 0.394 | 0.297 |
| X | - | 0.9816 | 0.9799 | 0.9860 | 0.9894 | 0.9748 | 0.9815 | 0.9748 | 0.9745 | 0.9718 | 0.9818 | 0.9782 | 0.9841 |
| 变量 | 单位 | 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NT | - | 97 | 96 | 87 | 76 |
| NE | - | 5 | 4 | 4 | 5 |
| NF | - | 40 | 37 | 32 | 31 |
| S | kmol/h | 1742.55 | 1721.84 | 1857.96 | 2030.24 |
| D | kg/h | 7664.23 | 5880.04 | 3783.23 | 1187.13 |
| RR | - | 7.07 | 9.45 | 13.09 | 30.44 |
| NT1 | - | 23 | 22 | 22 | 22 |
| NF1 | - | 8 | 9 | 9 | 9 |
| D1 | kg/h | 17030.01 | 18776.05 | 20832.12 | 23375.33 |
| RR1 | - | 0.79 | 0.64 | 0.59 | 0.56 |
表3 ACN水溶液萃取精馏工艺参数优化结果
Table 3 Optimization results of ACN-water-based extractive distillation process parameters
| 变量 | 单位 | 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NT | - | 97 | 96 | 87 | 76 |
| NE | - | 5 | 4 | 4 | 5 |
| NF | - | 40 | 37 | 32 | 31 |
| S | kmol/h | 1742.55 | 1721.84 | 1857.96 | 2030.24 |
| D | kg/h | 7664.23 | 5880.04 | 3783.23 | 1187.13 |
| RR | - | 7.07 | 9.45 | 13.09 | 30.44 |
| NT1 | - | 23 | 22 | 22 | 22 |
| NF1 | - | 8 | 9 | 9 | 9 |
| D1 | kg/h | 17030.01 | 18776.05 | 20832.12 | 23375.33 |
| RR1 | - | 0.79 | 0.64 | 0.59 | 0.56 |
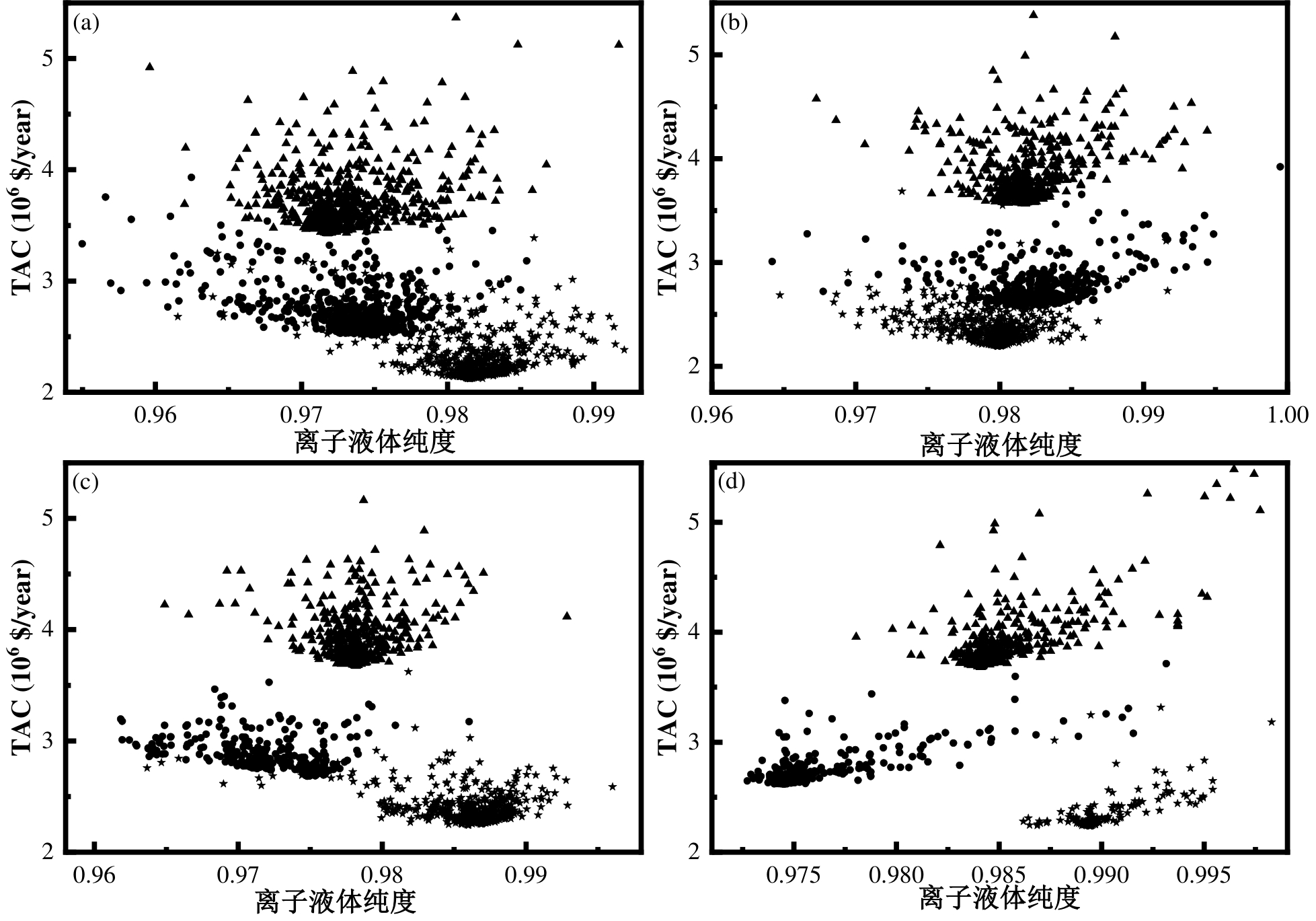
图6 不同丙烯进料的[MMIM][TFA]、[EMIM][TFA]和[BMIM][TFA]工艺的离子液体纯度对TAC的影响: (a) 70wt%; (b) 76.9wt%; (c) 85wt%; (d) 95wt%注:↔—[MMIM][TFA];●—[EMIM][TFA];⯅—[BMIM][TFA]
Fig.6 Effect of ionic liquid purity on TAC for [MMIM][TFA], [EMIM][TFA], and [BMIM][TFA] processes at different propylene feedstock: (a) 70wt%; (b) 76.9wt%; (c) 85wt%; (d) 95wt%
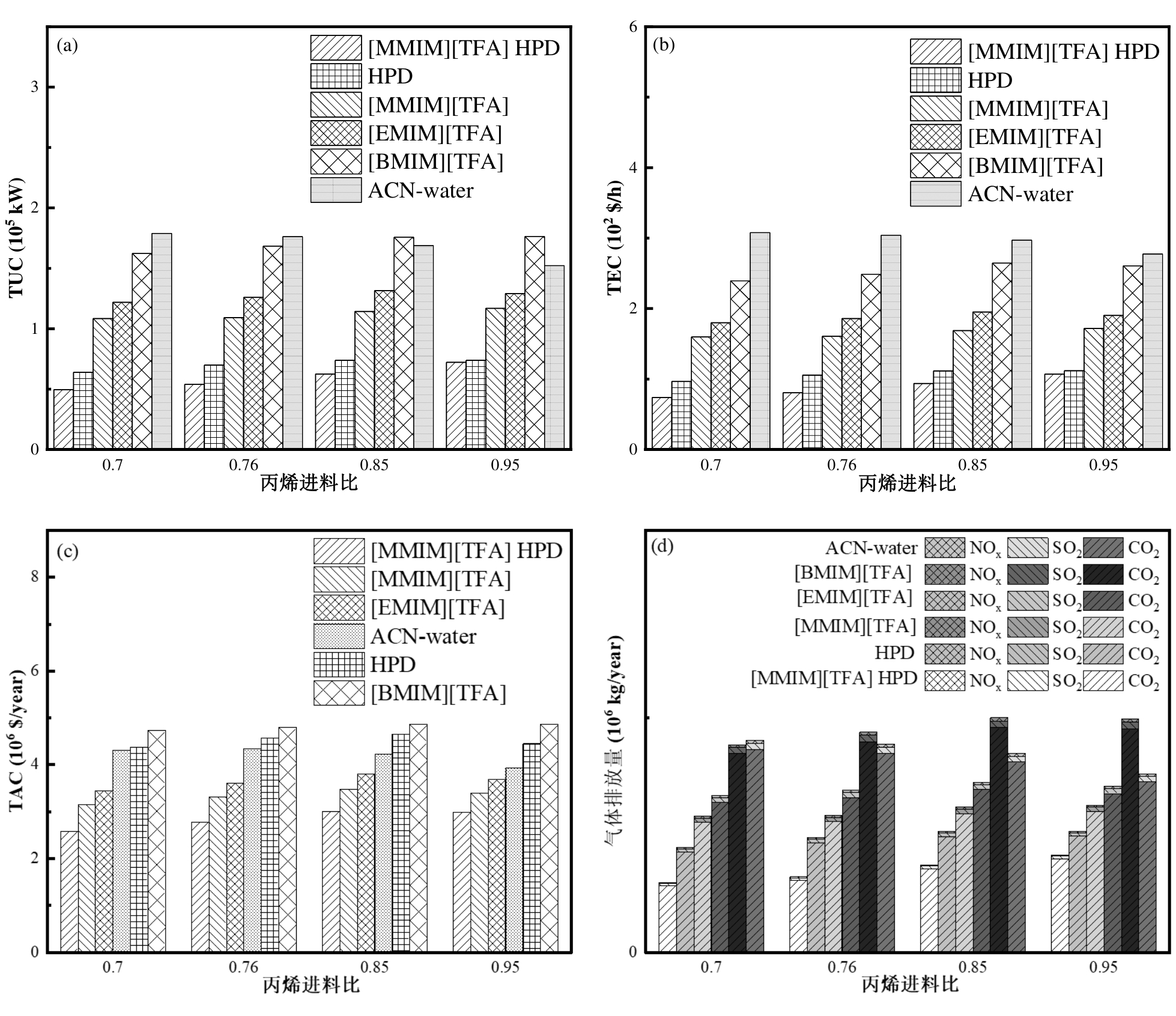
图7 不同丙烯进料下[MMIM][TFA]萃取精馏节能工艺和[MMIM][TFA]、[EMIM][TFA]、[BMIM][TFA]、ACN水溶液萃取精馏和HPD工艺的TUC (a)、TEC (b)、TAC (c)和气体排放(d)的比较
Fig.7 Comparisons of TUC (a), TEC (b), TAC (a) and gas emissions (b) for [MMIM][TFA] extractive distillation energy-saving process, [MMIM][TFA], [EMIM][TFA], [BMIM][TFA], ACN-water-based extractive distillation and HPD processes at different propylene feedstock.
| [1] | 王子宗, 刘罡, 王振维. 乙烯丙烯生产过程强化技术进展及思考[J]. 化工进展, 2023, 42(4): 1669-1676. |
| Wang Z Z, Liu G, Wang Z W. Progress and reflection on process intensification technology for ethylene/propylene production[J]. Chemical Industry and Engineering Progress, 2023, 42(4): 1669-1676. | |
| [2] | 李文学, 韩东, 杨卫兰. 中国丙烯及下游产品发展回顾及展望[J]. 现代化工, 2024, 44(5): 11-14. |
