化工学报 ›› 2024, Vol. 75 ›› Issue (5): 2001-2016.DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20231201
马旭1,2( ), 滕亚栋3,4, 刘杰3,4, 王宇璐1,2, 张鹏1(
), 滕亚栋3,4, 刘杰3,4, 王宇璐1,2, 张鹏1( ), 张莲海1, 姚万龙5, 展静1, 吴青柏1
), 张莲海1, 姚万龙5, 展静1, 吴青柏1
收稿日期:2023-11-21
修回日期:2024-03-27
出版日期:2024-05-25
发布日期:2024-06-25
通讯作者:
张鹏
作者简介:马旭(1996—),女,硕士研究生,maxu@nieer.ac.cn
基金资助:
Xu MA1,2( ), Yadong TENG3,4, Jie LIU3,4, Yulu WANG1,2, Peng ZHANG1(
), Yadong TENG3,4, Jie LIU3,4, Yulu WANG1,2, Peng ZHANG1( ), Lianhai ZHANG1, Wanlong YAO5, Jing ZHAN1, Qingbai WU1
), Lianhai ZHANG1, Wanlong YAO5, Jing ZHAN1, Qingbai WU1
Received:2023-11-21
Revised:2024-03-27
Online:2024-05-25
Published:2024-06-25
Contact:
Peng ZHANG
摘要:
对发电厂等大型点源释放的CO2捕集是减少人为CO2排放的一种选择,水合物法作为一种新型气体分离提纯技术,形成速率和水转化为水合物比率的强化是该技术关键。利用自主开发的喷雾水合物反应器进行了大水量(640 ml)和小水量(160 ml)碳捕集实验,考察了喷嘴孔径(0.1 mm和0.8 mm)、不同浓度十二烷基硫酸钠 (SDS)和L-蛋氨酸(L-Met)动力学促进剂对碳捕集效率及水合物生长特性的影响。实验结果表明:0.1 mm孔径喷嘴有利于CO2捕集。L-Met和SDS体系每摩尔水最终圈闭的CO2较纯水体系均提升1个数量级,而且低浓度(质量分数0.1%)促进剂效率优于高浓度(质量分数1%)。大水量实验SDS体系最终气体消耗量最高为0.0848 mol /mol H2O,为L-Met体系的1.4倍,但捕集速率L-Met体系优于SDS体系。小水量实验L-Met体系气体捕获量与捕集速率均优于SDS体系。促进剂浓度为0.1%(质量分数)时水合物爬壁生长角度是1%(质量分数)的1.8倍。综合评估,0.1%(质量分数)L-Met、0.1 mm喷嘴和小水量(3.33 ml/min)的注液方式共同作用,碳捕集性能最佳。上述实验结果为强化喷雾反应器中水合物法捕集烟道气中CO2提供参考与基础实验数据。
中图分类号:
马旭, 滕亚栋, 刘杰, 王宇璐, 张鹏, 张莲海, 姚万龙, 展静, 吴青柏. 喷雾法水合物法捕集分离烟道气中CO2[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(5): 2001-2016.
Xu MA, Yadong TENG, Jie LIU, Yulu WANG, Peng ZHANG, Lianhai ZHANG, Wanlong YAO, Jing ZHAN, Qingbai WU. CO2 capture and separation from flue gas by spraying hydrate method[J]. CIESC Journal, 2024, 75(5): 2001-2016.
| 体 系 | 编号 | 促进剂浓度/% (质量分数) | 雾化喷嘴孔径/mm | 原料气中CO2/%(摩尔分数) | 最终消耗的气体量/(mol/mol H2O) | 水转化为水合物比率/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CO2/N2/H2O | 1 | 纯水 | 0.8 | 14.35 | 0.0053 | 3.0 |
| 2 | 纯水 | 0.1 | 14.46 | 0.0061 | 3.5 | |
| CO2/N2/L-Met/H2O | 3 | 0.1 | 0.8 | 15.55 | 0.0587 | 33.5 |
| 4 | 1.0 | 0.8 | 16.87 | 0.0537 | 30.7 | |
| 5 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 19.08 | 0.0749 | 42.7 | |
