CIESC Journal ›› 2023, Vol. 74 ›› Issue (1): 313-329.DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20221268
• Reviews and monographs • Previous Articles Next Articles
Xin LI1,2( ), Shaojuan ZENG2, Kuilin PENG2, Lei YUAN2,3, Xiangping ZHANG1,2(
), Shaojuan ZENG2, Kuilin PENG2, Lei YUAN2,3, Xiangping ZHANG1,2( )
)
Received:2022-09-21
Revised:2022-11-28
Online:2023-03-20
Published:2023-01-05
Contact:
Xiangping ZHANG
李鑫1,2( ), 曾少娟2, 彭奎霖2, 袁磊2,3, 张香平1,2(
), 曾少娟2, 彭奎霖2, 袁磊2,3, 张香平1,2( )
)
通讯作者:
张香平
作者简介:李鑫(1996—),男,硕士研究生,lixin21@ipe.ac.cn
基金资助:CLC Number:
Xin LI, Shaojuan ZENG, Kuilin PENG, Lei YUAN, Xiangping ZHANG. Research progress and tendency of CO2 electrocatalytic reduction to syngas[J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(1): 313-329.
李鑫, 曾少娟, 彭奎霖, 袁磊, 张香平. CO2电催化还原制合成气研究进展及趋势[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(1): 313-329.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
| 反应 | 标准电极电势(vs RHE)/V |
|---|---|
| 2H++2e- | -0.42 |
| CO2 + 8H++ 8e- | -0.24 |
| CO2 + 6H++ 6e- | -0.38 |
| CO2 + 4H++ 4e- | -0.51 |
| CO2 + 2H++ 2e- | -0.52 |
| CO2 + 2H++ 2e- | -0.61 |
| 2CO2 + 12H++ 12e- | 0.064 |
| 2CO2 + 12H++ 12e- | 0.084 |
Table 1 Electrode potential for semi-reaction of CO2 electrocatalytic reduction [17-20]
| 反应 | 标准电极电势(vs RHE)/V |
|---|---|
| 2H++2e- | -0.42 |
| CO2 + 8H++ 8e- | -0.24 |
| CO2 + 6H++ 6e- | -0.38 |
| CO2 + 4H++ 4e- | -0.51 |
| CO2 + 2H++ 2e- | -0.52 |
| CO2 + 2H++ 2e- | -0.61 |
| 2CO2 + 12H++ 12e- | 0.064 |
| 2CO2 + 12H++ 12e- | 0.084 |
| CO/H2 | 下游产物 |
|---|---|
| 纯CO | CO电子特气 |
| 约1 | 氢甲酰化产品 |
| 0.5~1.0 | 费托合成品 |
| 约0.5 | 甲醇 |
| 0.3~0.5 | 甲烷 |
Table 2 CO/H2 ratios and corresponding downstream chemical products[19,21-24]
| CO/H2 | 下游产物 |
|---|---|
| 纯CO | CO电子特气 |
| 约1 | 氢甲酰化产品 |
| 0.5~1.0 | 费托合成品 |
| 约0.5 | 甲醇 |
| 0.3~0.5 | 甲烷 |
| 电极 | 电解液 | 电解槽 | 电势(vs RHE)/V | 电流密度/(mA/cm2) | CO/H2 | 文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cu-In | 0.1 mol/L KHCO3 | H | -1.1 | 20 | 2~9 | [ |
| CuZnAl | 0.5 mol/L NaHCO3 | H | -2.4 | 90 | 0.14~0.5 | [ |
| PdAg | 0.5 mol/L NaHCO3 | H | -0.9 | — | 2.7 | [ |
| PdCu | 0.5 mol/L NaHCO3 | H | -0.9 | — | 1.2 | [ |
| Zn-1P | 0.5 mol/L NaHCO3 | H | -1.27 | 90.4 | 0.09~11.4 | [ |
| Co3O4-CDots-C3N4 | 0.5 mol/L KHCO3 | H | -1.0 | 15 | 0.25~14.2 | [ |
| 3D N-CNTs/SS | 0.1 mol/L KHCO3 | H | -1.1 | 2 | 0.3~3 | [ |
| ZnO-C | 0.5 mol/L KHCO3 | H | -1.2 | 27.07 | 0.73~2 | [ |
| 4.3Pd-SnO2 | 0.5 mol/L KHCO3 | H | -0.6 | 10 | 0.28~4.2 | [ |
| Zn/Cu | 0.5 mol/L KHCO3 | H | -1.53 | 20.4 | 0.25~0.84 | [ |
| HPC-Co/CoPc | 1.0 mol/L KHCO3 | H | -0.86 | 225 | 0.26~0.95 | [ |
| CF-120 | 0.1 mol/L KHCO3 | H | -0.6 | ~8.5 | 0.33~2 | [ |
| Ag | 18%(mol)[Emim][BF4] | H | — | — | — | [ |
| Ru | Bu4NH2PO4 /MeCN | H | -1.2 | — | 0.45~49 | [ |
| MoO2 | MeCN/0.3 mol/L [Bmim][PF4] | H | -2.45 | 20 | 2~5 | [ |
| In2Se3/CP | [Bmim]PF6 | H | -2.3 | 90.1 | 0.33~24 | [ |
| Ag/TiO2 | 1 mol/L NaOH | GDE | -0.56 | ~-83 | 0.5~1.5 | [ |
| Cu-In | 1 mol/L KOH | GDE | -1.17 | ∼200 | 1.49~14.77 | [ |
| 4.3Pd-SnO2 | 0.5 mol/L KHCO3 | GDE | -0.9 | 100 | 0.26~9.2 | [ |
| HPC-Co/CoPc | 1.0 mol/L KOH | GDE | -0.6 | 880 | — | [ |
| PdH | 0.5 mol/L NaHCO3 | MEA | -0.9 | 200 | 0.25~1 | [ |
| BiO x /[Bmim]OTf | — | MEA | -3.8 V(full cell) | 200 | — | [ |
| Ni SA | — | MEA | -2.78 V(full cell) | ~50 | — | [ |
| NiO | — | SOEC | -1.3 | 620 | 0.5~2 | [ |
Table 3 Different system of CO2 electrocatalytic reduction to syngas
| 电极 | 电解液 | 电解槽 | 电势(vs RHE)/V | 电流密度/(mA/cm2) | CO/H2 | 文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cu-In | 0.1 mol/L KHCO3 | H | -1.1 | 20 | 2~9 | [ |
| CuZnAl | 0.5 mol/L NaHCO3 | H | -2.4 | 90 | 0.14~0.5 | [ |
| PdAg | 0.5 mol/L NaHCO3 | H | -0.9 | — | 2.7 | [ |
| PdCu | 0.5 mol/L NaHCO3 | H | -0.9 | — | 1.2 | [ |
| Zn-1P | 0.5 mol/L NaHCO3 | H | -1.27 | 90.4 | 0.09~11.4 | [ |
| Co3O4-CDots-C3N4 | 0.5 mol/L KHCO3 | H | -1.0 | 15 | 0.25~14.2 | [ |
