CIESC Journal ›› 2024, Vol. 75 ›› Issue (S1): 1-13.DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20240435
• Reviews and monographs • Previous Articles Next Articles
Yi ZHONG1( ), Shiyu ZHOU1, Lianchao JIU1, Yuxiao LI1, Haojiang WU1, Zhiyong ZHOU2(
), Shiyu ZHOU1, Lianchao JIU1, Yuxiao LI1, Haojiang WU1, Zhiyong ZHOU2( )
)
Received:2024-04-22
Revised:2024-05-11
Online:2024-12-17
Published:2024-12-25
Contact:
Zhiyong ZHOU
钟屹1( ), 周仕遇1, 纠连朝1, 李钰晓1, 吴豪江1, 周智勇2(
), 周仕遇1, 纠连朝1, 李钰晓1, 吴豪江1, 周智勇2( )
)
通讯作者:
周智勇
作者简介:钟屹(2002—),男,本科生,1724439674@qq.com
基金资助:CLC Number:
Yi ZHONG, Shiyu ZHOU, Lianchao JIU, Yuxiao LI, Haojiang WU, Zhiyong ZHOU. Research progress on direct remediation and regeneration of cathode materials from spent lithium iron phosphate batteries[J]. CIESC Journal, 2024, 75(S1): 1-13.
钟屹, 周仕遇, 纠连朝, 李钰晓, 吴豪江, 周智勇. 废旧磷酸铁锂电池正极材料直接修复再生研究进展[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(S1): 1-13.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
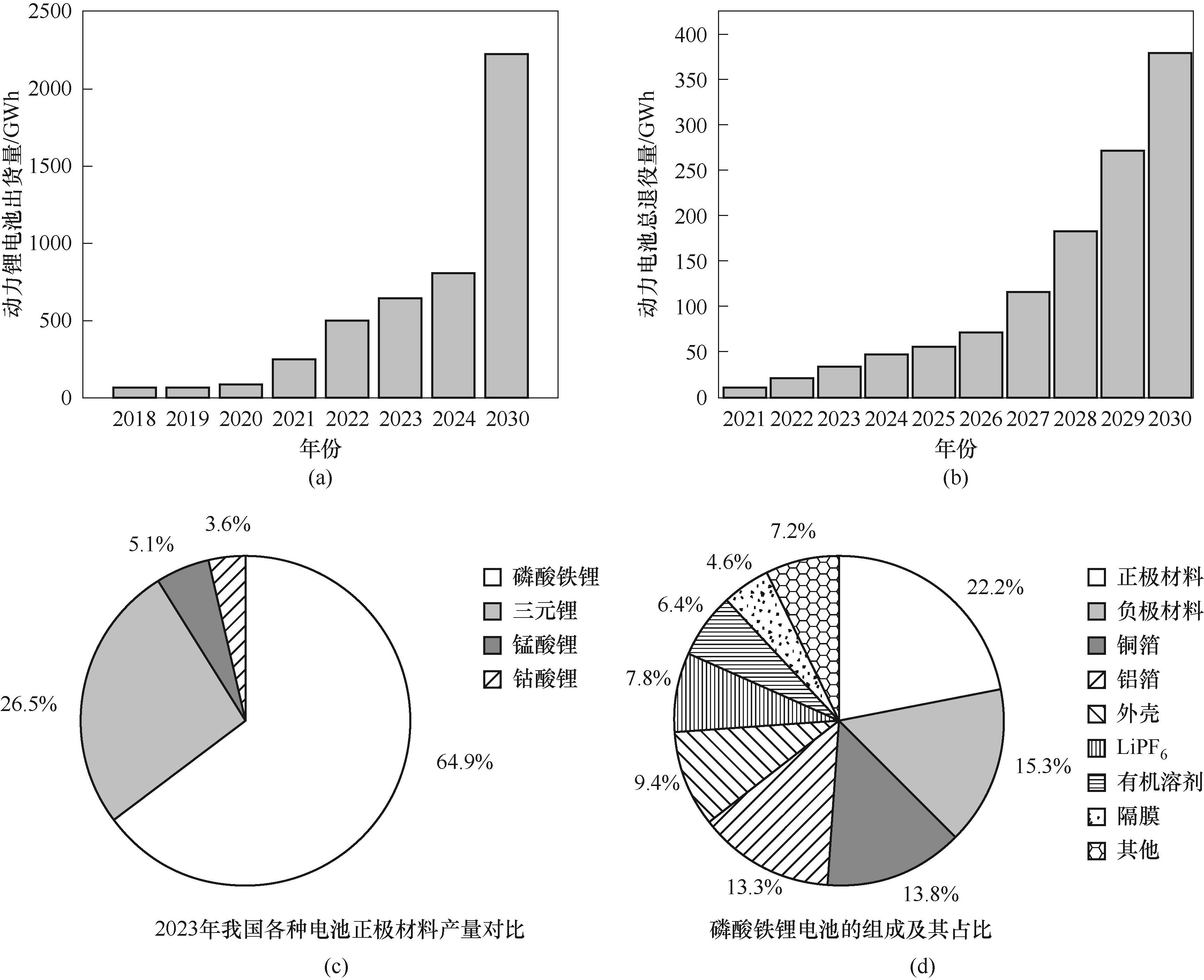
Fig.1 Shipment survey and forecast chart of power lithium battery (a); Total decommissioning survey and forecast chart of power lithium battery (b); Comparison of the production of various battery anode materials in China in 2023 (c); Composition and percentage of lithium iron phosphate battery (d)
| 主要结构 | 主要组成材料 | 含量/% | 成本/% | 潜在环境污染 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 电池壳 | 铝壳,铝塑复合膜 | 20~25 | 7~8 | 重金属污染 | |
| 电芯 | 正极 | 磷酸铁锂 | 25~30 | 76~78 | 重金属污染 |
| 负极 | 含碳石墨材料 | 14~19 | 7~8 | 粉尘污染 | |
| 隔膜 | 聚丙烯/聚乙烯 | 约5 | 约2 | 有机物污染 | |
| 电解液 | LiPF6溶液,碳酸乙烯酯,碳酸甲乙酯 | 10~15 | 约3 | 氟污染 | |
| 集流体 | 铝箔(正极) 铜箔(负极) | 10~16 | 3~4 | 重金属污染 | |
Table1 Main components and potential environmental pollution of lithium iron phosphate battery[44-45]
| 主要结构 | 主要组成材料 | 含量/% | 成本/% | 潜在环境污染 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 电池壳 | 铝壳,铝塑复合膜 | 20~25 | 7~8 | 重金属污染 | |
| 电芯 | 正极 | 磷酸铁锂 | 25~30 | 76~78 | 重金属污染 |
| 负极 | 含碳石墨材料 | 14~19 | 7~8 | 粉尘污染 | |
| 隔膜 | 聚丙烯/聚乙烯 | 约5 | 约2 | 有机物污染 | |
| 电解液 | LiPF6溶液,碳酸乙烯酯,碳酸甲乙酯 | 10~15 | 约3 | 氟污染 | |
| 集流体 | 铝箔(正极) 铜箔(负极) | 10~16 | 3~4 | 重金属污染 | |
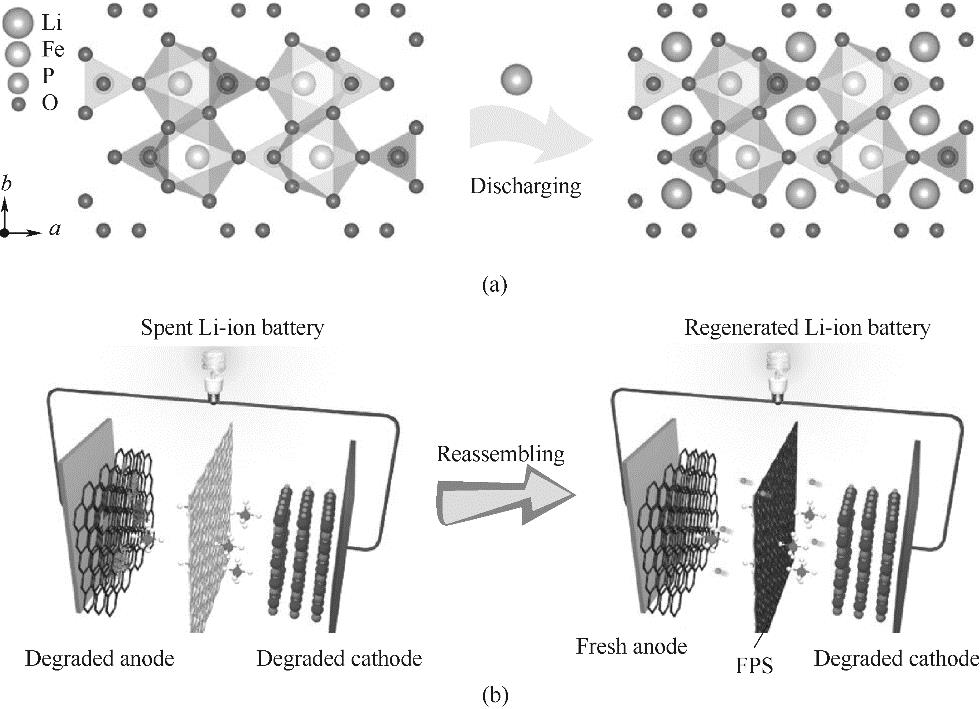
Fig.5 Electrochemical repair principle of lithium ion phosphate battery cathode materials (a); Schematic diagram of functional pre-lithiation diaphragm method for direct repair of lithium iron phosphate batteries (b)[72]
| 正极材料 | 添加物质 | 直接修复 再生方法 | 温度,时间 | 首次放电比容量/(mA·h/g) | 循环容量保持率 (测试条件) | 文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LFP | Li2CO3 | 固相烧结法 | 650℃,1 h | 140.4(0.2 C) | 95.32% (0.2 C,100次) | [ |
| LFP | 25%(质量分数)葡萄糖+10%(质量分数)Li2CO3 | 固相烧结法 | 350℃,2 h 650℃,12 h | 143(0.1 C) | 92.9% (0.1 C,100次) | [ |
| LFP | 5%(质量分数)CNTs+15%(质量分数)葡萄糖+5%(质量分数)Li2CO3 | 固相烧结法 | 350℃,2 h 650℃,12 h | 143.12(0.2 C) | 96.42% (0.2 C,100次) | [ |
| LFP | FC | 固相烧结法 | 350℃,2 h 600℃,8 h | 174.3(0.1 C) | 86.6% (10 C,1000次) | [ |
| LFP | CH3COOLi+15%(质量分数)蔗糖 | 固相烧结法 | 800℃,8 s | 152(0.1 C) | 108.6% (2 C,400次) | [ |
| LFP | Li2SO4+N2H4·H2O | 水热法 | 200℃,3 h 干燥10 h | 141.9(1 C) | 98.6% (1 C,200次) | [ |
| LFP | LiOH+H2O2+Li2CO3 | 水热法 固相烧结法 | 30℃,1 h 700℃,10 h | 146.3(1 C) | 84.9% (5 C,1000次) | [ |
