化工学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 76 ›› Issue (2): 466-483.DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20240783
• 综述与专论 • 上一篇
李舒月1( ), 王欢1,2, 周少强2, 毛志宏1, 张永民1(
), 王欢1,2, 周少强2, 毛志宏1, 张永民1( ), 王军武1, 吴秀花2
), 王军武1, 吴秀花2
收稿日期:2024-07-11
修回日期:2024-08-24
出版日期:2025-03-25
发布日期:2025-03-10
通讯作者:
张永民
作者简介:李舒月(1992—),女,博士,讲师,shuyue.li@cup.edu.cn
基金资助:
Shuyue LI1( ), Huan WANG1,2, Shaoqiang ZHOU2, Zhihong MAO1, Yongmin ZHANG1(
), Huan WANG1,2, Shaoqiang ZHOU2, Zhihong MAO1, Yongmin ZHANG1( ), Junwu WANG1, Xiuhua WU2
), Junwu WANG1, Xiuhua WU2
Received:2024-07-11
Revised:2024-08-24
Online:2025-03-25
Published:2025-03-10
Contact:
Yongmin ZHANG
摘要:
流化床技术在工业中应用广泛,其中天然铀转化、直接还原炼铁、化学链燃烧等工业过程中使用的是颗粒密度在4.0 g/cm3以上的重质颗粒,而传统化工、能源行业广泛使用的则是密度较小的轻质流化床颗粒。综述了重质颗粒流态化技术在工业中的应用情况,梳理了目前重质颗粒流态化基础的研究进展。已有的实验测量和数值模拟研究均表明重质颗粒的流态化行为与低密度颗粒存在显著差异,且针对低密度颗粒的一些研究规律并不能完全适用于重质颗粒流化床。当前,对重质颗粒的流态化基础研究尚不充分,特别是在流域转变、传热传质特性、颗粒混合分级特性、反应过程强化技术等研究方面,与传统低密度颗粒流态化的基础研究相比,存在巨大的基础研究空白。最后结合相关工业过程的需要,重点讨论了近期应重点补充的重质颗粒流态化基础研究的内容。
中图分类号:
李舒月, 王欢, 周少强, 毛志宏, 张永民, 王军武, 吴秀花. 重质颗粒流态化研究现状与展望[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(2): 466-483.
Shuyue LI, Huan WANG, Shaoqiang ZHOU, Zhihong MAO, Yongmin ZHANG, Junwu WANG, Xiuhua WU. Current status and prospects of research on fluidization characteristics of high-density particles[J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(2): 466-483.
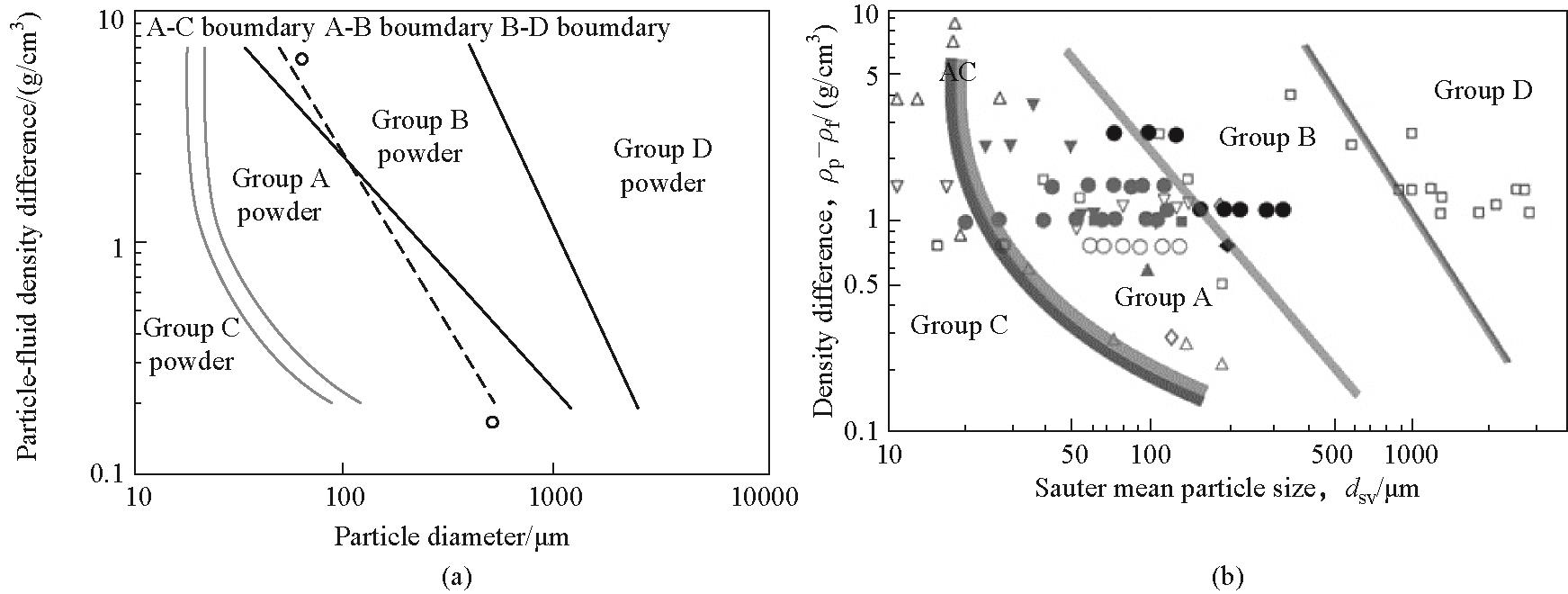
图1 (a)Geldart分类表征[1];(b)修正的Geldart流态化行为分类[5-14]
Fig.1 (a) Geldart classification of fluidization behavior[1]; (b) Modified Geldart classification of fluidization behavior[5-14]

图2 (a)模拟以及经验相关式得到的Uif、Umf和Uff随颗粒密度的变化;(b)模拟结果与经验公式Umf标准误差
Fig.2 (a) Variation of simulated Uif, Umf and Uff, and Umf predicted by empirical correlations with particle density; (b) Standard error of Umf
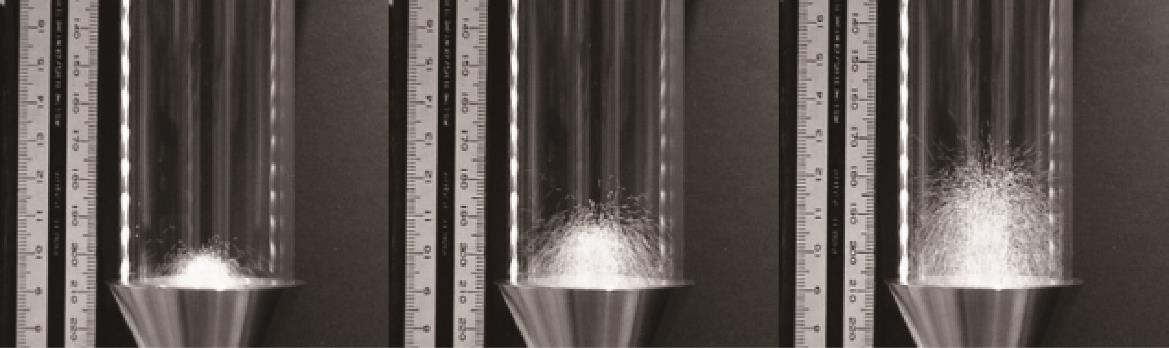
图9 ZrO2颗粒在60°锥形床中U/Ums分别为1.8、2.1、2.4的喷动行为实验[51-53]
Fig.9 Experimental study of spouting behavior of ZrO₂ particles in a 60 ° conical bed at U/Ums ratios of 1.8, 2.1, and 2.4[51-53]
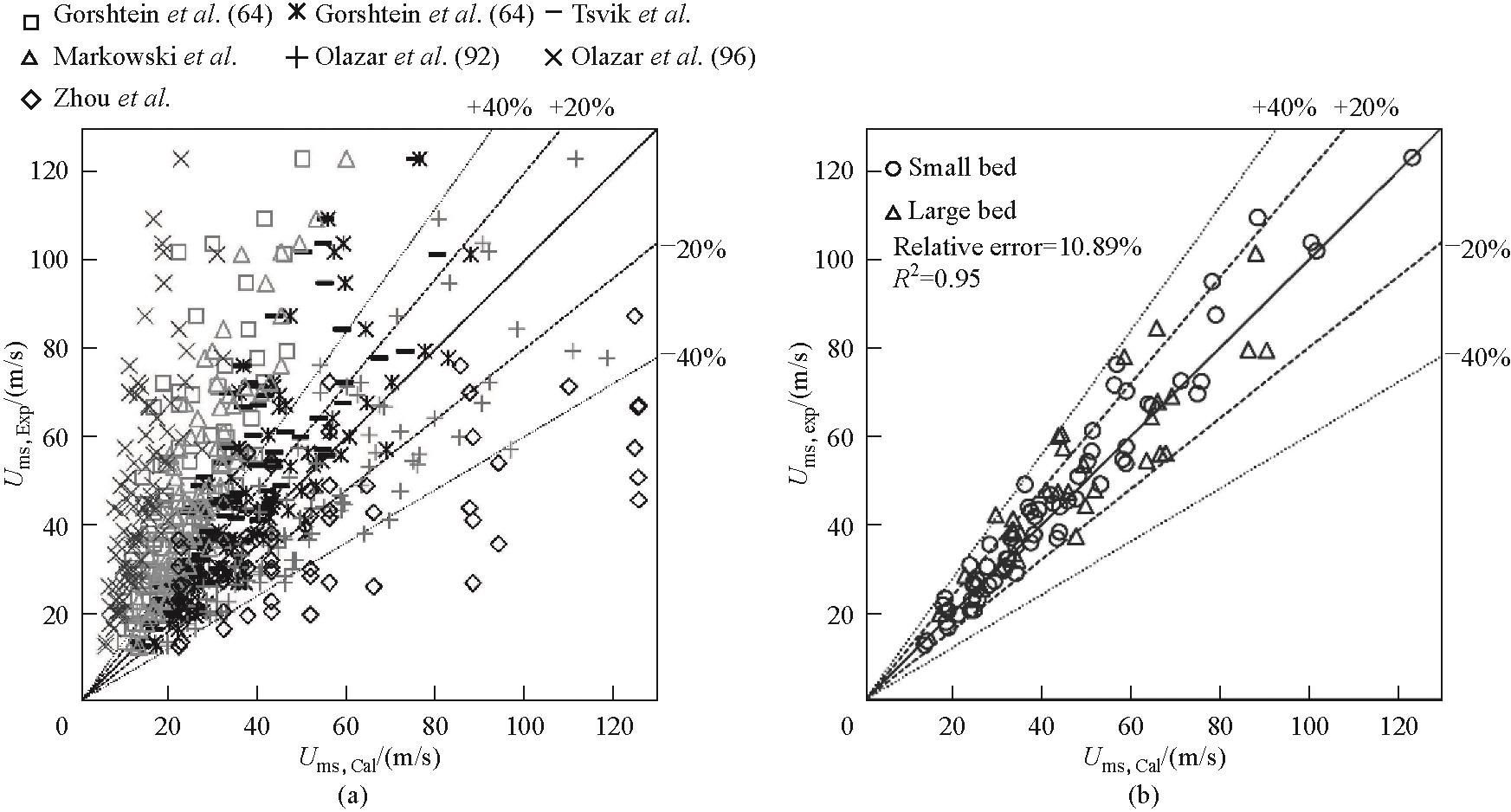
图10 (a)实验测量的最小喷动速度与文献中不同经验关联式预测值的比较;(b)Goldshan等[54]提出的最小喷动速度关联式与实验数据的比较
Fig.10 (a) Comparison of experimental minimum spouting velocity with predicted values from different empirical correlations in the literature; (b) Comparison of experimental data with the minimum spouting velocity correlation proposed by Goldshan et al.[54]
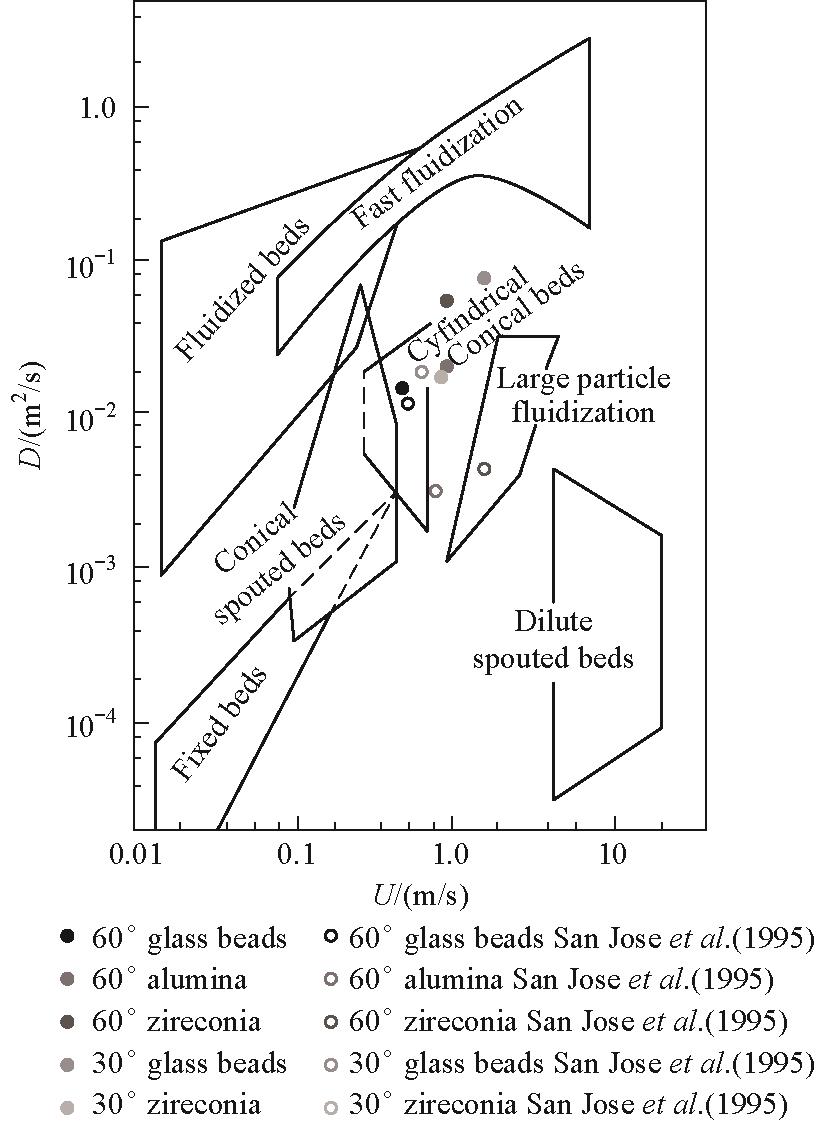
图11 Dogan实验得到气体扩散系数与San José基于低密度颗粒推导的气体扩散系数预测值的对比[55]
Fig.11 Comparison of gas diffusion coefficients obtained from Dogan's experiments with predicted values derived by San José for low-density particles[55]

图14 四种不同密度颗粒的实验结果:(a)颗粒流型;(b)与模拟结果相比进气气速与床层压降随颗粒密度的变化关系[92]
Fig.14 Experimental results for four different density particles: (a) Particle flow patterns; (b) Relationship between inlet gas velocity and bed pressure drop as a function of particle density compared with simulation results[92]
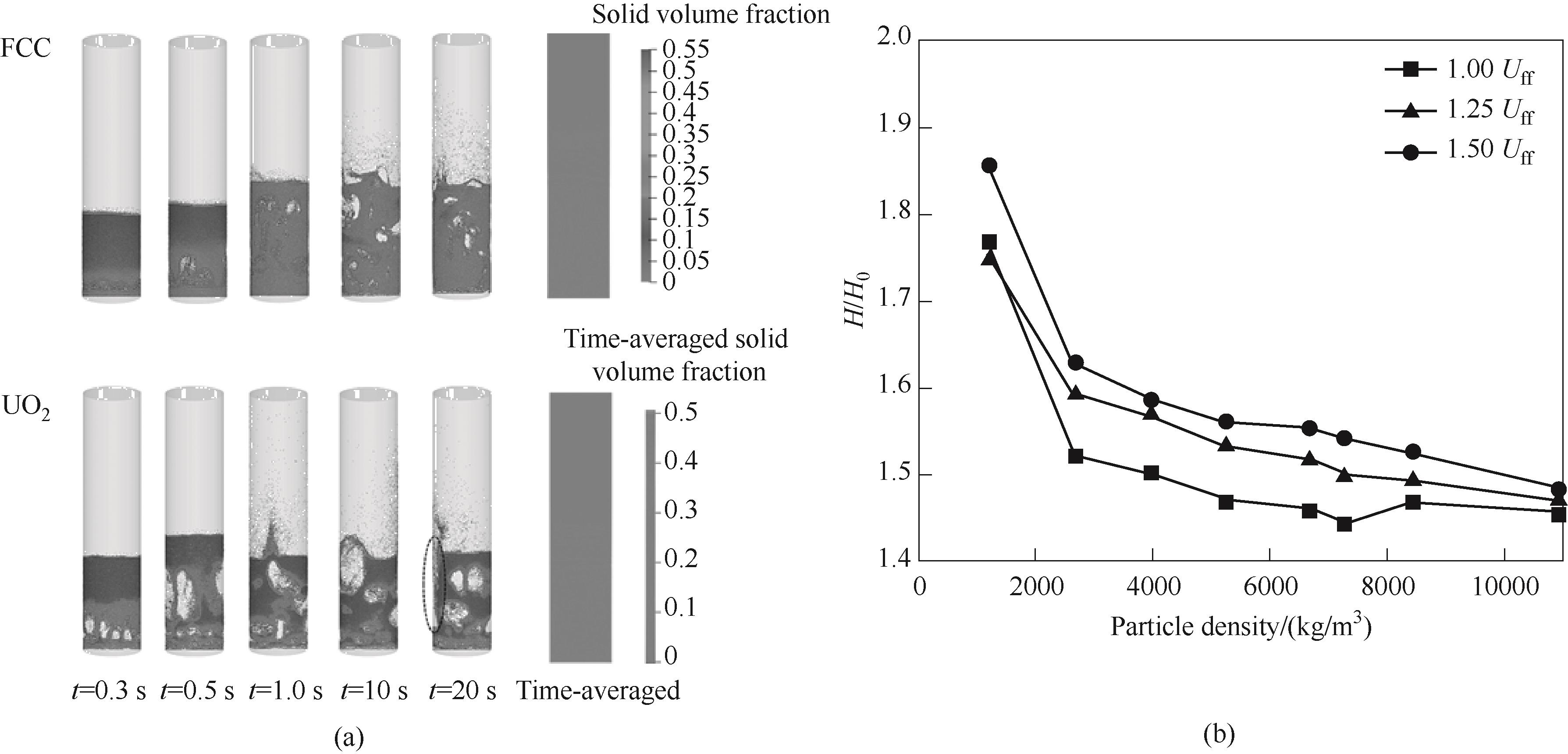
图15 (a)低密度FCC颗粒与重质UO2的充分流动状态对比;(b)颗粒密度和气速对床层膨胀率的影响[21-22]
Fig.15 (a) Comparison of the fully fluidized states between low-density FCC particles and high-density UO2 particles; (b) Effect of particle density and gas velocity on bed expansion ratio[21-22]
| 作者(年份) | 颗粒性质 | 主要结论 |
|---|---|---|
| Saxena et al.[ | Fe: Cu: | 施加外磁场可强化重质颗粒的流动性 |
| Zhou et al.[ | ZrO2: | 传统的经验公式无法准确预测ZrO2颗粒的最小喷动速度。本工作基于ZrO2实验数据建立了新的最小喷动速度关联式,并在关联式中包含了锥角、静床高度和颗粒粒径的影响 |
Cooper et al.[ Leaper[ | 焦炭: 金红石(Ti): 玻璃球: WC: | 与颗粒粒度差异相比,密度差异更能促使多组分颗粒在流化过程中分层 |
| Luckos et al.[ | 硅石(SiO2): 金红石(TiO2): 钛铁矿: 矿渣: | Ergun方程分别为钛铁矿和矿渣颗粒拟合了最小流化速度的相关性。这两个相关性都倾向于低估颗粒的最小流化速度 |
Pannala et al.[ Setarehshenas et al.[ | ZrO2: | 重质颗粒在喷动床床层中存在独有的不连贯喷动现象 |
| Formisani et al.[ | 玻璃球: 钢丸: 陶瓷球: | 密度不同的二元混合物的流化速度区间宽度与组分间的密度差距有关,同时还与初始体积分数和初始混合状态有关 |