| 6 | 1.0 | 0.1 | 13.19 | 0.0654 | 37.3 | |
| CO2/N2/SDS/H2O | 7 | 0.1 | 0.8 | 18.15 | 0.0848 | 48.4 |
| 8 | 1.0 | 0.8 | 13.67 | 0.0733 | 41.9 | |
| 9 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 15.34 | 0.0407 | 23.3 |
表1 大水量(640 ml)实验不同体系的实验条件以及实验结果(7.71 MPa,269.15 K)
Table 1 Experimental results in different 640 ml systems of SDS and L-Met promoters (7.71 MPa,269.15 K)
| 体 系 | 编号 | 促进剂浓度/% (质量分数) | 雾化喷嘴孔径/mm | 原料气中CO2/%(摩尔分数) | 最终消耗的气体量/(mol/mol H2O) | 水转化为水合物比率/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CO2/N2/H2O | 1 | 纯水 | 0.8 | 14.35 | 0.0053 | 3.0 |
| 2 | 纯水 | 0.1 | 14.46 | 0.0061 | 3.5 | |
| CO2/N2/L-Met/H2O | 3 | 0.1 | 0.8 | 15.55 | 0.0587 | 33.5 |
| 4 | 1.0 | 0.8 | 16.87 | 0.0537 | 30.7 | |
| 5 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 19.08 | 0.0749 | 42.7 | |
| 6 | 1.0 | 0.1 | 13.19 | 0.0654 | 37.3 | |
| CO2/N2/SDS/H2O | 7 | 0.1 | 0.8 | 18.15 | 0.0848 | 48.4 |
| 8 | 1.0 | 0.8 | 13.67 | 0.0733 | 41.9 | |
| 9 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 15.34 | 0.0407 | 23.3 |
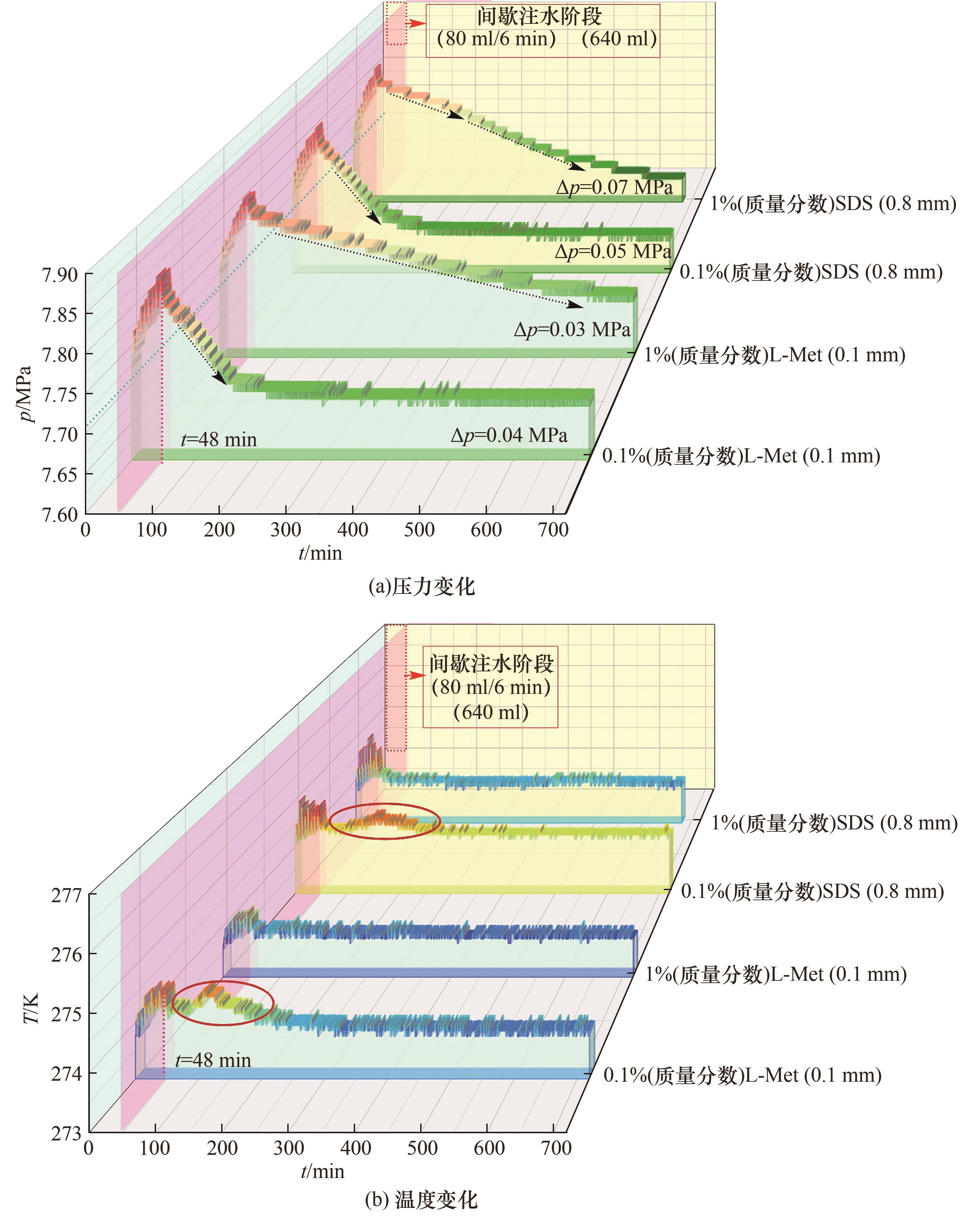
图4 SDS及L-Met体系在0.1%和1%(质量分数)浓度下的水合物生成过程温压变化对比
Fig.4 Temperature and pressure as functions of time during hydrate formation from solutions of CO2/H2O /SDS and CO2/H2O /L-Met respectively with concentrations of 0.1% and 1% (mass fraction)
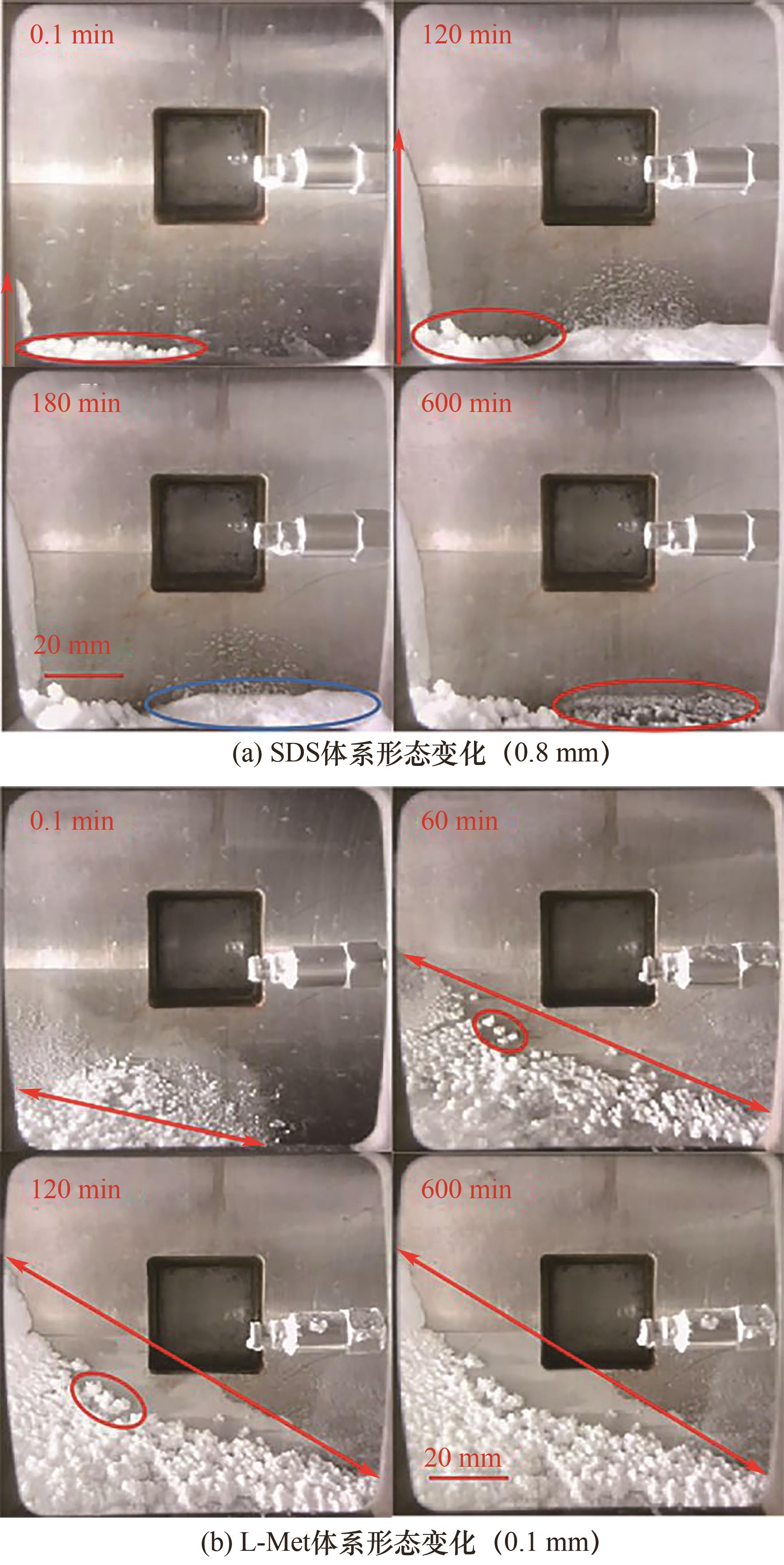
图5 0.1%(质量分数)SDS和L-Met体系水合物生成过程形态变化对比
Fig.5 Morphological changes during hydrate formation from solutions of CO2/H2O /SDS and CO2/H2O /L-Met with both 0.1% (mass fraction)
| 体 系 | 编号 | 促进剂浓度/% (质量分数) | 雾化喷嘴孔径/mm | 原料气中CO2/%(摩尔分数) | 最终消耗的气体量/(mol/mol H2O) | 水转化为水合物比率/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CO2/N2/H2O | 1 | 纯水 | 0.8 | 14.38 | 0.0075 | 4.3 |
| 2 | 纯水 | 0.1 | 14.53 | 0.0111 | 6.3 | |
| CO2/N2/L-Met/H2O | 3 | 0.1 | 0.8 | 16.64 | 0.1220 | 69.6 |
| 4 | 1.0 | 0.8 | 16.84 | 0.1306 | 74.5 | |
| 5 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 19.66 | 0.1599 | 91.2 | |
| 6 | 1.0 | 0.1 | 13.63 | 0.1319 | 75.2 | |
