化工学报 ›› 2021, Vol. 72 ›› Issue (6): 3349-3358.DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20201544
收稿日期:2020-11-01
修回日期:2021-02-07
出版日期:2021-06-05
发布日期:2021-06-05
通讯作者:
程芳琴
作者简介:马志斌(1987—),男,博士,副教授,基金资助:
MA Zhibin( ),ZHANG Sen,SHAN Xueyuan,GUO Yanxia,CHENG Fangqin(
),ZHANG Sen,SHAN Xueyuan,GUO Yanxia,CHENG Fangqin( )
)
Received:2020-11-01
Revised:2021-02-07
Online:2021-06-05
Published:2021-06-05
Contact:
CHENG Fangqin
摘要:
掌握煤中伴生有价微量元素在燃烧过程的迁移规律,对伴生元素的利用意义重大。选取4种高铝煤炭、1种煤泥和2种煤矸石等不同组成特性的样品为研究对象,采用逐级化学提取方法分析了锂(Li)、镓(Ga)和稀土(REE)在原料中的赋存形态,考察了以上元素在300~1100℃燃烧过程逸出情况和在燃烧灰中的富集行为,探讨了元素迁移规律与原料组成特性的关联。结果表明,Li、Ga和REE在7种样品中的赋存形态均以硅酸盐态为主,在燃烧过程的逸出率有与原料灰分呈负相关、与挥发分和含碳量呈正相关的趋势。以上元素在灰中均发生了不同程度的富集,REE的富集倍数高于Li和Ga。原料中微量元素含量和挥发分越高、灰分越低,同等燃烧条件下所得灰中微量元素的含量就越高。
中图分类号:
马志斌, 张森, 单雪媛, 郭彦霞, 程芳琴. 煤、煤泥和煤矸石燃烧过程锂镓稀土元素的迁移规律[J]. 化工学报, 2021, 72(6): 3349-3358.
MA Zhibin, ZHANG Sen, SHAN Xueyuan, GUO Yanxia, CHENG Fangqin. Migration of lithium, gallium and rare earth elements in coal, coal slime, and coal gangue during combustion[J]. CIESC Journal, 2021, 72(6): 3349-3358.
| 步骤 | 赋存状态 | 实验条件 |
|---|---|---|
| Ⅰ | 水溶态 | 8 g煤样+60 ml去离子水,25℃,24 h |
| Ⅱ | 离子交换态 | Ⅰ残渣+60 ml NH4Ac,25℃,24 h |
| Ⅲ | 有机结合态 | Ⅱ残渣+1.47 g/cm3 CHCl3,40℃干燥漂浮物,650℃灰化,+3 ml HNO3和3 ml HClO4,200℃,60 h |
| Ⅳ | 碳酸盐态 | Ⅱ残渣,乙醇冲洗,40℃干燥,+20 ml 0.5%HCl |
| Ⅴ | 硅酸盐态 | Ⅲ残渣+2.89 g/cm3 CHBr3,40℃干燥漂浮物,650℃灰化,+3 ml HNO3和3 ml HF,200℃,60 h |
| Ⅵ | 硫化物态 | Ⅲ残渣,水冲洗,40℃干燥,+HNO3,5 h |
表1 逐级化学提取方法实验步骤和条件
Table 1 Experimental conditions of stepwise chemical extraction method
| 步骤 | 赋存状态 | 实验条件 |
|---|---|---|
| Ⅰ | 水溶态 | 8 g煤样+60 ml去离子水,25℃,24 h |
| Ⅱ | 离子交换态 | Ⅰ残渣+60 ml NH4Ac,25℃,24 h |
| Ⅲ | 有机结合态 | Ⅱ残渣+1.47 g/cm3 CHCl3,40℃干燥漂浮物,650℃灰化,+3 ml HNO3和3 ml HClO4,200℃,60 h |
| Ⅳ | 碳酸盐态 | Ⅱ残渣,乙醇冲洗,40℃干燥,+20 ml 0.5%HCl |
| Ⅴ | 硅酸盐态 | Ⅲ残渣+2.89 g/cm3 CHBr3,40℃干燥漂浮物,650℃灰化,+3 ml HNO3和3 ml HF,200℃,60 h |
| Ⅵ | 硫化物态 | Ⅲ残渣,水冲洗,40℃干燥,+HNO3,5 h |
| 煤样 | 工业分析/%(质量, ad) | 元素分析/%(质量, ad) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mad | Aad | Vad | FC | C | H | N | S | |
| SZ | 1.7 | 23.6 | 31.4 | 43.2 | 79.7 | 5.1 | 1.3 | 1.5 |
| ZGE | 3.8 | 26.9 | 25.7 | 43.6 | 54.9 | 3.2 | 1.1 | 0.4 |