| de Vos et al.[ | 雾化硅铁: 研磨硅铁: | A类颗粒团聚临界粒径的经典概念不能充分描述重质的A类颗粒的夹带行为 |
| Chao et al.[ | 钢珠: 玻璃珠: | 密度主导的二元颗粒离析行为和颗粒的速度分布都依赖于表观气体速度 |
| Alekhine et al.[ | 重质青铜: | 观察到重质青铜颗粒在循环流化床中的“噎塞”极限 |
| Rodrigues et al.[ | W颗粒: | 重质的钨颗粒完全流化的床层膨胀率只有10% |
Saayman et al.[ | FeSi: | 向FeSi床层中添加细粉颗粒反而降低了鼓泡状态下密相床层的空隙率,使得反应器性能下降,这与以往低密度颗粒床层中的研究规律相反 |
| 刘坤等[ | HfO2: | 氧化铪床层开始流化时并没有像低密度颗粒床层一样出现均匀膨胀,而是局部首先出现气流通道 |
| Liu et al.[ | ZrO2: Fe: UO2: 玻璃珠: | 颗粒的密度与所需流化气速及床层压力之间存在着明显的正相关关系。当颗粒密度增加时,颗粒稳定喷动气速范围随密度增加而扩大,同时重质颗粒的不连贯喷动存在低密度颗粒不易存在的双频现象,说明重质颗粒在喷动床中存在独特的喷动现象 |
| Vanni et al.[ | W颗粒: | 重质颗粒的临界床径比常见的Geldart A类和B类颗粒的临界直径要大 |
Bournival et al.[ | PMMA: 玻璃珠: TiO2: | 重质颗粒在与气泡接触时因具有较大的惯性,容易从气泡表面掉落,而密度小的颗粒则更容易附着在气泡表面,阻碍气泡的凝聚 |
He et al.[ Zou et al.[ | 精铁矿石: | 锥形流化床可强化重质铁矿石颗粒的流化 |
Goldshan et al.[ | ZrO2: 增韧Al2O3: 玻璃珠: | 随着颗粒密度的增加,最大压降、稳定喷动压降以及最小喷动速度都会增加。随着密度的增加,功率谱密度函数显示出略低的振幅。以上现象认为是由于重质颗粒惯性力的增加造成的 |
| Kraft et al.[ | 青铜: | 研究的曳力模型不能很好地预测重质床料循环速率以及系统的压力分布 |
| Shao et al.[ | 煤: 砂: Al2O3: NiO: Fe2O3: | 随着颗粒密度的减小,最小流化速度降低 |
| McIntyre et al.[ | 钛铁矿石: | 通过实验测定的最小流化速度与常用的经验关联式存在较大误差 |
| Tsurμmaki et al.[ | 玻璃球: 铁-锰氧化物: 尖晶石: | 低密度材料的流化速度快于重质材料 |
Guo et al.[ Dogan et al.[ | ZrO2: 锆钙化Al2O3: Cu: | 重质颗粒要求更高的操作气体速度;重质颗粒与低密度颗粒在喷动床中存在不同的轴向气体混合行为 |
| Hessels et al.[ | 氧化铁: | 氢气还原实验中,得到远低于期望的1%的转化率 |
Mollick et al.[ | 玻璃球: ZrO2: WC: | 不同密度的颗粒最小喷动速度与床高的关系呈现出不同的指数关系,说明轻质颗粒与重质颗粒的喷动行为也遵循不同的规律 |
表1 重质颗粒流态化研究总结
Table 1 The summary of research on fluidization of high-density particles
| 作者(年份) | 颗粒性质 | 主要结论 |
|---|---|---|
| Saxena et al.[ | Fe: Cu: | 施加外磁场可强化重质颗粒的流动性 |
| Zhou et al.[ | ZrO2: | 传统的经验公式无法准确预测ZrO2颗粒的最小喷动速度。本工作基于ZrO2实验数据建立了新的最小喷动速度关联式,并在关联式中包含了锥角、静床高度和颗粒粒径的影响 |
Cooper et al.[ Leaper[ | 焦炭: 金红石(Ti): 玻璃球: WC: | 与颗粒粒度差异相比,密度差异更能促使多组分颗粒在流化过程中分层 |
| Luckos et al.[ | 硅石(SiO2): 金红石(TiO2): 钛铁矿: 矿渣: | Ergun方程分别为钛铁矿和矿渣颗粒拟合了最小流化速度的相关性。这两个相关性都倾向于低估颗粒的最小流化速度 |
Pannala et al.[ Setarehshenas et al.[ | ZrO2: | 重质颗粒在喷动床床层中存在独有的不连贯喷动现象 |
| Formisani et al.[ | 玻璃球: 钢丸: 陶瓷球: | 密度不同的二元混合物的流化速度区间宽度与组分间的密度差距有关,同时还与初始体积分数和初始混合状态有关 |
| de Vos et al.[ | 雾化硅铁: 研磨硅铁: | A类颗粒团聚临界粒径的经典概念不能充分描述重质的A类颗粒的夹带行为 |
| Chao et al.[ | 钢珠: 玻璃珠: | 密度主导的二元颗粒离析行为和颗粒的速度分布都依赖于表观气体速度 |
| Alekhine et al.[ | 重质青铜: | 观察到重质青铜颗粒在循环流化床中的“噎塞”极限 |
| Rodrigues et al.[ | W颗粒: | 重质的钨颗粒完全流化的床层膨胀率只有10% |
Saayman et al.[ | FeSi: | 向FeSi床层中添加细粉颗粒反而降低了鼓泡状态下密相床层的空隙率,使得反应器性能下降,这与以往低密度颗粒床层中的研究规律相反 |
| 刘坤等[ | HfO2: | 氧化铪床层开始流化时并没有像低密度颗粒床层一样出现均匀膨胀,而是局部首先出现气流通道 |
| Liu et al.[ | ZrO2: Fe: UO2: 玻璃珠: | 颗粒的密度与所需流化气速及床层压力之间存在着明显的正相关关系。当颗粒密度增加时,颗粒稳定喷动气速范围随密度增加而扩大,同时重质颗粒的不连贯喷动存在低密度颗粒不易存在的双频现象,说明重质颗粒在喷动床中存在独特的喷动现象 |
| Vanni et al.[ | W颗粒: | 重质颗粒的临界床径比常见的Geldart A类和B类颗粒的临界直径要大 |
Bournival et al.[ | PMMA: 玻璃珠: TiO2: | 重质颗粒在与气泡接触时因具有较大的惯性,容易从气泡表面掉落,而密度小的颗粒则更容易附着在气泡表面,阻碍气泡的凝聚 |
He et al.[ Zou et al.[ | 精铁矿石: | 锥形流化床可强化重质铁矿石颗粒的流化 |
Goldshan et al.[ | ZrO2: 增韧Al2O3: 玻璃珠: | 随着颗粒密度的增加,最大压降、稳定喷动压降以及最小喷动速度都会增加。随着密度的增加,功率谱密度函数显示出略低的振幅。以上现象认为是由于重质颗粒惯性力的增加造成的 |
| Kraft et al.[ | 青铜: | 研究的曳力模型不能很好地预测重质床料循环速率以及系统的压力分布 |
| Shao et al.[ | 煤: 砂: Al2O3: NiO: Fe2O3: | 随着颗粒密度的减小,最小流化速度降低 |
| McIntyre et al.[ | 钛铁矿石: | 通过实验测定的最小流化速度与常用的经验关联式存在较大误差 |
| Tsurμmaki et al.[ | 玻璃球: 铁-锰氧化物: 尖晶石: | 低密度材料的流化速度快于重质材料 |
Guo et al.[ Dogan et al.[ | ZrO2: 锆钙化Al2O3: Cu: | 重质颗粒要求更高的操作气体速度;重质颗粒与低密度颗粒在喷动床中存在不同的轴向气体混合行为 |
| Hessels et al.[ | 氧化铁: | 氢气还原实验中,得到远低于期望的1%的转化率 |
Mollick et al.[ | 玻璃球: ZrO2: WC: | 不同密度的颗粒最小喷动速度与床高的关系呈现出不同的指数关系,说明轻质颗粒与重质颗粒的喷动行为也遵循不同的规律 |
| 1 | Geldart D. Types of gas fluidization[J]. Powder Technology, 1973, 7(5): 285-292. |
| 2 | Grace J R, Bi X, Ellis N. Essentials of Fluidization Technology[M]. John Wiley & Sons, 2020. |
| 3 | 王荘, 吕潇, 邵媛媛, 等. 流态化的往昔寻觅及未来启示[J]. 化工学报, 2021, 72(12): 5904-5927. |
| Wang Z, Lyu X, Shao Y Y, et al. Early exploration of fluidization theory and its inspiration to the future[J]. CIESC Journal, 2021, 72(12): 5904-5927. | |
| 4 | 金涌. 流态化工程原理[M]. 北京: 清华大学出版社, 2001: 39-47. |
