化工学报 ›› 2020, Vol. 71 ›› Issue (8): 3535-3544.DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20200175
收稿日期:2020-02-24
修回日期:2020-05-12
出版日期:2020-08-05
发布日期:2020-08-05
通讯作者:
李斯琪
作者简介:刘坐东(1985—),男,博士,讲师,基金资助:
Zuodong LIU( ),Siqi LI(
),Siqi LI( ),Weiwei XING,Zhiming XU
),Weiwei XING,Zhiming XU
Received:2020-02-24
Revised:2020-05-12
Online:2020-08-05
Published:2020-08-05
Contact:
Siqi LI
摘要:
换热器微生物污垢问题普遍存在于能源化工领域,污垢的聚集会导致设备的流动阻力、燃料消耗和维护成本支出大幅度增加。本文采用复合纳米镀层来抑制和减轻换热表面的微生物污垢的附着和沉积。首先采用化学镀的方式,在板式换热器的不锈钢316板上镀覆 Ni-P-TiO2复合纳米镀层和对照性的Ni-P 镀层。基于板式换热器的微生物污垢在线监测实验系统,研究了镀覆Ni-P-TiO2复合纳米镀层的板式换热器微生物污垢特性。结果表明,清洁状态下,镀覆两种镀层的板式换热器其摩擦系数(f)和Nusselt数(Nu)相较未镀覆板式换热器均略有增加;微生物污垢实验后,相比较未镀覆的板式换热器,镀覆Ni-P镀层的板式换热器污垢热阻减少了8.36%~23.07%,而镀覆Ni-P-TiO2复合纳米镀层的板式换热器污垢热阻减少了16.6%~30.96%;在相同微生物污垢实验工况下,镀覆Ni-P-TiO2复合纳米镀层的板式换热器的摩擦系数(f)相比Ni-P镀层的低2.54%~11.82%,但Nu却明显高于Ni-P镀层达8.47%~9.45%,并且污垢热阻明显小于Ni-P镀层达10.66%~18.18%,镀覆Ni-P-TiO2复合纳米镀层的板式换热器展现了优异的强化传热性能和抑垢性能。
中图分类号:
刘坐东, 李斯琪, 邢维维, 徐志明. 板式换热器Ni-P-TiO2复合纳米镀层微生物污垢特性[J]. 化工学报, 2020, 71(8): 3535-3544.
Zuodong LIU, Siqi LI, Weiwei XING, Zhiming XU. Characteristics of microbial fouling on Ni-P- (nano) TiO2 composite coating of plate heat exchanger[J]. CIESC Journal, 2020, 71(8): 3535-3544.
| 材料 | 板片尺寸/mm | 波纹 形式 | 波纹深度/mm | 当量直径/mm | 单流道截面积/ m2 | 角孔直径/ mm | 板片厚度/mm | 换热面积/m2 | 波纹夹角/(°) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 316不锈钢 | 258×100 | 人字形 | 2 | 4 | 0.000167 | φ20 | 0.6 | 0.15 | 120 |
表1 待测板式换热器的尺寸参数
Table 1 Dimension parameters of the test plate heat exchanger
| 材料 | 板片尺寸/mm | 波纹 形式 | 波纹深度/mm | 当量直径/mm | 单流道截面积/ m2 | 角孔直径/ mm | 板片厚度/mm | 换热面积/m2 | 波纹夹角/(°) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 316不锈钢 | 258×100 | 人字形 | 2 | 4 | 0.000167 | φ20 | 0.6 | 0.15 | 120 |
| 表面 | θw/(°) | θDi/(°) | θEG/(°) | γLW/(mJ/m2) | γ-/(mJ/m2) | γ+/(mJ/m2) | γTOT/(mJ/m2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 不锈钢 | 95.0±0.6 | 25.7±0.8 | 48.6±0.5 | 44.56 | 2.29 | 0.81 | 47.09 |
| Ni-P镀层 | 84.3±0.5 | 28.6±1.8 | 43.5±2.5 | 44.83 | 1.41 | 0.29 | 46.11 |
| Ni-P-TiO2复合纳米镀层 | 64.3±2.4 | 38.4±1.2 | 58.8±0.8 | 41.15 | 9.58 | 0.41 | 44.29 |
表3 各表面的接触角以及表面能