| TKT | 4.3 | 28.7 | 27.7 | 39.2 | 50.3 | 3.2 | 0.9 | 0.9 |
| DT | 1.6 | 27.8 | 23.3 | 47.2 | 49.2 | 2.9 | 1.0 | 0.4 |
| SS | 4.3 | 27.2 | 36.8 | 31.6 | 55.7 | 3.8 | 1.2 | 1.6 |
| XY | 1.2 | 67.5 | 14.1 | 17.2 | 19.5 | 1.5 | 0.5 | 3.8 |
| PS | 2.3 | 70.2 | 16.2 | 11.3 | 12.2 | 1.8 | 0.8 | 2.1 |
表2 原料煤的工业分析和元素分析
Table 2 Proximate and ultimate analyses of coal samples
| 煤样 | 工业分析/%(质量, ad) | 元素分析/%(质量, ad) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mad | Aad | Vad | FC | C | H | N | S | |
| SZ | 1.7 | 23.6 | 31.4 | 43.2 | 79.7 | 5.1 | 1.3 | 1.5 |
| ZGE | 3.8 | 26.9 | 25.7 | 43.6 | 54.9 | 3.2 | 1.1 | 0.4 |
| TKT | 4.3 | 28.7 | 27.7 | 39.2 | 50.3 | 3.2 | 0.9 | 0.9 |
| DT | 1.6 | 27.8 | 23.3 | 47.2 | 49.2 | 2.9 | 1.0 | 0.4 |
| SS | 4.3 | 27.2 | 36.8 | 31.6 | 55.7 | 3.8 | 1.2 | 1.6 |
| XY | 1.2 | 67.5 | 14.1 | 17.2 | 19.5 | 1.5 | 0.5 | 3.8 |
| PS | 2.3 | 70.2 | 16.2 | 11.3 | 12.2 | 1.8 | 0.8 | 2.1 |
815℃ 灰样 | 化学组成/%(质量) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SiO2 | Al2O3 | Fe2O3 | K2O | CaO | SO3 | MgO | TiO2 | |
| SZ | 47.7 | 42.3 | 1.8 | 0.6 | 3.6 | 2.2 | 0.2 | 1.6 |
| ZGE | 44.2 | 52.3 | 0.7 | 0.2 | 0.8 | 0.7 | 0.1 | 1.0 |
| TKT | 49.7 | 41.2 | 2.3 | 0.1 | 2.9 | 1.0 | 0.2 | 1.4 |
| DT | 44.3 | 41.8 | 1.9 | 0.5 | 4.7 | 4.3 | 0.5 | 2.0 |
| SS | 46.5 | 40.9 | 4.4 | 0.6 | 2.7 | 3.1 | 0.4 | 1.4 |
| XY | 51.7 | 34.0 | 6.4 | 1.0 | 3.5 | 1.5 | 0.4 | 1.3 |
| PS | 51.4 | 41.1 | 4.5 | 0.6 | 0.2 | 0.5 | 0.2 | 1.5 |
表3 815℃灰样的化学组成
Table 3 Ash composition of coal samples
815℃ 灰样 | 化学组成/%(质量) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SiO2 | Al2O3 | Fe2O3 | K2O | CaO | SO3 | MgO | TiO2 | |
| SZ | 47.7 | 42.3 | 1.8 | 0.6 | 3.6 | 2.2 | 0.2 | 1.6 |
| ZGE | 44.2 | 52.3 | 0.7 | 0.2 | 0.8 | 0.7 | 0.1 | 1.0 |
| TKT | 49.7 | 41.2 | 2.3 | 0.1 | 2.9 | 1.0 | 0.2 | 1.4 |
| DT | 44.3 | 41.8 | 1.9 | 0.5 | 4.7 | 4.3 | 0.5 | 2.0 |
| SS | 46.5 | 40.9 | 4.4 | 0.6 | 2.7 | 3.1 | 0.4 | 1.4 |
| XY | 51.7 | 34.0 | 6.4 | 1.0 | 3.5 | 1.5 | 0.4 | 1.3 |
| PS | 51.4 | 41.1 | 4.5 | 0.6 | 0.2 | 0.5 | 0.2 | 1.5 |
| 样品 | 含量/(μg/g) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Li | Ga | REE | |
