化工学报 ›› 2019, Vol. 70 ›› Issue (3): 1198-1207.DOI: 10.11949/j.issn.0438-1157.20181233
收稿日期:2018-10-19
修回日期:2018-12-05
出版日期:2019-03-05
发布日期:2019-03-05
通讯作者:
徐存英
作者简介:<named-content content-type="corresp-name">段云彪</named-content>(1963—),男,高级实验师,<email>1037550651@qq.com</email>|徐存英(1971—),女,博士,教授,<email>xucunying@foxmail.com</email>
基金资助:
Yunbiao DUAN1( ),Cunying XU2,3(
),Cunying XU2,3( ),Xiang WANG2,Hai LIU2,Mengting HUANG2
),Xiang WANG2,Hai LIU2,Mengting HUANG2
Received:2018-10-19
Revised:2018-12-05
Online:2019-03-05
Published:2019-03-05
Contact:
Cunying XU
摘要:
以氯化胆碱-草酸低共熔溶剂(ChCl-OA DES)为溶剂,ZnO和Fe2O3为原料,通过简单的反溶剂沉淀法制备出不同掺杂浓度的Fe3+掺杂ZnO(Fe-ZnO)纳米结构。采用SEM、XRD、拉曼光谱、XPS等手段对所制Fe-ZnO结构与形貌进行了表征。结果表明,Fe-ZnO是由直径为20~30 nm纳米晶组装而成的微米棒。不同掺杂浓度的Fe-ZnO纳米晶均为六方铅锌矿结构,Fe3+很好地进入ZnO晶格。同时考察了所制Fe-ZnO的光吸收特性和光催化活性,发现Fe3+掺杂使其吸收峰红移至可见光范围,有效增强了可见光区域的催化活性。当Fe掺杂量为1.0%(atom)时,样品的光催化活性最好,比ZnO增大了约102倍。这说明Fe3+掺杂可改善ZnO对可见光光子的捕获能力。
中图分类号:
段云彪, 徐存英, 王祥, 刘海, 黄梦婷. 反溶剂沉淀法合成Fe3+掺杂ZnO纳米结构及其可见光催化性能[J]. 化工学报, 2019, 70(3): 1198-1207.
Yunbiao DUAN, Cunying XU, Xiang WANG, Hai LIU, Mengting HUANG. Synthesis of Fe3+-doped ZnO nanostructures by antisolvent precipitation method and their visible photocatalytic activity[J]. CIESC Journal, 2019, 70(3): 1198-1207.
| Fe3+掺杂量/%(atom) | 降解率/% | 降解率提高/% |
|---|---|---|
| 0.0 | 35.6 | 0 |
| 0.5 | 65.7 | 84.6 |
| 1.0 | 71.8 | 101.6 |
| 3.0 | 69.4 | 94.9 |
| 5.0 | 60.6 | 70.2 |
表1 纯ZnO和不同Fe3+掺杂量Fe-ZnO光催化降解RhB的比较
Table 1 Comparison of photocatalytic degradation of RhBbetween pure ZnO and different Fe3+ doping amount of Fe-ZnO
| Fe3+掺杂量/%(atom) | 降解率/% | 降解率提高/% |
|---|---|---|
| 0.0 | 35.6 | 0 |
| 0.5 | 65.7 | 84.6 |
| 1.0 | 71.8 | 101.6 |
| 3.0 | 69.4 | 94.9 |
| 5.0 | 60.6 | 70.2 |
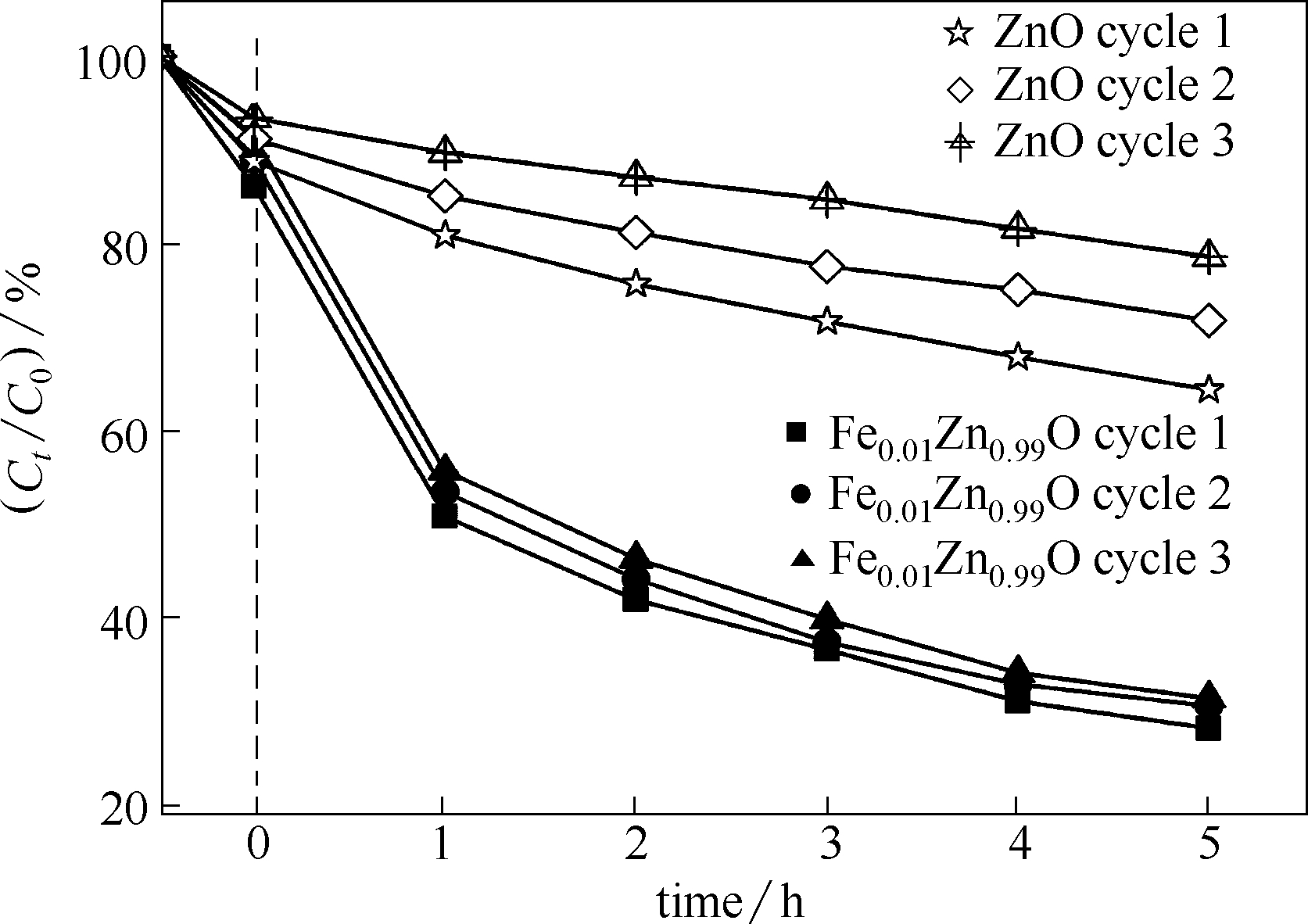
图9 Fe0.01Zn0.99O和纯ZnO催化剂在可见光照射下催化降解RhB的循环稳定性
Fig.9 Fe0.01Zn0.99O and ZnO for photodegradation of RhB under visible light( [RhB] = 10 mg/L, catalyst suspended = 3 g/L, pH = 9, T = 25℃)
| 1 | FortunaoE, BarquinhaP, PimentelA, et al. Recent advances in ZnO transparent thin film transistors[J]. Thin Solid Films, 2005, 487(1/2): 205-211. |
| 2 | SalehR, DjajaN F. UV light photocatalytic degradation of organic dyes with Fe-doped ZnO nanoparticles[J]. Superlattices and Microstructures, 2014, 74: 217-233. |
| 3 | WangY, ZhaoX, DuanL, et al. Structure, luminescence and photocatalytic activity of Mg-doped ZnO nanoparticles prepared by auto combustion method[J]. Materials Science in Semiconductor Processing, 2015, 29: 372-379. |
| 4 | 丁艳, 马歌, 李良超, 等. M2+(M= Cu, Cd, Ag, Fe) 掺杂氧化锌纳米粉晶的抗菌性能[J]. 无机化学学报, 2014, 30(2): 293-302. |
| DingY, MaG, LiL C, et al. Antibacterial activities of doped ZnO nano-powder with M2+ (M=Cu, Cd, Ag and Fe) [J]. Chinese Journal of Inorganic Chemistry, 2014, 30(2): 293-302. | |
