化工学报 ›› 2021, Vol. 72 ›› Issue (9): 4900-4909.DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20210282
刘怡静1,2( ),章骅1,2,邵立明1,2,何品晶1,2(
),章骅1,2,邵立明1,2,何品晶1,2( )
)
收稿日期:2021-02-22
修回日期:2021-04-19
出版日期:2021-09-05
发布日期:2021-09-05
通讯作者:
何品晶
作者简介:刘怡静(1994—),女,硕士研究生,基金资助:
Yijing LIU1,2( ),Hua ZHANG1,2,Liming SHAO1,2,Pinjing HE1,2(
),Hua ZHANG1,2,Liming SHAO1,2,Pinjing HE1,2( )
)
Received:2021-02-22
Revised:2021-04-19
Online:2021-09-05
Published:2021-09-05
Contact:
Pinjing HE
摘要:
采用氧弹法、浸提-氧弹法和管式炉-氧弹法分别测定生活垃圾组分中的总氯、无机/有机氯以及挥发态/固定态氯的含量,探究了生活垃圾中氯的形态和在热处理过程中的转化规律。结果表明,生活垃圾各组分的总氯含量(干基)为1.52~19.44 mg/g,其中,厨余类组分的氯含量最高,为8.38~19.44 mg/g。厨余类组分的无机氯含量占比高达90%以上,橡塑类组分的有机氯含量占比为46%~55%。热处理过程中,无机氯在空气气氛下更易转化成挥发态氯和固定态氯,在氮气气氛下更易转化成固定态氯和其他态氯;而有机氯则主要转化成挥发态氯。揭示生活垃圾各组分的氯形态及其在热处理过程中的转化规律,可以为生活垃圾热处理过程烟气处理和氯腐蚀控制提供理论依据和解决思路。
中图分类号:
刘怡静, 章骅, 邵立明, 何品晶. 生活垃圾中氯的赋存形态及热转化规律探究[J]. 化工学报, 2021, 72(9): 4900-4909.
Yijing LIU, Hua ZHANG, Liming SHAO, Pinjing HE. Occurrence of chlorine in municipal solid waste and its thermal transformation[J]. CIESC Journal, 2021, 72(9): 4900-4909.
| 组分 | 氯含量/% (干基) | 组分 | 氯含量/% (干基) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 厨余 | 0.11~2.74 | 橡胶和皮革 | 0.58~8 |
| 塑料 | 0.83~2.83 | 木材 | 0.05~0.29 |
| 纸张和硬纸板 | 0.15~0.71 | 玻璃 | 0.0081 |
| 纺织和地毯 | 0.36~1.1 | 其他 | 0.27~0.31 |
表1 生活垃圾组分的氯含量[14-18]
Table 1 Chlorine contents in the municipal solid waste components [14-18]
| 组分 | 氯含量/% (干基) | 组分 | 氯含量/% (干基) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 厨余 | 0.11~2.74 | 橡胶和皮革 | 0.58~8 |
| 塑料 | 0.83~2.83 | 木材 | 0.05~0.29 |
| 纸张和硬纸板 | 0.15~0.71 | 玻璃 | 0.0081 |
| 纺织和地毯 | 0.36~1.1 | 其他 | 0.27~0.31 |
| 样品名称 | 工业分析/%(质量) | 元素组成/%(质量,干基) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 含水率w① | 可燃分d① | 灰分d① | C | H | O | N | S | |
| H-厨余-1 | 79.4 | 82.4±0.3 | 17.6±0.3 | 46.7±0.4 | 6.8±0.1 | 22.8±0.3 | 4.1±0.2 | 0.47±0.09 |
| H-厨余-3 | 69.8 | 67.2±0.4 | 32.8±0.4 | 37.8±0.8 | 5.1±0.1 | 18.7±0.2 | 3.1±0.3 | 0.42±0.06 |
| H-橡塑 | 26.3 | 77.5±2.2 | 22.5±2.2 | 64.4±1.4 | 10.1±0.1 | 1.4±0.3 | 0.29±0.04 | 0.33±0.06 |
