化工学报 ›› 2024, Vol. 75 ›› Issue (9): 3028-3040.DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20240283
收稿日期:2024-03-08
修回日期:2024-04-19
出版日期:2024-09-25
发布日期:2024-10-10
通讯作者:
汪靖伦
作者简介:彭丹(1997—),女,硕士研究生,1197613686@qq.com
基金资助:
Dan PENG( ), Junjie LU, Wenjing NI, Yuan YANG, Jinglun WANG(
), Junjie LU, Wenjing NI, Yuan YANG, Jinglun WANG( )
)
Received:2024-03-08
Revised:2024-04-19
Online:2024-09-25
Published:2024-10-10
Contact:
Jinglun WANG
摘要:
钴酸锂(LiCoO2)具有高压实密度、高体积能量密度、优异的导电性能以及使用寿命长等优点,占据消费类电子产品的主要市场。LiCoO2材料的理论比容量高达274 mAh/g,而其在4.2 V的电压下比容量仅为140 mAh/g。随着消费类电子产品对高能量密度的迫切需求,提高LiCoO2材料工作电压成为当前研究的热点。材料改性和功能电解液设计是实现高电压LiCoO2电池的主要途径。相比较而言,功能电解液设计是一种高效且经济的途径,对高能量密度LiCoO2电池的研发具有重要意义。从高压有机溶剂、高压添加剂以及局部高浓度电解液三个方面入手,综述了近年来国内外高电压LiCoO2电池电解液的研究进展,重点阐述了电解液溶剂的氧化窗口、电极与电解液界面反应以及锂离子溶剂化结构对高电压LiCoO2电池性能的影响。最后,对高电压LiCoO2电池电解液的发展前景作出了总结和展望。
中图分类号:
彭丹, 卢俊杰, 倪文静, 杨媛, 汪靖伦. 高电压钴酸锂电池电解液研究进展[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(9): 3028-3040.
Dan PENG, Junjie LU, Wenjing NI, Yuan YANG, Jinglun WANG. Research progress of functional electrolyte for high-voltage LiCoO2 battery[J]. CIESC Journal, 2024, 75(9): 3028-3040.
| 电池体系 | 电解液 | 电压/V | 容量保持率/% | 文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Li/LiCoO2 | 1.2 mol/L LiPF6+0.15 mol/L LiDFOB-FEC∶DMC∶HFE (1∶1∶1,体积比) | 2.75~4.50 | 83.4(200 mA/g,300 cycles) | [ |
| Li/Li-Al-F@LiCoO2 | 1.0 mol/L LiPF6-FEC∶DFEC∶DMC (1∶1∶8,体积比) | 3.0~4.60 | >78.0(0.5 C,500 cycles) | [ |
| MCMB/LiCoO2 | 1.0 mol/L LiPF6-FEC∶FEMC∶TTE (3∶6∶1,质量比) | 3.0~4.45 | 76.0(0.5 C,100 cycles) | [ |
| Li/LiCoO2 | 1 mol/L LiPF6-MTFP | 2.8~4.50 | 97.0(25 mA/g,50 cycles) | [ |
| graphite/LiCoO2 | 1.0 mol/L LiPF6-FEC∶F5EON (1∶3,体积比) | 2.8~4.50 | 77.4(0.3 C,200 cycles) | [ |
| Li/LiCoO2 | 3.0 mol/L LiFSI-FMS | 3.0~4.60 | 92.5(0.2 C,100 cycles) | [ |
| 2.2 mol/L LiFSI-FMS | 3.0~4.50 | 95.0(0.2/0.5 C,400 cycles) | [ | |
| 1.5 mol/L LiFSI-TFTMS | 2.8~4.60 | 90.0(0.2/0.5 C,320 cycles) | [ |
表1 含氟溶剂在高压LiCoO2电池中的性能
Table 1 Electrochemical performances of fluorinated solvent for high-voltage LiCoO2 cells
| 电池体系 | 电解液 | 电压/V | 容量保持率/% | 文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Li/LiCoO2 | 1.2 mol/L LiPF6+0.15 mol/L LiDFOB-FEC∶DMC∶HFE (1∶1∶1,体积比) | 2.75~4.50 | 83.4(200 mA/g,300 cycles) | [ |
| Li/Li-Al-F@LiCoO2 | 1.0 mol/L LiPF6-FEC∶DFEC∶DMC (1∶1∶8,体积比) | 3.0~4.60 | >78.0(0.5 C,500 cycles) | [ |
| MCMB/LiCoO2 | 1.0 mol/L LiPF6-FEC∶FEMC∶TTE (3∶6∶1,质量比) | 3.0~4.45 | 76.0(0.5 C,100 cycles) | [ |
| Li/LiCoO2 | 1 mol/L LiPF6-MTFP | 2.8~4.50 | 97.0(25 mA/g,50 cycles) | [ |
| graphite/LiCoO2 | 1.0 mol/L LiPF6-FEC∶F5EON (1∶3,体积比) | 2.8~4.50 | 77.4(0.3 C,200 cycles) | [ |
| Li/LiCoO2 | 3.0 mol/L LiFSI-FMS | 3.0~4.60 | 92.5(0.2 C,100 cycles) | [ |
| 2.2 mol/L LiFSI-FMS | 3.0~4.50 | 95.0(0.2/0.5 C,400 cycles) | [ | |
| 1.5 mol/L LiFSI-TFTMS | 2.8~4.60 | 90.0(0.2/0.5 C,320 cycles) | [ |
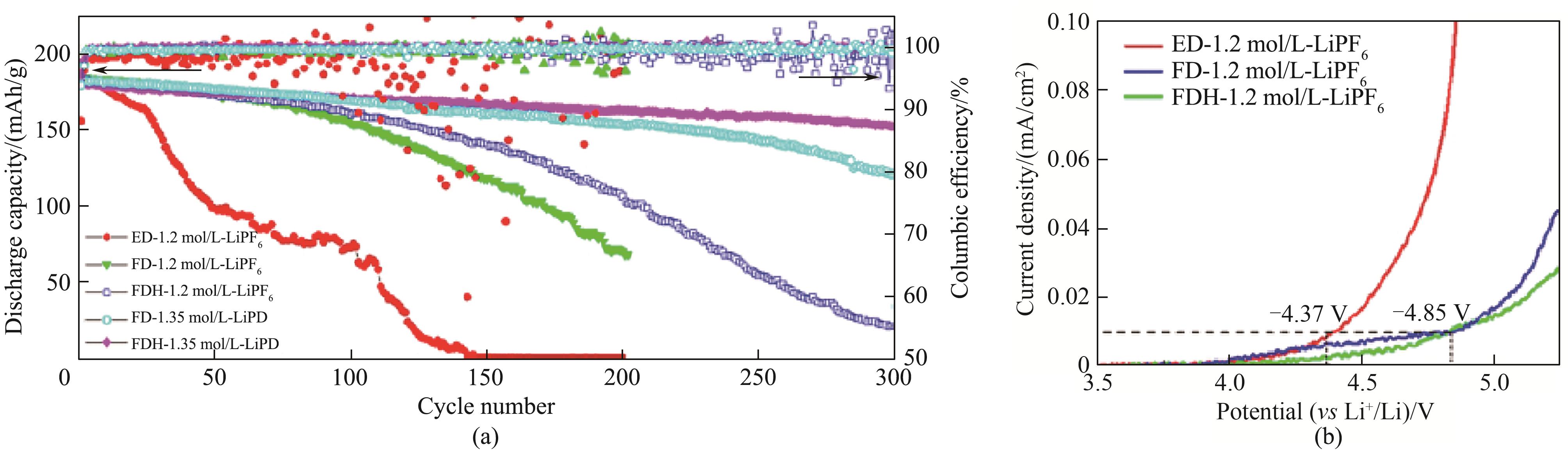
图2 高电压Li/LiCoO2电池在1.2 mol/L LiPF6+0.15 mol/L LiDFOB-FEC∶DMC∶HFE(1∶1∶1,体积比)电解液中的循环性能(a)和LSV图(b)[24]
Fig.2 Cycling performance of high-voltage Li/LiCoO2 cells in 1.2 mol/L LiPF6+0.15 mol/L LiDFOB-FEC∶DMC∶HFE (1∶1∶1, volume ratio) electrolytes (a) and LSV chart (b)[24]
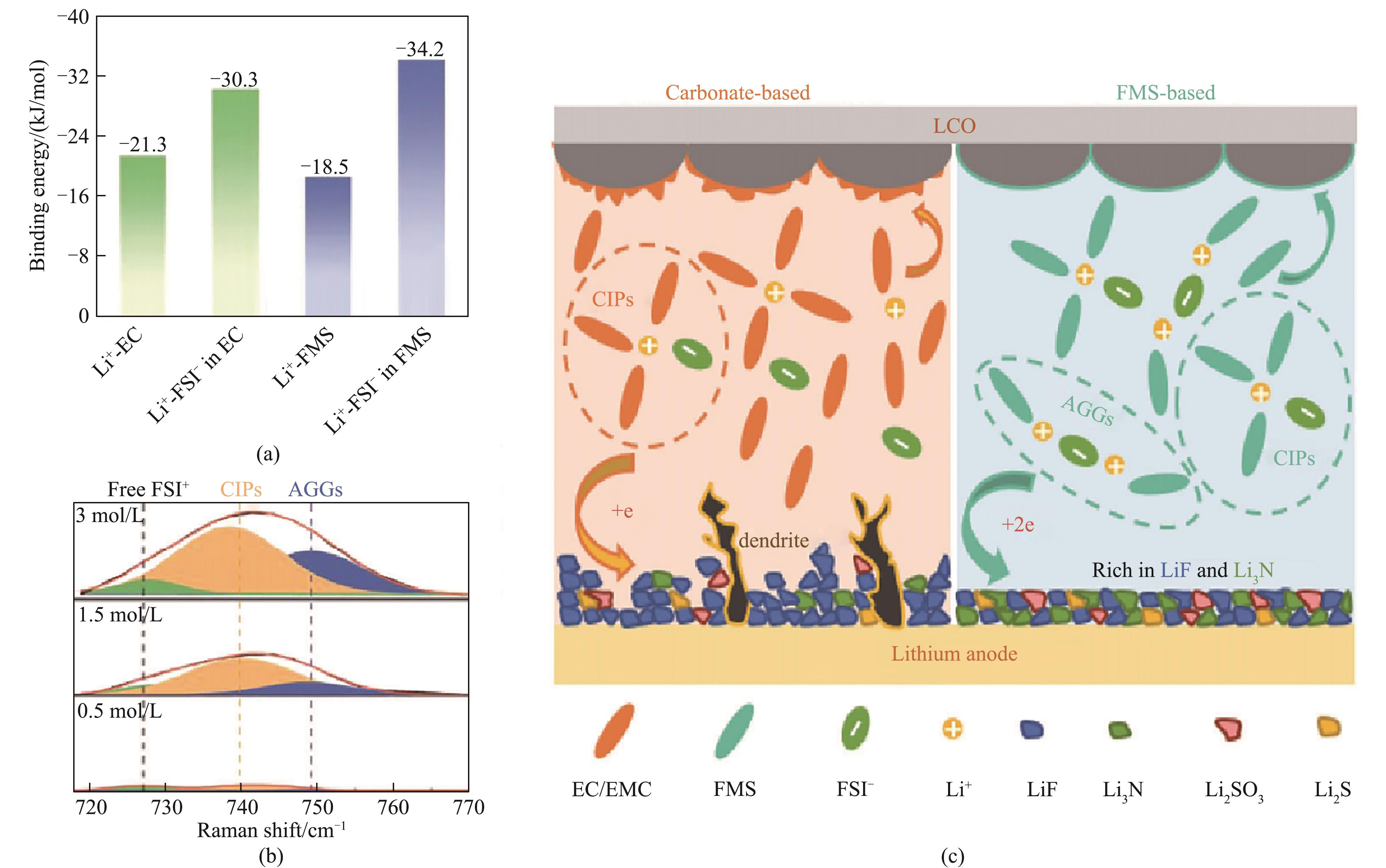
图3 Li+与各溶剂之间的结合能 (a),不同浓度FMS电解液的拉曼光谱 (b) 以及FMS基电解液形成SEI/CEI的机理示意图 (c)[29]
Fig.3 The binding energies between Li+ and various solvents (a); Raman spectra of different concentrations of FMS electrolytes (b); schematic diagram illustrating SEI/CEI formation mechanism of FMS-based electrolytes (c)[29]
| 电池体系 | 电解液 | 电压/V | 容量保持率/% | 文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| graphite/LiCoO2 | 1.0 mol/L LiPF6-EC∶PC∶DEC∶PP (1∶1∶1,质量比)+5.0%(质量分数) FEC+ 2.0%(质量分数) HTCN | 3.0~4.50 | 90.0(1.0 C,800 cycles) | [ |