| SZ | 197 | 34 | 128 |
| ZGE | 160 | 44 | 98 |
| TKT | 141 | 42 | 104 |
| DT | 120 | 30 | 121 |
| SS | 80 | 25 | 133 |
| XY | 84 | 26 | 85 |
| PS | 141 | 40 | 186 |
表4 原料中Li、Ga和REE元素含量
Table 4 Concentrations of Li, Ga, and REE in raw materials
| 样品 | 含量/(μg/g) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Li | Ga | REE | |
| SZ | 197 | 34 | 128 |
| ZGE | 160 | 44 | 98 |
| TKT | 141 | 42 | 104 |
| DT | 120 | 30 | 121 |
| SS | 80 | 25 | 133 |
| XY | 84 | 26 | 85 |
| PS | 141 | 40 | 186 |
| 样品 | Li含量/%(质量) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 水溶态 | 离子 交换态 | 有机态 | 碳酸 盐态 | 硅酸 盐态 | 硫酸 盐态 | |
| SZ | 4.2 | 1.9 | 5.8 | 2.5 | 85.7 | — |
| ZGE | 1.5 | 0.8 | 0.7 | 0.2 | 96.8 | — |
| TKT | 4.6 | 6.9 | 5.2 | 4.1 | 79.1 | — |
| DT | 0.5 | 5.4 | 2.7 | 0.7 | 90.7 | — |
| SS | 1.7 | 2.4 | 3.5 | 0.6 | 89.0 | 2.8 |
| XY | 1.8 | 0.2 | 2.5 | 0.8 | 94.7 | — |
| PS | 2.2 | 0.7 | 1.9 | 0.8 | 90.6 | 3.8 |
表5 各结合态中Li相对含量分布
Table 5 Distribution of Li in different forms
| 样品 | Li含量/%(质量) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 水溶态 | 离子 交换态 | 有机态 | 碳酸 盐态 | 硅酸 盐态 | 硫酸 盐态 | |
| SZ | 4.2 | 1.9 | 5.8 | 2.5 | 85.7 | — |
| ZGE | 1.5 | 0.8 | 0.7 | 0.2 | 96.8 | — |
| TKT | 4.6 | 6.9 | 5.2 | 4.1 | 79.1 | — |
| DT | 0.5 | 5.4 | 2.7 | 0.7 | 90.7 | — |
| SS | 1.7 | 2.4 | 3.5 | 0.6 | 89.0 | 2.8 |
| XY | 1.8 | 0.2 | 2.5 | 0.8 | 94.7 | — |
| PS | 2.2 | 0.7 | 1.9 | 0.8 | 90.6 | 3.8 |
| 样品 | Ga含量/%(质量) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 水溶态 | 离子 交换态 | 有机态 | 碳酸 盐态 | 硅酸 盐态 | 硫酸 盐态 | |
| SZ | 4.8 | 0.2 | 7.0 | 0.1 | 87.9 | — |
| ZGE | 0.4 | 0.2 | 0.5 | 0.1 | 98.8 | — |
| TKT | 2.7 | 4.7 | 2.1 | 3.8 | 86.7 | — |
| DT | 1.3 | 5.0 | 2.8 | 0.8 | 90.1 | — |
| SS | 2.6 | 1.7 | 3.9 | — | 91.8 | — |
| XY | 3.6 | 0.2 | 4.4 | 1.2 | 90.5 | — |
| PS | 0.9 | 0.1 | 0.3 | 0.3 | 98.1 | 0.2 |
表6 各结合态中Ga相对含量分布
Table 6 Distribution of Ga in different forms
| 样品 | Ga含量/%(质量) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 水溶态 | 离子 交换态 | 有机态 | 碳酸 盐态 | 硅酸 盐态 | 硫酸 盐态 | |
| SZ | 4.8 | 0.2 | 7.0 | 0.1 | 87.9 | — |
| ZGE | 0.4 | 0.2 | 0.5 | 0.1 | 98.8 | — |
| TKT | 2.7 | 4.7 | 2.1 | 3.8 | 86.7 | — |