| LFP | LiOH·H2O+DL-苹果酸 | 水热法 固相烧结法 | 100℃,6 h 650℃,3 h | 138.4(1 C) | 98.7% (1 C,200次) | [ |
| LFP | LiOH+柠檬酸+Li2CO3 | 水热法 固相烧结法 | 60℃,16 h 600℃,2 h | 162.0(0.2 C) | 100% (2 C,300次) | [ |
| LFP | LiOH·H2O+FeSO4·7H2O+H3PO4+C6H8O6+CNTs | 水热法 固相烧结法 | 200℃,6 h 600℃,10 h | 154.6(0.1C) | 90.9% (0.1 C,50次) | [ |
| LFP | LiOH·H2O+H3PO4+FeSO4·7H2O+[BMIM] BF4 | 水热法 固相烧结法 | 180℃,10 h 700℃,10 h | 162.2(0.1 C) 71.3(15 C) | 100% (0.1 C,40次) | [ |
| LFP | LiOH· H2O+H3PO4+FeSO4·7H2O+Ga | 水热法 固相烧结法 | 180℃,10 h 750℃,6 h | 154.5(1 C) | 98.77% (1 C,40次) | [ |
| LFP | Li2SO4 | 电化学法 | 室温 | 135.2(0.2 C) | 95.30% (1 C,500次) | [ |
| LFP | LiI | 电化学法 | 室温 | 126.6(0.1 C) | 65.5% (0.5 C,200次) | [ |
| LFP | Li2C2O4 | 电化学法 | 室温 | 152.0(0.05 C) | 90.7% (1 C,292次) | [ |
| LFP | Li2S/Co | 电化学法 | 室温 | 150.3(0.2 C) | 90.4% (0.2 C,200次) | [ |
Table 2 Summary of LFP direct repair regeneration methods
| 正极材料 | 添加物质 | 直接修复 再生方法 | 温度,时间 | 首次放电比容量/(mA·h/g) | 循环容量保持率 (测试条件) | 文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LFP | Li2CO3 | 固相烧结法 | 650℃,1 h | 140.4(0.2 C) | 95.32% (0.2 C,100次) | [ |
| LFP | 25%(质量分数)葡萄糖+10%(质量分数)Li2CO3 | 固相烧结法 | 350℃,2 h 650℃,12 h | 143(0.1 C) | 92.9% (0.1 C,100次) | [ |
| LFP | 5%(质量分数)CNTs+15%(质量分数)葡萄糖+5%(质量分数)Li2CO3 | 固相烧结法 | 350℃,2 h 650℃,12 h | 143.12(0.2 C) | 96.42% (0.2 C,100次) | [ |
| LFP | FC | 固相烧结法 | 350℃,2 h 600℃,8 h | 174.3(0.1 C) | 86.6% (10 C,1000次) | [ |
| LFP | CH3COOLi+15%(质量分数)蔗糖 | 固相烧结法 | 800℃,8 s | 152(0.1 C) | 108.6% (2 C,400次) | [ |
| LFP | Li2SO4+N2H4·H2O | 水热法 | 200℃,3 h 干燥10 h | 141.9(1 C) | 98.6% (1 C,200次) | [ |
| LFP | LiOH+H2O2+Li2CO3 | 水热法 固相烧结法 | 30℃,1 h 700℃,10 h | 146.3(1 C) | 84.9% (5 C,1000次) | [ |
| LFP | LiOH·H2O+DL-苹果酸 | 水热法 固相烧结法 | 100℃,6 h 650℃,3 h | 138.4(1 C) | 98.7% (1 C,200次) | [ |
| LFP | LiOH+柠檬酸+Li2CO3 | 水热法 固相烧结法 | 60℃,16 h 600℃,2 h | 162.0(0.2 C) | 100% (2 C,300次) | [ |
| LFP | LiOH·H2O+FeSO4·7H2O+H3PO4+C6H8O6+CNTs | 水热法 固相烧结法 | 200℃,6 h 600℃,10 h | 154.6(0.1C) | 90.9% (0.1 C,50次) | [ |
| LFP | LiOH·H2O+H3PO4+FeSO4·7H2O+[BMIM] BF4 | 水热法 固相烧结法 | 180℃,10 h 700℃,10 h | 162.2(0.1 C) 71.3(15 C) | 100% (0.1 C,40次) | [ |
| LFP | LiOH· H2O+H3PO4+FeSO4·7H2O+Ga | 水热法 固相烧结法 | 180℃,10 h 750℃,6 h | 154.5(1 C) | 98.77% (1 C,40次) | [ |
| LFP | Li2SO4 | 电化学法 | 室温 | 135.2(0.2 C) | 95.30% (1 C,500次) | [ |
| LFP | LiI | 电化学法 | 室温 | 126.6(0.1 C) | 65.5% (0.5 C,200次) | [ |
| LFP | Li2C2O4 | 电化学法 | 室温 | 152.0(0.05 C) | 90.7% (1 C,292次) | [ |
| LFP | Li2S/Co | 电化学法 | 室温 | 150.3(0.2 C) | 90.4% (0.2 C,200次) | [ |
| 1 | Bank M S, Swarzenski P W, Duarte C M, et al. Global plastic pollution observation system to aid policy[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2021, 55(12): 7770-7775. |
| 2 | Rogelj J, Geden O, Cowie A, et al. Net-zero emissions targets are vague: three ways to fix[J]. Nature, 2021, 591(7850): 365-368. |
| 3 | Rogelj J, Elzen D M, Höhne N, et al. Paris Agreement climate proposals need a boost to keep warming well below 2℃[J]. Nature, 2016, 534(7609): 631-639. |
| 4 | Wang F, Harindintwali J D, Yuan Z Z, et al. Technologies and perspectives for achieving carbon neutrality[J]. The Innovation, 2021, 2(4): 100180. |
