化工学报 ›› 2022, Vol. 73 ›› Issue (4): 1714-1723.DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20211584
孟文亮1,2( ),李贵贤1,2(
),李贵贤1,2( ),周怀荣1,2,李婧玮1,2,王健1,2,王可1,2,范学英3,王东亮1,2(
),周怀荣1,2,李婧玮1,2,王健1,2,王可1,2,范学英3,王东亮1,2( )
)
收稿日期:2021-11-09
修回日期:2021-12-22
出版日期:2022-04-05
发布日期:2022-04-25
通讯作者:
李贵贤,王东亮
作者简介:孟文亮(1996—),男,博士研究生,基金资助:
Wenliang MENG1,2( ),Guixian LI1,2(
),Guixian LI1,2( ),Huairong ZHOU1,2,Jingwei LI1,2,Jian WANG1,2,Ke WANG1,2,Xueying FAN3,Dongliang WANG1,2(
),Huairong ZHOU1,2,Jingwei LI1,2,Jian WANG1,2,Ke WANG1,2,Xueying FAN3,Dongliang WANG1,2( )
)
Received:2021-11-09
Revised:2021-12-22
Online:2022-04-05
Published:2022-04-25
Contact:
Guixian LI,Dongliang WANG
摘要:
在“碳达峰、碳中和”的背景下,传统煤制甲醇工艺存在CO2排放强度大、能耗高等问题成为制约煤制甲醇工艺发展的瓶颈问题。本研究基于外源性的绿氢,重构粉煤气化煤制甲醇工艺,省掉了空分单元、变换单元,开发了短流程低温甲醇洗单元,提出了粉煤气化集成绿氢的近零碳排放煤制甲醇新工艺。从碳元素利用率、CO2排放、成本分析等角度对新工艺进行了评价。结果表明,与传统煤制甲醇工艺相比,新工艺碳元素利用率从41.50%提高到95.77%,CO2直接排放量由1.939降低至0.035 t·(t MeOH)-1,通过分析H2价格与碳税对产品成本的影响发现,当氢气价格和碳税分别为10.36 CNY·(kg H2)-1和223.3 CNY·(t CO2)-1时,两种工艺的产品成本相当。新工艺不仅减少了煤制甲醇过程碳排放,而且可以提高可再生能源就地消纳能力,具有良好的应用前景。
中图分类号:
孟文亮, 李贵贤, 周怀荣, 李婧玮, 王健, 王可, 范学英, 王东亮. 绿氢重构的粉煤气化煤制甲醇近零碳排放工艺研究[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(4): 1714-1723.
Wenliang MENG, Guixian LI, Huairong ZHOU, Jingwei LI, Jian WANG, Ke WANG, Xueying FAN, Dongliang WANG. A novel coal to methanol process with near zero CO2 emission by pulverized coal gasification integrated green hydrogen[J]. CIESC Journal, 2022, 73(4): 1714-1723.
