化工学报 ›› 2022, Vol. 73 ›› Issue (7): 3099-3108.DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20220108
收稿日期:2022-01-19
修回日期:2022-03-19
出版日期:2022-07-05
发布日期:2022-08-01
通讯作者:
陈珺
作者简介:魏朋(1995—),男,硕士研究生,基金资助:
Peng WEI( ),Jun CHEN(
),Jun CHEN( ),Zhiguo WANG,Fei LIU
),Zhiguo WANG,Fei LIU
Received:2022-01-19
Revised:2022-03-19
Online:2022-07-05
Published:2022-08-01
Contact:
Jun CHEN
摘要:
在保证产品纯度的情况下,提出一种带额外色谱柱的双部分丢弃策略以提高模拟移动床的产率。通过将工艺点选取在纯提取产品和非纯提余产品区域以增大进料流量,并将由此导致的含较多杂质的提余产品暂时丢弃。丢弃的提余产品作为循环进料通入到一个额外色谱柱中以进一步分离,部分不能达到指定纯度的额外产品被永久丢弃。在模拟移动床和额外色谱柱处分别收集到的产品组成总产品。分析了工艺点的选取、提余产品的积分纯度阈值和额外产品的积分纯度阈值对总产品性能参数的影响。研究结果表明,所提策略能够以较高的回收率利用原料,且能够显著提高分离过程的产率,其分离效果优于传统的模拟移动床工艺和部分丢弃策略。
中图分类号:
魏朋, 陈珺, 王志国, 刘飞. 基于双部分丢弃的模拟移动床产率提高策略[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(7): 3099-3108.
Peng WEI, Jun CHEN, Zhiguo WANG, Fei LIU. Improved productivity strategy of simulated moving bed based on binary-partial-discard[J]. CIESC Journal, 2022, 73(7): 3099-3108.

图2 在模拟移动床的循环稳态下提余产品的浓度变化(A为强吸附组分,B为弱吸附组分)
Fig.2 The change of the concentration of the raffinate products under the cyclic steady state of the simulated moving bed
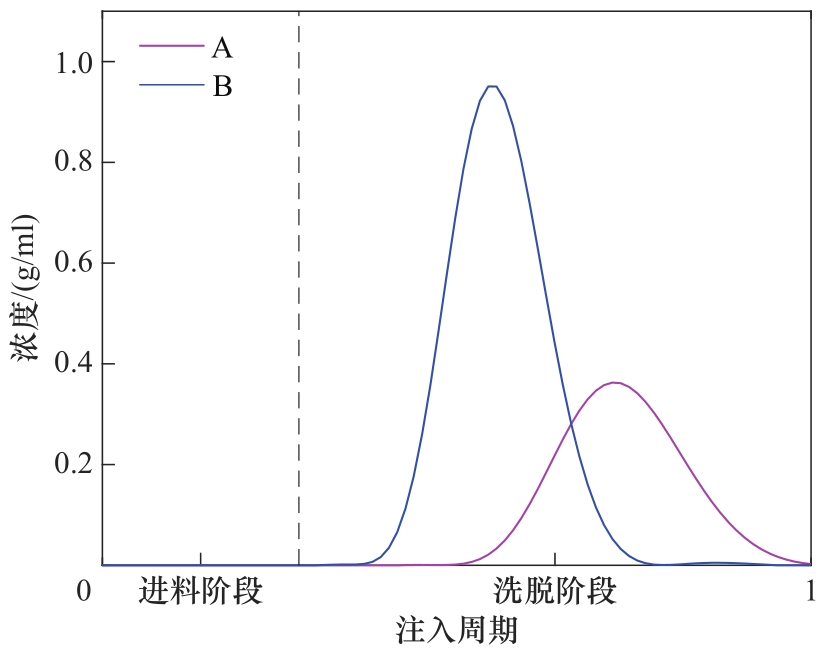
图5 在一个注入周期中额外色谱柱的出口浓度示意图(虚线表示每个注入周期中进料阶段和洗脱阶段的分界线;操作条件:进料中组分A和B的浓度分别为1.17和2.35 g/ml)
Fig.5 Schematic diagram of outlet concentration of the extra column during an injection cycle
| 模型参数 | 数值 | 初始工艺参数 | 数值 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 柱分布结构 | 2-2-2-2 | A的进料浓度 | 0.5 g/ml | ||
| 组分数 | 2 | B的进料浓度 | 0.5 g/ml | ||
| 柱长 | 53.6 cm | 进料液流量 | 0.0200 ml/s | ||
| 柱直径 | 2.6 cm | 洗脱液流量 | 0.0414 ml/s | ||
| 空隙率 | 0.38 | 提取液流量 | 0.0348 ml/s | ||
| 轴向扩散系数 | 0.0381 cm2/s | 提余液流量 | 0.0266 ml/s | ||
| A的亨利系数 | 0.54 | 循环液流量 | 0.0981 ml/s | ||
| B的亨利系数 | 0.28 | 切换时间 | 1552 s | ||
表1 模拟移动床的模型参数及初始工艺参数
Table 1 Model parameters and process parameters of the simulated moving bed
| 模型参数 | 数值 | 初始工艺参数 | 数值 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 柱分布结构 | 2-2-2-2 | A的进料浓度 | 0.5 g/ml | ||
| 组分数 | 2 | B的进料浓度 | 0.5 g/ml | ||
| 柱长 | 53.6 cm | 进料液流量 | 0.0200 ml/s | ||
| 柱直径 | 2.6 cm | 洗脱液流量 | 0.0414 ml/s | ||
| 空隙率 | 0.38 | 提取液流量 | 0.0348 ml/s | ||
| 轴向扩散系数 | 0.0381 cm2/s | 提余液流量 | 0.0266 ml/s | ||
| A的亨利系数 | 0.54 | 循环液流量 | 0.0981 ml/s | ||
| B的亨利系数 | 0.28 | 切换时间 | 1552 s | ||

图6 新工艺点处的流量比(mⅡ,?mⅢ)在mⅡ-mⅢ平面上的分布(p点表示初始工艺点,蓝点表示一组提高产率的工艺点)
Fig.6 The distribution of the flow ratio (mⅡ,?mⅢ) on the mⅡ-mⅢ plane at the new process point
