化工学报 ›› 2022, Vol. 73 ›› Issue (8): 3669-3678.DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20220207
收稿日期:2022-02-14
修回日期:2022-05-26
出版日期:2022-08-05
发布日期:2022-09-06
通讯作者:
李佳锡
作者简介:安绍杰(1997—),男,硕士研究生, 673686214@qq.com
基金资助:
Shaojie AN( ), Hongfeng XU, Si LI, Yuanhang XU, Jiaxi LI(
), Hongfeng XU, Si LI, Yuanhang XU, Jiaxi LI( )
)
Received:2022-02-14
Revised:2022-05-26
Online:2022-08-05
Published:2022-09-06
Contact:
Jiaxi LI
摘要:
谷胱甘肽过氧化物酶(GPx)是体内一种重要的抗氧化酶,对GPx的人工模拟能够拓展其体外应用,利用生命体内天然pH差异实现响应的pH敏感性GPx人工酶更是有着广泛的潜在应用。然而目前制备的pH敏感性GPx人工酶普遍存在活性较低的缺点,本文设计合成了同时含有高活性GPx催化中心和两个伯胺基团的乙胺单碲醚分子,酶促反应动力学的分析结果表明其二级反应速率常数高达101 L·mol-1·min-1数量级。pH=6时,乙胺单碲醚分子能够与葫芦[6]脲分子(CB[6])组装形成分子机器,此时活性中心被包埋于CB[6]的疏水空腔之中,仅能展现出(0.04±0.02)μmol·min-1·μmol-1的活性;pH=7时,分子机器部分分解,能够展现出高达(0.35±0.06)μmol·min-1·μmol-1的活性。因此,通过调控体系pH在6和7之间变化,借助分子机器的组装及部分分解调控人工酶活性的关闭与开启,从而构建了高活性的pH敏感性GPx人工酶。
中图分类号:
安绍杰, 许洪峰, 李思, 许远航, 李佳锡. 利用分子机器的组装与分解构建pH敏感性谷胱甘肽过氧化物人工酶[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(8): 3669-3678.
Shaojie AN, Hongfeng XU, Si LI, Yuanhang XU, Jiaxi LI. Construction of pH sensitive artificial glutathione peroxidase based on the formation and dissociation of molecular machine[J]. CIESC Journal, 2022, 73(8): 3669-3678.
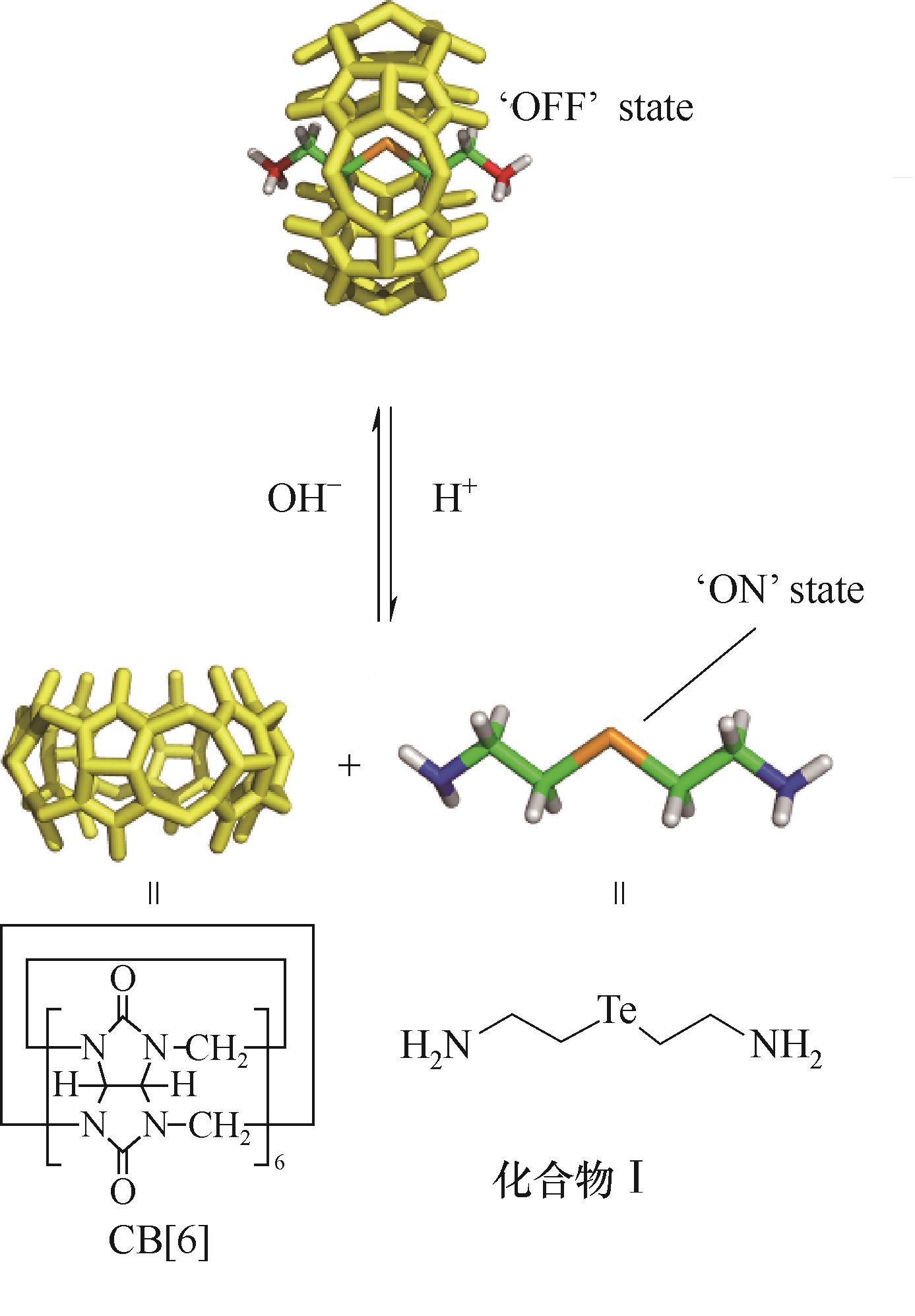
图1 利用分子机器的组装与分解构建pH敏感性谷胱甘肽过氧化物人工酶示意图
Fig.1 Schematic representation of pH sensitive artificial glutathione peroxidase based on the formation and dissociation of molecular machine

图3 化合物Ⅰ浓度分别为0、1、2、4 μmol·L-1条件下的催化曲线concentrations of compound Ⅰ/(μmol·L-1): a—0; b—1; c—2; d—4
Fig.3 Catalytic curves of different concentrations of compound Ⅰ by TNB assay system and GSH reductase-reduced NADPH coupled catalytic activity assay system at pH=7
