• •
收稿日期:2025-08-08
修回日期:2028-11-28
出版日期:2025-12-31
通讯作者:
姜祖明
基金资助:
Zuming Jiang( ), Qi Lv, Yu Liu, Fangjian Zhao, Binlin Pan, Xinyue Song
), Qi Lv, Yu Liu, Fangjian Zhao, Binlin Pan, Xinyue Song
Received:2025-08-08
Revised:2028-11-28
Online:2025-12-31
Contact:
Zuming Jiang
摘要:
针对高温高盐油藏条件下矿场在用粘弹性颗粒驱油剂热稳定性大幅下降的问题,采用聚乙烯基吡咯烷酮、丙烯酰胺,研发了一种具有半互穿网络结构(semi-IPN)的新型粘弹性颗粒驱油剂。通过调控PVP含量,系统研究了其耐温抗盐性能演化规律与结构解体机制。流变测试、微观形貌、粒径、水解度、核磁与红外光谱等多手段实验结果表明:PVP的引入可通过增强氢键密度与物理缠结结构,构建多级缓释破坏路径,实现水分子缔合、网络结构稳定与主链断裂的顺序调控。HP-PPG的老化过程依次经历PVP–水、PVP–PAM、PAM主链氢键的逐步断裂,展现出典型的“平台期”水分释放行为与最小水解度,显著优于矿场在用粘弹性颗粒驱油剂。
中图分类号:
姜祖明, 吕琦, 刘煜, 赵方剑, 潘斌林, 宋新玥. 新型粘弹性颗粒驱油剂耐温抗盐机理研究[J]. 化工学报, DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20250898.
Zuming Jiang, Qi Lv, Yu Liu, Fangjian Zhao, Binlin Pan, Xinyue Song. Mechanism study on temperature and salt resistance of novel viscoelastic particle-based oil displacement agents[J]. CIESC Journal, DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20250898.
| 矿化度 (mg/L) | H2O (mL) | NaCl (g) | CaCl2 (g) | MgCl2•6H2O (g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 30000 | 1000 | 27.3067 | 1.11 | 3.833 |
表1 盐水溶液成分
Table 1 The compositions of saline solutions with different salinities
| 矿化度 (mg/L) | H2O (mL) | NaCl (g) | CaCl2 (g) | MgCl2•6H2O (g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 30000 | 1000 | 27.3067 | 1.11 | 3.833 |
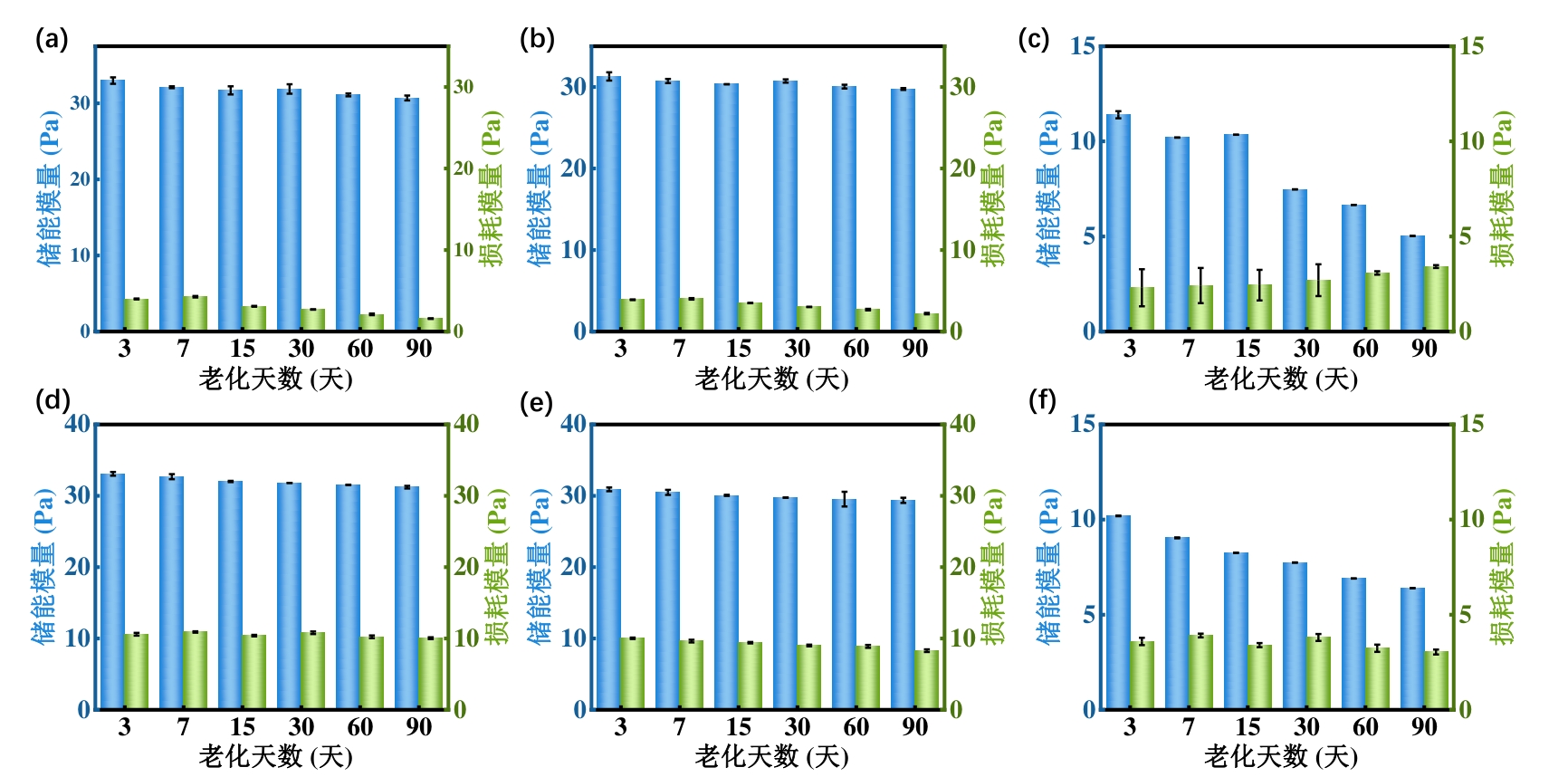
图1 85℃,盐水条件下(a)HP-PPG(b)LP-PPG(c)PPG;85℃,纯水条件下(d)HP-PPG(e)LP-PPG(f)PPG的储能模量(G′)和损耗模量(G'')随老化时间的变化
Fig.1 Evolution of storage modulus (G′) and loss modulus (G″) with aging time for (a) HP‑PPG, (b) LP‑PPG, and (c) PPG under saline conditions at 85 °C, and for (d) HP‑PPG, (e) LP‑PPG, and (f) PPG under pure water conditions at 85 °C
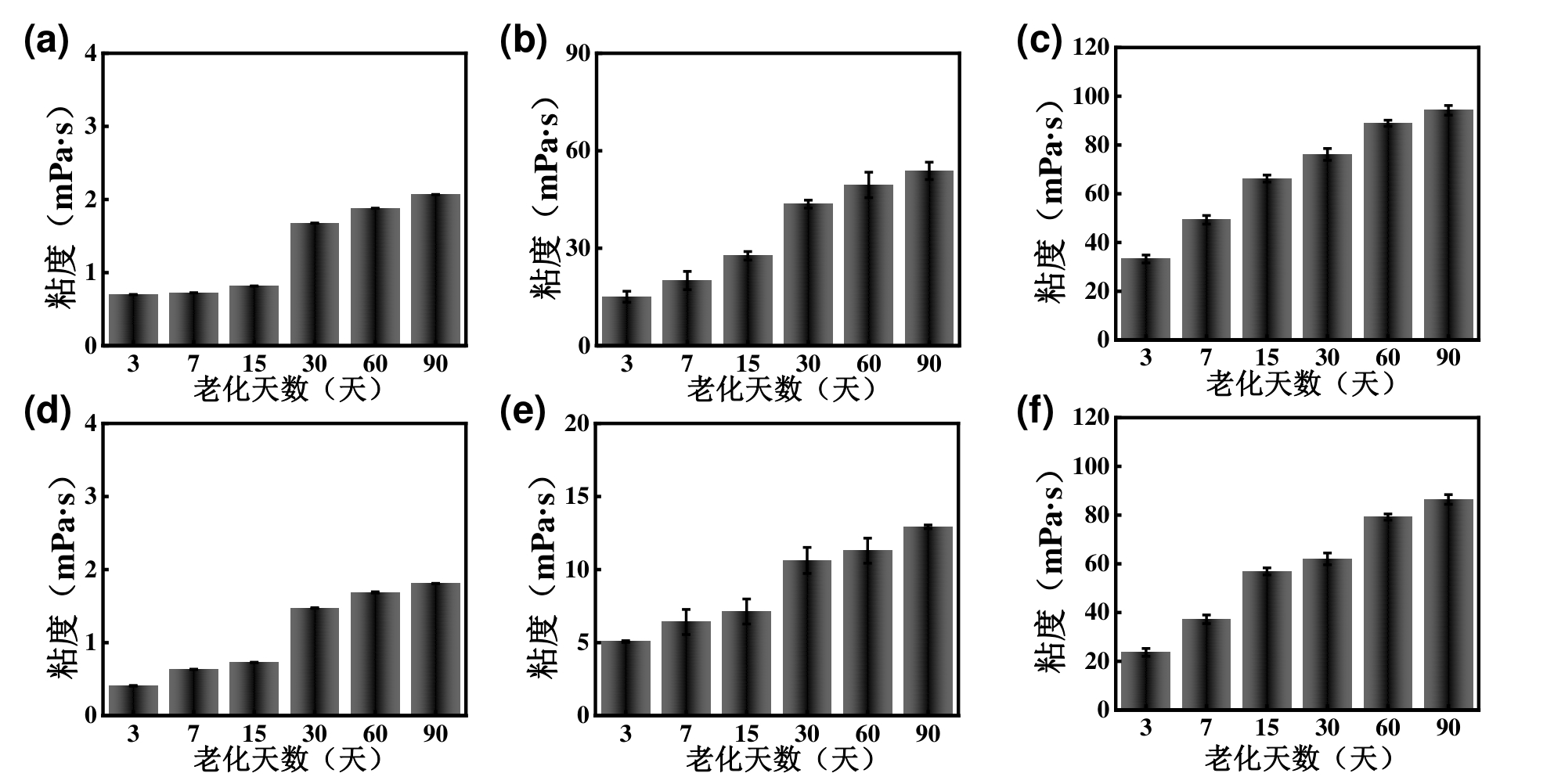
图2 85℃,盐水条件下(a)HP-PPG(b)LP-PPG(c)PPG;85℃,纯水条件下(d)HP-PPG(e)LP-PPG(f)PPG的粘度图