| Li/LiCoO2 | 1.0 mol/L LiPF6-EC∶EMC (3∶7,质量比)10%FEC+ 1.0%(质量分数) SUN/HTCN | 3.0~4.60 | 72.0 (1.0 C,300 cycles) 75.0(1.0 C,300 cycles) | [ |
| graphite/LiCoO2 | 1.0 mol/L LiPF6-EC∶DEC (1∶1,体积比)+0.1%(质量分数) TTEP | 3.0~4.40 | 90.72(1.0 C,130 cycles) | [ |
| Li/LiCoO2 | 1.0 mol/L LiPF6-EC∶DEC (3∶7,质量比)+0.2%(质量分数) TPPSe | 3.0~4.65 | 74.1(1.0 C,500 cycles) | [ |
| graphite/LiCoO2 | 1.15 mol/L LiPF6-EC∶PC∶DEC∶PP (1∶1∶1,质量比)+5.0%(质量分数) FEC+3.0%(质量分数) ADN+0.5%(质量分数) DMTMSP | 3.0~4.45 | 90.5(1.0 C,400 cycles) | [ |
| Li/LiCoO2 | 1.0 mol/L LiPF6-PC∶EC∶EMC (5∶25∶70,体积比)+2.0%(质量分数) TTFPB | 3.0~4.70 | 74.0(0.5 C,150 cycles) | [ |
| 1.0 mol/L LiPF6-EC∶DEC (3∶7,质量比)+0.5%(质量分数) TPCB | 3.0~4.60 | 82.2(1.0 C,200 cycles) | [ | |
| 1.0 mol/L LiPF6-EC∶DEC (3∶7,质量比)+0.1%(质量分数) TFPB | 3.0~4.60 | 84.6(1.0 C,200 cycles) | [ | |
| 1.0 mol/L LiPF6-EC∶EMC∶DEC (1∶1∶1,体积比)+2.0%(质量分数) TCEB | 2.75~4.50 | 78.2(1.0 C,200 cycles) | [ | |
| graphite/LiCoO2 | 1.0 mol/L LiPF6-EC∶EMC∶DEC (3∶5∶2,质量比)+1.0%(质量分数) LiDFOB | 3.0~4.50 | 80.2(1.0 C,300 cycles) | [ |
| Li/LiCoO2 | 1.0 mol/L LiPF6-EC∶DMC∶DEC (1∶1∶1,体积比)+1.0%(质量分数) BBSI | 3.0~4.60 | 81.3(0.5 C,300 cycles) | [ |
| graphite/LiCoO2 | 1.0 mol/L LiPF6-EC∶EMC (3∶7,质量比)+1.0%(质量分数) HBAG | 3.0~4.40 | 94.88(1.0 C,160 cycles) | [ |
| 1.0 mol/L LiPF6-EC∶EMC (3∶7,质量比)+1.0%(质量分数) MDFA | 3.0~4.45 | 93.1(1.0 C,100 cycles) | [ | |
| 1.0 mol/L LiPF6-EC∶EMC (3∶7,质量比)+1.0%(质量分数) PTSI | 3.0~4.40 | 95.3(0.5 C,200 cycles) | [ | |
| 1.0 mol/L LiPF6-EC∶DMC∶EMC (1∶1∶1,质量比)+0.5%(质量分数) DMSE | 3.0~4.50 | 66.5(0.2 C,100 cycles) | [ | |
| 1.0 mol/L LiPF6-EC∶EMC (3∶7,质量比)+1.0%(质量分数) TFBS | 3.0~4.50 | 96.8(0.5 C,100 cycles) | [ | |
| Li/LiCoO2 | 1.0 mol/L LiPF6-EC∶DEC (3∶7,质量比)+0.03%(质量分数) MMD | 3.0~4.60 | 83.5(1.0 C,200 cycles) | [ |
| graphite/LiCoO2 | 1.0 mol/L LiPF6-EC∶EMC (3∶7,体积比)+2.0%(质量分数) NPA | 3.0~4.60 | 77.1(0.3 C,200 cycles) | [ |
| graphite/LiCoO2 | 1.3 mol/L LiPF6-EC/PC/EB (10∶15∶75,体积比)+7% FEC+ 1% LiFMDFB+3% HTCN+0.2% TMSP | 3.0~4.55 | 51.8(1.5 C charge/ 0.5 C discharge,500 cycles) | [ |
| Li/LiCoO2 | 1.0 mol/L LiPF6-EC∶EMC (3∶7,质量比)+1.0%(质量分数) DMMA | 3.0~4.65 | 70.7(1.0 C,500 cycles) | [ |
表2 功能添加剂在高压LiCoO2电池中的性能
Table 2 Electrochemical performances of functional additives for high-voltage LiCoO2 cells
| 电池体系 | 电解液 | 电压/V | 容量保持率/% | 文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| graphite/LiCoO2 | 1.0 mol/L LiPF6-EC∶PC∶DEC∶PP (1∶1∶1,质量比)+5.0%(质量分数) FEC+ 2.0%(质量分数) HTCN | 3.0~4.50 | 90.0(1.0 C,800 cycles) | [ |
| Li/LiCoO2 | 1.0 mol/L LiPF6-EC∶EMC (3∶7,质量比)10%FEC+ 1.0%(质量分数) SUN/HTCN | 3.0~4.60 | 72.0 (1.0 C,300 cycles) 75.0(1.0 C,300 cycles) | [ |
| graphite/LiCoO2 | 1.0 mol/L LiPF6-EC∶DEC (1∶1,体积比)+0.1%(质量分数) TTEP | 3.0~4.40 | 90.72(1.0 C,130 cycles) | [ |
| Li/LiCoO2 | 1.0 mol/L LiPF6-EC∶DEC (3∶7,质量比)+0.2%(质量分数) TPPSe | 3.0~4.65 | 74.1(1.0 C,500 cycles) | [ |
| graphite/LiCoO2 | 1.15 mol/L LiPF6-EC∶PC∶DEC∶PP (1∶1∶1,质量比)+5.0%(质量分数) FEC+3.0%(质量分数) ADN+0.5%(质量分数) DMTMSP | 3.0~4.45 | 90.5(1.0 C,400 cycles) | [ |
| Li/LiCoO2 | 1.0 mol/L LiPF6-PC∶EC∶EMC (5∶25∶70,体积比)+2.0%(质量分数) TTFPB | 3.0~4.70 | 74.0(0.5 C,150 cycles) | [ |
| 1.0 mol/L LiPF6-EC∶DEC (3∶7,质量比)+0.5%(质量分数) TPCB | 3.0~4.60 | 82.2(1.0 C,200 cycles) | [ | |
| 1.0 mol/L LiPF6-EC∶DEC (3∶7,质量比)+0.1%(质量分数) TFPB | 3.0~4.60 | 84.6(1.0 C,200 cycles) | [ | |
| 1.0 mol/L LiPF6-EC∶EMC∶DEC (1∶1∶1,体积比)+2.0%(质量分数) TCEB | 2.75~4.50 | 78.2(1.0 C,200 cycles) | [ | |
| graphite/LiCoO2 | 1.0 mol/L LiPF6-EC∶EMC∶DEC (3∶5∶2,质量比)+1.0%(质量分数) LiDFOB | 3.0~4.50 | 80.2(1.0 C,300 cycles) | [ |
