化工学报 ›› 2023, Vol. 74 ›› Issue (6): 2351-2362.DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20230291
收稿日期:2023-03-27
修回日期:2023-05-31
出版日期:2023-06-05
发布日期:2023-07-27
通讯作者:
刘道银
作者简介:刘道银(1982—),男,博士,副教授,dyliu@seu.edu.cn
基金资助:
Daoyin LIU( ), Bingqi CHEN, Zuyang ZHANG, Yan WU
), Bingqi CHEN, Zuyang ZHANG, Yan WU
Received:2023-03-27
Revised:2023-05-31
Online:2023-06-05
Published:2023-07-27
Contact:
Daoyin LIU
摘要:
黏性颗粒多以聚团形式存在于气固两相系统中,流体施加于聚团的曳力对两相流动及传热传质起着至关重要的作用,而聚团的不规则、分形结构增加了曳力特性的复杂性。基于黏性离散单元方法生成不同分形结构的聚团,利用计算流体力学方法(CFD)直接求解分形聚团内部多孔结构的气流流动,得到了气体流过聚团时的周围与内部流场,研究了低Reynolds数(Re=0.1~10)条件下聚团结构特征对曳力的影响。结果表明:聚团的疏密程度显著影响聚团整体流场分布,多孔疏松结构增强了聚团的渗透性,使其与流体接触面积增加,所受曳力增加。分析不同结构聚团的曳力系数发现:除了聚团孔隙率、分形维数等结构参数的影响,气体流经聚团的方向也影响聚团曳力系数。在此基础上,综合考虑聚团分形维数、聚团与气流的夹角方向、Reynolds数拟合得到聚团曳力系数关联式。
中图分类号:
刘道银, 陈柄岐, 张祖扬, 吴琰. 颗粒聚团结构对曳力特性影响的数值模拟[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(6): 2351-2362.
Daoyin LIU, Bingqi CHEN, Zuyang ZHANG, Yan WU. Effect of agglomerate structure on drag force by numerical simulation[J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(6): 2351-2362.
| 聚团编号 | 颗粒速度/(m/s) | 回转半径/m | 分形维数 | 无量纲密度 | 孔隙度/% | 投影面积/m2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Agg-Ⅰ-1 | 0 | 2.62×10-5 | 2.94 | 0.87 | 12.73 | 3.96×10-9 |
| Agg-Ⅱ-1 | 0.1 | 3.12×10-5 | 2.74 | 0.51 | 48.66 | 5.22×10-9 |
| Agg-Ⅲ-1 | 0.5 | 4.05×10-5 | 2.48 | 0.24 | 76.39 | 3.44×10-9 |
| Agg-Ⅳ-1 | 1.0 | 5.90×10-5 | 2.19 | 0.08 | 92.39 | 9.08×10-9 |
表1 典型聚团结构特性表征
Table 1 Characteristics of typical agglomerates
| 聚团编号 | 颗粒速度/(m/s) | 回转半径/m | 分形维数 | 无量纲密度 | 孔隙度/% | 投影面积/m2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Agg-Ⅰ-1 | 0 | 2.62×10-5 | 2.94 | 0.87 | 12.73 | 3.96×10-9 |
| Agg-Ⅱ-1 | 0.1 | 3.12×10-5 | 2.74 | 0.51 | 48.66 | 5.22×10-9 |
| Agg-Ⅲ-1 | 0.5 | 4.05×10-5 | 2.48 | 0.24 | 76.39 | 3.44×10-9 |
| Agg-Ⅳ-1 | 1.0 | 5.90×10-5 | 2.19 | 0.08 | 92.39 | 9.08×10-9 |
| 参数 | 数值 |
|---|---|
| 计算域尺寸/(mm×mm×mm) | 0.6×0.3×0.3 |
| 组成聚团的原生颗粒粒径/μm | 5 |
| 组成聚团的原生颗粒个数 | 1000 |
| 原生颗粒密度/(kg/m3) | 400 |
| 流体密度/(kg/m3) | 1.225 |
| 流体黏度/(kg/(m·s)) | 1.7894×10-5 |
表2 CFD模拟参数
Table 2 Simulation parameters for CFD
| 参数 | 数值 |
|---|---|
| 计算域尺寸/(mm×mm×mm) | 0.6×0.3×0.3 |
| 组成聚团的原生颗粒粒径/μm | 5 |
| 组成聚团的原生颗粒个数 | 1000 |
| 原生颗粒密度/(kg/m3) | 400 |
| 流体密度/(kg/m3) | 1.225 |
| 流体黏度/(kg/(m·s)) | 1.7894×10-5 |