[H2O2]/ (mmol·L-1) | kcat /min-1 | KmGSH / (mol·L-1) | (kcat/KmGSH)/ (L·mol-1·min-1) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0.33 | 7.96 | 2.65 | 3.00 |
| 0.5 | 6.68 | 2.48 | 2.69 |
| 0.75 | 6.51 | 2.63 | 2.48 |
[GSH]/ (mmol·L-1) | kcat/ min-1 | (mol·L-1) | (kcat/ (L·mol-1·min-1) |
| 1.5 | 4.15 | 0.68 | 6.09 |
| 2 | 1.61 | 0.86 | 1.88 |
| 4 | 0.97 | 0.89 | 1.09 |
表1 化合物Ⅰ的表观动力学参数
Table 1 The apparent kinetic parameters of compound Ⅰ
[H2O2]/ (mmol·L-1) | kcat /min-1 | KmGSH / (mol·L-1) | (kcat/KmGSH)/ (L·mol-1·min-1) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0.33 | 7.96 | 2.65 | 3.00 |
| 0.5 | 6.68 | 2.48 | 2.69 |
| 0.75 | 6.51 | 2.63 | 2.48 |
[GSH]/ (mmol·L-1) | kcat/ min-1 | (mol·L-1) | (kcat/ (L·mol-1·min-1) |
| 1.5 | 4.15 | 0.68 | 6.09 |
| 2 | 1.61 | 0.86 | 1.88 |
| 4 | 0.97 | 0.89 | 1.09 |
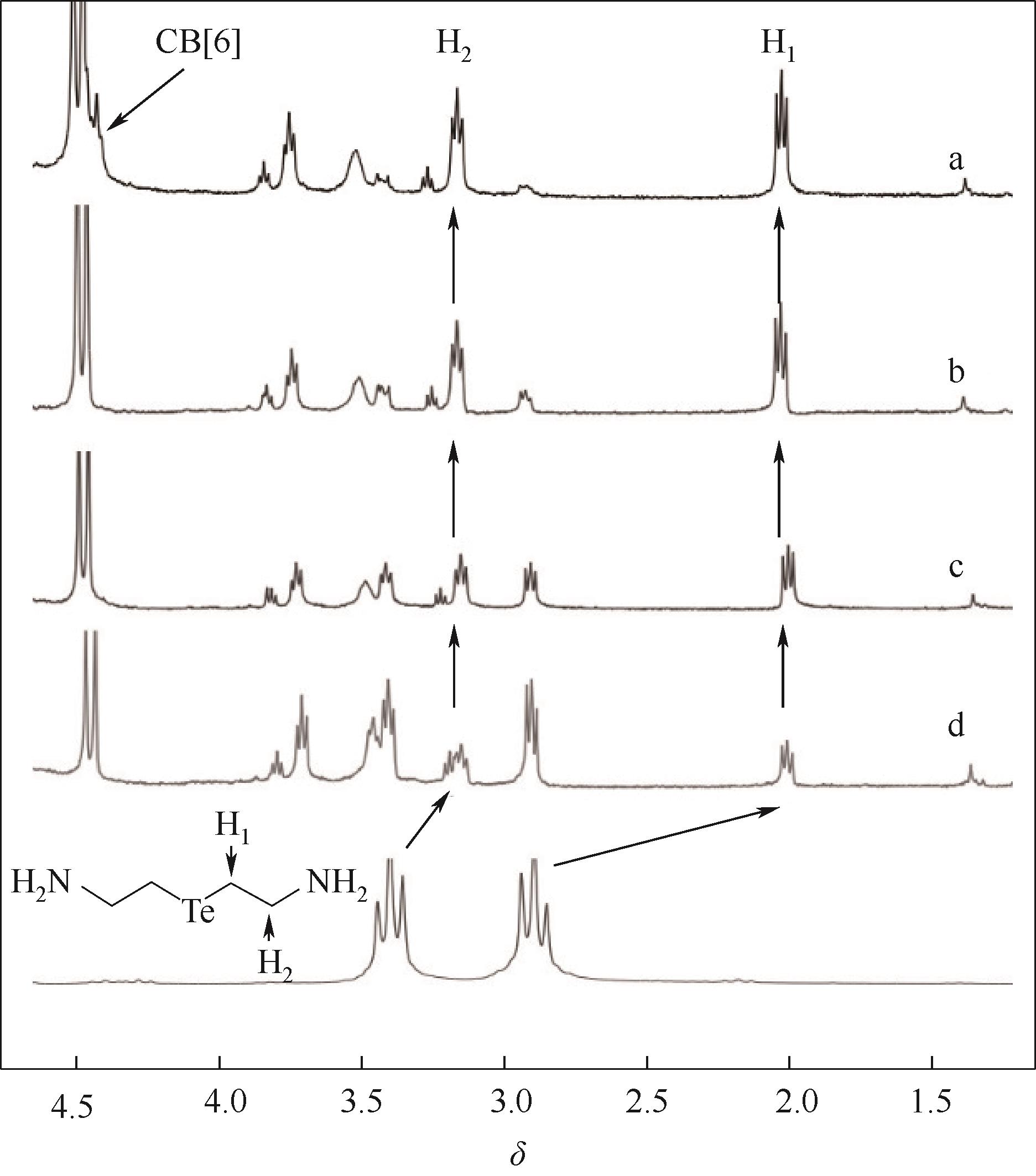
图7 化合物Ⅰ (5 mmol·L-1) 在pH=6时与不同浓度CB[6]混合物的部分1H NMR谱图concentration of CB[6] /(mmol·L-1): a—5; b—3.75; c—2.5; d—1.25
Fig.7 Partial 1H NMR spectra of mixtures of compound Ⅰ(5 mmol·L-1) with different amounts of CB[6] at pH=6
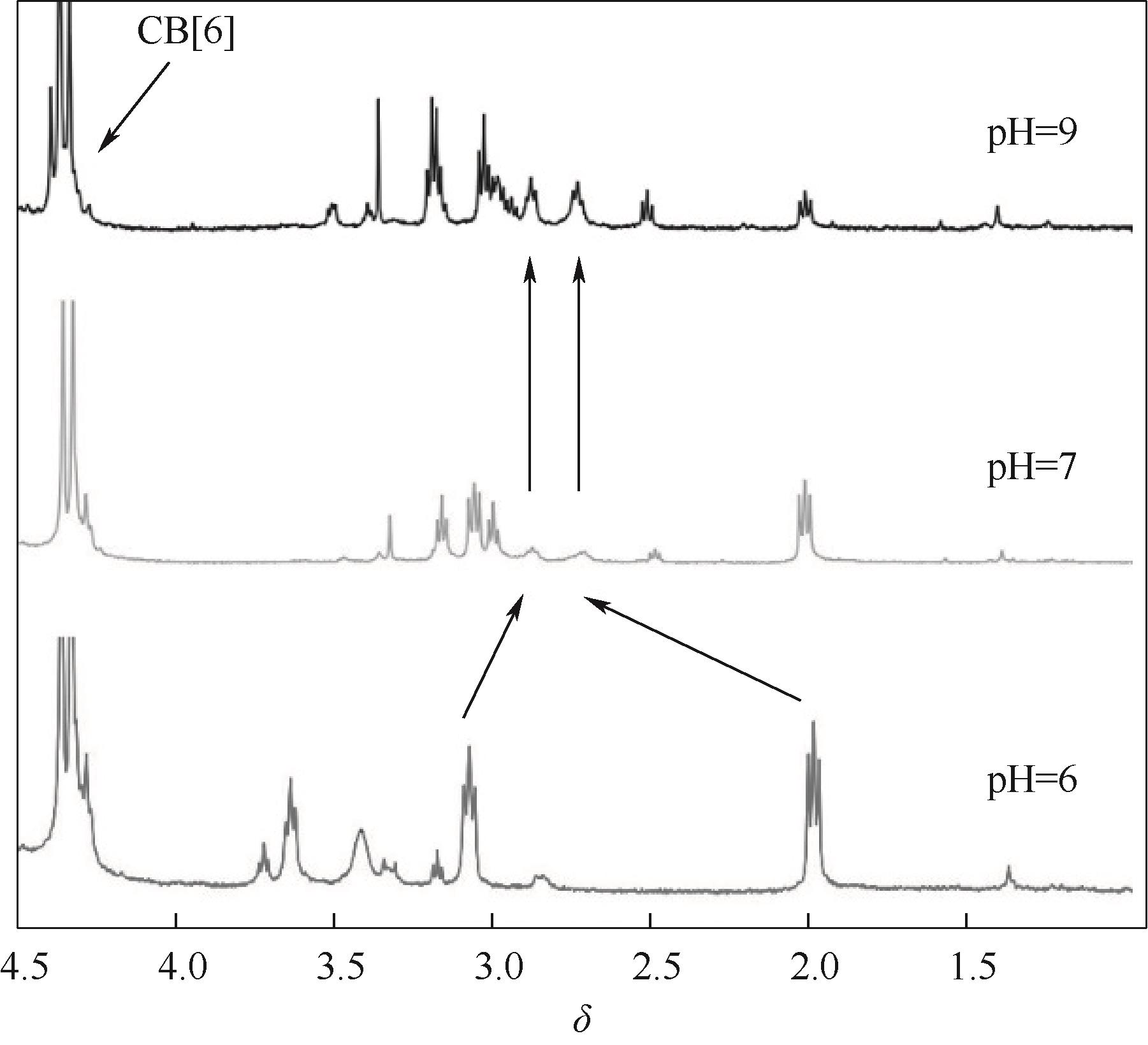
图8 化合物 Ⅰ (5 mmol·L-1)与 CB[6] (5 mmol·L-1) 在不同pH下的部分1 H NMR 谱图(500 MHz)
Fig.8 Partial 1H NMR spectra (500 MHz) of mixtures of compound Ⅰ (5 mmol·L-1) with CB[6] (5 mmol·L-1) at different pH

图9 pH=6时4 μmol·L-1化合物Ⅰ与空白(a),及浓度分别为4 μmol·L-1(b)、3 μmol·L-1(c)、2 μmol·L-1(d)、1 μmol·L-1(e)、0 μmol·L-1(f)的 CB[6]混合物的催化曲线
Fig.9 Catalytic curves of mixture of 4 μmol·L-1 compound Ⅰ and blank (a), 4 μmol·L-1 (b), 3 μmol·L-1 (c), 2 μmol·L-1 (d), 1 μmol·L-1 (e), 0 μmol·L-1 (f) CB[6] at pH=6
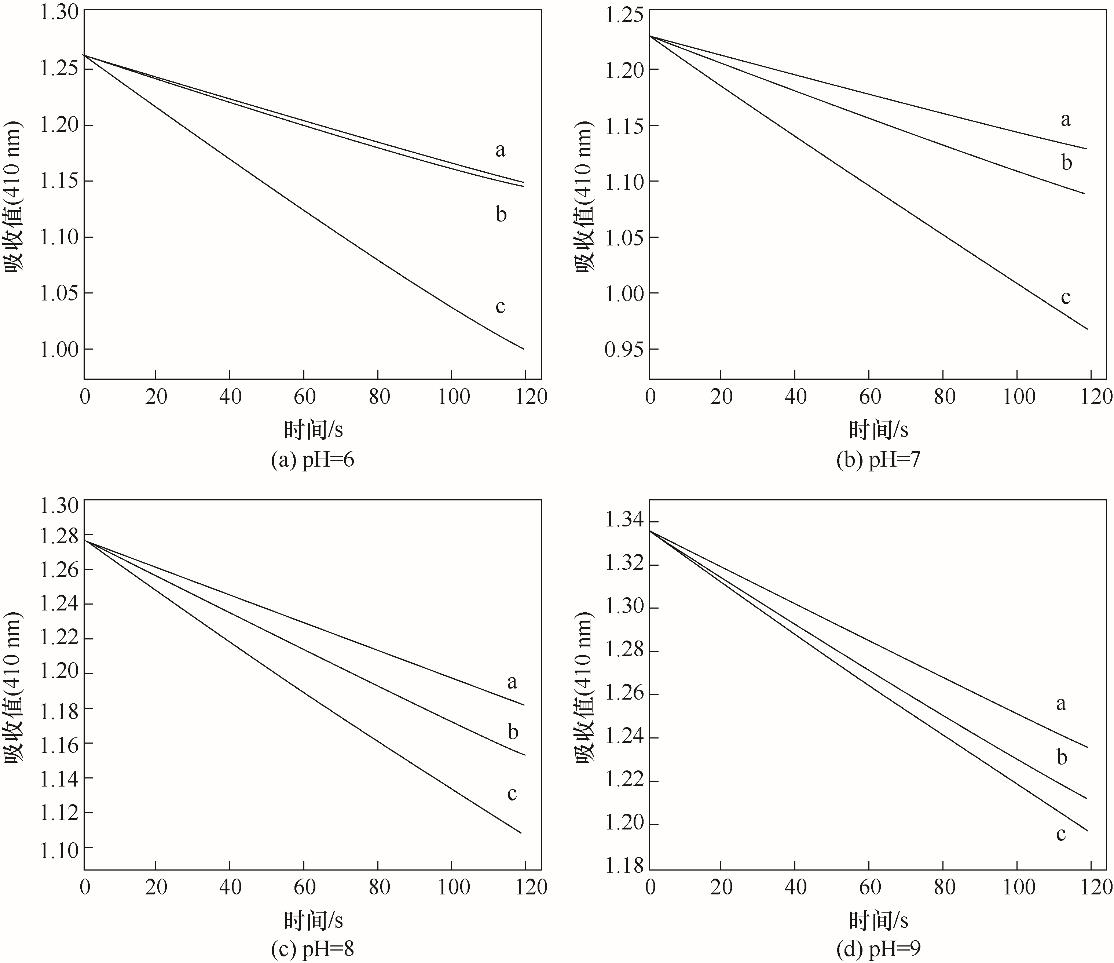