| H-纸类 | 61.1 | 88.3±0.9 | 11.7±0.9 | 41.0±0.2 | 6.20±0.01 | 39.7±1.1 | 0.41±0.05 | 0.146±0.001 |
| H-织物 | 29.3 | 98.0±0.2 | 2.0±0.2 | 58.6±0.5 | 5.1±0.2 | 32.9±0.2 | 0.93±0.07 | 0.15±0.03 |
| H-其他 | 6.6 | 13.3±1.7 | 86.7±1.7 | 6.7±0.1 | 1.20±0.07 | 4.3±0.3 | 0.52±0.01 | 0.42±0.01 |
| X-厨余-1 | 75.1 | 83.9±0.6 | 16.1±0.6 | 43.1±1.1 | 6.1±0.2 | 30.9±1.6 | 2.6±0.3 | 0.30±0.07 |
| X-厨余-2 | 76.2 | 87.3±0.5 | 12.7±0.5 | 51.5±0.2 | 7.74±0.08 | 22.5±0.5 | 3.8±0.2 | 0.55±0.04 |
| X-厨余-3 | 66.6 | 87.7±0.2 | 12.3±0.2 | 44.3±0.7 | 6.86±0.08 | 32.2±1.0 | 3.05±0.08 | 0.42±0.08 |
| X-橡塑 | 11.7 | 94.1±0.6 | 5.9±0.6 | 77.9±2.4 | 12.5±0.3 | 2.8±0.3 | 0.33±0.03 | 0.30±0.03 |
| X-纸类 | 24.7 | 89.5±0.3 | 10.5±0.3 | 41.6±0.7 | 5.8±0.3 | 41.6±0.6 | 0.07±0.01 | 0.08±0.01 |
| X-织物 | 4.7 | 98.93±0.03 | 1.07±0.03 | 79.6±0.2 | 12.9±0.3 | 6.1±0.5 | 0.010±0.001 | 0.05±0.01 |
| X-其他 | 4.3 | 18.4±1.0 | 81.6±1.0 | 11.4±2.2 | 1.9±0.4 | 4.9±1.5 | 0.005±0.001 | 0.042±0.002 |
表2 生活垃圾工业分析和元素组成
Table 2 Proximate analysis and elemental analysis results of municipal solid waste
| 样品名称 | 工业分析/%(质量) | 元素组成/%(质量,干基) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 含水率w① | 可燃分d① | 灰分d① | C | H | O | N | S | |
| H-厨余-1 | 79.4 | 82.4±0.3 | 17.6±0.3 | 46.7±0.4 | 6.8±0.1 | 22.8±0.3 | 4.1±0.2 | 0.47±0.09 |
| H-厨余-3 | 69.8 | 67.2±0.4 | 32.8±0.4 | 37.8±0.8 | 5.1±0.1 | 18.7±0.2 | 3.1±0.3 | 0.42±0.06 |
| H-橡塑 | 26.3 | 77.5±2.2 | 22.5±2.2 | 64.4±1.4 | 10.1±0.1 | 1.4±0.3 | 0.29±0.04 | 0.33±0.06 |
| H-纸类 | 61.1 | 88.3±0.9 | 11.7±0.9 | 41.0±0.2 | 6.20±0.01 | 39.7±1.1 | 0.41±0.05 | 0.146±0.001 |
| H-织物 | 29.3 | 98.0±0.2 | 2.0±0.2 | 58.6±0.5 | 5.1±0.2 | 32.9±0.2 | 0.93±0.07 | 0.15±0.03 |
| H-其他 | 6.6 | 13.3±1.7 | 86.7±1.7 | 6.7±0.1 | 1.20±0.07 | 4.3±0.3 | 0.52±0.01 | 0.42±0.01 |
| X-厨余-1 | 75.1 | 83.9±0.6 | 16.1±0.6 | 43.1±1.1 | 6.1±0.2 | 30.9±1.6 | 2.6±0.3 | 0.30±0.07 |
| X-厨余-2 | 76.2 | 87.3±0.5 | 12.7±0.5 | 51.5±0.2 | 7.74±0.08 | 22.5±0.5 | 3.8±0.2 | 0.55±0.04 |