Table 3 Contact angle and surface energy of each surface
| 表面 | θw/(°) | θDi/(°) | θEG/(°) | γLW/(mJ/m2) | γ-/(mJ/m2) | γ+/(mJ/m2) | γTOT/(mJ/m2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 不锈钢 | 95.0±0.6 | 25.7±0.8 | 48.6±0.5 | 44.56 | 2.29 | 0.81 | 47.09 |
| Ni-P镀层 | 84.3±0.5 | 28.6±1.8 | 43.5±2.5 | 44.83 | 1.41 | 0.29 | 46.11 |
| Ni-P-TiO2复合纳米镀层 | 64.3±2.4 | 38.4±1.2 | 58.8±0.8 | 41.15 | 9.58 | 0.41 | 44.29 |
| 测试液体 | (mJ/m2) | (mJ/m2) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
水 二碘甲烷 乙二醇 | 72.8 | 21.8 | 51.0 | 25.5 | 25.5 |
| 50.8 | 50.8 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| 48.0 | 29.0 | 19.0 | 1.92 | 47.0 |
表2 测试液体的表面能
Table 2 Surface energy of the test liquid
| 测试液体 | (mJ/m2) | (mJ/m2) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
水 二碘甲烷 乙二醇 | 72.8 | 21.8 | 51.0 | 25.5 | 25.5 |
| 50.8 | 50.8 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| 48.0 | 29.0 | 19.0 | 1.92 | 47.0 |
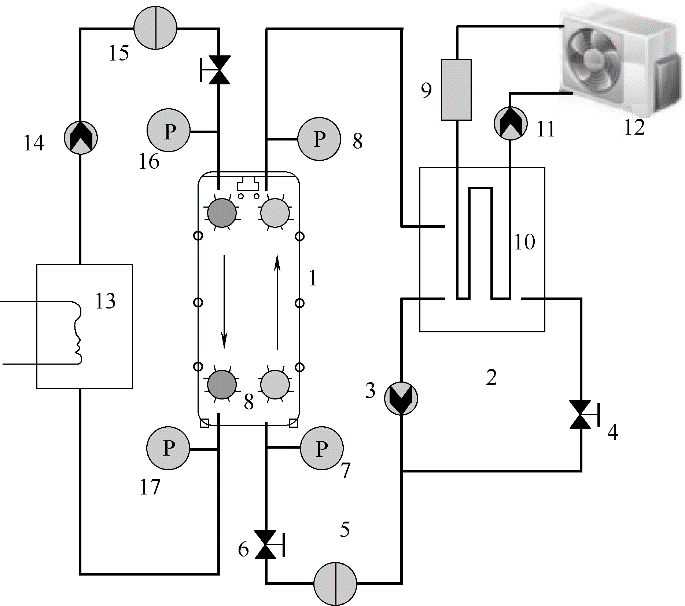
图2 实验系统图1—板式换热器;2—低温介质水箱;3—低温介质循环泵;4—旁通阀;5—冷端电磁流量计;6—冷端平衡阀;7—冷水进口压力表;8—冷水出口压力表;9—空冷水箱;10—散热器;11—空冷循环泵;12—换热扇;13—恒温水箱;14—高温介质循环泵;15—热端电磁流量计;16—热水进口压力表;17—热水出口压力表
Fig.2 Experimental system
| 温度 | 压力 | 体积流量 | 传热系数 | Nusselt数 | 范宁 摩擦系数f |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ±0.20% | ±0.11% | ±0.50% | ±6.69% | ±0.50% | ±0.51% |
表4 测量与计算的不确定度估计
Table 4 Uncertainty estimates for measurement and calculation
| 温度 | 压力 | 体积流量 | 传热系数 | Nusselt数 | 范宁 摩擦系数f |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ±0.20% | ±0.11% | ±0.50% | ±6.69% | ±0.50% | ±0.51% |
| Pt100热电阻 | 压差变送器 | 绕线电阻 | A/D转换器 | 电磁流量计 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.2% | 0.1% | 0.05% | 0.01% | 0.5% |
表5 仪器的不确定度
Table 5 Instrument uncertainty
| Pt100热电阻 | 压差变送器 | 绕线电阻 | A/D转换器 | 电磁流量计 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.2% | 0.1% | 0.05% | 0.01% | 0.5% |
| 表面 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 清洁状态 | 污垢状态 | 清洁状态 | 污垢状态 | |
| 不锈钢 | C=28.58,n=-0.57 | C=166.49,n=-0.73 | C=0.238,n=0.50 | C=0.052,n=0.69 |
| Ni-P镀层 | C=30.53,n=-0.59 | C=190.45,n-0.76 | C=0.245,n=0.51 | C=0.144,n=0.55 |