| 5 | Nitta N, Wu F X, Lee J T, et al. Li-ion battery materials: present and future[J]. Materials Today, 2015, 18(5): 252-264. |
| 6 | Alfaro-Algaba M, Ramirez J. Techno-economic and environmental disassembly planning of lithium-ion electric vehicle battery packs for remanufacturing[J]. Resource, Conservation and Recycling, 2020, 154: 104461. |
| 7 | Harper G, Sommerville R, Kendirck E, et al. Recycling lithium-ion batteries from electric vehicles[J]. Nature, 2019, 575(7781): 75-86. |
| 8 | Schmuch R, Wagner R, Hörpel G, et al. Performance and cost of materials for lithium-based rechargeable automotive batteries[J]. Nature Energy, 2018, 3(4): 267-278. |
| 9 | Winter M, Barnett B, Xu K. Before Li ion batteries[J]. Chemical Reviews, 2018, 118(23): 11433-11456. |
| 10 | Ji G J, Wang J X, Liang Z. Direct regeneration of degraded lithium-ion battery cathodes with a multifunctional organic lithium salt[J]. Nature Communication, 2023, 14(1): 584. |
| 11 | Yao Q, Xiao F Y, Lin C Y. Regeneration of spent lithium manganate into cation-doped and oxygen-deficient MnO2 cathodes toward ultralong lifespan and wide-temperature-tolerant aqueous Zn-ion batteries[J]. Battery Energy, 2023, 13(9): 20220065. |
| 12 | Wang J X, Ma J, Zhuang Z F, et al. Toward direct regeneration of spent lithium-ion batteries: a next-generation recycling method[J]. Chemical Reviews, 2024, 124(5): 2839-2887. |
| 13 | Wang L, Shen Y H, Liu Y L, et al. Electrochemical restoration of battery materials guided by synchrotron radiation technology for sustainable lithium-ion batteries[J]. Small Methods, 2023, 7(9): 2201658. |
| 14 | Xiao J F, Li J, Xu Z M. Novel approach for in situ recovery of lithium carbonate from spent lithium ion batteries using vacuum metallurgy[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2017, 51(20): 11960-11966. |
| 15 | Swain B. Recovery and recycling of lithium: a review[J]. Separation and Purification Technology, 2017, 172: 388-403. |
| 16 | Meshram P, Mishra A, Sahu R. Environmental impact of spent lithium ion batteries and green recycling perspectives by organic acids—A review[J]. Chemosphere, 2020, 242: 125291. |
| 17 | Xiao J F, Li J, Xu Z M. Challenges to future development of spent lithium ion batteries recovery from environmental and technological perspectives[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2020, 54(1): 9-25. |
| 18 | 王崇国, 刘广龙, 金小容, 等. 锂离子电池正极材料的研究进展[J]. 当代化工研究, 2023, 9: 12-14. |
| Wang C G, Liu G L, Jin X R, et al. Research progress of lithium-ion battery cathode material[J]. Modern Chemical Research, 2023, 9: 12-14. | |
| 19 | 王薇薇, 吴华珠, 赵斐, 等. 锂离子电池正极材料国内外专利分布及关键技术解析[J]. 中国科技信息, 2024, 4: 32-36. |
| Wang W W, Wu H Z, Zhao F, et al. Analysis of domestic and international patent distribution and key technologies of anode materials for lithium-ion batteries[J]. China Science and Technology Information, 2024, 4: 32-36. | |
| 20 | 梅洋, 张强. 锂离子电池磷酸铁锂正极材料的研究进展及预测[J]. 化工科技. DOI: 10.16664/j.cnki.issn1008-0511. 20240403.002 . |
| Mei Y, Zhang Q. Research progress and prediction of lithium iron phosphate cathode materials for lithium-ion batteries[J]. Science & Technology in Chemical Industry. DOI: 10.16664/j.cnki.issn1008-0511.20240403.002 . | |