| 5 | KumarR, UmarA, KumarG, et al. Ce-doped ZnO nanoparticles for efficient photocatalytic degradation of direct red-23 dye[J]. Ceramics International, 2015, 41(6): 7773-7782. |
| 6 | ShuklaS K, AgorkuE S, MittalH, et al. Synthesis, characterization and photoluminescence properties of Ce 3+-doped ZnO-nanophosphors[J]. Chemical Papers, 2014, 68(2): 217-222. |
| 7 | IsmailI M I, AslamM, AlmeelbiT, et al. Ce3+ impregnated ZnO: a highly efficient photocatalyst for sunlight mediated mineralization[J]. RSC Advances, 2014, 4(31): 16043-16046. |
| 8 | SharmaD K, SharmaK K, KumarV, et al. Effect of Ce doping on the structural, optical and magnetic properties of ZnO nanoparticles[J]. Journal of Materials Science: Materials in Electronics, 2016, 27(10): 10330-10335. |
| 9 | MayJ W, MaJ, BadaevaE, et al. Effect of excited-state structural relaxation on midgap excitations in Co2+-doped ZnO quantum dots[J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2014, 118(24): 13152-13156. |
| 10 | KumarS, SongT K, GautamS, et al. Structural, magnetic and electronic structure properties of Co doped ZnO nanoparticles[J]. Materials Research Bulletin, 2015, 66: 76-82. |
| 11 | RazaW, HaqueM M, MuneerM. Synthesis of visible light driven ZnO: characterization and photocatalytic performance[J]. Applied Surface Science, 2014, 322: 215-224. |
| 12 | KanevaN, BojinovaA, PapazovaK, et al. Photocatalytic purification of dye contaminated sea water by lanthanide (La3+, Ce3+, Eu3+) modified ZnO[J]. Catalysis Today, 2015, 252: 113-119. |
| 13 | ChenC, MaW, ZhaoJ. Semiconductor-mediated photodegradation of pollutants under visible-light irradiation[J]. Chem. Soc. Rev., 2010, 39: 4206-4219. |
| 14 | BaikJ M, KangT W, LeeJ L. Effects of N2O plasma treatment on magnetic properties of (Zn, Mn)O nanorods[J]. Nanotechnology, 2007, 18(9): 095703. |
| 15 | 翟英娇, 李金华, 陈新影, 等. 镉掺杂氧化锌纳米花的制备及其光催化活性[J]. 中国光学, 2014, 7(1): 124-130. |
| ZhaiY J, LiJ H, ChenX Y, et al. Preparation and photocatalytic activity of cadmium-doped zinc oxide nanoflowers[J]. China Optics, 2014, 7(1): 124-130. | |
| 16 | KolevaM E, AtanasovP A, NedialkovN N, et al. Role of vanadium content in ZnO thin films grown by pulsed laser deposition[J]. Applied Surface Science, 2007, 254(4): 1228-1231. |
| 17 | YimazS, ParlakM, ŞÖzcan, et al. Structural, optical and magnetic properties of Cr doped ZnO microrods prepared by spray pyrolysis method[J]. Applied Surface Science, 2011, 257(22): 9293-9298. |
| 18 | ShindeV R, GujarT P, LokhandeC D, et al. Mn doped and undoped ZnO films: a comparative structural, optical and electrical properties study[J]. Mater. Chem. Phys., 2006, 96: 326-330. |
