化工学报 ›› 2022, Vol. 73 ›› Issue (5): 2194-2205.DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20211588
郭志强1( ),燕可洲1(
),燕可洲1( ),张吉元2,柳丹丹2,高阳艳3,郭彦霞1
),张吉元2,柳丹丹2,高阳艳3,郭彦霞1
收稿日期:2021-11-09
修回日期:2022-01-27
出版日期:2022-05-05
发布日期:2022-05-24
通讯作者:
燕可洲
作者简介:郭志强(1996—),男,硕士研究生,基金资助:
Zhiqiang GUO1( ),Kezhou YAN1(
),Kezhou YAN1( ),Jiyuan ZHANG2,Dandan LIU2,Yangyan GAO3,Yanxia GUO1
),Jiyuan ZHANG2,Dandan LIU2,Yangyan GAO3,Yanxia GUO1
Received:2021-11-09
Revised:2022-01-27
Online:2022-05-05
Published:2022-05-24
Contact:
Kezhou YAN
摘要:
煤矸石或粉煤灰与赤泥协同钠化还原焙烧均可实现其所含铁、铝、硅等元素的形态转化,使其易于分离回收;但对于它们分别与赤泥协同钠化还原焙烧反应差异性及机制的研究目前尚未见报道。采用X射线衍射分析方法,分别考察了煤矸石-赤泥、粉煤灰-赤泥体系钠化还原焙烧过程中,气氛类型、钠助剂添加量、焙烧温度、焙烧时间对还原焙烧产物物相组成的影响规律,并对两个反应体系中铁磁化效果及铝硅活化效果的差异性进行分析。结果表明:在钠化还原焙烧过程中,煤矸石-赤泥、粉煤灰-赤泥体系均可同步实现含铁物相的磁化和铝硅物相的活化,且随着钠助剂添加量、焙烧温度、焙烧时间的变化,含铁物相和铝硅物相呈现规律性变化;在相同铁磁化和铝硅活化效果前提下,煤矸石-赤泥体系所需钠助剂添加量、焙烧温度和焙烧时间均略低于粉煤灰-赤泥体系,这主要与煤矸石、粉煤灰中所含还原性物质和铝硅矿物的赋存形态、含量及微观结构有关。研究将为煤矸石、粉煤灰等煤基固废与赤泥协同钠化还原焙烧回收有价元素的原料筛选提供理论指导。
中图分类号:
郭志强, 燕可洲, 张吉元, 柳丹丹, 高阳艳, 郭彦霞. 煤矸石/粉煤灰对赤泥钠化还原焙烧反应的影响机制[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(5): 2194-2205.
Zhiqiang GUO, Kezhou YAN, Jiyuan ZHANG, Dandan LIU, Yangyan GAO, Yanxia GUO. Influence mechanism of coal gangue / coal fly ash on the sodium reduction roasting reaction of red mud[J]. CIESC Journal, 2022, 73(5): 2194-2205.
| 物质 | Al2O3/% | SiO2/% | CaO/% | Na2O/% | Fe2O3/% | TiO2/% | MgO/% | K2O/% | LOI/% | Al/Si |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 煤矸石 | 21.06 | 41.36 | 0.95 | 0.43 | 2.52 | 0.77 | 0.50 | 2.00 | 23.4 | 0.61 |
| 粉煤灰 | 29.90 | 44.40 | 2.72 | 0.86 | 2.67 | 1.25 | 0.45 | 1.50 | 15.79 | 0.79 |
| 赤泥 | 27.40 | 22.40 | 19.40 | 9.89 | 7.81 | 3.95 | 0.92 | 0.81 | 7.42 | 1.43 |
表1 煤矸石、粉煤灰和赤泥主要化学组成
Table 1 Chemical compositions of coal gangue, coal fly ash and red mud
| 物质 | Al2O3/% | SiO2/% | CaO/% | Na2O/% | Fe2O3/% | TiO2/% | MgO/% | K2O/% | LOI/% | Al/Si |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 煤矸石 | 21.06 | 41.36 | 0.95 | 0.43 | 2.52 | 0.77 | 0.50 | 2.00 | 23.4 | 0.61 |
| 粉煤灰 | 29.90 | 44.40 | 2.72 | 0.86 | 2.67 | 1.25 | 0.45 | 1.50 | 15.79 | 0.79 |
| 赤泥 | 27.40 | 22.40 | 19.40 | 9.89 | 7.81 | 3.95 | 0.92 | 0.81 | 7.42 | 1.43 |