| Li/LiCoO2 | 1.0 mol/L LiPF6-EC∶DMC∶DEC (1∶1∶1,体积比)+1.0%(质量分数) BBSI | 3.0~4.60 | 81.3(0.5 C,300 cycles) | [ |
| graphite/LiCoO2 | 1.0 mol/L LiPF6-EC∶EMC (3∶7,质量比)+1.0%(质量分数) HBAG | 3.0~4.40 | 94.88(1.0 C,160 cycles) | [ |
| 1.0 mol/L LiPF6-EC∶EMC (3∶7,质量比)+1.0%(质量分数) MDFA | 3.0~4.45 | 93.1(1.0 C,100 cycles) | [ | |
| 1.0 mol/L LiPF6-EC∶EMC (3∶7,质量比)+1.0%(质量分数) PTSI | 3.0~4.40 | 95.3(0.5 C,200 cycles) | [ | |
| 1.0 mol/L LiPF6-EC∶DMC∶EMC (1∶1∶1,质量比)+0.5%(质量分数) DMSE | 3.0~4.50 | 66.5(0.2 C,100 cycles) | [ | |
| 1.0 mol/L LiPF6-EC∶EMC (3∶7,质量比)+1.0%(质量分数) TFBS | 3.0~4.50 | 96.8(0.5 C,100 cycles) | [ | |
| Li/LiCoO2 | 1.0 mol/L LiPF6-EC∶DEC (3∶7,质量比)+0.03%(质量分数) MMD | 3.0~4.60 | 83.5(1.0 C,200 cycles) | [ |
| graphite/LiCoO2 | 1.0 mol/L LiPF6-EC∶EMC (3∶7,体积比)+2.0%(质量分数) NPA | 3.0~4.60 | 77.1(0.3 C,200 cycles) | [ |
| graphite/LiCoO2 | 1.3 mol/L LiPF6-EC/PC/EB (10∶15∶75,体积比)+7% FEC+ 1% LiFMDFB+3% HTCN+0.2% TMSP | 3.0~4.55 | 51.8(1.5 C charge/ 0.5 C discharge,500 cycles) | [ |
| Li/LiCoO2 | 1.0 mol/L LiPF6-EC∶EMC (3∶7,质量比)+1.0%(质量分数) DMMA | 3.0~4.65 | 70.7(1.0 C,500 cycles) | [ |
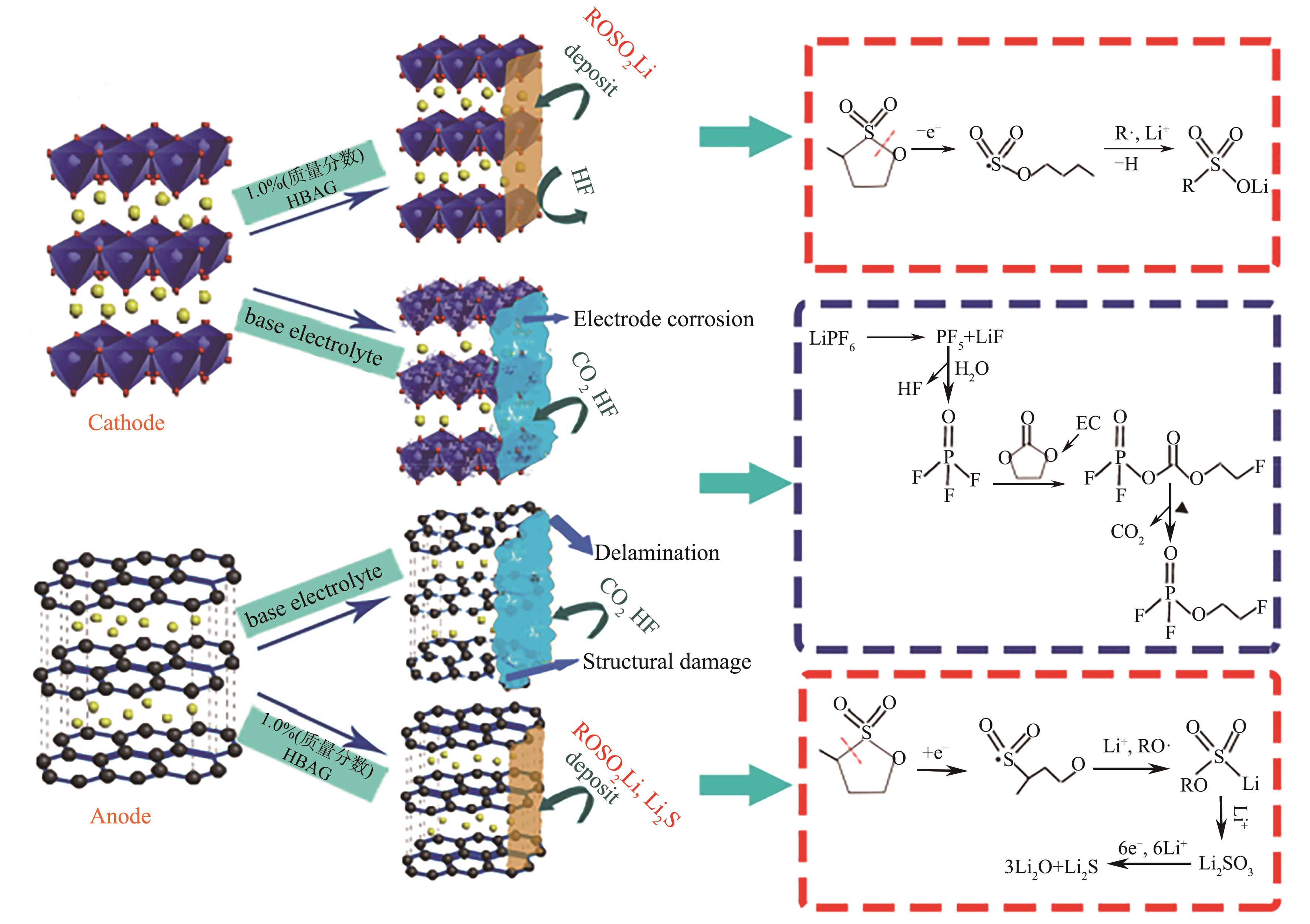
图8 HBAG氧化还原提高graphite/LiCoO2袋式电池性能的可能机制[49]
Fig.8 Possible mechanism for protective film formation by redox of HBAG to enhance the performance of graphite/LiCoO2 pouch cell[49]
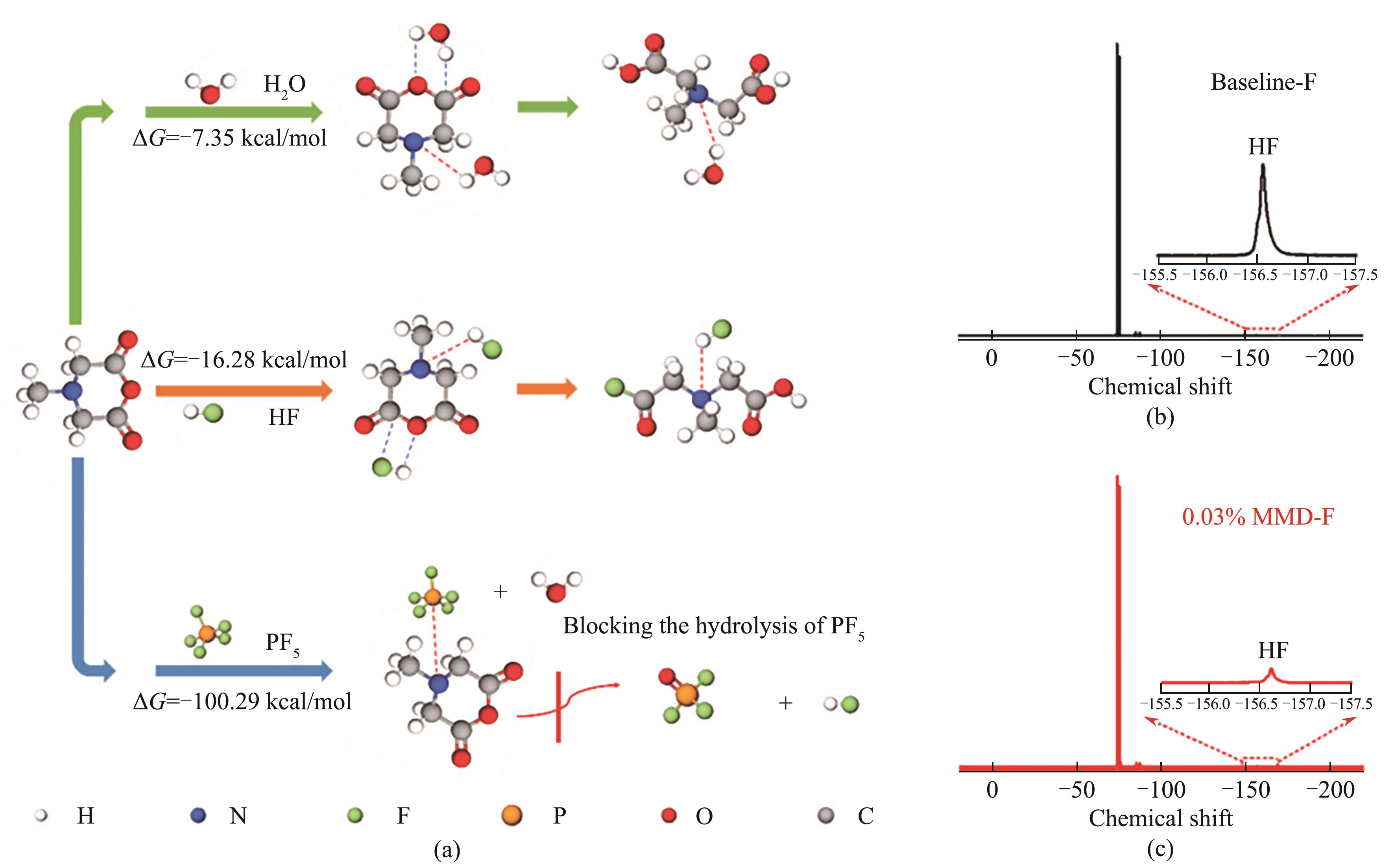
图10 MMD分子与水、HF和PF5反应的Gibbs自由能(ΔG) (a);电解液中加入0.06%的水并储存7 d后的19F NMR谱图:空白电解液(b);含0.03% MDD电解液(c)[54](1 cal=4.184 J)
Fig.10 Gibbs free energies (ΔG) of MMD reacting with H2O, HF and PF5 (a); 19F NMR spectra of baseline (b) and 0.03% MMD-containing electrolytes (c) added with 0.06% water after being stored for 7 d[54] (1 cal=4.184 J)
| 电池体系 | 电解液 | 容量保持率/% | 文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
3.0~4.50 V Li/LiCoO2 | [5 mol/L LiTFSI-MP-FEC (9∶1,体积比)]∶TTE(2∶1,质量比) | 87.7(1.0 C,300 cycles) | [ |
| 1.4 mol/L LiFSI-DME-TTME (1∶4,体积比) | 90.0(0.2 C charge/0.5 C discharge,170 cycles) | [ | |
| 1.9 mol/L LiFSI-DME-HM (2∶1,体积比) | 80.0(0.2 C charge/0.5 C discharge,505 cycles) | [ | |
| LiFSI∶DME∶FB∶3FB (1∶1.2∶2.8∶0.2,摩尔比) | 80.0(2.0 C,600 cycles) | [ | |
| 2.0 mol/L LiDFOB-DME∶DFEC (1∶1,体积比) | 82.32(0.3 C,1000 cycles) | [ | |
| 1.4 mol/L LiFSI-DME∶HFC (1∶3,摩尔比) | 88.0(0.2 C charge/0.5 C discharge,200 cycles) | [ |
表3 基于局部高浓度电解液(LHCE)的高压LiCoO2电池性能
Table 3 Electrochemical performances of high-voltage LiCoO2 cells based on localized high concentration electrolyte
| 电池体系 | 电解液 | 容量保持率/% | 文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
3.0~4.50 V Li/LiCoO2 | [5 mol/L LiTFSI-MP-FEC (9∶1,体积比)]∶TTE(2∶1,质量比) | 87.7(1.0 C,300 cycles) | [ |
| 1.4 mol/L LiFSI-DME-TTME (1∶4,体积比) | 90.0(0.2 C charge/0.5 C discharge,170 cycles) | [ | |
| 1.9 mol/L LiFSI-DME-HM (2∶1,体积比) | 80.0(0.2 C charge/0.5 C discharge,505 cycles) | [ | |
| LiFSI∶DME∶FB∶3FB (1∶1.2∶2.8∶0.2,摩尔比) | 80.0(2.0 C,600 cycles) | [ | |
| 2.0 mol/L LiDFOB-DME∶DFEC (1∶1,体积比) | 82.32(0.3 C,1000 cycles) | [ | |
| 1.4 mol/L LiFSI-DME∶HFC (1∶3,摩尔比) | 88.0(0.2 C charge/0.5 C discharge,200 cycles) | [ |
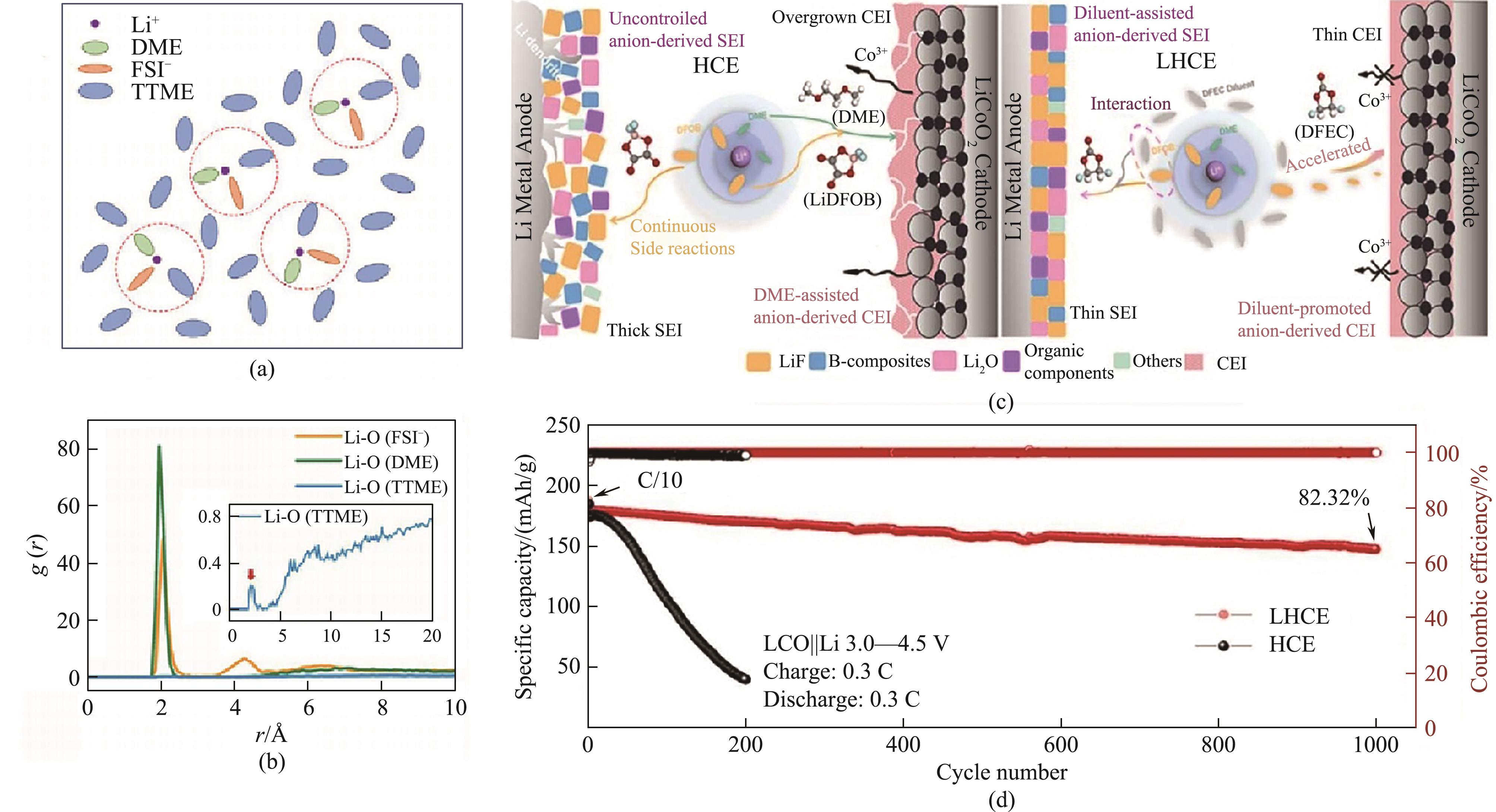
图11 TTME基电解液溶剂化结构示意图模型 (a); 在FSI-/DME/TTME中,Li+与O原子之间的径向分布函数(插图:TTME中Li+与O原子之间的径向分布函数) (b)[68]; DFEC在HCE、LHCE电解液形成的SEI/CEI示意图 (c)及在Li/LiCoO2电池中的循环性能图 (d)[71] (1 Å=0.1 nm)
Fig.11 Schematic illustration model of TTME based electrolyte solvation structure (a); radial distribution functions between Li+ and O atom in FSI-/DME/TTME (inset: radial distribution functions between Li+ and O atom in TTME) (b)[68]; schematic illustration of the electrolyte structure and the correspondingly formed SEI/CEI in DFEC based electrolyte (c) and cycling performance of Li/LiCoO2 cells (d)[71] (1 Å=0.1 nm)