| DT | 1.3 | 5.0 | 2.8 | 0.8 | 90.1 | — |
| SS | 2.6 | 1.7 | 3.9 | — | 91.8 | — |
| XY | 3.6 | 0.2 | 4.4 | 1.2 | 90.5 | — |
| PS | 0.9 | 0.1 | 0.3 | 0.3 | 98.1 | 0.2 |
| 样品 | REE含量/%(质量) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 水溶态 | 离子 交换态 | 有机态 | 碳酸 盐态 | 硅酸 盐态 | 硫酸 盐态 | |
| SZ | 4.8 | 3.6 | 8.3 | 2.9 | 80.3 | — |
| ZGE | 1.9 | 0.8 | 0.9 | 0.2 | 96.3 | — |
| TKT | 5.5 | 8.9 | 5.5 | 4.5 | 75.6 | — |
| DT | 1.0 | 9.0 | 4.6 | 1.1 | 84.4 | — |
| SS | 3.3 | 2.6 | 6.3 | — | 87.8 | — |
| XY | 2.0 | 0.3 | 2.9 | 1.4 | 93.5 | — |
| PS | 2.0 | 0.7 | 0.9 | 0.6 | 93.6 | 2.2 |
表7 各结合态中REE相对含量分布
Table 7 Distribution of REE in different forms
| 样品 | REE含量/%(质量) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 水溶态 | 离子 交换态 | 有机态 | 碳酸 盐态 | 硅酸 盐态 | 硫酸 盐态 | |
| SZ | 4.8 | 3.6 | 8.3 | 2.9 | 80.3 | — |
| ZGE | 1.9 | 0.8 | 0.9 | 0.2 | 96.3 | — |
| TKT | 5.5 | 8.9 | 5.5 | 4.5 | 75.6 | — |
| DT | 1.0 | 9.0 | 4.6 | 1.1 | 84.4 | — |
| SS | 3.3 | 2.6 | 6.3 | — | 87.8 | — |
| XY | 2.0 | 0.3 | 2.9 | 1.4 | 93.5 | — |
| PS | 2.0 | 0.7 | 0.9 | 0.6 | 93.6 | 2.2 |

图3 Li、Ga和REE逸出率与原料灰分(a)、挥发分(b)和含碳量(c)的关联
Fig.3 Correlation of Li, Ga and REE escape ratios during combustion with ash (a), volatiles (b) and carbon contents (c) in coal samples
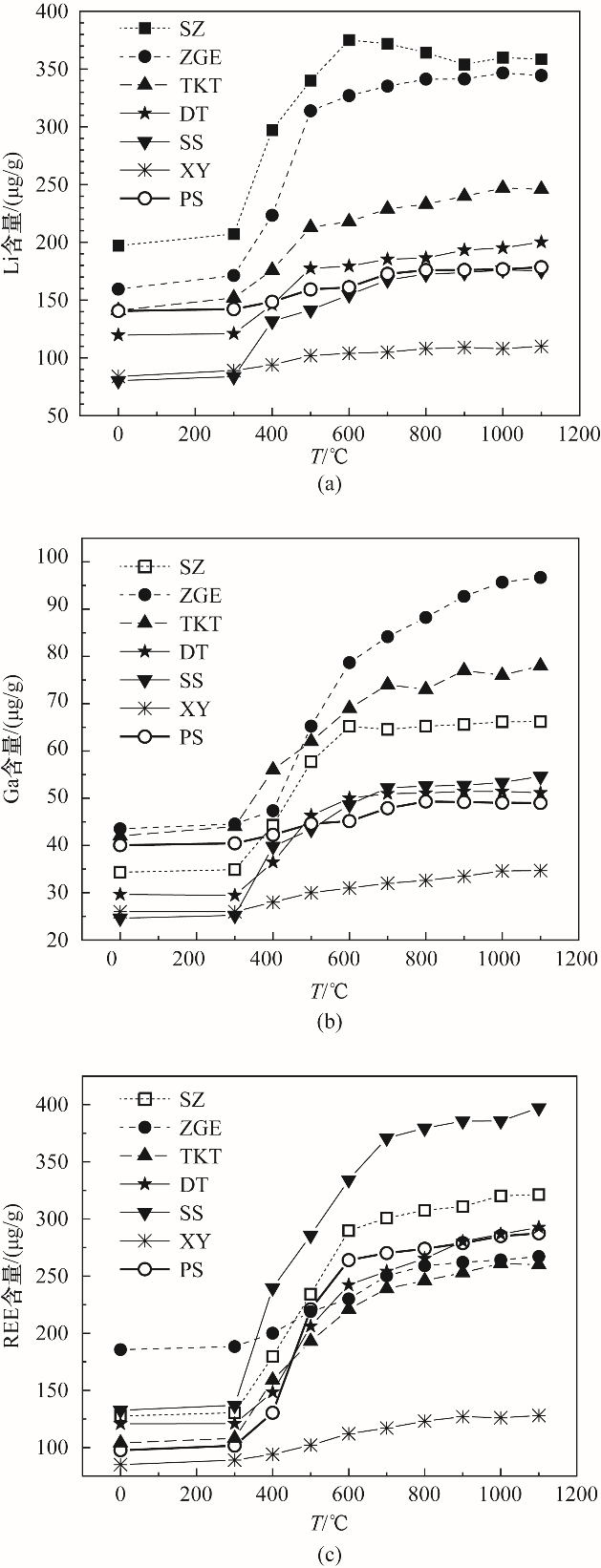
图5 7种样品不同温度燃烧灰中Li(a)、Ga(b)和REE(c)的含量变化
Fig.5 Variations of Li (a), Ga (b), and REE (c) concentrations in coal ash samples prepared at different temperatures
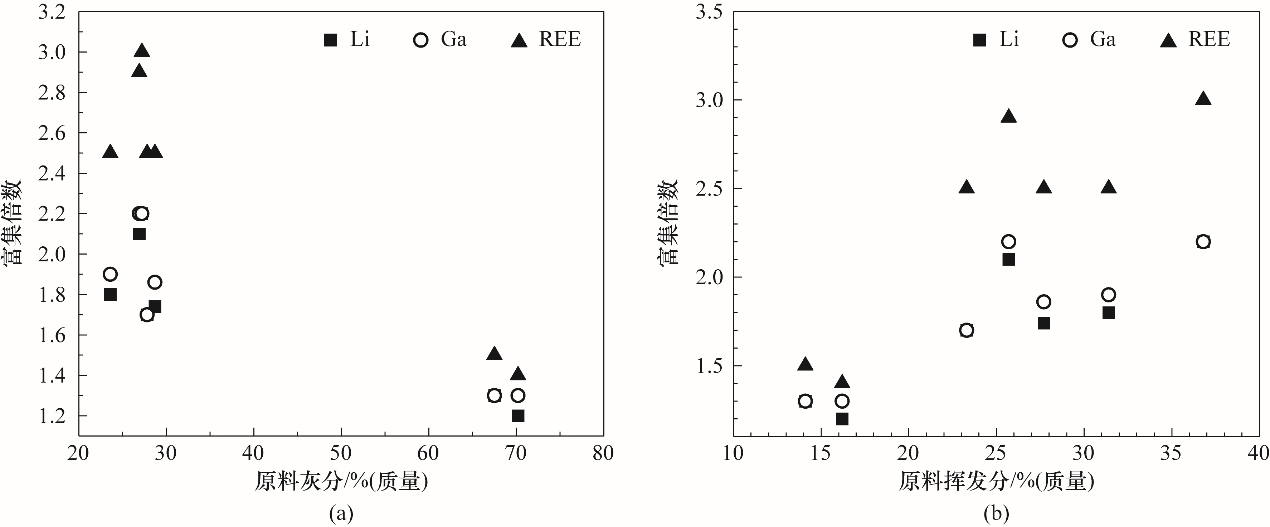
图7 Li、Ga和REE在灰中富集倍数与原料灰分(a)和挥发分(b)的关联
Fig.7 Correlation of Li, Ga and REE enrichment factors in ash with ash (a) and volatiles (b) contents in raw materials
| 1 | 王涛, 张新军. 煤中伴生矿产赋存状态及提取方法综述[J]. 矿产综合利用, 2019, (4): 21-25. |
| Wang T, Zhang X J. Summary of occurrence and extraction methods of associated minerals in coal [J]. Mult. Utiliz. Min. Res., 2019, (4): 21-25. | |
| 2 | Ma J L, Xiao L, Zhang K, et al. Geochemistry of carboniferous-permian coal from the Wujiawan Mine, Datong Coalfield, Northern China: modes of occurrence, origin of valuable trace elements, and potential industrial utilization [J]. Minerals, 2020, 10: 776-799. |