图1 煤矸石、粉煤灰和赤泥的XRD谱图1—石英(SiO2); 2—高岭石(Al2[Si2O5](OH)4); 3—莫来石(Al6Si2O13); 4—方钠石(Na8Al6O12(OH)2(H2O)2); 5—水化石榴石(Ca3Al2(SiO4)(OH)8); 6—潘诺霞石((K,Na)AlSiO4); 7—钠霞石(NaAlSiO4); 8—赤铁矿(Fe2O3)
Fig.1 XRD patterns of coal gangue, coal fly ash and red mud
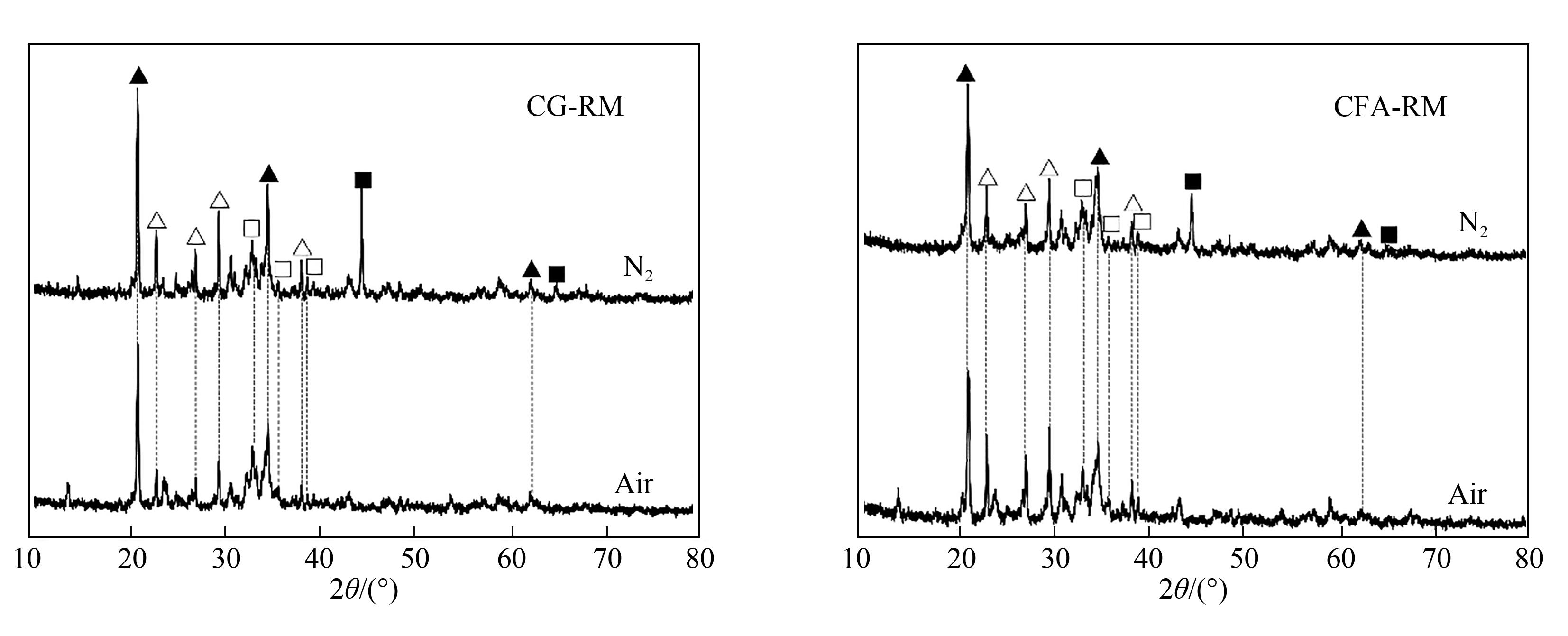
图2 不同气氛下CG-RM和CFA-RM体系钠化焙烧产物的XRD谱图(实验条件:Na∶Al∶Si=1.2∶1∶1,焙烧温度850℃,焙烧时间 120 min)△ 霞石(NaAlSiO4); ▲ 钠铝硅酸盐(Na6Al4Si4O17); □ 赤铁矿(Fe2O3); ■ 铁(Fe)
Fig.2 XRD patterns of the sodium roasting products of CG-RM and CFA-RM systems in different atmosphere

图3 不同钠助剂添加量下CG-RM和CFA-RM体系钠化还原焙烧产物的XRD谱图(实验条件:焙烧气氛 N2,焙烧温度 850°C,焙烧时间 120 min)△ 霞石(NaAlSiO4); ▲ 钠铝硅酸盐(Na6Al4Si4O17); ■ 铁(Fe)
Fig.3 XRD patterns of the sodium reduction roasting products of CG-RM and CFA-RM systems with different amount of sodium additive

图4 不同钠助剂添加量下CG-RM和CFA-RM体系钠化还原焙烧产物中活性相与磁性相的相对含量
Fig.4 Relative contents of active phase and magnetic phase in the sodium reduction roasting products of CG-RM and CFA-RM systems with different amount of sodium additives

图5 不同温度下CG-RM和CFA-RM体系钠化还原焙烧产物的XRD谱图(实验条件:焙烧气氛 N2,Na∶Al∶Si=1.2∶1∶1,焙烧时间 120 min)△ 霞石(NaAlSiO4); ▲ 钠铝硅酸盐(Na6Al4Si4O17); ■ 铁(Fe)
Fig.5 XRD patterns of the sodium reduction roasting products of CG-RM and CFA-RM systems in different temperature
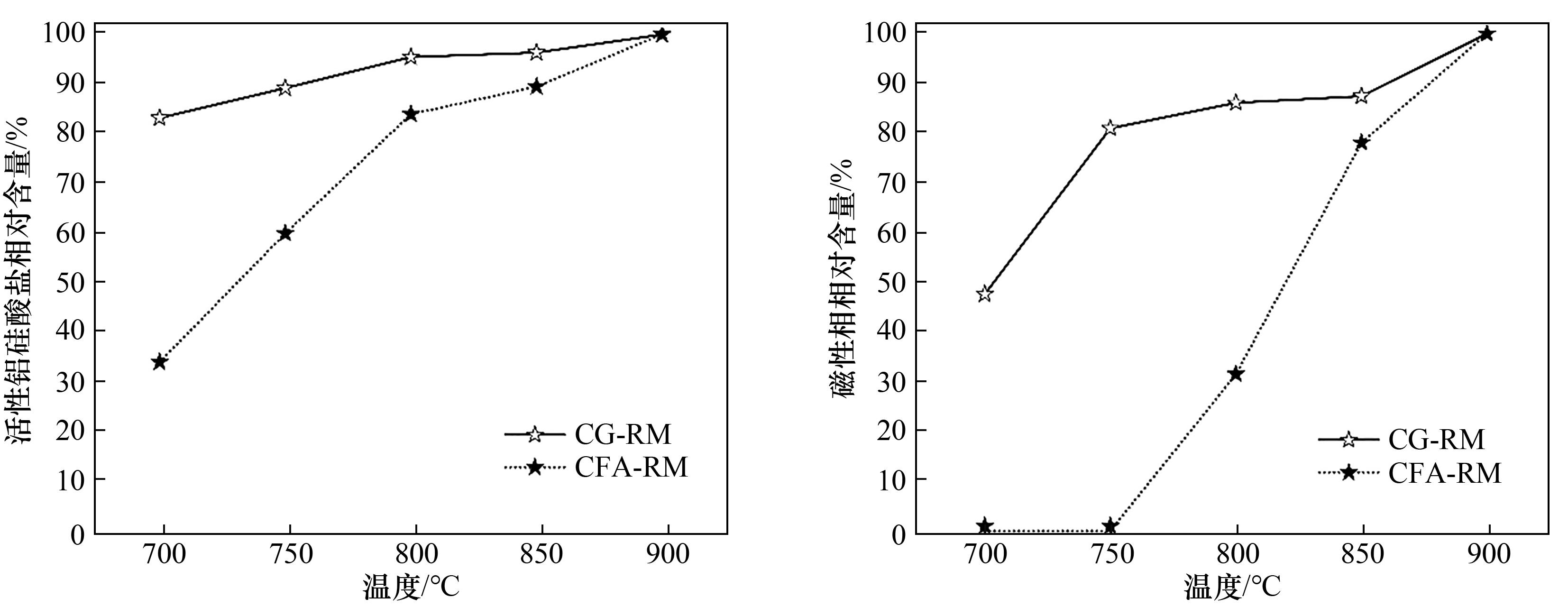
图6 不同温度下CG-RM和CFA-RM体系钠化还原焙烧产物中活性相与磁性相的相对含量
Fig.6 Relative contents of active phase and magnetic phase in the sodium reduction roasting products of CG-RM and CFA-RM systems in different temperature

图7 不同时间下CG-RM和CFA-RM体系钠化还原焙烧产物的XRD谱图(实验条件:焙烧气氛 N2,Na∶Al∶Si=1.2∶1∶1,焙烧温度850°C)△ 霞石(NaAlSiO4);▲ 钠铝硅酸盐(Na6Al4Si4O17); ■ 铁(Fe)
Fig.7 XRD patterns of the sodium reduction roasting products of CG-RM and CFA-RM systems at different time

图8 不同时间下CG-RM和CFA-RM体系钠化还原焙烧产物中活性相与磁性相的相对含量
Fig.8 Relative contents of active phase and magnetic phase in the sodium reduction roasting products of CG-RM and CFA-RM systems at different time
| 体系 | 钠铝硅比(mol) | 温度/℃ | 时间/min |
|---|---|---|---|
| 煤矸石-赤泥-碳酸钠 | 1.2∶1∶1 | 800 | 90 |
| 粉煤灰-赤泥-碳酸钠 | 1.5∶1∶1 | 850 | 150 |
表2 煤矸石-赤泥和粉煤灰-赤泥体系钠化还原焙烧优化实验条件差异
Table 2 Difference of optimum experimental conditions for sodium reduction roasting of coal gangue-red mud and coal fly ash-red mud systems
| 体系 | 钠铝硅比(mol) | 温度/℃ | 时间/min |
|---|---|---|---|
| 煤矸石-赤泥-碳酸钠 | 1.2∶1∶1 | 800 | 90 |