| Ni-P-TiO2复合纳米镀层 | C=42.35,n=-0.64 | C=267.25,n=-0.83 | C=0.161,n=0.59 | C=0.205,n=0.52 |
表6 不同表面的f及Nu相关性
Table 6 Correlation between friction factors and Nu on different surfaces
| 表面 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 清洁状态 | 污垢状态 | 清洁状态 | 污垢状态 | |
| 不锈钢 | C=28.58,n=-0.57 | C=166.49,n=-0.73 | C=0.238,n=0.50 | C=0.052,n=0.69 |
| Ni-P镀层 | C=30.53,n=-0.59 | C=190.45,n-0.76 | C=0.245,n=0.51 | C=0.144,n=0.55 |
| Ni-P-TiO2复合纳米镀层 | C=42.35,n=-0.64 | C=267.25,n=-0.83 | C=0.161,n=0.59 | C=0.205,n=0.52 |
| 表面 | 热阻波动范围/(m2·K/W) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 0.1 m/s | 0.2 m/s | 0.3 m/s | |
| 不锈钢表面 | -2.69×10-5~25.59×10-5 | -1.91×10-5~19.72×10-5 | -0.80×10-5~12.49×10-5 |
| Ni-P镀层 | -1.44×10-5~22.50×10-5 | -0.47×10-5~16.75×10-5 | -0.31×10-5~11.17×10-5 |
| Ni-P-TiO2复合纳米镀层 | -0.57×10-5~20.10×10-5 | -0.95×10-5~14.98×10-5 | -1.19×10-5~9.99×10-5 |
表7 不同流速下各表面污垢热阻的波动范围
Table 7 Fluctuation range of fouling resistance on different surfaces at different flow rates
| 表面 | 热阻波动范围/(m2·K/W) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 0.1 m/s | 0.2 m/s | 0.3 m/s | |
| 不锈钢表面 | -2.69×10-5~25.59×10-5 | -1.91×10-5~19.72×10-5 | -0.80×10-5~12.49×10-5 |
| Ni-P镀层 | -1.44×10-5~22.50×10-5 | -0.47×10-5~16.75×10-5 | -0.31×10-5~11.17×10-5 |
| Ni-P-TiO2复合纳米镀层 | -0.57×10-5~20.10×10-5 | -0.95×10-5~14.98×10-5 | -1.19×10-5~9.99×10-5 |
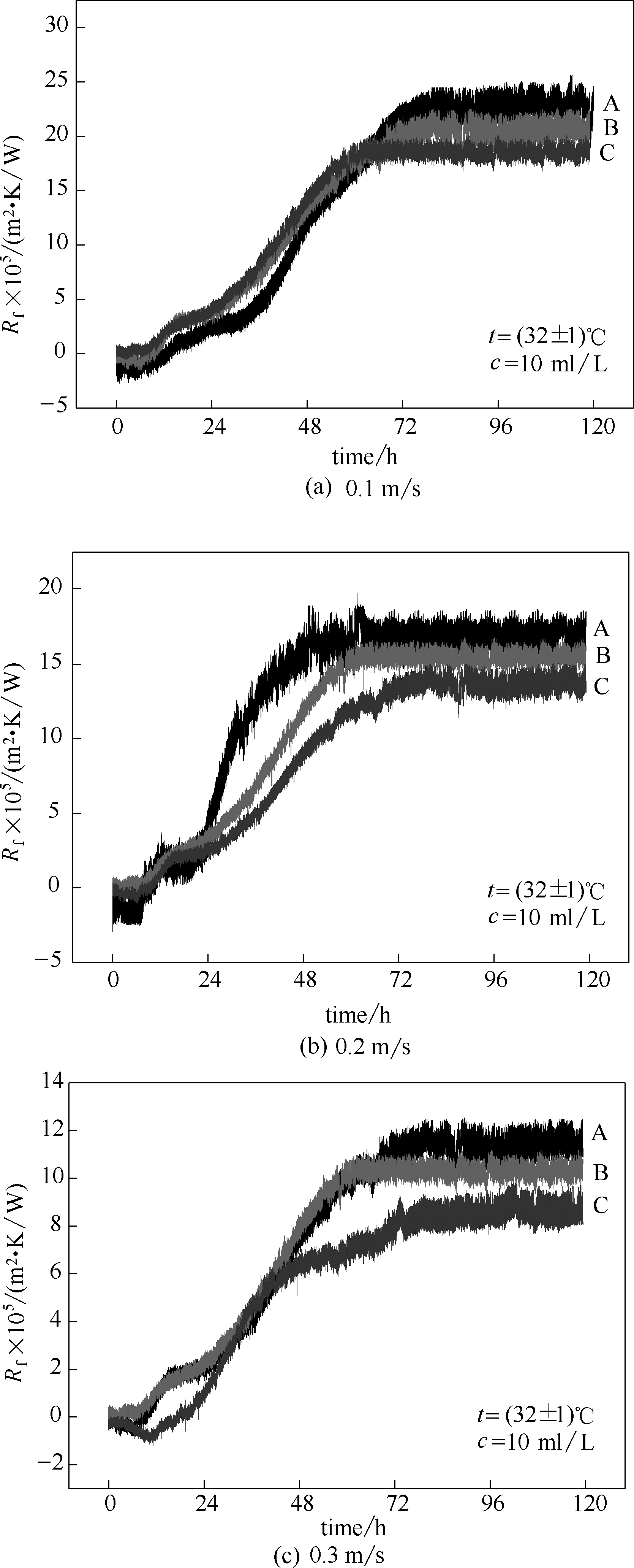
图6 不同流速下不锈钢316板片、Ni-P镀层和Ni-P-TiO2复合纳米镀层表面的污垢热阻A—不锈钢;B—Ni-P镀层;C—Ni-P-TiO2复合纳米镀层
Fig.6 Fouling resistance on stainless steel 316 plates, Ni-P coating and Ni-P-TiO2 composite coating at different flow rates
| 1 | 杨善让, 徐志明, 孙灵芳, 等. 换热设备污垢与对策[M]. 2版. 北京: 科学出版社, 2004: 17. |
| Yang S R, Xu Z M, Sun L F, et al. Fouling and Countermeasures of Heat Exchanger[M]. 2nd ed. Beijing: Science Press, 2004: 17. | |
| 2 | Yang Q, Wilson D I, Chen X, et al. Experimental investigation of interactions between the temperature field and biofouling in a synthetic treated sewage stream[J]. Biofouling, 2013, 29(5): 513-523. |
| 3 | Cao S X, Zhang Y H, Zhang J, et al. Experimental study on dynamic simulation for biofouling resistance prediction by least squares support vector machine[J]. Energy Procedia, 2012, 17(Part A): 74-78. |