| Run | Pu_A/% | Pu_B/% | Re_A/% | Re_B/% | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.2850 | 0.5489 | 97.61 | 95.10 | 90.57 | 96.50 |
| 2 | 0.2900 | 0.5539 | 98.21 | 94.07 | 89.42 | 97.44 |
| 3 | 0.2950 | 0.5589 | 98.68 | 92.93 | 88.17 | 98.26 |
| 4 | 0.3000 | 0.5639 | 99.07 | 91.77 | 86.74 | 98.89 |
| 5 | 0.3050 | 0.5689 | 99.35 | 90.56 | 85.22 | 99.40 |
| 6 | 0.3100 | 0.5739 | 99.56 | 89.16 | 83.72 | 99.90 |
| 24 | 0.4000 | 0.6639 | 99.90 | 67.17 | 51.04 | 99.90 |
| 25 | 0.4050 | 0.6689 | 99.90 | 66.37 | 49.17 | 99.91 |
| 26 | 0.4100 | 0.6739 | 99.91 | 65.62 | 47.31 | 99.93 |
表2 模拟移动床运行在新工艺点时所获得的性能参数
Table 2 The performance parameters obtained when the simulated moving bed runs at the new process point
| Run | Pu_A/% | Pu_B/% | Re_A/% | Re_B/% | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.2850 | 0.5489 | 97.61 | 95.10 | 90.57 | 96.50 |
| 2 | 0.2900 | 0.5539 | 98.21 | 94.07 | 89.42 | 97.44 |
| 3 | 0.2950 | 0.5589 | 98.68 | 92.93 | 88.17 | 98.26 |
| 4 | 0.3000 | 0.5639 | 99.07 | 91.77 | 86.74 | 98.89 |
| 5 | 0.3050 | 0.5689 | 99.35 | 90.56 | 85.22 | 99.40 |
| 6 | 0.3100 | 0.5739 | 99.56 | 89.16 | 83.72 | 99.90 |
| 24 | 0.4000 | 0.6639 | 99.90 | 67.17 | 51.04 | 99.90 |
| 25 | 0.4050 | 0.6689 | 99.90 | 66.37 | 49.17 | 99.91 |
| 26 | 0.4100 | 0.6739 | 99.91 | 65.62 | 47.31 | 99.93 |
| Run | 纯度阈值/% | 纯度/% | 回收率/% |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 98.00 | 98.02 | 69.91 |
| 2 | 98.10 | 98.11 | 69.21 |
| 3 | 98.20 | 98.23 | 68.26 |
| 4 | 98.30 | 98.31 | 67.56 |
| 5 | 98.40 | 98.42 | 66.61 |
| 6 | 98.50 | 98.51 | 65.91 |
| 7 | 98.60 | 98.61 | 64.96 |
| 15 | 99.40 | 99.41 | 53.92 |
| 16 | 99.50 | 99.50 | 51.34 |
| 17 | 99.60 | 99.60 | 47.37 |
表3 提余产品在不同纯度阈值下进行部分丢弃后的性能参数
Table 3 Performance parameters of raffinate products after partial-discard under different purity thresholds
| Run | 纯度阈值/% | 纯度/% | 回收率/% |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 98.00 | 98.02 | 69.91 |
| 2 | 98.10 | 98.11 | 69.21 |
| 3 | 98.20 | 98.23 | 68.26 |
| 4 | 98.30 | 98.31 | 67.56 |
| 5 | 98.40 | 98.42 | 66.61 |
| 6 | 98.50 | 98.51 | 65.91 |
| 7 | 98.60 | 98.61 | 64.96 |
| 15 | 99.40 | 99.41 | 53.92 |
| 16 | 99.50 | 99.50 | 51.34 |
| 17 | 99.60 | 99.60 | 47.37 |
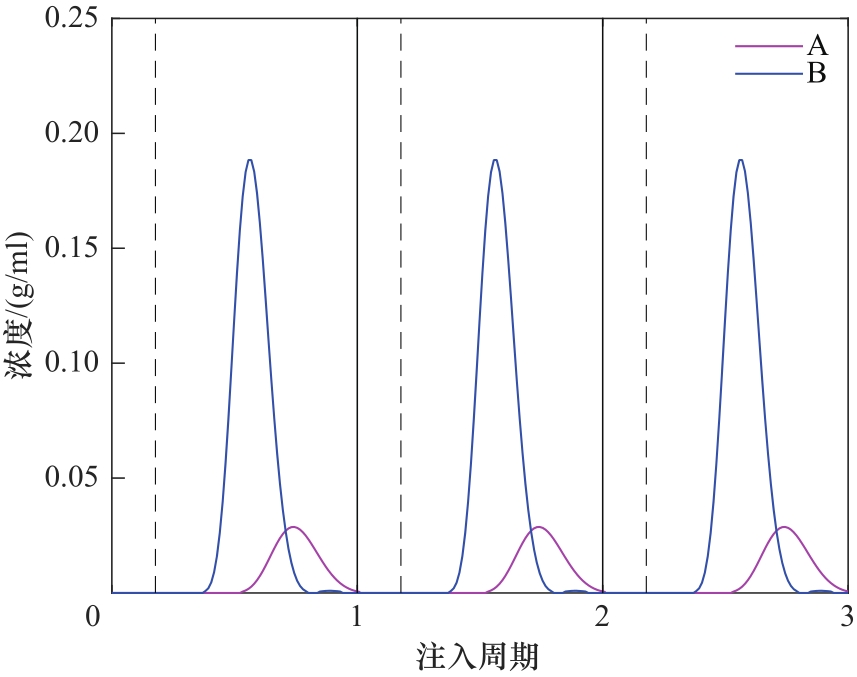
图9 额外产品的出口浓度示意图(实线表示相邻两个注入周期的分界线;虚线表示每个注入周期中进料阶段和洗脱阶段的分界线。操作条件:以表3中Run6下丢弃的提余产品作为额外色谱柱的进料)
Fig.9 Schematic diagram of outlet concentration of extra products