| Li W X, Han D, Yang W L. Review and outlook on development of China's propylene and its downstream products[J]. Modern Chemical Industry, 2024, 44(5): 11-14. | |
| [3] | Chen S, Chang X, Sun G D, et al. Propane dehydrogenation: catalyst development, new chemistry, and emerging technologies[J]. Chemical Society Reviews, 2021, 50(5): 3315-3354. |
| [4] | 谢磊, 安赵成, 崔莉程, 等. 气体分馏装置丙烯精馏塔的模拟与优化[J]. 炼油与化工, 2022, 33(2): 61-64. |
| Xie L, An Z C, Cui L C, et al. Simulation and optimization of propylene rectification tower in gas fractionation unit[J]. Refining and Chemical Industry, 2022, 33(2): 61-64. | |
| [5] | 叶启亮, 徐超洋, 王丽涛, 等. 隔壁精馏塔分离氯丙烯工艺模拟优化[J]. 化学工程, 2024, 52(10): 52-57. |
| Ye Q L, Xu C Y, Wang L T, et al. Simulation and optimization of separation of 3-chloropropene in dividing wall column[J]. Chemical Engineering (China), 2024, 52(10): 52-57. | |
| [6] | Woo H C, Kim Y H. Solvent selection for extractive distillation using molecular simulation[J]. AIChE Journal, 2019, 65(9): e16665. |
| [7] | Gui Y H, Guo C, Liang J C, et al. Thermo-kinetic synergy in separating dimethyl carbonate/methanol/water mixtures using ionic liquids-based mixed solvents[J]. Separation and Purification Technology, 2025, 356: 129849. |
| [8] | Guo C, Zheng Y, Wang S, et al. Energy-efficient heat pump-assisted pre-concentration integrated with sequential [EMIM][BF4] and ethylene glycol-based extractive distillation for enhanced recovery of ethanol and isopropyl alcohol from wastewater[J]. Separation and Purification Technology, 2025, 357: 130073. |
| [9] | Yu B Y, Chien I L. Design and optimization of the methanol-to-olefin process. part II: comparison of different methods for propylene/propane separation[J]. Chemical Engineering & Technology, 2016, 39(12): 2304-2311. |
| [10] | Cruz Valdez J A, Avilés Martínez A, Vallejo Montesinos J, et al. Maximizing propylene separation from propane by extractive distillation with aqueous N-methyl-2-pyrrolidone as separating agent[J]. Chemical Engineering & Technology, 2021, 44(9): 1726-1736. |
| [11] | 王键吉, 张锁江, 韩布兴. 前言: 离子液体前沿专刊[J]. 中国科学: 化学, 2021, 51(10): 1311-1312. |
| Wang J J, Zhang S J, Han B X. Preface: special issue on the frontiers of ionic liquids[J]. Scientia Sinica Chimica, 2021, 51(10): 1311-1312. | |
| [12] | Palomar J, Lemus J, Navarro P, et al. Process simulation and optimization on ionic liquids[J]. Chemical Reviews, 2024, 124(4): 1649-1737. |
