化工学报 ›› 2021, Vol. 72 ›› Issue (9): 4881-4891.DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20210212
收稿日期:2021-02-03
修回日期:2021-06-06
出版日期:2021-09-05
发布日期:2021-09-05
通讯作者:
韩昫身,于建国
作者简介:黄莉婷(1996—),女,硕士研究生,基金资助:
Liting HUANG1( ),Xushen HAN2(
),Xushen HAN2( ),Yan JIN3,Qiang MA4,Jianguo YU1(
),Yan JIN3,Qiang MA4,Jianguo YU1( )
)
Received:2021-02-03
Revised:2021-06-06
Online:2021-09-05
Published:2021-09-05
Contact:
Xushen HAN,Jianguo YU
摘要:
一般煤化工废水经过多级氧化处理后,反渗透淡水回用、浓水经蒸发产生难处理的“危废”,有机物的存在对“危废”循环利用有显著制约作用。以煤化工反渗透浓水为底物(TOC为233.4 mg/L,TDS为50.9 g/L,BOD5/COD仅为0.05),从不同菌源中筛选得到9株高效耐盐菌,经16S rDNA测序表明,这些菌株属于假单胞菌属、芽孢杆菌属及嗜盐单胞菌属。将9株耐盐菌配制成复合耐盐菌剂连续式运行处理实际废水,有机物去除率可达30%,为进一步提高去除率,经臭氧氧化预处理,有机物去除率可提高至40%,达到国内外较先进水平。根据气质联用分析,臭氧氧化预处理会破坏废水中环状物质的结构,提高复合耐盐菌剂对难降解有机物的去除效果。本研究为煤化工反渗透浓水中有机物的生物降解提供了可行性方案。
中图分类号:
黄莉婷, 韩昫身, 金艳, 马强, 于建国. 煤化工反渗透浓水的高效降解菌株筛选、鉴定及应用研究[J]. 化工学报, 2021, 72(9): 4881-4891.
Liting HUANG, Xushen HAN, Yan JIN, Qiang MA, Jianguo YU. Isolation, identification and application of highly efficient halotolerant strains for coal chemical reverse osmosis concentrate treatment[J]. CIESC Journal, 2021, 72(9): 4881-4891.
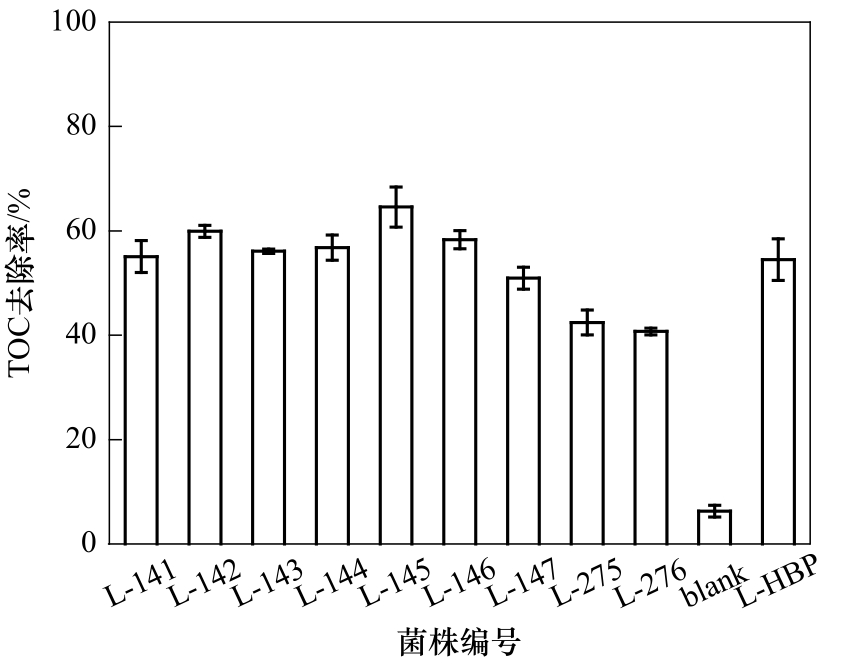
图3 耐盐菌对TOC的去除效果(blank—空白对照组;L-HBP—9株菌等比例复配制备的菌剂)
Fig.3 Degradation of TOC by halotolerant bacteria (blank—blank control; L-HBP—halotolerant bacteria preparation)
| 菌株编号 | 相似菌株 | 相似度/% | 序列号 |
|---|---|---|---|
| L-141 | Pseudomonas sp. HC2-4 | 100.00 | JF312947.1 |
| L-142 | Pseudomonas sp. strain P0u25 | 99.92 | MK737101.1 |
| L-143 | Bacillus sp. (in: Bacteria) strain CY1TSA7 | 99.79 | MH974115.1 |
| L-144 | Halomonas alkaliphila X3 | 100.00 | CP024811.1 |
| L-145 | Bacillus altitudinis strain HQ-51-Ba | 100.00 | CP040747.1 |
| L-146 | Bacillus altitudinis strain HQ-51-Ba | 99.85 | CP040747.1 |
| L-147 | Bacillus sp. (in: Bacteria) strain CY1TSA7 | 100.00 | MH974115.1 |
| L-275 | Bacillus flexus strain HDB-2 | 99.72 | MK178593.1 |
| L-276 | Bacillus altitudinis strain NPB34b | 100.00 | MT598007.1 |
表1 耐盐菌菌种鉴定
Table 1 Identification of screened halotolerant bacteria
| 菌株编号 | 相似菌株 | 相似度/% | 序列号 |
|---|---|---|---|
| L-141 | Pseudomonas sp. HC2-4 | 100.00 | JF312947.1 |
| L-142 | Pseudomonas sp. strain P0u25 | 99.92 | MK737101.1 |
| L-143 | Bacillus sp. (in: Bacteria) strain CY1TSA7 | 99.79 | MH974115.1 |
| L-144 | Halomonas alkaliphila X3 | 100.00 | CP024811.1 |
| L-145 | Bacillus altitudinis strain HQ-51-Ba | 100.00 | CP040747.1 |
| L-146 | Bacillus altitudinis strain HQ-51-Ba | 99.85 | CP040747.1 |
| L-147 | Bacillus sp. (in: Bacteria) strain CY1TSA7 | 100.00 | MH974115.1 |
| L-275 | Bacillus flexus strain HDB-2 | 99.72 | MK178593.1 |
| L-276 | Bacillus altitudinis strain NPB34b | 100.00 | MT598007.1 |