Fig.2 Viscosity diagrams of (a) HP-PPG, (b) LP-PPG and (c) PPG under saline conditions at 85℃; and viscosity diagrams of (d) HP-PPG, (e) LP-PPG and (f) PPG under pure water conditions at 85℃
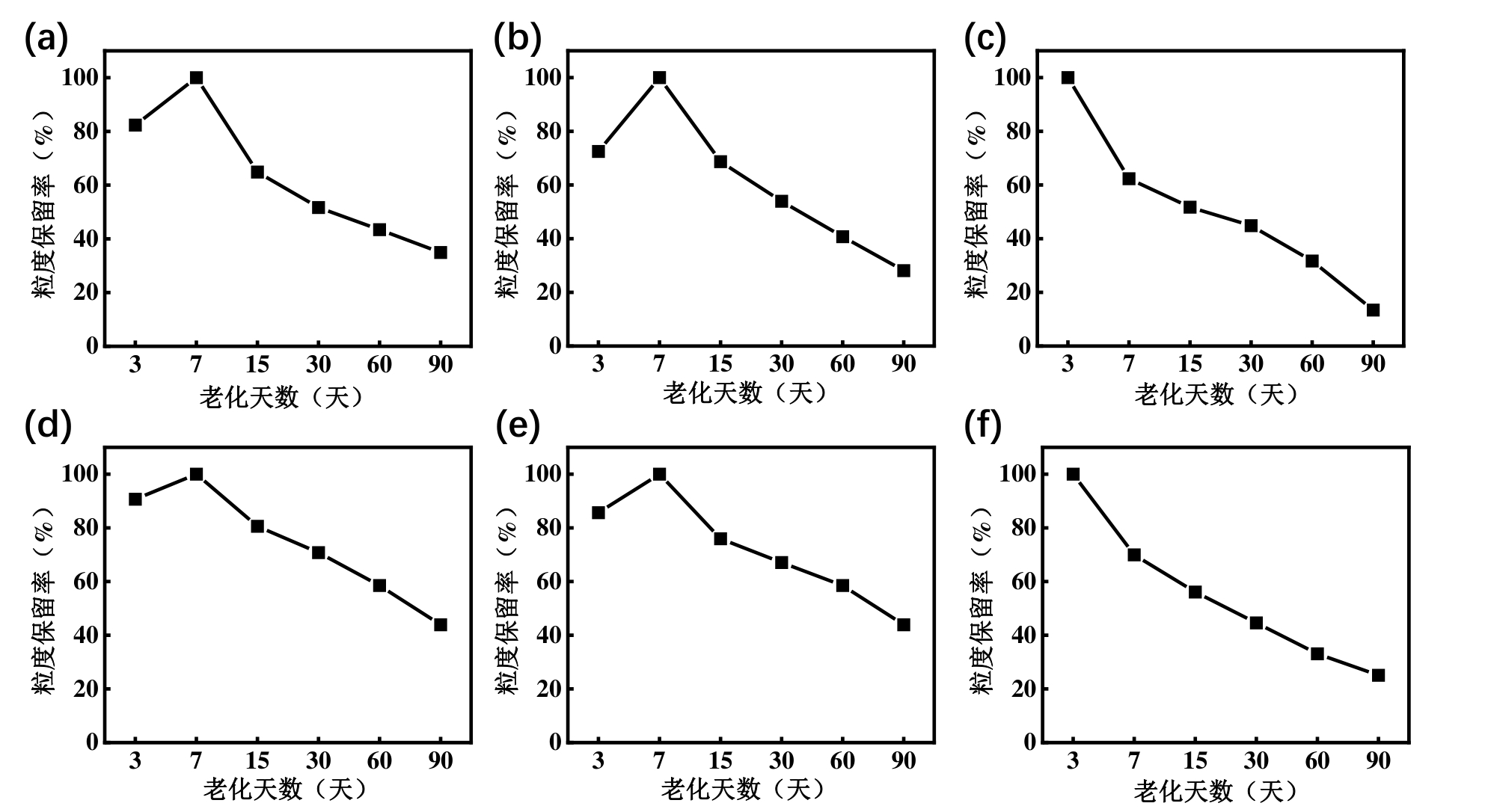
图3 85℃,盐水条件下(a)HP-PPG(b)LP-PPG(c)PPG;85℃,纯水条件下(d)HP-PPG(e)LP-PPG(f)PPG的粒度保留率图
Fig.3 Particle size retention rate diagrams of (a) HP-PPG, (b) LP-PPG and (c) PPG under saline conditions at 85℃; and particle size retention rate diagrams of (d) HP-PPG, (e) LP-PPG and (f) PPG under pure water conditions at 85℃.
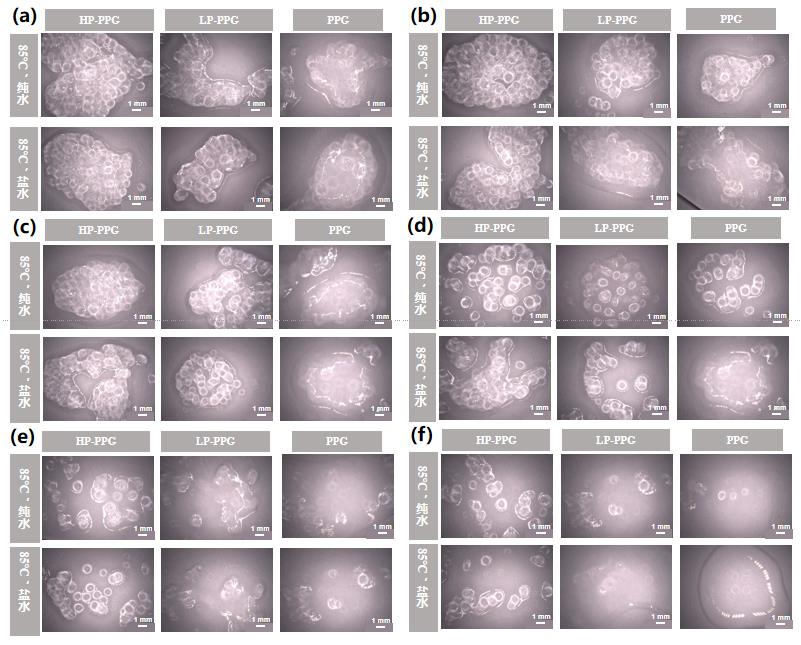
图4 各组样品在老化(a)3天(b)7天(c)15天(d)30天(e)60天(f)90天后的超景深示意图
Fig. 4 Ultra-depth of field diagrams of samples in each group after aging for (a) 3 days, (b) 7 days, (c) 15 days, (d) 30 days, (e) 60 days, and (f) 90 days.
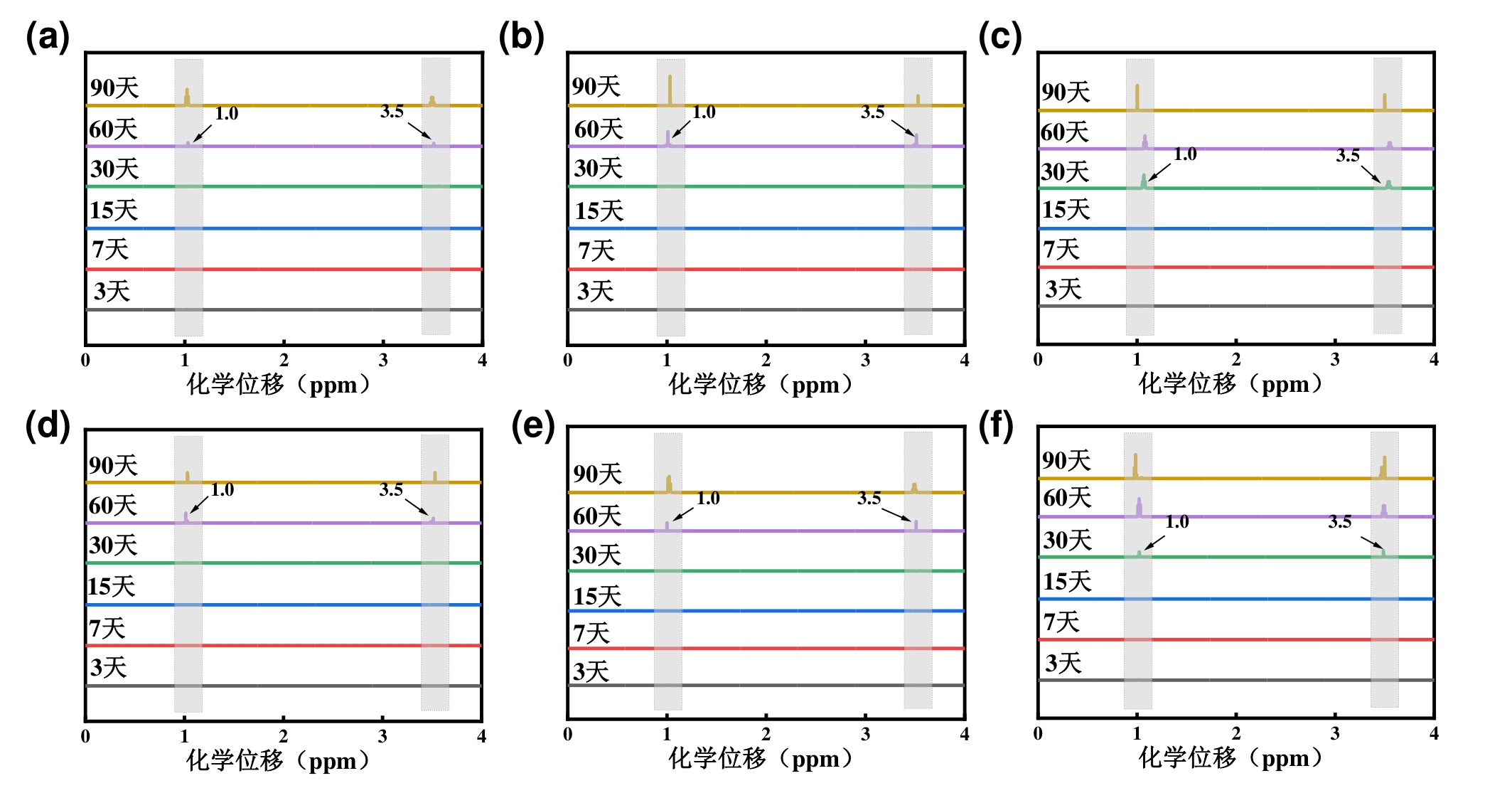
图5 85℃,盐水条件下(a)HP-PPG(b)LP-PPG(c)PPG;85℃,纯水条件下(d)HP-PPG(e)LP-PPG(f)PPG的核磁氢谱图
Fig. 5 ¹H NMR spectra of (a) HP-PPG, (b) LP-PPG and (c) PPG under saline conditions at 85℃; and¹H NMR spectra of (d) HP-PPG, (e) LP-PPG and (f) PPG under pure water conditions at 85℃
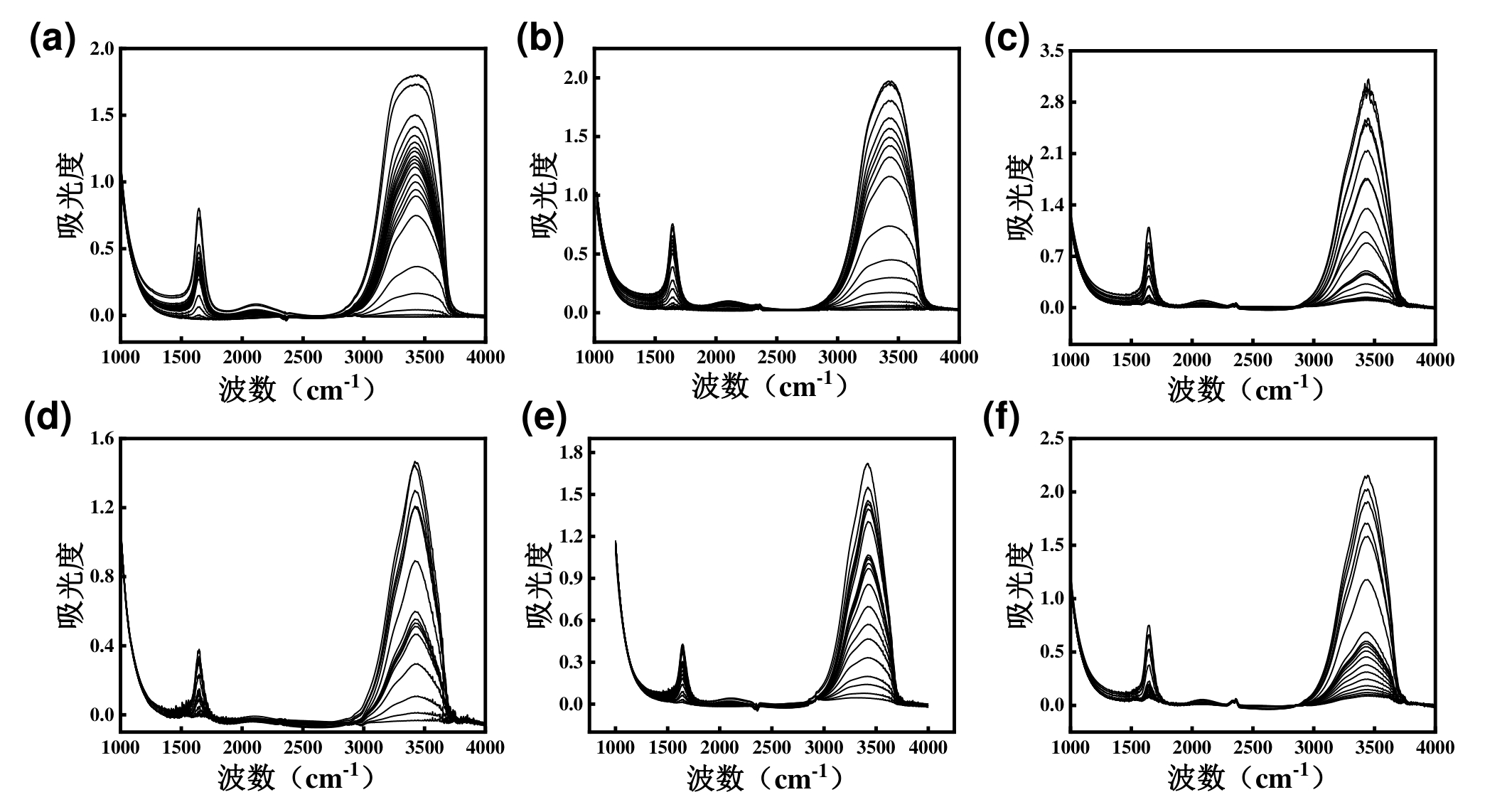
图6 85℃,纯水条件下(a)HP-PPG(b)LP-PPG(c)PPG;85℃,盐水条件下(d)HP-PPG(e)LP-PPG(f)PPG的一维红外谱图
Fig. 6 One-dimensional infrared spectra of (a) HP-PPG, (b) LP-PPG, and (c) PPG under pure water conditions at 85°C; and one-dimensional infrared spectra of (d) HP-PPG, (e) LP-PPG, and (f) PPG under salt water conditions at 85°C
| 自由水(%) | 弱氢键水(%) | 强氢键水(%) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 85℃,盐水,HP-PPG | 36.62 | 44.65 | 13.07 |
| 85℃,纯水,HP-PPG | 35.69 | 44.83 | 13.11 |
| 85℃,盐水,LP-PPG | 40.72 | 40.18 | 12.68 |
| 85℃,纯水,LP-PPG | 39.26 | 42.03 | 12.87 |
| 85℃,盐水,PPG | 49.92 | 38.85 | 11.23 |
| 85℃,纯水,PPG | 46.05 | 39.01 | 14.98 |
表2 六个体系中的水分的分布情况