| [13] | 容凡丁, 丁泽相, 曹义风, 等. 离子液体强化不饱和键差异化合物分离的研究进展[J]. 化工进展, 2024, 43(1): 198-214. |
| Rong F D, Ding Z X, Cao Y F, et al. Progress in enhanced separation of compounds differing in unsaturated bonds by ionic liquids[J]. Chemical Industry and Engineering Progress, 2024, 43(1): 198-214. | |
| [14] | Lei Y, Yu Z Y, Wei Z Q, et al. Energy-efficient separation of propylene/propane by introducing a tailor-made ionic liquid solvent[J]. Fuel, 2022, 326: 124930. |
| [15] | Kim H, Lee B, Lim D, et al. What is the best green propylene production pathway?: technical, economic, and environmental assessment[J]. Green Chemistry, 2021, 23(19): 7635-7645. |
| [16] | 国家市场监督管理总局, 中国国家标准化管理委员会. 聚合级丙烯: [S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2024. |
| State Administration for Market Regulation, Standardization Administration of the People's Republic of China. Propylene for polymerization: [S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China, 2024. | |
| [17] | Lei Z G, Zhang J G, Li Q S, et al. UNIFAC model for ionic liquids[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2009, 48(5): 2697-2704. |
| [18] | Lei Z G, Dai C N, Liu X, et al. Extension of the UNIFAC model for ionic liquids[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2012, 51(37): 12135-12144. |
| [19] | Dong Y C, Guo Y Y, Zhu R S, et al. UNIFAC model for ionic liquids. 2. revision and extension[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2020, 59(21): 10172-10184. |
| [20] | Zhu R S, Kang H W, Liu Q H, et al. UNIFAC model for ionic liquids: 3. revision and extension[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2024, 63(3): 1670-1679. |
| [21] | Lazzús J A, Pulgar-Villarroel G. A group contribution method to estimate the viscosity of ionic liquids at different temperatures[J]. Journal of Molecular Liquids, 2015, 209: 161-168. |
| [22] | Lazzús J A. A group contribution method to predict the melting point of ionic liquids[J]. Fluid Phase Equilibria, 2012, 313: 1-6. |
| [23] | Yang A, Wang W H, Sun S R, et al. Sustainable design and multi-objective optimization of eco-efficient extractive distillation with single and double entrainer(s) for separating the ternary azeotropic mixture tetrahydrofuran/ethanol/methanol[J]. Separation and Purification Technology, 2022, 285: 120413. |