| 菌株编号 | 革兰染色 | 氧化酶 | 触酶 | 淀粉酶 | 脲酶 | 吲哚 | 酪素水解 | 产H2S | 明胶水解 | 好氧/厌氧 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| L-141 | - | - | - | + | + | - | + | - | - | + |
| L-142 | + | - | - | - | + | - | + | - | - | + |
| L-143 | + | - | - | - | + | - | + | - | - | + |
| L-144 | + | - | - | - | + | - | + | - | - | + |
| L-145 | + | - | - | - | + | - | + | - | - | + |
| L-146 | + | - | - | - | + | - | + | - | - | + |
| L-147 | + | - | - | - | + | - | + | - | - | + |
| L-275 | + | - | - | - | + | - | + | - | - | + |
| L-276 | + | - | - | + | + | - | + | - | - | + |
表2 耐盐菌株的生理生化特性
Table 2 Physiological properties of halotolerant bacteria
| 菌株编号 | 革兰染色 | 氧化酶 | 触酶 | 淀粉酶 | 脲酶 | 吲哚 | 酪素水解 | 产H2S | 明胶水解 | 好氧/厌氧 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| L-141 | - | - | - | + | + | - | + | - | - | + |
| L-142 | + | - | - | - | + | - | + | - | - | + |
| L-143 | + | - | - | - | + | - | + | - | - | + |
| L-144 | + | - | - | - | + | - | + | - | - | + |
| L-145 | + | - | - | - | + | - | + | - | - | + |
| L-146 | + | - | - | - | + | - | + | - | - | + |
| L-147 | + | - | - | - | + | - | + | - | - | + |
| L-275 | + | - | - | - | + | - | + | - | - | + |
| L-276 | + | - | - | + | + | - | + | - | - | + |
| 煤化工反渗透浓水 | 复合耐盐菌剂法产水 | 臭氧预处理产水 | 臭氧预处理和复合耐盐菌剂法 联合工艺产水 | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 有机物成分 | 占比/% | 有机物成分 | 占比/% | 有机物成分 | 占比/% | 有机物成分 | 占比/% | ||||
| 乙二醇单丁醚 | 2.8 | 四氧杂环己烷 | 4.1 | 乙醇 | 8.5 | 5-乙酰氧基-6(1,2-环氧丙基)-5,6二氢吡喃-2-酮 | 4.5 | ||||
| 四氧杂环己烷 | 0.7 | ||||||||||
| 四氧杂环己烷 | 1.9 | 1-亚硝基-2-哌啶甲酸 | 3.1 | 二氯异乙醚 | 40.9 | 1-甲基-环戊烷羧酸 | 4.9 | ||||
| 1-亚硝基-2-哌啶甲酸 | 3.9 | 环己胺 | 2.5 | 3-己烯-2,5-二醇 | 5.5 | 3-乙基-2-甲基-1-戊烯 | 5.9 | ||||
| 硫代氨基甲酸,N-正环己基S-(2,5-二羟基苯基) | 2.7 | 5-甲基-4-乙烯-3-酮 | 4.5 | 2,3-双环呋喃 | 4.3 | 2,3-双环呋喃 | 5.7 | ||||
| 2,2-甲基-3-乙烯 | 6.5 | 2,3-双环呋喃 | 4.9 | 3-乙基-4-甲基-2-戊烯 | 3.9 | 2,4-二叔丁基苯酚 | 9.9 | ||||
| 2,3-双环呋喃 | 9.3 | 乙基环己烷 | 1.8 | 3-乙基-2-戊烯 | 1.4 | ||||||
| 5,5-二甲基-3-环己烯-1-醇 | 23.1 | 6-exo-vinyl-5-endo-norbornenol | 25.9 | 氯丙醇 | 0.6 | ||||||
| 对二氮杂环 | 2.4 | 2,6-环辛二烯-1-醇 | 2.1 | 二十烷 | 0.4 | ||||||
| 2,4-二叔丁基苯酚 | 2.8 | 2,4-二叔丁基苯酚 | 0.7 | ||||||||
| 二十六烷 | 0.8 | ||||||||||
表3 废水中有机物GC-MS分析
Table 3 Changes of organic compounds before and after biochemical treatment indicated by GC-MS
| 煤化工反渗透浓水 | 复合耐盐菌剂法产水 | 臭氧预处理产水 | 臭氧预处理和复合耐盐菌剂法 联合工艺产水 | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 有机物成分 | 占比/% | 有机物成分 | 占比/% | 有机物成分 | 占比/% | 有机物成分 | 占比/% | ||||
| 乙二醇单丁醚 | 2.8 | 四氧杂环己烷 | 4.1 | 乙醇 | 8.5 | 5-乙酰氧基-6(1,2-环氧丙基)-5,6二氢吡喃-2-酮 | 4.5 | ||||
| 四氧杂环己烷 | 0.7 | ||||||||||
| 四氧杂环己烷 | 1.9 | 1-亚硝基-2-哌啶甲酸 | 3.1 | 二氯异乙醚 | 40.9 | 1-甲基-环戊烷羧酸 | 4.9 | ||||
| 1-亚硝基-2-哌啶甲酸 | 3.9 | 环己胺 | 2.5 | 3-己烯-2,5-二醇 | 5.5 | 3-乙基-2-甲基-1-戊烯 | 5.9 | ||||
| 硫代氨基甲酸,N-正环己基S-(2,5-二羟基苯基) | 2.7 | 5-甲基-4-乙烯-3-酮 | 4.5 | 2,3-双环呋喃 | 4.3 | 2,3-双环呋喃 | 5.7 | ||||
| 2,2-甲基-3-乙烯 | 6.5 | 2,3-双环呋喃 | 4.9 | 3-乙基-4-甲基-2-戊烯 | 3.9 | 2,4-二叔丁基苯酚 | 9.9 | ||||
