• •
收稿日期:2025-09-28
修回日期:2025-11-26
出版日期:2026-01-19
通讯作者:
顾春鹏,韩长存
作者简介:张晨阳(2004—),男,本科生, chenyang23579@tju.edu.cn
基金资助:
Chenyang ZHANG1( ), Chunpeng GU2(
), Chunpeng GU2( ), Changcun HAN3(
), Changcun HAN3( )
)
Received:2025-09-28
Revised:2025-11-26
Online:2026-01-19
Contact:
Chunpeng GU, Changcun HAN
摘要:
工业化的快速推进加剧了全球对能源消耗与碳排放的担忧,氢能以其燃烧产物仅为水、来源丰富且燃烧热值高成为绿色能源体系的关键组成部分。光催化分解水制氢作为一种极具潜力的氢能生产技术,其效率和实用性受可见光利用率低、光生电荷载流子快速复合等因素制约。硫基光催化剂凭借硫掺杂带来的优势,在光催化领域展现出显著潜力,可通过修饰材料能带结构拓宽光响应范围、增强稳定性并抑制电荷复合。综述了硫基催化剂在光催化制氢中的最新研究进展,重点探讨了CdS、In2S3、ZnS、ZnIn2S4和CdZnS等典型硫基光催化剂的特性及改性策略,通过形貌工程、元素掺杂和负载助催化剂等手段,可有效提升光催化剂性能。本文为开发高效、稳定的光催化制氢催化剂提供了理论基础,助力全球能源结构向绿色转型。
中图分类号:
张晨阳, 顾春鹏, 韩长存. 硫基光催化剂在高效光催化制氢中研究进展[J]. 化工学报, DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20251084.
Chenyang ZHANG, Chunpeng GU, Changcun HAN. Recent advances and perspectives on sulfide-based photocatalysts for hydrogen production[J]. CIESC Journal, DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20251084.
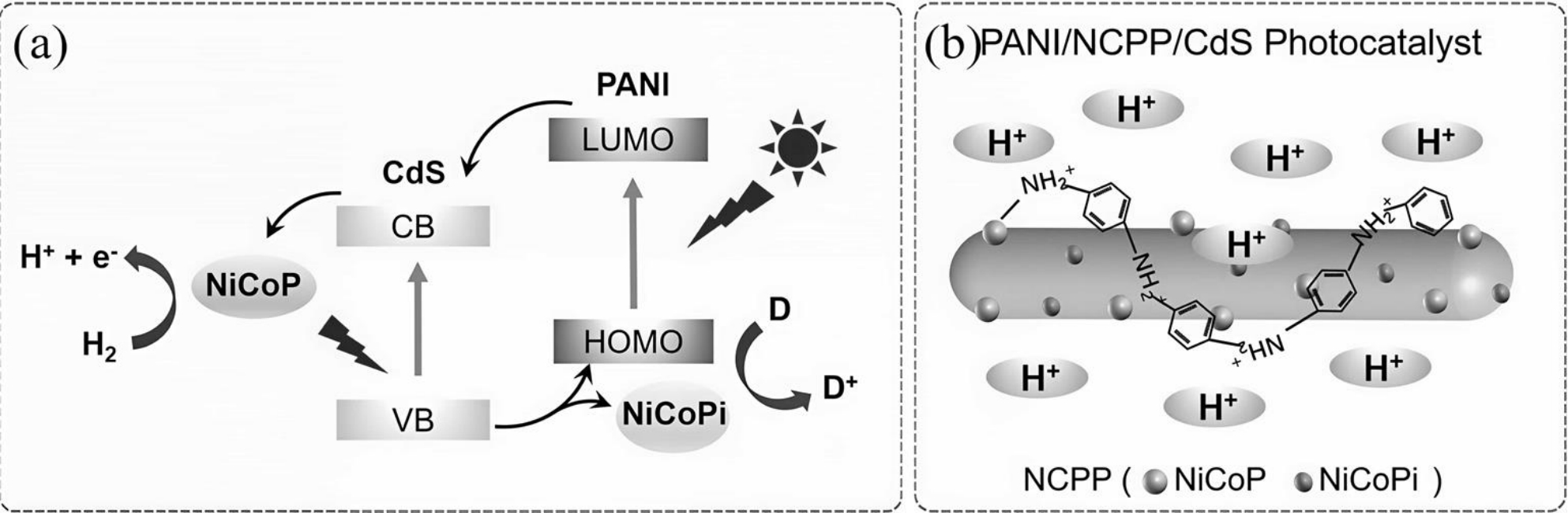
图2 (a)电荷分离及光催化机理示意图;(b)PANI和NCPP的CdS纳米棒示意图[30]
Fig.2 (a) Diagram illustrating charge separation and photocatalytic mechanism;(b) schematic of CdS nanorods loaded with PANI and NCPP[30]
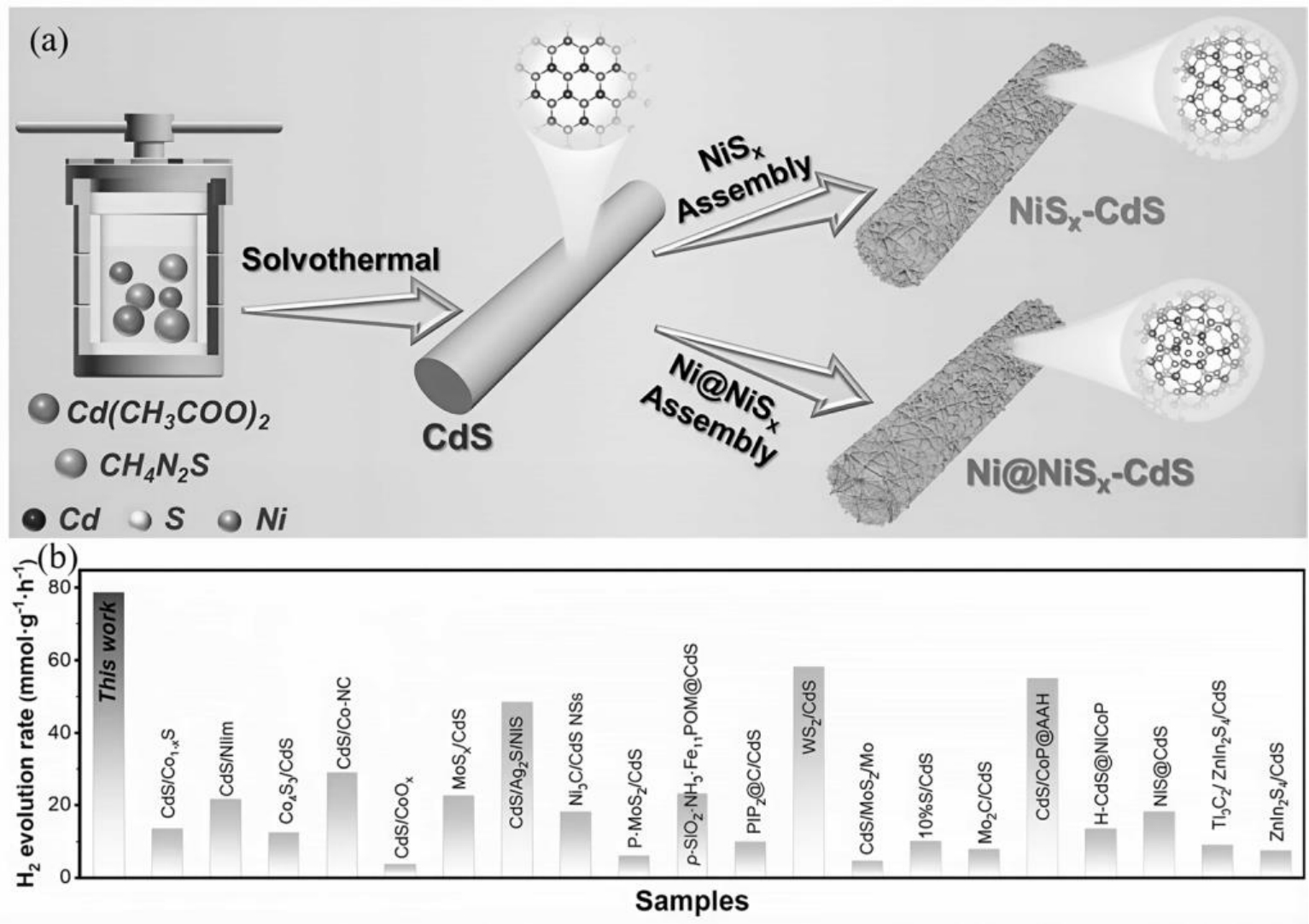
图3 (a)Ni@NiSx-CdS光催化剂的合成过程示意图;(b)不同CdS基光催化剂的析氢速率对比图[29]
Fig.3 (a) Schematic of the synthetic process; (b) comparison of the H2 evolution rate with other photocatalysts in recent works[29]
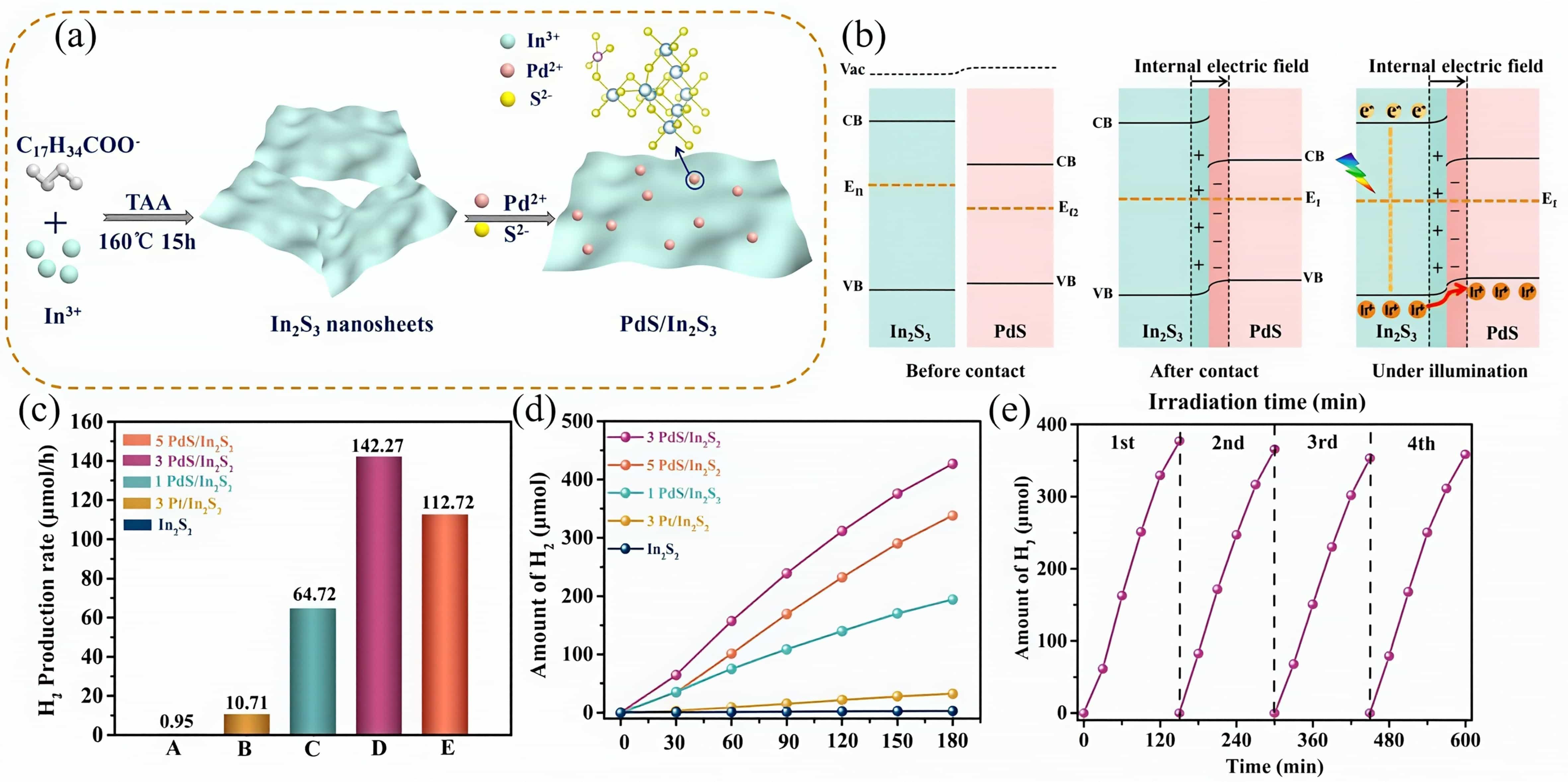
图4 PdS/In2S3催化剂的(a)制备流程示意图和(b)内建电场形成示意图;负载不同助催化剂和不同负载量的(c)产氢速率对比图和(d)产氢性能图;(e)3PdS/In2S3产氢稳定性测试[35]
Fig.4 Schematic illustration of (a)the fabrication for PdS/In2S3 catalyst and(b)the internal electric field formation between PdS and In2S3, Comparison of the hydrogen evolution rate (c) and amount of H2 generation(d)for the as-prepared samples;(e)stability test of H2 generation for the 3PdS/In2S3 composite[35]
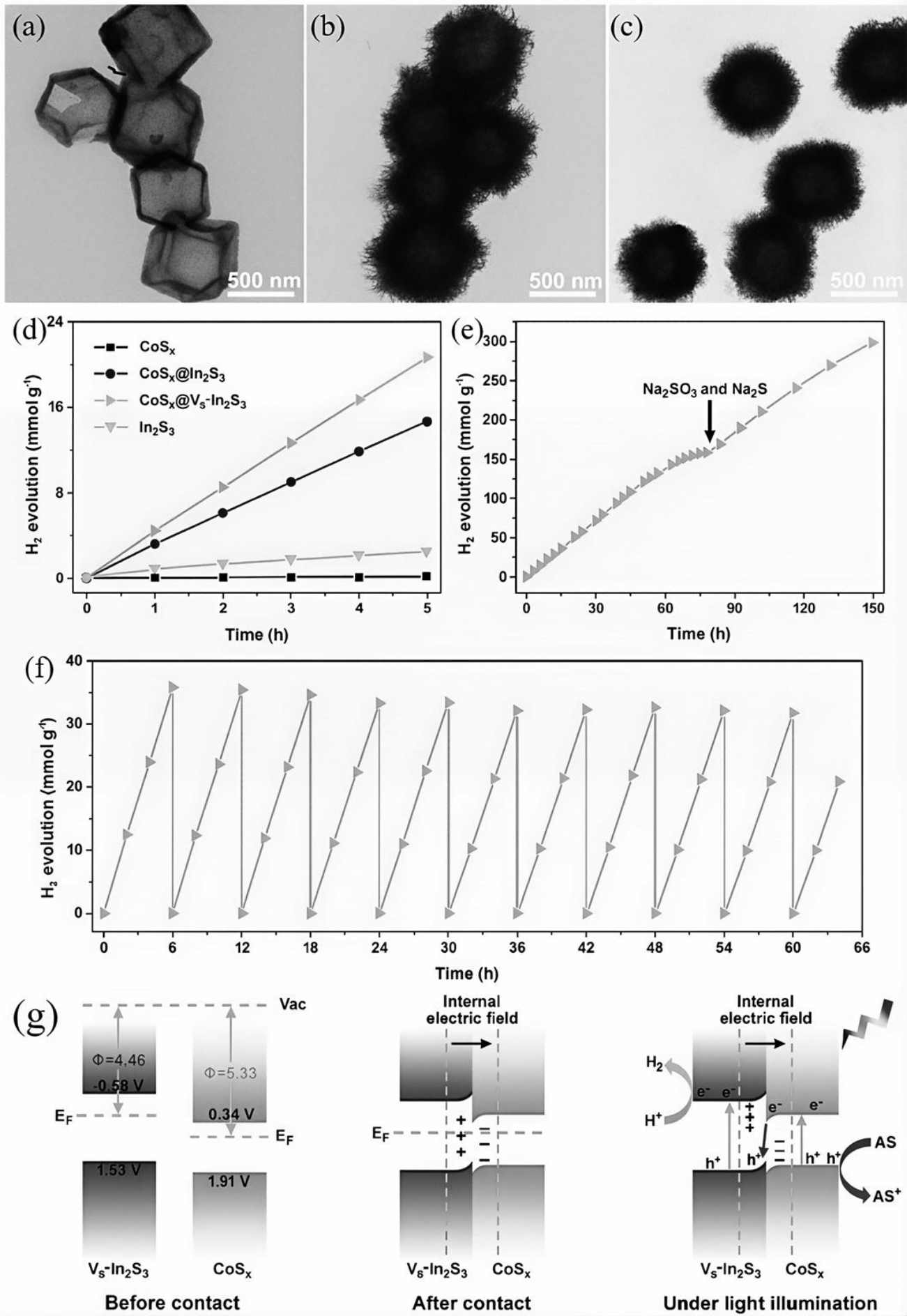
图5 透射电镜(TEM)图像:(a)CoSx;(b)CoSx@In2S3和(c)CoSx@Vs-In2S3;(d)光催化产氢性能图;CoSx@Vs-In2S3核壳光催化剂的(e)稳定性测试、(f)循环产氢测试和(g)产氢反应机制示意图[36]
Fig.5 (a–c) Transmission Electron Microscope(TEM) images of CoSx, CoSx@In2S3, and CoSx@Vs – In2S3, (d) Photocatalytic hydrogen-evolution rate of CoSx,In2S3, CoSx@In2S3, and CoSx@Vs – In2S3 catalysts; (e) uninterrupted stability tests of the CoSx@Vs – In2S3 core/shell photocatalysts;(f) recycling hydrogen-generation tests of the CoSx@Vs – In2S3 core/shell photocatalysts; (g)reaction mechanism for photocatalytic hydrogen evolution on the S-scheme CoSx@Vs – In2S3 heterojunction[36]
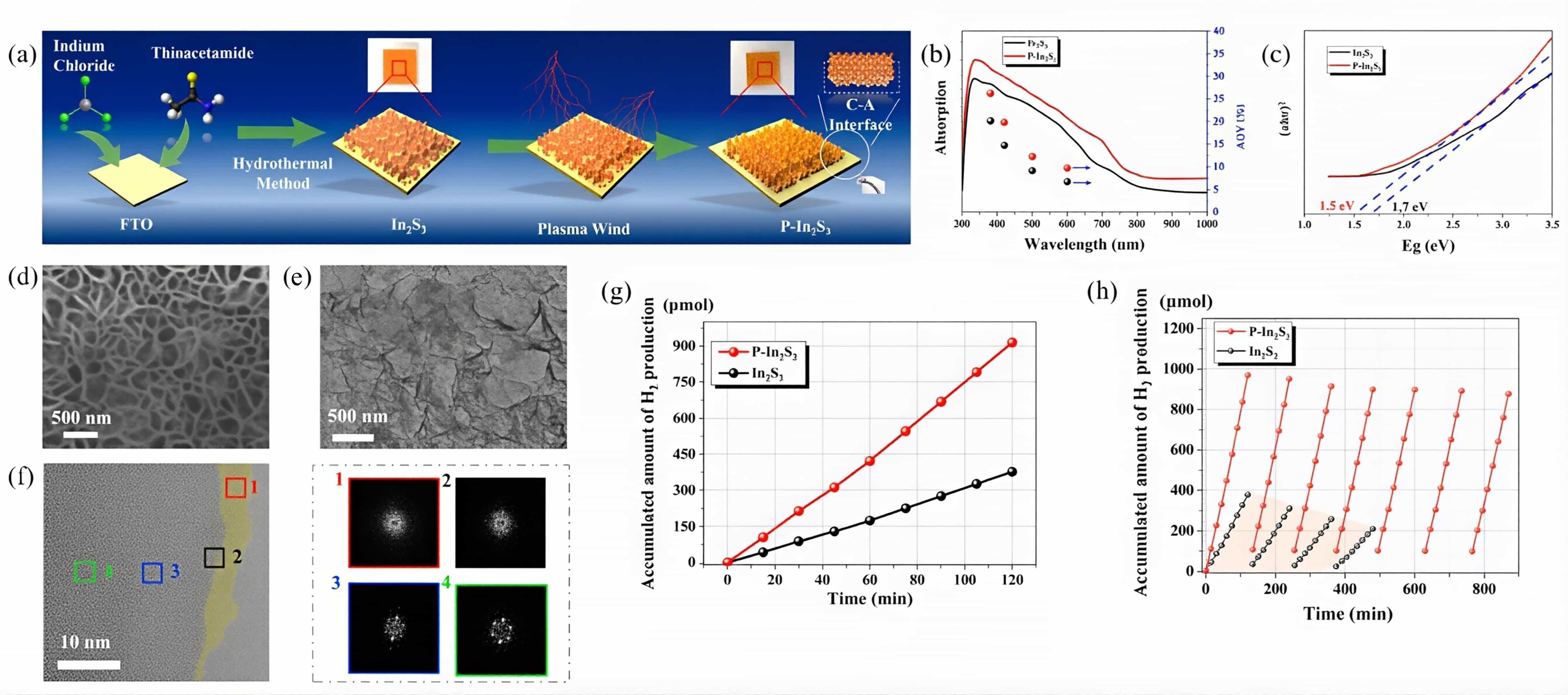
图6 (a)P-In2S3样品的制备流程示意图;(b)AQY;(c)基于光吸收光谱的带隙计算;P-In2S3样品的(d)扫描电子显微镜(SEM)、(e)TEM、(f)HRTEM图像,后方的四个方框区域显示了傅里叶变换;(g)不同样品的累积产氢量;(h)P-In2S3的七次光催化产氢循环与纯In2S3的四次循环对比[37]
Fig.6 (a)The schematic of the fabrication process of the sample P-In2S3,(b)the light absorption spectra and AQY, (c) the bandgap calculation based on the light absorption spectra,(d)the SEM image, (e) the TEM image, (f) the High-resolution SEM(HRTEM) image of the P-In2S3 sample. The Fourier transforms of the image involving the four box areas are displayed,(g) accumulated amount of hydrogen production of different samples, (h) seven photocatalytic hydrogen production cycles of the P-In2S3 vs. four cycles of the bare In2S3[37]
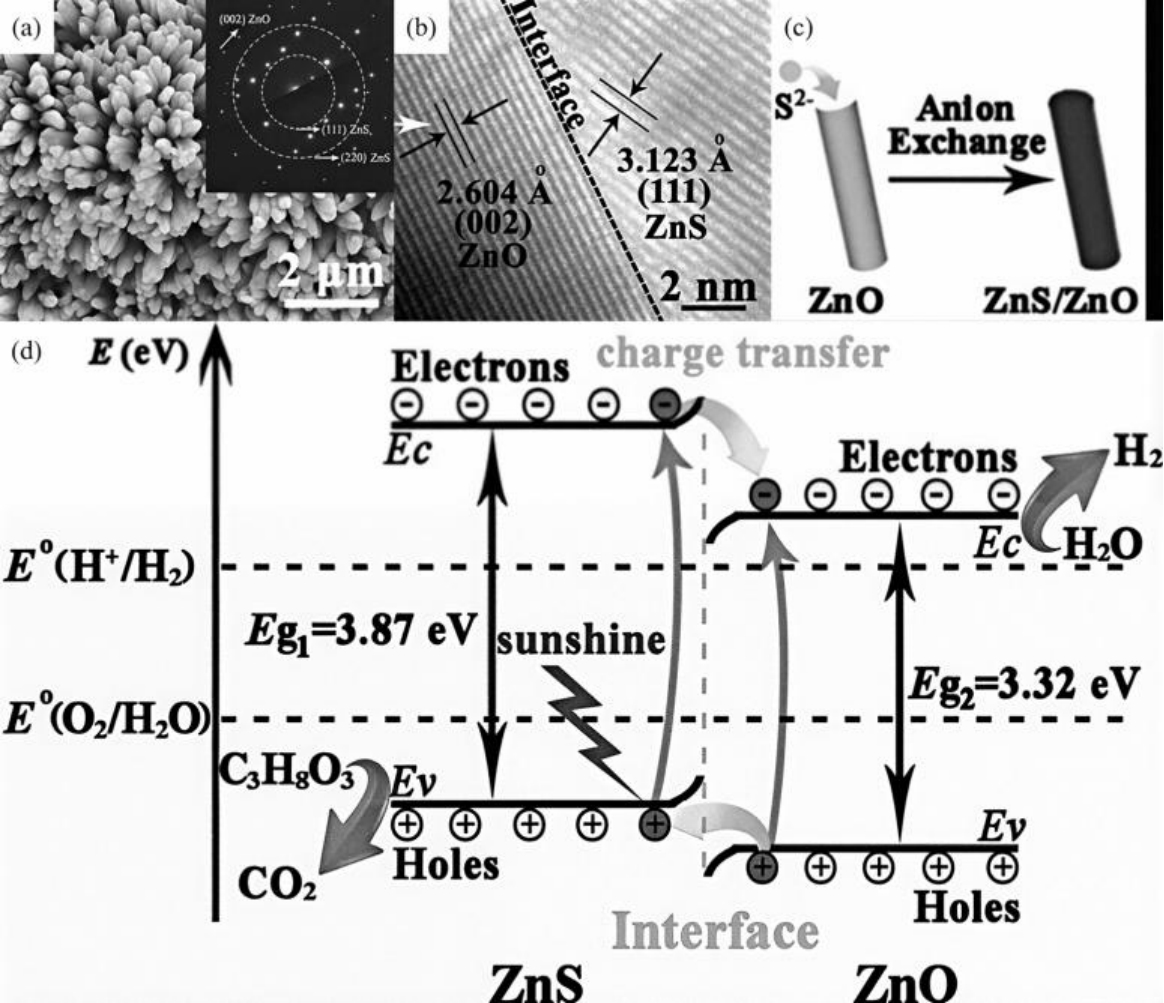
图7 ZnO/ZnS异质结构纳米棒阵列的(a)高分辨率SEM图像、(b)HRTEM图像;(c)ZnO核(黑色)上ZnS(灰色)壳的阴离子交换生长反应方案;(d)电荷转移过程[39]
Fig.7 (a)HRTEM images of ZnO/ZnS HNAs; inset: the crystallographic character of the single crystal ZnO core and the polycrystalline ZnS shell; (b) HRTEM images of a single ZnO/ZnS HNR; (c) scheme of the anion-exchange growing reaction for ZnS (grey) shell on ZnO core (black); (d) the charge-transfer process in ZnO/ZnS HNRAs[39]