| 1 | Kim K M, Lee J W, Kim S, et al. Advanced operating strategies to extend the applications of simulated moving bed chromatography[J]. Chemical Engineering & Technology, 2017, 40(12): 2163-2178. |
| 2 | Broughton D B, Gerhold C G. Continuous sorption process employing fixed bed of sorbent and moving inlets and outlets: US 2985589[P]. 1961-5-23. |
| 3 | Aniceto J P S, Silva C M. Simulated moving bed strategies and designs: from established systems to the latest developments[J]. Separation & Purification Reviews, 2015, 44(1): 41-73. |
| 4 | Faria R P, Rodrigues A E. Instrumental aspects of simulated moving bed chromatography[J]. Journal of Chromatography A, 2015, 1421: 82-102. |
| 5 | Lee J, Shin N C, Lim Y, et al. Modeling and simulation of a simulated moving bed for adsorptive para-xylene separation[J]. Korean Journal of Chemical Engineering, 2010, 27(2): 609-618. |
| 6 | van Duc Long N, Le T H, Kim J I, et al. Separation of D-psicose and D-fructose using simulated moving bed chromatography[J]. Journal of Separation Science, 2009, 32(11): 1987-1995. |
| 7 | Ribeiro A E, Gomes P S, Pais L S, et al. Chiral separation of ketoprofen enantiomers by preparative and simulated moving bed chromatography[J]. Separation Science and Technology, 2011, 46(11): 1726-1739. |
| 8 | Knutson H K, Holmqvist A, Andersson N, et al. Robust multi-objective optimization of chromatographic rare earth element separation[J]. Advances in Chemical Engineering and Science, 2017, 7(4): 477-493. |
| 9 | Minceva M, Rodrigues A E. Two-level optimization of an existing SMB for p-xylene separation[J]. Computers & Chemical Engineering, 2005, 29(10): 2215-2228. |
| 10 | 胡蓉, 杨明磊, 钱锋. 基于多目标教学优化算法在二甲苯吸附分离过程优化中的应用[J]. 化工学报, 2015, 66(1): 326-332. |
| Hu R, Yang M L, Qian F. Optimization of xylene adsorption separation process based on multi-objective teaching-learning-based optimization algorithm[J]. CIESC Journal, 2015, 66(1): 326-332. | |
| 11 | Matos J, Faria R P V, Nogueira I B R, et al. Optimization strategies for chiral separation by true moving bed chromatography using Particles Swarm Optimization (PSO) and new Parallel PSO variant[J]. Computers & Chemical Engineering, 2019, 123: 344-356. |
| 12 | Yu W F, Hidajat K, Ray A K. Optimization of reactive simulated moving bed and Varicol systems for hydrolysis of methyl acetate[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2005, 112(1/2/3): 57-72. |