| 3 | Sun Y Z, Zhao C L, Qin S J, et al. Occurrence of some valuable elements in the unique ‘high-aluminium coals’ from the Jungar coalfield, China [J]. Ore Geol. Rev., 2016, 72: 659–668. |
| 4 | Liu B J, Wang J Y, He H T, et al. Geochemistry of carboniferous coals from the Laoyaogou mine, Ningwu coalfield, Shanxi Province, Northern China: emphasis on the enrichment of valuable elements [J]. Fuel, 2020, 279: 118414-118425. |
| 5 | Wang J X, Wang Q, Shi J, et al. Distribution and enrichment mode of Li in the No. 11 coal seam from Pingshuo mining district, Shanxi province [J]. Energ. Explor. Exploit., 2015, 33(2): 203-215. |
| 6 | Xiao L, Zhao B, Duan P P, et al. Geochemical characteristics of trace elements in the No. 6 coal seam from the Chuancaogedan Mine, Jungar Coalfield, Inner Mongolia, China [J]. Minerals, 2016, 6: 28. |
| 7 | 陈健, 陈萍, 刘文中, 等. 煤系共伴生资源利用现状及两淮煤田前景分析[J]. 洁净煤技术, 2015, 21(6): 105-108. |
| Chen J, Chen P, Liu W Z, et al. Utilization of associated resources occurred in Chinese coal-bearing series and its prospects in Huainan and Huaibei coalfields [J]. Clean Coal Technol., 2015, 21(6): 105-108. | |
| 8 | Dai S F, Jiang Y F, Ward R C, et al. Mineralogical and geochemical compositions of the coal in the Guanbanwusu Mine, Inner Mongolia, China: further evidence for the existence of an Al (Ga and REE) ore deposit in the Jungar Coalfield [J]. Int. J. Coal Geol., 2012, 98: 10-40. |
| 9 | 白洪杰. 准格尔电煤燃烧过程中微量元素迁移规律[D]. 邯郸: 河北工程大学, 2014. |
| Bai H J. The trace elements migratory regularity during combustion process of coal of Junger power plant [D]. Handan: Hebei University of Engineering, 2014. | |
| 10 | Blissett R S, Smalley N, Rowson N A. An investigation into six coal fly ashes from the United Kingdom and Poland to evaluate rare earth element content [J]. Fuel, 2014, 119: 236-239. |
| 11 | Ma Z B, Shan X Y, Cheng F Q. Distribution characteristics of valuable elements, Al, Li, and Ga, and rare earth elements in feed coal, fly ash, and bottom ash from a 300 MW circulating fluidized bed boiler [J]. ACS Omega, 2019, 4: 6854-6863. |