| X-厨余-3 | 66.6 | 87.7±0.2 | 12.3±0.2 | 44.3±0.7 | 6.86±0.08 | 32.2±1.0 | 3.05±0.08 | 0.42±0.08 |
| X-橡塑 | 11.7 | 94.1±0.6 | 5.9±0.6 | 77.9±2.4 | 12.5±0.3 | 2.8±0.3 | 0.33±0.03 | 0.30±0.03 |
| X-纸类 | 24.7 | 89.5±0.3 | 10.5±0.3 | 41.6±0.7 | 5.8±0.3 | 41.6±0.6 | 0.07±0.01 | 0.08±0.01 |
| X-织物 | 4.7 | 98.93±0.03 | 1.07±0.03 | 79.6±0.2 | 12.9±0.3 | 6.1±0.5 | 0.010±0.001 | 0.05±0.01 |
| X-其他 | 4.3 | 18.4±1.0 | 81.6±1.0 | 11.4±2.2 | 1.9±0.4 | 4.9±1.5 | 0.005±0.001 | 0.042±0.002 |
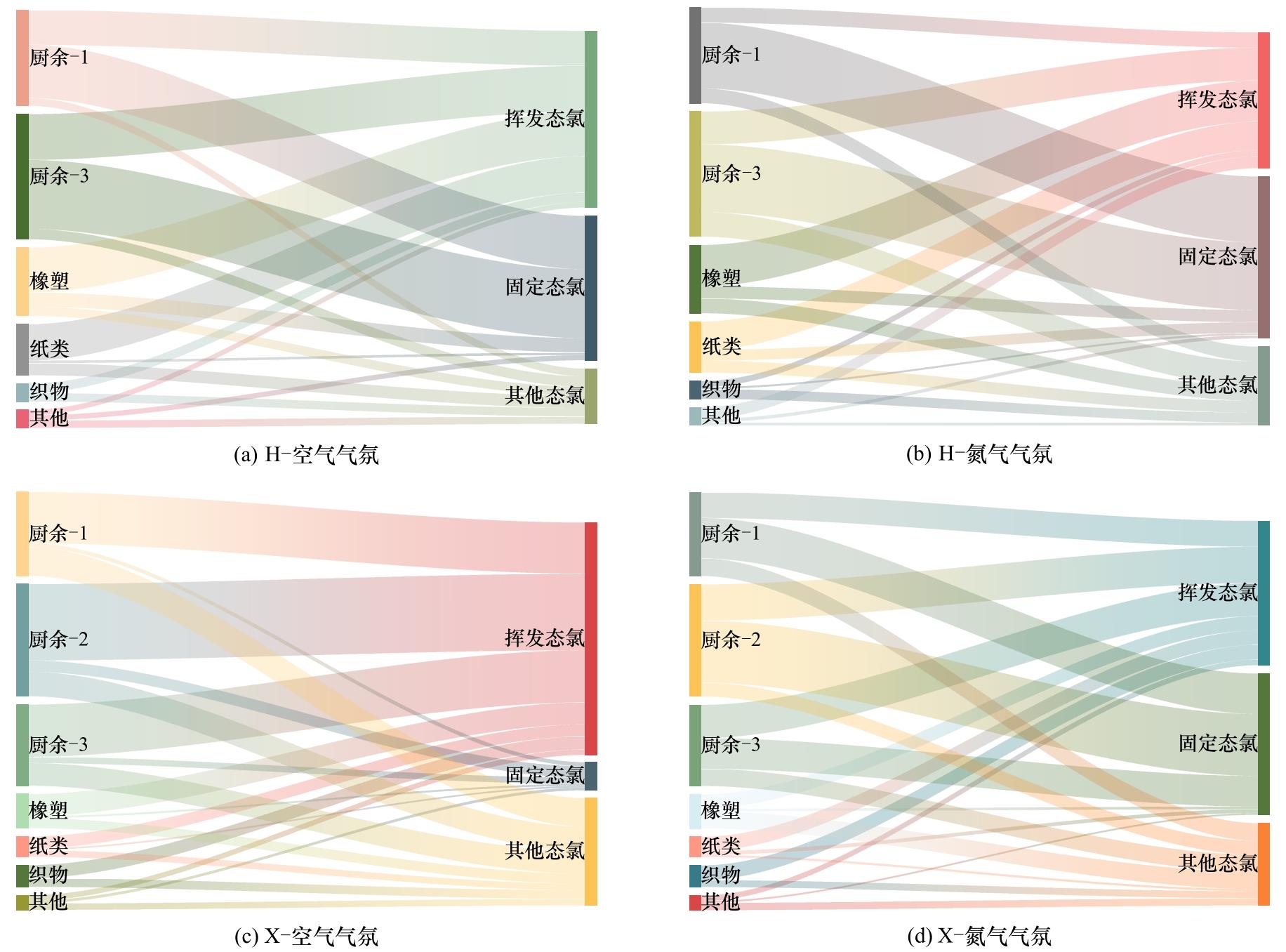
图5 热处理过程中生活垃圾各组分不同氯形态的迁移桑基图
Fig.5 Sankey diagram of migration of different chlorine forms in the municipal solid waste components during thermal treatment
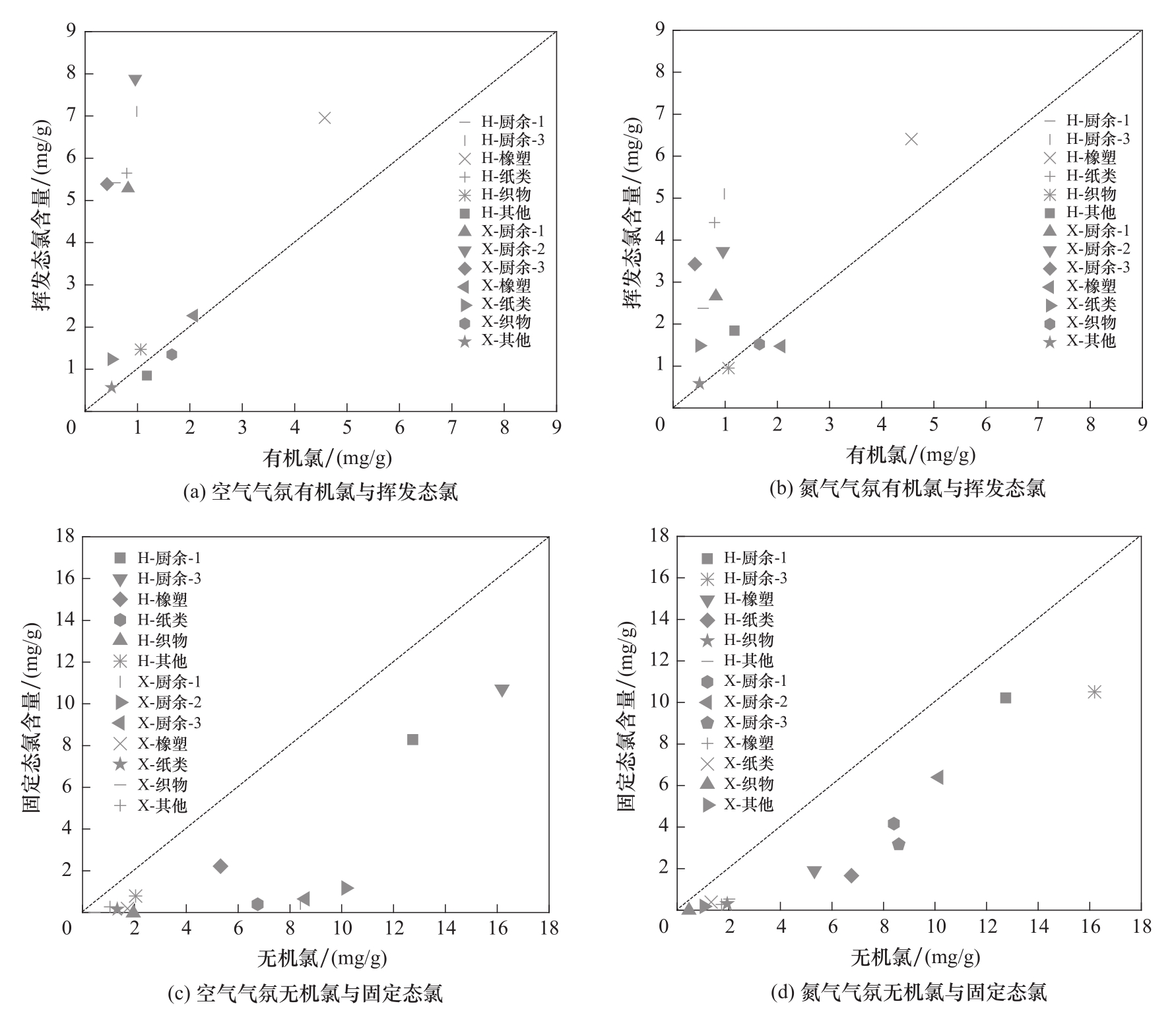
图6 不同气氛下生活垃圾各组分有机氯与挥发态氯含量、无机氯与固定态氯含量的关系
Fig.6 Relationship of organic chlorine and volatile chlorine content, inorganic chlorine and non-volatile chlorine content in municipal solid waste components in air and N2 atmospheres
| 氯形态 | 总氯 | 无机氯 | 有机氯 | 挥发态氯A① | 固定态氯A① | 其他态氯A① | 挥发态氯N① | 固定态氯N① | 其他态氯N① |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 总氯 | 1 | ||||||||
| 无机氯 | |||||||||
| 有机氯 | |||||||||
| 挥发态氯A① | |||||||||
| 固定态氯A① | |||||||||
| 其他态氯A① | |||||||||
| 挥发态氯N① | |||||||||
| 固定态氯N① | |||||||||
| 其他态氯N① | 1 |
表3 生活垃圾不同氯形态间的相关性分析
Table 3 Correlation analysis of different chlorine forms in municipal solid waste
| 氯形态 | 总氯 | 无机氯 | 有机氯 | 挥发态氯A① | 固定态氯A① | 其他态氯A① | 挥发态氯N① | 固定态氯N① | 其他态氯N① |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 总氯 | 1 | ||||||||
| 无机氯 | |||||||||
| 有机氯 | |||||||||
| 挥发态氯A① | |||||||||
| 固定态氯A① | |||||||||
| 其他态氯A① | |||||||||
| 挥发态氯N① | |||||||||
| 固定态氯N① | |||||||||
| 其他态氯N① | 1 |
| 主成分 | 总氯 | 无机氯 | 有机氯 | 挥发态氯A | 固定态氯A | 挥发态氯N | 固定态氯N |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PC1 | 0.966 | 0.988 | -0.199 | 0.781 | 0.871 | 0.563 | 0.981 |
| PC2 | 0.252 | 0.062 | 0.905 | 0.508 | -0.028 | 0.774 | -0.068 |
表4 主成分荷载
Table 4 Principal component loading