| Jin Y. Fluidization Engineering Principles[M]. Beijing: Tsinghua University Press, 2001: 39-47. | |
| 5 | Baerns M. Effect of interparticle adhesive forces on fluidization of fine particles[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Fundamentals, 1966, 5(4): 508-516. |
| 6 | Brekken R. Fluidization of flour in a stirred aerated bed[D]. Ames: Iowa State University, 1970. |
| 7 | de Jong J A H, Nomden J F. Homogeneous gas-solid fluidization[J]. Powder Technology, 1974, 9(2/3): 91-97. |
| 8 | Davies L, Richardson J. Gas interchange between bubbles and the continuous phase in a fluidized bed[J]. Trans. Inst. Chem. Eng., 1966, 44: 293. |
| 9 | Rietema K. Application of mechanical stress theory to fluidization[C]// Drinkenburg A A H. Proceedings of the International Symposium on Fluidization. Eindhoven, Netherlands: Eindhoven University of Technology, 1967: 154. |
| 10 | Godard K, Richardson J F. Bubble velocities and bed expansions in freely bubbling fluidised beds[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 1969, 24(4): 663-670. |
| 11 | Donsì G, Massimilla L. Bubble-free expansion of gas-fluidized beds of fine particles[J]. AIChE Journal, 1973, 19(6): 1104-1110. |
| 12 | Kehoe P, Davidson J. CHEMECA 70[C]//Inst. Chem. Eng. Symp. Ser. Melbourne, 1971, 33: 97. |
| 13 | Geldart D. The effect of particle size and size distribution on the behaviour of gas-fluidised beds[J]. Powder Technology, 1972, 6(4): 201-215. |
| 14 | Mathur K B, Epstein N. Dynamics of spouted beds[M]//Advances in Chemical Engineering. Amsterdam: Elsevier, 1974: 111-191. |
| 15 | Ozahi E, Gundogdu M Y, Carpinlioglu M Ö. A modification on Ergun's correlation for use in cylindrical packed beds with non-spherical particles[J]. Advanced Powder Technology, 2008, 19(4): 369-381. |
| 16 | Erdim E, Akgiray Ö, Demir İ. A revisit of pressure drop-flow rate correlations for packed beds of spheres[J]. Powder Technology, 2015, 283: 488-504. |
| 17 | Anantharaman A, Cocco R A, Chew J W. Evaluation of correlations for minimum fluidization velocity (Umf) in gas-solid fluidization[J]. Powder Technology, 2018, 323: 454-485. |
| 18 | Zhou Y, Wang T L, Zhu J. Investigation on minimum fluidization velocity in a modified Geldart's diagram[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2023, 453: 139984. |
| 19 | Terfous A, Hazzab A, Ghenaim A. Predicting the drag coefficient and settling velocity of spherical particles[J]. Powder Technology, 2013, 239: 12-20. |
| 20 | Wang J W. Continuum theory for dense gas-solid flow: a state-of-the-art review[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2020, 215: 115428. |
| 21 | Li S Y, Zhang Y M, Wang W J, et al. Multi-scale simulation of particle density effects on hydrodynamics in dense gas-solid fluidized beds[J]. Powder Technology, 2024, 435: 119394. |
| 22 | Li S Y, Zhang Y M, Wang W J, et al. Comparative analysis of particle density effects on initial fluidization in gas-solid fluidized beds[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2023, 477: 146966. |
| 23 | Bi X T. Gas and solid mixing in high-density CFB risers[J]. International Journal of Chemical Reactor Engineering, 2004. DOI: 10.2202/1542-6580.1080 . |
| 24 | Ma Q, Lei F L, Xu X, et al. Three-dimensional full-loop simulation of a high-density CFB with standpipe aeration experiments[J]. Powder Technology, 2017, 320: 574-585. |
| 25 | Wang X Y, Fan B G, Wang S D, et al. Gas-solid flow characteristics in high-density CFB[J]. Journal of Thermal Science, 2012, 21(4): 354-358. |
| 26 | 王俊峰. 铀转化工艺学[M]. 北京: 中国原子能出版社, 2012. |
| Wang J F. Uranium Conversion Technology[M]. Beijing: China Atomic Energy Press, 2012. | |
| 27 | 许贺卿. 铀化合物转化工艺学[M]. 北京: 原子能出版社, 1994. |
| Xu H Q. Uranium Compound Conversion Technology[M]. Beijing: Atomic Press, 1994. | |