| 3D N-CNTs/SS | 0.1 mol/L KHCO3 | H | -1.1 | 2 | 0.3~3 | [ |
| ZnO-C | 0.5 mol/L KHCO3 | H | -1.2 | 27.07 | 0.73~2 | [ |
| 4.3Pd-SnO2 | 0.5 mol/L KHCO3 | H | -0.6 | 10 | 0.28~4.2 | [ |
| Zn/Cu | 0.5 mol/L KHCO3 | H | -1.53 | 20.4 | 0.25~0.84 | [ |
| HPC-Co/CoPc | 1.0 mol/L KHCO3 | H | -0.86 | 225 | 0.26~0.95 | [ |
| CF-120 | 0.1 mol/L KHCO3 | H | -0.6 | ~8.5 | 0.33~2 | [ |
| Ag | 18%(mol)[Emim][BF4] | H | — | — | — | [ |
| Ru | Bu4NH2PO4 /MeCN | H | -1.2 | — | 0.45~49 | [ |
| MoO2 | MeCN/0.3 mol/L [Bmim][PF4] | H | -2.45 | 20 | 2~5 | [ |
| In2Se3/CP | [Bmim]PF6 | H | -2.3 | 90.1 | 0.33~24 | [ |
| Ag/TiO2 | 1 mol/L NaOH | GDE | -0.56 | ~-83 | 0.5~1.5 | [ |
| Cu-In | 1 mol/L KOH | GDE | -1.17 | ∼200 | 1.49~14.77 | [ |
| 4.3Pd-SnO2 | 0.5 mol/L KHCO3 | GDE | -0.9 | 100 | 0.26~9.2 | [ |
| HPC-Co/CoPc | 1.0 mol/L KOH | GDE | -0.6 | 880 | — | [ |
| PdH | 0.5 mol/L NaHCO3 | MEA | -0.9 | 200 | 0.25~1 | [ |
| BiO x /[Bmim]OTf | — | MEA | -3.8 V(full cell) | 200 | — | [ |
| Ni SA | — | MEA | -2.78 V(full cell) | ~50 | — | [ |
| NiO | — | SOEC | -1.3 | 620 | 0.5~2 | [ |

Fig.1 (a) Wall breaking and ring opening of carbon nanotube[31]; (b) Effect of different sizes nano Zn on CO/H2[50]; (c) Preparation of oxygen vacancy N-ZnO by rapid flame method[35]; (d) Construction of Pd-SnO2 interface[36]; (e) Dual single-cobalt atom-based carbon electrocatalyst for CO2RR and HER[38]
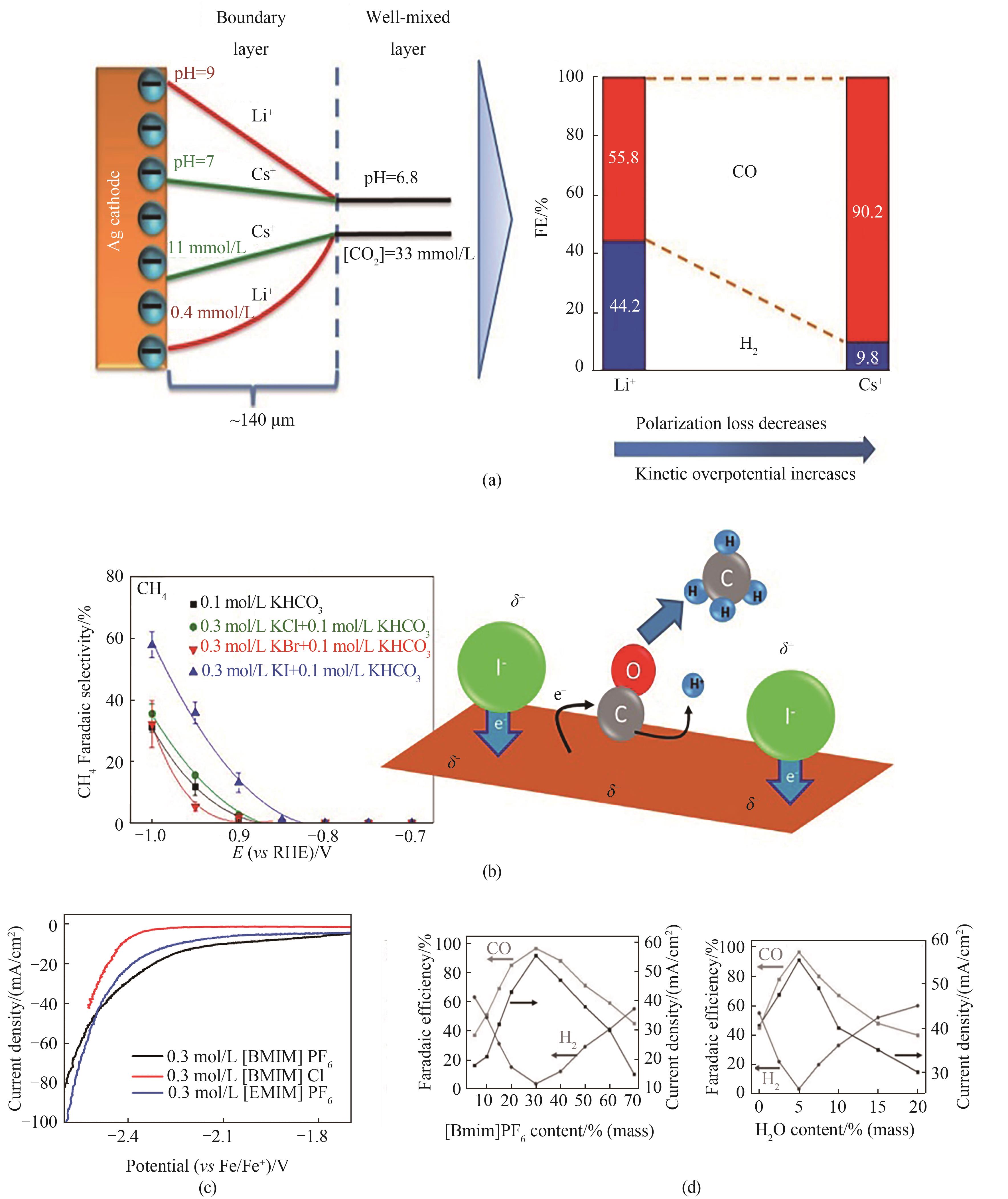
Fig.2 (a) Relationship between cation and pKa[64]; (b) Effect of halogen ion on product selectivity[66]; (c) Effect of different ionic liquids on current density[42]; (d) Adjust IL concentration and H2O content to regulate CO/H2 ratio[43]
| 1 | Global monitoring laboratory, earth system research laboratories[EB/OL]. . |
| 2 | Goeppert A, Czaun M, Surya Prakash G K, et al. Air as the renewable carbon source of the future: an overview of CO2 capture from the atmosphere[J]. Energy & Environmental Science, 2012, 5(7): 7833. |
| 3 | Nguyen T N, Dinh C T. Gas diffusion electrode design for electrochemical carbon dioxide reduction[J]. Chemical Society Reviews, 2020, 49(21): 7488-7504. |
| 4 | Tomboc G M, Choi S, Kwon T, et al. Potential link between Cu surface and selective CO2 electroreduction: perspective on future electrocatalyst designs[J]. Advanced Materials, 2020, 32(17): 1908398. |
| 5 | Rubin E S, Chen C, Rao A B. Cost and performance of fossil fuel power plants with CO2 capture and storage[J]. Energy Policy, 2007, 35(9): 4444-4454. |
| 6 | Hao L, Kang L, Huang H W, et al. Surface-halogenation-induced atomic-site activation and local charge separation for superb CO2 photoreduction[J]. Advanced Materials, 2019, 31(25): 1900546. |
| 7 | Li Y, Li B H, Zhang D N, et al. Crystalline carbon nitride supported copper single atoms for photocatalytic CO2 reduction with nearly 100% CO selectivity[J]. ACS Nano, 2020, 14(8): 10552-10561. |
| 8 | Heenemann M, Millet M M, Girgsdies F, et al. The mechanism of interfacial CO2 activation on Al doped Cu/ZnO[J]. ACS Catalysis, 2020, 10(10): 5672-5680. |
| 9 | Wang S W, Wu T J, Lin J, et al. Iron-potassium on single-walled carbon nanotubes as efficient catalyst for CO2 hydrogenation to heavy olefins[J]. ACS Catalysis, 2020, 10(11): 6389-6401. |
| 10 | Xu D, Ding M Y, Hong X L, et al. Selective C2+ alcohol synthesis from direct CO2 hydrogenation over a Cs-promoted Cu-Fe-Zn catalyst[J]. ACS Catalysis, 2020, 10(9): 5250-5260. |
| 11 | Ebaid M, Jiang K, Zhang Z M, et al. Production of C2/C3 oxygenates from planar copper nitride-derived mesoporous copper via electrochemical reduction of CO2 [J]. Chemistry of Materials, 2020, 32(7): 3304-3311. |
| 12 | Li J, Wu D H, Malkani A S, et al. Hydroxide is not a promoter of C2+ product formation in the electrochemical reduction of CO on copper[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2020, 59(11): 4464-4469. |
