化工学报 ›› 2023, Vol. 74 ›› Issue (2): 871-882.DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20221229
收稿日期:2022-09-09
修回日期:2022-12-06
出版日期:2023-02-05
发布日期:2023-03-21
通讯作者:
翁志焕
作者简介:胡月(1993—),女,硕士研究生,645912857@qq.com
基金资助:
Yue HU1,2( ), Shoujun MA1, Xigao JIAN1, Zhihuan WENG1(
), Shoujun MA1, Xigao JIAN1, Zhihuan WENG1( )
)
Received:2022-09-09
Revised:2022-12-06
Online:2023-02-05
Published:2023-03-21
Contact:
Zhihuan WENG
摘要:
通过两步一锅法制备了氨基封端的新型杂萘联苯聚芳醚腈(A-PPEN),其具有比常用的芳香二胺固化剂4,4′-二氨基二苯砜(DDS)更为优异的热稳定性。采用差示扫描量热法(DSC)研究了A-PPEN对间苯二酚基邻苯二甲腈树脂前体(DPPH)的固化过程,结果显示该固化体系具有自催化固化的特征,A-PPEN的投料比会影响体系的固化活性。另外研究了该固化体系的流变特性和热稳定性,结果表明树脂的5%热失重温度(Td5%)最高可达552.9℃,800℃时残炭率(Cy800)为78.6%,最低黏度可至0.06 Pa·s,具有优异的热稳定性和较宽的加工温度窗口。
中图分类号:
胡月, 马守骏, 蹇锡高, 翁志焕. 新型聚芳醚腈固化邻苯二甲腈树脂的研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(2): 871-882.
Yue HU, Shoujun MA, Xigao JIAN, Zhihuan WENG. Study on curing phthalonitrile resin with novel poly(phthalazinone ether nitrile)[J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(2): 871-882.

图7 不同含量A-PPEN固化DPPH树脂的峰值温度对应升温速率的拟合曲线
Fig.7 Temperature as a function of heating rates for DPPH phthalonitrile resins cured with different ratios of A-PPEN
| 固化剂 | 初始固化温度/℃ | Kissinger Ea/(kJ/mol) | Ozawa Ea/(kJ/mol) | A/s-1 | N | k/s-1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5%A-PPEN | 201.4 | 66.7 | 71.3 | 2.72✕106 | 0.89 | 0.173 |
| 10%A-PPEN | 195.0 | 76.5 | 80.5 | 4.88✕107 | 0.90 | 0.201 |
| 20%A-PPEN | 190.8 | 86.1 | 89.5 | 8.00✕108 | 0.91 | 0.232 |
| 30%A-PPEN | 191.1 | 93.1 | 96.1 | 5.15✕109 | 0.92 | 0.250 |
表1 不同含量A-PPEN固化DPPH的固化动力学参数
Table 1 Curing kinetic parameters of DPPH resins cured with different ratios of A-PPEN
| 固化剂 | 初始固化温度/℃ | Kissinger Ea/(kJ/mol) | Ozawa Ea/(kJ/mol) | A/s-1 | N | k/s-1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5%A-PPEN | 201.4 | 66.7 | 71.3 | 2.72✕106 | 0.89 | 0.173 |
| 10%A-PPEN | 195.0 | 76.5 | 80.5 | 4.88✕107 | 0.90 | 0.201 |
| 20%A-PPEN | 190.8 | 86.1 | 89.5 | 8.00✕108 | 0.91 | 0.232 |
| 30%A-PPEN | 191.1 | 93.1 | 96.1 | 5.15✕109 | 0.92 | 0.250 |

图8 不同升温速率下不同含量A-PPEN固化DPPH树脂的转化率对应温度曲线
Fig.8 Conversion as function of temperature for DPPH resins cured with different ratios of A-PPEN at various heating rates
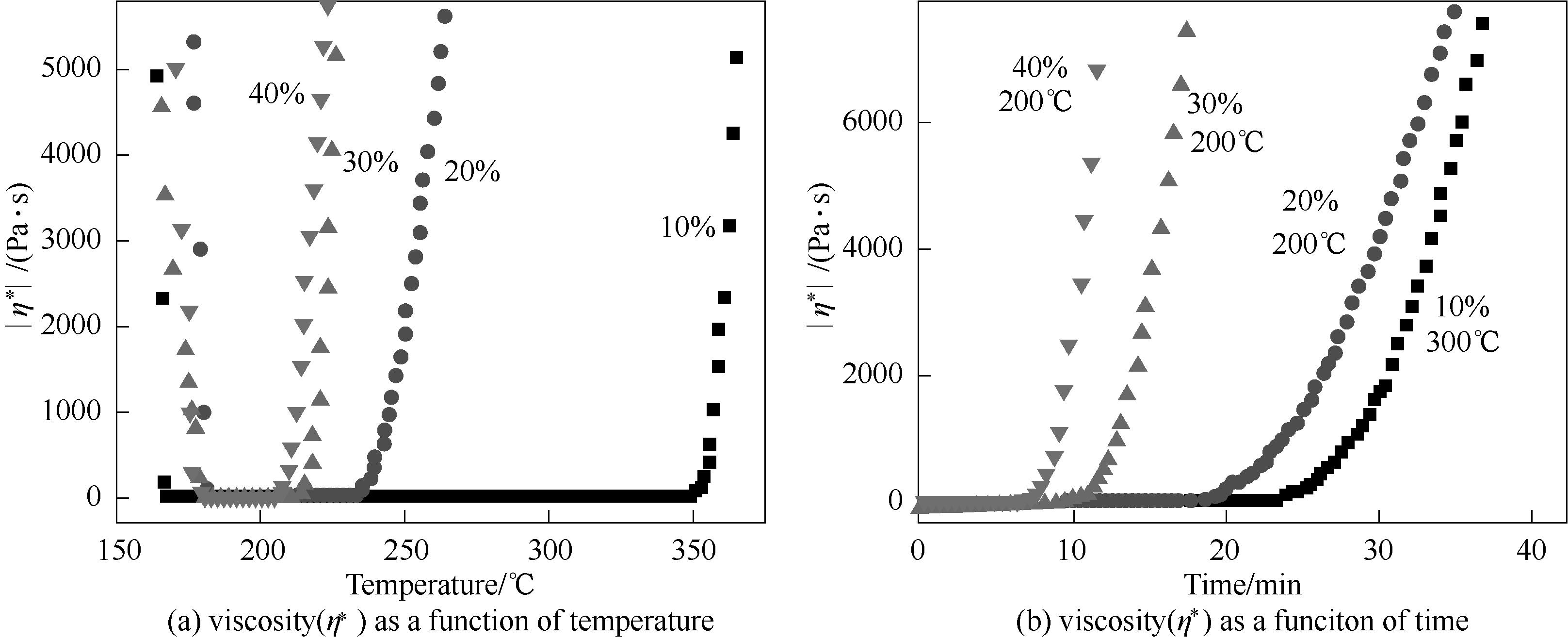
图11 不同含量A-PPEN固化DPPH树脂的黏度对应温度和时间的流变曲线
Fig.11 Complex viscosity(η* ) as a function of temperature and time for DPPH phthalonitrile resins cured with different ratios of A-PPEN