| 28 | Gupta C K, Sathiyamoorthy D. Fluid Bed Technology in Materials Processing[M]. Boca Raton: CRC Press, 1998. |
| 29 | 刘马林. 流化床-化学气相沉积技术在先进核燃料制备中的应用进展[J]. 化工进展, 2019, 38(4): 1646-1653. |
| Liu M L. Research activities on FB-CVD technology application in advanced nuclear fuel fabrication[J]. Chemical Industry and Engineering Progress, 2019, 38(4): 1646-1653. | |
| 30 | 刘荣正, 刘马林, 邵友林, 等. 流化床-化学气相沉积技术的应用及研究进展[J]. 化工进展, 2016, 35(5): 1263-1272. |
| Liu R Z, Liu M L, Shao Y L, et al. Application and research progress of fluidized bed-chemical vapor deposition technology[J]. Chemical Industry and Engineering Progress, 2016, 35(5): 1263-1272. | |
| 31 | Saeidi S, Talebi Amiri M, Saidina Amin N A, et al. Progress in reactors for high-temperature Fischer-Tropsch process: determination place of intensifier reactor perspective[J]. International Journal of Chemical Reactor Engineering, 2014, 12(1): 639-664. |
| 32 | de Vos W, Nicol W, du Toit E. Entrainment behaviour of high-density Geldart A powders with different shapes[J]. Powder Technology, 2009, 190(3): 297-303. |
| 33 | Cheng K, Virginie M, Ordomsky V V, et al. Pore size effects in high-temperature Fischer-Tropsch synthesis over supported iron catalysts[J]. Journal of Catalysis, 2015, 328: 139-150. |
| 34 | Duvenhage D J, Shingles T. Synthol reactor technology development[J]. Catalysis Today, 2002, 71(3/4): 301-305. |
| 35 | Steynberg A P, Espinoza R L, Jager B, et al. High temperature Fischer-Tropsch synthesis in commercial practice[J]. Applied Catalysis A: General, 1999, 186(1/2): 41-54. |
| 36 | Li S Y, Shen Y S. Numerical simulation of multiphase flow in a full coal-direct chemical looping combustion process[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2022, 248: 117233. |
| 37 | Li S Y, Zhuo Y T, Shen Y S. Modelling of multiphase reactive flows in a full-loop coal-direct chemical looping combustor[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2023, 457: 141306. |
| 38 | Siriwardane R, Tian H J, Miller D, et al. Fluidized bed testing of commercially prepared MgO-promoted hematite and CuO-Fe2O3 mixed metal oxide oxygen carriers for methane and coal chemical looping combustion[J]. Applied Energy, 2015, 157: 348-357. |
| 39 | Adánez-Rubio I, Bararpour S T, Abad A, et al. Performance evaluation of a Cu-based oxygen carrier impregnated onto ZrO2 for chemical-looping combustion (CLC)[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2020, 59(15): 7255-7266. |
| 40 | Mendiara T, Pérez R, Abad A, et al. Low-cost Fe-based oxygen carrier materials for the iG-CLC process with coal. 1[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2012, 51(50): 16216-16229. |
| 41 | Mendiara T, de Diego L F, García-Labiano F, et al. Behaviour of a bauxite waste material as oxygen carrier in a 500Wth CLC unit with coal[J]. International Journal of Greenhouse Gas Control, 2013, 17: 170-182. |
| 42 | Bischi A, Langørgen Ø, Morin J X, et al. Performance analysis of the cold flow model of a second generation chemical looping combustion reactor system[J]. Energy Procedia, 2011, 4: 449-456. |
| 43 | Ma K H, Deng J Y, Wang G, et al. Utilization and impacts of hydrogen in the ironmaking processes: a review from lab-scale basics to industrial practices[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2021, 46(52): 26646-26664. |
| 44 | Wang Y J, Zuo H B, Zhao J. Recent progress and development of ironmaking in China as of 2019: an overview[J]. Ironmaking & Steelmaking, 2020, 47(6): 640-649. |
| 45 | 田津. 非高炉炼铁新工艺的探索[D]. 天津: 天津大学, 2018. |
| Tian J. Exploration on new technology of non-blast furnace ironmaking[D]. Tianjin: Tianjin University, 2018. | |
| 46 | 张晓华, 师学峰, 赵凯, 等. 非高炉炼铁工艺流程发展现状及前景展望[J]. 矿产综合利用, 2020(2): 8-15. |
| Zhang X H, Shi X F, Zhao K, et al. Development status and prospect of smelting reduction ironmaking process[J]. Multipurpose Utilization of Mineral Resources, 2020(2): 8-15. | |