| 粉煤灰-赤泥-碳酸钠 | 1.5∶1∶1 | 850 | 150 |
| 物质 | 水分/% | 灰分/% | 挥发分/% | 固定碳/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 煤矸石 | 0.53 | 75.46 | 9.07 | 14.94 |
| 粉煤灰 | 0.17 | 88.81 | 1.66 | 9.36 |
表3 煤矸石和粉煤灰工业成分测试
Table 3 Industrial composition test of coal gangue and coal fly ash
| 物质 | 水分/% | 灰分/% | 挥发分/% | 固定碳/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 煤矸石 | 0.53 | 75.46 | 9.07 | 14.94 |
| 粉煤灰 | 0.17 | 88.81 | 1.66 | 9.36 |
| 项目 | 高岭石 | 莫来石 |
|---|---|---|
| 空间群 | C 1 C | P b n m |
| 晶胞体积 | 656.9 ?3 | 323.3 ?3 |
| 晶格参数 | a : 5.148 ? b : 8.920 ? c : 14.535 ? α : 90.000° β : 100.200° γ : 90.000° | a : 7.430 ? b : 7.580 ? c : 5.740 ? α : 90.000° β : 90.000° γ : 90.000° |
表4 高岭石和莫来石晶体结构基本参数
Table 4 Basic crystal structure parameters of kaolinite and mullite
| 项目 | 高岭石 | 莫来石 |
|---|---|---|
| 空间群 | C 1 C | P b n m |
| 晶胞体积 | 656.9 ?3 | 323.3 ?3 |
| 晶格参数 | a : 5.148 ? b : 8.920 ? c : 14.535 ? α : 90.000° β : 100.200° γ : 90.000° | a : 7.430 ? b : 7.580 ? c : 5.740 ? α : 90.000° β : 90.000° γ : 90.000° |
| 矿物 | 键类型 | 键长/nm | 重叠布局数 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 高岭石 | Si—O | 1.628 | 0.535 |
| Al—O | 2.420 | 0.0287 | |
| 莫来石 | Si—O | 1.624 | 0.588 |
| Al—O | 1.837 | 0.368 |
表5 高岭石和莫来石的平均键长和重叠布局数
Table 5 Average bond length and overlap number of kaolinite and mullite
| 矿物 | 键类型 | 键长/nm | 重叠布局数 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 高岭石 | Si—O | 1.628 | 0.535 |
| Al—O | 2.420 | 0.0287 | |
| 莫来石 | Si—O | 1.624 | 0.588 |
| Al—O | 1.837 | 0.368 |
| 1 | Reddy P S, Reddy N G, Serjun V Z, et al. Properties and assessment of applications of red mud (bauxite residue): current status and research needs[J]. Waste and Biomass Valorization, 2021, 12(3): 1185-1217. |
| 2 | Wang S H, Jin H X, Deng Y, et al. Comprehensive utilization status of red mud in China: a critical review[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2021, 289: 125136. |
| 3 | Khairul M A, Zanganeh J, Moghtaderi B. The composition, recycling and utilisation of Bayer red mud[J]. Resources, Conservation and Recycling, 2019, 141: 483-498. |
| 4 | Muraleedharan M, Nadir Y. Factors affecting the mechanical properties and microstructure of geopolymers from red mud and granite waste powder: a review[J]. Ceramics International, 2021, 47(10): 13257-13279. |