| 传统煤制甲醇工艺 | 近零碳排放的煤制甲醇新工艺 | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 煤气化单元 | 煤气化单元 | ||
| 气化温度/℃ | 1554 | 气化温度/℃ | 1554 |
| 气化压力/MPa | 8.8 | 气化压力/MPa | 8.8 |
| 煤转化率/% | >99 | 煤转化率/% | >99 |
| 水煤气变换单元 | 电解水制氢单元 | ||
| 高/低变温度/℃ | 350/220 | 工作效率/% | 70~90 |
| 压力/MPa | 3 | 工作压力/MPa | 3.2 |
| 蒸汽/CO摩尔比 | 0.94 | 能耗/(kWh·m-3) | 3.8~5.0 |
| 低温甲醇洗单元 | 短流程的低温甲醇洗单元 | ||
| H2S移除率/%(mol) | 100 | H2S移除率/%(mol) | 100 |
| CO2移除率/%(mol) | 96 | CO2移除率/%(mol) | 30 |
| 甲醇合成单元 | 甲醇合成单元 | ||
| 催化剂 | Cu/ZnO/Al2O3 | 催化剂 | Cu/ZnO/Al2O3 |
| 未反应气循环比/% | 99 | 未反应气循环比/% | 99 |
| 温度/℃ | 240 | 温度/℃ | 250 |
| 压力/MPa | 8 | 压力/MPa | 8 |
| 甲醇精馏单元 | 甲醇精馏单元 | ||
| 甲醇回收率/%(mol) | 99.9 | 甲醇回收率/%(mol) | 99.9 |
| 精甲醇纯度/%(mass) | 99.9 | 精甲醇纯度/%(mass) | 99.9 |
表2 工艺模拟的关键参数
Table 2 Key parameters for process simulation
| 传统煤制甲醇工艺 | 近零碳排放的煤制甲醇新工艺 | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 煤气化单元 | 煤气化单元 | ||
| 气化温度/℃ | 1554 | 气化温度/℃ | 1554 |
| 气化压力/MPa | 8.8 | 气化压力/MPa | 8.8 |
| 煤转化率/% | >99 | 煤转化率/% | >99 |
| 水煤气变换单元 | 电解水制氢单元 | ||
| 高/低变温度/℃ | 350/220 | 工作效率/% | 70~90 |
| 压力/MPa | 3 | 工作压力/MPa | 3.2 |
| 蒸汽/CO摩尔比 | 0.94 | 能耗/(kWh·m-3) | 3.8~5.0 |
| 低温甲醇洗单元 | 短流程的低温甲醇洗单元 | ||
| H2S移除率/%(mol) | 100 | H2S移除率/%(mol) | 100 |
| CO2移除率/%(mol) | 96 | CO2移除率/%(mol) | 30 |
| 甲醇合成单元 | 甲醇合成单元 | ||
| 催化剂 | Cu/ZnO/Al2O3 | 催化剂 | Cu/ZnO/Al2O3 |
| 未反应气循环比/% | 99 | 未反应气循环比/% | 99 |
| 温度/℃ | 240 | 温度/℃ | 250 |
| 压力/MPa | 8 | 压力/MPa | 8 |
| 甲醇精馏单元 | 甲醇精馏单元 | ||
| 甲醇回收率/%(mol) | 99.9 | 甲醇回收率/%(mol) | 99.9 |
| 精甲醇纯度/%(mass) | 99.9 | 精甲醇纯度/%(mass) | 99.9 |
| 流股 | 温度/℃ | 压力/MPa | 摩尔分数/% | 摩尔流量/ (kmol·h-1) | 质量流量/ (kg·h-1) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N2 | O2 | H2O | CO | CO2 | H2S | H2 | CH3OH | |||||
| 1 | 25 | 0.1 | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | 100000 | |
| 2 | 210 | 4 | 0.58 | 0 | 6.51 | 62.65 | 4.03 | 0.1 | 26.13 | 0 | 9841.63 | 208608 |
| 3 | 90 | 4 | 0.44 | 0 | 0.24 | 20.69 | 30.75 | 0.08 | 47.8 | 0 | 12798 | 262163 |
| 4 | 30 | 0.2 | 6.31 | 0 | 0 | 0.31 | 93.2 | 0 | 0.17 | 0.01 | 3240.81 | 138965 |
| 5 | 30 | 2.8 | 0.63 | 0 | 0 | 29.38 | 1.84 | 0 | 68.15 | 0 | 8965.75 | 94945 |
| 6 | 41 | 0.1 | 0 | 0 | 5.06 | 0 | 0.14 | 0 | 0 | 94.8 | 2904.73 | 91055 |
| 7 | 67 | 0.1 | 0 | 0 | 0.18 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 99.82 | 2755.83 | 88117.89 |
表3 传统煤制甲醇工艺模拟结果
Table 3 Simulation results at key points of the traditional coal to methanol process