| 21 | 李玉婷. 碳中和背景下锂离子电池正极材料的发展趋势及应对措施[J]. 化学与生物工程, 2022, 39(9): 7-10. |
| Li Y T. Development trend and countermeasures of lithium ion battery cathode materials under background of carbon neutralization[J]. Chemistry & Bioengineering, 2022, 39(9): 7-10. | |
| 22 | 兰凯惠, 吴利萍, 丁若兰, 等. 锂离子电池正极材料浅析[J]. 电工材料, 2023, 3: 49-52. |
| Lan K H, Wu L P, Ding R L, et al. A review of cathode materials for rechargeable lithium-ion batteries[J]. Electrical Engineering Materials, 2023, 3: 49-52. | |
| 23 | 周弋惟, 陈卓, 徐建鸿. 湿法冶金回收废旧锂电池正极材料的研究进展[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(1): 85-96. |
| Zhou Y W, Chen Z, Xu J H. Progress and prospect of recycling spent lithium battery cathode materials by hydrometallurgy[J]. CIESC Journal, 2022, 73(1): 85-96. | |
| 24 | 王振华, 彭代冲, 孙克宁. 锂离子电池隔膜材料研究进展[J]. 化工学报, 2018, 69(1): 282-294. |
| Wang Z H, Peng D C, Sun K N. Research progress of separator materials for lithium ion batteries[J]. CIESC Journal, 2018, 69(1): 282-294. | |
| 25 | Sheng O W, Hu H L, Liu T F, et al. Interfacial and ionic modulation of poly(ethylene oxide) electrolyte via localized iodization to enable dendrite-free lithium metal batteries[J]. Advanced Functional Materials, 2022, 32(14): 2111026. |
| 26 | Yan W, Fan K, Zheng L M, et al. Cluster-bridging-coordinated bimetallic metal-organic framework as high-performance anode material for lithium-ion storage[J]. Small Structures, 2021, 2(12): 2100122. |
| 27 | Zhao T Y, Li W L, Traversy M, et al. A review on the recycling of spent lithium iron phosphate batteries[J]. Journal of Environmental Management, 2024, 351: 119670. |
| 28 | Liao H Y, Zhao S W, Cai M Z, et al. Direct conversion of waste battery cathodes to high-volumetric-capacity anodes with assembled secondary‐particle morphology[J]. Advanced Energy Materials, 2023, 13(22): 2300596. |
| 29 | Yang T Z, Luo D, Yu A P, et al. Enabling future closed-loop recycling of spent lithium-ion batteries: direct cathode regeneration[J]. Advanced Material, 2023, 35(36): 2203218. |
| 30 | Zhu X H, Li Y J, Gong M Q, et al. Recycling valuable metals from spent lithium‐ion batteries using carbothermal shock method[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2023, 62(15): e202300074. |
| 31 | Lan Y Q, LI X K, Zhou G M, et al. Direct regenerating cathode materials from spent lithium-ion batteries[J]. Advanced Science, 2024, 11(1): 2304425. |
| 32 | Mrozik W, Rajaeifar M A, Heidrich O, et al. Environmental impacts, pollution sources and pathways of spent lithium-ion batteries[J]. Energy Environmental Science, 2021, 14(12): 6099-6121. |
| 33 | He Y Q, Yuan X, Zhang G W, et al. A critical review of current technologies for the liberation of electrode materials from foils in the recycling process of spent lithium-ion batteries[J]. Science of Total Environment, 2021, 766: 142382. |
| 34 | Xu P P, Yang Z Z, Yu X L, et al. Design and optimization of the direct recycling of spent Li-ion battery cathode materials[J]. ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering, 2021, 9(12): 4543-4553. |