| 13 | Ma L S, Hu W B, Mei B B, et al. Covalent triazine framework confined copper catalysts for selective electrochemical CO2 reduction: operando diagnosis of active sites[J]. ACS Catalysis, 2020, 10(8): 4534-4542. |
| 14 | Bouzon M, Perret A, Loreau O, et al. A synthetic alternative to canonical one-carbon metabolism[J]. ACS Synthetic Biology, 2017, 6(8): 1520-1533. |
| 15 | Döring V, Darii E, Yishai O, et al. Implementation of a reductive route of one-carbon assimilation in Escherichia coli through directed evolution[J]. ACS Synthetic Biology, 2018, 7(9): 2029-2036. |
| 16 | Zhang W J, Hu Y, Ma L B, et al. Progress and perspective of electrocatalytic CO2 reduction for renewable carbonaceous fuels and chemicals[J]. Advanced Science, 2017, 5(1): 1700275. |
| 17 | 张少阳, 商阳阳, 赵瑞花, 等. 电催化还原二氧化碳制一氧化碳催化剂研究进展[J]. 化工进展, 2022, 41(4): 1848-1857. |
| Zhang S Y, Shang Y Y, Zhao R H, et al. Research progress on catalysts for electrocatalytic reduction of carbon dioxide to carbon monoxide[J]. Chemical Industry and Engineering Progress, 2022, 41(4): 1848-1857. | |
| 18 | 孙睿, 徐跃, 刘建芳, 等. CO2催化还原转化为高附加值化学品[J]. 中国科学: 化学, 2018, 48(6): 547-561. |
| Sun R, Xu Y, Liu J F, et al. Recent progress in CO2 catalytic reduction to high value-added chemicals[J]. Scientia Sinica Chimica, 2018, 48(6): 547-561. | |
| 19 | 华亚妮, 冯少广, 党欣悦, 等. CO2电催化还原产合成气研究进展[J]. 化工进展, 2022, 41(3): 1224-1240. |
| Hua Y N, Feng S G, Dang X Y, et al. Research progress of CO2 electrocatalytic reduction to syngas[J]. Chemical Industry and Engineering Progress, 2022, 41(3): 1224-1240. | |
| 20 | 邵斌, 孙哲毅, 章云, 等. 二氧化碳转化为合成气及高附加值产品的研究进展[J]. 化工进展, 2022, 41(3): 1136-1151. |
| Shao B, Sun Z Y, Zhang Y, et al. Recent progresses in CO2 to syngas and high value-added products[J]. Chemical Industry and Engineering Progress, 2022, 41(3): 1136-1151. | |
| 21 | Wenzel M, Rihko-Struckmann L, Sundmacher K. Thermodynamic analysis and optimization of RWGS processes for solar syngas production from CO2 [J]. AIChE Journal, 2017, 63(1): 15-22. |
| 22 | Ma S C, Huang S D, Liu Z P. Dynamic coordination of cations and catalytic selectivity on zinc-chromium oxide alloys during syngas conversion[J]. Nature Catalysis, 2019, 2(8): 671-677. |
| 23 | 王茹洁, 赵华君, 齐彩娆, 等. 电催化还原CO2制单碳产物反应机理及催化剂研究进展[J]. 天然气化工—C1化学与化工, 2022, 47(2): 11-17. |
| Wang R J, Zhao H J, Qi C R, et al. Research progress on reaction mechanism and catalysts of electrocatalytic reduction of CO2 to single-carbon compounds[J]. Natural Gas Chemical Industry, 2022, 47(2): 11-17. | |
| 24 | Hua Y N, Wang J Y, Min T, et al. Electrochemical CO2 conversion towards syngas: recent catalysts and improving strategies for ratio-tunable syngas[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2022, 535: 231453. |
| 25 | Scarpa D, Sarno M. Single-atom catalysts for the electro-reduction of CO2 to syngas with a tunable CO/H2 ratio:a review[J]. Catalysts, 2022, 12(3): 275-284. |
| 26 | Gao D F, Arán-Ais R M, Jeon H S, et al. Rational catalyst and electrolyte design for CO2 electroreduction towards multicarbon products[J]. Nature Catalysis, 2019, 2(3): 198-210. |
| 27 | Chu M G, Chen C J, Wu Y H, et al. Enhanced CO2 electroreduction to ethylene via strong metal-support interaction[J]. Green Energy & Environment, 2022, 7(4): 792-798. |
| 28 | Clark E L, Ringe S, Tang M, et al. Influence of atomic surface structure on the activity of Ag for the electrochemical reduction of CO2 to CO[J]. ACS Catalysis, 2019, 9(5): 4006-4014. |
| 29 | Mahyoub S A, Qaraah F A, Yan S L, et al. 3D Cu/In nanocones by morphological and interface engineering design in achieving a high current density for electroreduction of CO2 to syngas under elevated pressure[J]. Journal of CO2 Utilization, 2022, 61: 102033. |
| 30 | Guzmán H, Roldán D, Sacco A, et al. CuZnAl-oxide nanopyramidal mesoporous materials for the electrocatalytic CO2 reduction to syngas: tuning of H2/CO ratio[J]. Nanomaterials, 2021, 11(11): 3052. |
