CIESC Journal ›› 2019, Vol. 70 ›› Issue (7): 2775-2785.DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20190027
• Material science and engineering, nanotechnology • Previous Articles Next Articles
Jihua ZHU( ),Yao CHEN,Xiulian QIU,Yuming HUANG,Cheng ZHENG,Wei YANG(
),Yao CHEN,Xiulian QIU,Yuming HUANG,Cheng ZHENG,Wei YANG( )
)
Received:2019-01-09
Revised:2019-04-16
Online:2019-07-05
Published:2019-07-05
Contact:
Wei YANG
通讯作者:
杨伟
作者简介:朱计划(1992—),男,硕士研究生,<email>497691268@qq.com</email>
基金资助:CLC Number:
Jihua ZHU, Yao CHEN, Xiulian QIU, Yuming HUANG, Cheng ZHENG, Wei YANG. Preparation of LiMn1-xMgxPO4/C cathode materials by microwave-assisted solvothermal method[J]. CIESC Journal, 2019, 70(7): 2775-2785.
朱计划, 陈姚, 丘秀莲, 黄宇明, 郑成, 杨伟. 微波辅助溶剂热法制备LiMn1-xMgxPO4/C正极材料[J]. 化工学报, 2019, 70(7): 2775-2785.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
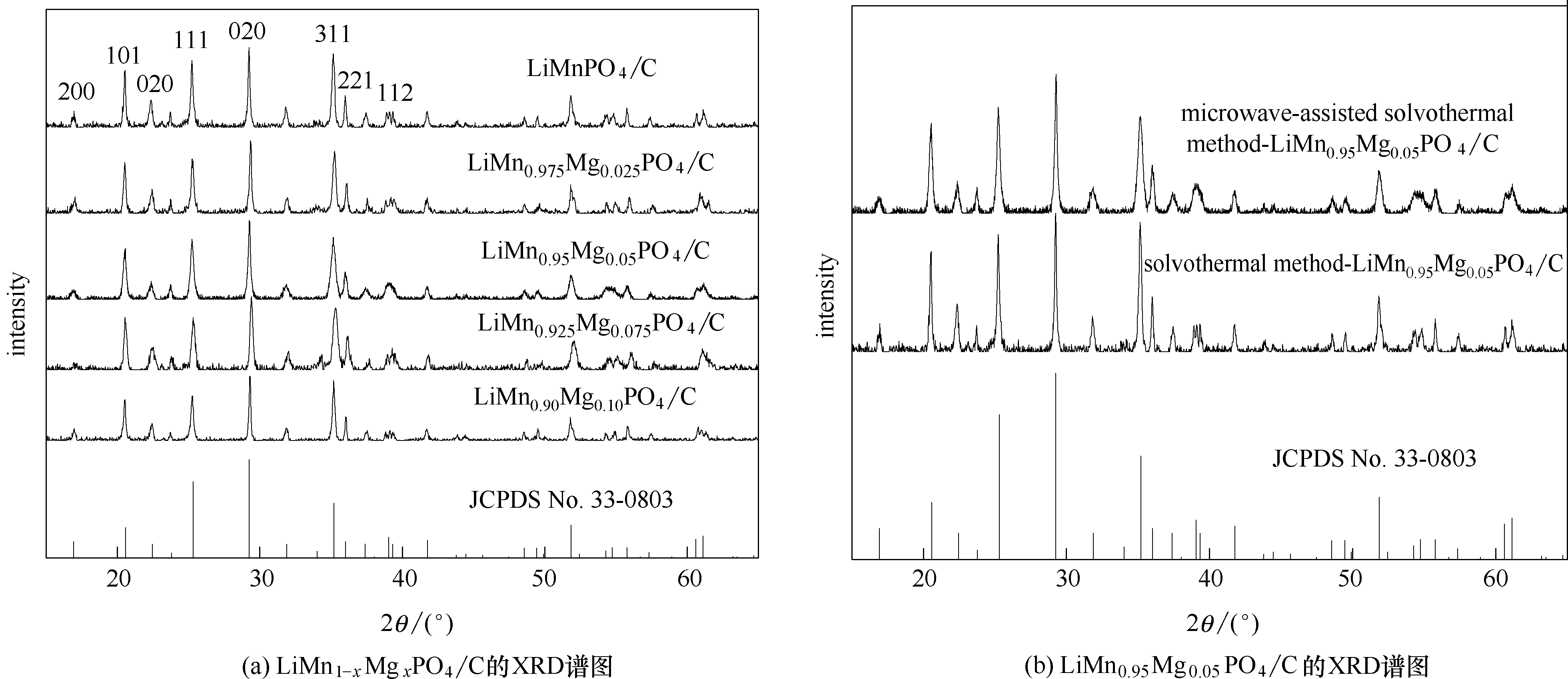
Fig.1 XRD patterns of microwave-assisted solvothermal samples of LiMn1-xMgxPO4/C (x = 0, 0.025, 0.05, 0.075 and 0.1) and LiMn0.95Mg0.05PO4/C synthesized through different routes
| 样品 | a/? | b/? | c/? | v/?3 | I020/I311 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LiMnPO4/C | 10.445 | 6.107 | 4.751 | 302.36 | 1.08 |
| LiMn0.975Mg0.025PO4/C | 10.438 | 6.102 | 4.758 | 301.85 | 1.16 |
| LiMn0.95Mg0.05PO4/C | 10.429 | 6.094 | 4.744 | 301.22 | 1.25 |
| LiMn0.925Mg0.075PO4/C | 10.421 | 6.085 | 4.742 | 300.71 | 1.18 |
| LiMn0.90Mg0.10PO4/C | 10.417 | 6.077 | 4.738 | 299.93 | 1.07 |
Table 1 Refined unit-cell parameters for LiMn1-xMgxPO4/C (x = 0, 0.025, 0.05, 0.075, 0.1)
| 样品 | a/? | b/? | c/? | v/?3 | I020/I311 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LiMnPO4/C | 10.445 | 6.107 | 4.751 | 302.36 | 1.08 |
| LiMn0.975Mg0.025PO4/C | 10.438 | 6.102 | 4.758 | 301.85 | 1.16 |
| LiMn0.95Mg0.05PO4/C | 10.429 | 6.094 | 4.744 | 301.22 | 1.25 |
| LiMn0.925Mg0.075PO4/C | 10.421 | 6.085 | 4.742 | 300.71 | 1.18 |
| LiMn0.90Mg0.10PO4/C | 10.417 | 6.077 | 4.738 | 299.93 | 1.07 |
