化工学报 ›› 2024, Vol. 75 ›› Issue (9): 3083-3093.DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20240348
收稿日期:2024-03-28
修回日期:2024-05-13
出版日期:2024-09-25
发布日期:2024-10-10
通讯作者:
徐强,郭烈锦
作者简介:罗欣怡(1999—),女,博士研究生,lxy15982992539@stu.xjtu.edu.cn
基金资助:
Xinyi LUO( ), Qiang XU(
), Qiang XU( ), Yonglu SHE, Tengfei NIE, Liejin GUO(
), Yonglu SHE, Tengfei NIE, Liejin GUO( )
)
Received:2024-03-28
Revised:2024-05-13
Online:2024-09-25
Published:2024-10-10
Contact:
Qiang XU, Liejin GUO
摘要:
光电极表面长时间连续生长的气泡是影响光电分解水制氢效率的重要因素。利用光电化学与气泡动力学多参数同步原位测量分析方法,系统研究了激光功率和电解池内压力对气泡动力学特性和气液界面传质过程的影响。结果表明,不同激光功率和压力下的气泡在脱离之前遵循相似的生长规律。气体质量产率在80 kPa取得极值,表明适当降低压力有利于气体的产生。此外,随着压力降低气泡脱离直径增大,周期缩短。对比考虑不同Marangoni力的力平衡模型,发现同时考虑浓度Marangoni力和热Marangoni力的力平衡模型对气泡脱离直径的预测误差小于5%,浓度Marangoni力是不同压力下影响气泡脱离直径的主要因素。通过求解传质系数,发现在低光电流密度内,不同压力条件下气液传质以单相自然微对流为主,但随着光电流密度的增大,气液界面扩张引起的气泡诱导微对流传质作用增强。
中图分类号:
罗欣怡, 徐强, 佘永璐, 聂腾飞, 郭烈锦. 光电分解水制氢气泡动力学特性及其传质机理研究[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(9): 3083-3093.
Xinyi LUO, Qiang XU, Yonglu SHE, Tengfei NIE, Liejin GUO. Study on bubble dynamic characteristics and mass transfer mechanism in photoelectrochemical water splitting for hydrogen production[J]. CIESC Journal, 2024, 75(9): 3083-3093.
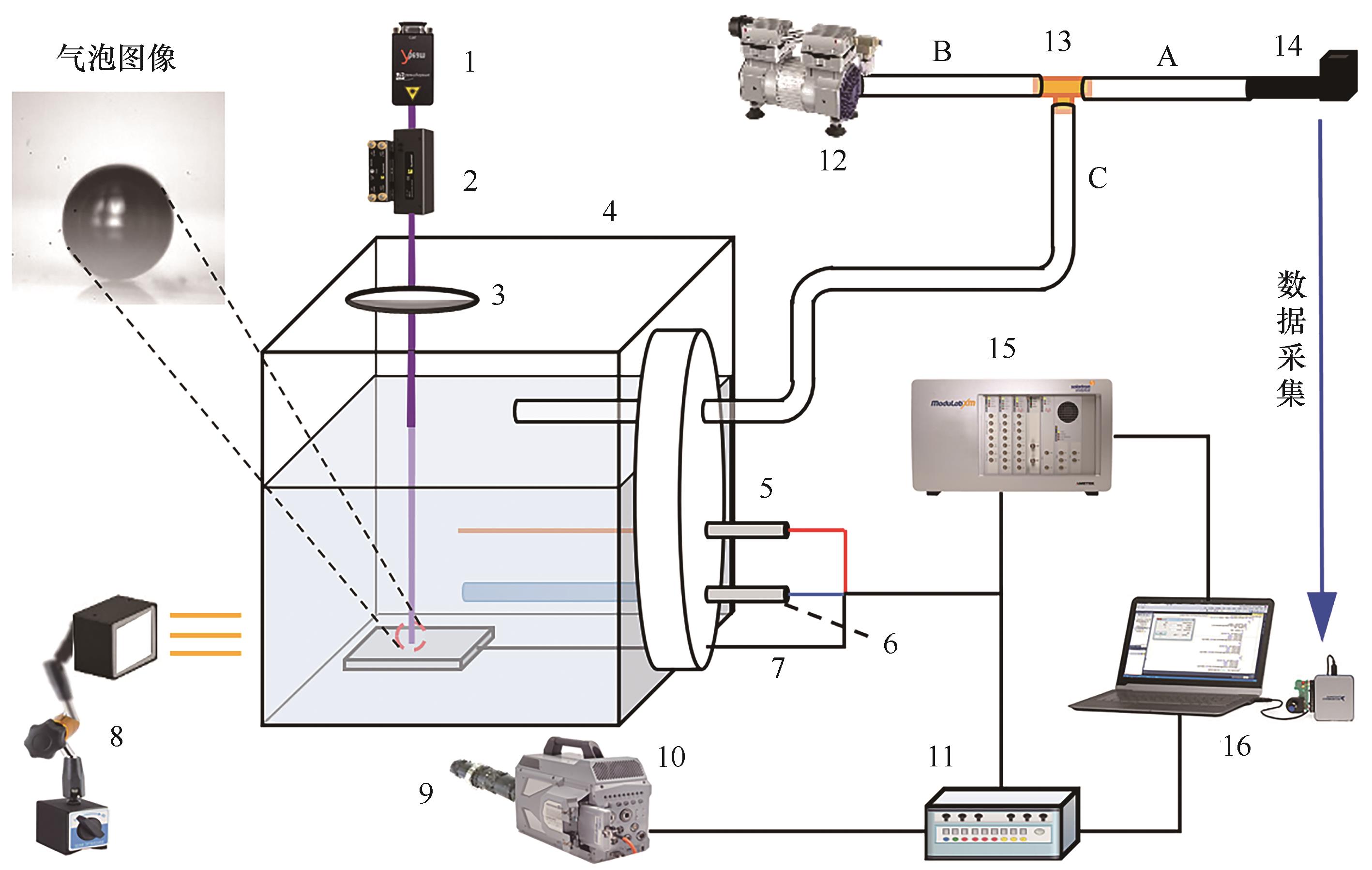
图1 光电分解水制氢气泡动力学与光电化学同步原位测试实验平台1—激光器;2—扩束器;3—光学透镜;4—密封电解池;5—铂丝电极(对电极);6—饱和Ag/AgCl电极(参比电极);7—TiO2薄膜电极(工作电极);8—LED光源;9—显微镜头;10—高速摄像机;11—同步器;12—真空泵;13—三通阀;14—压力传感器;15—电化学工作站;16—计算机及采集卡
Fig.1 Experimental platform for bubble dynamics and photoelectrochemical synchronous in-situ test in photoelectrochemical water splitting for hydrogen production
| 实验参数 | 数值 |
|---|---|
| 室温T/K | 293.15 |
| 大气压p0/kPa | 97 |
| 实验系统压力p/kPa | 60~97 |
| 电解液表面张力γ/(N·m-1) | 0.072 |
| 电解液密度ρL/(kg·m-3) | 1.0664×103 |
| 电解液运动黏度νL/(m2·s-1) | 10-6 |
| 激光光斑半径rlaser/nm | 500 |
| 激光功率W/mW | 8~12 |
| 外加偏压U(vs饱和Ag/AgCl)/V | 0.2 |
| 电化学工作站采样频率f/s-1 | 103 |
| 高速摄像机拍摄帧率v/(帧·s-1) | 103 |
| 高速摄像机分辨率 | 512×512 |
| 显微镜放大倍率 | 12.5 |
表1 单气泡动力学实验的参数设置
Table 1 Parameter settings for single bubble dynamics experiment
| 实验参数 | 数值 |
|---|---|
| 室温T/K | 293.15 |
| 大气压p0/kPa | 97 |
| 实验系统压力p/kPa | 60~97 |
| 电解液表面张力γ/(N·m-1) | 0.072 |
| 电解液密度ρL/(kg·m-3) | 1.0664×103 |
| 电解液运动黏度νL/(m2·s-1) | 10-6 |
| 激光光斑半径rlaser/nm | 500 |
| 激光功率W/mW | 8~12 |
| 外加偏压U(vs饱和Ag/AgCl)/V | 0.2 |
| 电化学工作站采样频率f/s-1 | 103 |
| 高速摄像机拍摄帧率v/(帧·s-1) | 103 |
| 高速摄像机分辨率 | 512×512 |
| 显微镜放大倍率 | 12.5 |
| 1 | Wolcott A, Smith W A, Kuykendall T R, et al. Photoelectrochemical water splitting using dense and aligned TiO2 nanorod arrays[J]. Small, 2009, 5(1): 104-111. |
| 2 | 郭烈锦, 曹振山, 王晔春, 等. 太阳能光催化分解水气泡动力学研究进展[J]. 西安交通大学学报, 2023, 57(3): 1-22. |
| Guo L J, Cao Z S, Wang Y C, et al. Review of bubble dynamics in solar photocatalytic water splitting[J]. Journal of Xi’an Jiaotong University, 2023, 57(3): 1-22. | |