| A-PPEN含量/% | 最低黏度/(Pa·s) | Tη<50/℃ | Tgel/℃ | 加工窗口/℃ | 加工时间/min |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10 | 0.060 | 167.5 | 350.4 | 182.9 | 23.1 |
| 20 | 0.098 | 181.9 | 233.9 | 42.0 | 17.7 |
| 30 | 0.218 | 179.2 | 213.4 | 34.2 | 9.8 |
| 40 | 0.443 | 178.9 | 206.9 | 28.0 | 6.9 |
表2 不同含量 A-PPEN 固化 DPPH 树脂的流变学参数
Table 2 Rheological parameters of DPPH reins cured with different ratios of A-PPEN
| A-PPEN含量/% | 最低黏度/(Pa·s) | Tη<50/℃ | Tgel/℃ | 加工窗口/℃ | 加工时间/min |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10 | 0.060 | 167.5 | 350.4 | 182.9 | 23.1 |
| 20 | 0.098 | 181.9 | 233.9 | 42.0 | 17.7 |
| 30 | 0.218 | 179.2 | 213.4 | 34.2 | 9.8 |
| 40 | 0.443 | 178.9 | 206.9 | 28.0 | 6.9 |
| A-PPEN含量 | 400℃ | 350℃ | 300℃ | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Td5%①/℃ | Cy800②/% | Td5%/℃ | Cy800/% | Td5%/℃ | Cy800/% | |
| 5% | 546.2 | 73.1 | 484.8 | 72.6 | 400.2 | 57.7 |
| 10% | 552.9 | 78.6 | 507.6 | 75.0 | 428.7 | 68.5 |
| 20% | 544.0 | 79.6 | 496.4 | 75.1 | 464.2 | 74.1 |
| 30% | 536.0 | 80.3 | 499.7 | 75.8 | 465.4 | 74.2 |
表3 不同后固化温度下不同含量A-PPEN固化DPPH树脂的热稳定性
Table 3 Thermal properties of DPPH resins cured with different ratios of A-PPEN under different post-curing temperature
| A-PPEN含量 | 400℃ | 350℃ | 300℃ | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Td5%①/℃ | Cy800②/% | Td5%/℃ | Cy800/% | Td5%/℃ | Cy800/% | |
| 5% | 546.2 | 73.1 | 484.8 | 72.6 | 400.2 | 57.7 |
| 10% | 552.9 | 78.6 | 507.6 | 75.0 | 428.7 | 68.5 |
| 20% | 544.0 | 79.6 | 496.4 | 75.1 | 464.2 | 74.1 |
| 30% | 536.0 | 80.3 | 499.7 | 75.8 | 465.4 | 74.2 |
| 1 | Zhao F H, Liu R J, Yu X Y, et al. A high temperature polymer of phthalonitrile-substituted phosphazene with low melting point and good thermal stability[J]. Journal of Applied Polymer Science, 2015, 132(39): 42606. |
| 2 | Nar I, Gül A, Sivaev I B, et al. Cobaltacarborane functionalized phthalocyanines: synthesis, photophysical, electrochemical and spectroelectrochemical properties[J]. Synthetic Metals, 2015, 210: 376-385. |
| 3 | Chen X G, Cai Y Q, Qu X W, et al. Preparation of a self-catalyzed amino-epoxy phthalonitrile resin with a large processing window[J]. Journal of Materials Science, 2022, 57(2): 1545-1553. |
| 4 | Ji S C, Yuan P, Hu J H, et al. A novel curing agent for phthalonitrile monomers: curing behaviors and properties of the polymer network[J]. Polymer, 2016, 84: 365-370. |
| 5 | Laskoski M, Clarke J S, Neal A, et al. Sustainable high-temperature phthalonitrile resins derived from resveratrol and dihydroresveratrol[J]. ChemistrySelect, 2016, 1(13): 3423-3427. |