Table 2 Water distributions in 6 systems
| 自由水(%) | 弱氢键水(%) | 强氢键水(%) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 85℃,盐水,HP-PPG | 36.62 | 44.65 | 13.07 |
| 85℃,纯水,HP-PPG | 35.69 | 44.83 | 13.11 |
| 85℃,盐水,LP-PPG | 40.72 | 40.18 | 12.68 |
| 85℃,纯水,LP-PPG | 39.26 | 42.03 | 12.87 |
| 85℃,盐水,PPG | 49.92 | 38.85 | 11.23 |
| 85℃,纯水,PPG | 46.05 | 39.01 | 14.98 |
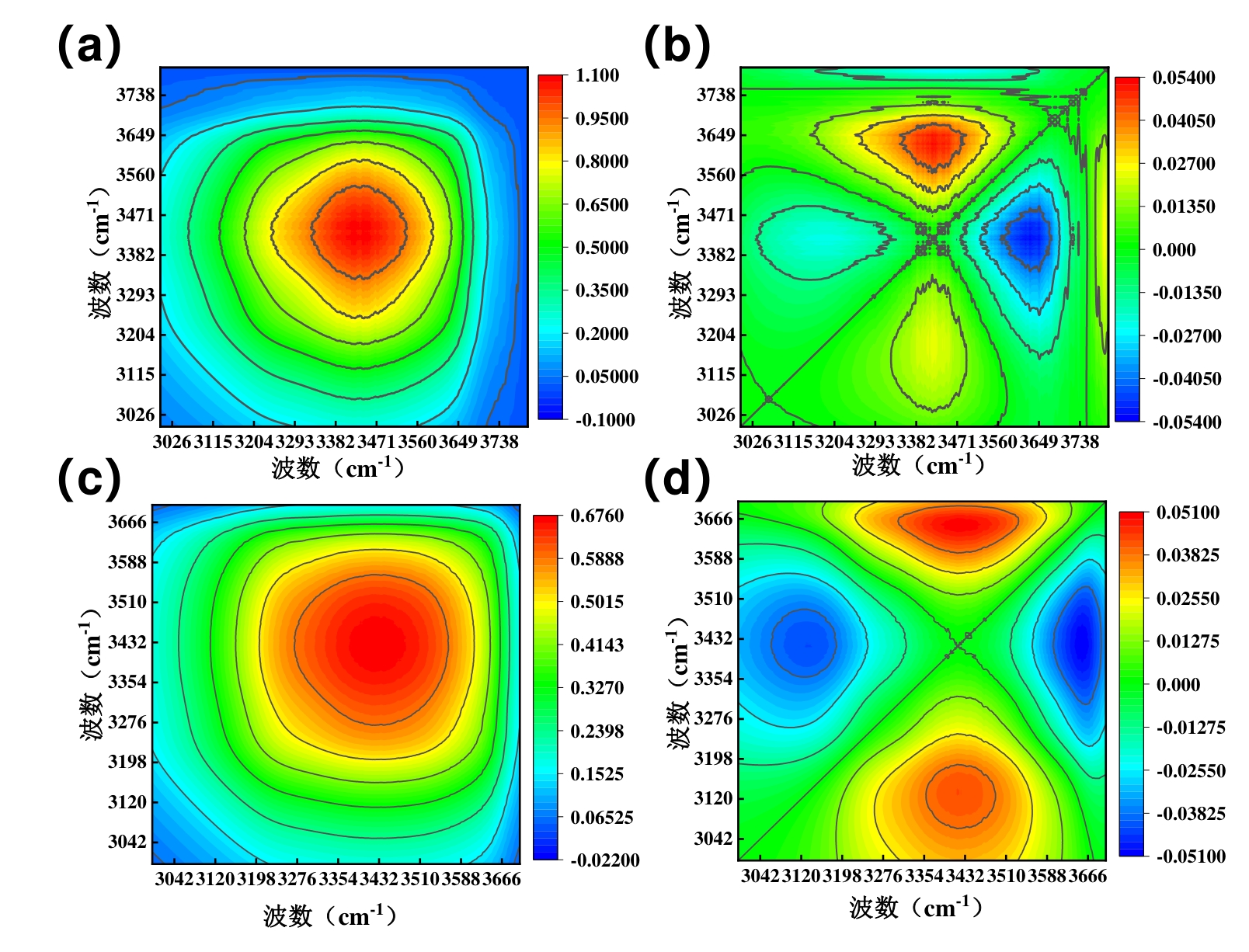
图8 HP-PPG在85℃,纯水条件下的(a)同步图(b)异步图;HP-PPG在85℃,盐水条件下的(c)同步图(d)异步图
Fig. 8 (a) Synchronous diagram and (b) asynchronous diagram of HP-PPG under the conditions of 85℃ and pure water; (c) synchronous diagram and (d) asynchronous diagram of HP-PPG under the conditions of 85℃ and salt water
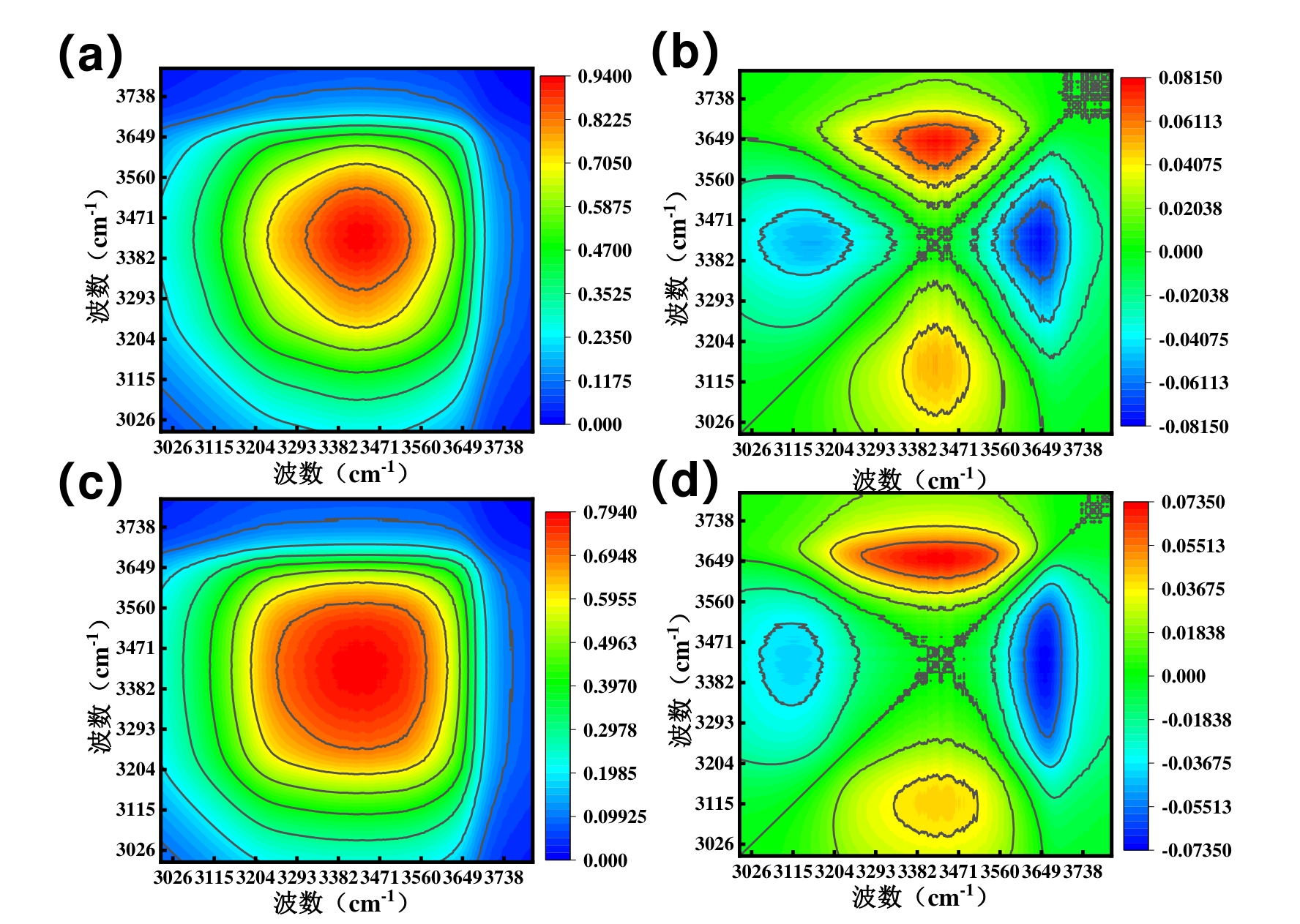
图9 LP-PPG在85℃,纯水条件下的(a)同步图(b)异步图;LP-PPG在85℃,盐水条件下的(c)同步图(d)异步图
Fig. 9 (a) Synchronous diagram and (b) asynchronous diagram of LP-PPG under the conditions of 85℃ and pure water; (c) synchronous diagram and (d) asynchronous diagram of LP-PPG under the conditions of 85℃ and salt water
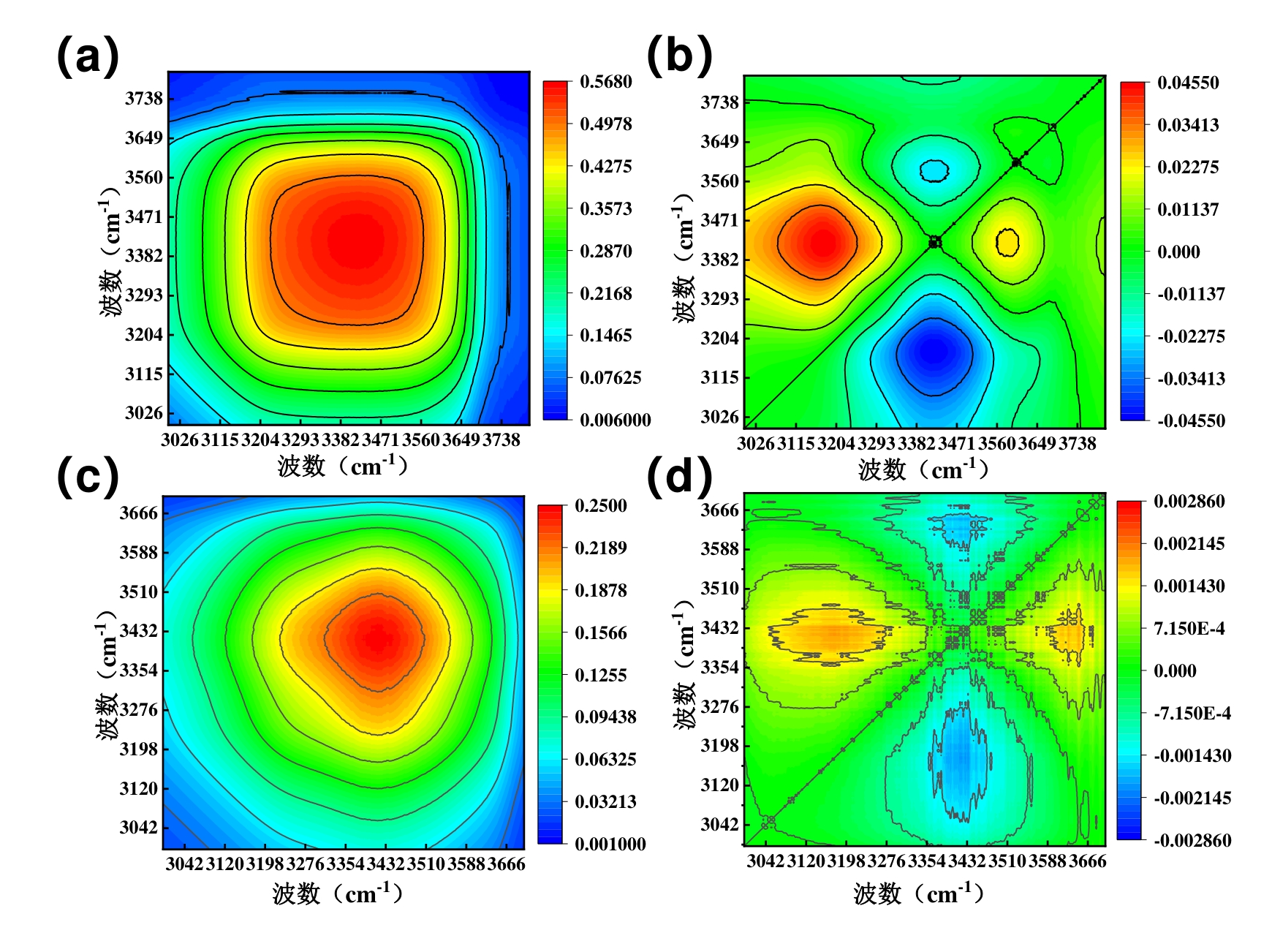
图10 PPG在85℃,纯水条件下的(a)同步图(b)异步图;PPG在85℃,盐水条件下的(c)同步图(d)异步图
Fig. 10 (a) Synchronous diagram and (b) asynchronous diagram of PPG under the conditions of 85℃ and pure water; (c) synchronous diagram and (d) asynchronous diagram of PPG under the conditions of 85℃ and salt water
| 85℃,盐水,PPG | 85℃,纯水,PPG | 85℃,盐水,HP-PPG | 85℃,纯水,HP-PPG | 85℃,盐水,LP-PPG | 85℃,纯水,LP-PPG | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 同步图 | 3422 | 3421 | 3419 | 3418 | 3420 | 3419 |
| 异步图 | 3123,3420 3626,3420 | 3159,3420 3420,3633 | 3164,3439 3629,3439 | 3169,3424 3612,3424 | 3422,3643 3135,3427 | 3420,3654 3418,3119 |
表3 六个体系中同步图谱与异步图谱的分析结果
Table 3 Results of synchronous and asynchronous maps in 6 systems
