化工学报 ›› 2021, Vol. 72 ›› Issue (12): 6122-6130.DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20211333
收稿日期:2021-09-14
修回日期:2021-11-09
出版日期:2021-12-05
发布日期:2021-12-22
通讯作者:
李凡星
作者简介:蔡润夏(1991—),男,博士后,Received:2021-09-14
Revised:2021-11-09
Online:2021-12-05
Published:2021-12-22
Contact:
Fanxing LI
Supported by:摘要:
CO2减排已经成为各国发展的重要议题之一。化工产业的传统分离过程由于?效率过低,往往会导致大量的能源浪费及CO2排放。作为一种典型的、耦合分离与反应的过程强化策略,化学链技术有利于实现产物分离、能量梯级利用,从而显著提升系统?效率。高通量计算与化学链技术的结合,可以针对不同化学反应,指导相应的化学链载氧体热力学性质的调变策略。以化学链空气分离、氧化脱氢和热化学储能三个典型过程为例,简述化学链过程中复杂载氧体热力学性质的调变策略。热力学分析表明,不同化学链流程中载氧体性质的优化方向和最优区间均存在显著差异。因此,未来化学链技术发展的重要方向之一,是针对不同的化工流程进行载氧体的精确调变,从而实现化工流程的最优化。
中图分类号:
蔡润夏, 李凡星. 复杂氧化物载氧体的调变策略及在过程强化中的应用[J]. 化工学报, 2021, 72(12): 6122-6130.
Runxia CAI, Fanxing LI. Tailoring the thermodynamic properties of complex oxides for thermochemical air separation and beyond[J]. CIESC Journal, 2021, 72(12): 6122-6130.
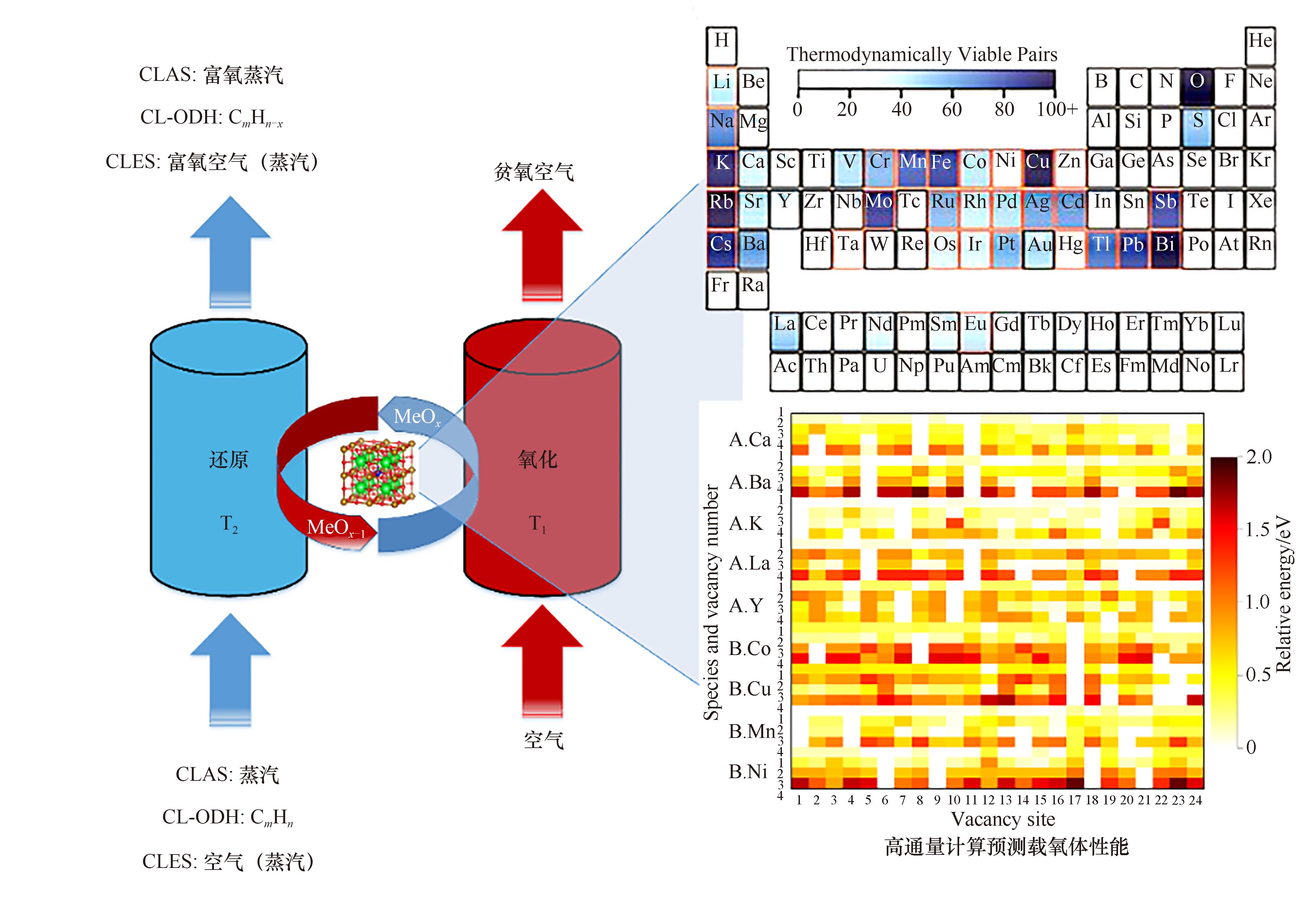
图1 化学链反应系统与载氧体热力学性质的计算预测示意图(右上图引自文献[35])
Fig.1 Schematics of a chemical looping reaction system and computationally predicted redox properties of complex oxides (the upper right figure was cited from Ref.[35])
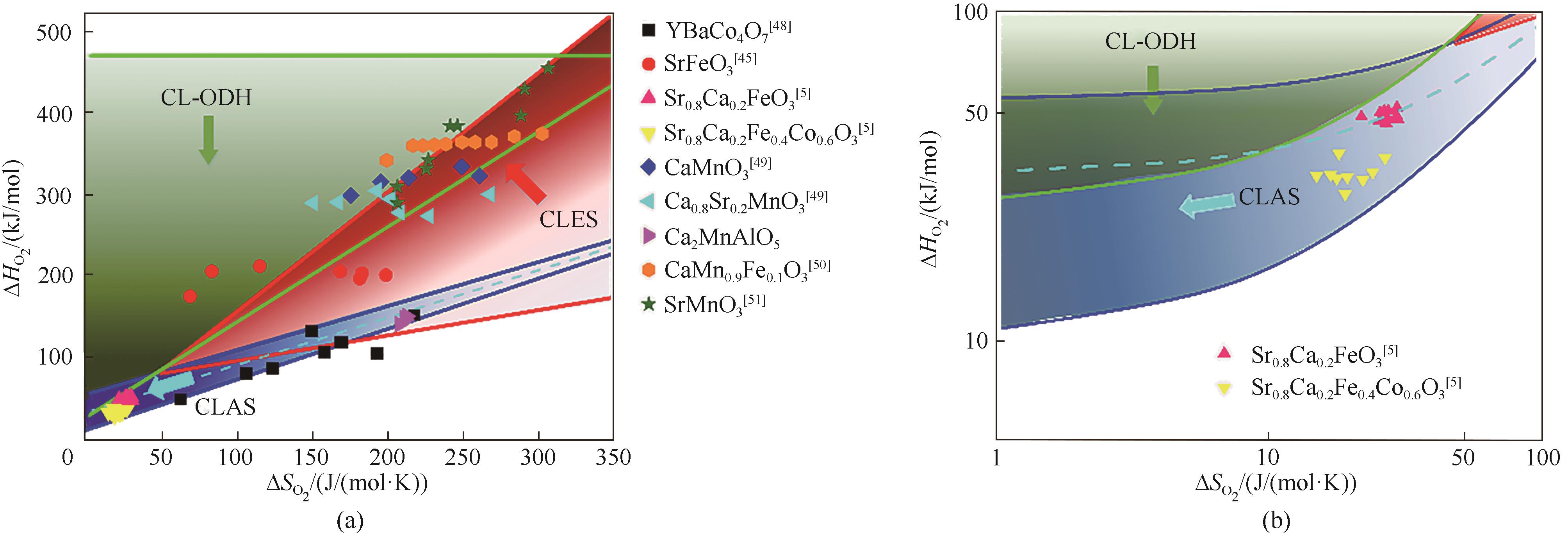
图2 针对不同化学链流程,载氧体热力学性质合适的分布区间:(a)全局视图;(b)低熵、低焓区域放大视图 (部分数据点引自文献[5,45,48-51],Ca2MnAlO5数据源于本课题组正在进行的实验工作)
Fig.2 Desired thermodynamic properties of complex oxides for different chemical looping process: (a) Overview; (b) Callout view of the low entropy and enthalpy region (Some data points were cited from Refs.[5,45,48-51], data for Ca2MnAlO5 were collected from an on-going experimental study in the authors’ research group)
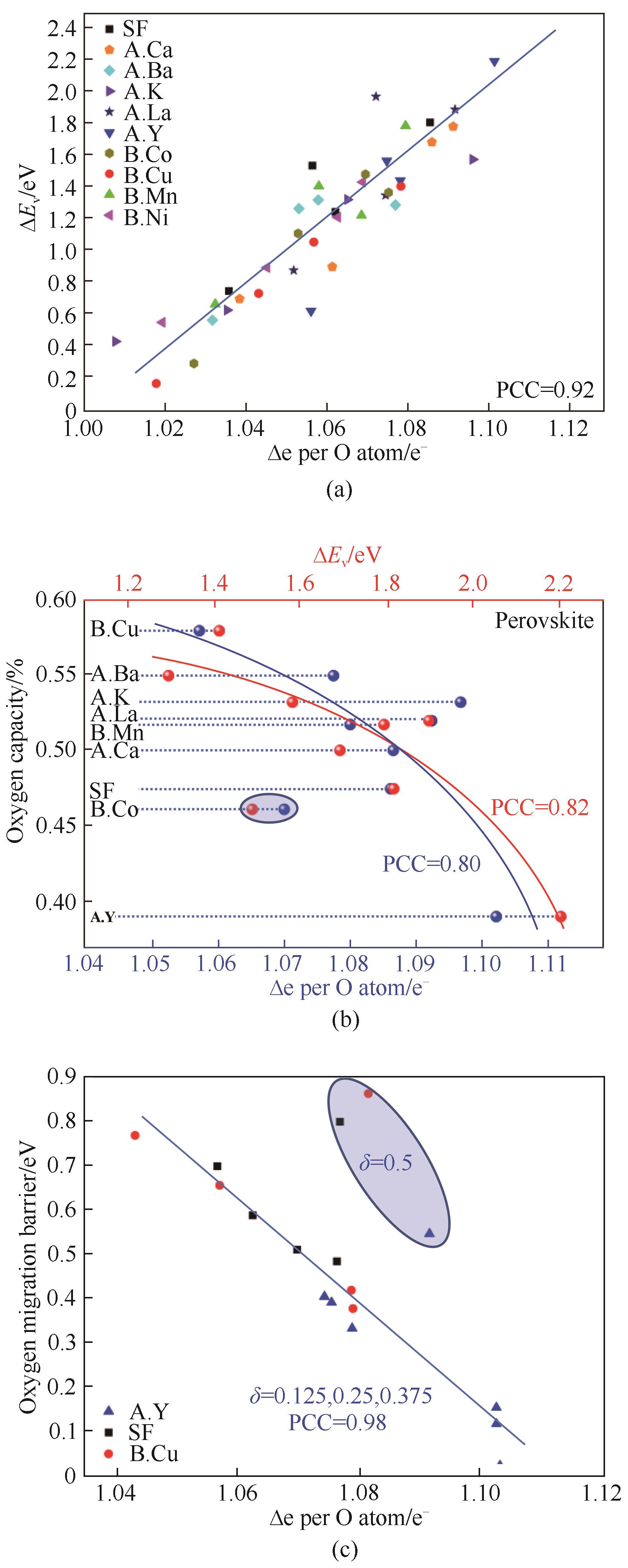
图3 DFT 指导和优化CLAS流程中SrxA1-xFeyB1-yO3-δ载氧体性质:(a)载氧体ΔEv和Δe存在线性关系;(b)实验测得700°C、1%~20%氧分压变压运行得到的氧容量与ΔEv和Δe有很强的关联性;(c)氧气传递能垒也与Δe相关[32]
Fig.3 DFT was used for the design and optimization of SrxA1-xFeyB1-yO3-δoxygen sorbents in the CLAS process: (a) Linear relationship between ΔEv and Δe was observed; (b) Experimental oxygen capacity at 700 °C within 1%-20% PO2 swing as functions of ΔEv and Δe; (c) Oxygen migration barrier as a function of Δe per O atom[32]
| 1 | Fan L S, Zeng L, Wang W, et al. Chemical looping processes for CO2 capture and carbonaceous fuel conversion—prospect and opportunity[J]. Energy & Environmental Science, 2012, 5(6): 7254. |
| 2 | Kenarsari S D, Yang D L, Jiang G D, et al. Review of recent advances in carbon dioxide separation and capture[J]. RSC Advances, 2013, 3(45): 22739. |
| 3 | Ritchie H, Roser M. CO₂ and greenhouse gas emissions[EB/OL]. 2020. . |