| 5 | 仇雅丽, 李长明, 王德亮, 等. 赤泥/煤基铁炭材料的制备及其脱除废水Cr(Ⅵ)的性能[J]. 化工学报, 2018, 69(7): 3216-3225. |
| Qiu Y L, Li C M, Wang D L, et al. Preparation of red mud/coal based material and its performance to remove Cr(Ⅵ) in waste water[J]. CIESC Journal, 2018, 69(7): 3216-3225. | |
| 6 | Wang M F, Liu X M. Applications of red mud as an environmental remediation material: a review[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2021, 408: 124420. |
| 7 | 王超, 李长明, 皇甫林, 等. 赤泥催化剂的制备及其对模拟烟气中微量氨的脱除性能[J]. 化工学报, 2019, 70(3): 1056-1064. |
| Wang C, Li C M, Huangfu L, et al. Preparation of red mud-based catalyst and performance for trace ammonia in simulative tail gas[J]. CIESC Journal, 2019, 70(3): 1056-1064. | |
| 8 | Liu X, Han Y X, He F Y, et al. Characteristic, hazard and iron recovery technology of red mud—a critical review[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2021, 420: 126542. |
| 9 | Hu G Y, Tang H H, He D D, et al. Selective extraction of sodium from red mud by dry digestion[J]. Minerals Engineering, 2021, 173: 107180. |
| 10 | Li S W, Pan J, Zhu D Q, et al. A new route for separation and recovery of Fe, Al and Ti from red mud[J]. Resources, Conservation and Recycling, 2021, 168: 105314. |
| 11 | Liu X, Gao P, Yuan S, et al. Clean utilization of high-iron red mud by suspension magnetization roasting[J]. Minerals Engineering, 2020, 157: 106553. |
| 12 | Yuan S, Liu X, Gao P, et al. A semi-industrial experiment of suspension magnetization roasting technology for separation of iron minerals from red mud[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2020, 394: 122579. |
| 13 | Wang J Y, Sun P P, Xue H M, et al. Red mud derived facile hydrothermal synthesis of hierarchical porous α-Fe2O3 microspheres as efficient adsorbents for removal of Congo red[J]. Journal of Physics and Chemistry of Solids, 2020, 140: 109379. |
| 14 | Zhu X B, Niu Z P, Li W, et al. A novel process for recovery of aluminum, iron, vanadium, scandium, titanium and silicon from red mud[J]. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 2020, 8(2): 103528. |