| 12 | Oboirien B O, Thulari V, North B C. Enrichment of trace elements in bottom ash from coal oxy-combustion: effect of coal types[J]. Appl. Energ., 2016, 177: 81-86. |
| 13 | Oboirien B O, Thulari V, North B C. Major and trace elements in coal bottom ash at different oxy coal combustion conditions [J]. Appl. Energ., 2014, 129: 207-216. |
| 14 | 陈怡伟. 热解过程煤中某些微量元素转化行为研究[D]. 合肥: 中国科学技术大学, 2008. |
| Chen Y W. The transformation behavior of some trace elements in coal during pyrolysis [D]. Hefei: University of Science and Technology of China, 2008. | |
| 15 | Ratafia-Brown J A. Overview of trace element partitioning in flames and furnaces of utility coal-fired boilers [J]. Fuel Process. Technol., 1994, 39(1/2/3): 139-157. |
| 16 | 杨建业. 煤热解中微量元素迁移规律的再探索[J]. 煤炭学报, 2013, 38(12): 2227-2233. |
| Yang J Y. Re-exploration on the law of trace elements migration during the pyrolysis of coal [J]. J. China Coal Soc., 2013, 38(12): 2227-2233 | |
| 17 | 杨建业, 张卫国, 邹建华. 煤中伴生稀有元素及其分布、迁移的几个规律 [J]. 稀有金属, 2020, 44(4): 440-448. |
| Yang J Y, Zhang W G, Zou J H. Distribution and migration regulations of associated elements in coal [J]. Chinese J. Rare Metals, 2020, 44(4): 440-448. | |
| 18 | 张森, 马志斌, 郭彦霞, 等. 三种气氛热处理过程朔州煤中锂和镓及稀土元素的迁移规律[J]. 煤炭转化, 2019, 42(2): 8-12. |
| Zhang S, Ma Z B, Guo Y X, et al. Migration of lithium, gallium and rare earth elements in Shuozhou coal during heat treatment process in three kinds of atmosphere [J]. Coal Conv., 2019, 42(2): 8-12. | |
| 19 | 王华. 陕北侏罗纪煤中微量元素赋存形态及迁移规律研究[D].西安: 西安科技大学, 2017. |
| Wang H. Study on the mode of occurrence and migration of trace elements in Shanbei Jurassic coals [D]. Xi'an: Xi'an University of Science and Technology, 2017. | |
| 20 | 邹潺, 王春波, 郭辉, 等. 燃煤过程中砷的赋存形态及其挥发特性 [J]. 化工学报, 2018, 69(4): 1670-1677. |
| Zou C, Wang C B, Guo H, et al. Volatilization characteristics and mode of occurrence of arsenic during coal combustion [J]. CIESC Journal, 2018, 69(4): 1670-1677. | |
| 21 | 刘慧敏, 王春波, 张月, 等. 温度和赋存形态对燃煤过程中砷迁移和释放的影响. 化工学报, 2015, 66(11): 4643-4651. |
| Liu H M, Wang C B, Zhang Y, et al. Effect of temperature and occurrence form of arsenic on its migration and volatilization during coal combustion [J]. CIESC Journal, 2015, 66(11): 4643-4651. | |