| 35 | Xu P P, Yu X L, Chen Z. A materials perspective on direct recycling of lithium‐ion batteries: principles, challenges and opportunities[J]. Advanced Functional Materials, 2023, 33(14): 2213168. |
| 36 | Li J L, Lu Y Q, Yang T R, et al. Water-based electrode manufacturing and direct recycling of lithium-ion battery electrodes—a green and sustainable manufacturing system[J]. iScience, 2020, 23(5): 101081. |
| 37 | Shin Y, Kim S, Park S, et al. A comprehensive review on the recovery of cathode active materials via direct recycling from spent Li-ion batteries[J]. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 2023, 187: 113693. |
| 38 | Wang T, Luo H M, Bai Y C, et al. Direct recycling of spent NCM cathodes through ionothermal lithiation[J]. Advanced Energy Materials, 2020, 10(30): 2001204. |
| 39 | Shi Y, Chen G, Chen Z. Effective regeneration of LiCoO2 from spent lithium-ion batteries: a direct approach towards high-performance active particles[J]. Green Chemistry, 2018, 20(4): 851-862. |
| 40 | Fan M, Chang X, Guo Y J, et al. Increased residual lithium compounds guided design for green recycling of spent lithium-ion cathodes[J]. Energy and Environmental Science, 2021, 14(3): 1461-1468. |
| 41 | Li Y K, Lv W G, Huang H L, et al. Recycling of spent lithium-ion batteries in view of green chemistry[J]. Green Chemistry, 2021, 23(17): 6139-6171. |
| 42 | 王猛, 张家靓, 陈永强, 等. 退役磷酸铁锂电池回收技术综述[J]. 有色金属(冶炼部分), 2023, (5): 100-110. |
| Wang M, Zhang J L, Chen Y Q, et al. Review on recycling technology of retired LiFePO4 batteries[J]. Non-Ferrous Metals (Smelting Part), 2023, (5): 100-110. | |
| 43 | 卫寿平, 孙杰, 周添, 等. 废旧锂离子电池中金属材料回收研究进展[J]. 储能科学与技术, 2017, 6(6): 1196-1207. |
| Wei S P, Sun J, Zhou T, et al. Research development of metals recovery from spent lithium-ion batteries[J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2017, 6(6): 1196-1207. | |
| 44 | 李洪枚, 姜亢. 废旧锂离子电池对环境污染的分析与对策[J]. 上海环境科学, 2004, 23(5): 201-203. |
| Li H M, Jiang K. An analysis of waste lithium-ion battery contamination to environment and its countermeasures[J]. Shanghai Environment Science, 2004, 23(5): 201-203. | |
| 45 | 任国庆. 废旧锂离子电池直接还原熔炼高效分离回收有价金属研究[D]. 长沙: 长沙矿冶研究院, 2014. |
| Ren G Q. Research of valuable metals separation and recovery from spent lithium-ion battery by reduction smelting[D]. Changsha: Changsha Research Institute of Mining and Metallurgy, 2014. | |
| 46 | Tiaan P, Steven M B, Guven A. The efficiency of black mass preparation by discharge and alkaline leaching for LIB recycling[J]. Minerals, 2022, 12(6): 753. |
| 47 | 蒋良兴, 郑文军, 张刚, 等. 废旧锂离子电池预处理的绿色放电技术研究[J]. 中南大学学报(自然科学版), 2023, 54(2): 684-693. |
| Jiang L X, Zheng W J, Zhang G, et al. Research on pretreatment green discharge technology of spent lithium-ion batteries[J]. Journal of Central South University (Natural Science Edition), 2023, 54(2): 684-693. | |
| 48 | 郭宇, 于刚强, 陈标华. 废锂离子电池的冶金回收工艺研究进展[J]. 北京工业大学学报, 2024, 50(2): 230-245. |
| Guo Y, Yu G Q, Chen B H. Research progress on metallurgical recovery process of waste lithium batteries[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Technology, 2024, 50(2): 230-245. | |
| 49 | 康飞, 孙峙, 卢雄辉. 面向分选的退役锂电池拆解设备与工艺研究[J]. 有色金属(选矿部分), 2023(2): 124-132. |