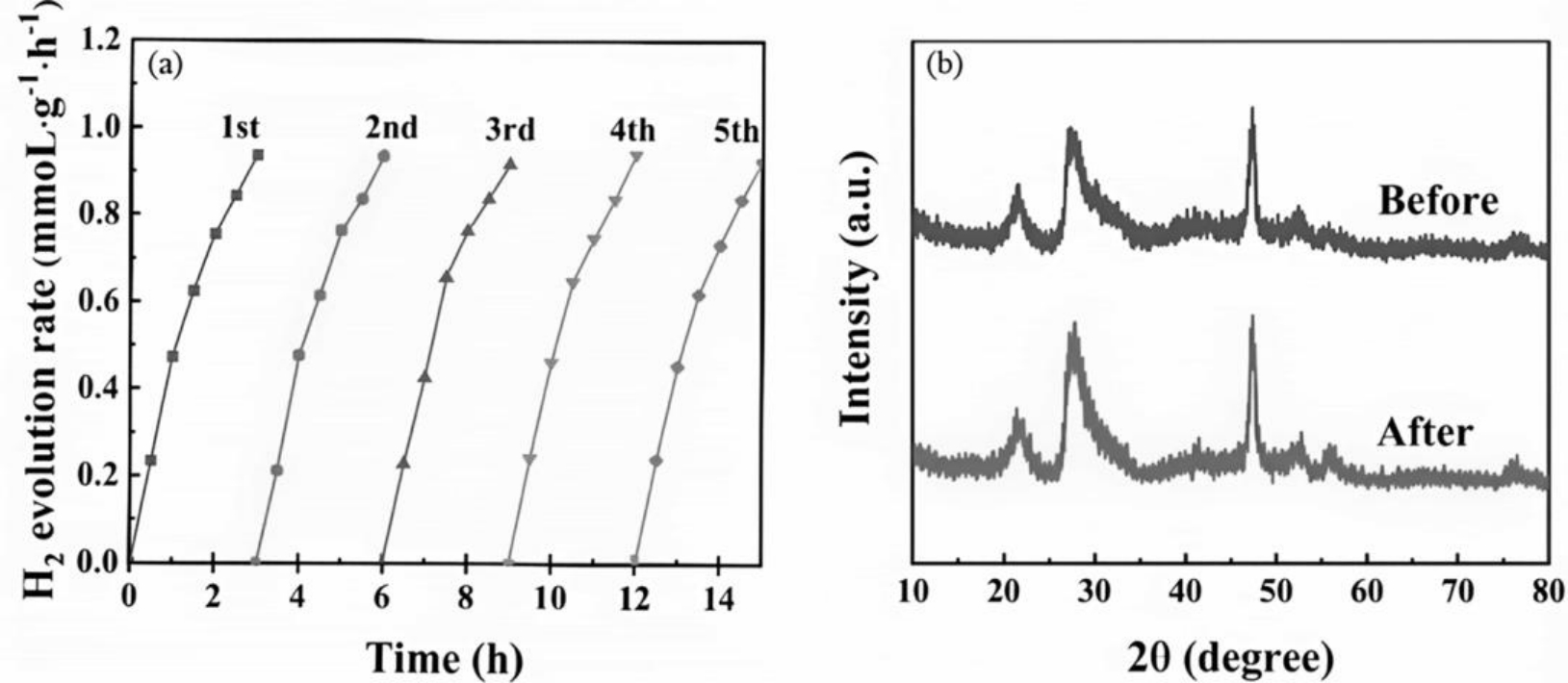
图8 (a)ZCZ-3的循环稳定性测试和(b)光催化析氢反应前后的XRD谱图[40]
Fig.8 (a)Cycle stability test of the ZCZ-3 and (b) XRD before and after photocatalytic hydrogen evolution reaction[40]
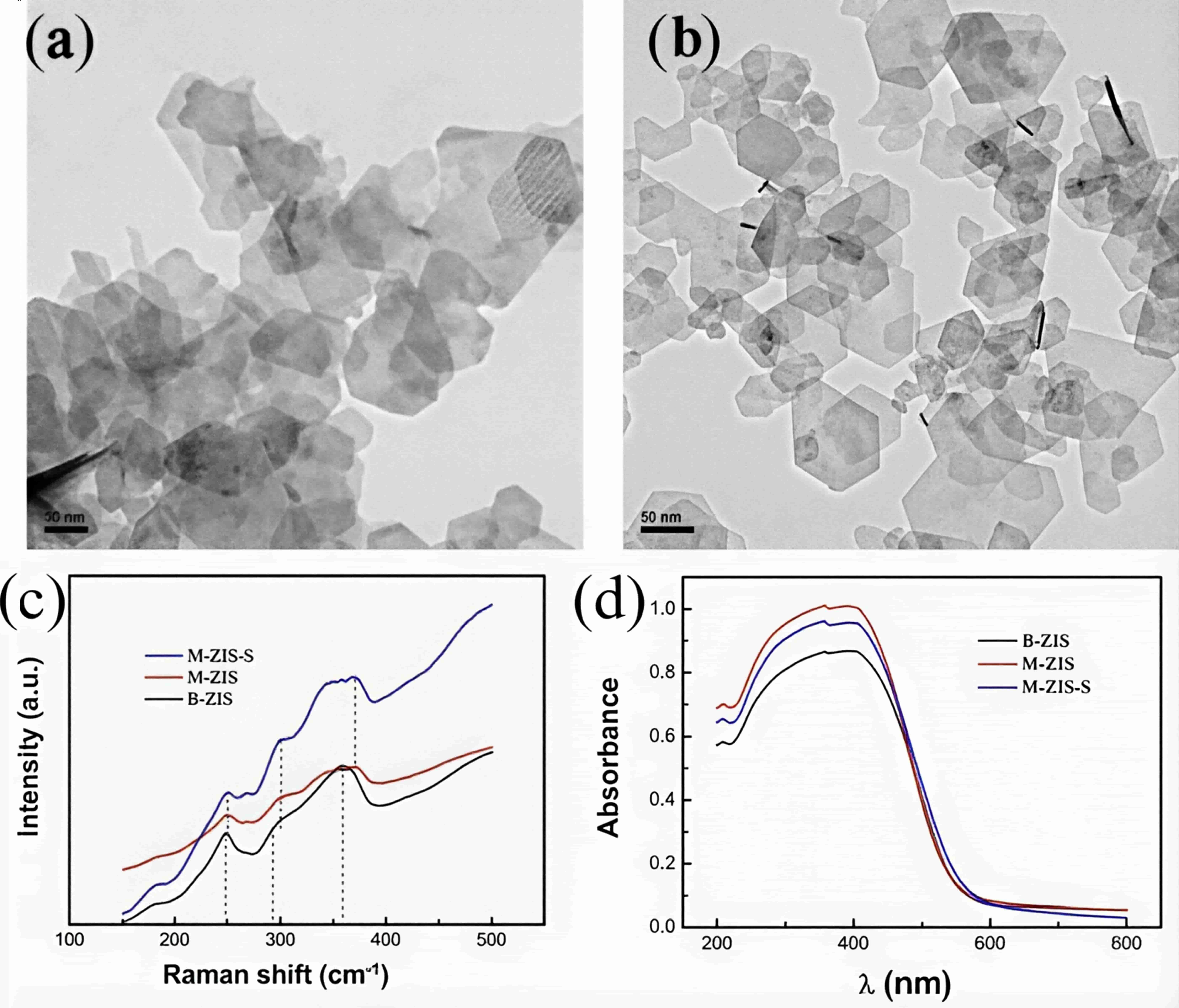
图10 (a)B-ZIS和(b)M-ZIS的TEM图像;B-ZIS、M-ZIS和M-ZIS-s的(c)拉曼光谱和(d)UV-vis 吸收光谱图[46]
Fig.10 The TEM images of (a)B-ZIS and (b)M-ZIS; (c) The Raman spectra and (d)UV–vis DRS of B-ZIS, M-ZIS and M-ZIS-S[46]
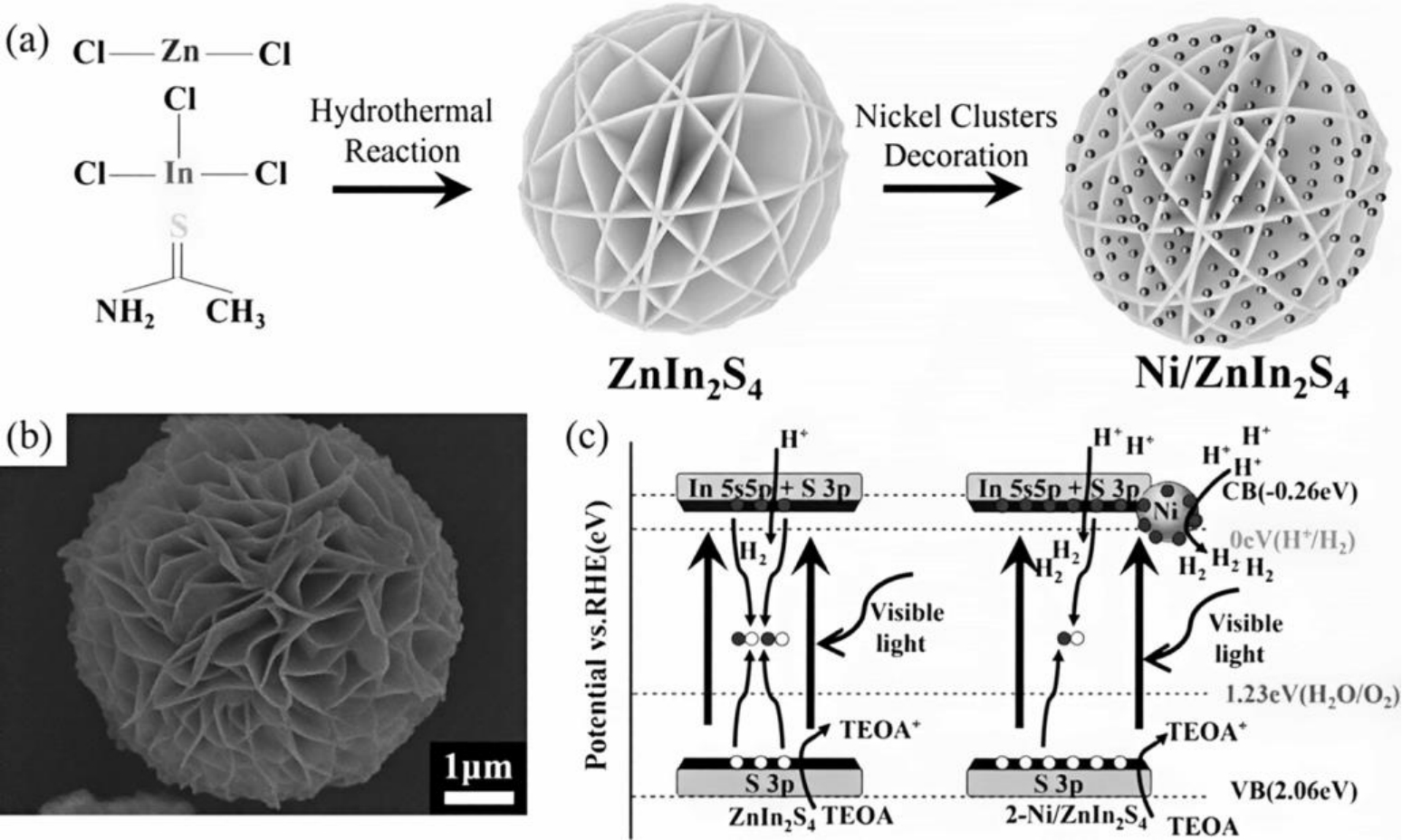
图11 (a)Ni/ZnIn2S4的合成过程示意图;(b)2 wt% Ni/ZnIn2S4的SEM图像;(c)ZnIn2S4和2 wt% Ni/ZnIn2S4的析氢反应机理示意图[47]
Fig.11 (a)the schematic synthetic process of Ni/ZnIn2S4;(b) SEM images of 2 wt%-Ni/ZnIn2S4;(c) the schemed mechanism of ZnIn2S4 and 2 wt%-Ni/ZnIn2S4 for H2 evolution[47]
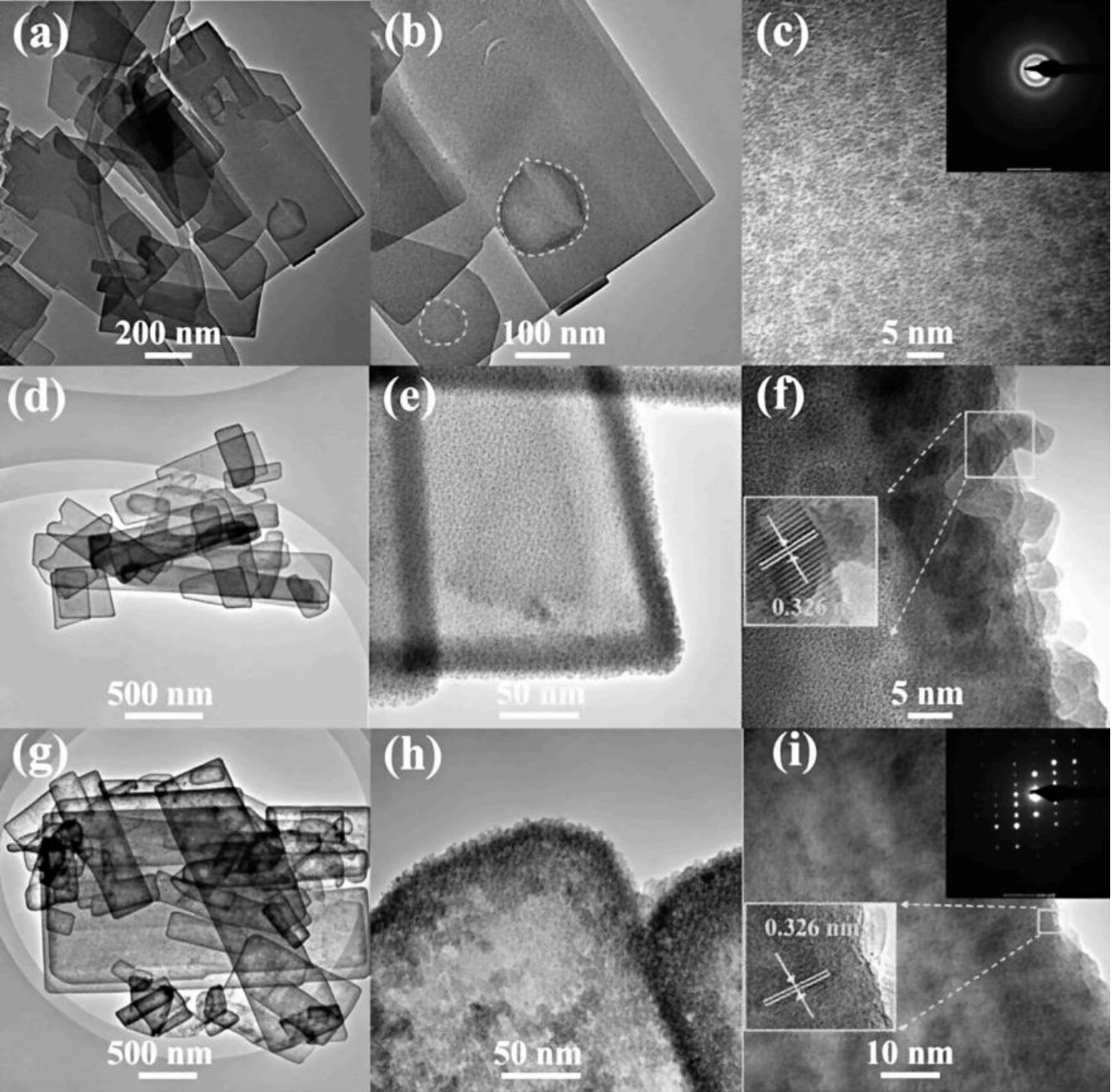
图12 TEM图像:(a–c)ZnS(en)0.5、(d–f)Cd0.5Zn0.5S(en)x和(g–i)Cd0.5Zn0.5S纳米片[51]
Fig.12 TEM images of ZnS(en)0.5 (a–c), Cd0.5Zn0.5S(en)x (d–f), and Cd0.5Zn0.5S (g–i) nanosheets[51]
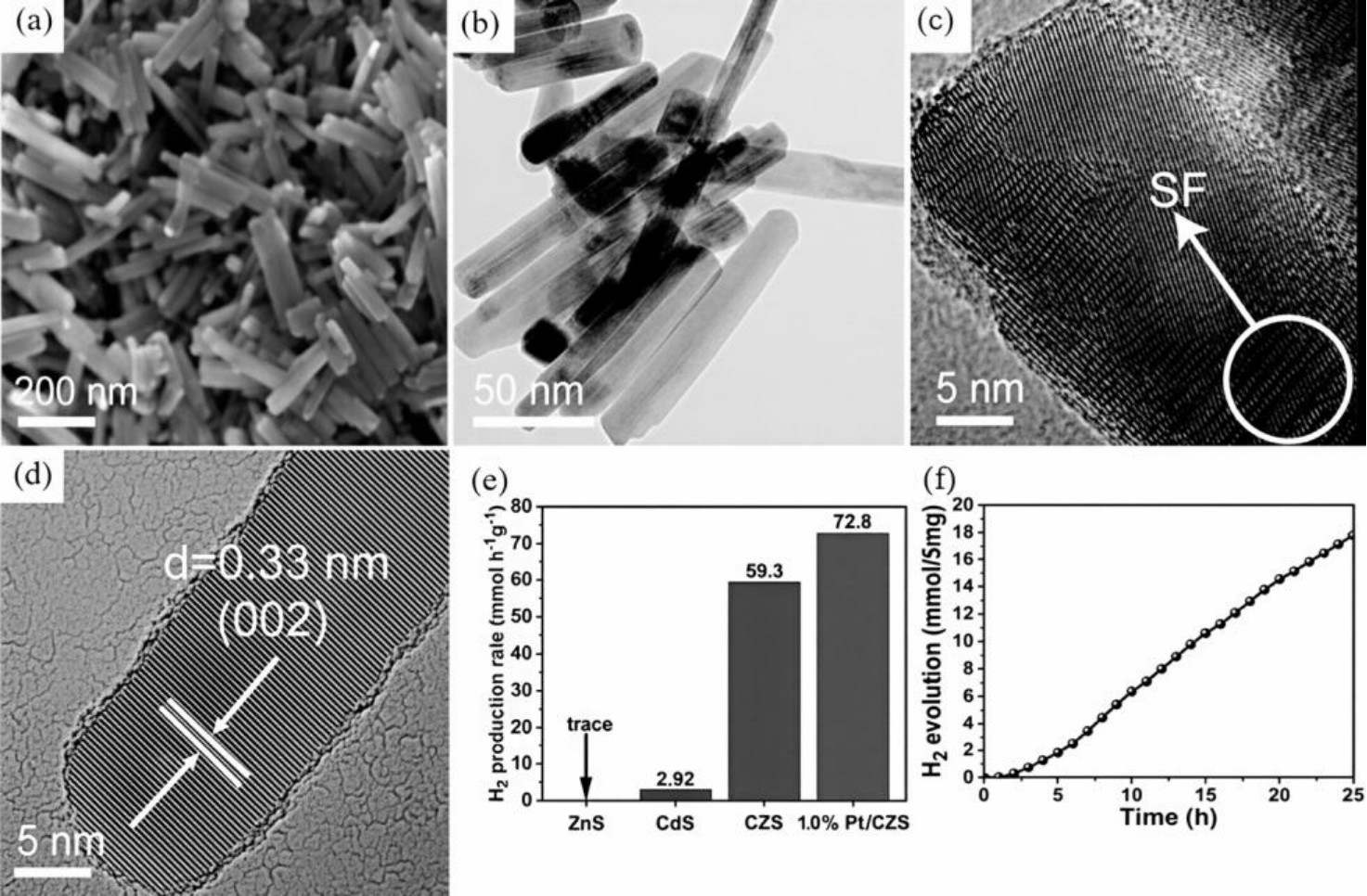
图13 CZS纳米棒的(a)SEM、(b)TEM和(c,d)HRTEM图像;(e)CdS、ZnS、CZS和1.0 wt% Pt/CZS的光催化析氢速率;(f)CZS在可见光照射下25 h的光催化稳定性[52]
Fig.13 (a) SEM, (b) TEM, and (c, d) HRTEM images of CZS nanorods; (e) Photocatalytic hydrogen evolution rates of CdS, ZnS, CZS, and 1.0 wt% Pt/CZS; (f) Photocatalytic stability of CZS under visible light irradiation for 25 h[52]
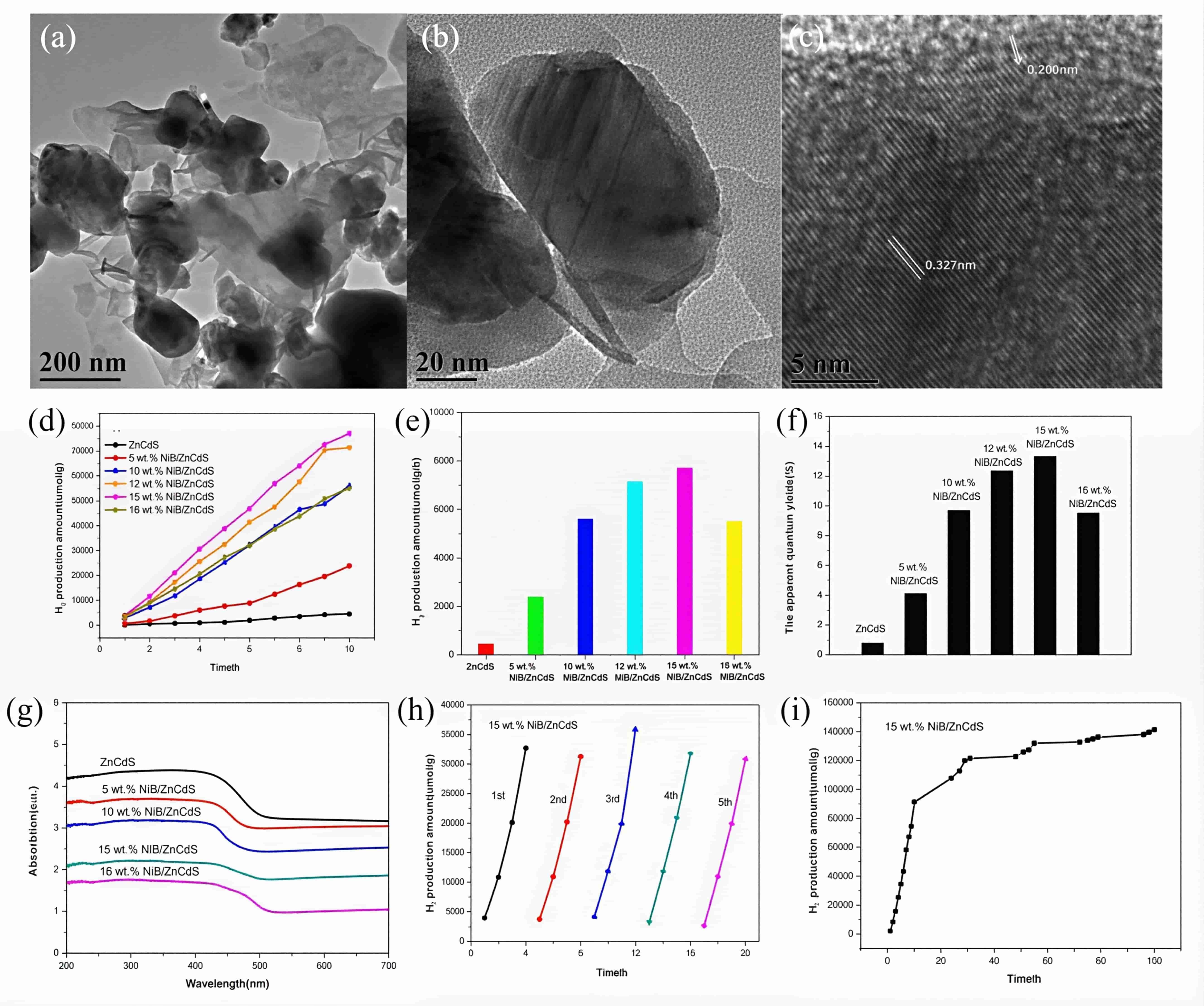
图14 (a-c)15 wt% NiB/ZnCdS的TEM图像;x wt% NiB/ZnCdS样品的(d)析氢量、(e)析氢速率、(f)AQY和(g)UV-vis吸收光谱;(h)15 wt% NiB/ZnCdS经5次循环后的析氢量和(i)稳定性[53]
Fig.14 (a-c)TEM image of 15 wt% NiB/ZnCdS(d) The H2 production amount of x wt% NiB/ZnCdS samples; (e)the H2 production rate of ZnCdS and NiB/ZnCdS;(f) the apparent quantum yields of ZnCdS samples with different contents of NiB;(g)UV-vis absorption spectra of NiB/ZnCdS samples and pure ZnCdS;(h)the H2 production amount of 15 wt% NiB/ZnCdS after 5 cycles;(i)the stability of 15 wt% NiB/ZnCdS[53]
| 催化剂基体类型 | 具体催化剂体系 | 析氢速率/ mmol·g-1·h-1 | 相对于纯相的提升倍数 | 突出特点 | 光源 | 空穴牺牲剂 | AQY | 文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CdS | PANI/NCPP/CdS | 170.3 | 426 | 双功能助催化剂(NiCoP/NiCoPi)+导电聚合物,质子吸附强化 | 可见光(λ>420 nm) | 乳酸 | 49%(420 nm) | [ |
| Ni@NiSx-CdS | 78.7 | 18.3 | 非晶-晶态异质结+ Cd-S-Ni键桥,梯度功函数驱动电子迁移 | 可见光 | 乳酸 | [ | ||
| 中空CdS({101}晶面) | 模板辅助阳离子交换制备,中空结构增强光吸收、缩短载流子迁移距离 | 可见光 | [ | |||||
| NiCoP-g-C3N4/CdS | 55.63 | 4.6 | 异质结构建+双助催化协同,量化电荷分离效率差异 | 可见光 | 乳酸 | 70%(420 nm) | [ | |
| In2S3 | PdS/In2S3(3 wt% PdS) | 142.27 | 149.8 | 0D-2D异质结+Pd-S-In键,内建电场定向转移空穴 | 可见光 | 0.35 M Na2S+0.25 M Na2SO3 | [ | |
| CoSx@Vs-In2S3 | 4.136 | 8.23 | 核-壳异质结+硫空位,In原子为高效析氢中心 | 可见光 | 0.35 M Na2S+0.25 M Na2SO3 | [ | ||
| P-In2S3(等离子体风表面非晶化) | 4.57 | 2.7 | 晶-非晶界面,S原子富集电子,抗光腐蚀 | 可见光 | TEOA | 26.2%(380 nm) | [ | |
| In2S3-WO3 | 5.1 | 5 | 2D-1D Type-II异质结,WO₃抑制光腐蚀、促进电荷分离 | AM 1.5G 模拟太阳光 | 0.5 M Na2SO4 | [ | ||
| ZnS | ZnO/ZnS HNRAs | 384 | 451.8 | n-p异质结,电子空穴跨界面转移,延长载流子寿命 | 模拟太阳光 | 无牺牲剂 | [ | |
| ZnIn2S4/CNTs/ZnS(ZCZ-3) | 未明确(活性稳定) | 三元异质结,ZnS结构稳定,抗分解抗变质 | 未明确 | 未明确 | [ | |||
| CdS/CuS/ZnS(C2C5) | 6.401 | 4 | Cd-Cu 共掺杂+三元异质结+硫/锌空位陷阱 | AM 1.5G 模拟太阳光 | 0.35 M Na2S+0.25 M Na2SO3 | 38.3%(425 nm) | [ | |
| ZnIn2S4 | M-ZIS(有序晶格) | 0.0082 | 2.5 | 微波辅助制备,晶格有序,载流子分离效率优 | 可见光 | TEOA | [ | |
| H-ZIS(硫空位缺陷) | 0.0033 | 硫空位丰富、晶格无序,缺陷充当复合中心 | 可见光 | TEOA | [ | |||
| M-ZIS-S(硫空位修饰) | 未明确(光吸收提升) | 硫空位窄化带隙,比表面积提升至 82.53 m²・g⁻¹ | 可见光 | TEOA | [ | |||
| Ni/ZnIn2S4(2 wt% Ni簇) | 22.2 | 10.6 | Ni簇提供活性位点,加速电子-空穴分离与迁移 | 可见光 | TEOA | 56.14%(450 nm) | [ | |
| ZnIn2S4/N-rGO | 2.85 | 9.7 | S型异质结+N掺杂rGO,增强电子传输与光吸收 | 可见光 | TEOA | 27.24%(420 nm) | [ | |
| CdZnS | 纯相CdZnS | 1.395 | 固溶体,可调控带隙,高比表面积 | 可见光 | 无(纯水) | [ | ||