| 2,3-双环呋喃 | 9.3 | 乙基环己烷 | 1.8 | 3-乙基-2-戊烯 | 1.4 | ||||||
| 5,5-二甲基-3-环己烯-1-醇 | 23.1 | 6-exo-vinyl-5-endo-norbornenol | 25.9 | 氯丙醇 | 0.6 | ||||||
| 对二氮杂环 | 2.4 | 2,6-环辛二烯-1-醇 | 2.1 | 二十烷 | 0.4 | ||||||
| 2,4-二叔丁基苯酚 | 2.8 | 2,4-二叔丁基苯酚 | 0.7 | ||||||||
| 二十六烷 | 0.8 | ||||||||||
| 46 | 任明, 孙淑英, 金艳, 等. 催化臭氧氧化法处理煤化工高盐废水[J]. 环境工程, 2018, 36(8): 54-59. |
| Ren M, Sun S Y, Jin Y, et al. Treatment of high-salt wastewater from coal chemical industry by catalytic ozone oxidation[J]. Environmental Engineering, 2018, 36(8): 54-59. | |
| 47 | Fang F, Han H J. Effect of catalytic ozonation coupling with activated carbon adsorption on organic compounds removal treating RO concentrate from coal gasification wastewater[J]. Ozone: Science & Engineering, 2018, 40(4): 275-283. |
| 48 | Ji Q H, Tabassum S, Hena S, et al. A review on the coal gasification wastewater treatment technologies: past, present and future outlook[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2016, 126: 38-55. |
| 1 | 任同伟, 俞彬, 阳春芳, 等. 煤化工高含盐废水资源化处理技术的工程应用研究[J]. 工业水处理, 2019, 39(2): 96-99. |
| Ren T W, Yu B, Yang C F, et al. Research on the engineering application of the recycling treatment technology of high salinity wastewater in coal chemical industry[J]. Industrial Water Treatment, 2019, 39(2): 96-99. | |
| 2 | 杜松, 金文标, 刘宁, 等. 煤化工高含盐废水有机物的去除研究[J]. 煤炭科学技术, 2019, 47(12): 221-225. |
| Du S, Jin W B, Liu N, et al. Study on removal of organic matter from high-salt wastewater in coal chemical industry[J]. Coal Science and Technology, 2019, 47(12): 221-225. | |
| 3 | 陈莉荣, 邬东, 谷振超, 等. 煤化工含盐废水的处理技术应用进展[J]. 工业水处理, 2019, 39(12): 12-18. |
| Chen L R, Wu D, Gu Z C, et al. Technology application on salt-containing wastewater treatment in coal chemical industry[J]. Industrial Water Treatment, 2019, 39(12): 12-18. | |
| 4 | 赵婷婷, 王真, 郑雯倩. 探讨煤化工废水的处理技术及应用[J]. 中国资源综合利用, 2019, 37(5): 64-66. |
| Zhao T T, Wang Z, Zheng W Q. Discussion on treatment technology and application of coal chemical wastewater[J]. China Resources Comprehensive Utilization, 2019, 37(5): 64-66. | |
| 5 | 曲风臣. 煤化工废水"零排放"技术要点及存在问题[J]. 化学工业, 2013, 31(Z1): 18-24. |
| Qu F C. The key technologies and problems of wastewater zero discharge in coal chemical industry[J]. Chemical Industry, 2013, 31(Z1): 18-24. | |
| 6 | Liu C, Chen X X, Zhang J, et al. Advanced treatment of bio-treated coal chemical wastewater by a novel combination of microbubble catalytic ozonation and biological process[J]. Separation and Purification Technology, 2018, 197: 295-301. |
| 7 | Zheng L X, Han X S, Han T, et al. Formulating a fully converged biorefining chain with zero wastewater generation by recycling stillage liquid to dry acid pretreatment operation[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2020, 318: 124077. |