| 流股 | 温度/℃ | 压力/MPa | 摩尔分数/% | 摩尔流量/ (kmol·h-1) | 质量流量/ (kg·h-1) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N2 | O2 | H2O | CO | CO2 | H2S | H2 | CH3OH | |||||
| 1 | 25 | 0.1 | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | 100000 | |
| 2 | 210 | 4 | 0.58 | 0 | 6.51 | 62.65 | 4.03 | 0.1 | 26.13 | 0 | 9841.63 | 208608 |
| 3 | 90 | 4 | 0.44 | 0 | 0.24 | 20.69 | 30.75 | 0.08 | 47.8 | 0 | 12798 | 262163 |
| 4 | 30 | 0.2 | 6.31 | 0 | 0 | 0.31 | 93.2 | 0 | 0.17 | 0.01 | 3240.81 | 138965 |
| 5 | 30 | 2.8 | 0.63 | 0 | 0 | 29.38 | 1.84 | 0 | 68.15 | 0 | 8965.75 | 94945 |
| 6 | 41 | 0.1 | 0 | 0 | 5.06 | 0 | 0.14 | 0 | 0 | 94.8 | 2904.73 | 91055 |
| 7 | 67 | 0.1 | 0 | 0 | 0.18 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 99.82 | 2755.83 | 88117.89 |
| 流股 | 温度/℃ | 压力/MPa | 摩尔分数/% | 摩尔流量/ (kmol·h-1) | 质量流量/ (kg·h-1) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N2 | O2 | H2O | CO | CO2 | H2S | H2 | CH3OH | |||||
| 1 | 25 | 0.1 | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | 100000 | |
| 2 | 86 | 3.2 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2343.75 | 75000 |
| 3 | 210 | 4 | 0.26 | 0 | 6.53 | 62.85 | 4.04 | 0.01 | 26.21 | 0 | 9841.63 | 208614 |
| 4 | 30 | 2.8 | 0.29 | 0 | 0 | 68.15 | 3.11 | 0 | 28.44 | 0 | 9062.82 | 191368 |
| 5 | 86 | 3.2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 11396.03 | 22792 |
| 6 | 41 | 0.1 | 0 | 0 | 3.75 | 0 | 0.13 | 0 | 0 | 96.12 | 6620.84 | 208758 |
| 7 | 67 | 0.1 | 0 | 0 | 0.18 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 99.82 | 6368.89 | 203646 |
表4 近零碳排放的煤制甲醇新工艺模拟结果
Table 4 Simulation results at key points of the novel process
| 流股 | 温度/℃ | 压力/MPa | 摩尔分数/% | 摩尔流量/ (kmol·h-1) | 质量流量/ (kg·h-1) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N2 | O2 | H2O | CO | CO2 | H2S | H2 | CH3OH | |||||
| 1 | 25 | 0.1 | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | 100000 | |
| 2 | 86 | 3.2 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2343.75 | 75000 |
| 3 | 210 | 4 | 0.26 | 0 | 6.53 | 62.85 | 4.04 | 0.01 | 26.21 | 0 | 9841.63 | 208614 |
| 4 | 30 | 2.8 | 0.29 | 0 | 0 | 68.15 | 3.11 | 0 | 28.44 | 0 | 9062.82 | 191368 |
| 5 | 86 | 3.2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 11396.03 | 22792 |
| 6 | 41 | 0.1 | 0 | 0 | 3.75 | 0 | 0.13 | 0 | 0 | 96.12 | 6620.84 | 208758 |
| 7 | 67 | 0.1 | 0 | 0 | 0.18 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 99.82 | 6368.89 | 203646 |
