化工学报 ›› 2024, Vol. 75 ›› Issue (9): 3133-3151.DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20240358
李舒月1( ), 王欢1,2, 周少强2, 毛志宏1, 张永民1(
), 王欢1,2, 周少强2, 毛志宏1, 张永民1( ), 王军武1, 吴秀花2
), 王军武1, 吴秀花2
收稿日期:2024-04-02
修回日期:2024-05-07
出版日期:2024-09-25
发布日期:2024-10-10
通讯作者:
张永民
作者简介:李舒月(1992—),女,博士,讲师,shuyue.li@cup.edu.cn
基金资助:
Shuyue LI1( ), Huan WANG1,2, Shaoqiang ZHOU2, Zhihong MAO1, Yongmin ZHANG1(
), Huan WANG1,2, Shaoqiang ZHOU2, Zhihong MAO1, Yongmin ZHANG1( ), Junwu WANG1, Xiuhua WU2
), Junwu WANG1, Xiuhua WU2
Received:2024-04-02
Revised:2024-05-07
Online:2024-09-25
Published:2024-10-10
Contact:
Yongmin ZHANG
摘要:
气固流化床因具有气固接触效率高、相间传质传热快等优点已用于天然铀转化工艺的多个环节,但目前对这类高密度颗粒系统的流化反应性能认识不足,难以对其精确设计和操控。采用计算颗粒流体力学(computational particle fluid dynamics, CPFD)方法对工业尺度连续U3O8还原流化床进行全三维数值模拟,对不同颗粒粒径分布的流化床还原系统中宏观气固流动、传热、反应特性等重要参数进行统计分析。结果显示,在氢气过量80%的条件下,3种不同粒径的颗粒在流化床中的流化状态均表现不佳,大部分区域颗粒处于非流化状态,床层膨胀率低。分析出口处产物分布发现,颗粒粒径越小产物的转化率越高,然而由于流化状态普遍较差,即便是在粒径较小的条件下转化率的总体水平仍然偏低。以上结果表明,在实际操作中可能需要进一步优化流化床的操作条件和结构形式,以提高流化效果和反应转化率。本研究期望能够为高密度颗粒在流化床中的流动与反应特性的深入认识提供新的视角和方法,为核化工及相关领域的技术进步提供有力支持。
中图分类号:
李舒月, 王欢, 周少强, 毛志宏, 张永民, 王军武, 吴秀花. 基于CPFD方法的U3O8氢还原流化床反应器数值模拟[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(9): 3133-3151.
Shuyue LI, Huan WANG, Shaoqiang ZHOU, Zhihong MAO, Yongmin ZHANG, Junwu WANG, Xiuhua WU. Numerical simulation of hydrogen reduction of U3O8 in fluidized bed reactors using CPFD method[J]. CIESC Journal, 2024, 75(9): 3133-3151.
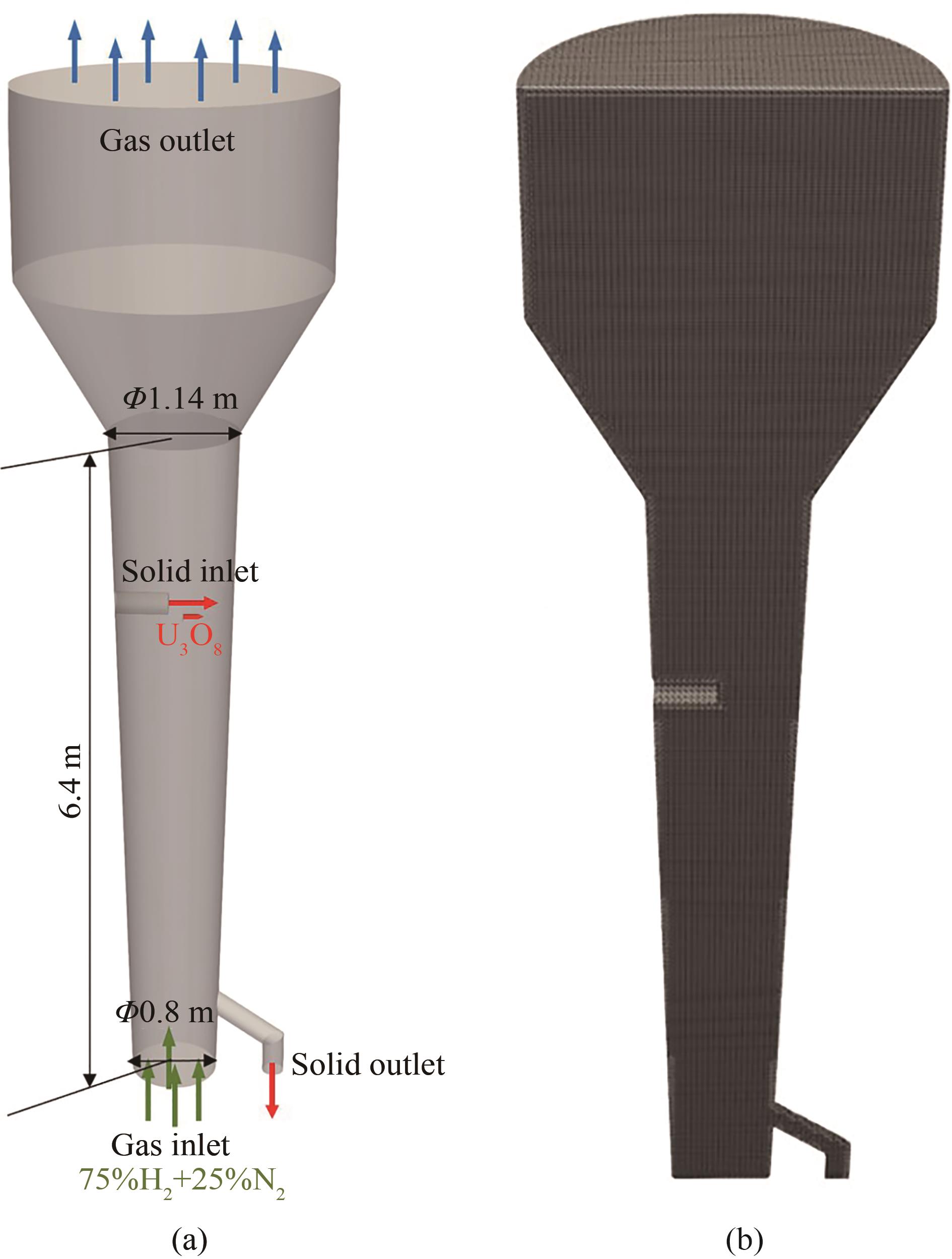
图2 (a) U3O8还原流化床反应器结构示意图; (b)三维模型网格划分剖面图
Fig.2 (a) Schematic diagram of the U3O8 reduction fluidized bed system structure; (b) cross-sectional mesh for three-dimensional model
| 操作参数 | 数值 |
|---|---|
| U3O8进料 | |
| 进料量 | |
| 进料温度 | 866 K |
| 密度 | 6690 kg/m3 |
| 气体进料 | |
| 进气量(H2过量80%) | 氢气量:3025.21 mol/h 氮气量:1008 mol/h 折算气速:0.064 m/s |
| 固体产物出口 | |
| 温度 | 866 K |
| 压力 | 400 kPa |
| 出料量 | 707.56 kg/h |
| UO2密度 | 6870 kg/m3 |
| 壁面条件 | 绝热壁面 |
表1 U3O8还原流化床反应器主要运行工况参数
Table 1 Main operating parameters of U3O8 reduction fluidized bed reactor
| 操作参数 | 数值 |
|---|---|
| U3O8进料 | |
| 进料量 | |
| 进料温度 | 866 K |
| 密度 | 6690 kg/m3 |
| 气体进料 | |
| 进气量(H2过量80%) | 氢气量:3025.21 mol/h 氮气量:1008 mol/h 折算气速:0.064 m/s |
| 固体产物出口 | |
| 温度 | 866 K |
| 压力 | 400 kPa |
| 出料量 | 707.56 kg/h |
| UO2密度 | 6870 kg/m3 |
| 壁面条件 | 绝热壁面 |
| 参数 | 数值 |
|---|---|
| 颗粒堆积体积分数 | 0.56 |