| Cd0.5Zn0.5S(en)ₓ(二维介孔超薄) | 1.395 | 模板转化法制备,厚度1.5 nm,孔径20.6 nm,高活性位点 | 可见光 | 无(纯水) | [ | |||
| Cd0.6Zn0.4S(1D纳米棒+硫空位) | 59.3 | 20 | 堆叠缺陷+硫空位,电子捕获位点丰富,电荷传输路径短 | 可见光 | 0.35 M Na2S+0.25 M Na2SO3 | [ | ||
| NiB/CdZnS(15 wt% NiB) | 8.137 | 17 | 非晶态NiB负载,不饱和配位原子为高效析氢中心 | 可见光 | TEOA | 13.3%(AQY) | [ | |
| Mo-Zn0.5Cd0.5S@NiCo2S4 | 未明确(双功能活性) | 掺杂-异质结协同,提升析氢与降解双功能 | 可见光 | [ | ||||
| CdZnS@Ti3C2Tx MXene | 未明确(活性提升) | 原位生长异质结,MXene增强电子传输 | 可见光 | TEOA | [ |
表1 典型硫基光催化剂析氢性能汇总表
Table 1 Summary Table of Hydrogen Evolution Performance of Typical Sulfide-Based Photocatalysts
| 催化剂基体类型 | 具体催化剂体系 | 析氢速率/ mmol·g-1·h-1 | 相对于纯相的提升倍数 | 突出特点 | 光源 | 空穴牺牲剂 | AQY | 文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CdS | PANI/NCPP/CdS | 170.3 | 426 | 双功能助催化剂(NiCoP/NiCoPi)+导电聚合物,质子吸附强化 | 可见光(λ>420 nm) | 乳酸 | 49%(420 nm) | [ |
| Ni@NiSx-CdS | 78.7 | 18.3 | 非晶-晶态异质结+ Cd-S-Ni键桥,梯度功函数驱动电子迁移 | 可见光 | 乳酸 | [ | ||
| 中空CdS({101}晶面) | 模板辅助阳离子交换制备,中空结构增强光吸收、缩短载流子迁移距离 | 可见光 | [ | |||||
| NiCoP-g-C3N4/CdS | 55.63 | 4.6 | 异质结构建+双助催化协同,量化电荷分离效率差异 | 可见光 | 乳酸 | 70%(420 nm) | [ | |
| In2S3 | PdS/In2S3(3 wt% PdS) | 142.27 | 149.8 | 0D-2D异质结+Pd-S-In键,内建电场定向转移空穴 | 可见光 | 0.35 M Na2S+0.25 M Na2SO3 | [ | |
| CoSx@Vs-In2S3 | 4.136 | 8.23 | 核-壳异质结+硫空位,In原子为高效析氢中心 | 可见光 | 0.35 M Na2S+0.25 M Na2SO3 | [ | ||
| P-In2S3(等离子体风表面非晶化) | 4.57 | 2.7 | 晶-非晶界面,S原子富集电子,抗光腐蚀 | 可见光 | TEOA | 26.2%(380 nm) | [ | |
| In2S3-WO3 | 5.1 | 5 | 2D-1D Type-II异质结,WO₃抑制光腐蚀、促进电荷分离 | AM 1.5G 模拟太阳光 | 0.5 M Na2SO4 | [ | ||
| ZnS | ZnO/ZnS HNRAs | 384 | 451.8 | n-p异质结,电子空穴跨界面转移,延长载流子寿命 | 模拟太阳光 | 无牺牲剂 | [ | |
| ZnIn2S4/CNTs/ZnS(ZCZ-3) | 未明确(活性稳定) | 三元异质结,ZnS结构稳定,抗分解抗变质 | 未明确 | 未明确 | [ | |||
| CdS/CuS/ZnS(C2C5) | 6.401 | 4 | Cd-Cu 共掺杂+三元异质结+硫/锌空位陷阱 | AM 1.5G 模拟太阳光 | 0.35 M Na2S+0.25 M Na2SO3 | 38.3%(425 nm) | [ | |
| ZnIn2S4 | M-ZIS(有序晶格) | 0.0082 | 2.5 | 微波辅助制备,晶格有序,载流子分离效率优 | 可见光 | TEOA | [ | |
| H-ZIS(硫空位缺陷) | 0.0033 | 硫空位丰富、晶格无序,缺陷充当复合中心 | 可见光 | TEOA | [ | |||
| M-ZIS-S(硫空位修饰) | 未明确(光吸收提升) | 硫空位窄化带隙,比表面积提升至 82.53 m²・g⁻¹ | 可见光 | TEOA | [ | |||
| Ni/ZnIn2S4(2 wt% Ni簇) | 22.2 | 10.6 | Ni簇提供活性位点,加速电子-空穴分离与迁移 | 可见光 | TEOA | 56.14%(450 nm) | [ | |
| ZnIn2S4/N-rGO | 2.85 | 9.7 | S型异质结+N掺杂rGO,增强电子传输与光吸收 | 可见光 | TEOA | 27.24%(420 nm) | [ | |
| CdZnS | 纯相CdZnS | 1.395 | 固溶体,可调控带隙,高比表面积 | 可见光 | 无(纯水) | [ | ||
| Cd0.5Zn0.5S(en)ₓ(二维介孔超薄) | 1.395 | 模板转化法制备,厚度1.5 nm,孔径20.6 nm,高活性位点 | 可见光 | 无(纯水) | [ | |||
| Cd0.6Zn0.4S(1D纳米棒+硫空位) | 59.3 | 20 | 堆叠缺陷+硫空位,电子捕获位点丰富,电荷传输路径短 | 可见光 | 0.35 M Na2S+0.25 M Na2SO3 | [ | ||
| NiB/CdZnS(15 wt% NiB) | 8.137 | 17 | 非晶态NiB负载,不饱和配位原子为高效析氢中心 | 可见光 | TEOA | 13.3%(AQY) | [ | |
| Mo-Zn0.5Cd0.5S@NiCo2S4 | 未明确(双功能活性) | 掺杂-异质结协同,提升析氢与降解双功能 | 可见光 | [ | ||||
| CdZnS@Ti3C2Tx MXene | 未明确(活性提升) | 原位生长异质结,MXene增强电子传输 | 可见光 | TEOA | [ |
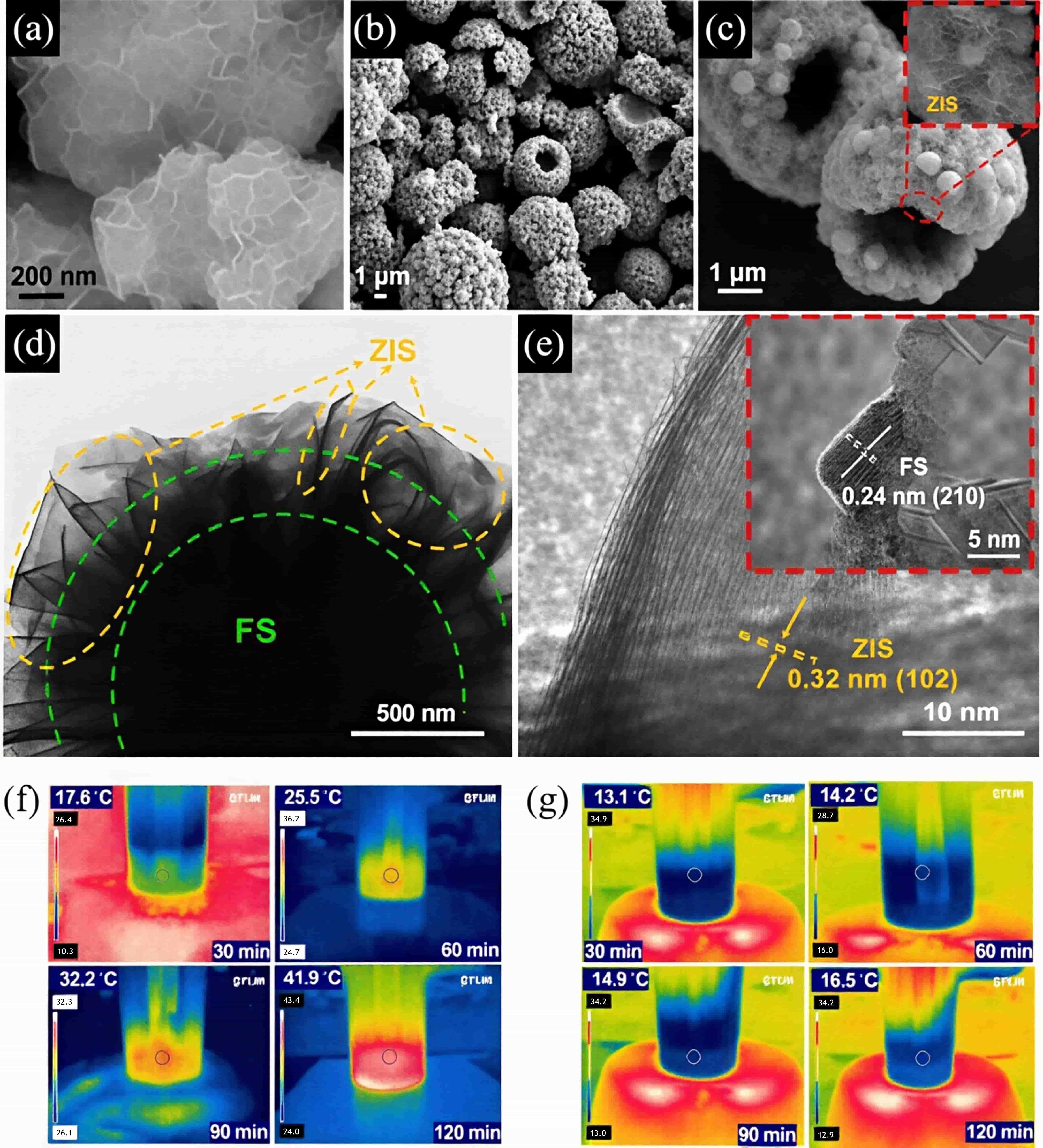

图15 (a)ZIS、(b)FS和(c)FS@ZIS-30的SEM图像;(d)FS@ZIS-30的TEM和(e)HRTEM图像;在AM 1.5G照射下,光热辅助光催化析氢实际反应过程中(f)FS@ZIS-30和(g)ZIS样品的温度分布图[56]
Fig.15 The SEM images of (a) ZIS, (b) FS and (c) FS@ZIS-30; (d) TEM and (e) HRTEM images of FS@ZIS-30; The temperature mapping images under AM 1.5G irradiation in the real reaction processes of photothermal-assisted photocatalytic H2 evolution for (f) FS@ZIS-30 and (g) ZIS samples[56]
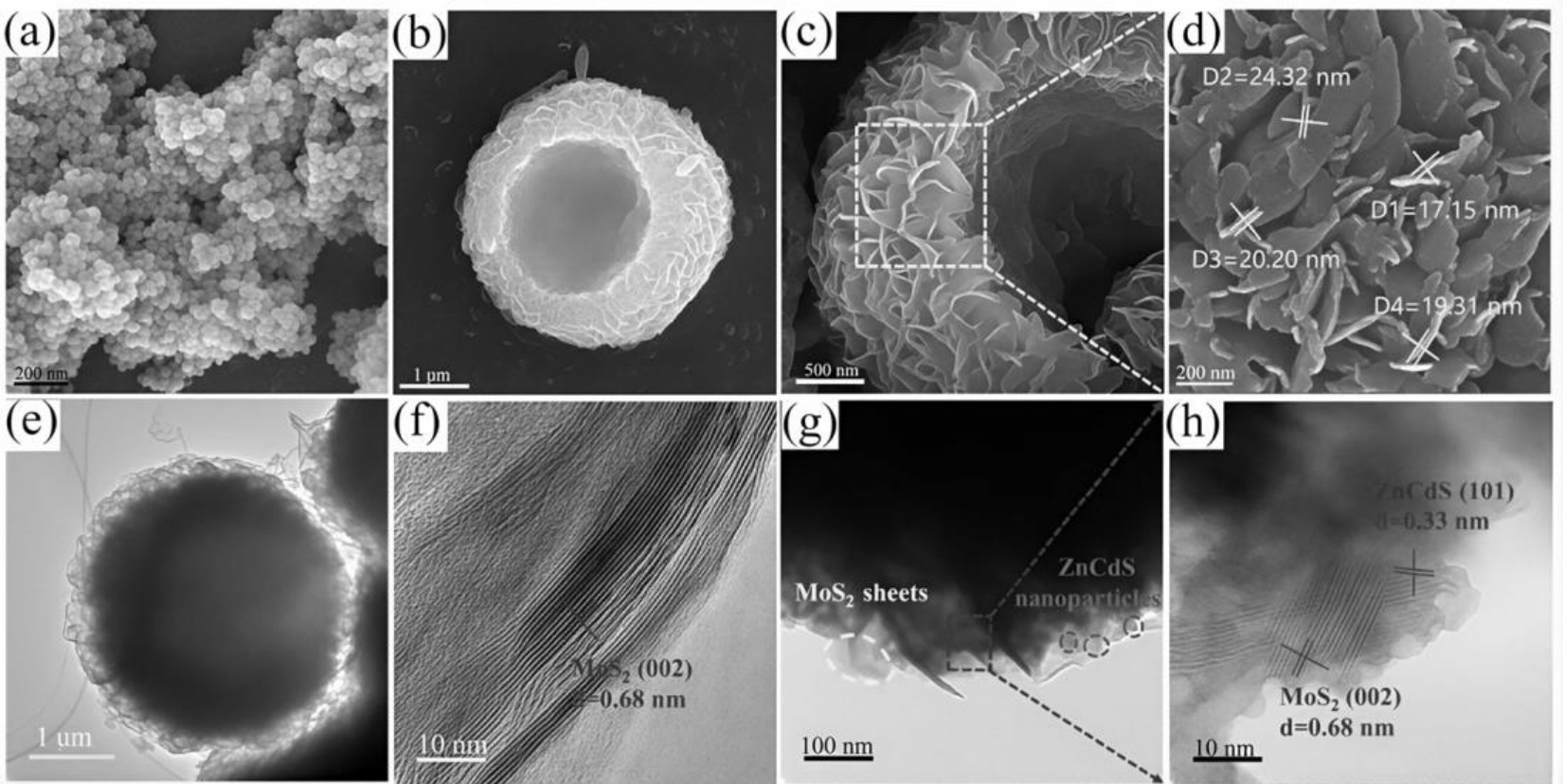
图16 (a)ZnCdS和(b-d)MoS2的的SEM图像。(e-f)MoS2的TEM和HRTEM图像,(g-h)10% M/ZCS的TEM和HRTEM图像[57]
Fig.16 SEM images of (a) ZnCdS and (b-d) MoS2. TEM and HRTEM images of (e-f) MoS2, (g-h) 10wt% M/ZCS[57]
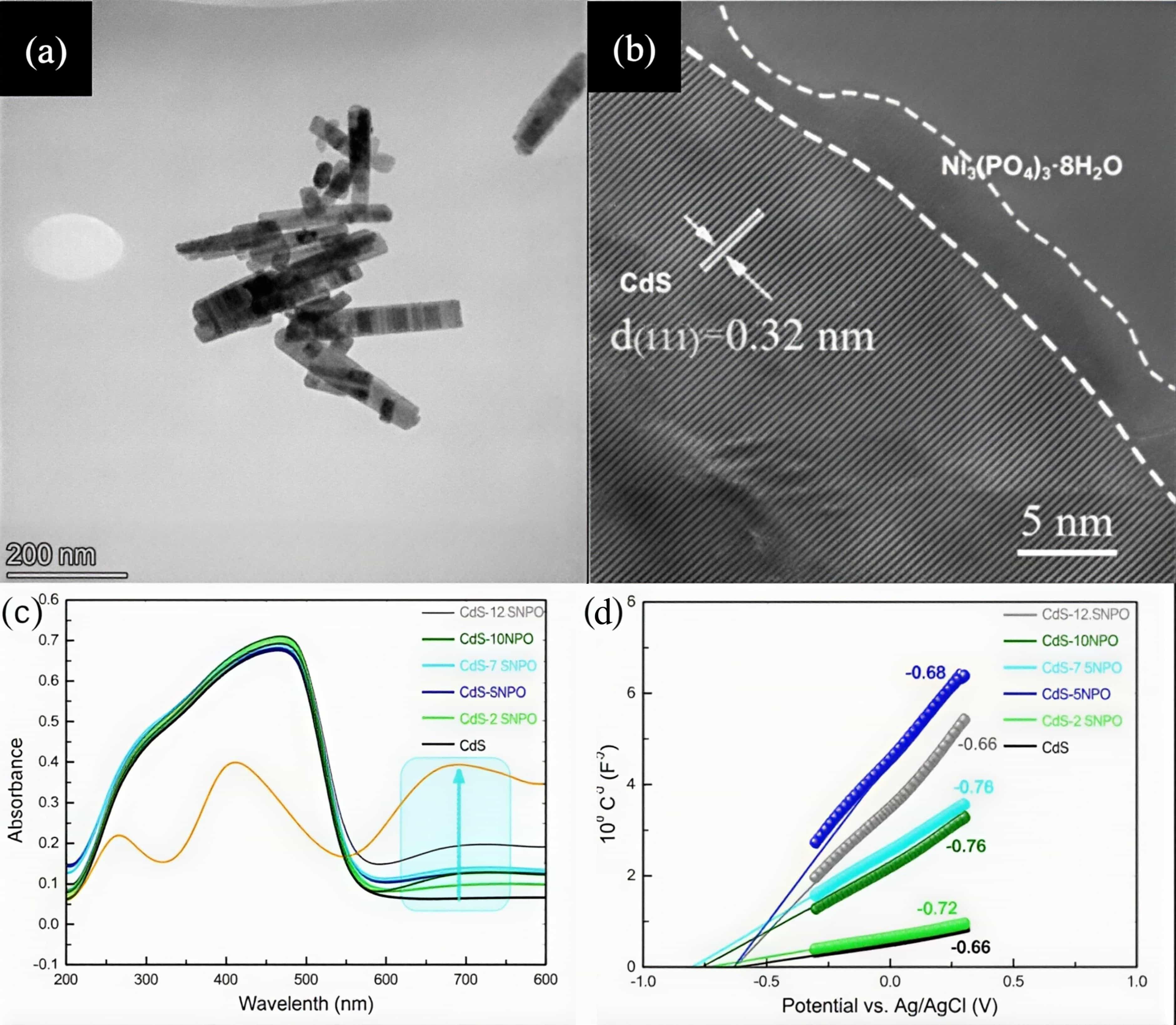
图20 CdS-7.5NPO的(a)TEM图像和(b)HRTEM图像;CdS-xNiPOi系列样品的(c)紫外-可见吸收光谱和(d)M-S曲线[65]注:CdS-xNPO series of samples[65]
Fig.20 (a)TEM and (b)HRTEM of CdS-7.5NPO; spectra of (c) UV–Vis absorption and (d) M-S plots of the