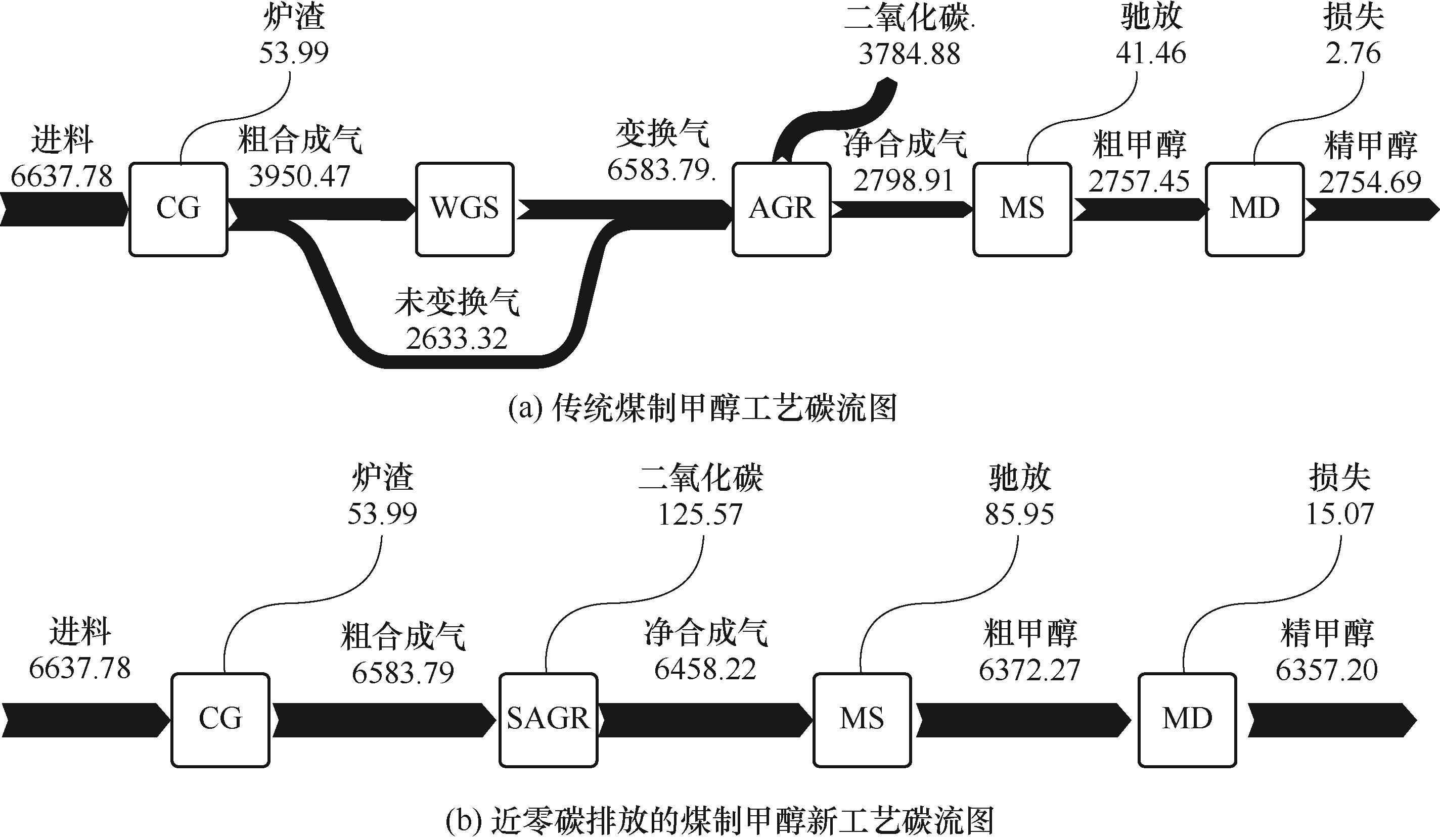
图7 碳流图(单位:kmol·h-1)CG—煤气化单元(coal gasification);WGS—水煤气变换单元(water gas shift);AGR—酸气脱除单元(acid gas removal);MS—甲醇合成单元(methanol synthesis);MD—甲醇精馏单元(methanol distillation);SAGR—短流程酸气脱除单元(simplified acid gas removal)
Fig.7 The diagram of carbon flow (unit: kmol·h-1)
| 工艺 | 能耗/(MJ·(kg MeOH))-1 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AS | CG | WGS | AGR | SAGR | MS | MD | |
| 传统煤制甲醇工艺 | 4.2 | -3.0 | -1.9 | 5.5 | — | -1.6 | 2.5 |
| 近零碳排放的煤制甲醇新工艺 | — | -1.3 | — | — | 0.8 | -1.6 | 2.4 |
表5 两种工艺不同单元能量消耗情况
Table 5 Energy consumption of different units in the two different processes
| 工艺 | 能耗/(MJ·(kg MeOH))-1 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AS | CG | WGS | AGR | SAGR | MS | MD | |
| 传统煤制甲醇工艺 | 4.2 | -3.0 | -1.9 | 5.5 | — | -1.6 | 2.5 |
| 近零碳排放的煤制甲醇新工艺 | — | -1.3 | — | — | 0.8 | -1.6 | 2.4 |
| 1 | Yang Q C, Li X F, Yang Q, et al. Opportunities for CO2 utilization in coal to green fuel process: optimal design and performance evaluation[J]. ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering, 2020, 8(3): 1329-1342. |
| 2 | Chen Q Q, Lv M, Gu Y, et al. Hybrid energy system for a coal-based chemical industry[J]. Joule, 2018, 2(4): 607-620. |
| 3 | Hosseini S E, Wahid M A. Hydrogen production from renewable and sustainable energy resources: promising green energy carrier for clean development[J]. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 2016, 57: 850-866. |
| 4 | 唐志永, 孙予罕, 江绵恒. 低碳复合能源系统——中国未来能源的解决方案和发展模式? [J].中国科学, 2013, 43(1): 116-124. |
| Tang Z Y, Sun Y H, Jiang M H. Low-carbon hybrid energy systems: future energy solutions and development models in China?[J]. Scientia sinica Chimica 43(1): 116-124. | |
| 5 | Xiang D, Yang S Y, Liu X, et al. Techno-economic performance of the coal-to-olefins process with CCS[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2014, 240: 45-54. |
| 6 | Chen J J, Yang S Y, Qian Y. A novel path for carbon-rich resource utilization with lower emission and higher efficiency: an integrated process of coal gasification and coking to methanol production[J]. Energy, 2019, 177: 304-318. |
| 7 | Zhang J P, Li Z W, Zhang Z H, et al. Techno-economic analysis of integrating a CO2 hydrogenation-to-methanol unit with a coal-to-methanol process for CO2 reduction[J]. ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering, 2020, 8(49): 18062-18070. |