| CO2/N2/SDS/H2O | 7 | 0.1 | 0.8 | 18.41 | 0.1187 | 67.7 |
| 8 | 1.0 | 0.8 | 13.95 | 0.0574 | 30.2 | |
| 9 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 15.56 | 0.0670 | 38.2 |
表2 小水量(160 ml)实验不同体系的实验条件及实验结果(7.71 MPa,269.15 K)
Table 2 Experimental results in different 160 ml systems of SDS and L-Met promoters (7.71 MPa,269.15 K)
| 体 系 | 编号 | 促进剂浓度/% (质量分数) | 雾化喷嘴孔径/mm | 原料气中CO2/%(摩尔分数) | 最终消耗的气体量/(mol/mol H2O) | 水转化为水合物比率/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CO2/N2/H2O | 1 | 纯水 | 0.8 | 14.38 | 0.0075 | 4.3 |
| 2 | 纯水 | 0.1 | 14.53 | 0.0111 | 6.3 | |
| CO2/N2/L-Met/H2O | 3 | 0.1 | 0.8 | 16.64 | 0.1220 | 69.6 |
| 4 | 1.0 | 0.8 | 16.84 | 0.1306 | 74.5 | |
| 5 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 19.66 | 0.1599 | 91.2 | |
| 6 | 1.0 | 0.1 | 13.63 | 0.1319 | 75.2 | |
| CO2/N2/SDS/H2O | 7 | 0.1 | 0.8 | 18.41 | 0.1187 | 67.7 |
| 8 | 1.0 | 0.8 | 13.95 | 0.0574 | 30.2 | |
| 9 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 15.56 | 0.0670 | 38.2 |
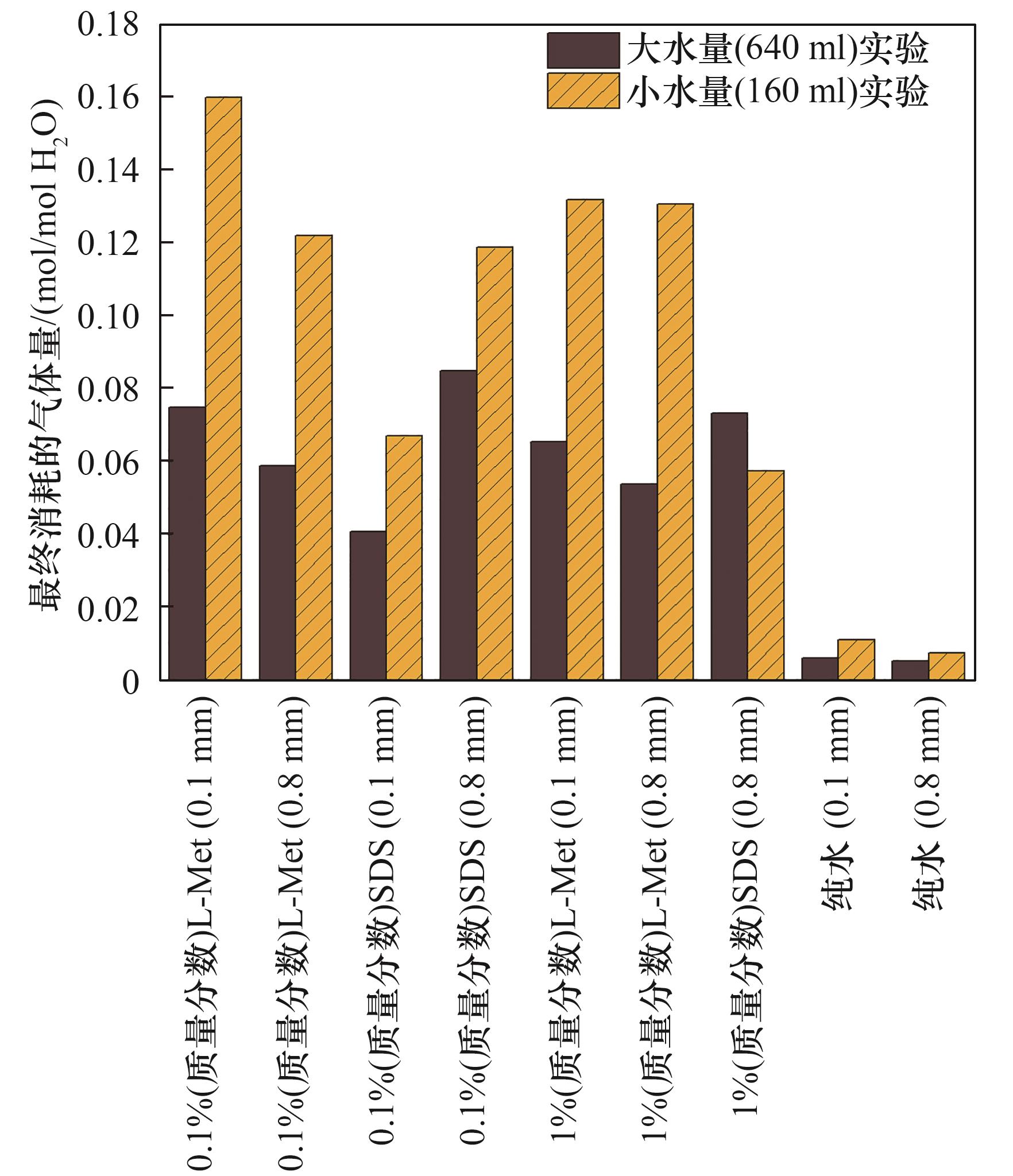
图6 大水量(640 ml)实验体系与小水量(160 ml)实验体系每摩尔水最终消耗的气体量对比
Fig.6 Comparison on final gas uptake per mole water for large water volume (640 ml) and the small (160 ml) systems
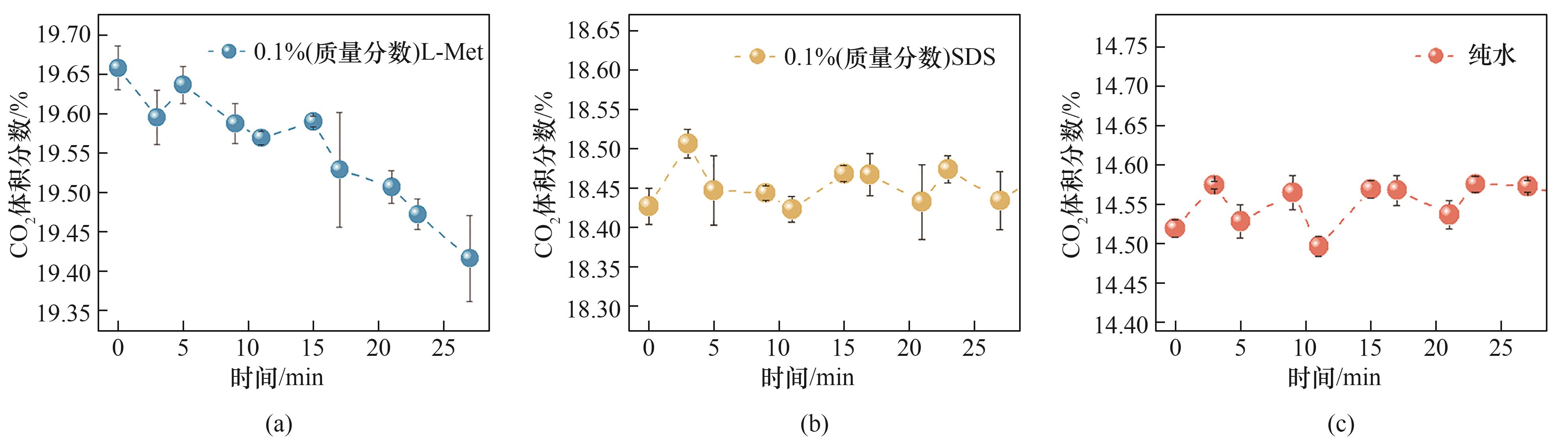
图11 不同体系中间歇注水阶段(24 min)气相CO2浓度变化
Fig.11 Variation of gas-phase CO2 concentration during the intermittent water injection stage (30 min) in different systems
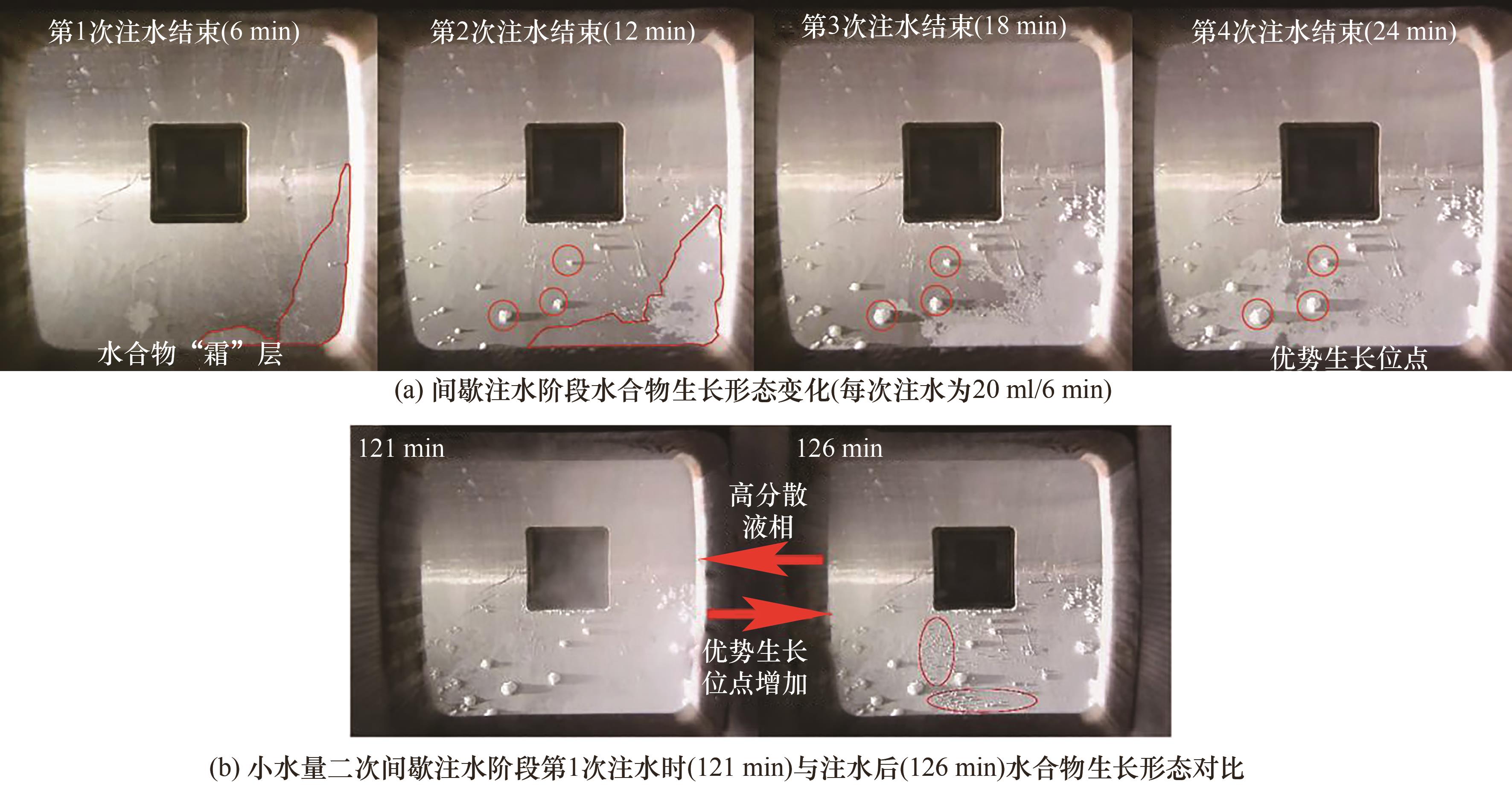
图12 0.1 mm喷嘴孔径下CO2/N2/0.1%(质量分数)L-Met/H2O体系水合物生长过程(视窗②)
Fig.12 Hydrate formation in CO2/N2/0.1% (mass fraction) L-Met/H2O system by using 0.1 mm nozzle aperture (Window 2)

图13 L-Met体系和SDS体系在不同浓度下(质量分数0.1%、1%)水合物生长最终形态
Fig.13 Final morphology of hydrate formation in L-Met system and SDS system at 0.1% and 1% (mass fraction)
| 1 | Lee H, Romero J. A report of the intergovernmental panel on climate change. contribution of working groups Ⅰ, Ⅱ and Ⅲ to the sixth assessment report of the intergovernmental panel on climate change[R]. Geneva: IPCC, 2023. |