| 13 | Zhang Z Y, Mazzotti M, Morbidelli M. PowerFeed operation of simulated moving bed units: changing flow-rates during the switching interval[J]. Journal of Chromatography A, 2003, 1006(1/2): 87-99. |
| 14 | Schramm H, Kienle A, Kaspereit M, et al. Improved operation of simulated moving bed processes through cyclic modulation of feed flow and feed concentration[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2003, 58(23/24): 5217-5227. |
| 15 | Katsuo S, Mazzotti M. Intermittent simulated moving bed chromatography: 2. Separation of Tröger’s base enantiomers[J]. Journal of Chromatography A, 2010, 1217(18): 3067-3075. |
| 16 | Shen B, Chen M J, Jiang H L, et al. Modeling study on a three-zone simulated moving bed without zone I[J]. Separation Science and Technology, 2011, 46(5): 695-701. |
| 17 | Bae Y S, Lee C H. Partial-discard strategy for obtaining high purity products using simulated moving bed chromatography[J]. Journal of Chromatography A, 2006, 1122(1/2): 161-173. |
| 18 | Keßler L C, Seidel-Morgenstern A. Improving performance of simulated moving bed chromatography by fractionation and feed-back of outlet streams[J]. Journal of Chromatography A, 2008, 1207(1/2): 55-71. |
| 19 | Kim K M, Lee H H, Lee C H. Improved performance of a simulated moving bed process by a recycling method in the partial-discard strategy[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2012, 51(29): 9835-9849. |
| 20 | Chung J W, Kim K M, Yoon T U, et al. Power partial-discard strategy to obtain improved performance for simulated moving bed chromatography[J]. Journal of Chromatography A, 2017, 1529: 72-80. |
| 21 | Han H S, Kim K M, Han K W, et al. Total-recycling partial-discard strategy for improved performance of simulated moving-bed chromatography[J]. Journal of Industrial and Engineering Chemistry, 2019, 79: 226-235. |
| 22 | Kim K M, Han K W, Kim S I, et al. Simulated moving bed with a product column for improving the separation performance[J]. Journal of Industrial and Engineering Chemistry, 2020, 88: 328-338. |
| 23 | Mazzotti M, Storti G, Morbidelli M. Optimal operation of simulated moving bed units for nonlinear chromatographic separations[J]. Journal of Chromatography A, 1997, 769(1): 3-24. |
| 24 | Mazzotti M. Equilibrium theory based design of simulated moving bed processes for a generalized Langmuir isotherm[J]. Journal of Chromatography A, 2006, 1126(1/2): 311-322. |
| 25 | Yao H M, Tian Y C, Tadé M O. Using wavelets for solving SMB separation process models[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2008, 47(15): 5585-5593. |