| 4 | 王洋, 张晓健, 陈雨乔, 等. 给水管网管壁铁细菌生长特性模拟及控制对策研究[J]. 环境科学, 2009, 30(11): 3293-3299. |
| Wang Y, Zhang X J, Chen Y Q, et al. Growth characteristics and control of iron bacteria on cast iron in drinking water distribution systems[J]. Environmental Science, 2009, 30(11): 3293-3299. | |
| 5 | 崔艳雨, 宁丽纳. 飞机油箱用材7075铝合金在积水环境中的微生物腐蚀规律[J]. 材料保护, 2014, 47(12): 29-32. |
| Cui Y Y, Ning L N. Microbial corrosion of 7075 aluminum alloy for aircraft fuel tank materials in water environment[J]. Materials Protection, 2014, 47(12): 29-32. | |
| 6 | 叶春松, 郝洪铎, 王天平, 等. 微生物菌剂处理循环冷却水的作用原理及其工业应用试验[J]. 环境工程, 2019, 37(8): 42-46. |
| Ye C S, Hao H D, Wang T P, et al. Principle of recirculating cooling water treated with microbial agents and its industrial test[J]. Environmental Engineering, 2019, 37(8): 42-46. | |
| 7 | 常思远, 方宇晴, 史琳, 等. Ca2+浓度对再生水源热泵系统中微生物污垢的影响及作用机理[J]. 制冷学报, 2016, 37(6): 55-60. |
| Chang S Y, Fang Y Q, Shi L, et al. Effect of Ca2+ concentration on microbial fouling in regenerative water source heat pump system and its mechanism[J]. Journal of Refrigeration, 2016, 37(6): 55-60. | |
| 8 | 杨帅. 海水板式换热器微生物污垢特性及传热强化的研究[D]. 青岛: 中国海洋大学, 2014. |
| Yang S. Study on microbial fouling characteristics and heat transfer enhancement of seawater plate heat exchangers[D]. Qingdao: Ocean University of China, 2014. | |
| 9 | 马东. 再生水宽流道板式换热器微生物污垢生长规律及其对传热性能影响的研究[D]. 西安: 西安建筑科技大学, 2017. |
| Ma D. Study on the growth law of microbial fouling and its influence on heat transfer performance of the wide-flow plate heat exchanger of recycled water[D]. Xi􀆳an: Xi􀆳an University of Architecture and Technology, 2017. | |
| 10 | 王蓉. 微生物污垢仿生换热模型及数值模拟[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学, 2018. |
| Wang R. Bionic heat transfer model and numerical simulation of microbial fouling[D]. Harbin: Harbin Institute of Technology, 2018. | |
| 11 | 王晶. 换热器表面蛋白质污垢的生长与清洗及抑垢研究[D]. 苏州: 苏州大学, 2018. |
| Wang J. Study of protein fouling on heat exchanger surface and anti-fouling[D]. Suzhou: Soochow University, 2018. | |