| 85℃,盐水,PPG | 85℃,纯水,PPG | 85℃,盐水,HP-PPG | 85℃,纯水,HP-PPG | 85℃,盐水,LP-PPG | 85℃,纯水,LP-PPG | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 同步图 | 3422 | 3421 | 3419 | 3418 | 3420 | 3419 |
| 异步图 | 3123,3420 3626,3420 | 3159,3420 3420,3633 | 3164,3439 3629,3439 | 3169,3424 3612,3424 | 3422,3643 3135,3427 | 3420,3654 3418,3119 |
| [1] | Elaf R, Hamza A, Nimir H, et al. Development of inorganically cross-linked sulfonated polyacrylamide preformed particle gels for conformance control: impact of anionic groups[J]. Energy & Fuels, 2024, 38(4): 2883-2897. |
| [2] | Almakimi A A, Liu J C, Bai B J, et al. Investigation of carbonate matrix damage and remediation methods for preformed particle gel conformance control treatments[J]. SPE Journal, 2024, 29(3): 1623-1634. |
| [3] | Pandit Y K, Mahto V, Gopalkrishnan Nair U. Titanium dioxide nanomaterial-reinforced particle gel: development, characterization, and performance evaluation for water shutoff jobs in heterogeneous reservoirs[J]. Energy & Fuels, 2024, 38(3): 1781-1798. |
| [4] | Raza A, Mahmoud M, Alafnan S, et al. Role of high-density brines in reservoir development stages: a review[J]. Energy Geoscience, 2024, 5(3): 100304. |
| [5] | Chai M J, Chai L W, Nourozieh H, et al. A technical, economic, and environmental assessment on dimethyl ether (DME) as a renewable solvent from carbon dioxide utilization (CCU) for heavy oil recovery: a real field in Surmont, Canada as case study[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2024, 482: 148936. |
| [6] | Yonguep E, Kapiamba K F, Kabamba K J, et al. Formation, stabilization and chemical demulsification of crude oil-in-water emulsions: a review[J]. Petroleum Research, 2022, 7(4): 459-472. |
| [7] | Hu J J, Zhang G C, Jiang P, et al. A new method of water control for horizontal wells in heavy oil reservoirs[J]. Geoenergy Science and Engineering, 2023, 222: 211391. |
