化工学报 ›› 2024, Vol. 75 ›› Issue (5): 2017-2025.DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20240102
武颖韬1( ), 费立涵1, 孔祥东1, 王帜2, 汤成龙1(
), 费立涵1, 孔祥东1, 王帜2, 汤成龙1( ), 黄佐华1
), 黄佐华1
收稿日期:2024-01-22
修回日期:2024-03-24
出版日期:2024-05-25
发布日期:2024-06-25
通讯作者:
汤成龙
作者简介:武颖韬(1993—),男,博士,讲师,wuyingtao@xjtu.edu.cn
基金资助:
Yingtao WU1( ), Lihan FEI1, Xiangdong KONG1, Zhi WANG2, Chenglong TANG1(
), Lihan FEI1, Xiangdong KONG1, Zhi WANG2, Chenglong TANG1( ), Zuohua HUANG1
), Zuohua HUANG1
Received:2024-01-22
Revised:2024-03-24
Online:2024-05-25
Published:2024-06-25
Contact:
Chenglong TANG
摘要:
利用落滴法对比了三种咪唑二氰胺离子液体分别掺混糠醇的自燃特性,使用高速摄相机和红外摄相机同步获得了燃料自燃过程的宏观、微观及红外图像;从液面下方拍摄了液滴与液池的混合反应过程。实验观察到了典型的三阶段自燃现象:铺展混合、气相产物生成及火核出现-火焰传播,使用着火延迟时间对燃料的自燃活性进行了定量表征,并计算了糠醇比例对混合燃料推进性能的影响。结果表明,糠醇添加可以显著降低混合燃料黏度,促进燃料与氧化剂的混合,加速自燃过程高温气雾产物的出现。混合燃料的着火延迟时间随糠醇添加比例非单调变化,着火延迟最短的掺混比随液滴速度的增加而增大;混合燃料推进性能受糠醇添加的影响较小。本研究可为自燃离子液体推进剂的开发及利用提供参考。
中图分类号:
武颖韬, 费立涵, 孔祥东, 王帜, 汤成龙, 黄佐华. 咪唑二氰胺离子液体掺混糠醇的自燃及推进性能[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(5): 2017-2025.
Yingtao WU, Lihan FEI, Xiangdong KONG, Zhi WANG, Chenglong TANG, Zuohua HUANG. Hypergolic ignition characteristics and propulsion performance of imidazolium dicyanamide ionic liquids blended with furfuryl alcohol[J]. CIESC Journal, 2024, 75(5): 2017-2025.
| 燃料 | 分子结构 | ρ/(g/cm3) | 黏度/(mPa·s) | σ/(mN/m) | ΔHf / (kJ/mol) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [AMIM][DCA] | 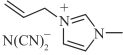 | 1.1 | 11.2 | 52.8 | 382.0 |
| [BMIM][DCA] | 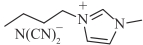 | 1.1 | 36.0 | 42.1 | 266.5 |
| [EMIM][DCA] | 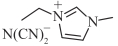 | 1.1 | 16.0 | 49.7 | 258.6 |
| FA | 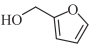 | 1.1 | 5.3 | 38.0 | -179.8 |
表1 燃料分子结构及室温下物性参数[16, 25, 27]
Table 1 Fuel molecular structures and physical properties at room temperature[16, 25, 27]
| 燃料 | 分子结构 | ρ/(g/cm3) | 黏度/(mPa·s) | σ/(mN/m) | ΔHf / (kJ/mol) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [AMIM][DCA] |  | 1.1 | 11.2 | 52.8 | 382.0 |
| [BMIM][DCA] | 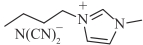 | 1.1 | 36.0 | 42.1 | 266.5 |
| [EMIM][DCA] |  | 1.1 | 16.0 | 49.7 | 258.6 |
| FA |  | 1.1 | 5.3 | 38.0 | -179.8 |
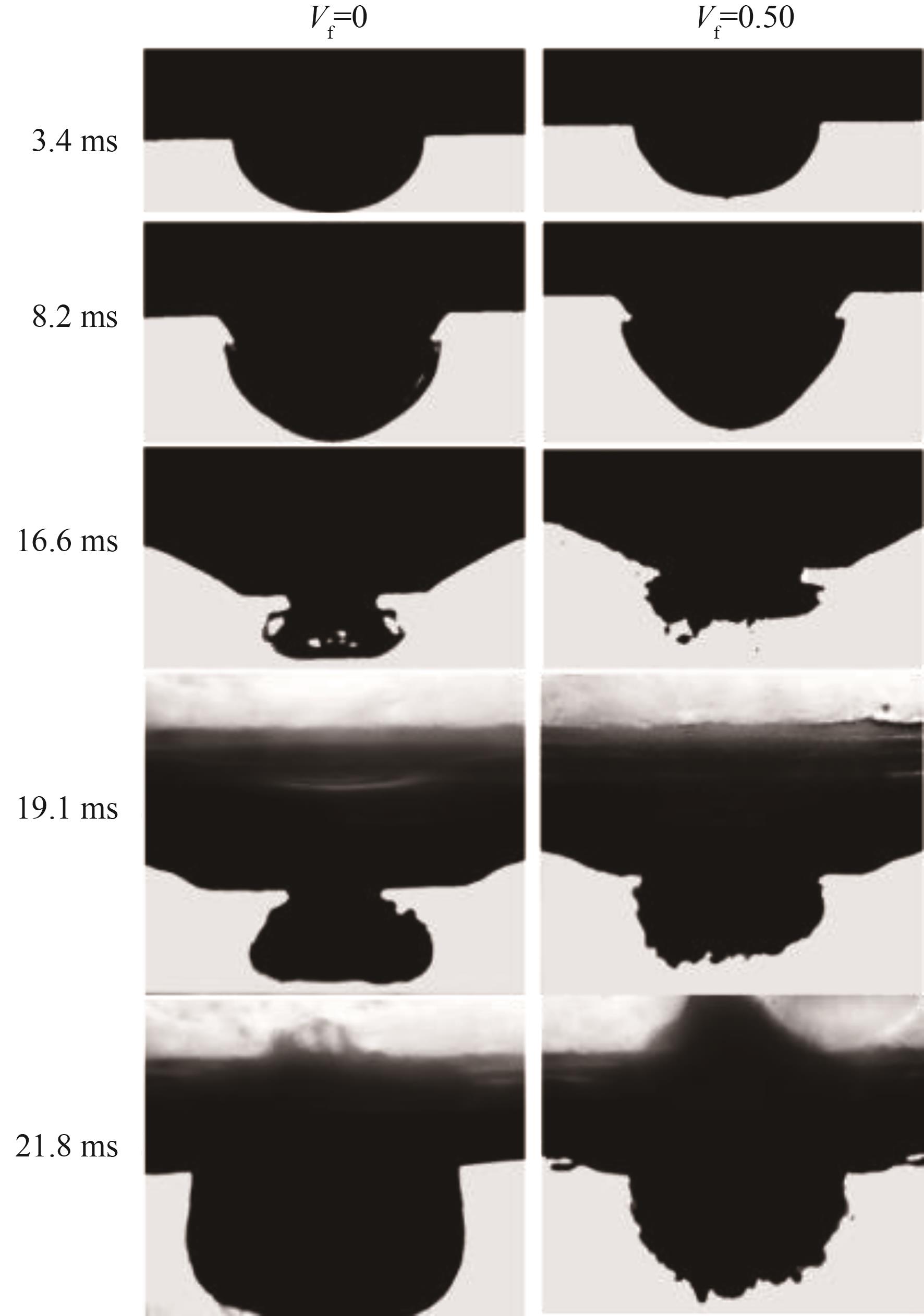
图5 纯[BMIM][DCA]与Vf = 0.50的[BMIM][DCA]/FA混合燃料自燃前期液面下图像
Fig.5 Morphology of pure [BMIM][DCA] and 50%FA/50%[BMIM][DCA] blend in the early stage of hypergolic ignition beneath the liquid surface
| 燃料 | C*/(m/s) | CF | Ivac/(m/s) | Isp/(m/s) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| [AMIM][DCA], Vf =0 | 1534.7 | 1.8236 | 2893.0 | 2798.8 |
| [AMIM][DCA], Vf =0.25 | 1529.2 | 1.8260 | 2887.4 | 2792.3 |