| 主成分 | 总氯 | 无机氯 | 有机氯 | 挥发态氯A | 固定态氯A | 挥发态氯N | 固定态氯N |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PC1 | 0.966 | 0.988 | -0.199 | 0.781 | 0.871 | 0.563 | 0.981 |
| PC2 | 0.252 | 0.062 | 0.905 | 0.508 | -0.028 | 0.774 | -0.068 |
| 1 | Zhang Y G, Chen Y, Meng A H, et al. Experimental and thermodynamic investigation on transfer of cadmium influenced by sulfur and chlorine during municipal solid waste (MSW) incineration[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2008, 153(1/2): 309-319. |
| 2 | 国家统计局. 中国统计年鉴[M]. 北京: 中国统计出版社, 2008-2019. |
| National Bureau of Statistics. China Statistical Yearbook[M]. Beijing: China Statistics Press, 2008-2019. | |
| 3 | Song J B, Sun Y, Jin L L. PESTEL analysis of the development of the waste-to-energy incineration industry in China[J]. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 2017, 80: 276-289. |
| 4 | Lee S H, Themelis N J, Castaldi M J. High-temperature corrosion in waste-to-energy boilers[J]. Journal of Thermal Spray Technology, 2007, 16(1): 104-110. |
| 5 | Ma W C, Hoffmann G, Schirmer M, et al. Chlorine characterization and thermal behavior in MSW and RDF[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2010, 178(1/2/3): 489-498. |
| 6 | Lu S Y, Yan J H, Li X D, et al. Effects of inorganic chlorine source on dioxin formation using fly ash from a fluidized bed incinerator[J]. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 2007, 19(6): 756-761. |
| 7 | Lu P, Huang Q X, Bourtsalas A C, et al. Review on fate of chlorine during thermal processing of solid wastes[J]. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 2019, 78: 13-28. |
| 8 | 章骅, 于思源, 邵立明, 等. 烟气净化工艺和焚烧炉类型对生活垃圾焚烧飞灰性质的影响[J]. 环境科学, 2018, 39(1): 467-476. |
| Zhang H, Yu S Y, Shao L M, et al. Influence of air pollution control (APC) systems and furnace type on the characteristics of APC residues from municipal solid waste incinerators[J]. Environmental Science, 2018, 39(1): 467-476. | |