| [8] | Hosseinzadehsadati S, Bonto M, Mokhtari R, et al. Modified salinity waterflooding in chalk reservoirs: a journey from rock and fluid interfaces to field scale applications[J]. Fuel, 2024, 356: 129461. |
| [9] | 曹绪龙, 石静, 张磊, 等. 高温高盐油藏化学驱提高采收率理论技术与矿场应用[J]. 油气地质与采收率, 2024, 31(5): 16-26. |
| Cao X L, Shi J, Zhang L, et al. Theoretical technology and field application of enhanced oil recovery by chemical flooding in high temperature and high salt reservoirs[J]. Petroleum Geology and Recovery Efficiency, 2024, 31(5): 16-26. | |
| [10] | 曹绪龙. 非均相复合驱油体系设计与性能评价[J]. 石油学报(石油加工), 2013, 29(1): 115-121. |
| Cao X L. Design and performance evaluation of heterogeneous composite flooding system[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica(Petroleum Processing Section), 2013, 29(1): 115-121. | |
| [11] | 崔晓红. 新型非均相复合驱油方法[J].石油学报, 2011, 32(1): 122-126. |
| Cui X H. A new heterogeneous composite oil displacement method[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2011, 32(1): 122-126. | |
| [12] | 孙焕泉. 聚合物驱后井网调整与非均相复合驱先导试验方案及矿场应用: 以孤岛油田中一区Ng3单元为例[J]. 油气地质与采收率, 2014, 21(2): 1-4. |
| Sun H Q. Pilot test scheme and field application of well pattern adjustment and heterogeneous composite flooding after polymer flooding: taking Ng3 unit in zone 1 of Gudao oilfield as an example[J]. Petroleum Geology and Recovery Efficiency, 2014, 21(2): 1-4. | |
| [13] | 孙焕泉, 曹绪龙, 李宗阳, 等. 基于储层孔喉匹配的非均相复合驱技术研究与矿场实践: 以胜坨油田一区沙二段1-3砂组聚合物驱后单元为例[J]. 油气地质与采收率, 2020, 27(5): 53-61. |
| Sun H Q, Cao X L, Li Z Y, et al. Research and Field Practice of Heterogeneous Composite Flooding Technology Based on Reservoir Pore-throat Matching: Taking the unit after polymer flooding of 1-3 sand group in the second member of Shahejie Formation in the first area of Shengtuo Oilfield as an example[J]. Petroleum Geology and Recovery Efficiency, 2020, 27(5): 53-61. | |