图10 分子机器的催化曲线a—空白; b—4 μmol·L-1化合物Ⅰ与CB[6]1∶1混合物; c—4 μmol·L-1化合物Ⅰ
Fig.10 Catalytic curves of molecular machinea—blank; b—4 μmol·L-1 mixture of compound Ⅰ and CB[6] at the ratio of 1∶1; c—4 μmol·L-1 compound Ⅰ

图11 pH在6~9时分子机器催化活性的相对值(a)及分子机器催化活性的绝对值(b)
Fig.11 Relative catalytic activities (a) and catalytic activities (b) of the molecular machine at a range of pH from 6 to 9
| 1 | Rattanawong K, Koiso N, Toda E, et al. Regulatory functions of ROS dynamics via glutathione metabolism and glutathione peroxidase activity in developing rice zygote[J]. The Plant Journal, 2021, 108(4): 1097-1115. |
| 2 | Chang C, Worley B L, Phaëton R, et al. Extracellular glutathione peroxidase GPx3 and its role in cancer[J]. Cancers, 2020, 12(8): 2197-2215. |
| 3 | Stolwijk J M, Falls-Hubert K C, Searby C C, et al. Simultaneous detection of the enzyme activities of GPx1 and GPx4 guide optimization of selenium in cell biological experiments[J]. Redox Biology, 2020, 32: 101518-101532. |
| 4 | Zhang M L, Wu H T, Chen W J, et al. Involvement of glutathione peroxidases in the occurrence and development of breast cancers[J]. Journal of Translational Medicine, 2020, 18(1): 247-257. |
| 5 | Pan T Z, Liu Y, Sun H C, et al. Reversible switch of a selenium-containing antioxidant system regulated by protein assembly[J]. ACS Catalysis, 2020, 10(17): 9735-9740. |
| 6 | Huang X, Liu X M, Luo Q, et al. Artificial selenoenzymes: designed and redesigned[J]. Chemical Society Reviews, 2011, 40(3): 1171-1184. |
| 7 | Mugesh G, du Mont W W, Sies H. Chemistry of biologically important synthetic organoselenium compounds[J]. Chemical Reviews, 2001, 101(7): 2125-2179. |