| 最大碰撞动量再定向系数/% | 40 |
| 切向颗粒-壁面碰撞恢复系数 | 0.99 |
| 法向颗粒-壁面碰撞恢复系数 | 0.3 |
| 回弹系数 | 0 |
| 颗粒应力模型的压力常数ps/Pa | 10 |
| 颗粒应力模型的无量纲常数β | 3 |
| 计算颗粒代表的实际颗粒数 | 125 |
| 颗粒应力模型的无量纲常数 α | 10-7 |
| 湍流模型 | LES |
表2 模拟参数及初始边界条件
Table 2 Simulation parameters and initial boundary conditions
| 参数 | 数值 |
|---|---|
| 颗粒堆积体积分数 | 0.56 |
| 最大碰撞动量再定向系数/% | 40 |
| 切向颗粒-壁面碰撞恢复系数 | 0.99 |
| 法向颗粒-壁面碰撞恢复系数 | 0.3 |
| 回弹系数 | 0 |
| 颗粒应力模型的压力常数ps/Pa | 10 |
| 颗粒应力模型的无量纲常数β | 3 |
| 计算颗粒代表的实际颗粒数 | 125 |
| 颗粒应力模型的无量纲常数 α | 10-7 |
| 湍流模型 | LES |
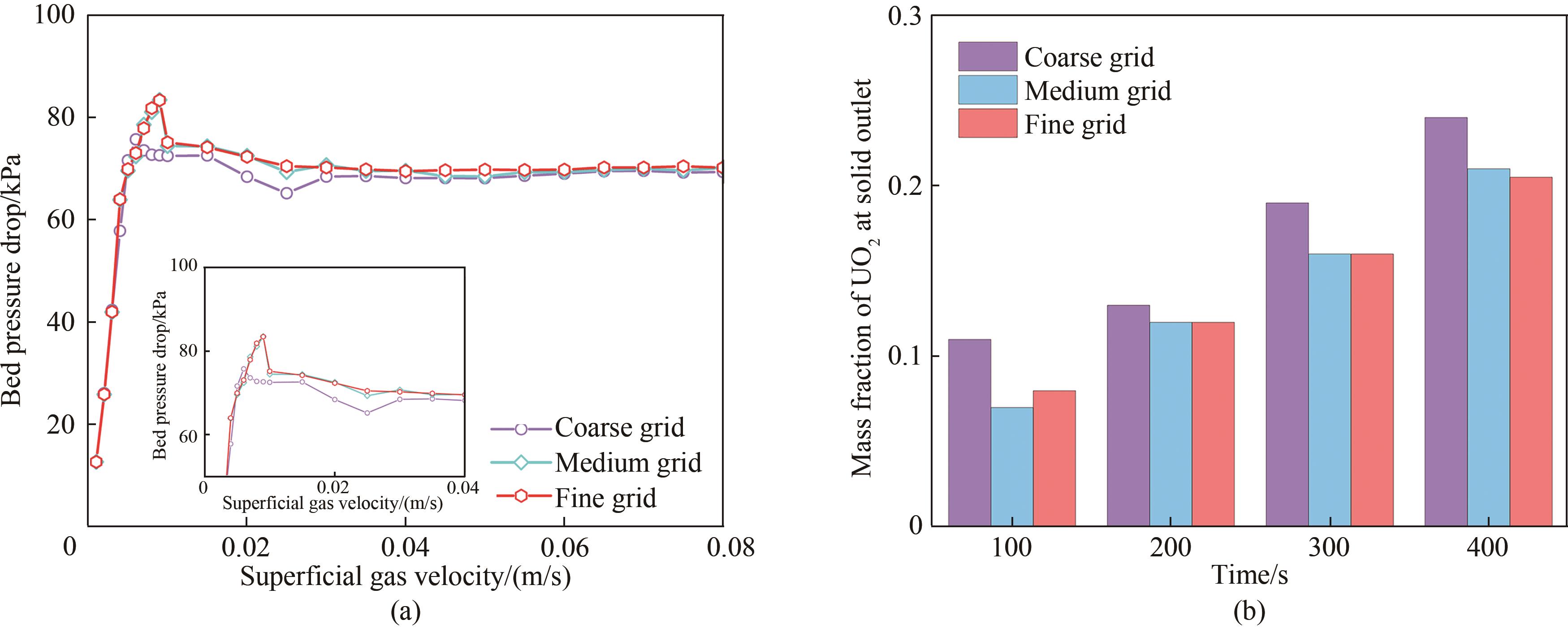
图3 不同网格数模拟的床层压降随流化风速的变化情况(a)和出口处UO2转化率随时间的变化情况(b)
Fig.3 Variation of bed pressure drop with fluidization velocity (a) and UO2 conversion with different grid number (b)
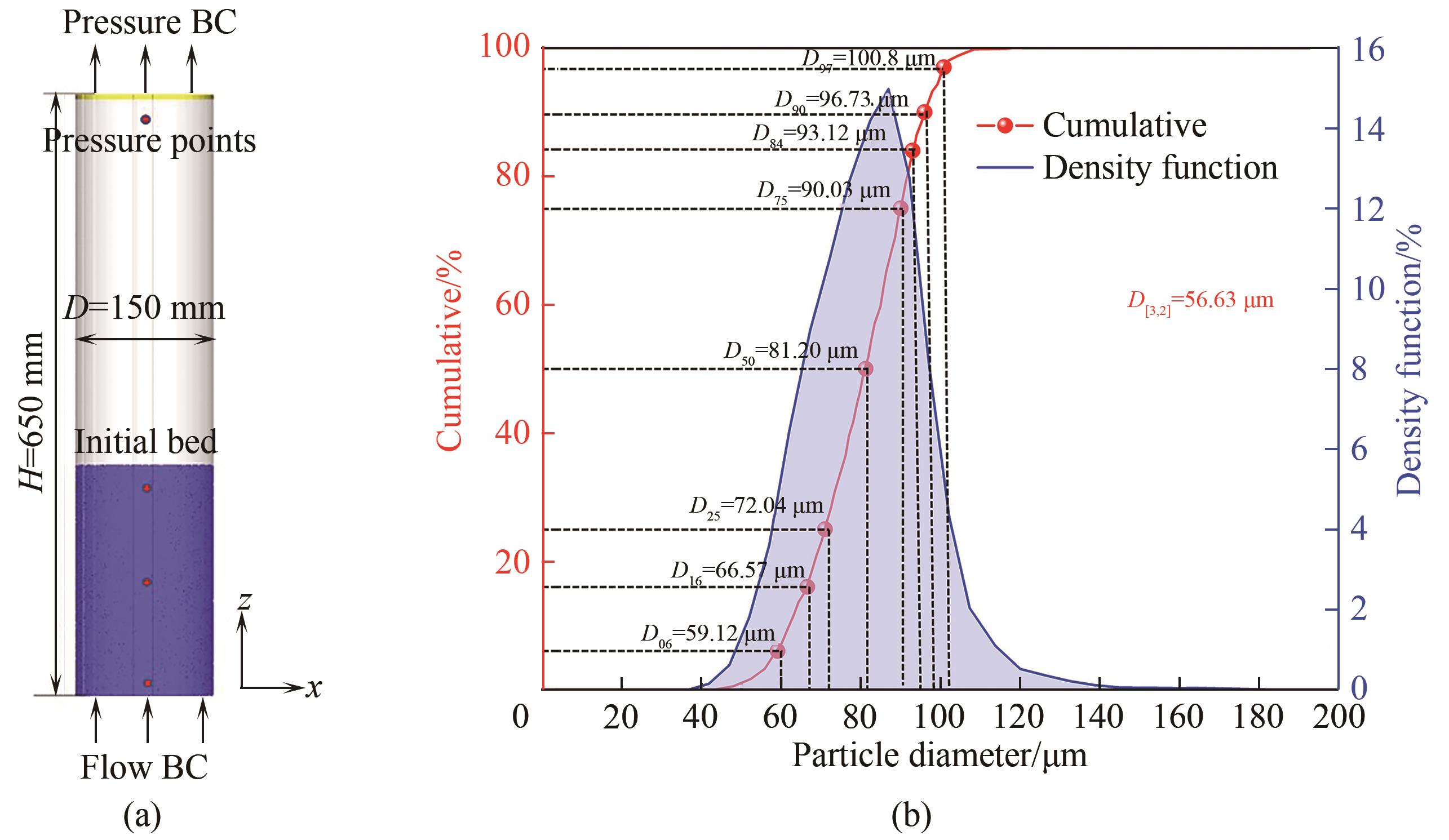
图5 (a) 基于实验室装置建立的三维鼓泡流化床模型;(b) 氧化铁颗粒粒径分布
Fig.5 (a) Three-dimensional model of a bubbling fluidized bed constructed based on laboratory apparatus; (b) particle size distribution of iron oxide particles
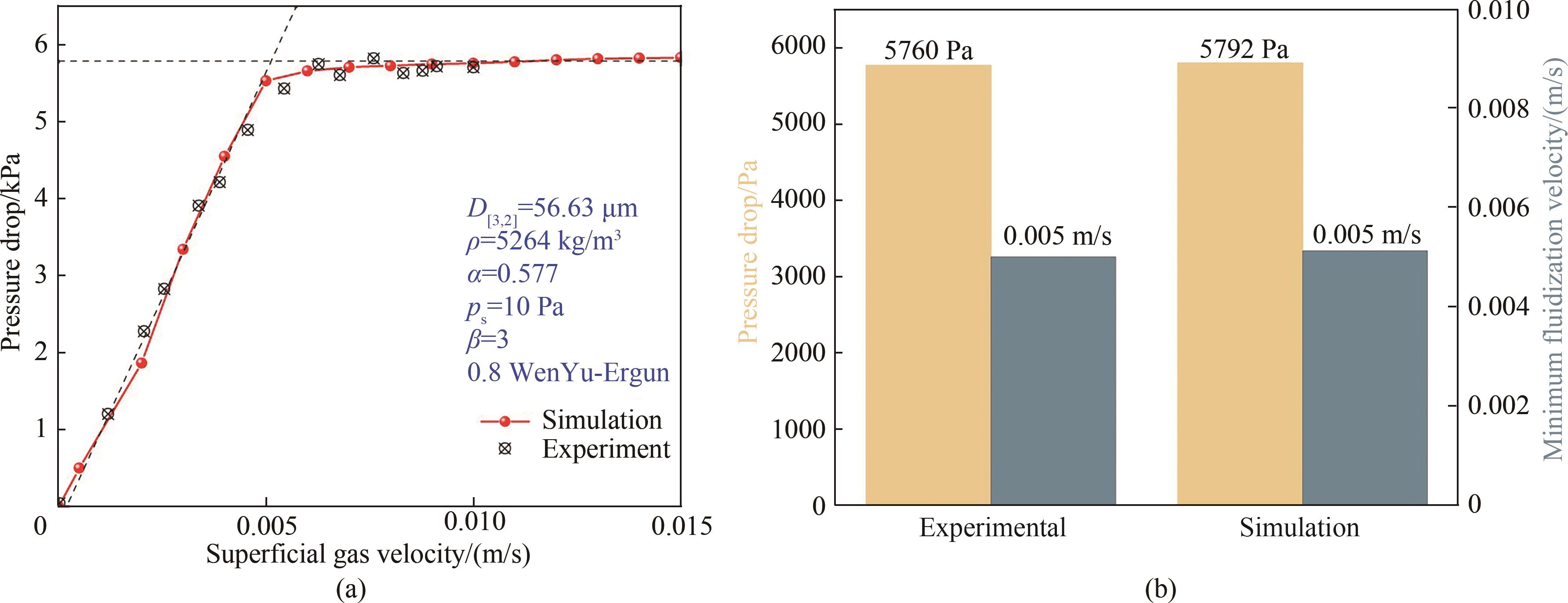
图6 (a)不同流化风速下的床层压降变化特性;(b)实验与数值模拟最大床层压降及最小流化速度预测值的对比
Fig.6 (a) Characteristics of bed pressure drop under different fluidization velocities; (b) comparison between experimental and simulation results for maximum bed pressure drop and predicted values of minimum fluidization velocity
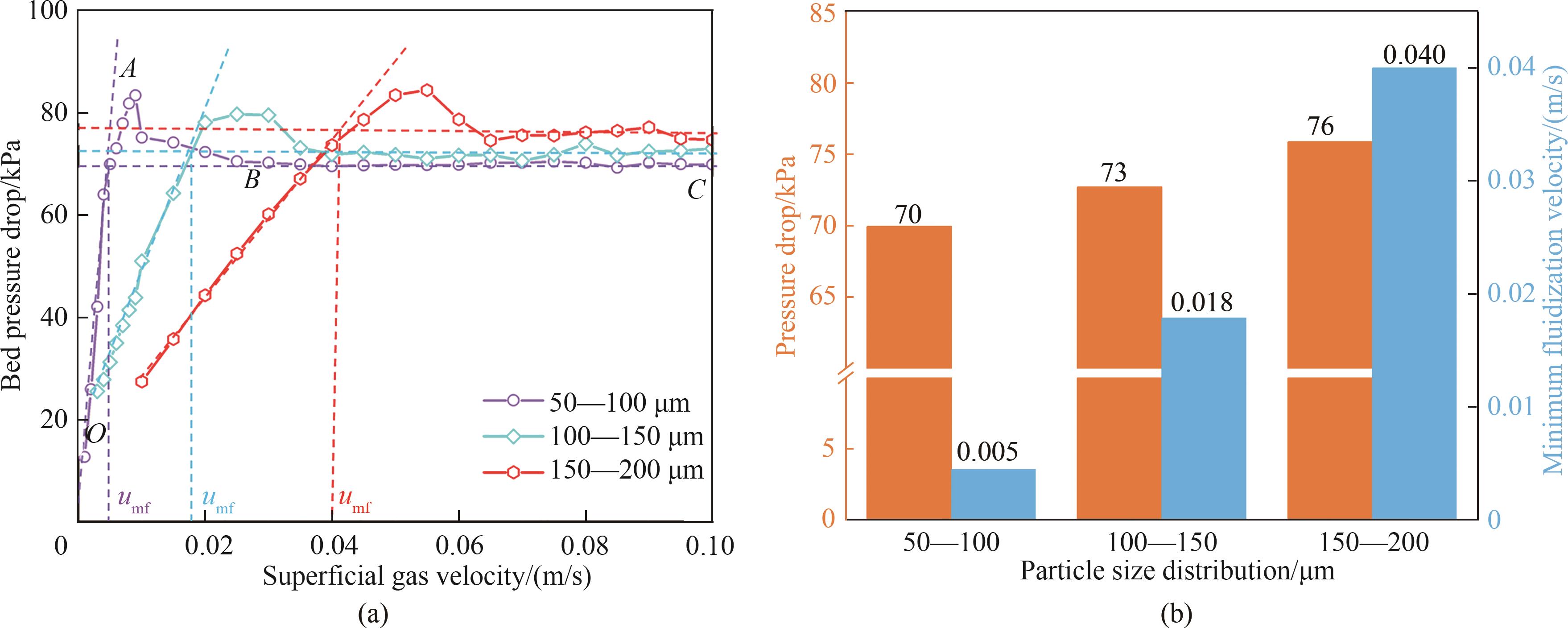
图7 不同颗粒粒径的热态U3O8还原反应器中床层压力随流化风速的变化曲线及流型划分(a)以及完全流化状态下的床层压降统计值和最小流化速度预测值(b)
Fig.7 Thermal U3O8 reduction reactor with different particle sizes: (a) bed pressure varying with fluidization velocity and flow pattern classification; (b) comparison of bed pressure drop under the fully fluidized state and minimum fluidization velocity
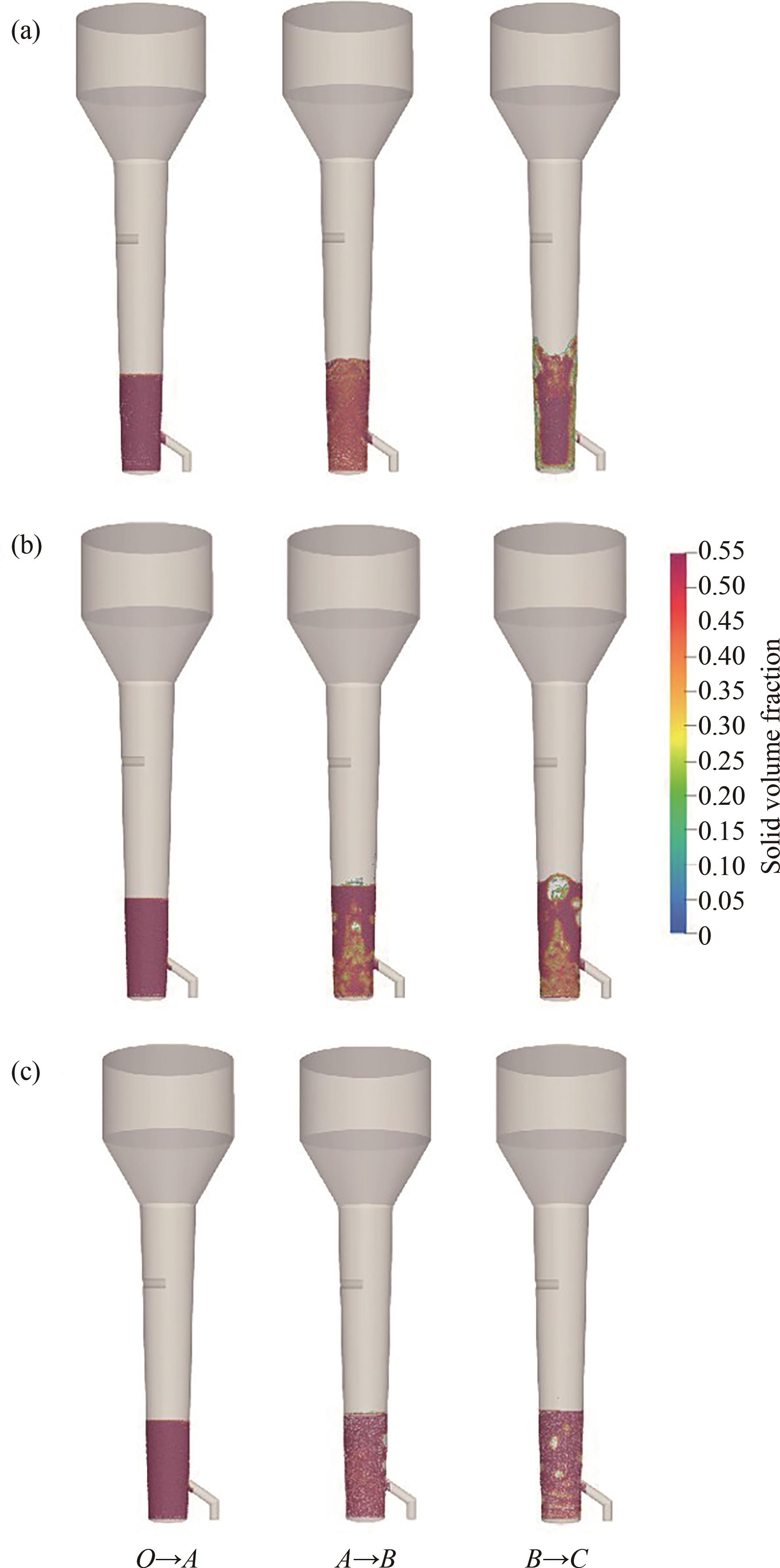
图8 不同流化风速下热态U3O8还原反应器床层颗粒分布:(a) 50~100 μm; (b)100~150 μm; (c)150~200 μm
Fig.8 Particle distribution in thermal U3O8 reduction reactor under different fluidization velocities: (a) 50—100μm; (b) 100—150 μm; (c) 150—200 μm
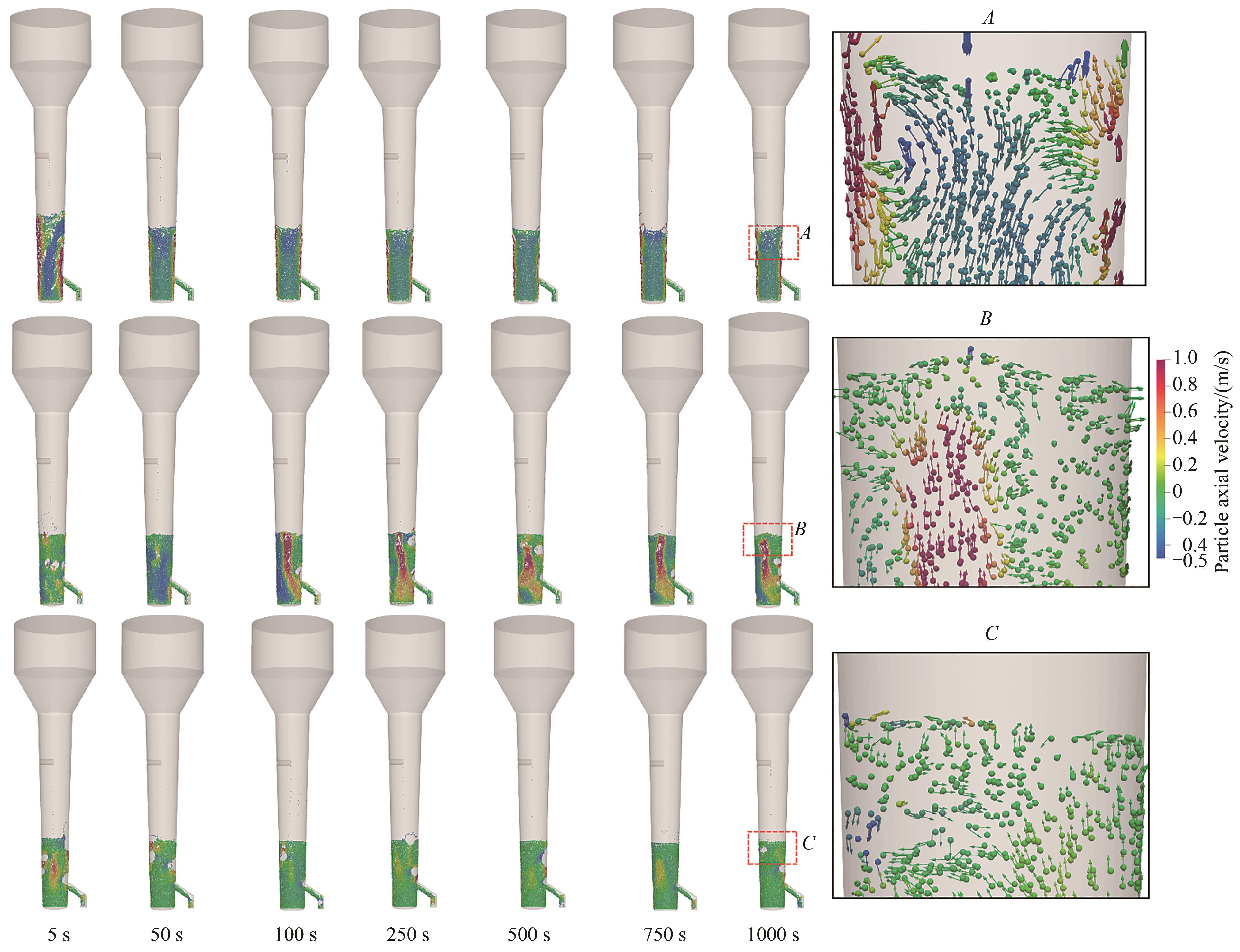
图9 氢气过剩80%(流化风速为0.064 m/s)情况下床层颗粒的瞬态分布(通过颗粒轴向速度着色)
Fig.9 Transient particles distribution with 80% excess hydrogen (fluidization velocity of 0.064 m/s, coloring based on particle axial velocity)
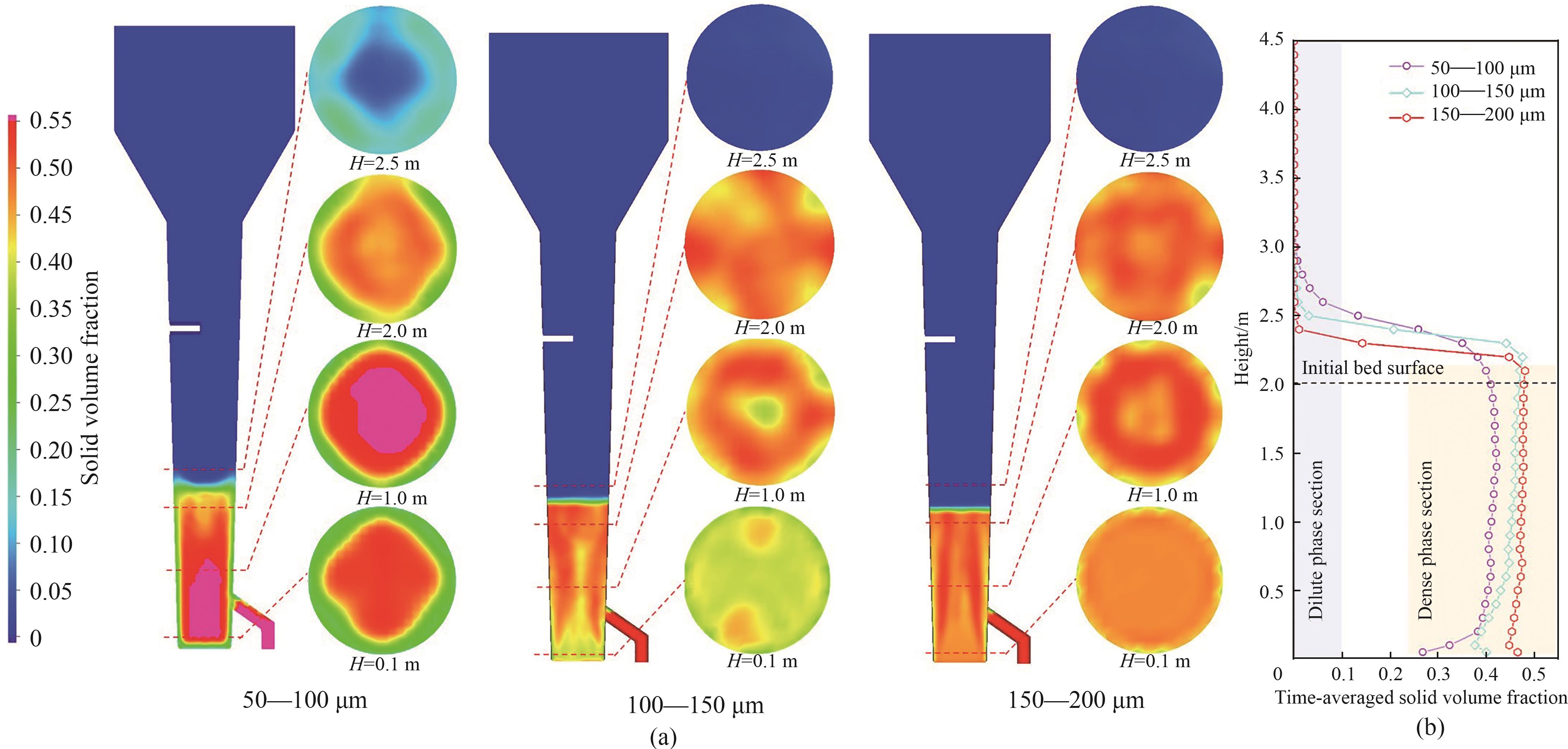
图10 (a)稳定流动状态下床层颗粒浓度时均分布云图;(b)不同高度反应器中床层颗粒浓度时均分布曲线