| 15 | Gao F, Zhang J H, Deng X J, et al. Comprehensive recovery of iron and aluminum from ordinary bayer red mud by reductive sintering-magnetic separation–digesting process[J]. JOM, 2019, 71(9): 2936-2943. |
| 16 | 马荣锴, 罗星, 冯吉福, 等. 赤泥还原提铁及钪的走向分析[J]. 有色金属工程, 2020, 10(2): 54-59. |
| Ma R K, Luo X, Feng J F, et al. Reduction extraction of iron from red mud and the scandium trend analysis[J]. Nonferrous Metals Engineering, 2020, 10(2): 54-59. | |
| 17 | 王丽明, 刘涛, 白春霞, 等. 山东某赤泥提铁试验研究[J]. 现代矿业, 2019, 35(11): 8-10. |
| Wang L M, Liu T, Bai C X, et al. Experimental study on iron extracting from red mud in Shandong[J]. Modern Mining, 2019, 35(11): 8-10. | |
| 18 | Agrawal S, Rayapudi V, Dhawan N. Comparison of microwave and conventional carbothermal reduction of red mud for recovery of iron values[J]. Minerals Engineering, 2019, 132: 202-210. |
| 19 | Liu J P, Li X Y, Lu Y S, et al. Effects of Na/Al ratio on mechanical properties and microstructure of red mud-coal metakaolin geopolymer[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2020, 263: 120653. |
| 20 | Wang X P, Sun T C, Wu S C, et al. A novel utilization of Bayer red mud through co-reduction with a limonitic laterite ore to prepare ferronickel[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2019, 216: 33-41. |
| 21 | Guo Y X, Zhao Q, Yan K Z, et al. Novel process for alumina extraction via the coupling treatment of coal gangue and bauxite red mud[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2014, 53(11): 4518-4521. |
| 22 | Guo Y X, Zhao Z S, Zhao Q, et al. Novel process of alumina extraction from coal fly ash by pre-desilicating-Na2CO3 activation-acid leaching technique[J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2017, 169: 418-425. |
| 23 | 郭玉梅, 曹丽琼, 郭彦霞, 等. 煤矸石和赤泥协同提取氧化铝过程矿相转变研究[J]. 化工学报, 2019, 70(4): 1542-1549. |
| Guo Y M, Cao L Q, Guo Y X, et al. Mineral transformation in process of combined extraction of alumina from coal gangue and red mud[J]. CIESC Journal, 2019, 70(4): 1542-1549. | |
| 24 | Guo Y X, Li J, Yan K Z, et al. A prospective process for alumina extraction via the co-treatment of coal fly ash and bauxite red mud: investigation of the process[J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2019, 186: 98-104. |
| 25 | 张吉元, 柳丹丹, 郭晓方, 等. 赤泥-煤矸石协同还原焙烧回收Fe、Al有价元素[J]. 环境工程学报, 2021, 15(10): 3306-3315. |