| 8 | Mugesh G, Singh H B. Heteroatom-directed aromatic lithiation: a versatile route to the synthesis of organochalcogen (Se, Te) compounds[J]. Accounts of Chemical Research, 2002, 35(4): 226-236. |
| 9 | Sies H. Ebselen, a selenoorganic compound as glutathione peroxidase mimic[J]. Free Radical Biology and Medicine, 1993, 14(3): 313-323. |
| 10 | Liu J Q, Gao S J, Luo G M, et al. Artificial imitation of glutathione peroxidase with 6-selenium-bridged β-cyclodextrin[J]. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications, 1998, 247(2): 397-400. |
| 11 | Luo G M, Zhu Z Q, Ding L, et al. Generation of selenium-containing abzyme by using chemical mutation[J]. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications, 1994, 198(3): 1240-1247. |
| 12 | Wu Z P, Hilvert D. Selenosubtilisin as a glutathione peroxidase mimic[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 1990, 112(14): 5647-5648. |
| 13 | Huang X, Yin Y Z, Liu J Q. Design of artificial selenoenzymes based on macromolecular scaffolds[J]. Macromolecular Bioscience, 2010, 10(12): 1385-1396. |
| 14 | Li J X, Wang Z R, Zhou J, et al. Construction of self-assembled vesicle nanoenzyme using cucurbit[8]uril-based supra-amphiphiles[J]. Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 2018, 558: 95-102. |
| 15 | Tang Y, Zhou L P, Li J X, et al. Giant nanotubes loaded with artificial peroxidase centers: self-assembly of supramolecular amphiphiles as a tool to functionalize nanotubes[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2010, 49(23): 3920-3924. |