Fig.10 (a) Time-averaged particle distribution in steady flow state; (b) time-averaged distribution of particle concentration at different heights in reactor
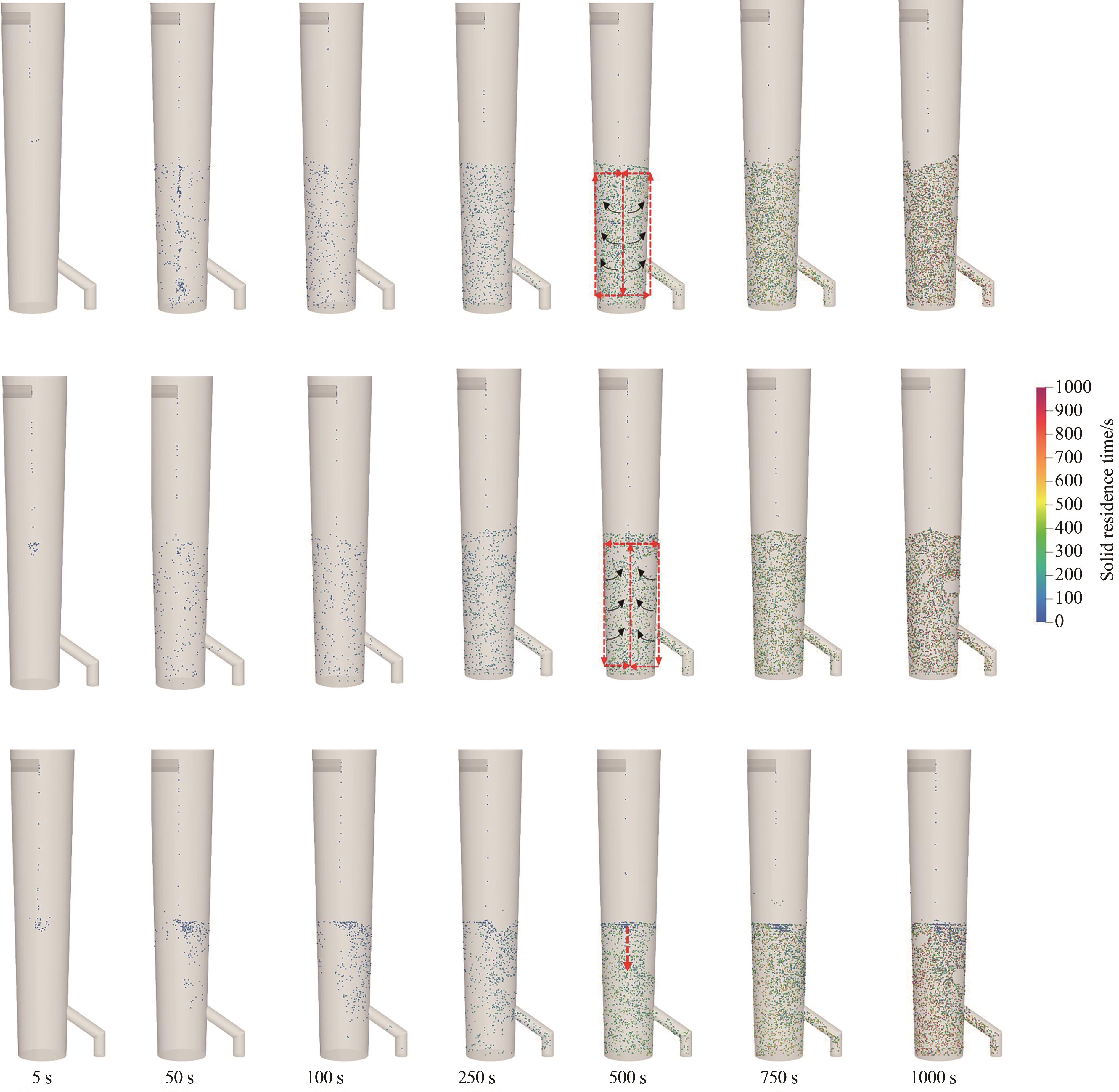
图12 不同粒径的新鲜入料颗粒在反应器内瞬时分布的演变过程(通过颗粒停留时间着色)
Fig.12 Evolution of instantaneous distribution of fresh feeding particles with different sizes inside reactor (coloring based on particle residence time)
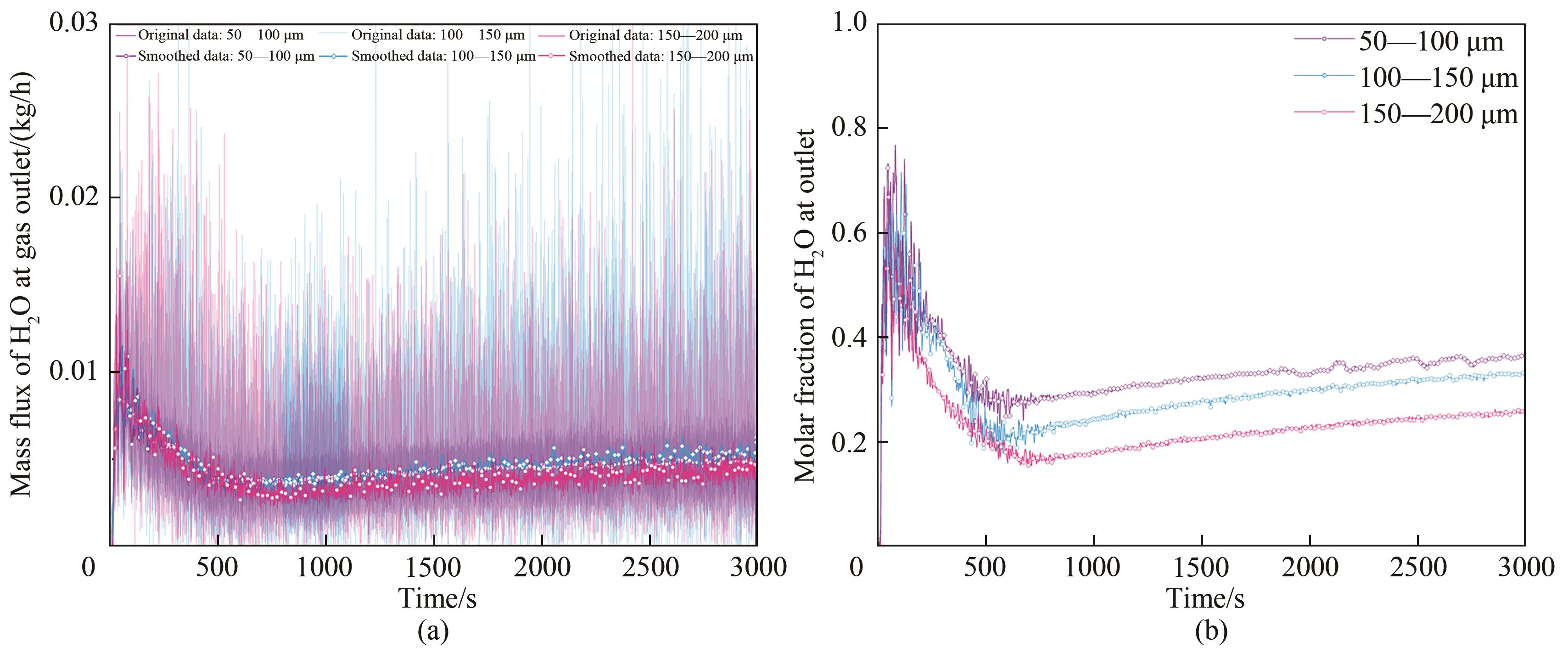
图13 不同颗粒粒径床层中反应器气体出口处H2O质量流率(a)和摩尔分数(b)随时间的变化
Fig.13 Time variation with mass flux (a) and mole fraction (b) of H2O at the gas outlet with different particle sizes
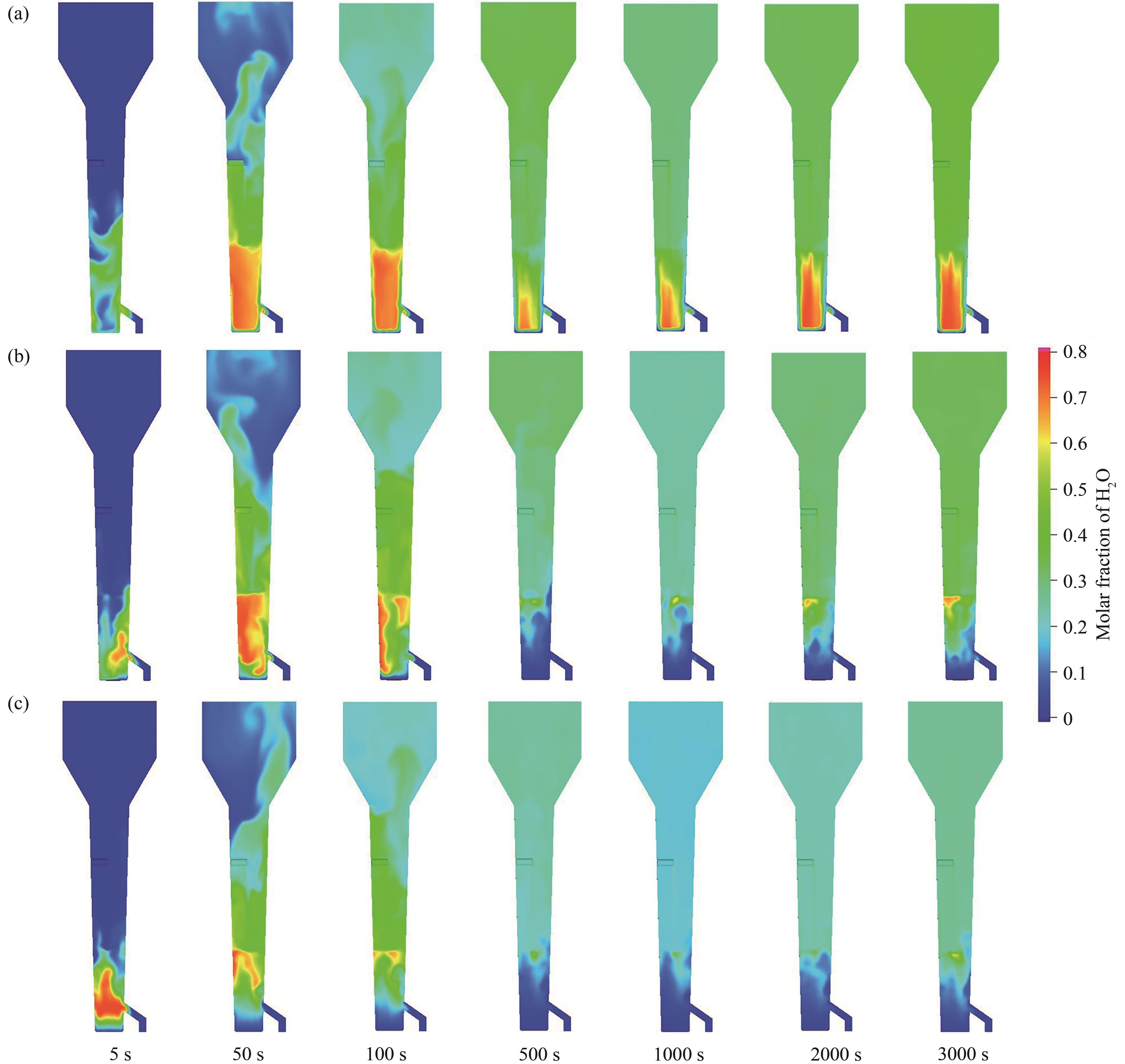
图14 U3O8还原反应器中产物H2O分布云图:(a) 50~100 μm; (b)100~150 μm; (c)150~200 μm
Fig14 H2O distribution in U3O8 reduction reactor: (a) 50—100 μm; (b) 100—150 μm; (c) 150—200 μm
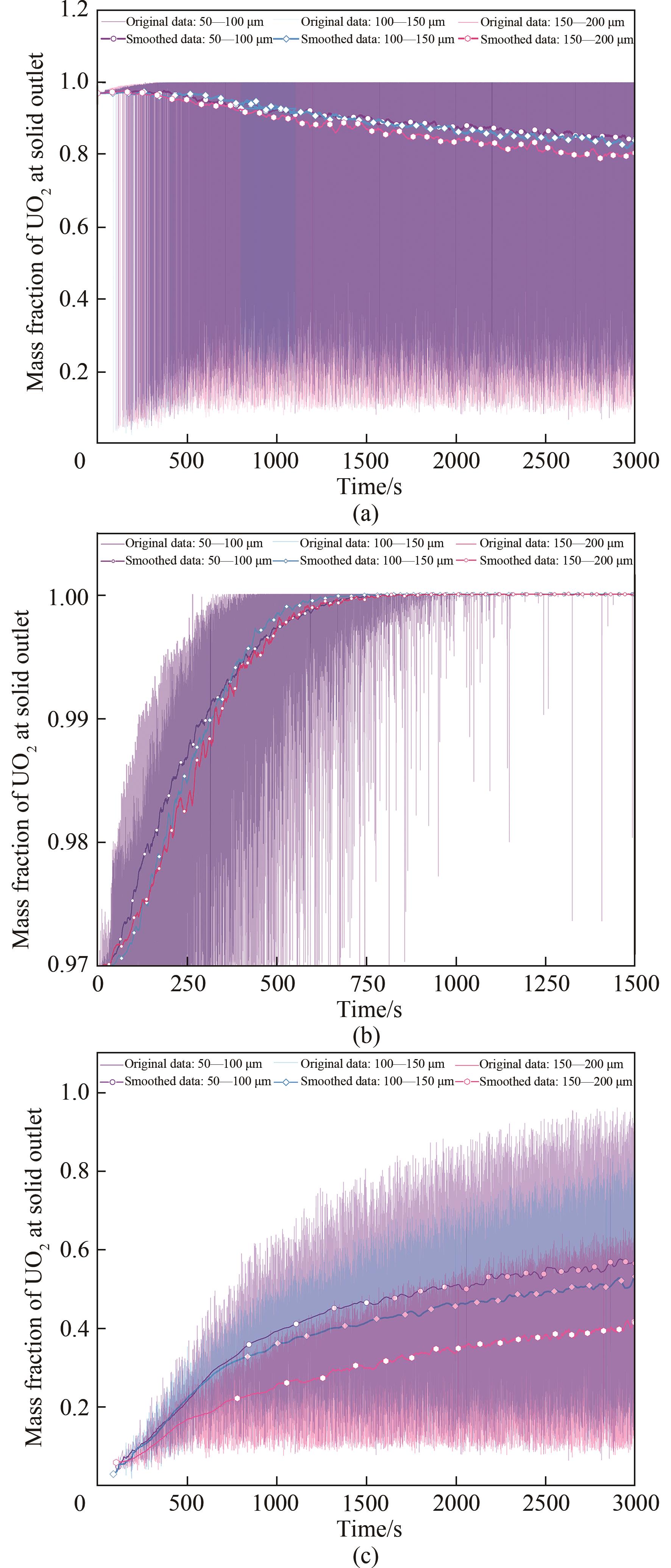
图15 不同颗粒粒径床层中固相出口处UO2组分质量分数随时间的变化:(a) 混合颗粒;(b) 初始堆料颗粒;(c)新鲜入料颗粒
Fig.15 Time variation with UO2 mass fraction of different particle sizes at solid outlet: (a) particle mixture; (b) initial packing particles; (c) fresh feeding particles
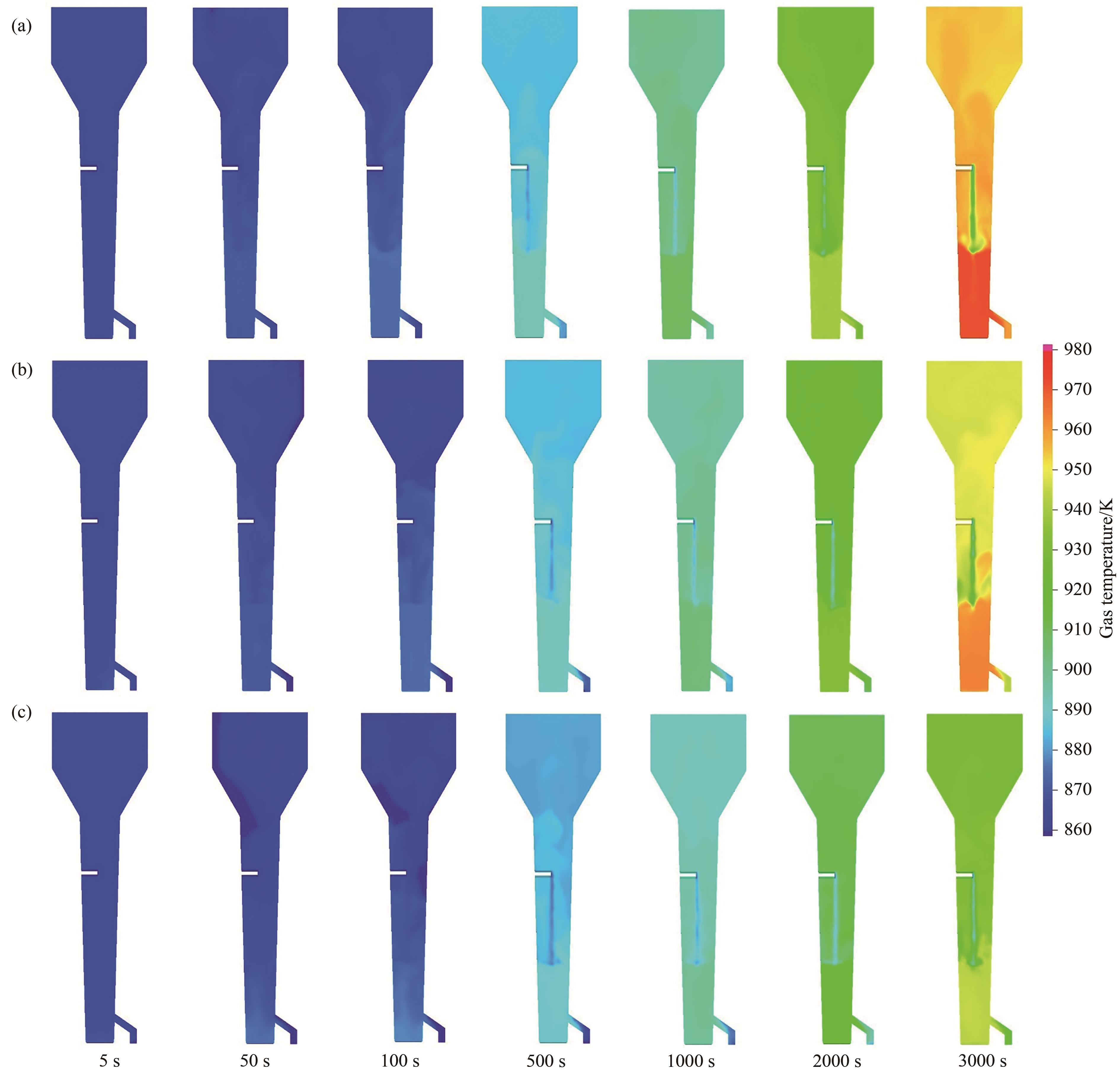
图16 不同颗粒粒径U3O8还原反应器中气体温度分布云图:(a)50~100 μm;(b)100~150 μm;(c)150~200 μm
Fig.16 Gas temperature distribution in U3O8 reduction reactors with different particle sizes: (a) 50—100 μm; (b) 100—150 μm; (c) 150—200 μm
| 1 | Murchie M P, Reid S J. Uranium conversion and enrichment[C]//Piro M H A. Advances in Nuclear Fuel Chemistry. Cambridge: Woodhead Publishing, 2020: 331-370. |
| 2 | 吴俊德, 徐乐昌, 牛洁, 等. 天然铀纯化与转化废物最小化对策建议[J]. 中国辐射卫生, 2022, 31(1): 74-78, 84. |
| Wu J D, Xu L C, Niu J, et al. A recommendation on minimization of wastes from natural uranium purification and conversion[J]. Chinese Journal of Radiological Health, 2022, 31(1): 74-78, 84. | |
| 3 | 刘马林. 化工流化床技术在铀燃料循环工业中的应用[J]. 化工进展, 2013, 32(3): 508-514, 548. |
| Liu M L. Review on application of fluidized bed technology in industry of uranium fuel cycle[J]. Chemical Industry and Engineering Progress, 2013, 32(3): 508-514, 548. | |
| 4 | 刘荣正, 刘马林, 邵友林, 等. 流化床-化学气相沉积技术的应用及研究进展[J]. 化工进展, 2016, 35(5): 1263-1272. |
| Liu R Z, Liu M L, Shao Y L, et al. Application and research progress of fluidized bed-chemical vapor deposition technology[J]. Chemical Industry and Engineering Progress, 2016, 35(5): 1263-1272. | |
| 5 | Oliver A J, Özberk E. Conversion of natural uranium[C]// Hore-Lacy I. Uranium for Nuclear Power. Amsterdam: Elsevier, 2016: 299-319. |