| 样品 | 比表面积/(m2/g) | 电导率/(S/cm) | 离子扩散系数/(cm2/s) | 碳含量/%(mass) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| LiMnPO4/C | 64.2 | 4.5×10-4 | 9.72×10-14 | 7.13 |
| LiMn0.975Mg0.025PO4/C | 79.9 | 6.3×10-4 | 1.56×10-13 | 7.21 |
| LiMn0.95Mg0.05PO4/C | 88.2 | 7.6×10-4 | 4.32×10-13 | 7.16 |
| LiMn0.925Mg0.075PO4/C | 82.8 | 5.4×10-4 | 1.95×10-13 | 7.08 |
| LiMn0.90Mg0.1PO4/C | 68.6 | 3.8×10-4 | 8.71×10-14 | 7.11 |
Table 2 Specific surface area, electronic conductivity,lithium-ion diffusion coefficients and carbon content of LiMn1-xMgxPO4/C
| 样品 | 比表面积/(m2/g) | 电导率/(S/cm) | 离子扩散系数/(cm2/s) | 碳含量/%(mass) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| LiMnPO4/C | 64.2 | 4.5×10-4 | 9.72×10-14 | 7.13 |
| LiMn0.975Mg0.025PO4/C | 79.9 | 6.3×10-4 | 1.56×10-13 | 7.21 |
| LiMn0.95Mg0.05PO4/C | 88.2 | 7.6×10-4 | 4.32×10-13 | 7.16 |
| LiMn0.925Mg0.075PO4/C | 82.8 | 5.4×10-4 | 1.95×10-13 | 7.08 |
| LiMn0.90Mg0.1PO4/C | 68.6 | 3.8×10-4 | 8.71×10-14 | 7.11 |
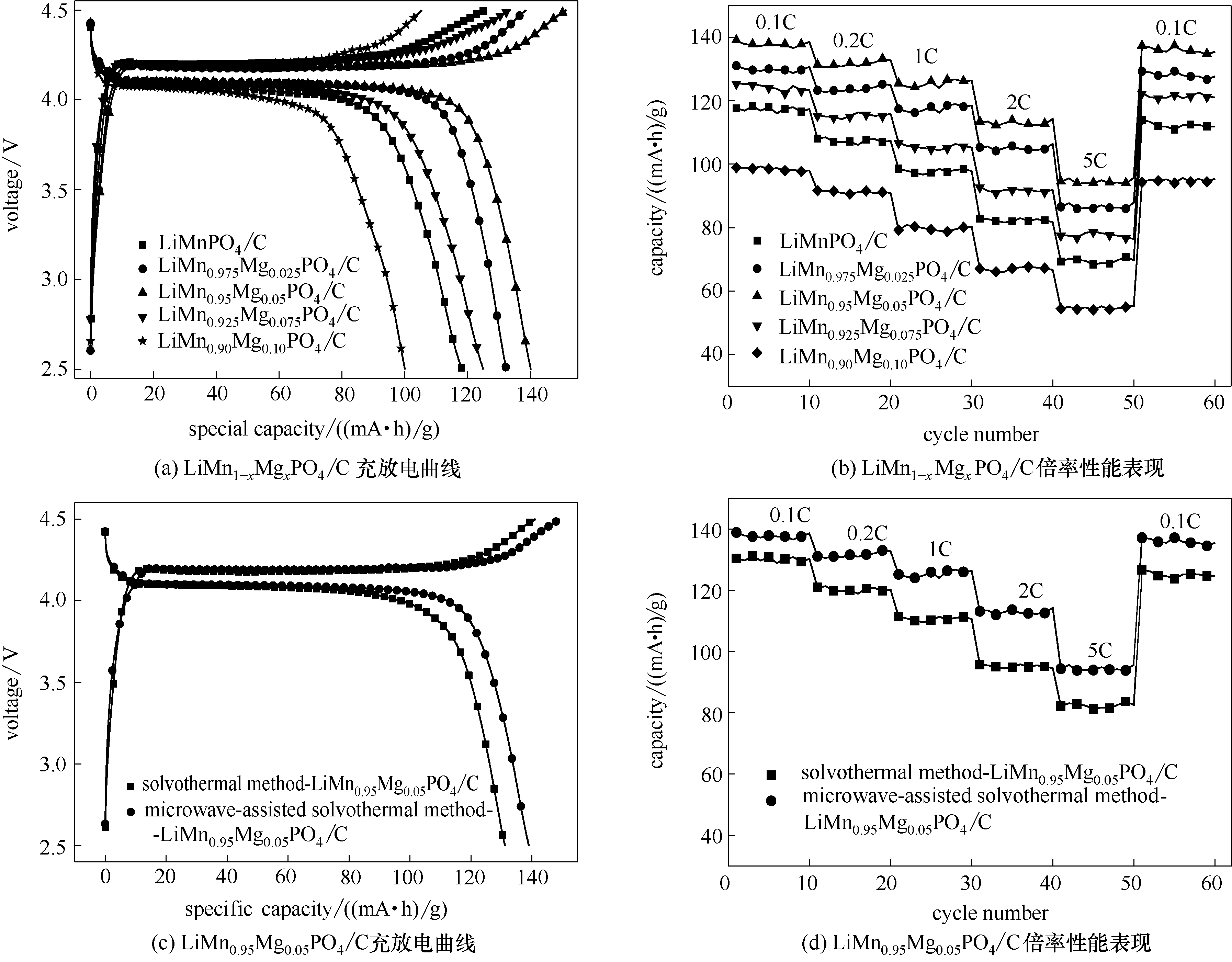
Fig.6 Charge/discharge diagrams (a) and rate capability(b) of microwave-assisted solvothermal samples of LiMn1-xMgxPO4/C (x = 0, 0.025, 0.05, 0.075, 0.1) and charge/discharge diagrams (c) and rate capability (d) of LiMn0.95Mg0.05PO4/C synthesized through different routes
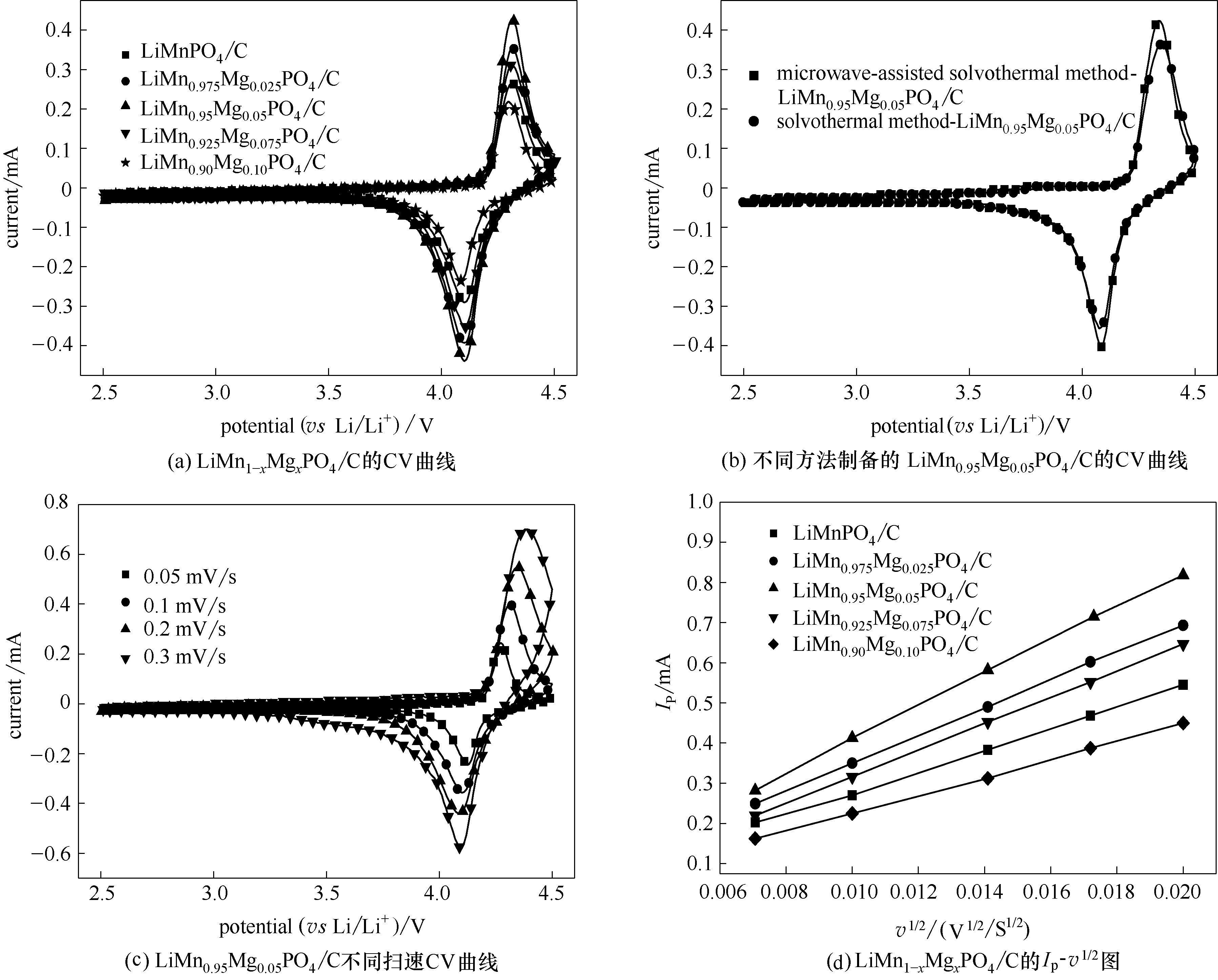
Fig.7 CV curves of microwave-assisted solvothermal samples of LiMn1-xMgxPO4/C (x = 0, 0.025, 0.05, 0.075, 0.1) (a) and LiMn0.95Mg0.05PO4/C synthesized through different routes(b) at a scan rate of 0.1 mV/s; LiMn0.95Mg0.05PO4/C synthesized through microwave-assisted solvothermal route at different scan rates (c), plots of cathodic peak current (Ip) as function of square root of scan rate (v1/2) (d)

Fig.8 EIS plots of microwave-assisted solvothermal samples of LiMn1-xMgxPO4/C (x = 0, 0.025, 0.05, 0.075, 0.1) (a) and LiMn0.95Mg0.05PO4/C synthesized through different routes (b)
| 1 | ArmandM, TarasconJ M. Building better batteries [J]. Nature, 2008, 451(7179): 652-657. |
| 2 | DunnB, KamathH, TarasconJ M. Electrical energy storage for the grid: a battery of choices [J]. Science, 2011, 334(6058):928-935. |