| [1] | Aghababaei N, Pourmadadi M, Mohebolkhames E, et al. Effect of electron-transfer cascade in g-C3N4/γ-Al2O3/TiO2 heterojunction on photocatalytic hydrogen production via water splitting[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2025, 173: 151395. [LinkOut] |
| [2] | Zhao X W, Bai X L, Zhai R, et al. Trap engineering in violet antimony phosphorus: Modulating photoelectron transfer pathways for enhanced photocatalytic hydrogen evolution[J]. Applied Catalysis B: Environment and Energy, 2025, 370: 125166. [LinkOut] |
| [3] | Brandon N P, Brandon J J. Hydrogen for a net-zero carbon world[J]. Engineering, 2023, 29: 8-10. [LinkOut] |
| [4] | Zhang Y J, Zhang W Y, Zhang X W, et al. Activating lattice oxygen based on energy band engineering in oxides for industrial water/saline oxidation[J]. Energy & Environmental Science, 2024, 17(10): 3347-3357. [LinkOut] |
| [5] | 孙仲顺, 刘根, 程春昱, 等. 生物质热化学转化制备绿氢研究进展[J]. 化工进展, 2025, 44(5): 2667-2682. |
| Sun Z S, Liu G, Cheng C Y, et al. Research progress on thermochemical conversion of biomass to green hydrogen[J]. Chemical Industry and Engineering Progress, 2025, 44(5): 2667-2682. [维普] | |
| [6] | Sayago-Carro R, Jiménez-Chavarriga L J, Fernández-García E, et al. Efficiency in photocatalytic production of hydrogen: energetic and sustainability implications[J]. Energy Advances, 2024, 3(11): 2738-2757. [LinkOut] |
| [7] | Ghosh S, Nakada A, Springer M A, et al. Identification of prime factors to maximize the photocatalytic hydrogen evolution of covalent organic frameworks[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2020, 142(21): 9752-9762. [PubMed] |
| [8] | Gong X J, Teng W K, Liu W, et al. A sucker-reactor polyoxometalate assembled superstructures for efficient photocatalytic nitrogen fixation[J]. Advanced Materials, 2025, 37(3): 2412924. [PubMed] |
| [9] | Hui Y Z, Wang M T, Guo S R, et al. Comprehensive review of development and applications of hydrogen energy technologies in China for carbon neutrality: Technology advances and challenges[J]. Energy Conversion and Management, 2024, 315: 118776. [LinkOut] |
| [10] | 葛全倩, 徐迈, 梁铣, 等. MOFs材料在光电催化领域应用的研究进展[J]. 化工进展, 2023, 42(9): 4692-4705. |
| Ge Q Q, Xu M, Liang X, et al. Research progress on the application of MOFs in photoelectrocatalysis[J]. Chemical Industry and Engineering Progress, 2023, 42(9): 4692-4705. [万方] | |
| [11] | Gao F Y, Zhang J Y, Jiang J Y, et al. Visible light-induced photocatalytic oxidation of gaseous ammonia on C surface-coated N-TiO2 catalyst: synthesis, properties and mechanism[J]. Separation and Purification Technology, 2025, 358: 130349. [LinkOut] |
| [12] | Li X X, Feng X Y, Meng D L, et al. Fabrication of TiO2/MOF type II heterojunction by growth of TiO2 on Cr-based MOF for enhanced photocatalytic hydrogen production[J]. Crystal Growth & Design, 2025, 25(4): 1182-1189. [LinkOut] |
| [13] | 张馨儿, 裴刘军, 周雨蝶, 等. 基于TiO2的光催化剂利用太阳能裂解水制氢研究进展[J]. 化工进展, 2025, 44(3): 1298-1308. |
| Zhang X E, Pei L J, Zhou Y D, et al. Progress of TiO2-based photocatalysts for hydrogen production by water splitting with solar energy[J]. Chemical Industry and Engineering Progress, 2025, 44(3): 1298-1308. [万方] | |
| [14] | 宋粉红, 王文光, 郭亮, 等. C元素修饰g-C3N4对TiO2的调控及复合材料光催化产氢性能研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(6): 2983-2994. |
| Song F H, Wang W G, Guo L, et al. Modulation of TiO2 by C-element modified g-C3N4 and photocatalytic hydrogen production performance of composites[J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(6): 2983-2994. [万方] | |
| [15] | Mahy J G, Lejeune L, Haynes T, et al. Crystalline ZnO photocatalysts prepared at ambient temperature: influence of morphology on p-nitrophenol degradation in water[J]. Catalysts, 2021, 11(10): 1182. [LinkOut] |