| [AMIM][DCA], Vf =0.50 | 1523.6 | 1.8284 | 2881.6 | 2785.7 |
| [AMIM][DCA], Vf =0.75 | 1517.7 | 1.8310 | 2875.7 | 2778.9 |
| [BMIM][DCA], Vf =0 | 1539.5 | 1.8257 | 2905.9 | 2810.8 |
| [BMIM][DCA], Vf =0.25 | 1533.3 | 1.8275 | 2897.7 | 2802.0 |
| [BMIM][DCA], Vf =0.50 | 1526.6 | 1.8294 | 2889.0 | 2792.7 |
| [BMIM][DCA], Vf =0.75 | 1519.4 | 1.8314 | 2879.7 | 2782.7 |
| [EMIM][DCA], Vf =0 | 1531.3 | 1.8243 | 2887.7 | 2793.6 |
| [EMIM][DCA], Vf =0.25 | 1526.6 | 1.8266 | 2883.4 | 2788.4 |
| [EMIM][DCA], Vf =0.50 | 1521.8 | 1.8288 | 2878.9 | 2783.1 |
| [EMIM][DCA], Vf =0.75 | 1516.8 | 1.8312 | 2874.4 | 2777.6 |
| FA | 1511.7 | 1.8336 | 2869.6 | 2771.9 |
表2 不同混合燃料的推进性能参数
Table 2 Propulsion performance parameters of different fuel blends
| 燃料 | C*/(m/s) | CF | Ivac/(m/s) | Isp/(m/s) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| [AMIM][DCA], Vf =0 | 1534.7 | 1.8236 | 2893.0 | 2798.8 |
| [AMIM][DCA], Vf =0.25 | 1529.2 | 1.8260 | 2887.4 | 2792.3 |
| [AMIM][DCA], Vf =0.50 | 1523.6 | 1.8284 | 2881.6 | 2785.7 |
| [AMIM][DCA], Vf =0.75 | 1517.7 | 1.8310 | 2875.7 | 2778.9 |
| [BMIM][DCA], Vf =0 | 1539.5 | 1.8257 | 2905.9 | 2810.8 |
| [BMIM][DCA], Vf =0.25 | 1533.3 | 1.8275 | 2897.7 | 2802.0 |
| [BMIM][DCA], Vf =0.50 | 1526.6 | 1.8294 | 2889.0 | 2792.7 |
| [BMIM][DCA], Vf =0.75 | 1519.4 | 1.8314 | 2879.7 | 2782.7 |
| [EMIM][DCA], Vf =0 | 1531.3 | 1.8243 | 2887.7 | 2793.6 |
| [EMIM][DCA], Vf =0.25 | 1526.6 | 1.8266 | 2883.4 | 2788.4 |
| [EMIM][DCA], Vf =0.50 | 1521.8 | 1.8288 | 2878.9 | 2783.1 |
| [EMIM][DCA], Vf =0.75 | 1516.8 | 1.8312 | 2874.4 | 2777.6 |
| FA | 1511.7 | 1.8336 | 2869.6 | 2771.9 |
| 1 | Salvador C A V, Costa F S. Vaporization lengths of hydrazine fuels burning with NTO[J]. Journal of Propulsion and Power, 2006, 22(6): 1362-1372. |
| 2 | Kulkarni S, Bagalkote V, Patil S, et al. Theoretical evaluation and experimental validation of performance parameters of new hypergolic liquid fuel blends with red fuming nitric acid as oxidizer[J]. Propellants, Explosives, Pyrotechnics, 2009, 34(6): 520-525. |
| 3 | Pichon S, Catoire L, Chaumeix N, et al. Search for green hypergolic propellants: gas-phase ethanol/nitrogen tetroxide reactivity[J]. Journal of Propulsion and Power, 2005, 21(6): 1057-1061. |
| 4 | Phillip J, Youngblood S, Grubelich M, et al. Development and testing of a nitrous-oxide/ethanol bi-propellant rocket engine[C]∥52nd AIAA/SAE/ASEE Joint Propulsion Conference. Reston, Virginia: AIAA, 2016: 5092. |
| 5 | Pasini A, Torre L, Pace G, et al. Pulsed chemical rocket with green high performance propellants[C]∥49th AIAA/ASME/SAE/ASEE Joint Propulsion Conference. Reston, Virginia: AIAA, 2013: 3756. |