| 3 | NittaN, WuF, LeeJ T, et al. Li-ion battery materials: present and future [J]. Materials Today, 2015, 18(5):252-264. |
| 4 | PadhiA K, NajundaswamyK S, GoodenoughJ B. Phospho-olivines as positive-electrode materials for rechargeable lithium batteries [J]. Journal of the Electrochemical Society, 1997, 144(4): 1188-1194. |
| 5 | MasquelierC, CroguennecL. Polyanionic (phosphates, silicates, sulfates) frameworks as electrode materials for rechargeable Li (or Na) batteries [J]. Chemical Reviews, 2013, 113(8):6552-6591. |
| 6 | AravindanV, GnanarajJ, LeeY S, et al. LiMnPO4—a next generation cathode material for lithium-ion batteries [J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2013, 1(11): 3518-3539. |
| 7 | DengY F, YangC X, ZouK X, et al. Recent advances of Mn-rich LiFe1-yMnyPO4 (0.5 ≤ y < 1.0) cathode materials for high energy density lithium ion batteries[J]. Advanced Energy Materials, 2017, 7(13): 1614-6840. |
| 8 | DevarajuM K, HonmaI. Hydrothermal and solvothermal process towards development of LiMPO4 (M=Fe, Mn) nanomaterials for lithium-ion batteries [J]. Advanced Energy Materials, 2012, 2(3):284-297. |
| 9 | MorganD, van der VenA, CederG. Li conductivity in LixMPO4 (M = Mn, Fe, Co, Ni) olivine materials [J]. Electrochemical and Solid State Letters, 2004, 7(2): A30-A32. |
| 10 | YamadaA, HosoyaM, ChungS C, et al. Olivine-type cathodes: achievements and problems[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2003, 119-121(6): 232-238. |
| 11 | ZhaoM, FuY, XuN, et al. High performance LiMnPO4/C prepared by a crystallite size control method[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2014, 2(36):15070-15077. |
| 12 | DinhH C, MhoS I, YeoI H, et al. Superior high rate capability of size-controlled LiMnPO4/C nanosheets with preferential orientation[J]. RSC Advances, 2015, 5(122):100709-100714. |
| 13 | LeiZ H, NaveedA, LeiJ Y, et al. High performance nano-sized LiMn1-xFexPO4 cathode materials for advanced lithium-ion batteries[J]. RSC Advances, 2017, 7 (69):43708-43715. |