| 3 | Swiegers G F, Terrett R N L, Tsekouras G, et al. The prospects of developing a highly energy-efficient water electrolyser by eliminating or mitigating bubble effects[J]. Sustainable Energy & Fuels, 2021, 5(5): 1280-1310. |
| 4 | Pinaud B A, Benck J D, Seitz L C, et al. Technical and economic feasibility of centralized facilities for solar hydrogen production via photocatalysis and photoelectrochemistry[J]. Energy & Environmental Science, 2013, 6(7): 1983-2002. |
| 5 | Maeda K, Domen K. Photocatalytic water splitting: recent progress and future challenges[J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry Letters, 2010, 1(18): 2655-2661. |
| 6 | Luo X Y, Xu Q, Nie T F, et al. Influence of subatmospheric pressure on bubble evolution on the TiO2 photoelectrode surface[J]. Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics, 2023, 25(23): 16086-16104. |
| 7 | Cao Z S, Wang Y C, Xu Q, et al. Visualization of bubble dynamic behaviors during photoelectrochemical water splitting with TiO2 photoelectrode[J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2020, 347: 136230. |
| 8 | Wang M S, Nie T F, She Y L, et al. Study on the behavior of single oxygen bubble regulated by salt concentration in photoelectrochemical water splitting[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2023, 48(61): 23387-23401. |
| 9 | Lu X L, Nie T F, Li X P, et al. Insight into pH-controlled bubble dynamics on a Pt electrode during electrochemical water splitting[J]. Physics of Fluids, 2023, 35(10): 103314. |
| 10 | Nie T F, Xu Q, She Y L, et al. The behavior of surface nanobubbles on different substrates in electrochemistry[J]. Journal of Molecular Liquids, 2024, 394: 123791. |
| 11 | She Y L, Xu Q, Nie T F, et al. In situ investigation of oxygen bubble evolution at photoanode surface affected by reaction temperature[J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2023, 127(29): 14197-14210. |
| 12 | Sielaff A, Dietl J, Herbert S, et al. The influence of system pressure on bubble coalescence in nucleate boiling[J]. Heat Transfer Engineering, 2014, 35(5): 420-429. |
| 13 | Matsushima H, Iida T, Fukunaka Y. Observation of bubble layer formed on hydrogen and oxygen gas-evolving electrode in a magnetic field[J]. Journal of Solid State Electrochemistry, 2012, 16(2): 617-623. |
| 14 | Timmermann J, Hoffmann M, Schlüter M. Influence of bubble bouncing on mass transfer and chemical reaction[J]. Chemical Engineering & Technology, 2016, 39(10): 1955-1962. |
| 15 | Vogt H, Stephan K. Local microprocesses at gas-evolving electrodes and their influence on mass transfer[J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2015, 155: 348-356. |
| 16 | Guo L J, Chen Y B, Su J Z, et al. Obstacles of solar-powered photocatalytic water splitting for hydrogen production: a perspective from energy flow and mass flow[J]. Energy, 2019, 172: 1079-1086. |