| 6 | Guo H, Chen Z R, Zhang J D, et al. Self-promoted curing phthalonitrile with high glass transition temperature for advanced composites[J]. Journal of Polymer Research, 2012, 19(7): 9918. |
| 7 | Zhang H D, Yan Z Y, Yang Z Z, et al. Synthesis, curing and thermal properties of the low melting point phthalonitrile resins containing glycidyl groups[J]. Polymer Bulletin, 2023, 80: 725-738. |
| 8 | Zong L S, Liu C, Zhang S H, et al. Enhanced thermal properties of phthalonitrile networks by cooperating phenyl-s-triazine moieties in backbones[J]. Polymer, 2015, 77: 177-188. |
| 9 | Sheng L P, Yin C P, Xiao J Y. A novel phthalonitrile monomer with low post cure temperature and short cure time[J]. RSC Advances, 2016, 6(27): 22204-22212. |
| 10 | Laskoski M, Keller T M, Qadri S B. Direct conversion of highly aromatic phthalonitrile thermosetting resins into carbon nanotube containing solids[J]. Polymer, 2007, 48(26): 7484-7489. |
| 11 | Huang Z T. The polymerization of aromatic and heterocyclic dinitriles[J]. Chinese Journal of Polymer Science, 1988, 6(1): 1-13. |
| 12 | Yu G P, Liu C, Wang J Y, et al. Heat-resistant aromatic s-triazine-containing ring-chain polymers based on bis(ether nitrile)s: synthesis and properties[J]. Polymer Degradation and Stability, 2010, 95(12): 2445-2452. |
| 13 | Qi Y, Weng Z H, Song C, et al. Deep eutectic solvent for curing of phthalonitrile resin: lower the curing temperature but improve the properties of thermosetting[J]. High Performance Polymers, 2021, 33(5): 538-545. |
| 14 | Keller T M, Price T R. Amine-cured bisphenol-linked phthalonitrile resins[J]. Journal of Macromolecular Science: Part A- Chemistry, 1982, 18(6): 931-937. |
| 15 | Pu Y, Xie H X, He X, et al. The curing reaction of phthalonitrile promoted by sulfhydryl groups with high curing activity[J]. Polymer, 2022, 252: 124948. |
| 16 | Chen Z W, Wang L Q, Lin J P, et al. A theoretical insight into the curing mechanism of phthalonitrile resins promoted by aromatic amines[J]. Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics: PCCP, 2021, 23(32): 17300-17309. |
| 17 | Liu C Z, Zhang B, Sun M M, et al. Novel low-melting bisphthalonitrile monomers: synthesis and their excellent adhesive performance[J]. European Polymer Journal, 2021, 153: 110511. |
| 18 | Hu J H, Xie H X, Zhu Z Z, et al. Reducing the melting point and curing temperature of aromatic cyano-based resins simultaneously through a Brønsted acid-base synergistic strategy[J]. Polymer, 2022, 246: 124745. |