| 14 | YanS Y, WangC Y, GuR M, et al. Enhanced kinetic behaviors of LiMn0.5Fe0.5PO4/C cathode material by Fe substitution and carbon coating[J]. Journal of Solid State Electrochemistry, 2015, 19(10): 2943-2950. |
| 15 | OhS M, OhS W, YoonC S, et al. High-performance carbon-LiMnPO4 nanocomposite cathode for lithium batteries[J]. Advanced Functional Materials, 2010, 20(19): 3260-3265. |
| 16 | WangF X, WangXW, ChangZ, et al. Electrode materials with tailored facets for electrochemical energy storage [J]. Nanoscale Horizons, 2016, 1(4): 272-289. |
| 17 | JungY H, ParkW B, PyoM, et al. A multi-element doping design for a high-performance LiMnPO4 cathode via metaheuristics computation [J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2017, 5(19): 8939-8945 |
| 18 | LuQ, HutchingsG S, ZhouY, et al. Nanostructured flexible Mg-modified LiMnPO4 matrix as high-rate cathode materials for Li-ion batteries [J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2014, 2(18): 6368-6373. |
| 19 | WangY, YangH, WuC Y, et al. Facile and controllable one-pot synthesis of nickel-doped LiMn0.8Fe0.2PO4 nanosheets as high performance cathode materials for lithium-ion batteries[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2017, 5(35):18674-18683. |
| 20 | DuanJ G, HuG R, CaoY B, et al. Synthesis of high-performance Fe-Mg-co-doped LiMnPO4/C via a mechano-chemical liquid-phase activation technique[J]. Ionics, 2016, 22(5): 609-619 |
| 21 | ZhangJ, LuoS, WangQ, et al. Yttrium substituting in Mn site to improve electrochemical kinetics activity of sol-gel synthesized LiMnPO4/C as cathode for lithium ion battery [J]. Journal of Solid State Electrochemistry, 2017, 21(11): 3189-3194. |
| 22 | WangC, LiS, HanY, et al. Assembly of LiMnPO4 nanoplates into microclusters as a high-performance cathode in lithium-ion batteries [J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2017, 9(33): 27618-27624 |
| 23 | PanX, GaoZ. Hydrothermal synthesis and electrochemical properties of dispersed LiMnPO4 wedges[J]. Crystengcomm, 2013, 15(38): 7808-7814. |