| Kang F, Sun Z, Lu X H. Research on decommissioned lithium battery disassembly equipment and technology for separation [J]. Non-Ferrous Metals (Mineral Processing Part), 2023(2): 124-132. | |
| 50 | Wang X, Gaustad G, Babbitt C W. Targeting high value metals in lithium⁃ion battery recycling via shredding and size-based separation[J]. Waste Management, 2016, 51: 204⁃213. |
| 51 | Sovacool B K, Kester J, Noel L, et al. Contested visions and sociotechnical expectations of electric mobility and vehicle⁃to⁃grid innovation in five Nordic countries[J]. Environmental Innovation and Societal Transitions, 2019, 31: 170⁃183. |
| 52 | Chen X P, Li S Z, Wang Y, et al. Recycling of LiFePO4 cathode materials from spent lithium-ion batteries through ultrasound-assisted Fenton reaction and lithium compensation[J]. Waste Management, 2021, 136: 67-75. |
| 53 | Sun L, Qiu K Q. Organic oxalate as leachant and precipitant for the recovery of valuable metals from spent lithium-ion batteries[J]. Waste Management, 2012, 32: 1575-1582. |
| 54 | Jin Y C, Zhang T, Zhang M D. Advancesin intelligent regeneration of cathode materials for sustainable lithium-ion batteries[J]. Advanced Energy Materials, 2022, 12(36): 2201526. |
| 55 | Li X L, Zhang J, Song D W, et al. Direct regeneration of recycled cathode material mixture from scrapped LiFePO4 batteries[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2017, 345: 78-84. |
| 56 | Qi C, Wang S H, Zhu X K, et al. Environmental-friendly low-cost direct regeneration of cathode material from spent LiFePO4 [J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2022, 924: 166612. |
| 57 | Song L, Qi C, Wang S H, et al. Direct regeneration of waste LiFePO4 cathode materials with a solid-phase method promoted by activated CNTs[J]. Waste Management, 2023, 157: 141-148. |
| 58 | Wang X F, Feng Z J, Hou X L, et al. Fluorine doped carbon coating of LiFePO4 as a cathode material for lithium-ion batteries[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2020, 379: 122371. |
| 59 | Zheng S H, Wang X T, Gu Z Y, et al. Direct and rapid regeneration of spent LiFePO4 cathodes via a high-temperature shock strategy[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2023, 587: 233697. |
| 60 | Gao H P, Tran D, Chen Z. Seeking direct cathode regeneration for more efficient lithium-ion battery recycling[J]. Current Opinion in Electrochemistry, 2022, 31: 100875. |
| 61 | Jin H, Zhang J L, Wang D D, et al. Facile and efficient recovery of lithium from spent LiFePO4 batteries via air oxidation-water leaching at room temperature[J]. Green Chemistry, 2022, 24: 152-162. |
| 62 | Macarena K, Samuel A H, James N O, et al. Lithium iron phosphate/carbon (LFP/C) composite using nanocellulose as a reducing agent and carbon source[J]. Polymers, 2023, 15(12): 2628. |
| 63 | Christian H, Thomas L, Jan D, et al. Recycling of lithium-ion batteries: a novel method to separate coating and foil of electrodes[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2015, 108: 301-311. |
| 64 | Xu Y L, Zhang B C, Ge Z F, et al. Direct recovery of degraded LiFePO4 cathode via mild chemical relithiation strategy[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2023, 477: 147201. |