| 4 | BoroumandJazi G, Rismanchi B, Saidur R. A review on exergy analysis of industrial sector[J]. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 2013, 27: 198-203. |
| 5 | Dou J, Krzystowczyk E, Wang X J, et al. A- and B-site codoped SrFeO3 oxygen sorbents for enhanced chemical looping air separation[J]. ChemSusChem, 2020, 13(2): 385-393. |
| 6 | Al-Muslim H, Dincer I. Thermodynamic analysis of crude oil distillation systems[J]. International Journal of Energy Research, 2005, 29(7): 637-655. |
| 7 | El-Sayed Y M. Designing desalination systems for higher productivity[J]. Desalination, 2001, 134(1/2/3): 129-158. |
| 8 | Zhu X, Imtiaz Q, Donat F, et al. Chemical looping beyond combustion—a perspective[J]. Energy & Environmental Science, 2020, 13(3): 772-804. |
| 9 | Zhu X, Li K Z, Neal L, et al. Perovskites as geo-inspired oxygen storage materials for chemical looping and three-way catalysis: a perspective[J]. ACS Catalysis, 2018, 8(9): 8213-8236. |
| 10 | Zeng L, Cheng Z, Fan J A, et al. Metal oxide redox chemistry for chemical looping processes[J]. Nature Reviews Chemistry, 2018, 2(11): 349-364. |
| 11 | Adanez J, Abad A, Garcia-Labiano F, et al. Progress in chemical-looping combustion and reforming technologies[J]. Progress in Energy and Combustion Science, 2012, 38(2): 215-282. |
| 12 | Zhao X, Zhou H, Sikarwar V S, et al. Biomass-based chemical looping technologies: the good, the bad and the future[J]. Energy & Environmental Science, 2017, 10(9): 1885-1910. |
| 13 | Lyngfelt A, Leckner B, Mattisson T. A fluidized-bed combustion process with inherent CO2 separation: application of chemical-looping combustion[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2001, 56(10): 3101-3113. |
| 14 | Xu L, Wang J N, Li Z S, et al. Experimental study of cement-supported CuO oxygen carriers in chemical looping with oxygen uncoupling (CLOU)[J]. Energy & Fuels, 2013, 27(3): 1522-1530. |
| 15 | Ma J C, Zhao H B, Tian X, et al. Chemical looping combustion of coal in a 5 kWth interconnected fluidized bed reactor using hematite as oxygen carrier[J]. Applied Energy, 2015, 157: 304-313. |
| 16 | Fan J M, Hong H, Jin H G. Life cycle global warming impact of CO2 capture by in situ gasification chemical looping combustion using ilmenite oxygen carriers[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2019, 234: 568-578. |
| 17 | Zheng Y E, Li K Z, Wang H, et al. Designed oxygen carriers from macroporous LaFeO3 supported CeO2 for chemical-looping reforming of methane[J]. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 2017, 202: 51-63. |