| 9 | Wang P, Hu Y, Cheng H F. Municipal solid waste (MSW) incineration fly ash as an important source of heavy metal pollution in China[J]. Environmental Pollution, 2019, 252: 461-475. |
| 10 | Renou S, Givaudan J G, Poulain S, et al. Landfill leachate treatment: review and opportunity[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2008, 150(3): 468-493. |
| 11 | Kjeldsen P, Barlaz M A, Rooker A P, et al. Present and long-term composition of MSW landfill leachate: a review[J]. Critical Reviews in Environmental Science and Technology, 2002, 32(4): 297-336. |
| 12 | Beníšek M, Kukučka P, Mariani G, et al. Dioxins and dioxin-like compounds in composts and digestates from European countries as determined by the in vitro bioassay and chemical analysis[J]. Chemosphere, 2015, 122: 168-175. |
| 13 | Wang H, Ge D D, Cheng Z W, et al. Improved understanding of dissolved organic matter transformation in concentrated leachate induced by hydroxyl radicals and reactive chlorine species[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2020, 387: 121702. |
| 14 | Nasrullah M, Vainikka P, Hannula J, et al. Elemental balance of SRF production process: solid recovered fuel produced from municipal solid waste[J]. Waste Management and Research, 2016, 34(1): 38-46. |
| 15 | Zhou H, Meng A H, Long Y Q, et al. An overview of characteristics of municipal solid waste fuel in China: physical, chemical composition and heating value[J]. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 2014, 36: 107-122. |
| 16 | Becidan M, Sørum L, Lindberg D. Impact of municipal solid waste (MSW) quality on the behavior of alkali metals and trace elements during combustion: a thermodynamic equilibrium analysis[J]. Energy & Fuels, 2010, 24(6): 3446-3455. |
| 17 | Watanabe N, Yamamoto O, Sakai M, et al. Combustible and incombustible speciation of Cl and S in various components of municipal solid waste[J]. Waste Management, 2004, 24(6): 623-632. |
| 18 | 卿山, 王华, 吴桢芬, 等. 城市垃圾中生物质在热分析仪中燃烧的动力学模型研究[J]. 环境污染与防治, 2005, 27(7): 493-497. |