| 6 | Schneider S, Hawkins T, Rosander M, et al. Ionic liquids as hypergolic fuels[J]. Energy & Fuels, 2008, 22(4): 2871-2872. |
| 7 | Kelkar M S, Maginn E J. Effect of temperature and water content on the shear viscosity of the ionic liquid 1-ethyl-3-methylimidazolium bis(trifluoromethanesulfonyl)imide as studied by atomistic simulations[J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry. B, 2007, 111(18): 4867-4876. |
| 8 | Zhang Q H, Shreeve J M. Energetic ionic liquids as explosives and propellant fuels: a new journey of ionic liquid chemistry[J]. Chemical Reviews, 2014, 114(20): 10527-10574. |
| 9 | Zhang Y Q, Shreeve J M. Dicyanoborate-based ionic liquids as hypergolic fluids[J]. Angewandte Chemie, 2011, 50(4): 935-937. |
| 10 | 黄实. 新型高能低毒液体推进剂的合成及点火性能研究[D]. 绵阳: 中国工程物理研究院, 2016. |
| Huang S. Study on synthesis and ignition performance of new high-energy and low-toxicity liquid propellant[D].Mianyang: China Academy of Engineering Physics, 2016. | |
| 11 | Sutton G P. History of Liquid Propellant Rocket Engines[M]. Reston, Virginia.: American Institute of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2006. |
| 12 | Liu Y, Guo Y, Fei L H, et al. Experimental study on hypergolic ignition and non-ignition for dicyanamide-based ionic liquids at low impact velocity conditions[J]. Energetic Materials Frontiers, 2021, 2(4): 241-248. |
| 13 | He L, Tao G H, Parrish D A, et al. Nitrocyanamide-based ionic liquids and their potential applications as hypergolic fuels[J]. Chemistry, 2010, 16(19): 5736-5743. |
| 14 | Newsome D A, Vaghjiani G L, Sengupta D. An ab initio based structure property relationship for prediction of ignition delay of hypergolic ionic liquids[J]. Propellants, Explosives, Pyrotechnics, 2015, 40(5): 759-764. |
| 15 | Khomik S V, Usachev S V, Medvedev S P, et al. Ignition characteristics of hypergolic fuels with various N-substituents[J]. Proceedings of the Combustion Institute, 2019, 37(3): 3311-3317. |
| 16 | Li J L, Weng X Y, Tang C L, et al. The ignition process measurements and performance evaluations for hypergolic ionic liquid fuels: [EMIm][DCA] and [BMIm][DCA][J]. Fuel, 2018, 215: 612-618. |
| 17 | 杜增晖, 孙策, 李钰潼, 等. 咪唑二氰胺类离子液体在白色发烟硝酸中自燃特性的实验研究[J]. 西安交通大学学报, 2022, 56(4): 13-22. |
| Du Z H, Sun C, Li Y T, et al. Experimental study on hypergolic characteristics of imidazolium dicyanamide ionic liquids in white Fuming nitric acid[J]. Journal of Xi’an Jiaotong University, 2022, 56(4): 13-22. | |
| 18 | 翁欣妍, 杜宗罡, 于君, 等. 含BH3(CN)BH2(CN)-阴离子的离子液体自着火过程的实验研究[J]. 含能材料, 2018, 26(7): 557-564. |