| [24] | Yang A, Kong Z Y, Sunarso J. Design and optimisation of novel hybrid side-stream reactive-extractive distillation for recovery of isopropyl alcohol and ethyl acetate from wastewater[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2023, 451: 138563. |
| [25] | Yang A, Zou H C, Chien I L, et al. Optimal design and effective control of triple-column extractive distillation for separating ethyl acetate/ethanol/water with multiazeotrope[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2019, 58(17): 7265-7283. |
| [26] | Heris M K. Multi-Objective PSO in MATLAB[EB/OL]. 2015. . |
| [27] | Frisch M J, Trucks G W, Schlegel H B. Gaussian 16, RevisionC. 01, Gaussian[EB/OL]. 2019. . |
| [28] | Lu T. Molclus Program, 1.8.5Version. Beijing Kein Research Center for Natural Science[EB/OL]. 2019. . |
| [29] | Stewart J J P. MOPAC: a semiempirical molecular orbital program[J]. Journal of Computer-Aided Molecular Design, 1990, 4(1): 1-103. |
| [30] | Chai J D, Head-Gordon M. Long-range corrected hybrid density functionals with damped atom–atom dispersion corrections[J]. Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics, 2008, 10(44): 6615-6620. |
| [31] | Lu T, Chen Q X. Independent gradient model based on Hirshfeld partition: a new method for visual study of interactions in chemical systems[J]. Journal of Computational Chemistry, 2022, 43(8): 539-555. |
| [32] | Lu T, Liu Z Y, Chen Q X. Comment on "18 and 12–Member carbon rings (cyclo[n]carbons)–A density functional study"[J]. Materials Science and Engineering: B, 2021, 273:115425. |
| [33] | Liang J C, Guo C, Liu X Y, et al. Economic and environmental benefits of novel process of ionic liquids-based toluene absorption from exhaust gas at atmospheric pressure[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2024, 470: 143283. |
| [34] | Guo C, Luo K, Hou W, et al. A novel [MMIM]-based ionic liquid extractive distillation process for achieving liquid-phase propylene at 1.8 MPa with enhanced energy-economic-environmental benefits[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2025, 525: 146579. |
| [35] | Chen H, Li X G, He L, et al. Energy, exergy, economic, and environmental analysis for methyl acetate hydrolysis process with heat integrated technology used[J]. Energy Conversion and Management, 2020, 216:112919. |