| 24 | GuoH, WuC, XieJ, et al. Controllable synthesis of high-performance LiMnPO4 nanocrystals by a facile one-spot solvothermal process[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2014, 2(27): 10581-10588. |
| 25 | AssatG, ManthiramA. Rapid microwave-assisted solvothermal synthesis of non-olivine cecum polymorphs of LiMPO4 (M = Mn, Fe, Co, and Ni) at low temperature and pressure[J]. Inorganic Chemistry, 2015, 54(20): 10015-10022. |
| 26 | ZhuJ N, LiW C, ChengF, et al. Synthesis of LiMnPO4/C with superior performance as Li-ion battery cathodes by a two-stage microwave solvothermal process[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2015, 3(26): 13920-13925. |
| 27 | ÖAhmet. Positive effects of a particular type of microwave-assisted methodology on the electrochemical properties of olivine LiMPO4 (M=Fe, Co and Ni) cathode materials[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2018, 331: 501-509. |
| 28 | CuiY T, XuN, KouL Q, et al. Enhanced electrochemical performance of different morphological LiMnPO4/C nanoparticles from hollow-sphere Li3PO4 precursor via a delicate polyol-assisted hydrothermal method [J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2014, 249(3): 42-47. |
| 29 | GuoH, WuC, LiaoL, et al. Performance improvement of lithium manganese phosphate by controllable morphology tailoring with acid-engaged nano engineering[J]. Inorganic Chemistry, 2015, 54(2): 667-674. |
| 30 | WangL, ZhangH, LiuQ, et al. Modifying high-voltage olivine-type LiMnPO4 cathode via Mg substitution in high-orientation crystal [J]. ACS Applied Energy Materials, 2018, 1(11): 5928-5935. |
| 31 | HuC, YiH, FangH, et al. Improving the electrochemical activity of LiMnPO4via Mn-site co-substitution with Fe and Mg [J]. Electrochemistry Communications, 2010, 12(12): 1784-1787. |
| 32 | KumarP R, VenkateswarluM, MisraM, et al. Enhanced conductivity and electrical relaxation studies of carbon-coated LiMnPO4 nanorods[J]. Ionics, 2012, 19(3): 461-469. |