| 31 | Pan F P, Li B Y, Sarnello E, et al. Atomically dispersed iron-nitrogen sites on hierarchically mesoporous carbon nanotube and graphene nanoribbon networks for CO2 reduction[J]. ACS Nano, 2020, 14(5): 5506-5516. |
| 32 | Li P S, Liu J Y, Bi J H, et al. Tuning the efficiency and product composition for electrocatalytic CO2 reduction to syngas over zinc films by morphology and wettability[J]. Green Chemistry, 2022, 24(4): 1439-1444. |
| 33 | Guo S J, Zhao S Q, Wu X Q, et al. A Co3O4-CDots-C3N4 three component electrocatalyst design concept for efficient and tunable CO2 reduction to syngas[J]. Nature Communications, 2017, 8: 1828. |
| 34 | Liu K H, Zhong H X, Yang X Y, et al. Composition-tunable synthesis of “clean” syngas via a one-step synthesis of metal-free pyridinic-N-enriched self-supported CNTs: the synergy of electrocatalyst pyrolysis temperature and potential[J]. Green Chemistry, 2017, 19(18): 4284-4288. |
| 35 | Ma C, Zou X Y, Li A, et al. Rapid flame synthesis of carbon doped defective ZnO for electrocatalytic CO2 reduction to syngas[J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2022, 411: 140098. |
| 36 | He H C, Xia D, Yu X, et al. Pd-SnO2 interface enables synthesis of syngas with controllable H2/CO ratios by electrocatalytic reduction of CO2 [J]. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 2022, 312: 121392. |
| 37 | Chen P, Jiao Y, Zhu Y H, et al. Syngas production from electrocatalytic CO2 reduction with high energetic efficiency and current density[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2019, 7(13): 7675-7682. |
| 38 | Ni W P, Liu Z X, Guo X G, et al. Dual single-cobalt atom-based carbon electrocatalysts for efficient CO2 to syngas conversion with industrial current densities[J]. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 2021, 291: 120092. |
| 39 | Li H Q, Xiao N, Wang Y W, et al. Nitrogen-doped tubular carbon foam electrodes for efficient electroreduction of CO2 to syngas with potential-independent CO/H2 ratios[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2019, 7(32): 18852-18860. |
| 40 | Rosen B A, Salehi-Khojin A, Thorson M R, et al. Ionic liquid-mediated selective conversion of CO2 to CO at low overpotentials[J]. Science, 2011, 334(6056): 643-644. |
| 41 | Chen Z F, Kang P, Zhang M T, et al. Making syngas electrocatalytically using a polypyridyl ruthenium catalyst[J]. Chemical Communications, 2014, 50(3): 335-337. |
| 42 | Oh Y, Hu X L. Ionic liquids enhance the electrochemical CO2 reduction catalyzed by MoO2 [J]. Chemical Communications, 2015, 51(71): 13698-13701. |
| 43 | Yang D X, Zhu Q G, Sun X F, et al. Electrosynthesis of a defective indium selenide with 3D structure on a substrate for tunable CO2 electroreduction to syngas[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2020, 59(6): 2354-2359. |
| 44 | Kim Y E, Kim B, Lee W, et al. Highly tunable syngas production by electrocatalytic reduction of CO2 using Ag/TiO2 catalysts[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2021, 413: 127448. |
| 45 | Xiang H, Rasul S, Hou B, et al. Copper-indium binary catalyst on a gas diffusion electrode for high-performance CO2 electrochemical reduction with record CO production efficiency[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2020, 12(1): 601-608. |
| 46 | Li Y C, Zhou D K, Yan Z F, et al. Electrolysis of CO2 to syngas in bipolar membrane-based electrochemical cells[J]. ACS Energy Letters, 2016, 1(6): 1149-1153. |
| 47 | Jiang K, Siahrostami S, Zheng T T, et al. Isolated Ni single atoms in graphene nanosheets for high-performance CO2 reduction[J]. Energy & Environmental Science, 2018, 11(4): 893-903. |
| 48 | Song Y F, Zhou Z W, Zhang X M, et al. Pure CO2 electrolysis over an Ni/YSZ cathode in a solid oxide electrolysis cell[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2018, 6(28): 13661-13667. |
| 49 | Zhu W L, Zhang Y J, Zhang H Y, et al. Active and selective conversion of CO2 to CO on ultrathin Au nanowires[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2014, 136(46): 16132-16135. |
