化工学报 ›› 2023, Vol. 74 ›› Issue (5): 1904-1913.DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20230340
收稿日期:2023-04-06
修回日期:2023-05-07
出版日期:2023-05-05
发布日期:2023-06-29
通讯作者:
姜晓滨
作者简介:李正涛(1997—),男,硕士研究生,zhengtaoli@mail.dlut.edu.cn
基金资助:
Zhengtao LI( ), Zhijie YUAN, Gaohong HE, Xiaobin JIANG(
), Zhijie YUAN, Gaohong HE, Xiaobin JIANG( )
)
Received:2023-04-06
Revised:2023-05-07
Online:2023-05-05
Published:2023-06-29
Contact:
Xiaobin JIANG
摘要:
盐水微液滴蒸发结晶在海水淡化、晶体制备、药物预混合和颗粒筛选中具有非常重要的作用。通过计算流体动力学模型,对不同疏水界面传热系数和不同直径疏水平台上的NaCl盐水液滴蒸发过程开展模拟研究,主要通过模拟预测了液滴内流体在温度和浓度差作用下的环流演变机制。模拟结果通过光学可视化和红外热成像仪进行了验证。结果表明,常温蒸发下,NaCl液滴内部的环流主要由Rayleigh对流和溶质Marangoni效应主导。不同的固液界面传热系数会影响液滴的升温速率和温度分布,当温差大于一定值时,热Marangoni效应可以主导液滴内部环流。基于Rayleigh数和Marangoni数的调控区间制得了流场演变相图,有效地预测液滴内部的环流状态。盐水液滴内环流方向和持续时间可以通过调整热Marangoni效应来控制,从而影响最终蒸发结晶的晶体形貌和沉积分布。这项工作可以为蒸发界面设计、蒸发结晶的过程控制等提供理论依据。
中图分类号:
李正涛, 袁志杰, 贺高红, 姜晓滨. 疏水界面上的NaCl液滴蒸发过程内环流调控机制研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(5): 1904-1913.
Zhengtao LI, Zhijie YUAN, Gaohong HE, Xiaobin JIANG. Study of the mechanism of internal circulation regulation during evaporation of NaCl droplets on hydrophobic interface[J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(5): 1904-1913.
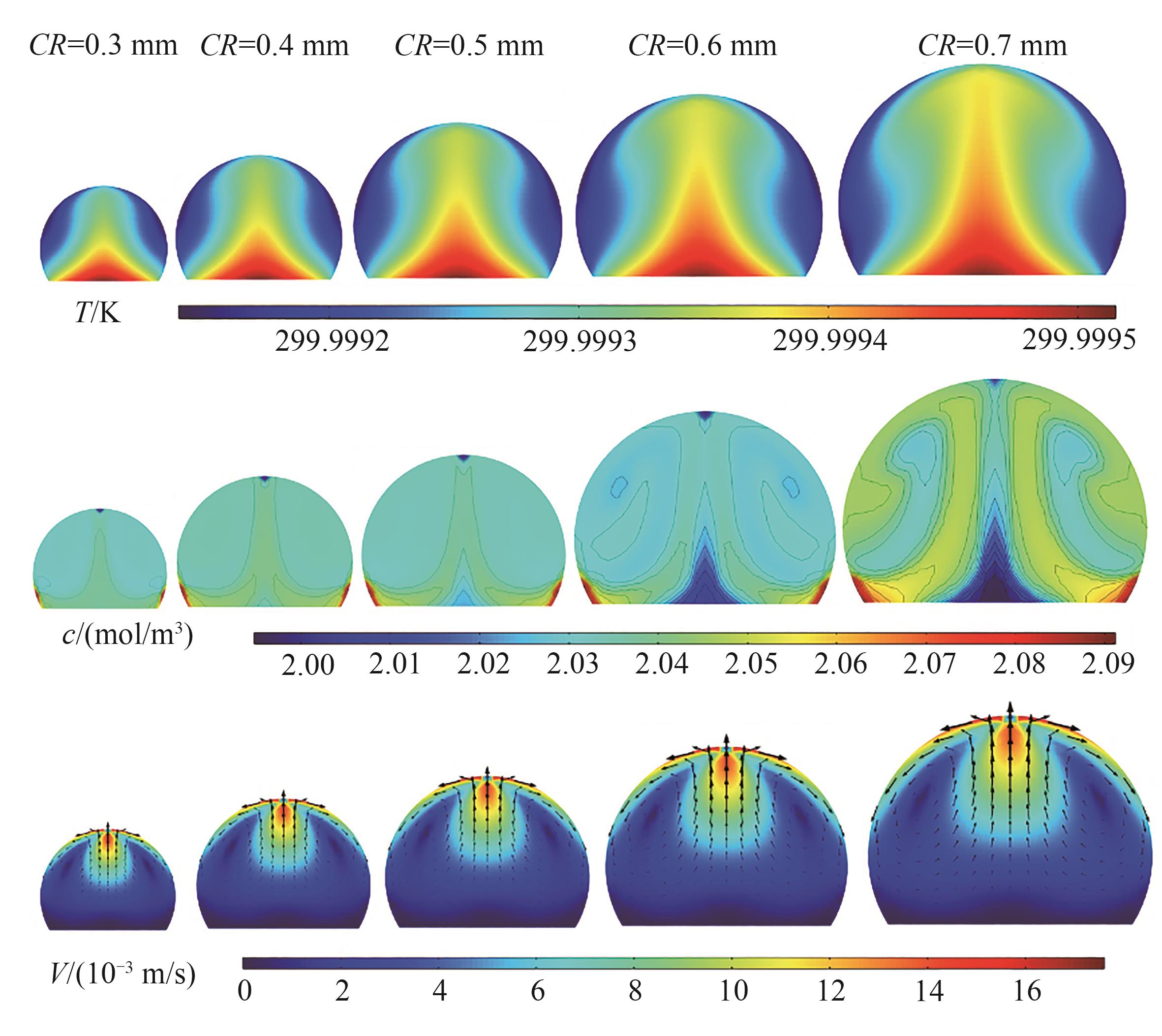
图6 接触角为120°不同接触半径液滴的温度、浓度和速度云图
Fig.6 Temperature, concentration and velocity clouds for droplets with different contact radius at a contact angle of 120°
| 1 | Xu R N, Wang G Y, Jiang P X. Spray cooling on enhanced surfaces: a review of the progress and mechanisms[J]. Journal of Electronic Packaging, 2022, 144(1): 010802. |
| 2 | 沈胜强, 周士鹤, 牟兴森, 等. 大型低温多效蒸发海水淡化装置传热过程热力损失分析[J]. 化工学报, 2014, 65(9): 3366-3374. |
| Shen S Q, Zhou S H, Mu X S, et al. Analysis of thermodynamic losses of heat transfer process in large-scale LT-MED desalination plant[J]. CIESC Journal, 2014, 65(9): 3366-3374. | |
| 3 | Tijing L D, Woo Y C, Choi J S, et al. Fouling and its control in membrane distillation—a review[J]. Journal of Membrane Science, 2015, 475: 215-244. |
| 4 | Garcia-Cordero J L, Fan Z H. Sessile droplets for chemical and biological assays[J]. Lab on a Chip, 2017, 17(13): 2150-2166. |
| 5 | Hernandez-Perez R, Fan Z H, Garcia-Cordero J L. Evaporation-driven bioassays in suspended droplets[J]. Analytical Chemistry, 2016, 88(14): 7312-7317. |
| 6 | Wong T S, Chen T H, Shen X Y, et al. Nanochromatography driven by the coffee ring effect[J]. Analytical Chemistry, 2011, 83(6): 1871-1873. |