| [14] | 姜祖明. 黏弹性颗粒驱油剂的制备与性能[J]. 塑料工业, 2020, 48(4): 148-152. |
| Jiang Z M. Preparation and properties of branched preformed particle gel[J]. China Plastics Industry, 2020, 48(4): 148-152. | |
| [15] | 孙焕泉, 曹绪龙, 黄光速, 等. 一种部分支化部分交联聚合物驱油剂及其制备方法: CN110590994A[P]. 2019-05-10. |
| [16] | 姜祖明, 石静, 元福卿, 等. HPAM/PPG颗粒悬浮液驱油体系增黏机制的分子模拟[J]. 中国石油大学学报(自然科学版), 2023, 47(3): 190-196. |
| Jiang Z M, Shi J, Yuan F Q, et al. Molecular simulation of viscosity-increasing mechanism for polymer/PPG particle suspension flooding system[J]. Journal of China University of Petroleum (Edition of Natural Science), 2023, 47(3): 190-196. | |
| [17] | 苏智青, 姜祖明, 黄光速, 等. 部分交联聚丙烯酰胺的合成机理[J]. 高分子材料科学与工程, 2012, 28(5): 53-56. |
| Su Z Q, Jiang Z M, Huang G S, et al. Synthesis mechanism of partially crosslinked polyacrylamide[J]. Polymer Materials Science & Engineering, 2012, 28(5): 53-56. | |
| [18] | 刘煜. 黏弹性颗粒驱油剂在多孔介质中的渗流规律[J]. 科学技术与工程, 2017, 17(24): 218-222. |
| Liu Y. Seepage law of viscoelastic particle oil displacement agent in porous media[J]. Science Technology and Engineering, 2017, 17(24): 218-222. | |
| [19] | Xiong C M, Wei F L, Li W T, et al. Mechanism of polyacrylamide hydrogel instability on high-temperature conditions[J]. ACS Omega, 2018, 3(9): 10716-10724. |
| [20] | Leon-Cecilla A, Gila-Vilchez C, Vazquez-Perez F J, et al. Highly deformable and strongly magnetic semi-interpenetrating hydrogels based on alginate or cellulose[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 2024, 260: 129368. |
| [21] | Bongiovanni Abel S, Busatto C A, Karp F, et al. Weaving the next generation of (bio)materials: Semi-interpenetrated and interpenetrated polymeric networks for biomedical applications[J]. Advances in Colloid and Interface Science, 2023, 321: 103026. |