| 18 | Song T, Shen L H. Review of reactor for chemical looping combustion of solid fuels[J]. International Journal of Greenhouse Gas Control, 2018, 76: 92-110. |
| 19 | Bao J H, Li Z S, Cai N S. Promoting the reduction reactivity of ilmenite by introducing foreign ions in chemical looping combustion[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2013, 52(18): 6119-6128. |
| 20 | He F, Li H B, Zhao Z L. Advancements in development of chemical-looping combustion: a review[J]. International Journal of Chemical Engineering, 2009, 2009: 1-16. |
| 21 | Fan J M, Hong H, Zhu L, et al. Thermodynamic and environmental evaluation of biomass and coal co-fuelled gasification chemical looping combustion with CO2 capture for combined cooling, heating and power production[J]. Applied Energy, 2017, 195: 861-876. |
| 22 | Voitic G, Hacker V. Recent advancements in chemical looping water splitting for the production of hydrogen[J]. RSC Advances, 2016, 6(100): 98267-98296. |
| 23 | Gao Y F, Neal L M, Ding D, et al. Recent advances in intensified ethylene production—a review[J]. ACS Catalysis, 2019, 9(9): 8592-8621. |
| 24 | Li F X, Kim H R, Sridhar D, et al. Syngas chemical looping gasification process: oxygen carrier particle selection and performance[J]. Energy & Fuels, 2009, 23(8): 4182-4189. |
| 25 | Bao J H, Li Z S, Cai N S. Interaction between iron-based oxygen carrier and four coal ashes during chemical looping combustion[J]. Applied Energy, 2014, 115: 549-558. |
| 26 | Ge H J, Guo W J, Shen L H, et al. Biomass gasification using chemical looping in a 25 kWth reactor with natural hematite as oxygen carrier[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2016, 286: 174-183. |
| 27 | Zhao K, He F, Huang Z, et al. Perovskite-type oxides LaFe1-xCoxO3 for chemical looping steam methane reforming to syngas and hydrogen co-production[J]. Applied Energy, 2016, 168: 193-203. |
| 28 | Zhu Y Y, Jin N N, Liu R L, et al. Bimetallic BaFe2MAl9O19 (M=Mn, Ni, and Co) hexaaluminates as oxygen carriers for chemical looping dry reforming of methane[J]. Applied Energy, 2020, 258: 114070. |
| 29 | Kang Y, Han Y J, Tian M, et al. Promoted methane conversion to syngas over Fe-based garnets via chemical looping[J]. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 2020, 278: 119305. |
| 30 | Lyngfelt A. Chemical-looping combustion of solid fuels—status of development[J]. Applied Energy, 2014, 113: 1869-1873. |