| 22 | Qin S J, Lu Q F, Li Y H, et al. Relationships between trace elements and organic matter in coals [J]. J. Geochem. Explor., 2018, 188: 101-110. |
| 23 | Zou J H, Cheng L F, Guo Y C, et al. Mineralogical and geochemical characteristics of lithium and rare earth elements in high-sulfur coal from the Donggou Mine, Chongqing, Southwestern China [J]. Minerals, 2020, 10: 627-643. |
| 24 | 薄朋慧. 煤和煤灰中"三稀"元素的地球化学特征及其在燃烧中的迁移[D]. 邯郸: 河北工程大学, 2020. |
| Bo P H. Geochemical characteristics of TREs in coal and coal ash and their migration during combustion [D]. Handan: Hebei University of Engineering, 2020. | |
| 25 | 覃轩.大同煤田煤中微量元素富集特征及共生关系成因研究[J]. 煤炭科学技术, 2019, 47( 11) : 189-195. |
| Tan X. Study on enrichment characteristics of trace elements and genesis of symbiotic relationship of coal in Datong Coalfield [J]. Coal Sci. Technol., 2019, 47(11): 189-195. | |
| 26 | Li J, Zhuang X G, Yuan W, et al. Mineral composition and geochemical characteristics of the Li-Ga-rich coals in the Buertaohai-Tianjiashipan mining district, Jungar Coalfield, Inner Mongolia [J]. Int. J. Coal Geol., 2016, 167: 157–175. |
| 27 | Zhao C L, Liu B J, Xiao L, et al. Significant enrichment of Ga, Rb, Cs, REEs and Y in the Jurassic No. 6 coal in the Iqe Coalfield, northern Qaidam Basin, China—a hidden gem [J]. Ore Geol. Rev., 2017, 83: 1–13. |
| 28 | 党钾涛. 气流床煤粉气化煤中微量元素的迁移与配分[D]. 北京: 中国矿业大学(北京), 2017. |
| Dang J T. Migration and partition of trace elements in coal during gasification in entrained-flow gasifier [D]. Beijing: China University of Mining & Technology (Beijing), 2017. | |
| 29 | Sorokin A P, Konyushok A A, Ageev O A, et al. Distribution of rare earth and selected trace elements in combustion products of Yerkovetskoe brown coal deposit (Amur Region, Russia) [J]. Energ. Explor. Exploit., 2019, 37(6): 1721-1736. |
| 30 | Hower J C, Fu B, Dai S F. Geochemical partitioning from pulverized coal to fly ash and bottom ash [J]. Fuel, 2020, 279: 118542-118554. |
| 31 | 张勇, 王西勃, 孙莹莹, 等. 煤灰化过程中有益元素镓的迁移和变化特征——以内蒙古准格尔富镓煤为例 [J]. 矿物岩石地球化学通报, 2008, 27(2): 133-136. |