| 聚团编号 | 分形维数 | 回转半径/m | 无量纲密度 | 孔隙度/% | 投影面积/m2 | 等效直径/m | Reynolds数 | 来流速度/(m/s) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Agg-Ⅳ-5 | 2.35 | 4.75×10-5 | 0.15 | 85.39 | 4.18×10-9 | 7.30×10-5 | 0.1 | 0.02002 |
| 0.15 | 0.03002 | |||||||
| 0.2 | 0.04003 | |||||||
| 0.5 | 0.10008 | |||||||
| 1 | 0.20015 | |||||||
| 2 | 0.40031 | |||||||
| 5 | 1.00077 | |||||||
| 10 | 2.00155 |
表3 不同Reynolds数的流场模拟工况设置
Table 3 The condition settings for simulations at different Re
| 聚团编号 | 分形维数 | 回转半径/m | 无量纲密度 | 孔隙度/% | 投影面积/m2 | 等效直径/m | Reynolds数 | 来流速度/(m/s) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Agg-Ⅳ-5 | 2.35 | 4.75×10-5 | 0.15 | 85.39 | 4.18×10-9 | 7.30×10-5 | 0.1 | 0.02002 |
| 0.15 | 0.03002 | |||||||
| 0.2 | 0.04003 | |||||||
| 0.5 | 0.10008 | |||||||
| 1 | 0.20015 | |||||||
| 2 | 0.40031 | |||||||
| 5 | 1.00077 | |||||||
| 10 | 2.00155 |
| 聚团编号 | Reynolds数 | 聚团和来流方向夹角/(˚) | 投影面积/(10-9 m2) | 等效直径/(10-5 m) | 来流速度/(m/s) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Agg-Ⅳ-5 | 0.1 | 0 | 4.18 | 7.30 | 0.020015 |
| 30 | 4.64 | 7.69 | 0.018995 | ||
| 60 | 6.07 | 8.79 | 0.016614 | ||
| 90 | 6.95 | 9.41 | 0.015520 | ||
| 120 | 6.67 | 9.22 | 0.015847 | ||
| 150 | 5.43 | 8.32 | 0.017556 | ||
| 180 | 4.18 | 7.30 | 0.020015 |
表4 不同聚团方向的流场模拟工况设置
Table 4 The condition settings for simulations at different agglomerate orientations
| 聚团编号 | Reynolds数 | 聚团和来流方向夹角/(˚) | 投影面积/(10-9 m2) | 等效直径/(10-5 m) | 来流速度/(m/s) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Agg-Ⅳ-5 | 0.1 | 0 | 4.18 | 7.30 | 0.020015 |
| 30 | 4.64 | 7.69 | 0.018995 | ||
| 60 | 6.07 | 8.79 | 0.016614 | ||
| 90 | 6.95 | 9.41 | 0.015520 | ||
| 120 | 6.67 | 9.22 | 0.015847 | ||
| 150 | 5.43 | 8.32 | 0.017556 | ||
| 180 | 4.18 | 7.30 | 0.020015 |
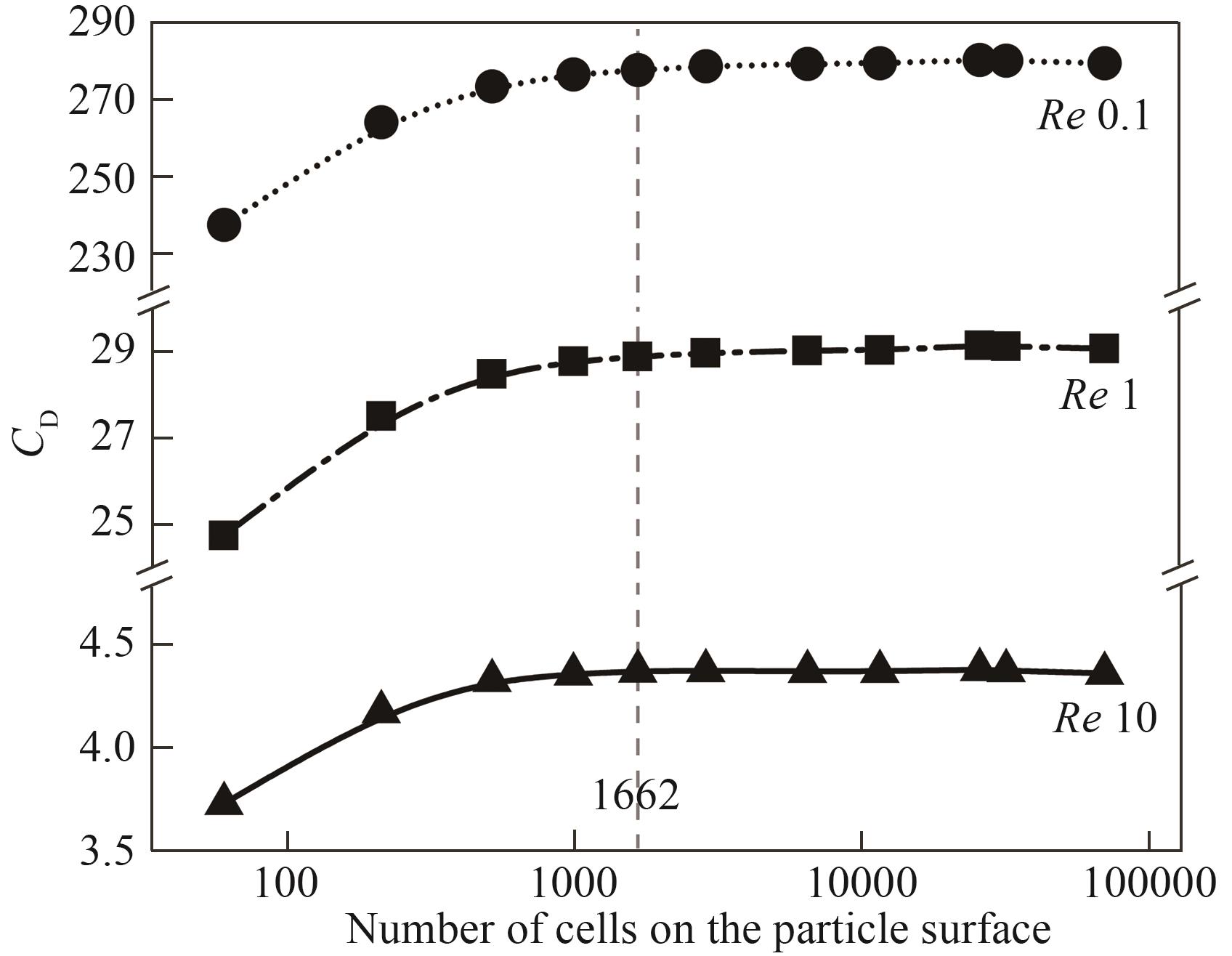
图3 表面网格数量对Reynolds数Re=0.1、1、10下单颗粒曳力系数的影响
Fig.3 Effect of number of surface cells on the predicted drag coefficient at Re=0.1, 1, 10 for a single particle
| 1 | Flesch J C, Spicer P T, Pratsinis S E. Laminar and turbulent shear-induced flocculation of fractal aggregates[J]. AIChE Journal, 1999, 45(5): 1114-1124. |
| 2 | 刘荣正, 刘马林, 邵友林, 等. 流化床-化学气相沉积技术的应用及研究进展[J]. 化工进展, 2016, 35(5): 1263-1272. |
| Liu R Z, Liu M L, Shao Y L, et al. Application and research progress of fluidized bed-chemical vapor deposition technology[J]. Chemical Industry and Engineering Progress, 2016, 35(5): 1263-1272. | |