| 33 | ZhaoY, PengL L, LiuB R, et al. Single-crystalline LiFePO4 nanosheets for high-rate Li-ion batteries [J]. Nano Letters, 2014, 14(5): 2849-2853. |
| 34 | BakenovZ, TaniguchiI. LiMn1-xMgxPO4/C cathodes for lithium batteries prepared by a combination of spray pyrolysis with wet ball milling [J]. Journal of the Electrochemical Society, 2010, 157(4): A430-A436. |
| [1] | Yepin CHENG, Daqing HU, Yisha XU, Huayan LIU, Hanfeng LU, Guokai CUI. Application of ionic liquid-based deep eutectic solvents for CO2 conversion [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(9): 3640-3653. |
| [2] | Yuanchao LIU, Bin GUAN, Jianbin ZHONG, Yifan XU, Xuhao JIANG, Duan LI. Investigation of thermoelectric transport properties of single-layer XSe2 (X=Zr/Hf) [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(9): 3968-3978. |
| [3] | Yali HU, Junyong HU, Suxia MA, Yukun SUN, Xueyi TAN, Jiaxin HUANG, Fengyuan YANG. Development of novel working fluid and study on electrochemical characteristics of reverse electrodialysis heat engine [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(8): 3513-3521. |
| [4] | Jiaqi CHEN, Wanyu ZHAO, Ruichong YAO, Daolin HOU, Sheying DONG. Synthesis of pistachio shell-based carbon dots and their corrosion inhibition behavior on Q235 carbon steel [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(8): 3446-3456. |
| [5] | Jiali GE, Tuxiang GUAN, Xinmin QIU, Jian WU, Liming SHEN, Ningzhong BAO. Synthesis of FeF3 nanoparticles covered by vertical porous carbon for high performance Li-ion battery cathode [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(7): 3058-3067. |
| [6] | Yuanhao QU, Wenyi DENG, Xiaodan XIE, Yaxin SU. Study on electro-osmotic dewatering of sludge assisted by activated carbon/graphite [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(7): 3038-3050. |
| [7] | Mengmeng ZHANG, Dong YAN, Yongfeng SHEN, Wencui LI. Effect of electrolyte types on the storage behaviors of anions and cations for dual-ion batteries [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(7): 3116-3126. |