| 31 | Vieten J, Bulfin B, Huck P, et al. Materials design of perovskite solid solutions for thermochemical applications[J]. Energy & Environmental Science, 2019, 12(4): 1369-1384. |
| 32 | Wang X J, Krzystowczyk E, Dou J, et al. Net electronic charge as an effective electronic descriptor for oxygen release and transport properties of SrFeO3-based oxygen sorbents[J]. Chemistry of Materials, 2021, 33(7): 2446-2456. |
| 33 | Lau C Y, Dunstan M T, Hu W T, et al. Large scale in silico screening of materials for carbon capture through chemical looping[J]. Energy & Environmental Science, 2017, 10(3): 818-831. |
| 34 | Emery A A, Saal J E, Kirklin S, et al. High-throughput computational screening of perovskites for thermochemical water splitting applications[J]. Chemistry of Materials, 2016, 28(16):5621-5634. |
| 35 | Singstock N R, Bartel C J, Holder A M, et al. High-throughput analysis of materials for chemical looping processes[J]. Advanced Energy Materials, 2020, 10(27): 2000685. |
| 36 | Air separation plant market by process (cryogenic, non-cryogenic), (nitrogen gas, oxygen, argon, others), end-use industry (iron & steel, oil & gas, chemical, healthcare, others) and region-global forecast to 2026[EB/OL].2021.. |
| 37 | Fu Q, Kansha Y, Song C F, et al. A cryogenic air separation process based on self-heat recuperation for oxy-combustion plants[J]. Applied Energy, 2016, 162: 1114-1121. |
| 38 | Moghtaderi B. Application of chemical looping concept for air separation at high temperatures[J]. Energy & Fuels, 2010, 24(1): 190-198. |
| 39 | Tian X, Wei Y J, Zhao H B. Using a hierarchically-structured CuO@TiO2-Al2O3 oxygen carrier for chemical looping air separation in a paralleled fluidized bed reactor[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2018, 334: 611-618. |
| 40 | Popczun E J, Jia T, Natesakhawat S, et al. Investigation of Sr0.7Ca0.3FeO3 oxygen carriers with variable cobalt B-site substitution[J]. ChemSusChem, 2021, 14(8): 1893-1901. |
| 41 | Xu M, Wu H C, Lin Y S, et al. Simulation and optimization of pressure swing adsorption process for high-temperature air separation by perovskite sorbents[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2018, 354: 62-74. |
| 42 | Dou J, Krzystowczyk E, Wang X J, et al. Sr1-xCaxFe1-yCoyO3-δ as facile and tunable oxygen sorbents for chemical looping air separation[J]. Journal of Physics: Energy, 2020, 2(2): 025007. |