| 2 | Liu H J, Were P, Li Q, et al. Worldwide status of CCUS technologies and their development and challenges in China[J]. Geofluids, 2017, 2017: 6126505. |
| 3 | Gupta M, Coyle I, Thambimuthu K. CO2 capture technologies and opportunities in Canada[C]//1st Canadian CC&S Technology Roadmap Workshop. Canada: CANMET Energy Technology Centre Natural Resources Canada, 2003: 18-19. |
| 4 | Pellegrini G, Strube R, Manfrida G. Comparative study of chemical absorbents in postcombustion CO2 capture[J]. Energy, 2010, 35(2): 851-857. |
| 5 | Martunus, Helwani Z, Wiheeb A D, et al. Improved carbon dioxide capture using metal reinforced hydrotalcite under wet conditions[J]. International Journal of Greenhouse Gas Control, 2012, 7: 127-136. |
| 6 | Dou B L, Song Y C, Liu Y G, et al. High temperature CO2 capture using calcium oxide sorbent in a fixed-bed reactor[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2010, 183(1/2/3): 759-765. |
| 7 | Sevilla M, Fuertes A B. CO2 adsorption by activated templated carbons[J]. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 2012, 366(1): 147-154. |
| 8 | Zanganeh K E, Shafeen A, Salvador C. CO2 capture and development of an advanced pilot-scale cryogenic separation and compression unit[J]. Energy Procedia, 2009, 1(1): 247-252. |
| 9 | Sloan E D, Koh C A, Koh C A. Clathrate Hydrates of Natural Gases[M]. New York: CRC Press, 2007: 685-692. |
| 10 | Park S, Lee S, Lee Y, et al. CO2 capture from simulated fuel gas mixtures using semiclathrate hydrates formed by quaternary ammonium salts[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2013, 47(13): 7571-7577. |
| 11 | Zhang P, Wu Q B, Mu C C. Influence of temperature on methane hydrate formation[J]. Scientific Reports, 2017, 7: 7904. |
| 12 | Kang S P, Lee H, Lee C S, et al. Hydrate phase equilibria of the guest mixtures containing CO2, N2 and tetrahydrofuran[J]. Fluid Phase Equilibria, 2001, 185(1/2): 101-109. |
| 13 | Linga P, Kumar R, Englezos P. Gas hydrate formation from hydrogen/carbon dioxide and nitrogen/carbon dioxide gas mixtures[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2007, 62(16): 4268-4276. |