| 16 | Liu X M, Silks L, Liu C P, et al. Incorporation of tellurocysteine into glutathione transferase generates high glutathione peroxidase efficiency[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2009, 48(11): 2020-2023. |
| 17 | Dong Z Y, Luo Q, Liu J Q. Artificial enzymes based on supramolecular scaffolds[J]. Chemical Society Reviews, 2012, 41(23): 7890-7908. |
| 18 | Raynal M, Ballester P, Vidal-Ferran A, et al. Supramolecular catalysis ( Ⅱ ) : Artificial enzyme mimics[J]. Chemical Society Reviews, 2014, 43(5): 1734-1787. |
| 19 | Wu P, Xiao R Q, Zhang C Q, et al. Photoregulating catalytic activity of cyclodextrin-based artificial glutathione peroxidase by charged azobenzene[J]. Catalysis Letters, 2010, 138(1/2): 62-67. |
| 20 | Yin Y Z, Jiao S F, Lang C, et al. A supramolecular microgel glutathione peroxidase mimic with temperature responsive activity[J]. Soft Matter, 2014, 10(19): 3374-3385. |
| 21 | Yin Y Z, Jiao S F, Zhang R R, et al. Construction of a smart microgel glutathione peroxidase mimic based on supramolecular self-assembly[J]. Soft Matter, 2015, 11(26): 5301-5312. |
| 22 | Li J X, Si C Y, Sun H C, et al. Reversible pH-controlled switching of an artificial antioxidant selenoenzyme based on pseudorotaxane formation and dissociation[J]. Chemical Communications (Cambridge, England), 2015, 51(49): 9987-9990. |
| 23 | Li J X, Jia W L, Ma G H, et al. Construction of pH sensitive smart glutathione peroxidase (GPx) mimics based on pH responsive pseudorotaxanes[J]. Organic & Biomolecular Chemistry, 2020, 18(16): 3125-3134. |
| 24 | Yu C M, Meng X, Liu X, et al. Switchable supramolecular jalousie constructed from a fluorenone macrocycle[J]. Chemistry of Materials, 2022, 34(1): 358-365. |