| Weng X Y, Du Z G, Yu J, et al. Experimental study of hypergolic process of ionic liquids with BH3(CN)BH2(CN)- anion[J]. Chinese Journal of Energetic Materials, 2018, 26(7): 557-564. | |
| 19 | 王镜淇, 张星, 陈雪娇, 等. 与硝基氧化剂快速自燃的绿色燃料研究进展[J]. 宇航总体技术, 2022, 6(3): 40-48. |
| Wang J Q, Zhang X, Chen X J, et al. Investigation of nitro-oxidizers based green hypergolic fuels with superior low ignition delay[J]. Astronautical Systems Engineering Technology, 2022, 6(3): 40-48. | |
| 20 | Munjal N L. Ignition catalysts for furfuryl alcohol-red fuming nitric acid bipropellant[J]. AIAA Journal, 1970, 8(5): 980-981. |
| 21 | Kulkarni S G, Bagalkote V S. Studies on pre-ignition reactions of hydrocarbon-based rocket fuels hypergolic with red fuming nitric acid as oxidizer[J]. Journal of Energetic Materials, 2010, 28(3): 173-188. |
| 22 | Chalmpes N, Bourlinos A B, Talande S, et al. Nanocarbon from rocket fuel waste: the case of furfuryl alcohol-fuming nitric acid hypergolic pair[J]. Nanomaterials, 2020, 11(1): 1. |
| 23 | James O O, Maity S, Usman L A, et al. Towards the conversion of carbohydrate biomass feedstocks to biofuels via hydroxylmethylfurfural[J]. Energy & Environmental Science, 2010, 3(12): 1833-1850. |
| 24 | Nandiwale K Y, Pande A M, Bokade V V. One step synthesis of ethyl levulinate biofuel by ethanolysis of renewable furfuryl alcohol over hierarchical zeolite catalyst[J]. RSC Advances, 2015, 5(97): 79224-79231. |
| 25 | Bhosale M V K, Kulkarni S G, Kulkarni P S. Ionic liquid and biofuel blend: a low-cost and high performance hypergolic fuel for propulsion application[J]. ChemistrySelect, 2016, 1(9): 1921-1925. |
| 26 | Wu Y T, Wang Z, Fei L H, et al. An experimental study on the hypergolic process enhanced by pre-ignition heat release: [AMIM][DCA]/furfuryl alcohol blends reacting with white fuming nitric acid[J]. Fuel, 2022, 326: 125103. |
| 27 | Sun C G, Tang S K, Zhang X W. Hypergolicity evaluation and prediction of ionic liquids based on hypergolic reactive groups[J]. Combustion and Flame, 2019, 205: 441-445. |
| 28 | Jia F F, Sun K, Zhang P, et al. Marangoni effect on the impact of droplets onto a liquid-gas interface[J]. Physical Review Fluids, 2020, 5(7): 073605. |
| 29 | Maples R E. Petroleum Refinery Process Economics[M]. 2nd ed. Tulsa, Okla.: PennWell Corp., 2000. |
| 30 | Li J L, Fan W, Weng X Y, et al. Experimental observation of hypergolic ignition of superbase-derived ionic liquids[J]. Journal of Propulsion and Power, 2018, 34(1): 125-132. |
| 31 | Weng X Y, Tang C L, Li J L, et al. Coulomb explosion and ultra-fast hypergolic ignition of borohydride-rich ionic liquids with WFNA[J]. Combustion and Flame, 2018, 194: 464-471. |