| Qing S, Wang H, Wu Z F, et al. Study on characteristics of combustion of municipal solid waste with thermal analyzers[J]. Environmental Pollution & Control, 2005, 27(7): 493-497. | |
| 19 | Silva R B, Fragoso R, Sanches C, et al. Which chlorine ions are currently being quantified as total chlorine on solid alternative fuels?[J]. Fuel Processing Technology, 2014, 128: 61-67. |
| 20 | Rahim M U, Gao X P, Wu H W. A method for the quantification of chlorine in low-rank solid fuels[J]. Energy & Fuels, 2013, 27(11): 6992-6999. |
| 21 | Yang Z Z, Tian S C, Ji R, et al. Effect of water-washing on the co-removal of chlorine and heavy metals in air pollution control residue from MSW incineration[J]. Waste Management, 2017, 68: 221-231. |
| 22 | Hwang I H, Matsuto T, Tanaka N. Water-soluble characteristics of chlorine in char derived from municipal solid wastes[J]. Waste Management, 2006, 26(6): 571-579. |
| 23 | Chen W S, Chang F C, Shen Y H, et al. Removal of chloride from MSWI fly ash[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2012, 237/238: 116-120. |
| 24 | Pereira É R, Welz B, Lopez A H D, et al. Strontium mono-chloride—a new molecule for the determination of chlorine using high-resolution graphite furnace molecular absorption spectrometry and direct solid sample analysis[J]. Spectrochimica Acta Part B: Atomic Spectroscopy, 2014, 102: 1-6. |
| 25 | Knudsen J N, Jensen P A, Dam-Johansen K. Transformation and release to the gas phase of Cl, K, and S during combustion of annual biomass[J]. Energy & Fuels, 2004, 18(5): 1385-1399. |
| 26 | Ma W C, Wenga T, Frandsen F J, et al. The fate of chlorine during MSW incineration: vaporization, transformation, deposition, corrosion and remedies[J]. Progress in Energy and Combustion Science, 2020, 76: 100789. |
| 27 | 刘正, 周向东. 锦纶织物耐久性阻燃剂的合成及应用[J]. 印染助剂, 2020, 37(9): 28-31. |
| Liu Z, Zhou X D. Synthesis and application of durable flame retardant for nylon fabric[J].Textile Auxiliaries, 2020, 37(9): 28-31. | |
| 28 | 谭飞, 黄成, 纪柏林, 等. 卤胺抗菌剂稳定乳液的制备及整理织物抗菌性能[J]. 印染, 2020, 46(1): 5-10. |