| 6 | Raffo-Caiado A C, Begovich J M, Ferrada J J, et al. Model of a generic natural uranium conversion plant—Suggested measures to strengthen international safeguards[R]. Oak Ridge National Laboratory, Tennessee, 2009. |
| 7 | Gupta C K, Sathiyamoorthy D. Fluid Bed Technology in Materials Processing[M]. Boca Raton, Fla: CRC Press, 1999. |
| 8 | Cappia F, Cullison M, Chen T, et al. Grain subdivision and structural modifications by high-energy heavy ions in UO2 with different initial grain size[J]. Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research Section B: Beam Interactions with Materials and Atoms, 2022, 515: 48-60. |
| 9 | Lindroos M, Vajragupta N, Heikinheimo J, et al. Micromechanical modeling of single crystal and polycrystalline UO2 at elevated temperatures[J]. Journal of Nuclear Materials, 2023, 573: 154127. |
| 10 | Qiu M F, Chen Z, Jiang L, et al. Numerical simulation of uranium tetrafluoride fluorination in a multistage spouted bed using the improved CFD-DEM chemical reaction model[J]. Particuology, 2023, 75: 119-136. |
| 11 | Du Z, Liu J Y, Liu F, et al. Relationship of particle size, reaction and sticking behavior of iron ore fines toward efficient fluidized bed reduction[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2022, 447: 137588. |
| 12 | de Vos W, Nicol W, du Toit E. Entrainment behaviour of high-density Geldart A powders with different shapes[J]. Powder Technology, 2009, 190(3): 297-303. |
| 13 | Bischi A, Langørgen Ø, Morin J X, et al. Performance analysis of the cold flow model of a second generation chemical looping combustion reactor system[J]. Energy Procedia, 2011, 4: 449-456. |
| 14 | Pierson H O. Handbook of Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD): Principles, Technology, and Applications[M]. 2nd ed. Norwich, N.Y.: Noyes Publications, 1999. |
| 15 | Grace J R, Bi X T, Ellis N. Essentials of Fluidization Technology[M]. Weinheim: John Wiley & Sons, 2020. |
| 16 | 王荘, 吕潇, 邵媛媛, 等. 流态化的往昔寻觅及未来启示[J]. 化工学报, 2021, 72(12): 5904-5927. |
| Wang Z, Lyu X, Shao Y Y, et al. Early exploration of fluidization theory and its inspiration to the future[J]. CIESC Journal, 2021, 72(12): 5904-5927. | |