| 32 | Kim T, Assary R S, Marshall C L, et al. Acid-catalyzed furfuryl alcohol polymerization: characterizations of molecular structure and thermodynamic properties[J]. ChemCatChem, 2011, 3(9): 1451-1458. |
| 33 | Gordon S, Mcbride B. Computer program for calculation of complex chemical equilibrium compositions and applications(Ⅰ): Analysis[CP]. NASA Reference Publication 1311, 1994. |
| 34 | Mcbride B, Gordon S. Computer program for calculation of complex chemical equilibrium compositions and applications(Ⅱ): User manual and program description[CP]. NASA Reference Publication 1311, 1996. |
| [1] | 李静, 张方芳, 王帅帅, 徐建华, 张朋远. 凹腔结构对正丁烷部分预混火焰可燃极限的影响[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(5): 2081-2090. |
| [2] | 王金山, 王世学, 朱禹. 冷却表面温差对高温质子交换膜燃料电池性能的影响[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(5): 2026-2035. |
| [3] | 冯彬彬, 卢明佳, 黄志宏, 常译文, 崔志明. 碳载体在质子交换膜燃料电池中的应用及优化[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(4): 1469-1484. |
| [4] | 贾旭东, 杨博龙, 程前, 李雪丽, 向中华. 分步负载金属法制备铁钴双金属位点高效氧还原电催化剂[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(4): 1578-1593. |
| [5] | 申州洋, 薛康, 刘青, 史成香, 邹吉军, 张香文, 潘伦. 吸热型纳米流体燃料研究进展[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(4): 1167-1182. |
| [6] | 王瑞瑞, 金颖, 刘玉梅, 李梦悦, 朱胜文, 闫瑞一, 刘瑞霞. 聚合离子液体设计及催化环己烷选择性氧化性能研究[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(4): 1552-1564. |
| [7] | 张劲, 郭志斌, 罗来明, 卢善富, 相艳. 5 kW重整甲醇高温质子交换膜燃料电池系统设计与性能[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(4): 1697-1704. |
| [8] | 孙铭泽, 黄鹤来, 牛志强. 铂基氧还原催化剂:从单晶电极到拓展表面纳米材料[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(4): 1256-1269. |
| [9] | 蒋方涛, 钱刚, 周兴贵, 段学志, 张晶. 基于[bmim][BF4]相转移催化的氟代碳酸乙烯酯高效合成[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(4): 1543-1551. |
| [10] | 周辛梓, 李增辉, 孟现阳, 吴江涛. 低温下高纯空气黏度实验研究[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(3): 782-788. |
| [11] | 张领先, 刘斌, 邓琳, 任宇航. 基于改进TSO优化Xception的PEMFC故障诊断[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(3): 945-955. |
| [12] | 谭耀文, 姜攀星, 杜青, 余婉秋, 温小飞, 詹志刚. 工作电压对PEMFC膜电极衰退影响模拟研究[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(3): 974-986. |
| [13] | 詹小斌, 王会彬, 蒋亚龙, 史铁林. 声共振混合器高黏度流体混合的功耗特性研究[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(2): 531-542. |
| [14] | 肖拥君, 时兆翀, 万仁, 宋璠, 彭昌军, 刘洪来. 反向传播神经网络用于预测离子液体的自扩散系数[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(2): 429-438. |
| [15] | 陈宏, 江坤, 唐廷江, 黄易元, 池滨, 廖世军. 大功率质子交换膜燃料电池电堆膜电极一致性研究[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(2): 637-646. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备 11010102001995号
京公网安备 11010102001995号