| 1 | Li J, Zuo P J. Research progress on low-temperature graphite anode and electrolyte optimization for lithium-ion batteries[J]. Scientia Sinica Chimica, 2022, 52(10): 1824-1833. |
| 2 | Zheng J M, Kan W H, Manthiram A. Role of Mn content on the electrochemical properties of nickel-rich layered LiNi0.8– x Co0.1Mn0.1+ x O2 (0.0≤x≤0.08) cathodes for lithium-ion batteries[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2015, 7(12): 6926-6934. |
| 3 | Qin D M, Cheng F Y, Zhang W, et al. Electrolyte regulating and interface engineering for high voltage LiCoO2 lithium metal batteries[J]. Applied Surface Science, 2023, 616: 156447. |
| 4 | Liu X, Fu A, Lin J D, et al. Constructing a stabilized cathode electrolyte interphase for high-voltage LiCoO2 batteries via the phenylmaleic anhydride additive[J]. ACS Applied Energy Materials, 2023, 6(3): 2001-2009. |
| 5 | Lyu Y C, Wu X, Wang K, et al. An overview on the advances of LiCoO2 cathodes for lithium-ion batteries[J]. Advanced Energy Materials, 2021, 11(2): 2000982. |
| 6 | Wang X, Wu Q, Li S Y, et al. Lithium-aluminum-phosphate coating enables stable 4.6 V cycling performance of LiCoO2 at room temperature and beyond[J]. Energy Storage Materials, 2021, 37: 67-76. |
| 7 | Lin C, Li J, Yin Z W, et al. Structural understanding for high-voltage stabilization of lithium cobalt oxide[J]. Advanced Materials, 2024, 36(6): 2307404. |
| 8 | Xue W J, Gao R, Shi Z, et al. Stabilizing electrode-electrolyte interfaces to realize high-voltage Li||LiCoO2 batteries by a sulfonamide-based electrolyte[J]. Energy & Environmental Science, 2021, 14(11): 6030-6040. |
| 9 | Guo K L, Qi S H, Wang H P, et al. High-voltage electrolyte chemistry for lithium batteries[J]. Small Science, 2022, 2(5): 2100107. |
| 10 | Wu Q, Zhang B, Lu Y Y. Progress and perspective of high-voltage lithium cobalt oxide in lithium-ion batteries[J]. Journal of Energy Chemistry, 2022, 74: 283-308. |
| 11 | 陈喜, 杨春利, 黄江龙, 等. 高电压钴酸锂正极材料研究进展[J]. 材料导报, 2023, 37(13): 39-52. |
| Chen X, Yang C L, Huang J L, et al. Research progress of high voltage lithium cobalt oxide cathode materials[J]. Materials Reports, 2023, 37(13): 39-52. | |
| 12 | 张思东, 刘园, 祁慕尧, 等. 表面限域掺杂提升高比能正极材料稳定性[J]. 物理化学学报, 2021, 37(11): 88-100. |
| Zhang S D, Liu Y, Qi M Y, et al. Localized surface doping for improved stability of high energy cathode materials[J]. Acta Physico-Chimica Sinica, 2021, 37(11): 88-100. | |
| 13 | Xu K. Electrolytes and interphases in Li-ion batteries and beyond[J]. Chemical Reviews, 2014, 114(23): 11503-11618. |
| 14 | Xu J J, Zhang J X, Pollard T P, et al. Electrolyte design for Li-ion batteries under extreme operating conditions[J]. Nature, 2023, 614(7949): 694-700. |
| 15 | 胡华坤, 薛文东, 蒋朋, 等. 锂离子电池安全添加剂的研究进展[J]. 化工进展, 2022, 41(10): 5441-5455. |
| Hu H K, Xue W D, Jiang P, et al. Research progress of safety additives for lithium ion batteries[J]. Chemical Industry and Engineering Progress, 2022, 41(10): 5441-5455. | |
| 16 | Sun Z Y, Zhao J W, Zhu M, et al. Critical problems and modification strategies of realizing high-voltage LiCoO2 cathode from electrolyte engineering[J]. Advanced Energy Materials, 2024, 14(8): 2303498. |
| 17 | Zhao H J, Yu X Q, Li J D, et al. Film-forming electrolyte additives for rechargeable lithium-ion batteries: progress and outlook[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2019, 7(15): 8700-8722. |
| 18 | Chen S M, Wen K H, Fan J T, et al. Progress and future prospects of high-voltage and high-safety electrolytes in advanced lithium batteries: from liquid to solid electrolytes[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2018, 6(25): 11631-11663. |