| Zhang Y, Wang X B, Sun Y Y, et al. Migration and variation of gallium in coal ashing: a case study of gallium-rich coal, Jungar, Inner Mongolia [J]. Bull. Miner. Petrol. Geochem., 2008, 27(2): 133-136. |
| [1] | 张曼铮, 肖猛, 闫沛伟, 苗政, 徐进良, 纪献兵. 危废焚烧处理耦合有机朗肯循环系统工质筛选与热力学优化[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(8): 3502-3512. |
| [2] | 曾如宾, 沈中杰, 梁钦锋, 许建良, 代正华, 刘海峰. 基于分子动力学模拟的Fe2O3纳米颗粒烧结机制研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(8): 3353-3365. |
| [3] | 韩晨, 司徒友珉, 朱斌, 许建良, 郭晓镭, 刘海峰. 协同处理废液的多喷嘴粉煤气化炉内反应流动研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(8): 3266-3278. |
| [4] | 屈园浩, 邓文义, 谢晓丹, 苏亚欣. 活性炭/石墨辅助污泥电渗脱水研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(7): 3038-3050. |
| [5] | 陈朝光, 贾玉香, 汪锰. 以低浓度废酸驱动中和渗析脱盐的模拟与验证[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(6): 2486-2494. |
| [6] | 刘定平, 陈爱桦, 张向阳, 何文浩, 王海. 铝灰半干法水解脱氮研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(3): 1294-1302. |
| [7] | 罗欣宜, 冯超, 刘晶, 乔瑜. 污泥不同热处理工艺产物磷的浸出回收实验研究[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(9): 4034-4044. |
| [8] | 刘新华, 韩振南, 韩健, 梁斌, 张楠, 胡善伟, 白丁荣, 许光文. 基于热解与燃烧反应重构的低NO x 解耦燃烧原理与技术[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(8): 3355-3368. |
| [9] | 何聪, 钟文琪, 周冠文, 陈曦. 高海拔地区水泥生料悬浮炉分解特性研究[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(5): 2120-2129. |
| [10] | 李雪, 东明, 张璜, 谢俊. 潮湿环境下微尺度颗粒撞击平板的动力学研究[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(5): 1940-1946. |
| [11] | 郭志强, 燕可洲, 张吉元, 柳丹丹, 高阳艳, 郭彦霞. 煤矸石/粉煤灰对赤泥钠化还原焙烧反应的影响机制[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(5): 2194-2205. |
| [12] | 许世佩, 王超, 李庆远, 张炳康, 许世伟, 张雪琴, 王诗颖, 丛梦晓. 氧化钙对油基钻屑热脱附产物影响的研究[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(4): 1724-1731. |
| [13] | 李文怀, 周嵬. 高氧离子电导钙钛矿的影响因素分析和设计策略[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(4): 1455-1471. |
| [14] | 邬云飞, 栾小丽, 刘飞. 基于迁移学习的2,6-二甲酚纯度近红外光谱在线检测[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(2): 782-791. |
| [15] | 刘轩, 苏银皎, 滕阳, 张锴, 王鹏程, 李丽锋, 李圳. 超低排放燃煤机组硒的迁移转化及飞灰对其富集特性[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(2): 923-932. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备 11010102001995号
京公网安备 11010102001995号