| 19 | Han Y, Tang D H, Wang G X, et al. Phthalonitrile resins derived from vanillin: synthesis, curing behavior, and thermal properties[J]. Chinese Journal of Polymer Science, 2020, 38(1): 72-83. |
| 20 | Yang W J, Qi J Y, Tan W, et al. Study on aromatic nitrile-based resins containing both phthalonitrile and dicyanoimidazole groups[J]. Polymer, 2022, 255: 125118. |
| 21 | Wang T, Shi C Y, Dayo A Q, et al. Synthesis and properties of novel self-catalytic phthalonitrile monomers with aliphatic chain and their copolymerization with multi-functional fluorene-based benzoxazine monomers[J]. European Polymer Journal, 2021, 161: 110862. |
| 22 | Kolesnikov T I, Orlova A M, Tsegelskaya A Y, et al. Dual-curing propargyl-phthalonitrile imide-based thermoset: synthesis, characterization and curing behavior[J]. European Polymer Journal, 2021, 161: 110865. |
| 23 | Weng Z H, Hu Y, Qi Y, et al. Enhanced properties of phthalonitrile resins under lower curing temperature via complex curing agent[J]. Polymers for Advanced Technologies, 2020, 31(2): 233-239. |
| 24 | Vyazovkin S. Computational aspects of kinetic analysis[J]. Thermochimica Acta, 2000, 355(1/2): 155-163. |
| 25 | Dickinson C F, Heal G R. A review of the ICTAC kinetics project, 2000[J]. Thermochimica Acta, 2009, 494(1/2): 15-25. |
| 26 | 刘晓东, 程珏, 林欣, 等. 环氧树脂和环氧/环硫树脂与胺的固化反应动力学[J]. 化工学报, 2013, 64(11): 4046-4053. |
| Liu X D, Cheng J, Lin X, et al. Curing kinetics of epoxy resins/amine system and epoxy/episulfide resin/amine system[J]. CIESC Journal, 2013, 64(11): 4046-4053. | |
| 27 | Vyazovkin S, Burnham A K, Criado J M, et al. ICTAC Kinetics Committee recommendations for performing kinetic computations on thermal analysis data[J]. Thermochimica Acta, 2011, 520(1/2): 1-19. |
| 28 | 贾展宁. 中低分子量聚乙醇酸合成研究及诱发降解探索[M]. 北京:北京理工大学出版社, 2019: 53. |
| Jia Z N. The Synthesis and Trigger Biodegradation of Medium or Low Molecular Weight Polyglycolic Acid[M]. Beijing: Beijing Institute of Technology Press, 2019: 53. | |
| 29 | 杨泽, 胡冬冬, 刘涛, 等. 高压气体氛围中的聚氨酯非等温固化动力学[J]. 化工学报, 2018, 69(11): 4728-4736. |
| Yang Z, Hu D D, Liu T, et al. Non-isothermal curing kinetics of polyurethane under high-pressure gas atmosphere[J]. CIESC Journal, 2018, 69(11): 4728-4736. | |
| 30 | Weng Z H, Qi Y, Zong L S, et al. Multiple-SO3H functioned ionic liquid as efficient curing agent for phthalonitrile-terminated poly(phthalazinone ether nitrile)[J]. Chinese Chemical Letters, 2017, 28(5): 1069-1073. |