| 19 | ShishodiaP K. Effect of cobalt doping on ZnO thin films deposited by sol-gel method[J]. Thin Solid Films, 2016, 612: 55-60. |
| 20 | ZhaoX, LiuE, RamanujanR V, et al. Effects of rapid thermal annealing on structural, magnetic and optical properties of Ni-doped ZnO thin films[J]. Current Applied Physics, 2012, 12(3): 834-840. |
| 21 | HouD L, YeX J, MengH J, et al. Magnetic properties of n-type Cu-doped ZnO thin films[J]. Applied Physics Letters, 2007, 90(14): 142502. |
| 22 | SrivastavaA, KumarN, KhareS. Enhancement in UV emission and band gap by Fe doping in ZnO thin films[J]. Opto-Electronics Review, 2014, 22(1): 68-76. |
| 23 | YiS S, CuiJ B, LiS, et al. Enhanced visible-light photocatalytic activity of Fe/ZnO for Rhodamine B degradation and its photogenerated charge transfer properties[J]. Applied Surface Science, 2014, 319: 230-236. |
| 24 | SalehR, DjajaN F. UV light photocatalytic degradation of organic dyes with Fe-doped ZnO nanoparticles[J]. Superlattices and Microstructures, 2014, 74: 217-233. |
| 25 | LmaiF, MoubahR, AmiriE A, et al. Spin wave study and optical properties in Fe-doped ZnO thin films prepared by spray pyrolysis technique[J]. Optical Materials, 2016, 57: 28-33. |
| 26 | WuX, WeiZ, ZhangL, et al. Optical and magnetic properties of Fe doped ZnO nanoparticles obtained by hydrothermal synthesis[J]. Journal of Nanomaterials, 2014, 2014: 1-6. |
| 27 | LiX, HouM, HanB, et al. Solubility of CO2 in a choline chloride+ urea eutectic mixture[J]. Journal of Chemical & Engineering Data, 2008, 53(2): 548-550. |
| 28 | AbbottA P, CullisP M, GibsonM J, et al. Extraction of glycerol from biodiesel into a eutectic based ionic liquid[J]. Green Chemistry, 2007, 9(8): 868-872. |
| 29 | PhadtareS B, ShankarlingG S. Halogenation reactions in biodegradable solvent: efficient bromination of substituted 1-aminoanthra-9, 10-quinone in deep eutectic solvent (choline chloride: urea) [J]. Green Chemistry, 2010, 12(3): 458-462. |
| 30 | HarishkumarH N, MahadevanK M, MasagalliJ N, et al. Synthesis and fluorescence study of phenylcoumarin / cyanophenylbenzocoumarin-3-carboxylates[J]. Organic Comm-unications, 2012, 5(4): 196-208. |
| 31 | PawaP M, JaragK J, ShankarlingG S. Environmentally benign and energy efficient methodology for condensation: an interesting facet to the classical Perkin reaction[J]. Green Chemistry, 2011, 13(8): 2130-2134. |
| 32 | SutrisnoA, LiuL, DongJ, et al. Solid-state 91Zr NMR characterization of layered and three-dimensional framework zirconium phosphates[J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2012, 116(32): 17070-17081. |