| 26 | Minceva M, Rodrigues A E. Modeling and simulation of a simulated moving bed for the separation of p-xylene[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2002, 41(14): 3454-3461. |
| 27 | Klatt K U, Hanisch F, Dünnebier G. Model-based control of a simulated moving bed chromatographic process for the separation of fructose and glucose[J]. Journal of Process Control, 2002, 12(2): 203-219. |
| [1] | 陈哲文, 魏俊杰, 张玉明. 超临界水煤气化耦合SOFC发电系统集成及其能量转化机制[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(9): 3888-3902. |
| [2] | 齐聪, 丁子, 余杰, 汤茂清, 梁林. 基于选择吸收纳米薄膜的太阳能温差发电特性研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(9): 3921-3930. |
| [3] | 文兆伦, 李沛睿, 张忠林, 杜晓, 侯起旺, 刘叶刚, 郝晓刚, 官国清. 基于自热再生的隔壁塔深冷空分工艺设计及优化[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(7): 2988-2998. |
| [4] | 江锦波, 彭新, 许文烜, 门日秀, 刘畅, 彭旭东. 泵出型螺旋槽油气密封泄漏特性及参数影响研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(6): 2538-2554. |
| [5] | 孙永尧, 高秋英, 曾文广, 王佳铭, 陈艺飞, 周永哲, 贺高红, 阮雪华. 面向含氮油田伴生气提质利用的膜耦合分离工艺设计优化[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(5): 2034-2045. |
| [6] | 刘尚豪, 贾胜坤, 罗祎青, 袁希钢. 基于梯度提升决策树的三组元精馏流程结构最优化[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(5): 2075-2087. |
| [7] | 周必茂, 许世森, 王肖肖, 刘刚, 李小宇, 任永强, 谭厚章. 烧嘴偏转角度对气化炉渣层分布特性的影响[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(5): 1939-1949. |
| [8] | 王泽栋, 石至平, 刘丽艳. 考虑气泡非均匀耗散的矩形反应器声流场数值模拟及结构优化[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(5): 1965-1973. |
| [9] | 李纪元, 李金旺, 周刘伟. 不同扰流结构冷板传热性能研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(4): 1474-1488. |
| [10] | 许文烜, 江锦波, 彭新, 门日秀, 刘畅, 彭旭东. 宽速域三种典型型槽油气密封泄漏与成膜特性对比研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(4): 1660-1679. |
| [11] | 陈俊先, 姬忠礼, 赵瑜, 张倩, 周岩, 刘猛, 刘震. 基于微波技术的天然气管道内颗粒物在线检测方法研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(3): 1042-1053. |
| [12] | 魏进家, 刘蕾, 杨小平. 面向高热流电子器件散热的环路热管研究进展[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(1): 60-73. |
| [13] | 陈玉弓, 陈昊, 黄耀松. 基于分子反应动力学模拟的六甲基二硅氧烷热解机理研究[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(7): 2844-2857. |
| [14] | 赵涛岩, 曹江涛, 李平, 冯琳, 商瑀. 区间二型模糊免疫PID在环己烷无催化氧化温度控制系统中的应用[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(7): 3166-3173. |
| [15] | 万景, 张霖, 樊亚超, 刘勰民, 骆培成, 张锋, 张志炳. 基于介尺度PBM模型的生物反应器放大模拟及实验研究[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(6): 2698-2707. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备 11010102001995号
京公网安备 11010102001995号