| 43 | Cai R X, Dou J, Krzystowczyk E, et al. Chemical looping air separation with Sr0.8Ca0.2Fe0.9Co0.1O3-δ perovskite sorbent: packed bed modeling, verification, and optimization[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2022, 429: 132370. |
| 44 | Cormos C C. Energy and cost efficient manganese chemical looping air separation cycle for decarbonized power generation based on oxy-fuel combustion and gasification[J]. Energy, 2020, 191: 116579. |
| 45 | Bulfin B, Lapp J, Richter S, et al. Air separation and selective oxygen pumping via temperature and pressure swing oxygen adsorption using a redox cycle of SrFeO3 perovskite[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2019, 203: 68-75. |
| 46 | Saghafifar M, Scott S A. The use of high decomposition temperature materials for chemical looping electricity storage[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2021, 423: 128789. |
| 47 | Krzystowczyk E, Wang X J, Dou J, et al. Substituted SrFeO3 as robust oxygen sorbents for thermochemical air separation: correlating redox performance with compositional and structural properties[J]. Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics, 2020, 22(16): 8924-8932. |
| 48 | Tsvetkov D S, Maram P S, Tsvetkova N S, et al. High-resolution thermochemical study of phase stability and rapid oxygen incorporation in YBaCo4–xZnxO7+δ 114-cobaltites[J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry A, 2018, 122(50): 9597-9604. |
| 49 | Bulfin B, Vieten J, Starr D E, et al. Redox chemistry of CaMnO3 and Ca0.8Sr0.2MnO3 oxygen storage perovskites[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2017, 5(17): 7912-7919. |
| 50 | Mastronardo E, Qian X, Coronado J M, et al. Impact of La doping on the thermochemical heat storage properties of CaMnO3-δ[J]. Journal of Energy Storage, 2021, 40: 102793. |
| 51 | Vieten J, Bulfin B, Senholdt M, et al. Redox thermodynamics and phase composition in the system SrFeO3- δ-SrMnO3- δ [J]. Solid State Ionics, 2017, 308: 149-155. |
| 52 | Krzystowczyk E, Haribal V, Dou J, et al. Chemical looping air separation using a perovskite-based oxygen sorbent: system design and process analysis[J]. ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering, 2021, 9(36): 12185-12195. |
| 53 | Cavani F, Ballarini N, Cericola A. Oxidative dehydrogenation of ethane and propane: How far from commercial implementation? [J]. Catalysis Today, 2007, 127(1/2/3/4): 113-131. |
| 54 | Dudek R B, Tian X, Blivin M, et al. Perovskite oxides for redox oxidative cracking of n-hexane under a cyclic redox scheme[J]. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 2019, 246: 30-40. |