| [22] | Chatterjee S, Ghosal K, Kumar M, et al. A detailed discussion on interpenetrating polymer network (IPN) based drug delivery system for the advancement of health care system[J]. Journal of Drug Delivery Science and Technology, 2023, 79: 104095. |
| [23] | Ahmadian M, Jaymand M. Interpenetrating polymer network hydrogels for removal of synthetic dyes: a comprehensive review[J]. Coordination Chemistry Reviews, 2023, 486: 215152. |
| [24] | Wang Z B, Liu Y T, Huang W A, et al. Preparation and performance evaluation of a plugging agent with an interpenetrating polymer network[J]. Gels, 2023, 9(3): 205. |
| [25] | Xu Q J, Yuan Z Y, Wang C C, et al. Tough semi-interpenetrating polyvinylpyrrolidone/polyacrylamide hydrogels enabled by bioinspired hydrogen-bonding induced phase separation[J]. Chinese Journal of Polymer Science, 2024, 42(5): 591-603. |
| [26] | 关岚, 盛京, 黄定海. 聚合物/水混合体系中水的状态和性质的研究[J]. 高分子通报, 2010, 12: 38-42. |
| Guan L, Sheng J, Huang D H. Study on the state and properties of water in polymer/water mixed system[J]. Polymer Bulletin, 2010, 12: 38-42. | |
| [27] | Mizuno K, Mabuchi K, Miyagawa T, et al. IR study of hydrogen bonds in halogenoalcohol–water mixtures[J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry A, 1997, 101(7): 1366-1369. |
| [28] | Paul J B, Provencal R A, Chapo C, et al. Infrared cavity ringdown spectroscopy of the water cluster bending vibrations[J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry A, 1999, 103(16): 2972-2974. |
| [29] | Noda I. Generalized two-dimensional correlation method applicable to infrared, Raman, and other types of spectroscopy[J]. Applied Spectroscopy, 1993, 47(9): 1329-1336. |
| [1] | 周光正, 钟子翰, 黄彦群, 王学重. 基于原位成像与图像分析技术的结晶过程智能监测[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(9): 4351-4368. |
| [2] | 戴元燊, 邵之江, 陈伟锋, 陈宁. 基于粒数衡算方程的三元前体结晶过程粒度分布动态预测方法[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(8): 4119-4128. |