| 12 | Chen X, Yang Q R, Wang R H, et al. Experimental study of the growth characteristics of microbial fouling on sewage heat exchanger surface[J]. Applied Thermal Engineering, 2018, 128: 426-433. |
| 13 | Chandra K, Mahanti A, Singh A P, et al. Microbiologically influenced corrosion of 70/30 cupronickel tubes of a heat-exchanger[J]. Engineering Failure Analysis, 2019, 105: 1328-1339. |
| 14 | Li N, Yang Q, Yao E, et al. Synergism between particulate and microbial fouling on a heat transfer surface using treated sewage water[J]. Applied Thermal Engineering, 2019, 105: 791-802. |
| 15 | Zouaghi S, Six T, Nuns N, et al. Influence of stainless steel surface properties on whey protein fouling under industrial processing conditions[J]. Journal of Food Engineering, 2018, 228: 38-49. |
| 16 | 吕昌旗, 孙玲玲, 王云汉, 等. 换热设备污垢热阻和腐蚀监测技术综述[J]. 现代工业经济和信息化, 2016, 6(6): 73. |
| Lyu C Q, Sun L L, Wang Y H, et al. Review of fouling resistance and corrosion monitoring techniques for heat exchange equipment[J]. Modern Industrial Economy and Information Technology, 2016, 6(6): 73. | |
| 17 | 郭静. 金属材料的表面腐蚀与防护措施分析[J]. 科学技术创新, 2018, (21): 171-172. |
| Guo J. Analysis of surface corrosion and protective measures of metal materials[J]. Science and Technology Innovation, 2018, (21): 171-172. | |
| 18 | 冯刚. 石油化工行业不锈钢的常见腐蚀分析与涂层防护[J]. 涂层与防护, 2018, 39(8): 4-7. |
| Feng G. Corrosion analysis and coating protection for stainless steel in petrochemical industry[J]. Coating and Protection, 2018, 39(8): 4-7. | |
| 19 | Powell C A. Preventing biofouling with copper-nickel alloys[J]. Mater World, 1994, 2(4): 181-183. |
| 20 | 程延海, 朱真才, 韩正铜, 等. 镀层换热表面凝结传热实验研究[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2010, 30(8): 27-31. |
| Cheng Y H, Zhu Z C, Han Z T, et al. Experimental study on condensation and heat transfer of coating heat exchange surface[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2010, 30(8): 27-31. | |
| 21 | Cheng Y H, Zou Y, Cheng L, et al. Effect of the microstructures on the properties of Ni-P deposits on heat transfer surface[J]. Surface and Coatings Technology, 2009, 203(12): 1559-1564. |
| 22 | 杨倩鹏, 田磊, 常思远, 等. 换热表面镀银抑制微生物污垢综合分析[J]. 工程热物理学报, 2014, (2): 354-357. |