| 3 | Wang W, Lu B N, Geng J W, et al. Mesoscale drag modeling: a critical review[J]. Current Opinion in Chemical Engineering, 2020, 29: 96-103. |
| 4 | 万韶六, 欧阳洁. 颗粒团绕流曳力系数的LBM计算[J]. 化工学报, 2008, 59(1): 58-63. |
| Wan S L, Ouyang J. Evaluation of drag coefficient on particles in cluster by using lattice Boltzmann method[J]. Journal of Chemical Industry and Engineering(China), 2008, 59(1): 58-63. | |
| 5 | 祁晗璐, 王嘉骏, 顾雪萍, 等. 黏性颗粒团聚机理及流化特性研究进展[J]. 过程工程学报, 2019, 19(1): 55-63. |
| Qi H L, Wang J J, Gu X P, et al. Research progress on agglomeration mechanisms and fluidization behavior of cohesive particles[J]. The Chinese Journal of Process Engineering, 2019, 19(1): 55-63. | |
| 6 | Chen S, Chen P Z, Fu J H. Drag and lift forces acting on linear and irregular agglomerates formed by spherical particles[J]. Physics of Fluids, 2022, 34(2): 023307. |
| 7 | Tsou G W, Wu R M, Yen P S, et al. Advective flow and floc permeability[J]. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 2002, 250(2): 400-408. |
| 8 | Wu R M, Feng W H, Tsai I H, et al. An estimate of activated-sludge floc permeability: a novel hydrodynamic approach[J]. Water Environment Research, 1998, 70(7): 1258-1264. |
| 9 | Wang S W, Liu H P, Yang C Y. Structure and drag characteristics of fluidized nanoparticle agglomerates at the bottom of the bed[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2019, 58(42): 19693-19701. |
| 10 | Johnson C P, Li X Y, Logan B E. Settling velocities of fractal aggregates[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 1996, 30(6): 1911-1918. |
| 11 | Xiao F, Li X Y, Wang D S. Three-dimensional CFD simulation of the flow field around and through particle aggregates[J]. Colloids and Surfaces A-Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 2013, 436: 1034-1040. |
| 12 | Rogak S N, Flagan R C. Stokes drag on self-similar clusters of spheres[J]. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 1990, 134(1): 206-218. |
| 13 | Li D, Bai X F, Li P, et al. A dynamic cluster structure-dependent drag coefficient model applied to the riser in high density circulating fluidized bed[J]. Advanced Powder Technology, 2022, 33(2): 103418. |
| 14 | Bhattacharyya S, Dhinakaran S, Khalili A. Fluid motion around and through a porous cylinder[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2006, 61(13): 4451-4461. |