| Zhang J Y, Liu D D, Guo X F, et al. Valuable element recovery of Fe and Al by reduction roasting of red mud and coal gangue[J]. Chinese Journal of Environmental Engineering, 2021, 15(10): 3306-3315. | |
| 26 | 孙亮, 李玉虎, 宋健清, 等. 焙烧制度对稀土精矿中铁、铝等杂质浸出行为的影响[J]. 有色金属科学与工程, 2021, 12(4): 27-32, 81. |
| Sun L, Li Y H, Song J Q, et al. Effects of roasting system on the leaching behavior of iron and aluminum impurities in rare earth concentrates[J]. Nonferrous Metals Science and Engineering, 2021, 12(4): 27-32, 81. | |
| 27 | 孙开, 王维, 张子阳, 等. 高铁赤泥碳热还原制备镍铁合金[J]. 粉末冶金材料科学与工程, 2021, 26(6): 560-566. |
| Sun K, Wang W, Zhang Z Y, et al. Preparation of Ni-Fe alloy by carbothermal reduction of high iron red mud[J]. Materials Science and Engineering of Powder Metallurgy, 2021, 26(6): 560-566. | |
| 28 | 姜涛, 刘牡丹, 李光辉, 等. 钠盐对高铝褐铁矿还原焙烧铝铁分离的影响[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2010, 20(6): 1226-1233. |
| Jiang T, Liu M D, Li G H, et al. Effects of sodium-salt on Al-Fe separation by reduction roasting for high-aluminum content limonite[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2010, 20(6): 1226-1233. | |
| 29 | 冉敬, 郭创锋, 杜谷, 等. X射线衍射全谱拟合法分析蓝晶石的矿物含量[J]. 岩矿测试, 2019, 38(6): 660-667. |
| Ran J, Guo C F, Du G, et al. Quantitative analysis of mineral composition of kyanite by X-ray diffraction with rietveld refinement method[J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2019, 38(6): 660-667. | |
| 30 | 宋刘斌, 黎安娴, 肖忠良, 等. 第一性原理在锂离子电池电极材料中的应用研究[J]. 化工学报, 2019, 70(6): 2051-2059. |
| Song L B, Li A X, Xiao Z L, et al. Application research status of first-principles in lithium-ion battery electrode materials[J]. CIESC Journal, 2019, 70(6): 2051-2059. | |
| 31 | Li X J, Hayashi J I, Li C Z. FT-Raman spectroscopic study of the evolution of char structure during the pyrolysis of a Victorian brown coal[J]. Fuel, 2006, 85(12/13): 1700-1707. |
| 32 | Gruner J W. The crystal structure of kaolinite[J]. Zeitschrift Für Kristallographie-Crystalline Materials, 1932, 83(1/2/3/4/5/6): 75-88. |
| 33 | Taylor W H. ⅩⅩⅧ . The structure of sillimanite and mullite[J]. Zeitschrift Für Kristallographie-Crystalline Materials, 1928, 68(1/2/3/4/5/6): 503-521. |