| 47 | 唐利刚. 宽粒级加重质流化床的数值模拟及分选特性[D]. 徐州: 中国矿业大学, 2010. |
| Tang L G. Numerical simulation and separation characteristics of wide-size-range medium-solids fluidized beds[D]. Xuzhou: China University of Mining and Technology, 2010. | |
| 48 | 王松. 基于二元加重质特征参数的气固流化床床层特性及分选行为研究[D]. 徐州: 中国矿业大学, 2023. |
| Wang S. Study on bed characteristics and separation behavior of gas-solid fluidized bed based on characteristic parameters of binary weighting materials[D]. Xuzhou: China University of Mining and Technology, 2023. | |
| 49 | Fu Z J, Zhu J, Barghi S, et al. Mixing and segregation behavior in an air dense medium fluidized bed with binary mixtures for dry coal beneficiation[J]. Powder Technology, 2020, 371: 161-169. |
| 50 | Sahu A K, Biswal S K, Parida A. Development of air dense medium fluidized bed technology for dry beneficiation of coal—a review[J]. International Journal of Coal Preparation and Utilization, 2009, 29(4): 216-241. |
| 51 | Zhou J, Bruns D D, Finney C E, et al. Hydrodynamic correlations with experimental results from cold mockup spouted beds for nuclear fuel particle coating[C]//AIChE Annual Meeting. Cincinnati, Ohio, 2005. |
| 52 | Zhou J D, Bruns D D. Minimum spouting velocity of dense particles in shallow spouted beds[J]. The Canadian Journal of Chemical Engineering, 2012, 90(3): 558-564. |
| 53 | Zhou J D. Characterizing and modeling the hydrodynamics of shallow spouted beds[D]. Knoxville: University of Tennessee, 2008. |
| 54 | Golshan S, Yaman O, Koksal M, et al. A new correlation for minimum spouting velocity for conical spouted beds operating with high density particles[J]. Experimental Thermal and Fluid Science, 2018, 96: 358-370. |
| 55 | Guo L H, Wang G Q, Zhang F, et al. Effect of temperature on the minimum spouting velocity of heavy particles in conical spouted bed used for nuclear fuel coating[J]. Experimental Thermal and Fluid Science, 2023, 144: 110876. |
| 56 | Dogan N, Koksal M, Kulah G. Axial gas mixing in conical spouted beds with high density particles[J]. Particuology, 2023, 81: 45-57. |
| 57 | San José M J, Olazar M, Peñas F J, et al. Correlation for calculation of the gas dispersion coefficient in conical spouted beds[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 1995, 50(13): 2161-2172. |
| 58 | Mollick P K, Tellabide M, Bolaños M, et al. Functional variation of minimum spouting velocity with static bed height in conical spouted beds[J]. Chemical Engineering Research and Design, 2024, 208: 204-208. |
| 59 | 刘坤, 陈松, 王力军. 高密度颗粒相HfO2的流态化特性研究[J]. 稀有金属, 2015, 39(7): 617-622. |
| Liu K, Chen S, Wang L J. Fluidization characteristics of high-density particles of HfO2 [J]. Chinese Journal of Rare Metals, 2015, 39(7): 617-622. | |
| 60 | Rodriguez P, Caussat B, Ablitzer C, et al. Fluidization and coating of very dense powders by fluidized bed chemical vapour deposition[J]. Chemical Engineering Research and Design, 2013, 91(12): 2477-2483. |
| 61 | Rodriguez P, Caussat B, Ablitzer C, et al. Fluidization and coating of very dense powders by fluidized bed CVD[C]//Proc. Congrès de la société française de génie des procédés. Lille, France, 2011. |
| 62 | Vanni F, Caussat B, Ablitzer C, et al. Effects of reducing the reactor diameter on the fluidization of a very dense powder[J]. Powder Technology, 2015, 277: 268-274. |
| 63 | Vanni F, Caussat B, Ablitzer C, et al. Silicon coating on very dense tungsten particles by fluidized bed CVD for nuclear application[J]. Physica Status Solidi (a), 2015, 212(7): 1599-1606. |
| 64 | Vanni F, Montaigu M, Caussat B, et al. Fluidized-bed chemical vapor deposition of silicon on very dense tungsten powder[J]. Chemical Engineering & Technology, 2015, 38(7): 1254-1260. |
| 65 | Saayman J, Ellis N, Nicol W. Fluidization of high-density particles: the influence of fines on reactor performance[J]. Powder Technology, 2013, 245: 48-55. |