| 17 | Zhong Y, Gao J, Guo Z, et al. Mechanism and prevention of agglomeration/defluidization during fluidized-bed reduction of iron ore [C]//Shatokha V. Iron Ores and Iron Oxide Materials. Rijeka: IntechOpen, 2018: 105. |
| 18 | Rodriguez P, Caussat B, Ablitzer C, et al. Fluidization and coating of very dense powders by fluidized bed chemical vapour deposition[J]. Chemical Engineering Research and Design, 2013, 91(12): 2477-2483. |
| 19 | Zhong Y W, Wang Z, Guo Z C, et al. Defluidization behavior of iron powders at elevated temperature: influence of fluidizing gas and particle adhesion[J]. Powder Technology, 2012, 230: 225-231. |
| 20 | Vanni F, Caussat B, Ablitzer C, et al. Effects of reducing the reactor diameter on the fluidization of a very dense powder[J]. Powder Technology, 2015, 277: 268-274. |
| 21 | Saayman J, Ellis N, Nicol W. Fluidization of high-density particles: the influence of fines on reactor performance[J]. Powder Technology, 2013, 245: 48-55. |
| 22 | Bournival G, Ata S, Wanless E J. Behavior of bubble interfaces stabilized by particles of different densities[J]. Langmuir, 2016, 32(25): 6226-6238. |
| 23 | Liu M L, Wen Y Y, Liu R Z, et al. Investigation of fluidization behavior of high density particle in spouted bed using CFD-DEM coupling method[J]. Powder Technology, 2015, 280: 72-82. |
| 24 | Jiang L, Qiu M F, Liu R Z, et al. CFD-DEM simulation of high density particles fluidization behaviors in 3D conical spouted beds[J]. Particuology, 2024, 88: 266-281. |
| 25 | Li S Y, Zhang Y M, Wang W J, et al. Multi-scale simulation of particle density effects on hydrodynamics in dense gas-solid fluidized beds[J]. Powder Technology, 2024, 435: 119394. |
| 26 | Li S Y, Zhang Y M, Wang W J, et al. Comparative analysis of particle density effects on initial fluidization in gas-solid fluidized beds[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2023, 477: 146966. |
| 27 | Lan B, Xu J, Lu S, et al. Direct reduction of iron-ore with hydrogen in fluidized beds: a coarse-grained CFD-DEM-IBM study[J]. Powder Technology, 2024, 438: 119624. |
| 28 | Smagorinsky J. General circulation experiments with the primitive equations (Ⅰ): The basic experiment[J]. Monthly Weather Review, 1963, 91(3): 99-164. |
| 29 | Gan J Q, Zhou Z Y, Yu A B. Particle scale study of heat transfer in packed and fluidized beds of ellipsoidal particles[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2016, 144: 201-215. |