| 19 | 胡素琴, 杨改, 蔡飞鹏, 等. 离子液体基锂离子电池电解液的应用与性能改进[J]. 化工学报, 2011, 62(S2): 1-6. |
| Hu S Q, Yang G, Cai F P, et al. Application of ionic liquids-based Li-ion battery electrolyte and improvement of electrochemical properties[J]. CIESC Journal, 2011, 62(S2): 1-6. | |
| 20 | 于喆, 张建军, 刘亭亭, 等. 二次电池用局部高浓度电解质的研究进展与展望[J]. 化学学报, 2020, 78(2): 114-124. |
| Yu Z, Zhang J J, Liu T T, et al. Research progress and perspectives of localized high-concentration electrolytes for secondary batteries[J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2020, 78(2): 114-124. | |
| 21 | Guan D C, Hu G R, Peng Z D, et al. A nonflammable low-concentration electrolyte for lithium-ion batteries[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2022, 10(23): 12575-12587. |
| 22 | Li Z Z, Chen Y F, Yun X R, et al. Critical review of fluorinated electrolytes for high-performance lithium metal batteries[J]. Advanced Functional Materials, 2023, 33(32): 2300502. |
| 23 | Wang Y Q, Wu Z Z, Azad F M, et al. Fluorination in advanced battery design[J]. Nature Reviews Materials, 2024, 9: 119-133. |
| 24 | Lin S S, Zhao J B. Functional electrolyte of fluorinated ether and ester for stabilizing both 4.5 V LiCoO2 cathode and lithium metal anode[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2020, 12(7): 8316-8323. |
| 25 | Fan T J, Kai W, Harika V K, et al. Operating highly stable LiCoO2 cathodes up to 4.6 V by using an effective integration of surface engineering and electrolyte solutions selection[J]. Advanced Functional Materials, 2022, 32(33): 2204972. |
| 26 | Peng L G, He Q R, He L, et al. Improved electrochemical performance of a LiCoO2/MCMB cell by regulating fluorinated electrolytes[J]. RSC Advances, 2021, 11(49): 30763-30770. |
| 27 | Ugata Y, Yukishita K, Kazahaya N, et al. Nonflammable fluorinated ester-based electrolytes for safe and high-energy batteries with LiCoO2 [J]. Chemistry of Materials, 2023, 35(9): 3686-3693. |
| 28 | Zhou X, Peng D, Deng K Q, et al. Synthesis and characterization of novel fluorinated nitriles as non-flammable and high-voltage electrolytes for lithium/lithium-ion batteries[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2023, 557: 232557. |
| 29 | Li Y Q, Liu M Z, Wang K, et al. Single-solvent-based electrolyte enabling a high-voltage lithium-metal battery with long cycle life[J]. Advanced Energy Materials, 2023, 13(30): 2300918. |
| 30 | Sun C C, Li R H, Zhu C N, et al. High-voltage Li metal batteries enabled by adsorption-defluorination mechanism[J]. ACS Energy Letters, 2023, 8(10): 4119-4128. |
| 31 | Chen L, Zhang H K, Li R H, et al. Dynamic shielding of electrified interface enables high-voltage lithium batteries[J]. Chem, 2024, 10(4): 1196-1212. |
| 32 | Wang W L, Zeng X Y, Hu H L, et al. 1,2,3,4-tetrakis(2-cyanoethoxy)butane (TCEB)-assisted construction of self-repair electrode interface films to improve the performance of 4.5 V pouch LiCoO2/artificial graphite full cells operating at 45 ℃[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2021, 13(50): 59925-59936. |
| 33 | Zhao J T, Liang Y, Zhang X, et al. In situ construction of uniform and robust cathode-electrolyte interphase for Li‐rich layered oxides[J]. Advanced Functional Materials, 2021, 31(8): 2009192. |
| 34 | Li T T, Lin J L, Xing L D, et al. Insight into the contribution of nitriles as electrolyte additives to the improved performances of the LiCoO2 cathode[J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry Letters, 2022, 13(37): 8801-8807. |