| 31 | 王哲, 祖愿, 胡方圆, 等. 含杂萘联苯结构的环氧树脂固化动力学分析[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(2): 681-688. |
| Wang Z, Zu Y, Hu F Y, et al. Kinetic analysis of curing of epoxy resin containing phthalazinone structure[J]. CIESC Journal, 2022, 73(2): 681-688. | |
| 32 | Hu J H, Xie H X, Zhu Z Z, et al. Reducing the melting point and curing temperature of aromatic cyano-based resins simultaneously through a Brønsted acid-base synergistic strategy[J]. Polymer, 2022, 246: 124745. |
| [1] | 毕丽森, 刘斌, 胡恒祥, 曾涛, 李卓睿, 宋健飞, 吴翰铭. 粗糙界面上纳米液滴蒸发模式的分子动力学研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(S1): 172-178. |
| [2] | 于宏鑫, 邵双全. 水结晶过程的分子动力学模拟分析[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(S1): 250-258. |
| [3] | 金正浩, 封立杰, 李舒宏. 氨水溶液交叉型再吸收式热泵的能量及 分析[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(S1): 53-63. 分析[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(S1): 53-63. |
| [4] | 程成, 段钟弟, 孙浩然, 胡海涛, 薛鸿祥. 表面微结构对析晶沉积特性影响的格子Boltzmann模拟[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(S1): 74-86. |
| [5] | 肖明堃, 杨光, 黄永华, 吴静怡. 浸没孔液氧气泡动力学数值研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(S1): 87-95. |
| [6] | 郑佳丽, 李志会, 赵新强, 王延吉. 离子液体催化合成2-氰基呋喃反应动力学研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(9): 3708-3715. |
| [7] | 范孝雄, 郝丽芳, 范垂钢, 李松庚. LaMnO3/生物炭催化剂低温NH3-SCR催化脱硝性能研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(9): 3821-3830. |
| [8] | 杨越, 张丹, 郑巨淦, 涂茂萍, 杨庆忠. NaCl水溶液喷射闪蒸-掺混蒸发的实验研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(8): 3279-3291. |
| [9] | 汪林正, 陆俞冰, 张睿智, 罗永浩. 基于分子动力学模拟的VOCs热氧化特性分析[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(8): 3242-3255. |
| [10] | 曾如宾, 沈中杰, 梁钦锋, 许建良, 代正华, 刘海峰. 基于分子动力学模拟的Fe2O3纳米颗粒烧结机制研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(8): 3353-3365. |
| [11] | 李锦潼, 邱顺, 孙文寿. 煤浆法烟气脱硫中草酸和紫外线强化煤砷浸出过程[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(8): 3522-3532. |
| [12] | 张蒙蒙, 颜冬, 沈永峰, 李文翠. 电解液类型对双离子电池阴阳离子储存行为的影响[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(7): 3116-3126. |
| [13] | 何宣志, 何永清, 闻桂叶, 焦凤. 磁液液滴颈部自相似破裂行为[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(7): 2889-2897. |
| [14] | 王杰, 丘晓琳, 赵烨, 刘鑫洋, 韩忠强, 许雍, 蒋文瀚. 聚电解质静电沉积改性PHBV抗氧化膜的制备与性能研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(7): 3068-3078. |
| [15] | 刘杰, 吴立盛, 李锦锦, 罗正鸿, 周寅宁. 含乙烯基胺酯键聚醚类可逆交联聚合物的制备及性能研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(7): 3051-3057. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备 11010102001995号
京公网安备 11010102001995号