| 14 | Seo Y T, Kang S P, Lee H E, et al. Hydrate phase equilibria for gas mixtures containing carbon dioxide: a proof-of-concept to carbon dioxide recovery from multicomponent gas stream[J]. Korean Journal of Chemical Engineering, 2000, 17(6): 659-667. |
| 15 | Kutergin O B, Melnikov V P, Nesterov A N. Influence of surfactants on the mechanism and kinetics of the formation of gas hydrates[J]. Doklady Akademii Nauk, 1992, 323(3): 549-553. |
| 16 | 郎雪梅, 樊栓狮, 王燕鸿, 等. 笼型水合物为能源化工带来新机遇[J]. 化工进展, 2021, 40(9): 4703-4710. |
| Lang X M, Fan S S, Wang Y H, et al. Opportunities for energy and chemical engineering through clathrate hydrates[J]. Chemical Industry and Engineering Progress, 2021, 40(9): 4703-4710. | |
| 17 | Molokitina N S, Nesterov A N, Podenko L S, et al. Carbon dioxide hydrate formation with SDS: further insights into mechanism of gas hydrate growth in the presence of surfactant[J]. Fuel, 2019, 235: 1400-1411. |
| 18 | Linga P, Kumar R, Lee J D, et al. A new apparatus to enhance the rate of gas hydrate formation: application to capture of carbon dioxide[J]. International Journal of Greenhouse Gas Control, 2010, 4(4): 630-637. |
| 19 | Li G, Liu D P, Xie Y M, et al. Study on effect factors for CO2 hydrate rapid formation in a water-spraying apparatus[J]. Energy & Fuels, 2010, 24(8): 4590-4597. |
| 20 | 石定贤, 赵建忠, 赵阳升. 水合物合成喷雾强化机理研究[J]. 辽宁工程技术大学学报, 2006, 25(1): 131-133. |
| Shi D X, Zhao J Z, Zhao Y S. Research on atomization strengthening mechanics for hydrate formation[J]. Journal of Liaoning Technical University, 2006, 25(1): 131-133. | |
| 21 | Sloan E D. Fundamental principles and applications of natural gas hydrates[J]. Nature, 2003, 426: 353-359. |
| 22 | Hassanpouryouzband A, Joonaki E, Farahani M V, et al. Gas hydrates in sustainable chemistry[J]. Chemical Society Reviews, 2020, 49(15): 5225-5309. |