| 7 | Jeong H, Han C, Cho S, et al. Analysis of extracellular vesicles using coffee ring[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2018, 10(27): 22877-22882. |
| 8 | Deegan R D, Bakajin O, Dupont T F, et al. Capillary flow as the cause of ring stains from dried liquid drops[J]. Nature, 1997, 389(6653): 827-829. |
| 9 | Hu H, Larson R G. Marangoni effect reverses coffee-ring depositions[J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry. B, 2006, 110(14): 7090-7094. |
| 10 | Hu H, Larson R G. Analysis of the effects of Marangoni stresses on the microflow in an evaporating sessile droplet[J]. Langmuir, 2005, 21(9): 3972-3980. |
| 11 | Hu H, Larson R G. Analysis of the microfluid flow in an evaporating sessile droplet[J]. Langmuir, 2005, 21(9): 3963-3971. |
| 12 | Hu H, Larson R G. Evaporation of a sessile droplet on a substrate[J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry B, 2002, 106(6): 1334-1344. |
| 13 | Lee S J, Hong J, Choi Y S. Evaporation-induced flows inside a confined droplet of diluted saline solution[J]. Langmuir, 2014, 30(26): 7710-7715. |
| 14 | Mampallil D, Eral H B. A review on suppression and utilization of the coffee-ring effect[J]. Advances in Colloid and Interface Science, 2018, 252: 38-54. |
| 15 | Kaneda M, Takao Y, Jun F K. Thermal and solutal effects on convection inside a polymer solution droplet on a substrate[J]. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 2010, 53(21/22): 4448-4457. |
| 16 | Misyura S Y, Volkov R S, Filatova A S. Interaction of two drops at different temperatures: the role of thermocapillary convection and surfactant[J]. Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 2018, 559: 275-283. |
| 17 | Strizhak P A, Volkov R S, Misyura S Y, et al. The role of convection in gas and liquid phases at droplet evaporation[J]. International Journal of Thermal Sciences, 2018, 134: 421-439. |
| 18 | Wang Z Y, Karapetsas G, Valluri P, et al. Dynamics of hygroscopic aqueous solution droplets undergoing evaporation or vapour absorption[J]. Journal of Fluid Mechanics, 2021, 912: A2. |
| 19 | 金铭, 胡定华, 李强, 等. Al2O3纳米流体液滴蒸发特性的数值模拟研究[J]. 化工学报, 2019, 70(11): 4199-4206. |
| Jin M, Hu D H, Li Q, et al. Simulation of sessile nanofluid droplet evaporation character[J]. CIESC Journal, 2019, 70(11): 4199-4206. | |
| 20 | Kim J H, Park S B, Kim J H, et al. Polymer transports inside evaporating water droplets at various substrate temperatures[J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2011, 115(31): 15375-15383. |