| 50 | Han K, Ngene P, De Jongh P. Structure dependent product selectivity for CO2 electroreduction on ZnO derived catalysts[J]. ChemCatChem, 2021, 13(8): 1998-2004. |
| 51 | Qin B H, Li Y H, Fu H Q, et al. Electrochemical reduction of CO2 into tunable syngas production by regulating the crystal facets of earth-abundant Zn catalyst[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2018, 10(24): 20530-20539. |
| 52 | Xiong B, Yang Y J, Liu J, et al. Crystal orientation effects on the electrochemical conversion of CO2 to syngas over Cu-M (M=Ag, Ni, Zn, Cd, and Pd) bimetal catalysts[J]. Applied Surface Science, 2021, 567: 150839. |
| 53 | Cao K L, Ji Y J, Bai S X, et al. A wide range of CO:H2 syngas ratios enabled by a tellurization-induced amorphous telluride–palladium surface[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2021, 9(34): 18349-18355. |
| 54 | Xie C L, Niu Z Q, Kim D, et al. Surface and interface control in nanoparticle catalysis[J]. Chemical Reviews, 2020, 120(2): 1184-1249. |
| 55 | Luo W, Xie W, Mutschler R, et al. Selective and stable electroreduction of CO2 to CO at the copper/indium interface[J]. ACS Catalysis, 2018, 8(7): 6571-6581. |
| 56 | Wang X, Lv J, Zhang J X, et al. Hierarchical heterostructure of SnO2 confined on CuS nanosheets for efficient electrocatalytic CO2 reduction[J]. Nanoscale, 2020, 12(2): 772-784. |
| 57 | Zhang L L, Ren Y J, Liu W G, et al. Single-atom catalyst: a rising star for green synthesis of fine chemicals[J]. National Science Review, 2018, 5(5): 653-672. |
| 58 | Zhang L L, Zhou M X, Wang A Q, et al. Selective hydrogenation over supported metal catalysts: from nanoparticles to single atoms[J]. Chemical Reviews, 2020, 120(2): 683-733. |
| 59 | He Q, Liu D B, Lee J H, et al. Electrochemical conversion of CO2 to syngas with controllable CO/H2 ratios over Co and Ni single-atom catalysts[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2020, 59(8): 3033-3037. |
| 60 | Deng B W, Huang M, Zhao X L, et al. Interfacial electrolyte effects on electrocatalytic CO2 reduction[J]. ACS Catalysis, 2022, 12(1): 331-362. |
| 61 | Sa Y J, Lee C W, Lee S Y, et al. Catalyst-electrolyte interface chemistry for electrochemical CO2 reduction[J]. Chemical Society Reviews, 2020, 49(18): 6632-6665. |
| 62 | Gutiérrez-Sánchez O, Daems N, Offermans W, et al. The inhibition of the proton donor ability of bicarbonate promotes the electrochemical conversion of CO2 in bicarbonate solutions[J]. Journal of CO2 Utilization, 2021, 48: 101521. |
| 63 | Zhong Y, Xu Y, Ma J, et al. An artificial electrode/electrolyte interface for CO2 electroreduction by cation surfactant self-assembly[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2020, 59(43): 19095-19101. |
| 64 | Singh M R, Kwon Y, Lum Y, et al. Hydrolysis of electrolyte cations enhances the electrochemical reduction of CO2 over Ag and Cu[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2016, 138(39): 13006-13012. |
| 65 | Malkani A S, Anibal J, Xu B J. Cation effect on interfacial CO2 concentration in the electrochemical CO2 reduction reaction[J]. ACS Catalysis, 2020, 10(24): 14871-14876. |
| 66 | Varela A S, Ju W, Reier T, et al. Tuning the catalytic activity and selectivity of Cu for CO2 electroreduction in the presence of halides[J]. ACS Catalysis, 2016, 6(4): 2136-2144. |
| 67 | 张香平, 曾少娟, 冯佳奇, 等.CO2化工:离子微环境调控的CO2绿色高效转化[J]. 中国科学:化学, 2020, 50(2): 282-298. |
| Zhang X P, Zeng S J, Feng J Q, et al. CO2 chemical engineering: CO2 green conversion enhanced by ionic liquid microhabitat[J]. Scientia Sinica Chimica, 2020, 50(2): 282-298. | |
| 68 | Dong K, Liu X M, Dong H F, et al. Multiscale studies on ionic liquids[J]. Chemical Reviews, 2017, 117(10): 6636-6695. |
| 69 | Vasilyev D V, Shyshkanov S, Shirzadi E, et al. Principal descriptors of ionic liquid co-catalysts for the electrochemical reduction of CO2 [J]. ACS Applied Energy Materials, 2020, 3(5): 4690-4698. |