| 30 | Kuang S B, Yu A B. Micromechanic modeling and analysis of the flow regimes in horizontal pneumatic conveying[J]. AIChE Journal, 2011, 57(10): 2708-2725. |
| 31 | Snider D M. An incompressible three-dimensional multiphase particle-in-cell model for dense particle flows[J]. Journal of Computational Physics, 2001, 170(2): 523-549. |
| 32 | Harris S E, Crighton D G. Solitons, solitary waves, and voidage disturbances in gas-fluidized beds[J]. Journal of Fluid Mechanics, 1994, 266: 243-276. |
| 33 | Wen C Y. Mechanics of fluidization[J]. Fluid Particle Technology, Chemical Engineering Progress Symposium Series, 1966, 62:100-111. |
| 34 | Hamilton M A, Reinking Z, Whitty K J, et al. Application of MP-PIC on dual interconnected chemical looping cold flow system: validation process with hydrodynamic experiments[R]. Salt Lake City, UT: Univ of Utah, 2018. |
| 35 | Adkins B D, Kapur N, Dudley T, et al. Experimental validation of CFD hydrodynamic models for catalytic fast pyrolysis[J]. Powder Technology, 2017, 316: 725-739. |
| 36 | Reinking Z, Shim H S, Whitty K J, et al. Computational simulation of a 100 kW dual circulating fluidized bed reactor processing coal by chemical looping with oxygen uncoupling[J]. International Journal of Greenhouse Gas Control, 2019, 90: 102795. |
| 37 | Zafiryadis F, Jensen A D, Laxminarayan Y, et al. Predicting cold gas-solid flow in a pilot-scale dual-circulating fluidized bed: validation of computational particle fluid dynamics model[J]. Powder Technology, 2021, 381: 25-43. |
| 38 | Wheeler V J. The diffusion and solubility of hydrogen in uranium dioxide single crystals[J]. Journal of Nuclear Materials, 1971, 40(2): 189-194. |
| 39 | Le Page A H, Fane A G. The kinetics of hydrogen reduction of UO3 and U3O8 derived from ammonium diuranate[J]. Journal of Inorganic and Nuclear Chemistry, 1974, 36(1): 87-92. |
| 40 | 王俊峰. 铀转化工艺学[M]. 北京: 中国原子能出版社, 2012. |
| Wang J F. Uranium Conversion Technology [M]. Beijing: China Atomic Energy Press, 2012. | |
| 41 | 许贺卿. 铀化合物转化工艺学[M]. 北京: 原子能出版社, 1994. |
| Xu H Q. Uranium Compound Conversion Technology[M]. Beijing: Atomic Press, 1994. | |
| 42 | Dell R M, Wheeler V J. Chemical reactivity of uranium trioxide Part 1—Conversion to U3O8, UO2 and UF4 [J]. Transactions of the Faraday Society, 1962, 58: 1590-1607. |