| 21 | Teng L, Wang W F, Huang X, et al. Evaporation of sessile droplet on surfaces with various wettability[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2023, 268: 118413. |
| 22 | Li Y X, Lv P Y, Diddens C, et al. Evaporation-triggered segregation of sessile binary droplets[J]. Physical Review Letters, 2018, 120(22): 224501. |
| 23 | van Gaalen R T, Wijshoff H M A, Kuerten J G M, et al. Competition between thermal and surfactant-induced Marangoni flow in evaporating sessile droplets[J]. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 2022, 622: 892-903. |
| 24 | Kumar V, Dash S. Patterns during evaporative crystallization of a saline droplet[J]. Langmuir, 2022, 38(33): 10265-10273. |
| 25 | 金艳艳, 单彦广. 水-乙醇二元混合固着液滴的蒸发特性[J]. 化工学报, 2018, 69(7): 2908-2915. |
| Jin Y Y, Shan Y G. Evaporation characteristics of sessile ethanol-water mixture droplets[J]. CIESC Journal, 2018, 69(7): 2908-2915. | |
| 26 | Gavrilina A A, Barash L Y. Modeling unsteady Bénard-marangoni instabilities in drying volatile droplets on a heated substrate[J]. Journal of Experimental and Theoretical Physics, 2021, 132(2): 302-312. |
| 27 | Efstratiou M, Christy J, Sefiane K. Crystallization-driven flows within evaporating aqueous saline droplets[J]. Langmuir, 2020, 36(18): 4995-5002. |
| 28 | Li Y X, Diddens C, Lv P Y, et al. Gravitational effect in evaporating binary microdroplets[J]. Physical Review Letters, 2019, 122(11): 114501. |
| 29 | Savino R, Monti R. Buoyancy and surface-tension-driven convection in hanging-drop protein crystallizer[J]. Journal of Crystal Growth, 1996, 165(3): 308-318. |
| 30 | A M J Edwards, S Atkinson P, S Cheung C, et al. Density-driven flows in evaporating binary liquid droplets[J]. Physical Review Letters, 2018, 121(18): 184501. |
| 31 | Kang K H, Lim H C, Lee H W, et al. Evaporation-induced saline Rayleigh convection inside a colloidal droplet[J]. Physics of Fluids, 2013, 25(4): 042001. |
| 32 | Pradhan T K, Panigrahi P K. Evaporation induced natural convection inside a droplet of aqueous solution placed on a superhydrophobic surface[J]. Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 2017, 530: 1-12. |
| 33 | Diddens C, Li Y X, Lohse D. Competing Marangoni and Rayleigh convection in evaporating binary droplets[J]. Journal of Fluid Mechanics, 2021, 914: A23. |
| 34 | Yuan Z J, Li Z T, Wu M Y, et al. Shaping droplet by semiflexible micro crystallizer for high quality crystal harvest[J]. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 2023, 629: 334-345. |