| 70 | Tanner E E L, Batchelor-Mcauley C, Compton R G. Carbon dioxide reduction in room-temperature ionic liquids: the effect of the choice of electrode material, cation, and anion[J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2016, 120(46): 26442-26447. |
| 71 | Monroe M M, Lobaccaro P, Lum Y, et al. Membraneless laminar flow cell for electrocatalytic CO2 reduction with liquid product separation[J]. Journal of Physics D: Applied Physics, 2017, 50(15): 154006. |
| 72 | Zhu P, Wang H T. High-purity and high-concentration liquid fuels through CO2 electroreduction[J]. Nature Catalysis, 2021, 4(11): 943-951. |
| 73 | Mohd Adli N, Shan W T, Hwang S, et al. Engineering atomically dispersed FeN4 active sites for CO2 electroreduction[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2021, 60(2): 1022-1032. |
| 74 | Sheng X D, Ge W X, Jiang H L, et al. Engineering the Ni-N-C catalyst microenvironment enabling CO2 electroreduction with nearly 100% CO selectivity in acid[J]. Advanced Materials, 2022, 34(38): e2201295. |
| 75 | Wicks J, Jue M L, Beck V A, et al. 3D-printable fluoropolymer gas diffusion layers for CO2 electroreduction[J]. Advanced Materials, 2021, 33(7): 2003855. |
| 76 | Song Y F, Zhang X M, Xie K, et al. High-temperature CO2 electrolysis in solid oxide electrolysis cells: developments, challenges, and prospects[J]. Advanced Materials, 2019, 31(50): 1902033. |
| 77 | Zhang X Y, O’Brien J E, O’Brien R C, et al. Improved durability of SOEC stacks for high temperature electrolysis[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2013, 38(1): 20-28. |
| 78 | Fan H, Han M F. Improved performance and stability of Ag-infiltrated nanocomposite La0.6Sr0.4Co0.2Fe0.8O3- δ -(Y2O3)0.08(ZrO2)0.92 oxygen electrode for H2O/CO2 co-electrolysis[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2016, 336: 179-185. |
| 79 | Zhou Y J, Zhou Z W, Song Y F, et al. Enhancing CO2 electrolysis performance with vanadium-doped perovskite cathode in solid oxide electrolysis cell[J]. Nano Energy, 2018, 50: 43-51. |
| 80 | Jin S, Hao Z M, Zhang K, et al. Advances and challenges for the electrochemical reduction of CO2 to CO: from fundamentals to industrialization[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2021, 60(38): 20627-20648. |
| 81 | Daiyan R, Chen R, Kumar P, et al. Tunable syngas production through CO2 electroreduction on cobalt-carbon composite electrocatalyst[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2020, 12(8): 9307-9315. |
| 82 | Charles D, John N. Mathematical modeling of CO2 reduction to CO in aqueous electrolytes (Ⅱ): Study of an electrolysis cell making syngas (CO+H2) from CO2 and H2O reduction at room temperature[J]. Joural of The Electrochemical Society, 2010, 157(12:) 1911-1926. |
| 83 | Pan F P, Yang Y. Designing CO2 reduction electrode materials by morphology and interface engineering[J]. Energy & Environmental Science, 2020, 13(8): 2275-2309. |
| 84 | Seifitokaldani A, Gabardo C M, Burdyny T, et al. Hydronium-induced switching between CO2 electroreduction pathways[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2018, 140(11): 3833-3837. |
| 85 | Ge W X, Chen Y X, Fan Y, et al. Dynamically formed surfactant assembly at the electrified electrode-electrolyte interface boosting CO2 electroreduction[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2022, 144(14): 6613-6622. |
| 86 | 江重阳, 冯佳奇, 曾少娟, 等.CO2电化学还原过程中电解质研究现状及趋势[J]. 科学通报, 2021, 66(7): 716-727. |
| Jiang C Y, Feng J Q, Zeng S J, et al. Research status and trend of electrolytes in the CO2 electrochemical reduction[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2021, 66(7): 716-727. | |
| 87 | 冯建朋, 张香平, 尚大伟, 等.离子液体中电化学还原CO2研究评述与展望[J]. 化工学报, 2018, 69(1): 69-75. |
| Feng J P, Zhang X P, Shang D W, et al. Review and prospect of CO2 electro-reduction in ionic liquids[J]. CIESC Journal, 2018, 69(1): 69-75. | |