| [16] | Xiao X P, Li S J, Zuo L Y, et al. Twin S-scheme heterojunction ZnO/UiO-66-NH2@ZnIn2S4 rhombic octahedra for efficient photocatalytic H2 evolution[J]. Advanced Functional Materials, 2025, 35(31): 2418778. [LinkOut] |
| [17] | Mansour S, Akkari R, Soto E, et al. Pt–BiVO4/TiO2 composites as Z-scheme photocatalysts for hydrogen production from ethanol: the effect of BiVO4 and Pt on the photocatalytic efficiency[J]. New Journal of Chemistry, 2021, 45(9): 4481-4495. [LinkOut] |
| [18] | Liu B Y, Wang X, Zhang Y J, et al. A standalone bismuth vanadate-silicon artificial leaf achieving 8.4% efficiency for hydrogen production[J]. Nature Communications, 2025, 16: 2792. [LinkOut] |
| [19] | Wang H R, Bai Y Y, Wang R L, et al. Boosting photoelectrochemical water splitting: enhanced hole transport in BiVO4 photoanodes via interfacial coupling[J]. Catalysis Science & Technology, 2025, 15(2): 405-415. [LinkOut] |
| [20] | Wang K L, Yang Y, Farhan S, et al. S-scheme p-n junction Na0.6CoO2/g-C3N4 heterostructure as an efficient photocatalyst for green hydrogen production: fabrication, characterization and mechanisms[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2024, 490: 151408. [LinkOut] |
| [21] | Han X, Liu Q N, Qian A, et al. Transition-metal single atom anchored on MoS2 for enhancing photocatalytic hydrogen production of g-C3N4 photocatalysts[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2023, 15(22): 26670-26681. [LinkOut] |
| [22] | 潘锦波,沈胜,周伟,等。光催化产氢研究进展 [J]. 物理化学学报,2020, 36 (3): 1905068. |
| Pan J B, Shen S, Zhou W, et al. Recent progress in photocatalytic hydrogen evolution[J]. Acta. Phys.-Chim. Sin., 2020, (3): 40-56. [LinkOut] | |
| [23] | Bootz P, Frank K, Eichhorn J, et al. S-scheme interface between K–C3N4 and FePS3 fosters photocatalytic H2 evolution[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2024, 16(47): 65610-65619.[LinkOut] |
| [24] | Mohammad A, Chandra P, Khan M E, et al. Sulfur-doped graphitic carbon nitride: Tailored nanostructures for photocatalytic, sensing, and energy storage applications[J]. Advances in Colloid and Interface Science, 2023, 322: 103048. [LinkOut] |
| [25] | Zhang H B, Wang Z L, Zhang J F, et al. Metal-sulfide-based heterojunction photocatalysts: Principles, impact, applications, and in-situ characterization[J]. Chinese Journal of Catalysis, 2023, 49: 42-67. [LinkOut] |
| [26] | Zhang M Y, Hu Q Y, Ma K W, et al. Pyroelectric effect in CdS nanorods decorated with a molecular co-catalyst for hydrogen evolution[J]. Nano Energy, 2020, 73: 104810. [LinkOut] |
| [27] | Hong F Y, Jing T, Wang S, et al. Defect engineering of ZnIn2S4 photocatalysts for enhanced hydrogen evolution reaction[J]. Coatings, 2025, 15(9): 1061. [LinkOut] |
| [28] | Rahman M H, Yang J Q, Sun Y J, et al. Defect engineering in ZnIn2X4 (X=S, Se, Te) semiconductors for improved photocatalysis[J]. Surfaces and Interfaces, 2023, 39: 102960. [LinkOut] |
| [29] | Zhang X L, Wu F, Li G C, et al. Modulating electronic structure and sulfur p-band center by anchoring amorphous Ni@NiSx on crystalline CdS for expediting photocatalytic H2 evolution[J]. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 2024, 342: 123398. [LinkOut] |
| [30] | Zhao Y, Fang X, Chen L, et al. Improved proton adsorption and charge separation on cadmium sulfides for photocatalytic hydrogen production[J]. Energy Technology, 2022, 10(12): 2200300. [LinkOut] |
| [31] | Ding M Y, Cui S S, Lin Z X, et al. Crystal facet engineering of hollow cadmium sulfide for efficient photocatalytic hydrogen evolution[J]. Applied Catalysis B: Environment and Energy, 2024, 357: 124333. [LinkOut] |