| 17 | Jianu O A, Rosen M A, Naterer G F, et al. Two-phase bubble flow and convective mass transfer in water splitting processes[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2015, 40(11): 4047-4055. |
| 18 | Cao Z S, Zhang B, Feng Y Y, et al. Mass transfer mechanism during bubble evolution on the surface of photoelectrode[J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2022, 434: 141293. |
| 19 | Wang M S, Xu Q, Nie T F, et al. Growth characteristics and the mass transfer mechanism of single bubble on a photoelectrode at different electrolyte concentrations[J]. Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics, 2023, 25(41): 28497-28509. |
| 20 | 韩宁宁, 许壮, 何广利. 电解水制高压氢气——技术挑战与研究进展[J]. 储能科学与技术, 2024, 13(2): 626-633. |
| Han N N, Xu Z, He G L. Pressurized water electrolysis—Challenge and recent progress[J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2024, 13(2): 626-633. | |
| 21 | Fujishima A, Zhang X T, Tryk D. TiO2 photocatalysis and related surface phenomena[J]. Surface Science Reports, 2008, 63(12): 515-582. |
| 22 | van der Linde P, Peñas-López P, Moreno Soto Á, et al. Gas bubble evolution on microstructured silicon substrates[J]. Energy & Environmental Science, 2018, 11(12): 3452-3462. |
| 23 | Brandon N P, Kelsall G H. Growth kinetics of bubbles electrogenerated at microelectrodes[J]. Journal of Applied Electrochemistry, 1985, 15(4): 475-484. |
| 24 | Lu X L, Nie T F, Yadav D, et al. Enhancing hydrogen bubble release from a microelectrode through precise tuning of Marangoni forces with nonionic surfactant[J]. Physics of Fluids, 2024, 36(1): 013335. |
| 25 | Matsushima H, Kiuchi D, Fukunaka Y, et al. Single bubble growth during water electrolysis under microgravity[J]. Electrochemistry Communications, 2009, 11(8): 1721-1723. |
| 26 | Robinson A J, Judd R L. The dynamics of spherical bubble growth[J]. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 2004, 47(23): 5101-5113. |
| 27 | Scriven L E. On the dynamics of phase growth[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 1959, 10(1/2): 1-13. |
| 28 | Hu X W, Wang Y C, Guo L J, et al. Diffusion-controlled growth of oxygen bubble evolved from nanorod-array TiO2 photoelectrode[J]. Advances in Condensed Matter Physics, 2014, 2014: 970891. |
| 29 | Liu H B, Pan L M, Wen J. Numerical simulation of hydrogen bubble growth at an electrode surface[J]. The Canadian Journal of Chemical Engineering, 2016, 94(1): 192-199. |
| 30 | Hu X W, Cao Z S, Wang Y C, et al. Single photogenerated bubble at gas-evolving TiO2 nanorod-array electrode[J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2016, 202: 175-185. |
| 31 | Nie T F, Li Z Q, Luo X Y, et al. Single bubble dynamics on a TiO2 photoelectrode surface during photoelectrochemical water splitting[J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2022, 436: 141394. |