| 25 | Yang Z Y, Liu Z J, Yuan L H. Recent advances of photoresponsive supramolecular switches[J]. Asian Journal of Organic Chemistry, 2021, 10(1): 74-90. |
| 26 | Blanco-Gómez A, Cortón P, Barravecchia L, et al. Controlled binding of organic guests by stimuli-responsive macrocycles[J]. Chemical Society Reviews, 2020, 49(12): 3834-3862. |
| 27 | Wang X P, Jia F, Yang L P, et al. Conformationally adaptive macrocycles with flipping aromatic sidewalls[J]. Chemical Society Reviews, 2020, 49(13): 4176-4188. |
| 28 | Zhang L, Wang H X, Li S, et al. Supramolecular chiroptical switches[J]. Chemical Society Reviews, 2020, 49(24): 9095-9120. |
| 29 | 许国贺, 李杰, 邓瑾妮, 等. 基于主客体识别的刺激响应型分子梭[J]. 化学进展, 2015, 27(12): 1732-1742. |
| Xu G H, Li J, Deng J N, et al. Molecular shuttles based on host-guest recognition driven by external-stimuli[J]. Progress in Chemistry, 2015, 27(12): 1732-1742. | |
| 30 | Cong H, Ni X L, Xiao X, et al. Synthesis and separation of cucurbit[n]urils and their derivatives[J]. Organic & Biomolecular Chemistry, 2016, 14(19): 4335-4364. |
| 31 | Dong Z Y, Liu J Q, Mao S Z, et al. Aryl thiol substrate 3-carboxy-4-nitrobenzenethiol strongly stimulating thiol peroxidase activity of glutathione peroxidase mimic 2, 2'-ditellurobis(2-deoxy-beta-cyclodextrin)[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2004, 126(50): 16395-16404. |
| 32 | Engman L, Stern D, Cotgreave I A, et al. Thiol peroxidase activity of diaryl ditellurides as determined by a proton NMR method[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 1992, 114(25): 9737-9743. |
| 33 | Engman L, Stern D, Pelcman M, et al. Thiol peroxidase activity of diorganyl tellurides[J]. The Journal of Organic Chemistry, 1994, 59(8): 1973-1979. |