| [32] | Islam A, Malek A, Islam M T, et al. Next frontier in photocatalytic hydrogen production through CdS heterojunctions[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2025, 101: 173-211. [LinkOut] |
| [33] | Liu S B, Wang Y J, Zhang Y Z, et al. In-MOF-derived In2S3/Bi2S3 heterojunction for enhanced photocatalytic hydrogen production[J]. Frontiers in Energy, 2023, 17(5): 654-663. [LinkOut] |
| [34] | Cai Y, Wang S J, Liu B, et al. Semi-transparent and stable In2S3/CdTe heterojunction photoanodes for unbiased photoelectrochemical water splitting[J]. Nature Communications, 2025, 16: 5105. [LinkOut] |
| [35] | Zhang R Y, Jia X W, Li Y R, et al. Oxidation co-catalyst modified In2S3 with efficient interfacial charge transfer for boosting photocatalytic H2 evolution[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2022, 47(60): 25300-25308. [LinkOut] |
| [36] | Zhang J, Zhao W X, Qian C H, et al. Facile construction of a sulfur vacancy defect-decorated CoSx@In2S3 core/shell heterojunction for efficient visible-light-driven photocatalytic hydrogen evolution[J]. Dalton Transactions, 2023, 52(36): 12899-12908. [LinkOut] |
| [37] | Guo S H, Luo H, Duan X C, et al. Plasma-wind-assisted In2S3 preparation with an amorphous surface structure for enhanced photocatalytic hydrogen production[J]. Nanomaterials, 2022, 12(10): 1761. [LinkOut] |
| [38] | Kaur N, Kodan N, Sharma D, et al. 2D-In2S3 nanoflakes/1D-WO3 nanorods heterojunction with enhanced absorption and photoresponse for photoelectrochemical water splitting[J]. Renewable Energy, 2025, 240: 122229. [LinkOut] |
| [39] | Bao D, Gao P, Zhu X Y, et al. ZnO/ZnS heterostructured nanorod arrays and their efficient photocatalytic hydrogen evolution[J]. Chemistry – A European Journal, 2015, 21(36): 12728-12734. [LinkOut] |
| [40] | Zhang C M, Gao K Y, Zhu H B, et al. Fast interlayer charge separation and transmission in ZnIn2S4/CNTs/ZnS heterojunctions for efficient photocatalytic hydrogen evolution[J]. ChemCatChem, 2022, 14(12): e202200225. [LinkOut] |
| [41] | Kang E, Kim J H. Highly boosted photocatalytic H2 production from ZnS particles assisted by Cd-Cu co-doping[J]. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 2023, 11(3): 109833. [LinkOut] |
| [42] | Ma H Q, Mao Z X, Liu W, et al. Ni(OH)2 nanoparticle-modified Co9S8/ZnIn2S4 heterojunction for boosting photocatalytic H2 production[J]. Crystal Growth & Design, 2024, 24(11): 4312-4321. [LinkOut] |
| [43] | Liu W, Ye F R, Zhao Y H, et al. Cobalt phosphate co-catalysts and boron-doped ZnIn2S4 nanosheets for efficient photocatalytic hydrogen conversion[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2024, 79: 106-114. [LinkOut] |
| [44] | Li L L, Ma D K, Xu Q L, et al. Constructing hierarchical ZnIn2S4/g-C3N4 S-scheme heterojunction for boosted CO2 photoreduction performance[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2022, 437: 135153. [LinkOut] |
| [45] | Su Y H, Wei Z H, Lian Y B, et al. Defect-driven electroless deposition and activation of platinum sites on ZnIn2S4 nanosheets for accelerated kinetics of photocatalytic hydrogen production[J]. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 2023, 334: 122827. |
| [46] | Du C, Zhang Q, Lin Z Y, et al. Half-unit-cell ZnIn2S4 monolayer with sulfur vacancies for photocatalytic hydrogen evolution[J]. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 2019, 248: 193-201. [LinkOut] |
| [47] | Chen J, Wu S J, Cui W J, et al. Nickel clusters accelerating hierarchical zinc indium sulfide nanoflowers for unprecedented visible-light hydrogen production[J]. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 2022, 608: 504-512. [LinkOut] |