| 65 | Gupta V, Yu X L, Gao H P, et al. Scalable direct recycling of cathode black mass from spent lithium‐ion batteries[J]. Advanced Energy Materials, 2023, 13(6): 2203093. |
| 66 | Yang J Y, Zhou K, Gong R, et al. Direct regeneration of spent LiFePO4 materials via a green and economical one-step hydrothermal process[J]. Journal of Environmental Management, 2023, 348:119384. |
| 67 | Xu P P, Dai Q, Gao H P, et al. Efficient direct recycling of lithium-ion battery cathodes by targeted healing[J]. Joule, 2020, 4(12): 2609-2626. |
| 68 | Feng W J, Cao Yue, Zhao X, et al. Effect of carbon nanotubes on the electrochemical performance of LiFePO4 particles in lithium ion batteries[J]. International Journal of Electrochemical Science, 2017, 12(6): 5199-5207. |
| 69 | Meng Y S, Li Y Z, Xia J, et al. F-doped LiFePO4@N/B/F-doped carbon as high performance cathode materials for Li-ion batteries[J]. Applied Surface Science, 2019, 476: 761-768. |
| 70 | Yi D W, Cui X M, Li N L, et al. Enhancement of electrochemical performance of LiFePO4@C by Ga coating[J]. ACS Omega, 2020, 5(17): 9752-9758. |
| 71 | Ganter, Matthew J, Brian J, et al. Cathode refunctionalization as a lithium ion battery recycling alternative[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2014, 256: 274-280. |
| 72 | Fan M, Meng Q H, Chang X, et al. In situ electrochemical regeneration of degraded LiFePO4 electrode with functionalized prelithiation separator[J]. Advanced Energy Materials, 2022, 12(18): 2103630. |
| 73 | Peng D Z, Wang X W, Wang S B, et al. Efficient regeneration of retired LiFePO4 cathode by combining spontaneous and electrically driven processes[J]. Green Chemistry, 2022, 24(11): 4544-4556. |
| 74 | Wang T, Yu X S, Fan M, et al. Direct regeneration of spent LiFePO4 via a graphite prelithiation strategy[J]. Chemical Communications, 2020, 56(2): 245-248. |
| 75 | Rao Z X, Wu J Y, He B, et al. A prelithiation separator for compensating the initial capacity loss of lithium-ion batteries[J]. Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2021, 13(32): 38194-38201. |
| 76 | Sun J, Jiang Z Y, Li S, et al. A sustainable revival process for defective LiFePO4 cathodes through the synergy of defect-targeted healing and in-situ construction of 3D-interconnected porous carbon networks[J]. Waste Management, 2023, 158: 125-135. |
| 77 | Wu C, Jiang J Y, He B, et al. Direct regeneration of spent Li-ion battery cathodes via chemical relithiation reaction[J]. ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering, 2021, 9(48): 16384-16393. |
| 78 | Zhao X X, Wang X T, Guo J Z, et al. Dynamic Li+ capture through ligand-chain interaction for the regeneration of depleted LiFePO4 cathode[J]. Advanced Materials, 2024, 36(14): e2308927. |
| [1] | Angran ZHAO, Yongqiang HAN, Zhipeng WANG, Pengfei LI, Yawei XU, Huiling TONG. Experimental study on simultaneous desulfurization and denitrification of red mud at low temperature [J]. CIESC Journal, 2024, 75(S1): 276-282. |