| 8 | Bian C, Chen H, Song X F, et al. Metastable zone width and the primary nucleation kinetics for cooling crystallization of NaNO3 from NaCl-NaNO3-H2O system[J]. Journal of Crystal Growth, 2019, 518: 5-13. |
| 9 | Bian C, Chen H, Song X F, et al. Effects of organic pollutants on the fractional crystallization of NaNO3 from high-saline wastewater[J]. Journal of Crystal Growth, 2020, 540: 125656. |
| 10 | Liu J, Ou H S, Wei C H, et al. Novel multistep physical/chemical and biological integrated system for coking wastewater treatment: technical and economic feasibility[J]. Journal of Water Process Engineering, 2016, 10: 98-103. |
| 11 | Huang Y, Hou X L, Liu S T, et al. Correspondence analysis of bio-refractory compounds degradation and microbiological community distribution in anaerobic filter for coking wastewater treatment[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2016, 304: 864-872. |
| 12 | Pradhan S, Fan L H, Roddick F A, et al. Impact of salinity on organic matter and nitrogen removal from a municipal wastewater RO concentrate using biologically activated carbon coupled with UV/H2O2[J]. Water Research, 2016, 94: 103-110. |
| 13 | Pradhan S, Fan L H, Roddick F A. Removing organic and nitrogen content from a highly saline municipal wastewater reverse osmosis concentrate by UV/H2O2-BAC treatment[J]. Chemosphere, 2015, 136: 198-203. |
| 14 | Jia S Y, Han Y X, Zhuang H F, et al. Simultaneous removal of organic matter and salt ions from coal gasification wastewater RO concentrate and microorganisms succession in a MBR[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2017, 241: 517-524. |
| 15 | Liu R K, Wang Q, Li M, et al. Advanced treatment of coal chemical reverse osmosis concentrate with three-stage MABR[J]. RSC Advances, 2020, 10(17): 10178-10187. |
| 16 | Lan M C, Li M, Liu J, et al. Coal chemical reverse osmosis concentrate treatment by membrane-aerated biofilm reactor system[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2018, 270: 120-128. |
| 17 | Liu X D, Wu S J, Zhang D J, et al. Simultaneous pyridine biodegradation and nitrogen removal in an aerobic granular system[J]. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 2018, 67: 318-329. |
| 18 | 唐婧, 屈姗姗, 傅金祥, 等. 复合菌剂强化处理高盐废水脱氮效果[J]. 环境工程学报, 2015, 9(6): 2699-2705. |
| Tang J, Qu S S, Fu J X, et al. Efficiency of saline wastewater denitrification by bioaugmentation with composite microbial inoculum[J]. Chinese Journal of Environmental Engineering, 2015, 9(6): 2699-2705. | |
| 19 | Abou-Elela S I, Kamel M M, Fawzy M E. Biological treatment of saline wastewater using a salt-tolerant microorganism[J]. Desalination, 2010, 250(1): 1-5. |
| 20 | Zhuang X L, Han Z, Bai Z H, et al. Progress in decontamination by halophilic microorganisms in saline wastewater and soil[J]. Environmental Pollution, 2010, 158(5): 1119-1126. |