| 66 | Bournival G, Ata S, Wanless E J. Behavior of bubble interfaces stabilized by particles of different densities[J]. Langmuir, 2016, 32(25): 6226-6238 |
| 67 | McIntyre C J, Symonds R T, Lu D Y, et al. Experimental evaluation of hydrodynamics and tube-to-bed heat transfer of fluidized ilmenite ore particles at elevated pressures[J]. Powder Technology, 2020, 376: 697-707. |
| 68 | Luckos A, Hoed P D. A study into the hydrodynamic behaviour of heavy minerals in a circulating fluidized bed[C]// Luckos A, Smit P. IFSA 2005, Industrial Fluidization South Africa. Johannesburg: South African Institute of Mining and Metallurgy, 2005: 345-355. |
| 69 | Luckos A, Reynolds Q G, Hoed P D. An analysis of pressure fluctuations in a CFB of heavy minerals[C]// Berruti F, Bi X, Pugsley T. The 12th International Conference on Fluidization - New Horizons in Fluidization Engineering. ECI Symposium Series. London, Canada: The University of Western Ontario, 2007. |
| 70 | He S Y, Sun H Y, Hu C Q, et al. Direct reduction of fine iron ore concentrate in a conical fluidized bed[J]. Powder Technology, 2017, 313: 161-168. |
| 71 | Zou Z, Zhang X, Yan D, et al. Experimental investigation and CFD study of direct reduction of iron ore in the conical fluidized bed[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2024, 300: 120586. |
| 72 | Plaul F, Bohm C, Schenk J. Fluidized-bed technology for the production of iron products for steelmaking[J]. Journal of the South African Institute of Mining & Metallurgy, 2009, 109(2): 121-128. |
| 73 | Langston B G, Stephens F M. Self-agglomerating fluidized-bed reduction. Is it an answer to the economic treatment of fine iron concentrates produced from low-grade ores?[J]. JOM - Journal of the Minerals, Metals and Materials Society, 1960, 12(4): 312-316. |
| 74 | Hessels C J M, Lelivelt D W J, Stevens N C, et al. Minimum fluidization velocity and reduction behavior of combusted iron powder in a fluidized bed[J]. Fuel, 2023, 342: 127710. |
| 75 | Fauquet-Alekhine P. Gas-particles flow transitions for high density powder[C]//Proceedings of the World Congress on Engineering 2012, Vol III. London, U.K.: WCE, 2012. |
| 76 | Yang T Y, Leu L P. Study of transition velocities from bubbling to turbulent fluidization by statistic and wavelet multi-resolution analysis on absolute pressure fluctuations[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2008, 63(7): 1950-1970. |
| 77 | Nienow A W, Rowe P N, Cheung L Y L. A quantitative analysis of the mixing of two segregating powders of different density in a gas-fluidised bed[J]. Powder Technology, 1978, 20(1): 89-97. |
| 78 | Chiba S, Nienow A W, Chiba T, et al. Fluidised binary mixtures in which the denser component may be flotsam[J]. Powder Technology, 1980, 26(1): 1-10. |
| 79 | Cooper S, Coronella C J. CFD simulations of particle mixing in a binary fluidized bed[J]. Powder Technology, 2005, 151(1/2/3): 27-36. |
| 80 | Rasul M G, Rudolph V, Carsky M. Segregation potential in binary gas fluidized beds[J]. Powder Technology, 1999, 103(2): 175-181. |
| 81 | Leaper M C, Seville J P K, Hilal N, et al. Investigating the dynamics of segregation of high jetsam binary batch fluidised bed systems[J]. Chemical Engineering and Processing: Process Intensification, 2004, 43(2): 187-192. |
| 82 | Formisani B, Girimonte R, Longo T. The fluidization pattern of density-segregating binary mixtures[J]. Chemical Engineering Research and Design, 2008, 86(4): 344-348. |
| 83 | Formisani B, Girimonte R, Vivacqua V. Fluidization of mixtures of two solids differing in density or size[J]. AIChE Journal, 2011, 57(9): 2325-2333. |
| 84 | Zhu Q H, Cao Y L, Zhang Q, et al. Universal methodology of measuring properties for particles based on their settled state in fluidized bed[J]. Fuel, 2024, 377: 132733. |