| [48] | Ullah S, Chen Y E, Javed J, et al. Engineering of visible light-activated ZnIn2S4/N-rGO S-scheme heterojunction photocatalyst for H2 generation[J]. Surfaces and Interfaces, 2024, 54: 105147. [LinkOut] |
| [49] | 牛杰, 王亮, 孟祥超, 等. Mo-Zn0.5Cd0.5S@NiCo2S4掺杂-异质结体系的制备及其双功能光催化性能研究[J]. 聊城大学学报(自然科学版), 2024, 37(1): 36-45. |
| Niu J, Wang L, Meng X C, et al. Preparation of Mo-Zn0.5Cd0.5S@NiCo2S4 doped-heterojunction system and its bifunctional photocatalytic performance[J]. Journal of Liaocheng University (Natural Science Edition), 2024, 37(1): 36-45. [万方] | |
| [50] | Li Z L, Zhao Y, Deng Q L, et al. In situ growth of CdZnS Nanoparticles@Ti3C2T x MXene nanosheet heterojunctions for boosted visible-light-driven photocatalytic hydrogen evolution[J]. Nanomaterials, 2023, 13(15): 2261. [LinkOut] |
| [51] | Xue W H, Chang W X, Hu X Y, et al. 2D mesoporous ultrathin Cd0.5Zn0.5S nanosheet: Fabrication mechanism and application potential for photocatalytic H2 evolution[J]. Chinese Journal of Catalysis, 2021, 42(1): 152-163. [LinkOut] |
| [52] | Yu K, Huang H B, Zeng X Y, et al. CdZnS nanorods with rich sulphur vacancies for highly efficient photocatalytic hydrogen production[J]. Chemical Communications, 2020, 56(56): 7765-7768. [LinkOut] |
| [53] | Song L M, Zhang S J, Liu D, et al. High-performance hydrogen evolution of NiB/ZnCdS under visible light irradiation[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2020, 45(15): 8234-8242. [LinkOut] |
| [54] | Conesa J C. Sulfide-based photocatalysts using visible light, with special focus on In2S3, SnS2 and ZnIn2S4 [J]. Catalysts, 2022, 12(1): 40. [LinkOut] |
| [55] | Zhang D D, Gao Z Y, Yang D J, et al. Crystal-interface-mediated self-assembly of ZnIn2S4/CdS S-scheme heterojunctions toward efficient photocatalytic hydrogen production[J]. Carbon Energy, 2025, 7(6): e707. [LinkOut] |
| [56] | Chen K Y, Shi Y X, Shu P, et al. Construction of core–shell FeS2@ZnIn2S4 hollow hierarchical structure S-scheme heterojunction for boosted photothermal-assisted photocatalytic H2 production[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2023, 454: 140053. [LinkOut] |
| [57] | Liu N, Yu H, Liu Y B, et al. A novel hierarchical S-scheme heterojunction of 0D/3D Zn0.5Cd0.5S nanoparticles/hollow micro-flower MoS2 for improved photocatalytic hydrogen evolution[J]. Applied Surface Science, 2023, 632: 157579. [LinkOut] |
| [58] | Fang H M, Cai J J, Li H J, et al. Fabrication of ultrathin two-dimensional/two-dimensional MoS2/ZnIn2S4 hybrid nanosheets for highly efficient visible-light-driven photocatalytic hydrogen evolution[J]. ACS Applied Energy Materials, 2022, 5(7): 8232-8240. [LinkOut] |
| [59] | Liu W X, Chen J M, Pan X L, et al. Ultrathin nickel-doped ZnIn2S4 nanosheets with sulfur vacancies for efficient photocatalytic hydrogen evolution[J]. ChemCatChem, 2021, 13(24): 5148-5155. [LinkOut] |
| [60] | Feng K T, Wang C X, Hu X Y, et al. Highly efficient photocatalytic H2 evolution over Ni-doped Mn0.5Cd0.5S nanorods under visible light[J]. International Journal of Energy Research, 2022, 46(14): 20828-20837. [LinkOut] |
| [61] | Chen H F, Zhu Y W, Wu J, et al. Cu-doped ZnCdS-based photocatalyst for efficient photocatalytic hydrogen production by photothermal assistance[J]. Case Studies in Thermal Engineering, 2024, 61: 104970. [LinkOut] |
| [62] | Wu K L, Shang Y H, Li H Z, et al. Synthesis and hydrogen production performance of MoP/a-TiO2/co-ZnIn2S4 flower-like composite photocatalysts[J]. Molecules, 2023, 28(11): 4350. [LinkOut] |