| 88 | Yang D W, Li Q Y, Shen F X, et al. Electrochemical impedance studies of CO2 reduction in ionic liquid/organic solvent electrolyte on Au electrode[J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2016, 189: 32-37. |
| 89 | Sun L Y, Ramesha G K, Kamat P V, et al. Switching the reaction course of electrochemical CO2 reduction with ionic liquids[J]. Langmuir, 2014, 30(21): 6302-6308. |
| 90 | DiMeglio J L, Rosenthal J. Selective conversion of CO2 to CO with high efficiency using an inexpensive bismuth-based electrocatalyst[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2013, 135(24): 8798-8801. |
| 91 | Lau G P S, Schreier M, Vasilyev D, et al. New insights into the role of imidazolium-based promoters for the electroreduction of CO2 on a silver electrode[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2016, 138(25): 7820-7823. |
| 92 | Liang S Y, Huang L, Gao Y S, et al. Electrochemical reduction of CO2 to CO over transition metal/N-doped carbon catalysts: the active sites and reaction mechanism[J]. Advanced Science, 2021, 8(24): 2102886. |
| 93 | Chen Z S, Zhang G X, Chen H R, et al. Multi-metallic catalysts for the electroreduction of carbon dioxide: recent advances and perspectives[J]. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 2022, 155: 111922. |
| 94 | Gui J J, Zhang K F, Zhan X W, et al. Nitrogen-doped porous carbon nanosheets as a robust catalyst for tunable CO2 electroreduction to syngas[J]. Sustainable Energy & Fuels, 2022, 6(6): 1512-1518. |
| 95 | Yan W Y, Zhang C, Liu L. Hierarchically porous CuAg via 3D printing/dealloying for tunable CO2 reduction to syngas[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2021, 13(38): 45385-45393. |
| 96 | Luo H Q, Li B, Ma J G, et al. Surface modification of nano-Cu2O for controlling CO2 electrochemical reduction to ethylene and syngas[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2022, 61(11): e202116736. |
| 97 | Lu Q, Jiao F. Electrochemical CO2 reduction: electrocatalyst, reaction mechanism, and process engineering[J]. Nano Energy, 2016, 29: 439-456. |
| 98 | Yan X X, Gu M Y, Wang Y, et al. In-situ growth of Ni nanoparticle-encapsulated N-doped carbon nanotubes on carbon nanorods for efficient hydrogen evolution electrocatalysis[J]. Nano Research, 2020, 13(4): 975-982. |
| 99 | Ismail A M, Samu G F, Balog Á, et al. Composition-dependent electrocatalytic behavior of Au-Sn bimetallic nanoparticles in carbon dioxide reduction[J]. ACS Energy Letters, 2019, 4(1): 48-53. |
| 100 | Zou X Y, Ma C, Li A, et al. Nanoparticle-assisted Ni-Co binary single-atom catalysts supported on carbon nanotubes for efficient electroreduction of CO2 to syngas with controllable CO/H2 ratios[J]. ACS Applied Energy Materials, 2021, 4(9): 9572-9581. |
| 101 | Liang Z, Song L P, Sun M Z, et al. Tunable CO/H2 ratios of electrochemical reduction of CO2 through the Zn-La dual atomic catalysts[J]. Science Advances, 2021, 7(47): eabl4915. |
| 102 | Sullivan I, Goryachev A, Digdaya I A, et al. Coupling electrochemical CO2 conversion with CO2 capture[J]. Nature Catalysis, 2021, 4(11): 952-958. |
| 103 | Lee G, Li Y C, Kim J Y, et al. Electrochemical upgrade of CO2 from amine capture solution[J]. Nature Energy, 2021, 6(1): 46-53. |
| 104 | Huang Y Y, Yang R, Anandhababu G, et al. Cobalt/iron(oxides) heterostructures for efficient oxygen evolution and benzyl alcohol oxidation reactions[J]. ACS Energy Letters, 2018, 3(8): 1854-1860. |
| 105 | Verma S, Lu S, Kenis P J A. Co-electrolysis of CO2 and glycerol as a pathway to carbon chemicals with improved technoeconomics due to low electricity consumption[J]. Nature Energy, 2019, 4(6): 466-474. |
| 106 | Li T F, Cao Y, He J F, et al. Electrolytic CO2 reduction in tandem with oxidative organic chemistry[J]. ACS Central Science, 2017, 3(7): 778-783. |