| 55 | Dudek R B, Li F X. Selective hydrogen combustion as an effective approach for intensified chemical production via the chemical looping strategy[J]. Fuel Processing Technology, 2021, 218: 106827. |
| 56 | Zhu X, Gao Y F, Wang X J, et al. A tailored multi-functional catalyst for ultra-efficient styrene production under a cyclic redox scheme[J]. Nature Communications, 2021, 12(1): 1329. |
| 57 | Chen S, Chang X, Sun G D, et al. Propane dehydrogenation: catalyst development, new chemistry, and emerging technologies[J]. Chemical Society Reviews, 2021, 50(5): 3315-3354. |
| 58 | Chen S, Zeng L, Mu R T, et al. Modulating lattice oxygen in dual-functional Mo-V-O mixed oxides for chemical looping oxidative dehydrogenation[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2019, 141(47): 18653-18657. |
| 59 | Ding W X, Zhao K, Jiang S C, et al. Alkali-metal enhanced LaMnO3 perovskite oxides for chemical looping oxidative dehydrogenation of ethane[J]. Applied Catalysis A: General, 2021, 609: 117910. |
| 60 | Neal L M, Yusuf S, Sofranko J A, et al. Oxidative dehydrogenation of ethane: a chemical looping approach[J]. Energy Technology, 2016, 4(10): 1200-1208. |
| 61 | Yusuf S, Haribal V, Jackson D, et al. Mixed iron-manganese oxides as redox catalysts for chemical looping-oxidative dehydrogenation of ethane with tailorable heat of reactions[J]. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 2019, 257: 117885. |
| 62 | Gao Y F, Wang X J, Liu J C, et al. A molten carbonate shell modified perovskite redox catalyst for anaerobic oxidative dehydrogenation of ethane[J]. Science Advances, 2020, 6(17): eaaz9339. |
| 63 | Liu J C, Gao Y F, Wang X J, et al. Molten-salt-mediated carbon dioxide capture and superequilibrium utilization with ethane oxidative dehydrogenation[J]. Cell Reports Physical Science, 2021, 2(7): 100503. |
| 64 | Wang T, Gao Y F, Liu Y Z, et al. Core-shell Na2WO4/CuMn2O4 oxygen carrier with high oxygen capacity for chemical looping oxidative dehydrogenation of ethane[J]. Fuel, 2021, 303: 121286. |
| 65 | Tian X, Zheng C H, Li F X, et al. Co and Mo co-doped Fe2O3 for selective ethylene production via chemical looping oxidative dehydrogenation[J]. ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering, 2021, 9(23): 8002-8011. |
| 66 | Brody L, Neal L M, Haribal V, et al. Ethane to liquids via a chemical looping approach—redox catalyst demonstration and process analysis[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2021, 417: 128886. |