| 34 | Vessman K, Ekstroem M, Berglund M, et al. Catalytic antioxidant activity of diaryl tellurides in a two-phase lipid peroxidation model[J]. The Journal of Organic Chemistry, 1995, 60(14): 4461-4467. |
| 35 | Mugesh G, Panda A, Singh H B, et al. Glutathione peroxidase-like antioxidant activity of diaryl diselenides: a mechanistic study[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2001, 123(5): 839-850. |
| 36 | Engman L, Stern D, Cotgreave I A, et al. Thiol peroxidase activity of diaryl ditellurides as determined by a proton NMR method[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 1992, 114(25): 9737-9743. |
| 37 | Sies H, Masumoto H. Ebselen as a glutathione peroxidase mimic and as a scavenger of peroxynitrite[J]. Advances in Pharmacology, 1996, 38: 229-246. |
| 38 | Ba L A, Döring M, Jamier V, et al. Tellurium: an element with great biological potency and potential[J]. Organic & Biomolecular Chemistry, 2010, 8(19): 4203-4216. |
| 39 | Jun S I, Lee J W, Sakamoto S, et al. Rotaxane-based molecular switch with fluorescence signaling[J]. Tetrahedron Letters, 2000, 41(4): 471-475. |
| 40 | Lagona J, Mukhopadhyay P, Chakrabarti S, et al. The cucurbit[n]uril family[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2005, 44(31): 4844-4870. |
| [1] | 程业品, 胡达清, 徐奕莎, 刘华彦, 卢晗锋, 崔国凯. 离子液体基低共熔溶剂在转化CO2中的应用[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(9): 3640-3653. |
| [2] | 陈杰, 林永胜, 肖恺, 杨臣, 邱挺. 胆碱基碱性离子液体催化合成仲丁醇性能研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(9): 3716-3730. |
| [3] | 李艺彤, 郭航, 陈浩, 叶芳. 催化剂非均匀分布的质子交换膜燃料电池操作条件研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(9): 3831-3840. |