| 85 | Zhang Q, Liu W K, Cao Y L, et al. Diverse gas-solid magnetized fluidized beds with different magnetic fields[J]. Powder Technology, 2024, 433: 119241. |
| 86 | Saxena S C, Wu W Y. Hydrodynamic characteristics of magnetically stabilized fluidized admixture beds of iron and copper particles[J]. The Canadian Journal of Chemical Engineering, 1999, 77(2): 312-318. |
| 87 | Zhu Q H, Li H Z, Huang Q S. Magnetized fluidized bed with binary admixture of magnetizable and nonmagnetizable particles[J]. Reviews in Chemical Engineering, 2021, 37(2): 305-338. |
| 88 | Wang J J, Han Y, Gu X P, et al. Effect of agitation on the fluidization behavior of a gas-solid fluidized bed with a frame impeller[J]. AIChE Journal, 2013, 59(4): 1066-1074. |
| 89 | Ramamurthy K, Subbaraju K. Bed expansion characteristics of annular liquid-fluidized beds[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Process Design and Development, 1973, 12(2): 184-189. |
| 90 | Zhang J P, Grace J R, Epstein N, et al. Flow regime identification in gas-liquid flow and three-phase fluidized beds[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 1997, 52(21/22): 3979-3992. |
| 91 | Ghatage S V, Peng Z B, Sathe M J, et al. Stability analysis in solid-liquid fluidized beds: experimental and computational[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2014, 256: 169-186. |
| 92 | Liu M L, Wen Y Y, Liu R Z, et al. Investigation of fluidization behavior of high density particle in spouted bed using CFD-DEM coupling method[J]. Powder Technology, 2015, 280: 72-82. |
| 93 | Jiang L, Qiu M F, Liu R Z, et al. CFD-DEM simulation of high density particles fluidization behaviors in 3D conical spouted beds[J]. Particuology, 2024, 88: 266-281. |
| 94 | Pannala S, Daw C, Finney C, et al. Simulating the dynamics of spouted-bed nuclear fuel coaters[J]. Chemical Vapor Deposition, 2007, 13(9): 481-490. |
| 95 | Setarehshenas N, Hosseini S H, Esfahany M N, et al. Impacts of solid-phase wall boundary condition on CFD simulation of conical spouted beds containing heavy zirconia particles[J]. Journal of the Taiwan Institute of Chemical Engineers, 2016, 64: 146-156. |
| 96 | Shao Y J, Gu J R, Zhong W Q, et al. Determination of minimum fluidization velocity in fluidized bed at elevated pressures and temperatures using CFD simulations[J]. Powder Technology, 2019, 350: 81-90. |
| 97 | Shao Y J, Li Z Z, Zhong W Q, et al. Minimum fluidization velocity of particles with different size distributions at elevated pressures and temperatures[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2020, 216: 115555. |
| 98 | Tsurumaki G, Bellan S, Matsubara K, et al. Fluidization behavior of redox metal oxide and spinel particles to develop high-energy-density thermal energy storage system for concentrated solar power applications[J]. Journal of Thermal Science and Technology, 2022, 17(2): 22-61-22-00061. |
| 99 | Chao Z X, Wang Y F, Jakobsen J P, et al. Multi-fluid modeling of density segregation in a dense binary fluidized bed[J]. Particuology, 2012, 10(1): 62-71. |
| 100 | Lan B, Xu J, Lu S, et al. Direct reduction of iron-ore with hydrogen in fluidized beds: a coarse-grained CFD-DEM-IBM study[J]. Powder Technology, 2024, 438: 119624. |
| 101 | McIntyre C J, Hughes R W, Macchi A, et al. Computational modeling of high pressure bubbling fluidized bed hydrodynamics using ilmenite particles[J]. Powder Technology, 2022, 402: 117332. |
| 102 | Kraft S, Kirnbauer F, Hofbauer H. Influence of drag laws on pressure and bed material recirculation rate in a cold flow model of an 8MW dual fluidized bed system by means of CPFD[J]. Particuology, 2018, 36: 70-81. |
| 103 | Zou Z, Li H Z, Zhu Q S, et al. Experimental study and numerical simulation of bubbling fluidized beds with fine particles in two and three dimensions[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2013, 52(33): 11302-11312. |