| 35 | 汪靖伦, 冉琴, 韩冲宇, 等. 锂离子电池有机硅功能电解液[J]. 化学进展, 2020, 32(4): 467-480. |
| Wang J L, Ran Q, Han C Y, et al. Organosilicon functionalized electrolytes for lithium-ion batteries[J]. Progress in Chemistry, 2020, 32(4): 467-480. | |
| 36 | Huang Y Q, Li R H, Weng S T, et al. Eco-friendly electrolytes via a robust bond design for high-energy Li metal batteries[J]. Energy & Environmental Science, 2022, 15(10): 4349-4361. |
| 37 | 胡华坤, 薛文东, 霍思达, 等. 锂离子电池电解液SEI成膜添加剂的研究进展[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(4): 1436-1454. |
| Hu H K, Xue W D, Huo S D, et al. Review of SEI film forming additives for electrolyte of lithium ion battery[J]. CIESC Journal, 2022, 73(4): 1436-1454. | |
| 38 | Tang C, Chen Y W, Zhang Z F, et al. Stable cycling of practical high-voltage LiCoO2 pouch cell via electrolyte modification[J]. Nano Research, 2023, 16(3): 3864-3871. |
| 39 | Yang X R, Lin M, Zheng G R, et al. Enabling stable high-voltage LiCoO2 operation by using synergetic interfacial modification strategy[J]. Advanced Functional Materials, 2020, 30(43): 2004664. |
| 40 | Liang X, Huang J, Zheng Y, et al. Tris(2-(thiophen-2-yl) ethyl) phosphate to synergistically enhance electronic and ionic conductivities of cathode electrolyte interphase in high-voltage lithium ion batteries[J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2019, 316: 228-235. |
| 41 | Fu A, Lin J D, Zheng J M, et al. Additive evolved stabilized dual electrode-electrolyte interphases propelling the high-voltage Li||LiCoO2 batteries up to 4.7 V[J]. Nano Energy, 2024, 119: 109095. |
| 42 | Liao X Q, Zhang C M, Li F, et al. Dimethyl trimethylsilyl phosphite as a novel electrolyte additive for high voltage layered lithium cobaltate-based lithium ion batteries[J]. New Journal of Chemistry, 2021, 45(6): 3160-3168. |
| 43 | Wu D X, Zhu C L, Wang H P, et al. Mechanically and thermally stable cathode electrolyte interphase enables high-temperature, high-voltage Li||LiCoO2 batteries[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2024, 63(7): e202315608. |
| 44 | Zou Y, Cheng Y, Lin J D, et al. Boosting high voltage cycling of LiCoO2 cathode via triisopropanolamine cyclic borate electrolyte additive[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2022, 532: 231372. |
| 45 | Zou Y, Fu A, Zhang J, et al. Stabilizing the LiCoO2 interface at high voltage with an electrolyte additive 2,4,6-tris(4-fluorophenyl)boroxin[J]. ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering, 2021, 9(44): 15042-15052. |
| 46 | Zhang Z, Liu F Y, Huang Z Y, et al. Enhancing the electrochemical performance of a high-voltage LiCoO2 cathode with a bifunctional electrolyte additive[J]. ACS Applied Energy Materials, 2021, 4(11): 12954-12964. |
| 47 | Li B, Shao Y X, He J J, et al. Cyclability improvement of high voltage lithium cobalt oxide/graphite battery by use of lithium difluoro (oxalate) borate electrolyte additive[J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2022, 426: 140783. |
| 48 | Guo K L, Zhu C L, Wang H P, et al. Conductive Li+ moieties-rich cathode electrolyte interphase with electrolyte additive for 4.6 V well-cycled Li||LiCoO2 batteries[J]. Advanced Energy Materials, 2023, 13(20): 2204272. |
| 49 | Lei W P, Deng X, Zuo X X, et al. 4-Hydroxy-2-butanesulfonic acid gamma-sultone as a bifunctional electrolyte additive for LiCoO2/graphite batteries with enhanced performances[J]. ACS Applied Energy Materials, 2021, 4(6): 5877-5887. |
| 50 | Xiang F Y, Wang P P, Cheng H. Methyl 2,2-difluoro-2-(fluorosulfonyl) acetate as a novel electrolyte additive for high-voltage LiCoO2/graphite pouch Li-ion cells[J]. Energy Technology, 2020, 8(5): 1901277. |