| [36] | Luo K, Guo C, Liang J C, et al. Energy and cost-efficient ionic liquids extractive distillation for producing electronic and polymer-grade propylene with emphasis on feedstock variability[J]. Separation and Purification Technology, 2025, 358: 130258. |
| [1] | 张晓钰, 兰金鑫, 黎昕, 曹石林, 高海丽, 马晓娟. [Emim]Ac-[Emim]OH-DMSO三元体系溶解纤维素的研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(7): 3226-3234. |
| [2] | 李琳, 王明媚, 宋二伟, 王雯雯, 张耀昌, 王二强. 异戊二烯-正戊烷分离工艺的热力学分析及优化[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(6): 2549-2558. |
| [3] | 崔家馨, 殷梦凡, 郑涛, 刘晗, 张睿, 刘植昌, 刘海燕, 徐春明, 孟祥海. 铝铜双金属离子液体在1-己烯/正己烷分离中的应用[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(2): 686-694. |
| [4] | 张奇, 张睿, 郑涛, 曹欣, 刘植昌, 刘海燕, 徐春明, 张荣, 孟祥海. 基于分子模拟的新型双阳离子质子型离子液体捕集CO2研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(2): 797-811. |
| [5] | 冯海军, 章冰璇, 周健. 图神经网络模型预测和解释离子液体毒性的研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(1): 93-106. |
| [6] | 邱知, 谭明. 聚离子液体膜的制备及其在低钠高钾健康酱油中的应用[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(S1): 244-250. |
| [7] | 杜海燕, 朱凯, 游峰, 王金凤, 赵一帆, 张楠, 李英. 用于应变传感器的自愈合抗冻离子水凝胶[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(7): 2709-2722. |
| [8] | 张广宇, 付然飞, 孙冰, 袁俊聪, 冯翔, 杨朝合, 徐伟. CO2-环氧丙烷合成碳酸丙烯酯:氢键供体效应研究[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(6): 2243-2251. |
| [9] | 武颖韬, 费立涵, 孔祥东, 王帜, 汤成龙, 黄佐华. 咪唑二氰胺离子液体掺混糠醇的自燃及推进性能[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(5): 2017-2025. |
| [10] | 蒋方涛, 钱刚, 周兴贵, 段学志, 张晶. 基于[bmim][BF4]相转移催化的氟代碳酸乙烯酯高效合成[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(4): 1543-1551. |
| [11] | 王瑞瑞, 金颖, 刘玉梅, 李梦悦, 朱胜文, 闫瑞一, 刘瑞霞. 聚合离子液体设计及催化环己烷选择性氧化性能研究[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(4): 1552-1564. |
| [12] | 肖拥君, 时兆翀, 万仁, 宋璠, 彭昌军, 刘洪来. 反向传播神经网络用于预测离子液体的自扩散系数[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(2): 429-438. |
| [13] | 冯咪, 张杰, 吕兴梅. 基于胆碱类离子液体的高纯甲壳素一步提取分离[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(11): 4286-4297. |
| [14] | 赵非凡, 朱佳媚, 康洁, 檀亮, 段靖瑜. 三丁基(丙基)季 离子液体对VOCs的吸收性能及机理[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(10): 3669-3680. 离子液体对VOCs的吸收性能及机理[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(10): 3669-3680. |
| [15] | 蒋斯麒, 胡玉峰, 程永强, 刘清华, 雷志刚. 离子液体萃取分离FCC柴油中双环芳香性硫氮组分:实验和分子机理[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(10): 3651-3659. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备 11010102001995号
京公网安备 11010102001995号