| Yang Q P, Tian L, Chang S Y, et al. Comprehensive analysis of inhibition of microbial fouling by silver plating on heat exchange surface[J]. Journal of Engineering Thermophysics, 2014, (2): 354-357. | |
| 23 | Huang K, Goddard J M. Influence of fluid milk product composition on fouling and cleaning of Ni–PTFE modified stainless steel heat exchanger surfaces[J]. Journal of Food Engineering, 2015(158): 22-29. |
| 24 | Zhao Q, Liu C, Su X, et al. Antibacterial characteristics of electroless plating Ni–P–TiO2 coatings[J]. Applied Surface Science, 2013, 274: 101-104. |
| 25 | Jindal S, Anand S, Metzger L, et al. Short communication: a comparison of biofilm development on stainless steel and modified-surface plate heat exchangers during a 17-h milk pasteurization run[J]. Journal of Dairy Science, 2018, 101(4): 2921-2926. |
| 26 | Oldani V, Biella S, Bianchi C L, et al. Perfluoropolyethers coatings design for fouling reduction on heat transfer stainless-steel surfaces[J]. Heat Transfer Engineering, 2016, 37: 210-219. |
| 27 | Balasubramanian S, Puri V M. Thermal energy savings in pilot-scale plate heat exchanger system during product processing using modified surfaces[J]. Journal of Food Engineering, 2009, 91(4): 608-611. |
| 28 | Lukas S, Wolfgang A, Stephan S, et al. Fouling mitigation in food processes by modification of heat transfer surfaces: a review[J]. Food and Bioproducts Processing, 2020, 121: 1-19. |
| 29 | 罗敏, 司徒振明. 液体界面张力的测定方法——悬滴法[J]. 材料工程, 1989, (2): 23-26. |
| Luo M, Situ Z M. Method for measuring liquid interfacial tension— method of hanging-drop[J]. Materials Engineering, 1989, (2): 23-26. | |
| 30 | Bellon-Fontaine M N, Rault J, Oss V. Microbial adhesion to solvents: a novel method to determine the electron-donor/electron-acceptor or Lewis acid-base properties of microbial cells[J]. Colloids & Surface B, 1996, 7(1/2): 47-53. |
| 31 | 张海泉. 板式换热器热工与阻力性能测试及计算方法研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学, 2006. |
| Zhang H Q. Testing and calculate method study on thermal performance and flow pressure drop characteristics of a plate heat exchanger[D]. Harbin: Harbin Institute of Technology, 2006. | |