| 43 | Kavazauri R, Pokrovskiy S A, Baranov V G, et al. Thermal properties of nonstoichiometry uranium dioxide[J]. IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering, 2016, 130(1): 012025. |
| 44 | Niksiar A, Rahimi A. Design of a moving bed reactor for the production of uranium tetrafluoride based on mathematical modeling[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2010, 65(10): 3147-3157. |
| 45 | Park J Y, Levenspiel O. The crackling core model for the reaction of solid particles[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 1975, 30(10): 1207-1214. |
| 46 | 闫树仁, 梁咏诗, 张永民. 深层鼓泡床内偏涌现象的实验研究与数值模拟[J]. 化工学报, 2014, 65(12): 4775-4784. |
| Yan S R, Liang Y S, Zhang Y M. Experimental study and numerical simulation on jet streaming in deep bubbling fluidized-bed[J]. CIESC Journal, 2014, 65(12): 4775-4784. | |
| 47 | Issangya A S, Knowlton T, Karri S. Detection of gas bypassing due to jet streaming in deep fluidized beds of group A particles[C]//Berruti F, Bi X, Pugsley T. The 12th International Conference on Fluidization-New Horizons in Fluidization Engineering. ECI Symposium Series. Vancouver, Canada: ECI Digital Archives, 2007:775-782. |
| 48 | Sau D C, Mohanty S, Biswal K C. Minimum fluidization velocities and maximum bed pressure drops for gas-solid tapered fluidized beds[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2007, 132(1/2/3): 151-157. |
| 49 | Schaafsma S H, Marx T, Hoffmann A C. Investigation of the particle flowpattern and segregation in tapered fluidized bed granulators[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2006, 61(14): 4467-4475. |
| 50 | Hua L N, Zhao H, Li J, et al. Eulerian–Eulerian simulation of irregular particles in dense gas–solid fluidized beds[J]. Powder Technology, 2015, 284: 299-311. |
| 51 | Reuge N, Cadoret L, Coufort-Saudejaud C, et al. Multifluid Eulerian modeling of dense gas-solids fluidized bed hydrodynamics: influence of the dissipation parameters[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2008, 63(22): 5540-5551. |
| 52 | Sau D C, Mohanty S, Biswal K C. Experimental studies and empirical models for the prediction of bed expansion in gas–solid tapered fluidized beds[J]. Chemical Engineering and Processing: Process Intensification, 2010, 49(4): 418-424. |