| 35 | Han M G, Li J, He G H, et al. Tailored 3D printed micro-crystallization chip for versatile and high-efficiency droplet evaporative crystallization[J]. Lab on a Chip, 2019, 19(5): 767-777. |
| 36 | Misyura S Y, Strizhak P A, Volkov R S, et al. The influence of the wall microtexture on functional properties and heat transfer[J]. Journal of Molecular Liquids, 2019, 294: 111670. |
| 37 | Ristenpart W D, Kim P G, Domingues C, et al. Influence of substrate conductivity on circulation reversal in evaporating drops[J]. Physical Review Letters, 2007, 99(23): 234502. |
| [1] | 张思雨, 殷勇高, 贾鹏琦, 叶威. 双U型地埋管群跨季节蓄热特性研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(S1): 295-301. |
| [2] | 肖明堃, 杨光, 黄永华, 吴静怡. 浸没孔液氧气泡动力学数值研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(S1): 87-95. |
| [3] | 温凯杰, 郭力, 夏诏杰, 陈建华. 一种耦合CFD与深度学习的气固快速模拟方法[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(9): 3775-3785. |
| [4] | 汪林正, 陆俞冰, 张睿智, 罗永浩. 基于分子动力学模拟的VOCs热氧化特性分析[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(8): 3242-3255. |
| [5] | 邢雷, 苗春雨, 蒋明虎, 赵立新, 李新亚. 井下微型气液旋流分离器优化设计与性能分析[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(8): 3394-3406. |
| [6] | 岳林静, 廖艺涵, 薛源, 李雪洁, 李玉星, 刘翠伟. 凹坑缺陷对厚孔板喉部空化流动特性影响研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(8): 3292-3308. |
| [7] | 牛超, 沈胜强, 杨艳, 潘泊年, 李熠桥. 甲烷BOG喷射器流动过程计算与性能分析[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(7): 2858-2868. |
| [8] | 何晓崐, 刘锐, 薛园, 左然. MOCVD生长AlN单晶薄膜的气相和表面化学反应综述[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(7): 2800-2813. |
| [9] | 邵远哲, 赵忠盖, 刘飞. 基于共同趋势模型的非平稳过程质量相关故障检测方法[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(6): 2522-2537. |
| [10] | 刘道银, 陈柄岐, 张祖扬, 吴琰. 颗粒聚团结构对曳力特性影响的数值模拟[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(6): 2351-2362. |
| [11] | 李晨曦, 刘永峰, 张璐, 刘海峰, 宋金瓯, 何旭. O2/CO2氛围下正庚烷的燃烧机理研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(5): 2157-2169. |
| [12] | 董鑫, 单永瑞, 刘易诺, 冯颖, 张建伟. 非牛顿流体气泡羽流涡特性数值模拟研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(5): 1950-1964. |
| [13] | 周艾然, 陆平, 夏建辉, 李冬勤, 郭杰, 杜明, 董立春. 氯化钛白氧化反应器结疤问题分析及数值模拟[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(4): 1499-1508. |
| [14] | 李亚飞, 邓建强, 何阳. 跨临界CO2快速膨胀过程中非平衡冷凝和闪蒸机理的数值研究[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(7): 2912-2923. |
| [15] | 魏琳, 郭剑, 廖梓豪, Dafalla Ahmed Mohmed, 蒋方明. 空气流量对空冷燃料电池电堆性能的影响研究[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(7): 3222-3231. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备 11010102001995号
京公网安备 11010102001995号