| 15 | Yu P, Zeng Y, Lee T S, et al. Steady flow around and through a permeable circular cylinder[J]. Computers & Fluids, 2011, 42(1): 1-12. |
| 16 | Noymer P D, Glicksman L R, Devendran A. Drag on a permeable cylinder in steady flow at moderate Reynolds numbers[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 1998, 53(16): 2859-2869. |
| 17 | 王利民, 邱小平, 李静海. 气固两相流介尺度LBM-DEM模型[J]. 计算力学学报, 2015, 32(5): 685-692. |
| Wang L M, Qiu X P, Li J H. Mesoscale LBM-DEM model for gas-solid two-phase flow[J]. Chinese Journal of Computational Mechanics, 2015, 32(5): 685-692. | |
| 18 | 蒋鸣, 周强. 气固流化床介尺度结构形成机制及过滤曳力模型研究进展[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(6): 2468-2485. |
| Jiang M, Zhou Q. Progress on mechanisms of mesoscale structures and mesoscale drag model in gas-solid fluidized beds[J]. CIESC Journal, 2022, 73(6): 2468-2485. | |
| 19 | Binder C, Feichtinger C, Schmid H J, et al. Simulation of the hydrodynamic drag of aggregated particles[J]. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 2006, 301(1): 155-167. |
| 20 | Dietzel M, Sommerfeld M. Numerical calculation of flow resistance for agglomerates with different morphology by the lattice-Boltzmann method[J]. Powder Technology, 2013, 250: 122-137. |
| 21 | Dietzel M, Ernst M, Sommerfeld M. Application of the lattice-Boltzmann method for particle-laden flows: point-particles and fully resolved particles[J]. Flow Turbulence and Combustion, 2016, 97(2): 539-570. |
| 22 | Wittig K, Nikrityuk P, Richter A. Drag coefficient and Nusselt number for porous particles under laminar flow conditions[J]. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 2017, 112: 1005-1016. |
| 23 | Li X, Ouyang J, Wang X D, et al. A drag force formula for heterogeneous granular flow systems based on finite average statistical method[J]. Particuology, 2021, 55: 94-107. |
| 24 | Dodds D, Sarhan A R, Naser J. Experimental and numerical study of drag forces on particles in clusters[J]. Powder Technology, 2020, 371: 195-208. |
| 25 | Chen X, Song N, Jiang M, et al. A microscopic gas-solid drag model considering the effect of interface between dilute and dense phases[J]. International Journal of Multiphase Flow, 2020, 128: 103266. |
| 26 | Chen X, Ma T, Zhou Q. Theoretical and numerical analysis of drag force at the interface between the dilute and dense phases[J]. Physics of Fluids, 2022, 34(9): 093306. |