| [8] | Meibo XING, Zhongtian ZHANG, Dongliang JING, Hongfa ZHANG. Enhanced phase change energy storage/release properties by combining porous materials and water-based carbon nanotube under magnetic regulation [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(7): 3093-3102. |
| [9] | Qin YANG, Chuanjian QIN, Mingzi LI, Wenjing YANG, Weijie ZHAO, Hu LIU. Fabrication and properties of dual shape memory MXene based hydrogels for flexible sensor [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(6): 2699-2707. |
| [10] | Yuanchao LIU, Xuhao JIANG, Ke SHAO, Yifan XU, Jianbin ZHONG, Zhuan LI. Influence of geometrical dimensions and defects on the thermal transport properties of graphyne nanoribbons [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(6): 2708-2716. |
| [11] | Tan ZHANG, Guang LIU, Jinping LI, Yuhan SUN. Performance regulation strategies of Ru-based nitrogen reduction electrocatalysts [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(6): 2264-2280. |
| [12] | Xueyan WEI, Yong QIAN. Experimental study on the low to medium temperature oxidation characteristics and kinetics of micro-size iron powder [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(6): 2624-2638. |
| [13] | Chengze WANG, Kaili GU, Jinhua ZHANG, Jianxuan SHI, Yiwei LIU, Jinxiang LI. Sulfidation couples with aging to enhance the reactivity of zerovalent iron toward Cr(Ⅵ) in water [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(5): 2197-2206. |
| [14] | Xu GUO, Yongzheng ZHANG, Houbing XIA, Na YANG, Zhenzhen ZHU, Jingyao QI. Research progress in the removal of water pollutants by carbon-based materials via electrooxidation [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(5): 1862-1874. |
| [15] | Zheng ZHANG, Yongping HE, Haidong SUN, Rongzi ZHANG, Zhengping SUN, Jinlan CHEN, Yixuan ZHENG, Xiao DU, Xiaogang HAO. Electrochemically switched ion exchange device with serpentine flow field for selective extraction of lithium [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(5): 2022-2033. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||