| 33 | MaldonadoM, OleksiakM D, ChintaS, et al. Controlling crystal polymorphism in organic-free synthesis of Na-zeolites[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2013, 135(7): 2641-2652. |
| 34 | LiaoH G, JiangY X, ZhouZ Y, et al. Shape-controlled synthesis of gold nanoparticles in deep eutectic solvents for studies of structure-functionality relationships in electrocatalysis[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2008, 47(47): 9100-9103. |
| 35 | AbbottA P, CapperG, DaviesD L, et al. Selective extraction of metals from mixed oxide matrixes using choline-based ionic liquids[J]. Inorganic Chemistry, 2005, 44(19): 6497-6499. |
| 36 | DongJ Y, HsuY J, WongD S H, et al. Growth of ZnO nanostructures with controllable morphology using a facile green antisolvent method[J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2010, 114(19): 8867-8872. |
| 37 | ShaktiN, GuptaP S. Structural and optical properties of sol-gel prepared ZnO thin film[J]. Applied Physics Research, 2010, 2(1): 19-28. |
| 38 | BundesmannC, AshkenovN, SchubertM, et al. Raman scattering in ZnO thin films doped with Fe, Sb, Al, Ga, and Li[J]. Applied Physics Letters, 2003, 83(10): 1974-1976. |
| 39 | WangJ B, HuangG J, ZhongX L, et al. Raman scattering and high temperature ferromagnetism of Mn-doped ZnO nanoparticles[J]. Applied Physics Letters, 2006, 88(25): 252502. |
| 40 | SinghP, KaushalA, KaurD. Mn-doped ZnO nanocrystalline thin films prepared by ultrasonic spray pyrolysis[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2009, 471(1/2): 11-15. |
| 41 | KaramatS, RawatR S, LeeP, et al. Structural, elemental, optical and magnetic study of Fe doped ZnO and impurity phase formation[J]. Progress in Natural Science: Materials International, 2014, 24(2): 142-149. |
| 42 | RambuA P, NicaV, DobromirM. Influence of Fe-doping on the optical and electrical properties of ZnO films[J]. Superlattices and Microstructures, 2013, 59: 87-96. |
| 43 | CuiJ, SunJ, LiuX, et al. Fabrication of hierarchical flower-like porous ZnO nanostructures from layered ZnC2O4·3Zn(OH)2 and gas sensing properties[J]. Applied Surface Science, 2014, 308: 17-23. |
| 44 | RajaK, RameshP S, D. StructuralGeetha, FTIR and photoluminescence studies of Fe doped ZnO nanopowder by co-precipitation method[J]. Spectrochimica Acta Part A: Molecular and Biomolecular Spectroscopy, 2014, 131: 183-188. |
| 45 | MitraP, MondalS. Structural and morphological characterization of ZnO thin films synthesized by SILAR[J]. Progress in Theoretical and Applied Physics, 2013, 1: 17-31. |
| 46 | ParraP A, PeralesP O, SinghalR, et al. Structural, optical, and magnetic characterization of monodisperse Fe-doped ZnO nanocrystals[J]. Journal of Applied Physics, 2008, 103(7): 07D121. |