| 51 | Zhang L D, Zuo X X, Zhu T M, et al. 1- (P-toluenesulfonyl)imidazole (PTSI) as the novel bifunctional electrolyte for LiCoO2-based cells with improved performance at high voltage[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2021, 491: 229596. |
| 52 | Zheng X Z, Huang T, Fang G H, et al. Di(methylsulfonyl) ethane: new electrolyte additive for enhancing LiCoO2/electrolyte interface stability under high voltage[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2019, 11(39): 36244-36251. |
| 53 | Zhang L D, Zuo X X, Zhu T M, et al. A new fluorinated sultone as multifunctional electrolyte additive for high-performance LiCoO2/graphite cell[J]. ChemElectroChem, 2021, 8(13): 2534-2544. |
| 54 | Zou Y, Zhang J, Lin J D, et al. Improving interfacial stability of high voltage LiCoO2-based cells with 4-methylmorpholine-2,6-dione additive[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2022, 524: 231049. |
| 55 | Bizuneh G G, Zhu C L, Huang J D, et al. Constructing highly Li+ conductive electrode electrolyte interphases for 4.6 V Li||LiCoO2 batteries via electrolyte additive engineering[J]. Small Methods, 2023, 7(9): e2300079. |
| 56 | Kim S, Lee J A, Lee D G, et al. Designing electrolytes for stable operation of high-voltage LiCoO2 in lithium-ion batteries[J]. ACS Energy Letters, 2024, 9(1): 262-270. |
| 57 | Fu A, Xu C J, Lin J D, et al. Enabling interfacial stability of LiCoO2 batteries at an ultrahigh cutoff voltage ≥4.65 V via a synergetic electrolyte strategy[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2023, 11(7): 3703-3716. |
| 58 | 占佳琦, 邢丽丹. 锂离子电池正极材料过渡金属离子溶出的危害及抑制研究[J]. 材料研究与应用, 2023, 17(5): 902-911. |
| Zhan J Q, Xing L D. Study on the detriment and inhibition of the dissolution of transition metal ions in cathode materials of lithium-ion batteries[J]. Materials Research and Application, 2023, 17(5): 902-911. | |
| 59 | 蒋志敏, 王莉, 沈旻, 等. 锂离子电池正极界面修饰用电解液添加剂[J]. 化学进展, 2019, 31(5): 699-713. |
| Jiang Z M, Wang L, Shen M, et al. Electrolyte additives for interfacial modification of cathodes in lithium ion battery[J]. Progress in Chemistry, 2019, 31(5): 699-713. | |
| 60 | Wang W L, Hu H L, Zeng X Y, et al. Bifunctional mechanism and electrochemical performance of self-healing nitrile ether electrolyte additives in 4.5 V LiCoO2/artificial graphite lithium-ion batteries[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2022, 542: 231799. |
| 61 | 程伟江, 汪何琦, 高翔, 等. 锂离子电池硅基负极电解液成膜添加剂的研究进展[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(2): 571-584. |
| Cheng W J, Wang H Q, Gao X, et al. Research progress on film-forming electrolyte additives for Si-based lithium-ion batteries[J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(2): 571-584. | |
| 62 | Yan G C, Li X H, Wang Z X, et al. Tris(trimethylsilyl)phosphate: a film-forming additive for high voltage cathode material in lithium-ion batteries[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2014, 248: 1306-1311. |
| 63 | Lee H S, Yang X Q, Xiang C L, et al. The synthesis of a new family of boron-based anion receptors and the study of their effect on ion pair dissociation and conductivity of lithium salts in nonaqueous solutions[J]. Journal of the Electrochemical Society, 1998, 145(8): 2813-2818. |
| 64 | Wang F, Lin Y X, Suo L M, et al. Stabilizing high voltage LiCoO2 cathode in aqueous electrolyte with interphase-forming additive[J]. Energy & Environmental Science, 2016, 9(12): 3666-3673. |
| 65 | 余笑颖. 含硫添加剂对高电压下锂离子电池性能影响研究[D]. 杭州: 浙江大学, 2019. |