| [3] | 高照, 吴熙, 夏丹, 张霖宙. 石油加工分子管理平台热力学及分离单元模块开发[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(7): 3212-3225. |
| [4] | 郭乃胜, 朱小波, 王双, 陈平, 褚召阳, 王志臣. 聚氨酯改性沥青高低温性能及影响因素的研究进展[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(6): 2505-2523. |
| [5] | 何燎, 李俊, 高梦舒, 刘东阳, 张宇豪, 赵亮, 高金森, 徐春明. 石油烃中芳烃分离技术研究进展[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(5): 1909-1926. |
| [6] | 蔡本安, 张建新, 龙城君, 杜乔琛, 车勋建, 张义迎, 蔡伟华. 喷雾闪蒸制备微纳米颗粒[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(3): 1334-1345. |
| [7] | 贾文龙, 肖欢, 冷翔宇, 黄巧竞, 刘程玮, 吴瑕. 原油储罐重质沉积物超声波空化微射流清洗实验及数值模拟[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(3): 1288-1296. |
| [8] | 肖志华, 房浩楠, 郑方植, 孙冬, 陶丽达, 李永峰, 徐春明, 马新龙. NaCl辅助构筑高性能沥青基硬炭负极材料[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(2): 846-857. |
| [9] | 常斐, 师人博, 刘士花, 高文倩, 王一飞, 郑镔, 焦怡萱, 蓝兴英, 徐春明, 韩晔华. 石化行业产品生命周期碳足迹评价研究现状及展望[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(2): 419-437. |
| [10] | 陈弋翀, 贾星雨, 钟文宇, 施俞晖, 彭瑶, 孙嘉阳, 胡冬冬, 赵玲. 具有梯度结构的微孔热塑性聚氨酯及其性能[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(2): 897-908. |
| [11] | 雷宇寰, 赵秋阳, 董宇, 张延龙, 郭烈锦. 超临界水稠油改质反应动力学研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(11): 5544-5553. |
| [12] | 王俊英, 金辉. 超临界CO2与石油烃溶解度参数的分子动力学研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(11): 5788-5798. |
| [13] | 方延玮, 柳冠青, 张易阳, 朱泽鹏, 方筑, 李水清. 变比例广义粗粒化方法的多颗粒场景验证[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(11): 5630-5644. |
| [14] | 刘子琦, 王吉, 俞海, 张宇宁. PDMS微通道冷凝流动导致弹性壁面变形的研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(10): 5076-5092. |
| [15] | 黄俊豪, 庞克亮, 孙方远, 刘福军, 谷致远, 韩龙, 段衍泉, 冯妍卉. 干熄炉料钟结构对焦炭布料粒径均匀度影响的模拟研究[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(S1): 158-169. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备 11010102001995号
京公网安备 11010102001995号