| 47 | 李奡麒, 陈玉娟, 胡晓宇, 等. 低共熔溶剂辅助水热法合成分层球状微/纳米 ZnO 晶体及其光催化性能[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2015, 36(1): 165-170. |
| LiW Q, ChenY J, HuX Y, et al. Synthesis of layered spherical micro/nano ZnO crystals by hydrothermal solvent-assisted hydrothermal method[J]. Chemical Journal of Chinese Universities, 2015, 36(1): 165-170. | |
| 48 | ZhangQ, LiuJ K, WangJ D, et al. Atmospheric self-induction synthesis and enhanced visible light photocatalytic performance of Fe3+ doped Ag-ZnO mesocrystals[J]. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res., 2014, 53:13236-13246 |
| [1] | 范孝雄, 郝丽芳, 范垂钢, 李松庚. LaMnO3/生物炭催化剂低温NH3-SCR催化脱硝性能研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(9): 3821-3830. |
| [2] | 吴雷, 刘姣, 李长聪, 周军, 叶干, 刘田田, 朱瑞玉, 张秋利, 宋永辉. 低阶粉煤催化微波热解制备含碳纳米管的高附加值改性兰炭末[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(9): 3956-3967. |
| [3] | 李艺彤, 郭航, 陈浩, 叶芳. 催化剂非均匀分布的质子交换膜燃料电池操作条件研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(9): 3831-3840. |
| [4] | 程业品, 胡达清, 徐奕莎, 刘华彦, 卢晗锋, 崔国凯. 离子液体基低共熔溶剂在转化CO2中的应用[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(9): 3640-3653. |
| [5] | 陈杰, 林永胜, 肖恺, 杨臣, 邱挺. 胆碱基碱性离子液体催化合成仲丁醇性能研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(9): 3716-3730. |
| [6] | 杨学金, 杨金涛, 宁平, 王访, 宋晓双, 贾丽娟, 冯嘉予. 剧毒气体PH3的干法净化技术研究进展[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(9): 3742-3755. |
| [7] | 胡兴枝, 张皓焱, 庄境坤, 范雨晴, 张开银, 向军. 嵌有超小CeO2纳米粒子的碳纳米纤维的制备及其吸波性能[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(8): 3584-3596. |
| [8] | 杨菲菲, 赵世熙, 周维, 倪中海. Sn掺杂的In2O3催化CO2选择性加氢制甲醇[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(8): 3366-3374. |
| [9] | 李凯旋, 谭伟, 张曼玉, 徐志豪, 王旭裕, 纪红兵. 富含零价钴活性位点的钴氮碳/活性炭设计及甲醛催化氧化应用研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(8): 3342-3352. |
| [10] | 杨欣, 彭啸, 薛凯茹, 苏梦威, 吴燕. 分子印迹-TiO2光电催化降解增溶PHE废水性能研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(8): 3564-3571. |
| [11] | 陈雅鑫, 袁航, 刘冠章, 毛磊, 杨纯, 张瑞芳, 张光亚. 蛋白质纳米笼介导的酶自固定化研究进展[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(7): 2773-2782. |
| [12] | 吴文涛, 褚良永, 张玲洁, 谭伟民, 沈丽明, 暴宁钟. 腰果酚生物基自愈合微胶囊的高效制备工艺研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(7): 3103-3115. |
| [13] | 汤晓玲, 王嘉瑞, 朱玄烨, 郑仁朝. 基于Pickering乳液的卤醇脱卤酶催化合成手性环氧氯丙烷[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(7): 2926-2934. |
| [14] | 余娅洁, 李静茹, 周树锋, 李清彪, 詹国武. 基于天然生物模板构建纳米材料及集成催化剂研究进展[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(7): 2735-2752. |
| [15] | 王志龙, 杨烨, 赵真真, 田涛, 赵桐, 崔亚辉. 搅拌时间和混合顺序对锂离子电池正极浆料分散特性的影响[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(7): 3127-3138. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备 11010102001995号
京公网安备 11010102001995号