| Yu X Y. Effects of sulfur-containing electrolyte additives on high-voltage lithium ion batteries[D]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang University, 2019. | |
| 66 | Liu M Z, Vatamanu J, Chen X L, et al. Hydrolysis of LiPF6-containing electrolyte at high voltage[J]. ACS Energy Letters, 2021, 6(6): 2096-2102. |
| 67 | Lai P B, Huang B Y, Deng X D, et al. A localized high concentration carboxylic ester-based electrolyte for high-voltage and low temperature lithium batteries[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2023, 461: 141904. |
| 68 | Wang R, Li J W, Han B, et al. Unique double-layer solid electrolyte interphase formed with fluorinated ether-based electrolytes for high-voltage lithium metal batteries[J]. Journal of Energy Chemistry, 2024, 88: 532-542. |
| 69 | Zhang J B, Zhang H K, Li R H, et al. Diluent decomposition-assisted formation of LiF-rich solid-electrolyte interfaces enables high-energy Li-metal batteries[J]. Journal of Energy Chemistry, 2023, 78: 71-79. |
| 70 | Zhang H, Zeng Z Q, He R J, et al. 1,3,5-Trifluorobenzene and fluorobenzene co-assisted electrolyte with thermodynamic and interfacial stabilities for high-voltage lithium metal battery[J]. Energy Storage Materials, 2022, 48: 393-402. |
| 71 | Luo C H, Liu Q, Wang X S, et al. Synergistic-effect of diluent to reinforce anion-solvation-derived interfacial chemistry for 4.5 V-class Li||LiCoO2 batteries[J]. Nano Energy, 2023, 109: 108323. |
| 72 | Wu Z C, Li R H, Zhang S Q, et al. Deciphering and modulating energetics of solvation structure enables aggressive high-voltage chemistry of Li metal batteries[J]. Chem, 2023, 9(3): 650-664. |
| [1] | 王舒英, 左涛, 石志伟, 范小明, 张卫新. 阳离子交换树脂基介孔石墨化碳合成与储钠性能[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(9): 3338-3347. |
| [2] | 罗欣怡, 徐强, 佘永璐, 聂腾飞, 郭烈锦. 光电分解水制氢气泡动力学特性及其传质机理研究[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(9): 3083-3093. |
| [3] | 左磊, 王军锋, 高健, 王道睿. 电场调控生物柴油液滴燃烧行为[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(8): 2983-2990. |
| [4] | 王天闻, 闫肃, 赵梦园, 杨天让, 刘建国. 固体氧化物电池空气电极铬中毒机理及抗铬性能研究进展[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(6): 2091-2108. |
| [5] | 江洋, 彭长宏, 陈伟, 周豪, 马忠彬, 李洪博, 邱在容, 张国鹏, 周康根. 废旧磷酸铁锂粉料综合回收中试研究[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(6): 2353-2361. |
| [6] | 裴欣哲, 孙朱行, 林钰翔, 张朝阳, 钱勇, 吕兴才. 电催化分解液氨阳极材料的研究[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(5): 1843-1854. |
| [7] | 孙铭泽, 黄鹤来, 牛志强. 铂基氧还原催化剂:从单晶电极到拓展表面纳米材料[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(4): 1256-1269. |
| [8] | 李云璇, 刘新悦, 陈熙, 刘文, 周明月, 蓝兴英. 基于固液氧化还原靶向反应的能量存储技术:材料、器件及动力学[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(4): 1222-1240. |
| [9] | 贾旭东, 杨博龙, 程前, 李雪丽, 向中华. 分步负载金属法制备铁钴双金属位点高效氧还原电催化剂[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(4): 1578-1593. |
| [10] | 严孝清, 赵瑛, 张宇哲, 欧鸿辉, 黄起中, 胡华贵, 杨贵东. 五重孪晶铜纳米线@聚吡咯制备及其电催化硝酸盐还原制氨[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(4): 1519-1532. |
| [11] | 李昂, 赵振宇, 李洪, 高鑫. 微波诱导高分散Pd/FeP催化剂构筑及其电催化性能研究[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(4): 1594-1606. |
| [12] | 吴希, 孙博, 刘银东, 齐传磊, 陈凯毅, 王路海, 许崇, 李永峰. 钠离子电池沥青基碳负极材料制备技术研究进展[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(4): 1270-1283. |
| [13] | 吴吉昊, 陈涛, 刘思宇, 刘梦柯, 杨卷. 双功能活化制备沥青基硬炭用于钠离子电池负极[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(3): 1019-1027. |
| [14] | 郭邦军, 贾理男, 张希. 全固态硫化物锂电池中NCM正极及其界面研究[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(3): 743-759. |
| [15] | 潘娜, 田昌, 怀兰坤, 刘玉玉, 张芬芬, 高晓梅, 刘伟, 闫良国, 赵艳侠. 聚合铝钛基絮凝剂的合成与应用[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(3): 1009-1018. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备 11010102001995号
京公网安备 11010102001995号