| 32 | Bernardin J D, Mudawar I, Walsh C B, et al. Contact angle temperature dependence for water droplets on practical aluminum surfaces[J]. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 1997, 40(5): 1017-1033. |
| 33 | Lax M. Temperature rise induced by a laser beam[J]. Journal of Applied Physics, 1977, 48(9): 3919-3924. |
| 34 | Mun J, Kim S W, Kato R, et al. Measurement of the thermal conductivity of TiO2 thin films by using the thermo-reflectance method[J]. Thermochimica Acta, 2007, 455(1/2): 55-59. |
| 35 | Brian P L T. Effect of Gibbs adsorption on Marangoni instability[J]. AIChE Journal, 1971, 17(4): 765-772. |
| 36 | Hardy S C. The motion of bubbles in a vertical temperature gradient[J]. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 1979, 69(1): 157-162. |
| 37 | Lubetkin S. Thermal Marangoni effects on gas bubbles are generally accompanied by solutal Marangoni effects [J]. Langmuir, 2003, 19(26): 10774-10778. |
| 38 | Lubetkin S. The motion of electrolytic gas bubbles near electrodes[J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2002, 48(4): 357-375. |
| 39 | Luo X Y, Xu Q, Ye X M, et al. Mass transfer mechanism of single bubble evolution on TiO2 electrode surface under decreased pressure[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2024, 61: 859-872. |
| 40 | Ye X M, Xu Q, Nie T F, et al. Study on bubble dynamics in photoelectrochemical water splitting with low-rate flow fields[J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2023, 127(45): 22085-22096. |
| 41 | Vogt H. The concentration overpotential of gas evolving electrodes as a multiple problem of mass transfer[J]. Journal of the Electrochemical Society, 1990, 137(4): 1179-1184. |
| 42 | Vogt H. Interfacial supersaturation at gas evolving electrodes[J]. Journal of Applied Electrochemistry, 1993, 23(12): 1323-1325. |
| 43 | Vogt H. On the gas-evolution efficiency of electrodes(Ⅱ): Numerical analysis[J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2011, 56(5): 2404-2410. |
| 44 | Vogt H. The role of single-phase free convection in mass transfer at gas evolving electrodes (Ⅰ): Theoretical[J]. Electrochimica Acta, 1993, 38(10): 1421-1426. |
| 45 | Reddy Karri S B. Dynamics of bubble departure in micro-gravity[J]. Chemical Engineering Communications, 1988, 70(1): 127-135. |
| 46 | Siegel R, Keshock E G. Effects of reduced gravity on nucleate boiling bubble dynamics in saturated water[J]. AIChE Journal, 1964, 10(4): 509-517. |
| 47 | Beer H, Borrow P, Best R. Nucleate Boiling, Bubble Growth and Dynamics. Heat Transfer in Boiling[M]. New York: Academic Press, 1977: 21-52. |
| 48 | Fritz W. Berechnung des maximalvolume von dampfblasen[J]. Physik Zeitschr, 1935, 36: 379-384. |