| 27 | Ma T, Li Y, Zhou Q, et al. Microscale drag model considering the effect of interface between dense and dilute phases for gas-solid suspensions at moderate Reynolds numbers[J]. International Journal of Multiphase Flow, 2022, 157: 104270. |
| 28 | Liu D Y, Wang Z, Chen X P, et al. Simulation of agglomerate breakage and restructuring in shear flows: coupled effects of shear gradient, surface energy and initial structure[J]. Powder Technology, 2018, 336: 102-111. |
| 29 | Mroczka J, Wozniak M, Onofri F R A. Algorithms and methods for analysis of the optical structure factor of fractal aggregates[J]. Metrology and Measurement Systems, 2012, 19(3): 459-470. |
| 30 | Froeschke S, Kohler S, Weber A P, et al. Impact fragmentation of nanoparticle agglomerates[J]. Journal of Aerosol Science, 2003, 34(3): 275-287. |
| 31 | Kanniah V, Wu P, Mandzy N, et al. Fractal analysis as a complimentary technique for characterizing nanoparticle size distributions[J]. Powder Technology, 2012, 226: 189-198. |
| 32 | Goudeli E, Eggersdorfer M L, Pratsinis S E. Coagulation-agglomeration of fractal-like particles: structure and self-preserving size distribution[J]. Langmuir, 2015, 31(4): 1320-1327. |
| 33 | Tenneti S, Subramaniam S. Particle-resolved direct numerical simulation for gas-solid flow model development[J]. Annual Review of Fluid Mechanics, 2014, 46: 199-230. |
| 34 | Johnson T A, Patel V C. Flow past a sphere up to a Reynolds number of 300[J]. Journal of Fluid Mechanics, 1999, 378: 19-70. |
| 35 | Schlichting H, Gersten K. Fundamentals of boundary-layer theory[M]//Boundary-Layer Theory. Berlin Heidelberg: Springer-Verlag, 2000: 29-49. |
| 36 | Rong L W, Dong K J, Yu A B. Lattice-Boltzmann simulation of fluid flow through packed beds of uniform spheres: effect of porosity[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2013, 99: 44-58. |
| 37 | Mola I A, Fawell P D, Small M. Particle-resolved direct numerical simulation of drag force on permeable, non-spherical aggregates[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2020, 218: 115582. |
| 38 | Militzer J, Kan J M, Hamdullahpur F, et al. Drag coefficient for axisymmetric flow around individual spheroidal particles[J]. Powder Technology, 1989, 57(3): 193-195. |
| 39 | Bushell G C, Yan Y D, Woodfield D, et al. On techniques for the measurement of the mass fractal dimension of aggregates[J]. Advances in Colloid and Interface Science, 2002, 95(1): 1-50. |