| 23 | Prasad P S R, Sai Kiran B. Clathrate hydrates of greenhouse gases in the presence of natural amino acids: storage, transportation and separation applications[J]. Scientific Reports, 2018, 8: 8560. |
| 24 | Prasad P S, Kiran B S. Are the amino acids thermodynamic inhibitors or kinetic promoters for carbon dioxide hydrates?[J]. Journal of Natural Gas Science and Engineering, 2018, 52: 461-466. |
| 25 | Bavoh C B, Nashed O, Khan M S, et al. The impact of amino acids on methane hydrate phase boundary and formation kinetics[J]. Journal of Chemical Thermodynamics, 2018, 117: 48-53. |
| 26 | Cai Y H, Chen Y L, Li Q J, et al. CO2 hydrate formation promoted by a natural amino acid l-methionine for possible application to CO2 capture and storage[J]. Energy Technology, 2017, 5(8): 1195-1199. |
| 27 | Liu X J, Ren J J, Chen D Y, et al. Comparison of SDS and L-methionine in promoting CO2 hydrate kinetics: implication for hydrate-based CO2 storage[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2022, 438: 135504. |
| 28 | Pandey J S, Daas Y, Sieverts M, et al. Insights into CO2 capture by flue gas hydrate formation using selected amino acids and surfactant[C]// IUPAC 50th General Assembly. Paris, France, 2019: 1. |
| 29 | Jarrahian A, Nakhaee A. Hydrate-liquid-vapor equilibrium condition of N2+CO2+H2O system: measurement and modeling[J]. Fuel, 2019, 237: 769-774. |
| 30 | Sun S C, Liu C L, Meng Q G. Hydrate phase equilibrium of binary guest-mixtures containing CO2 and N2 in various systems[J]. Journal of Chemical Thermodynamics, 2015, 84: 1-6. |
| 31 | Ballard A L. A non-ideal hydrate solid solution model for a multi-phase equilibria program[D]. Golden: Colorado School of Mines, 2002. |
| 32 | Kumar R, Englezos P, Moudrakovski I, et al. Structural and compositional characterization of hydrates formed from CO2/H2 and CO2/H2/C3H8 gas mixtures in relation to simultaneous CO2 capture and H2 production[J]. AIChE Journal, 2009, 55(6): 1584-94. |
| 33 | Davidson D W, Leaist D G, Hesse R. Oxygen-18 enrichment in the water of a clathrate hydrate[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1983, 47(12): 2293-2295. |