| 21 | 金艳, 张永红, 宋兴福, 等. 一株降解页岩气采出水耐盐菌的分离鉴定与特性[J]. 华东理工大学学报(自然科学版), 2020, 46(6): 722-729. |
| Jin Y, Zhang Y H, Song X F, et al. Identification and characteristics of a salt-tolerant bacteria for shale gas produced water treatment[J]. Journal of East China University of Science and Technology, 2020, 46(6): 722-729. | |
| 22 | 金艳, 张永红, 宋兴福, 等. 耐盐菌MBR系统处理页岩气采出水性能及膜污染特性[J]. 华东理工大学学报(自然科学版), 2020, 46(6): 730-736. |
| Jin Y, Zhang Y H, Song X F, et al. Performance and membrane fouling of produced water from shale gas treated by MBR system with salt-tolerant bacteria[J]. Journal of East China University of Science and Technology, 2020, 46(6): 730-736. | |
| 23 | Tamura K, Peterson D, Peterson N, et al. MEGA5: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis using maximum likelihood, evolutionary distance, and maximum parsimony methods[J]. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 2011, 28(10): 2731-2739. |
| 24 | Thompson J D, Higgins D G, Gibson T J. CLUSTAL W: improving the sensitivity of progressive multiple sequence alignment through sequence weighting, position-specific gap penalties and weight matrix choice[J]. Nucleic Acids Research, 1994, 22(22): 4673-4680. |
| 25 | 孟凡旭, 吴敏, 张会斌, 等. 阿牙克库木湖嗜盐菌的分离及功能酶的筛选[J]. 浙江大学学报(理学版), 2006, 33(6): 671-675. |
| Meng F X, Wu M, Zhang H B, et al. Isolation and enzyme screening of halophilesfrom Ayakekum Lake[J]. Journal of Zhejiang University (Science Edition), 2006, 33(6): 671-675. | |
| 26 | 王晓丽, 于建国. 一个甲烷氧化菌株的分离、鉴定及其特性研究[J]. 微生物学通报, 2008, 35(6): 934-938. |
| Wang X L, Yu J G. Isolation, identification and characterization of a methanotrophic strain[J]. Microbiology, 2008, 35(6): 934-938. | |
| 27 | 张浩, 刘玉香, 呼婷婷, 等. 一株苯胺降解菌的分离及其降解特性[J]. 环境工程学报, 2015, 9(12): 6154-6160. |
| Zhang H, Liu Y X, Hu T T, et al. Isolation and characterization of an aniline-degrading bacterium[J]. Chinese Journal of Environmental Engineering, 2015, 9(12): 6154-6160. | |
| 28 | 高廷耀, 顾国维, 周琪. 水污染控制工程[M]. 北京: 高等教育出版社, 2007. |
| Gao T Y, Gu G W, Zhou Q. Water Pollution Control Engineering [M]. Beijing: Higher Education Press, 2007. | |
| 29 | Ahmadi M, Ahmadmoazzam M, Saeedi R, et al. Biological treatment of a saline and recalcitrant petrochemical wastewater by using a newly isolated halo-tolerant bacterial consortium in MBBR[J]. Desalination and Water Treatment, 2019, 167: 84-95. |
| 30 | Qu J H, Chen X L, Zhou J, et al. Treatment of real sodium saccharin wastewater using multistage contact oxidation reactor and microbial community analysis[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2019, 289: 121714. |