| [4] | 杨学金, 杨金涛, 宁平, 王访, 宋晓双, 贾丽娟, 冯嘉予. 剧毒气体PH3的干法净化技术研究进展[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(9): 3742-3755. |
| [5] | 范孝雄, 郝丽芳, 范垂钢, 李松庚. LaMnO3/生物炭催化剂低温NH3-SCR催化脱硝性能研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(9): 3821-3830. |
| [6] | 吴雷, 刘姣, 李长聪, 周军, 叶干, 刘田田, 朱瑞玉, 张秋利, 宋永辉. 低阶粉煤催化微波热解制备含碳纳米管的高附加值改性兰炭末[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(9): 3956-3967. |
| [7] | 孟令玎, 崇汝青, 孙菲雪, 孟子晖, 刘文芳. 改性聚乙烯膜和氧化硅固定化碳酸酐酶[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(8): 3472-3484. |
| [8] | 杨欣, 彭啸, 薛凯茹, 苏梦威, 吴燕. 分子印迹-TiO2光电催化降解增溶PHE废水性能研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(8): 3564-3571. |
| [9] | 杨菲菲, 赵世熙, 周维, 倪中海. Sn掺杂的In2O3催化CO2选择性加氢制甲醇[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(8): 3366-3374. |
| [10] | 李凯旋, 谭伟, 张曼玉, 徐志豪, 王旭裕, 纪红兵. 富含零价钴活性位点的钴氮碳/活性炭设计及甲醛催化氧化应用研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(8): 3342-3352. |
| [11] | 陈雅鑫, 袁航, 刘冠章, 毛磊, 杨纯, 张瑞芳, 张光亚. 蛋白质纳米笼介导的酶自固定化研究进展[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(7): 2773-2782. |
| [12] | 汤晓玲, 王嘉瑞, 朱玄烨, 郑仁朝. 基于Pickering乳液的卤醇脱卤酶催化合成手性环氧氯丙烷[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(7): 2926-2934. |
| [13] | 余娅洁, 李静茹, 周树锋, 李清彪, 詹国武. 基于天然生物模板构建纳米材料及集成催化剂研究进展[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(7): 2735-2752. |
| [14] | 李盼, 马俊洋, 陈志豪, 王丽, 郭耘. Ru/α-MnO2催化剂形貌对NH3-SCO反应性能的影响[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(7): 2908-2918. |
| [15] | 涂玉明, 邵高燕, 陈健杰, 刘凤, 田世超, 周智勇, 任钟旗. 钙基催化剂的设计合成及应用研究进展[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(7): 2717-2734. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备 11010102001995号
京公网安备 11010102001995号