| 40 | Holzer A, Sommerfeld M. New simple correlation formula for the drag coefficient of non-spherical particles[J]. Powder Technology, 2008, 184(3): 361-365. |
| 41 | Beinert S, Kwade A, Schilde C. Strategies for multi-scale simulation of fine grinding and dispersing processes: drag coefficient and fracture of fractal aggregates[J]. Advanced Powder Technology, 2018, 29(3): 707-718. |
| [1] | 张思雨, 殷勇高, 贾鹏琦, 叶威. 双U型地埋管群跨季节蓄热特性研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(S1): 295-301. |
| [2] | 肖明堃, 杨光, 黄永华, 吴静怡. 浸没孔液氧气泡动力学数值研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(S1): 87-95. |
| [3] | 温凯杰, 郭力, 夏诏杰, 陈建华. 一种耦合CFD与深度学习的气固快速模拟方法[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(9): 3775-3785. |
| [4] | 张佳怡, 何佳莉, 谢江鹏, 王健, 赵鹬, 张栋强. 渗透汽化技术用于锂电池生产中N-甲基吡咯烷酮回收的研究进展[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(8): 3203-3215. |
| [5] | 岳林静, 廖艺涵, 薛源, 李雪洁, 李玉星, 刘翠伟. 凹坑缺陷对厚孔板喉部空化流动特性影响研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(8): 3292-3308. |
| [6] | 邢雷, 苗春雨, 蒋明虎, 赵立新, 李新亚. 井下微型气液旋流分离器优化设计与性能分析[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(8): 3394-3406. |
| [7] | 汪林正, 陆俞冰, 张睿智, 罗永浩. 基于分子动力学模拟的VOCs热氧化特性分析[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(8): 3242-3255. |
| [8] | 牛超, 沈胜强, 杨艳, 潘泊年, 李熠桥. 甲烷BOG喷射器流动过程计算与性能分析[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(7): 2858-2868. |
| [9] | 何晓崐, 刘锐, 薛园, 左然. MOCVD生长AlN单晶薄膜的气相和表面化学反应综述[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(7): 2800-2813. |
| [10] | 屈园浩, 邓文义, 谢晓丹, 苏亚欣. 活性炭/石墨辅助污泥电渗脱水研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(7): 3038-3050. |
| [11] | 贾晓宇, 杨剑, 王博, 林梅, 王秋旺. 金属丝网毛细特性的孔隙尺度数值分析[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(5): 1928-1938. |
| [12] | 李晨曦, 刘永峰, 张璐, 刘海峰, 宋金瓯, 何旭. O2/CO2氛围下正庚烷的燃烧机理研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(5): 2157-2169. |
| [13] | 董鑫, 单永瑞, 刘易诺, 冯颖, 张建伟. 非牛顿流体气泡羽流涡特性数值模拟研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(5): 1950-1964. |
| [14] | 袁子涵, 王淑彦, 邵宝力, 谢磊, 陈曦, 马一玫. 基于幂律液固曳力模型流化床内湿颗粒流动特性的研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(5): 2000-2012. |
| [15] | 李正涛, 袁志杰, 贺高红, 姜晓滨. 疏水界面上的NaCl液滴蒸发过程内环流调控机制研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(5): 1904-1913. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备 11010102001995号
京公网安备 11010102001995号