| 8 | 刘硕士, 杨思宇, 顾竞芳, 等. 气煤联供实现资源高效利用和碳减排技术进展[J]. 化工进展, 2019, 38(1): 664-671. |
| Liu S S, Yang S Y, Gu J F, et al. Review on coal and gas co-feed processes for better resource use and lower carbon emission[J]. Chemical Industry and Engineering Progress, 2019, 38(1): 664-671. | |
| 9 | Qin Z, Zhai G F, Wu X M, et al. Carbon footprint evaluation of coal-to-methanol chain with the hierarchical attribution management and life cycle assessment[J]. Energy Conversion and Management, 2016, 124: 168-179. |
| 10 | 金涌, 周禹成, 胡山鹰. 低碳理念指导的煤化工产业发展探讨[J]. 化工学报, 2012, 63(1): 3-8. |
| Jin Y, Zhou Y C, Hu S Y. Discussion on development of coal chemical industry using low-carbon concept[J]. CIESC Journal, 2012, 63(1): 3-8. | |
| 11 | Qin Z, Bhattacharya S, Tang K, et al. Effects of gasification condition on the overall performance of methanol-electricity polygeneration system[J]. Energy Conversion and Management, 2019, 184: 362-373. |
| 12 | 黄宏, 杨思宇. 一种低能耗捕集CO2煤基甲醇和电力联产过程设计[J]. 化工学报, 2017, 68(10): 3860-3869. |
| Huang H, Yang S Y. Design of a coal based methanol and power polygeneration process with low energy consumption for CO2 capture[J]. CIESC Journal, 2017, 68(10): 3860-3869. | |
| 13 | Wang D L, Meng W L, Zhou H R, et al. Green hydrogen coupling with CO2 utilization of coal-to-methanol for high methanol productivity and low CO2 emission[J]. Energy, 2021, 231: 120970. |
| 14 | 东赫, 刘金昌, 解强, 等. 典型气流床煤气化炉气化过程的建模[J]. 化工进展, 2016, 35(8): 2426-2431. |
| Dong H, Liu J C, Xie Q, et al. Modeling of coal gasification reaction in typical entrained-flow coal gasifiers[J]. Chemical Industry and Engineering Progress, 2016, 35(8): 2426-2431. | |
| 15 | Qin S Y, Chang S Y, Yao Q. Modeling, thermodynamic and techno-economic analysis of coal-to-liquids process with different entrained flow coal gasifiers[J]. Applied Energy, 2018, 229: 413-432. |
| 16 | Park N, Park M J, Ha K S, et al. Modeling and analysis of a methanol synthesis process using a mixed reforming reactor: perspective on methanol production and CO2 utilization[J]. Fuel, 2014, 129: 163-172. |
| 17 | Bussche K M V, Froment G F. A steady-state kinetic model for methanol synthesis and the water gas shift reaction on a commercial Cu/ZnO/Al2O3 catalyst[J]. Journal of Catalysis, 1996, 161(1): 1-10. |
| 18 | Cui C T, Sun J S, Li X G. A hybrid design combining double-effect thermal integration and heat pump to the methanol distillation process for improving energy efficiency[J]. Chemical Engineering and Processing: Process Intensification, 2017, 119: 81-92. |