| [63] | Yang J H, Wang D E, Han H X, et al. Roles of cocatalysts in photocatalysis and photoelectrocatalysis[J]. Accounts of Chemical Research, 2013, 46(8): 1900-1909. [LinkOut] |
| [64] | Jia Y L, Wang Z Z, Qiao X Q, et al. A synergistic effect between S-scheme heterojunction and Noble-metal free cocatalyst to promote the hydrogen evolution of ZnO/CdS/MoS2 photocatalyst[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2021, 424: 130368. [LinkOut] |
| [65] | Tang B L, Lv B, Yu G P, et al. Non-noble metal based nickel phosphate decorated CdS nanorods for persistent and efficient solar-to-hydrogen conversion[J]. Surfaces and Interfaces, 2023, 41: 103325. [LinkOut] |
| [66] | Li S, Li Y B, Yin W Q, et al. Boosting the photocatalytic hydrogen production activity of marigold-like Zn2In2S5 by using noble-metal-free Ni2P as cocatalyst[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2024, 56: 596-603. [LinkOut] |
| [67] | Li B F, Guo W Y, Lu X F, et al. Position-selected cocatalyst modification on a Z-scheme Cd0.5Zn0.5S/NiTiO3 photocatalyst for boosted H2 evolution[J]. Materials Reports: Energy, 2023, 3(4): 100230. [LinkOut] |
| [68] | Yin X L, Jing Y N, Li L L, et al. Deposition state of CoS significantly affects the photocatalytic H2 generation performance of CdS–CoS heterostructure[J]. Ceramics International, 2024, 50(16): 28715-28723. [LinkOut] |
| [69] | Xu J, Kang Q, Peng B, et al. Engineering single-atom catalysts for sulfur electrochemistry in metal–sulfur batteries[J]. Journal of Energy Chemistry, 2025, 106: 768-790. [LinkOut] |
| [70] | Lian Z C, Wu H X, Yang W W, et al. Atomically dispersed metal-site electrocatalysts for high-performance lithium-sulfur batteries[J]. Chem Catalysis, 2023, 3(12): 100824. [LinkOut] |
| [1] | 赵维, 邢文乐, 韩朝旭, 袁兴中, 蒋龙波. g-C3N4基非金属异质结光催化降解水中有机污染物的研究进展[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(9): 4752-4769. |
| [2] | 佟丽丽, 陈英, 艾敏华, 舒玉美, 张香文, 邹吉军, 潘伦. ZnO/WO3异质结光催化环烯烃[2+2]环加成制备高能量密度燃料[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(9): 4882-4892. |
| [3] | 郭铮铮, 赵一丹, 王辅强, 裴璐, 靳彦岭, 任芳, 任鹏刚. 异质结构MoS2/RGO/NiFe2O4复合材料的构筑及电磁波吸收性能研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(7): 3719-3732. |
| [4] | 王三龙, 王跃霖, 曹宇. 基于相异质结的高效无机钙钛矿太阳能电池的性能研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(3): 1346-1352. |
| [5] | 刘彦贝, 王若名, 刘娟, Raza Taimoor, 陆玉正, Raza Rizwan, 朱斌, 李松波, 安胜利, 云斯宁. CeO2@La0.6Sr0.4Co0.2Fe0.8O3-δ 电解质的制备及半导体离子燃料电池性能研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(3): 1353-1362. |
| [6] | 皮若冰, 周云龙. 直接Z型异质结体系光催化还原二氧化碳研究进展[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(10): 3379-3400. |
| [7] | 李勇, 高佳琦, 杜超, 赵亚丽, 李伯琼, 申倩倩, 贾虎生, 薛晋波. Ni@C@TiO2核壳双重异质结的构筑及光热催化分解水产氢[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(6): 2458-2467. |
| [8] | 柴亚婷, 路家伟, 王蕊欣, 焦纬洲. 碳纸自支撑N掺杂碳纳米管复合MoC/NiCo异质结构的电解水析氧性能[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(12): 4904-4913. |
| [9] | 周国莉, 韩项珂, 武文佳, 王景涛, 张毛娃, 李凤丽. 异质结构g-C3N4@AM层状膜构筑及纳滤性能研究[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(2): 941-950. |
| [10] | 李燕, 蹇亮, 茅沁怡, 潘成思, 蒋平平, 朱永法, 董玉明. 构建Bi2O2CO3/g-C3N4异质结光催化完全氧化苯甲醇至苯甲醛[J]. 化工学报, 2021, 72(8): 4166-4176. |
| [11] | 王艳, 徐进良, 李文. 不同种类超临界流体异质结构及相变分析[J]. 化工学报, 2021, 72(4): 1906-1919. |
| [12] | 张开莲, 杨凯, 李笑笑, 梁若雯, 管婕, 李文强, 黄健, 余长林, 戴文新. 一步水热合成In2S3/CdIn2S4异质结微球及其光催化性能[J]. 化工学报, 2020, 71(8): 3602-3613. |
| [13] | 杨金曼, 朱兴旺, 周固礼, 许晖, 李华明. MOFs诱导中空Co3O4/CdIn2S4合成及光催化CO2还原性能研究[J]. 化工学报, 2020, 71(6): 2780-2787. |
| [14] | 陈克龙, 黄建花. g-C3N4-CdS-NiS2复合纳米管的制备及可见光催化分解水制氢[J]. 化工学报, 2020, 71(1): 397-408. |
| [15] | 郭月莹, 谢建良, 彭波. 可见高吸收红外高反射薄膜制备及光学特性研究[J]. 化工学报, 2019, 70(6): 2325-2333. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备 11010102001995号
京公网安备 11010102001995号