| 49 | Chen J W, Guo L J, Hu X W, et al. Dynamics of single bubble departure from TiO2 nanorod-array photoelectrode[J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2018, 274: 57-66. |
| 50 | Stephan K, Vogt H. A model for correlating mass transfer data at gas evolving electrodes[J]. Electrochimica Acta, 1979, 24(1): 11-18. |
| 51 | Colombet D, Legendre D, Tuttlies U, et al. On single bubble mass transfer in a volatile liquid[J]. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 2018, 125: 1144-1155. |
| 52 | Vogt H. The role of single-phase free convection in mass transfer at gas evolving electrodes (Ⅱ): Experimental verification[J]. Electrochimica Acta, 1993, 38(10): 1427-1431. |
| 53 | Lochiel A C, Calderbank P H. Mass transfer in the continuous phase around axisymmetric bodies of revolution[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 1964, 19(7): 471-484. |
| [1] | 王军锋, 张俊杰, 张伟, 王家乐, 双舒炎, 张亚栋. 液相放电等离子体分解甲醇制氢:电极配置的优化[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(9): 3277-3286. |
| [2] | 杨子驰, 谢冰琪, 石瑞莘, 雷虹, 陈晨, 周才金, 张吉松. 套管膜式微反应器内高效安全的气液传质-反应过程研究进展[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(9): 3011-3027. |
| [3] | 唐昊, 胡定华, 李强, 张轩畅, 韩俊杰. 抗加速度双切线弧流道内气泡动力学行为数值与可视化研究[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(9): 3074-3082. |
| [4] | 王冉, 王焕, 熊晓云, 关慧敏, 郑云锋, 陈彩琳, 秦玉才, 宋丽娟. FCC催化剂传质强化活性位利用效率的可视化分析[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(9): 3198-3209. |
| [5] | 罗正航, 李敬宇, 陈伟雄, 种道彤, 严俊杰. 摇摆运动下低流率蒸汽冷凝换热特性和气泡受力数值模拟[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(8): 2800-2811. |
| [6] | 曲玖哲, 杨鹏, 杨绪飞, 张伟, 宇波, 孙东亮, 王晓东. 硅基微柱簇阵列微通道流动沸腾实验研究[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(8): 2840-2851. |
| [7] | 曹佳蕾, 孙立岩, 曾德望, 尹凡, 高子翔, 肖睿. 双流化床化学链制氢反应器的数值模拟[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(8): 2865-2874. |
| [8] | 丁家琦, 刘海涛, 赵普, 朱香凝, 王晓放, 谢蓉. 煤炭超临界水制氢反应器内多相流场智能滚动预测研究[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(8): 2886-2896. |
| [9] | 童永祺, 程杰, 林海, 陈曦, 赵海波. 10 MWth化学链燃烧反应装置的CPFD模拟[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(8): 2949-2959. |
| [10] | 郑晓园, 蔡炎嶙, 应芝, 王波, 豆斌林. 污水污泥磷形态亚临界水热转化研究[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(8): 2970-2982. |
| [11] | 杨锦蕊, 郑宏飞, 马兴龙, 金日辉, 梁深. 两级叠置式加湿除湿海水淡化装置性能研究[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(7): 2446-2454. |
| [12] | 赵赫, 费滢洁, 朱春英, 付涛涛, 马友光. 高黏体系中纳米颗粒稳定气泡的形变及破裂行为[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(6): 2180-2189. |
| [13] | 关朝阳, 黄国庆, 张一喃, 陈宏霞, 杜小泽. 泡沫铜导离气泡强化流动沸腾换热实验研究[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(5): 1765-1776. |
| [14] | 汪威, 白旭, 赵翔, 马学良, 林纬, 喻九阳. 基于响应面法的气浮旋流分离条件优化[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(5): 1929-1938. |
| [15] | 王金山, 王世学, 朱禹. 冷却表面温差对高温质子交换膜燃料电池性能的影响[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(5): 2026-2035. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备 11010102001995号
京公网安备 11010102001995号