| Tan F, Huang C, Ji B L, et al. Preparation of stabilized halogen antibacterial emulsion and the antibacterial properties of finished fabrics[J].China Dyeing & Finishing, 2020, 46(1): 5-10. | |
| 29 | Aracil I, Font R, Conesa J A. Semivolatile and volatile compounds from the pyrolysis and combustion of polyvinyl chloride[J]. Journal of Analytical and Applied Pyrolysis, 2005, 74(1/2): 465-478. |
| 30 | Yu J, Sun L S, Ma C, et al. Thermal degradation of PVC: a review[J]. Waste Management, 2016, 48: 300-314. |
| 31 | Kikuchi R, Kukacka J, Raschman R. Grouping of mixed waste plastics according to chlorine content[J]. Separation and Purification Technology, 2008, 61(1): 75-81. |
| 32 | Kanters M J, van Nispen R, Louw R, et al. Chlorine input and chlorophenol emission in the lab-scale combustion of municipal solid waste[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 1996, 30(7): 2121-2126. |
| 33 | Aho M, Ferrer E. Importance of coal ash composition in protecting the boiler against chlorine deposition during combustion of chlorine-rich biomass[J]. Fuel, 2005, 84(2/3): 201-212. |
| 34 | Du S L, Wang X H, Shao J G, et al. Releasing behavior of chlorine and fluorine during agricultural waste pyrolysis[J]. Energy, 2014, 74: 295-300. |
| 35 | Gui B, Qiao Y, Wan D, et al. Nascent tar formation during polyvinylchloride (PVC) pyrolysis[J]. Proceedings of the Combustion Institute, 2013, 34(2): 2321-2329. |
| 36 | Wey M Y, Chen J C, Wu H Y, et al. Formations and controls of HCl and PAHs by different additives during waste incineration[J]. Fuel, 2006, 85(5/6): 755-763. |
| 37 | López A, de Marco I, Caballero B M, et al. Dechlorination of fuels in pyrolysis of PVC containing plastic wastes[J]. Fuel Processing Technology, 2011, 92(2): 253-260. |
| 38 | Wang Z Q, Huang H T, Li H B, et al. HCl formation from RDF pyrolysis and combustion in a spouting-moving bed reactor[J]. Energy & Fuels, 2002, 16(3): 608-614. |