| 19 | Liu X, Yang S Y, Hu Z G, et al. Simulation and assessment of an integrated acid gas removal process with higher CO2 capture rate[J]. Computers & Chemical Engineering, 2015, 83: 48-57. |
| 20 | Sun L, Smith R. Rectisol wash process simulation and analysis[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2013, 39: 321-328. |
| 21 | 赵鹏飞, 李水弟, 王立志. 低温甲醇洗技术及其在煤化工中的应用[J]. 化工进展, 2012, 31(11): 2442-2448. |
| Zhao P F, Li S D, Wang L Z. Rectisol technology and its application in coal chemical industry[J]. Chemical Industry and Engineering Progress, 2012, 31(11): 2442-2448. | |
| 22 | 贾欣, 赵文星, 王建成, 等. 低温甲醇洗吸收塔产出液再生过程模拟研究[J]. 天然气化工(C1化学与化工), 2019, 44(3): 65-70. |
| Jia X, Zhao W X, Wang J C, et al. Regeneration process simulation of the output fluid from rectisol absorber[J]. Natural Gas Chemical Industry, 2019, 44(3): 65-70. | |
| 23 | Yang Q C, Zhang J L, Chu G Y, et al. Optimal design, thermodynamic and economic analysis of coal to ethylene glycol processes integrated with various methane reforming technologies for CO2 reduction[J]. Energy Conversion and Management, 2021, 244: 114538. |
| 24 | Yang Q C, Zhu S, Yang Q, et al. Comparative techno-economic analysis of oil-based and coal-based ethylene glycol processes[J]. Energy Conversion and Management, 2019, 198: 111814. |
| 25 | Yi Q, Wu G S, Gong M H, et al. A feasibility study for CO2 recycle assistance with coke oven gas to synthetic natural gas[J]. Applied Energy, 2017, 193: 149-161. |
| 26 | Zhang D Q, Duan R H, Li H W, et al. Optimal design, thermodynamic, cost and CO2 emission analyses of coal-to-methanol process integrated with chemical looping air separation and hydrogen technology[J]. Energy, 2020, 203: 117876. |
| 27 | Li M X, Zhuang Y, Zhang L, et al. Conceptual design and techno-economic analysis for a coal-to-SNG/methanol polygeneration process in series and parallel reactors with integration of waste heat recovery[J]. Energy Conversion and Management, 2020, 214: 112890. |
| 28 | 杨庆, 许思敏, 张大伟, 等. 石油与煤路线制乙二醇过程的技术经济分析[J]. 化工学报, 2020, 71(5): 2164-2172. |
| Yang Q, Xu S M, Zhang D W, et al. Techno-economic analysis of oil and coal to ethylene glycol processes[J]. CIESC Journal, 2020, 71(5): 2164-2172. | |