| 34 | Ripmeester J A, Ratcliffe C I. Low-temperature cross-polarization/magic angle spinning carbon-13 NMR of solid methane hydrates: structure, cage occupancy, and hydration number[J]. Journal of Physical Chemistry, 1988, 92(2): 337-339. |
| 35 | Kang S P, Lee H E. Recovery of CO2 from flue gas using gas hydrate: thermodynamic verification through phase equilibrium measurements[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2000, 34(20): 4397-4400. |
| 36 | Seo Y T, Moudrakovski I L, Ripmeester J A, et al. Efficient recovery of CO2 from flue gas by clathrate hydrate formation in porous silica gels[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2005, 39(7): 2315-2319. |
| 37 | Li Y, Maria Gambelli A, Chen J Z, et al. Experimental study on the competition between carbon dioxide hydrate and ice below the freezing point[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2023, 268: 118426. |
| 38 | Linga P. Separation of carbon dioxide from flue gas (post-combustion capture) via gas hydrate crystallization[D]. Vancouver: University of British Columbia, 2009. |
| 39 | Burla S K, Pinnelli S R P. Enrichment of gas storage in clathrate hydrates by optimizing the molar liquid water-gas ratio[J]. RSC Advances, 2022, 12(4): 2074-2082. |
| 40 | Zhang X, Huang Y L, Ma Z S, et al. Hydrogen-bond memory and water-skin supersolidity resolving the Mpemba paradox[J]. Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics: PCCP, 2014, 16(42): 22995-23002. |
| 41 | 张学民, 李洋, 姚泽, 等. 表面活性剂对气体水合物生成过程的定量影响[J]. 过程工程学报, 2018, 18(2): 356-360. |
| Zhang X M, Li Y, Yao Z, et al. Quantitative influence of surfactant on the formation process for gas hydrate[J]. Chinese Journal of Process Engineering, 2018, 18(2): 356-360. | |
| 42 | Colbeck S C. Capillary bonding of wet surfaces—the effects of contact angle and surface roughness[J]. Journal of Adhesion Science and Technology, 1997, 11(3): 359-371. |