| 32 | 徐志明, 贾玉婷, 王丙林, 等. 板式换热器铁细菌生物污垢特性的实验分析[J]. 化工学报, 2014, 65(8): 3178-3183. |
| Xu Z M, Jia Y T, Wang B L, et al. Experimental analysis on bio-fouling of iron bacteria on plate heat exchanger[J].CIESC Journal, 2014, 65(8): 3178-3183. | |
| 33 | Webb R L. Heat transfer and friction characteristics of internal helical-rib roughness[J]. Journal of Heat Transfer, 2000, 122(1): 134-142. |
| [1] | 张义飞, 刘舫辰, 张双星, 杜文静. 超临界二氧化碳用印刷电路板式换热器性能分析[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(S1): 183-190. |
| [2] | 程成, 段钟弟, 孙浩然, 胡海涛, 薛鸿祥. 表面微结构对析晶沉积特性影响的格子Boltzmann模拟[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(S1): 74-86. |
| [3] | 晁京伟, 许嘉兴, 李廷贤. 基于无管束蒸发换热强化策略的吸附热池的供热性能研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(S1): 302-310. |
| [4] | 黄磊, 孔令学, 白进, 李怀柱, 郭振兴, 白宗庆, 李平, 李文. 油页岩添加对准东高钠煤灰熔融行为影响的研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(5): 2123-2135. |
| [5] | 何洋, 高森虎, 吴青云, 张明理, 龙涛, 牛佩, 高景辉, 孟颖琪. 析湿工况下平直开缝翅片传热传质特性的数值研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(3): 1073-1081. |
| [6] | 王兵兵, 王超, 徐志明. 圆筒电极抑制换热表面CaCO3污垢沉积特性研究[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(2): 634-642. |
| [7] | 张舒蕾, 李冰杰, 蒋健, 董新宇, 刘璐. 凸面恒温基底上固着液滴蒸发特性研究[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(12): 5537-5546. |
| [8] | 刘坐东, 王禹晨, 邢维维, 赵波, 徐志明. 复合改性表面抑制颗粒污垢积聚特性分析[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(11): 4928-4937. |
| [9] | 顾鋆鋆, 黎睿, 吴兴熠, 汤显强, 胡艳平. 电动导排孔隙水对泥-水界面氮释放通量的控制效果研究[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(11): 5118-5127. |
| [10] | 谢瑶, 李剑锐, 胡海涛. 印刷电路板式换热器内超临界甲烷流动换热特性模拟[J]. 化工学报, 2021, 72(S1): 203-209. |
| [11] | 金默, 刘道银, 陈晓平. 基于离散元方法的高碱煤灰沉积过程数值模拟研究[J]. 化工学报, 2021, 72(4): 1939-1946. |
| [12] | 彭冬根, 徐少华. 蒸发冷却条件下管内LiCl和CaCl2溶液降膜除湿性能对比[J]. 化工学报, 2020, 71(4): 1554-1561. |
| [13] | 张毅,张冠敏,冷学礼,屈晓航,田茂诚. 无霜空气源热泵技术研究进展[J]. 化工学报, 2020, 71(12): 5400-5419. |
| [14] | 丛健,高蓬辉,张东海,周晋鹏,张正函. 超声波对液滴冻结状态及传热的影响[J]. 化工学报, 2020, 71(11): 5117-5128. |
| [15] | 李钰冰, 杨茉, 陆廷康, 戴正华. 具有质热源的方腔内对流传热传质及其非线性特性[J]. 化工学报, 2019, 70(S2): 130-137. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备 11010102001995号
京公网安备 11010102001995号