| [1] | 邵苛苛, 宋孟杰, 江正勇, 张旋, 张龙, 高润淼, 甄泽康. 水平方向上冰中受陷气泡形成和分布实验研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(S1): 161-164. |
| [2] | 连梦雅, 谈莹莹, 王林, 陈枫, 曹艺飞. 地下水预热新风一体化热泵空调系统制热性能研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(S1): 311-319. |
| [3] | 黄琮琪, 吴一梅, 陈建业, 邵双全. 碱性电解水制氢装置热管理系统仿真研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(S1): 320-328. |
| [4] | 金正浩, 封立杰, 李舒宏. 氨水溶液交叉型再吸收式热泵的能量及 分析[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(S1): 53-63. 分析[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(S1): 53-63. |
| [5] | 米泽豪, 花儿. 基于DFT和COSMO-RS理论研究多元胺型离子液体吸收SO2气体[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(9): 3681-3696. |
| [6] | 李艺彤, 郭航, 陈浩, 叶芳. 催化剂非均匀分布的质子交换膜燃料电池操作条件研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(9): 3831-3840. |
| [7] | 王浩, 王振雷. 基于自适应谱方法的裂解炉烧焦模型化简策略[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(9): 3855-3864. |
| [8] | 韩晨, 司徒友珉, 朱斌, 许建良, 郭晓镭, 刘海峰. 协同处理废液的多喷嘴粉煤气化炉内反应流动研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(8): 3266-3278. |
| [9] | 杨越, 张丹, 郑巨淦, 涂茂萍, 杨庆忠. NaCl水溶液喷射闪蒸-掺混蒸发的实验研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(8): 3279-3291. |
| [10] | 张瑞航, 曹潘, 杨锋, 李昆, 肖朋, 邓春, 刘蓓, 孙长宇, 陈光进. ZIF-8纳米流体天然气乙烷回收工艺的产品纯度关键影响因素分析[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(8): 3386-3393. |
| [11] | 胡兴枝, 张皓焱, 庄境坤, 范雨晴, 张开银, 向军. 嵌有超小CeO2纳米粒子的碳纳米纤维的制备及其吸波性能[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(8): 3584-3596. |
| [12] | 张曼铮, 肖猛, 闫沛伟, 苗政, 徐进良, 纪献兵. 危废焚烧处理耦合有机朗肯循环系统工质筛选与热力学优化[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(8): 3502-3512. |
| [13] | 屈园浩, 邓文义, 谢晓丹, 苏亚欣. 活性炭/石墨辅助污泥电渗脱水研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(7): 3038-3050. |
| [14] | 邵伟明, 韩文学, 宋伟, 杨勇, 陈灿, 赵东亚. 基于分布式贝叶斯隐马尔可夫回归的动态软测量建模方法[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(6): 2495-2502. |
| [15] | 郑志航, 马郡男, 闫子涵, 卢春喜. 提升管射流影响区内压力脉动特性研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(6): 2335-2350. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备 11010102001995号
京公网安备 11010102001995号