| 31 | Yan Y X, Yang J, Zhu Z Y, et al. Enhancing performance evaluation and microbial community analysis of the biofilter for toluene removal by adding polyethylene glycol-600 into the nutrient solution[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2021, 330: 124954. |
| 32 | Wang Q, Wu X G, Jiang L H, et al. Effective degradation of di-n-butyl phthalate by reusable, magnetic Fe3O4 nanoparticle-immobilized Pseudomonas sp. W1 and its application in simulation[J]. Chemosphere, 2020, 250: 126339. |
| 33 | Wang J L, Zhou J, Wang Y M, et al. Efficient nitrogen removal in a modified sequencing batch biofilm reactor treating hypersaline mustard tuber wastewater: the potential multiple pathways and key microorganisms[J]. Water Research, 2020, 177: 115734. |
| 34 | Zerva I, Remmas N, Melidis P, et al. Biotreatment efficiency, hydrolytic potential and bacterial community dynamics in an immobilized cell bioreactor treating caper processing wastewater under highly saline conditions[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2021, 325: 124694. |
| 35 | Haddadi A, Shavandi M. Biodegradation of phenol in hypersaline conditions by Halomonas sp strain PH2-2 isolated from saline soil[J]. International Biodeterioration & Biodegradation, 2013, 85: 29-34. |
| 36 | Piubeli F, Grossman M J, Fantinatti-Garboggini F, et al. Enhanced reduction of COD and aromatics in petroleum-produced water using indigenous microorganisms and nutrient addition[J]. International Biodeterioration & Biodegradation, 2012, 68: 78-84. |
| 37 | Fimlaid K A, Shen A. Diverse mechanisms regulate sporulation sigma factor activity in the Firmicutes[J]. Current Opinion in Microbiology, 2015, 24: 88-95. |
| 38 | Khanpour-Alikelayeh E, Partovinia A, Talebi A, et al. Investigation of Bacilluslicheniformis in the biodegradation of Iranian heavy crude oil: a two-stage sequential approach containing factor-screening and optimization[J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 2020, 205: 111103. |
| 39 | Koops H P, Pommerening-Röser A. Distribution and ecophysiology of the nitrifying bacteria emphasizing cultured species[J]. FEMS Microbiology Ecology, 2001, 37(1): 1-9. |
| 40 | Santorelli M, Maurelli L, Pocsfalvi G, et al. Isolation and characterisation of a novel alpha-amylase from the extreme haloarchaeon Haloterrigena turkmenica[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 2016, 92: 174-184. |
| 41 | Kargi F, Dinçer A R. Saline wastewater treatment by halophile-supplemented activated sludge culture in an aerated rotating biodisc contactor[J]. Enzyme and Microbial Technology, 1998, 22(6): 427-433. |
| 42 | Hou M, Li W, Li H, et al. Performance and bacterial characteristics of aerobic granular sludge in response to alternating salinity[J]. International Biodeterioration & Biodegradation, 2019, 142: 211-217. |