| 29 | Xiang D, Li P, Yuan X Y, et al. Highly efficient carbon utilization of coal-to-methanol process integrated with chemical looping hydrogen and air separation technology: process modeling and parameter optimization[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2020, 258: 120910. |
| 30 | 王科, 刘永艳. 2020 年中国碳市场回顾与展望[J]. 北京理工大学学报(社会科学版), 2020, 22(2): 10-19. |
| Wang K, Liu Y Y. China's carbon market: reviews and prospects for 2020[J]. Journal of Beijing Institute of Technology (Social Sciences Edition), 2020, 22(2): 10-19. |
| [1] | 宋瑞涛, 王派, 王云鹏, 李敏霞, 党超镔, 陈振国, 童欢, 周佳琦. 二氧化碳直接蒸发冰场排管内流动沸腾换热数值模拟分析[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(S1): 96-103. |
| [2] | 张义飞, 刘舫辰, 张双星, 杜文静. 超临界二氧化碳用印刷电路板式换热器性能分析[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(S1): 183-190. |
| [3] | 程业品, 胡达清, 徐奕莎, 刘华彦, 卢晗锋, 崔国凯. 离子液体基低共熔溶剂在转化CO2中的应用[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(9): 3640-3653. |
| [4] | 陈哲文, 魏俊杰, 张玉明. 超临界水煤气化耦合SOFC发电系统集成及其能量转化机制[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(9): 3888-3902. |
| [5] | 齐聪, 丁子, 余杰, 汤茂清, 梁林. 基于选择吸收纳米薄膜的太阳能温差发电特性研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(9): 3921-3930. |
| [6] | 郑玉圆, 葛志伟, 韩翔宇, 王亮, 陈海生. 中高温钙基材料热化学储热的研究进展与展望[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(8): 3171-3192. |
| [7] | 杨菲菲, 赵世熙, 周维, 倪中海. Sn掺杂的In2O3催化CO2选择性加氢制甲醇[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(8): 3366-3374. |
| [8] | 洪瑞, 袁宝强, 杜文静. 垂直上升管内超临界二氧化碳传热恶化机理分析[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(8): 3309-3319. |
| [9] | 文兆伦, 李沛睿, 张忠林, 杜晓, 侯起旺, 刘叶刚, 郝晓刚, 官国清. 基于自热再生的隔壁塔深冷空分工艺设计及优化[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(7): 2988-2998. |
| [10] | 张琦钰, 高利军, 苏宇航, 马晓博, 王翊丞, 张亚婷, 胡超. 碳基催化材料在电化学还原二氧化碳中的研究进展[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(7): 2753-2772. |
| [11] | 李贵贤, 曹阿波, 孟文亮, 王东亮, 杨勇, 周怀荣. 耦合固体氧化物电解槽的CO2制甲醇过程设计与评价研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(7): 2999-3009. |
| [12] | 邵远哲, 赵忠盖, 刘飞. 基于共同趋势模型的非平稳过程质量相关故障检测方法[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(6): 2522-2537. |
| [13] | 毛磊, 刘冠章, 袁航, 张光亚. 可捕集CO2的纳米碳酸酐酶粒子的高效制备及性能研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(6): 2589-2598. |
| [14] | 江锦波, 彭新, 许文烜, 门日秀, 刘畅, 彭旭东. 泵出型螺旋槽油气密封泄漏特性及参数影响研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(6): 2538-2554. |
| [15] | 蔺彩虹, 王丽, 吴瑜, 刘鹏, 杨江峰, 李晋平. 沸石中碱金属阳离子对CO2/N2O吸附分离性能的影响[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(5): 2013-2021. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备 11010102001995号
京公网安备 11010102001995号