| 104 | Komatina M, Gudenau H W. The sticking problem during direct reduction of fine iron ore in the fluidized bed[J]. Metalurgija-Journal of Metallurgy, 2004, 10(4): 309-328. |
| 105 | Guo L, Bao Q P, Gao J T, et al. A review on prevention of sticking during fluidized bed reduction of fine iron ore[J]. ISIJ International, 2020, 60(1): 1-17. |
| 106 | Chang J, Yang S Q, Zhang K. A particle-to-particle heat transfer model for dense gas-solid fluidized bed of binary mixture[J]. Chemical Engineering Research and Design, 2011, 89(7): 894-903. |
| 107 | Baker C G J, Geldart D. An investigation into the slugging characteristics of large particles[J]. Powder Technology, 1978, 19(2): 177-187. |
| 108 | Gao Z L, Chai X S, Zhou E H, et al. Effect of the distributor plugging ways on fluidization quality and particle stratification in air dense medium fluidized bed[J]. International Journal of Mining Science and Technology, 2020, 30(6): 883-888. |
| 109 | Mikami T, Kamiya H, Horio M. The mechanism of defluidization of iron particles in a fluidized bed[J]. Powder Technology, 1996, 89(3): 231-238. |
| 110 | Jerndal E, Mattisson T, Lyngfelt A. Investigation of different NiO/NiAl2O4 particles as oxygen carriers for chemical-looping combustion[J]. Energy & Fuels, 2009, 23(2): 665-676. |
| 111 | Jerndal E, Mattisson T, Thijs I, et al. Investigation of NiO/NiAl2O4 oxygen carriers for chemical-looping combustion produced by spray-drying[J]. International Journal of Greenhouse Gas Control, 2010, 4(1): 23-35. |
| 112 | Zhong Y W, Wang Z, Guo Z C, et al. Defluidization behavior of iron powders at elevated temperature: influence of fluidizing gas and particle adhesion[J]. Powder Technology, 2012, 230: 225-231. |
| [1] | 刘萍, 邱雨生, 李世婧, 孙瑞奇, 申晨. 微通道内纳米流体传热流动特性[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(1): 184-197. |
| [2] | 韩志敏, 周相宇, 张宏宇, 徐志明. 不同粗糙元结构下CaCO3污垢局部沉积特性[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(1): 151-160. |
| [3] | 韩启沃, 刘永峰, 裴普成, 张璐, 姚圣卓. 工作温度对PEMFC水分布、质子传输及性能影响分析[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(1): 374-384. |
| [4] | 邓志诚, 杨欢, 王斯民, 王家瑞. 微混燃烧器中微管结构对氢燃料掺混效果与燃烧性能影响[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(1): 335-347. |
| [5] | 王瀚彬, 胡帅, 毕丰雷, 李隽森, 贺来宾. 新型波纹翅片金属氢化物反应器的放氢性能有限元分析[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(1): 221-230. |
| [6] | 高羡明, 杨汶轩, 卢少辉, 任晓松, 卢方财. 双槽道结构对超疏水表面液滴合并弹跳的影响[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(1): 208-220. |
| [7] | 任冠宇, 张义飞, 李新泽, 杜文静. 翼型印刷电路板式换热器流动传热特性数值研究[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(S1): 108-117. |
| [8] | 杨勇, 祖子轩, 李煜坤, 王东亮, 范宗良, 周怀荣. T型圆柱形微通道内CO2碱液吸收数值模拟[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(S1): 135-142. |
| [9] | 黄俊豪, 庞克亮, 孙方远, 刘福军, 谷致远, 韩龙, 段衍泉, 冯妍卉. 干熄炉料钟结构对焦炭布料粒径均匀度影响的模拟研究[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(S1): 158-169. |
| [10] | 董新宇, 边龙飞, 杨怡怡, 张宇轩, 刘璐, 王腾. 冷却条件下倾斜上升管S-CO2流动与传热特性研究[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(S1): 195-205. |
| [11] | 郭骐瑞, 任丽媛, 陈康, 黄翔宇, 马卫华, 肖乐勤, 周伟良. 用于HTPB推进剂浆料的静态混合管数值模拟[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(S1): 206-216. |
| [12] | 李匡奚, 于佩潜, 王江云, 魏浩然, 郑志刚, 冯留海. 微气泡旋流气浮装置内流动分析与结构优化[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(S1): 223-234. |
| [13] | 汪张洲, 唐天琪, 夏嘉俊, 何玉荣. 基于复合相变材料的电池热管理性能模拟[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(S1): 329-338. |
| [14] | 胡俭, 姜静华, 范生军, 刘建浩, 邹海江, 蔡皖龙, 王沣浩. 中深层U型地埋管换热器取热特性研究[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(S1): 76-84. |
| [15] | 李舒月, 王欢, 周少强, 毛志宏, 张永民, 王军武, 吴秀花. 基于CPFD方法的U3O8氢还原流化床反应器数值模拟[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(9): 3133-3151. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备 11010102001995号
京公网安备 11010102001995号