| 107 | Wei X F, Li Y, Chen L S, et al. Formic acid electro-synthesis by concurrent cathodic CO2 reduction and anodic CH3OH oxidation[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2021, 60(6): 3148-3155. |
| [1] | Baomin DAI, Qilong WANG, Shengchun LIU, Jianing ZHANG, Xinhai LI, Fandi ZONG. Thermodynamic performance analysis of combined cooling and heating system based on combination of CO2 with the zeotropic refrigerant assisted subcooled [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(S1): 64-73. |
| [2] | Tianyang YANG, Huiming ZOU, Hui ZHOU, Chunlei WANG, Changqing TIAN. Experimental investigation on heating performance of vapor-injection CO2 heat pump for electric vehicles at -30℃ [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(S1): 272-279. |
| [3] | Lei WU, Jiao LIU, Changcong LI, Jun ZHOU, Gan YE, Tiantian LIU, Ruiyu ZHU, Qiuli ZHANG, Yonghui SONG. Catalytic microwave pyrolysis of low-rank pulverized coal for preparation of high value-added modified bluecoke powders containing carbon nanotubes [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(9): 3956-3967. |
| [4] | Yitong LI, Hang GUO, Hao CHEN, Fang YE. Study on operating conditions of proton exchange membrane fuel cells with non-uniform catalyst distributions [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(9): 3831-3840. |
| [5] | Meisi CHEN, Weida CHEN, Xinyao LI, Shangyu LI, Youting WU, Feng ZHANG, Zhibing ZHANG. Advances in silicon-based ionic liquid microparticle enhanced gas capture and conversion [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(9): 3628-3639. |
| [6] | Jie CHEN, Yongsheng LIN, Kai XIAO, Chen YANG, Ting QIU. Study on catalytic synthesis of sec-butanol by tunable choline-based basic ionic liquids [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(9): 3716-3730. |
| [7] | Xuejin YANG, Jintao YANG, Ping NING, Fang WANG, Xiaoshuang SONG, Lijuan JIA, Jiayu FENG. Research progress in dry purification technology of highly toxic gas PH3 [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(9): 3742-3755. |
| [8] | Xin YANG, Xiao PENG, Kairu XUE, Mengwei SU, Yan WU. Preparation of molecularly imprinted-TiO2 and its properties of photoelectrocatalytic degradation of solubilized PHE [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(8): 3564-3571. |
| [9] | Linqi YAN, Zhenlei WANG. Multi-step predictive soft sensor modeling based on STA-BiLSTM-LightGBM combined model [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(8): 3407-3418. |
| [10] | Rubin ZENG, Zhongjie SHEN, Qinfeng LIANG, Jianliang XU, Zhenghua DAI, Haifeng LIU. Study of the sintering mechanism of Fe2O3 nanoparticles based on molecular dynamics simulation [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(8): 3353-3365. |
| [11] | Feifei YANG, Shixi ZHAO, Wei ZHOU, Zhonghai NI. Sn doped In2O3 catalyst for selective hydrogenation of CO2 to methanol [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(8): 3366-3374. |
| [12] | Kaixuan LI, Wei TAN, Manyu ZHANG, Zhihao XU, Xuyu WANG, Hongbing JI. Design of cobalt-nitrogen-carbon/activated carbon rich in zero valent cobalt active site and application of catalytic oxidation of formaldehyde [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(8): 3342-3352. |
| [13] | Mengmeng ZHANG, Dong YAN, Yongfeng SHEN, Wencui LI. Effect of electrolyte types on the storage behaviors of anions and cations for dual-ion batteries [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(7): 3116-3126. |
| [14] | Ji CHEN, Ze HONG, Zhao LEI, Qiang LING, Zhigang ZHAO, Chenhui PENG, Ping CUI. Study on coke dissolution loss reaction and its mechanism based on molecular dynamics simulations [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(7): 2935-2946. |
| [15] | Yajie YU, Jingru LI, Shufeng ZHOU, Qingbiao LI, Guowu ZHAN. Construction of nanomaterial and integrated catalyst based on biological template: a review [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(7): 2735-2752. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||