| 34 | 丁治英, 敬珊珊, 陈启元. 含锌矿物的微观结构与反应活性[J]. 中国科技论文, 2015, 10(18): 2178-2181, 2186. |
| Ding Z Y, Jing S S, Chen Q Y. Microstructures and reaction activity of zinc - bearing minerals[J]. China Sciencepaper, 2015, 10(18): 2178-2181, 2186. |
| [1] | 胡超, 董玉明, 张伟, 张红玲, 周鹏, 徐红彬. 浓硫酸活化五氧化二钒制备高浓度全钒液流电池正极电解液[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(S1): 338-345. |
| [2] | 范孝雄, 郝丽芳, 范垂钢, 李松庚. LaMnO3/生物炭催化剂低温NH3-SCR催化脱硝性能研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(9): 3821-3830. |
| [3] | 韩晨, 司徒友珉, 朱斌, 许建良, 郭晓镭, 刘海峰. 协同处理废液的多喷嘴粉煤气化炉内反应流动研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(8): 3266-3278. |
| [4] | 张曼铮, 肖猛, 闫沛伟, 苗政, 徐进良, 纪献兵. 危废焚烧处理耦合有机朗肯循环系统工质筛选与热力学优化[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(8): 3502-3512. |
| [5] | 曾如宾, 沈中杰, 梁钦锋, 许建良, 代正华, 刘海峰. 基于分子动力学模拟的Fe2O3纳米颗粒烧结机制研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(8): 3353-3365. |
| [6] | 屈园浩, 邓文义, 谢晓丹, 苏亚欣. 活性炭/石墨辅助污泥电渗脱水研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(7): 3038-3050. |
| [7] | 康超, 乔金鹏, 杨胜超, 彭超, 付元鹏, 刘斌, 刘建荣, Aleksandrova Tatiana, 段晨龙. 煤矸石中有价关键金属活化提取研究进展[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(7): 2783-2799. |
| [8] | 李盼, 马俊洋, 陈志豪, 王丽, 郭耘. Ru/α-MnO2催化剂形貌对NH3-SCO反应性能的影响[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(7): 2908-2918. |
| [9] | 张琦钰, 高利军, 苏宇航, 马晓博, 王翊丞, 张亚婷, 胡超. 碳基催化材料在电化学还原二氧化碳中的研究进展[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(7): 2753-2772. |
| [10] | 卫雪岩, 钱勇. 微米级铁粉燃料中低温氧化反应特性及其动力学研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(6): 2624-2638. |
| [11] | 陈朝光, 贾玉香, 汪锰. 以低浓度废酸驱动中和渗析脱盐的模拟与验证[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(6): 2486-2494. |
| [12] | 张艳梅, 袁涛, 李江, 刘亚洁, 孙占学. 高效SRB混合菌群构建及其在酸胁迫条件下的性能研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(6): 2599-2610. |
| [13] | 胡南, 陶德敏, 杨照岚, 王学兵, 张向旭, 刘玉龙, 丁德馨. 铁炭微电解与硫酸盐还原菌耦合修复铀尾矿库渗滤水的研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(6): 2655-2667. |
| [14] | 张谭, 刘光, 李晋平, 孙予罕. Ru基氮还原电催化剂性能调控策略[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(6): 2264-2280. |
| [15] | 李瑞康, 何盈盈, 卢维鹏, 王园园, 丁皓东, 骆勇名. 电化学强化钴基阴极活化过一硫酸盐的研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(5): 2207-2216. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备 11010102001995号
京公网安备 11010102001995号