| 53 | Li D D, Zhao B D, Lu S, et al. Physics-informed dynamic mode decomposition for short-term and long-term prediction of gas-solid flows[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2024, 289: 119849. |
| 54 | Xie Z Z, Gu X Y, Shen Y S. A machine learning study of predicting mixing and segregation behaviors in a bidisperse solid-liquid fluidized bed[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2022, 61(24): 8551-8565. |
| [1] | 陈巨辉, 苏潼, 李丹, 陈立伟, 吕文生, 孟凡奇. 翅形扰流片作用下的微通道换热特性[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(9): 3122-3132. |
| [2] | 豆少军, 郝亮. PEMFC催化层耦合气体电荷传输过程的介观模拟[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(8): 3002-3010. |
| [3] | 钱啸宇, 阮璇, 李水清. 外加电场下电介质颗粒层结构重构与悬浮[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(8): 2756-2762. |
| [4] | 朱子良, 王爽, 姜宇昂, 林梅, 王秋旺. 欧拉-拉格朗日迭代固-液相变算法[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(8): 2763-2776. |
| [5] | 邓爱明, 何玉荣, 唐天琪, 胡彦伟. 导流板对喷雾流化床内颗粒生长过程影响的模拟[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(8): 2787-2799. |
| [6] | 金虎, 杨帆, 戴梦瑶. 基于格子Boltzmann方法的液滴在圆柱壁面上运动过程研究[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(8): 2897-2908. |
| [7] | 韩志敏, 李江, 陈则齐, 刘威, 徐志明. 脉动流通道内不同纵向涡发生器的颗粒污垢特性[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(7): 2486-2496. |
| [8] | 方立昌, 李梓龙, 陈博, 苏政, 贾莉斯, 王智彬, 陈颖. 基于相变微胶囊悬浮液的芯片阵列冷却特性研究[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(7): 2455-2464. |
| [9] | 卢飞, 鲁波娜, 许光文. 气固微型流化床反应分析仪的理想流型判据分析[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(6): 2201-2213. |
| [10] | 黄斌, 丰生杰, 傅程, 张威. 液滴撞击单丝铺展特性的数值研究[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(6): 2233-2242. |
| [11] | 李娟, 曹耀文, 朱章钰, 石雷, 李佳. 仿生正形尾鳍结构微通道流动与传热特性数值研究及结构优化[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(5): 1802-1815. |
| [12] | 王金山, 王世学, 朱禹. 冷却表面温差对高温质子交换膜燃料电池性能的影响[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(5): 2026-2035. |
| [13] | 李怡菲, 董新宇, 王为术, 刘璐, 赵一璠. 微肋板表面干冰升华喷雾冷却传热数值模拟[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(5): 1830-1842. |
| [14] | 刘帆, 张芫通, 陶成, 胡成玉, 杨小平, 魏进家. 歧管式射流微通道液冷散热性能[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(5): 1777-1786. |
| [15] | 李静, 张方芳, 王帅帅, 徐建华, 张朋远. 凹腔结构对正丁烷部分预混火焰可燃极限的影响[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(5): 2081-2090. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备 11010102001995号
京公网安备 11010102001995号