| 43 | Wang D X, Han Y X, Han H J, et al. Enhanced treatment of Fischer-Tropsch wastewater using up-flow anaerobic sludge blanket system coupled with micro-electrolysis cell: a pilot scale study[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2017, 238: 333-342. |
| 44 | 俞汉青, 郑煜铭, 顾国维, 等. 活性污泥对四种非极性有机物的吸附[J]. 环境科学学报, 2003, 23(4): 546-548. |
| Yu H Q, Zheng Y M, Gu G W, et al. Sorption of four non-poplar organic compounds by activated sludge[J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 2003, 23(4): 546-548. | |
| 45 | Álvarez P M, Beltrán F J, Pocostales J P, et al. Preparation and structural characterization of Co/Al2O3 catalysts for the ozonation of pyruvic acid[J]. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 2007, 72(3/4): 322-330. |
| [1] | 杨百玉, 寇悦, 姜峻韬, 詹亚力, 王庆宏, 陈春茂. 炼化碱渣湿式氧化预处理过程DOM的化学转化特征[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(9): 3912-3920. |
| [2] | 杨欣, 彭啸, 薛凯茹, 苏梦威, 吴燕. 分子印迹-TiO2光电催化降解增溶PHE废水性能研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(8): 3564-3571. |
| [3] | 吕龙义, 及文博, 韩沐达, 李伟光, 高文芳, 刘晓阳, 孙丽, 王鹏飞, 任芝军, 张光明. 铁基导电材料强化厌氧去除卤代有机污染物:研究进展及未来展望[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(8): 3193-3202. |
| [4] | 朱理想, 罗默也, 张晓东, 龙涛, 余冉. 醌指纹法指示三氯乙烯污染土功能微生物活性应用研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(6): 2647-2654. |
| [5] | 张艳梅, 袁涛, 李江, 刘亚洁, 孙占学. 高效SRB混合菌群构建及其在酸胁迫条件下的性能研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(6): 2599-2610. |
| [6] | 张兰河, 赖青燚, 王铁铮, 关潇卓, 张明爽, 程欣, 徐小惠, 贾艳萍. H2O2对SBR脱氮效率和污泥性能的影响[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(5): 2186-2196. |
| [7] | 李瑞康, 何盈盈, 卢维鹏, 王园园, 丁皓东, 骆勇名. 电化学强化钴基阴极活化过一硫酸盐的研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(5): 2207-2216. |
| [8] | 张建华, 陈萌萌, 孙雅雯, 彭永臻. 部分短程硝化同步除磷耦合Anammox实现生活污水高效脱氮除磷[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(5): 2147-2156. |
| [9] | 吴学红, 栾林林, 陈亚南, 赵敏, 吕财, 刘勇. 可降解柔性相变薄膜的制备及其热性能[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(4): 1818-1826. |
| [10] | 胡香凝, 尹渊博, 袁辰, 是赟, 刘翠伟, 胡其会, 杨文, 李玉星. 成品油在土壤中运移可视化的实验研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(4): 1827-1835. |
| [11] | 徐银, 蔡洁, 陈露, 彭宇, 刘夫珍, 张晖. 异相可见光催化耦合过硫酸盐活化技术在水污染控制中的研究进展[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(3): 995-1009. |
| [12] | 祖凌鑫, 胡荣庭, 李鑫, 陈余道, 陈广林. 木质生物质化学组分的碳释放产物特征和反硝化利用程度[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(3): 1332-1342. |
| [13] | 刘定平, 陈爱桦, 张向阳, 何文浩, 王海. 铝灰半干法水解脱氮研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(3): 1294-1302. |
| [14] | 闫新龙, 黄志刚, 胡清勋, 张新, 胡晓燕. Cu/Co掺杂多孔炭活化过硫酸盐降解水中硝基酚研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(3): 1102-1112. |
| [15] | 王思琪, 顾天宇, 陈献富, 王通, 李佳, 柯威, 李小锋, 范益群. 陶瓷膜用于杜仲叶提取液澄清的分离特性与膜污染机制研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(3): 1113-1125. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备 11010102001995号
京公网安备 11010102001995号