| [2] | Shugang HU, Guoqing TIAN, Wenjuan LIU, Guangfei XU, Huaqing LIU, Jian ZHANG, Yanlong WANG. Preparation of nanoscale zero-valent iron and its application of reduction and oxidation technology [J]. CIESC Journal, 2024, 75(9): 3041-3055. |
| [3] | Wenfang GAO, Han CUI, Yiran SUN, Jiaqing PENG, Rui ZHU, Ran XIA, Xinyu ZHANG, Jiaqi LI, Xueliang WANG, Zhi SUN, Longyi LYU. A critical review on environmental impact assessment of typical metal production processes [J]. CIESC Journal, 2024, 75(9): 3056-3073. |
| [4] | Xiaoyuan ZHENG, Yanlin CAI, Zhi YING, Bo WANG, Binlin DOU. Phosphorus transformation during subcritical hydrothermal conversion of sewage sludge [J]. CIESC Journal, 2024, 75(8): 2970-2982. |
| [5] | Hongrui LI, Chunxi HUANG, Xiaodong HONG, Zuwei LIAO, Jingdai WANG, Yongrong YANG. An adaptive variable-step homotopy-based algorithm for process simulation with cyclic streams [J]. CIESC Journal, 2024, 75(7): 2604-2612. |
| [6] | Junxia MA, Lintao LI, Weili XIONG. A semi-supervised soft sensor modeling method based on the Tri-training GPR [J]. CIESC Journal, 2024, 75(7): 2613-2623. |
| [7] | Han ZHANG, Shuning ZHANG, Ke LIU, Guanlong DENG. Particle size prediction of cobalt oxalate synthesis process based on slow feature analysis and least squares support vector regression [J]. CIESC Journal, 2024, 75(6): 2313-2321. |
| [8] | Baofeng WANG, Shugao WANG, Fangqin CHENG. Progress in preparation and CO2 adsorption properties of solid waste-based sulfur-doped porous carbon materials [J]. CIESC Journal, 2024, 75(2): 395-411. |
| [9] | Qiong SUN, Fuxin YANG, Houzhang TAN, Xiaopo WANG. Simulation study of CO2 capture from flue gas by deep eutectic solvent [J]. CIESC Journal, 2024, 75(10): 3705-3717. |
| [10] | Jiawen LIU, Wencheng XIA, Feng WU, Yaoli PENG, Guangyuan XIE. Mechanism study on mechanochemical solid-phase oxidation recovery of spent LiFePO4 batteries [J]. CIESC Journal, 2024, 75(10): 3775-3782. |
| [11] | Ruimin CHE, Wenqiu ZHENG, Xiaoyu WANG, Xin LI, Feng XU. Research progress on homogeneous processing of cellulose in ionic liquids [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(9): 3615-3627. |
| [12] | Chen HAN, Youmin SITU, Bin ZHU, Jianliang XU, Xiaolei GUO, Haifeng LIU. Study of reaction and flow characteristics in multi-nozzle pulverized coal gasifier with co-processing of wastewater [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(8): 3266-3278. |
| [13] | Manzheng ZHANG, Meng XIAO, Peiwei YAN, Zheng MIAO, Jinliang XU, Xianbing JI. Working fluid screening and thermodynamic optimization of hazardous waste incineration coupled organic Rankine cycle system [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(8): 3502-3512. |
| [14] | Yuanhao QU, Wenyi DENG, Xiaodan XIE, Yaxin SU. Study on electro-osmotic dewatering of sludge assisted by activated carbon/graphite [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(7): 3038-3050. |
| [15] | Zhaolun WEN, Peirui LI, Zhonglin ZHANG, Xiao DU, Qiwang HOU, Yegang LIU, Xiaogang HAO, Guoqing GUAN. Design and optimization of cryogenic air separation process with dividing wall column based on self-heat regeneration [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(7): 2988-2998. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||