| [1] | 刘礼豪, 黄婷, 雍宇, 罗昕浩, 赵泽明, 宋尚飞, 史博会, 陈光进, 宫敬. 含粉砂盐水体系甲烷水合物生成与固相沉积规律[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(5): 1987-2000. |
| [2] | 李怡菲, 董新宇, 王为术, 刘璐, 赵一璠. 微肋板表面干冰升华喷雾冷却传热数值模拟[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(5): 1830-1842. |
| [3] | 臧雅晴, 张益钧, 王金钊, 王倩, 李殿卿, 冯俊婷, 段雪. 基于反应耦合的低能耗水合氯化钙脱水制无水氯化钙[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(4): 1508-1518. |
| [4] | 王佳琪, 魏皓琦, 苟阿静, 刘佳兴, 周昕霖, 葛坤. 纳米粒子作用下CO2水合物生成机理研究[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(3): 956-966. |
| [5] | 陶明清, 慕明昊, 程滕, 王博. 喷雾耦合降温强化旋风分离器脱除细颗粒物的研究[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(2): 584-592. |
| [6] | 赵若晗, 黄蒙蒙, 朱春英, 付涛涛, 高习群, 马友光. 缩口T型微通道内纳米流体吸收CO2的流动与传质研究[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(1): 221-230. |
| [7] | 李晓阳, 李东, 陶明磊, 周致富, 张灵怡, 苏力争, 张天宁, 李智, 陈斌. 多喷嘴喷雾冷却表面传热特性实验研究[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(1): 231-241. |
| [8] | 于旭东, 李琪, 陈念粗, 杜理, 任思颖, 曾英. 三元体系KCl + CaCl2 + H2O 298.2、323.2及348.2 K相平衡研究及计算[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(8): 3256-3265. |
| [9] | 陈天华, 刘兆轩, 韩群, 张程宾, 李文明. 喷雾冷却换热强化研究进展及影响因素[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(8): 3149-3170. |
| [10] | 李彬, 徐正虎, 姜爽, 张天永. 双氧水催化氧化法清洁高效合成促进剂CBS[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(7): 2919-2925. |
| [11] | 毛磊, 刘冠章, 袁航, 张光亚. 可捕集CO2的纳米碳酸酐酶粒子的高效制备及性能研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(6): 2589-2598. |
| [12] | 龙臻, 王谨航, 任俊杰, 何勇, 周雪冰, 梁德青. 离子液体协同PVCap抑制天然气水合物生成实验研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(6): 2639-2646. |
| [13] | 徐文超, 孙志高, 李翠敏, 李娟, 黄海峰. 静态条件下表面活性剂E-1310对HCFC-141b水合物生成的影响[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(5): 2179-2185. |
| [14] | 王皓, 唐思扬, 钟山, 梁斌. MEA吸收CO2富液解吸过程中固体颗粒表面的强化作用分析[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(4): 1539-1548. |
| [15] | 李明川, 樊栓狮, 徐赋海, 卢惠东, 李晓军. 水合物热分解Stefan相变模型解的存在性及Laplace变换求解[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(4): 1746-1754. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备 11010102001995号
京公网安备 11010102001995号