| 67 | Yusuf S, Neal L M, Li F X. Effect of promoters on manganese-containing mixed metal oxides for oxidative dehydrogenation of ethane via a cyclic redox scheme[J]. ACS Catalysis, 2017, 7(8): 5163-5173. |
| 68 | Gao Y F, Neal L M, Li F X. Li-promoted LaxSr2–xFeO4–δ core–shell redox catalysts for oxidative dehydrogenation of ethane under a cyclic redox scheme[J]. ACS Catalysis, 2016, 6(11): 7293-7302. |
| 69 | Haribal V P, Neal L M, Li F X. Oxidative dehydrogenation of ethane under a cyclic redox scheme—process simulations and analysis[J]. Energy, 2017, 119: 1024-1035. |
| 70 | Yusuf S, Neal L, Haribal V, et al. Manganese silicate based redox catalysts for greener ethylene production via chemical looping - oxidative dehydrogenation of ethane[J]. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 2018, 232: 77-85. |
| 71 | Neal L M, Haribal V P, Li F X. Intensified ethylene production via chemical looping through an exergetically efficient redox scheme[J]. iScience, 2019, 19: 894-904. |
| 72 | Imponenti L, Albrecht K J, Wands J W, et al. Thermochemical energy storage in strontium-doped calcium manganites for concentrating solar power applications[J]. Solar Energy, 2017, 151: 1-13. |
| 73 | Saghafifar M, Schnellmann M A, Scott S A. Chemical looping electricity storage[J]. Applied Energy, 2020, 279: 115553. |
| 74 | Sunku Prasad J, Muthukumar P, Desai F, et al. A critical review of high-temperature reversible thermochemical energy storage systems[J]. Applied Energy, 2019, 254: 113733. |
| 75 | Sarbu I, Sebarchievici C. A comprehensive review of thermal energy storage[J]. Sustainability, 2018, 10(1): 191. |
| 76 | Bell S, Steinberg T, Will G. Corrosion mechanisms in molten salt thermal energy storage for concentrating solar power[J]. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 2019, 114: 109328. |
| 77 | Yan Y L, Wang K, Clough P T, et al. Developments in calcium/chemical looping and metal oxide redox cycles for high-temperature thermochemical energy storage: a review[J]. Fuel Processing Technology, 2020, 199: 106280. |
| 78 | Jin F, Xu C, Yu H Y, et al. CaCo0.05Mn0.95O3–δ: a promising perovskite solid solution for solar thermochemical energy storage[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2021, 13(3): 3856-3866. |
| 79 | Chen X Y, Kubota M, Yamashita S, et al. Investigation of Sr-based perovskites for redox-type thermochemical energy storage media at medium-high temperature[J]. Journal of Energy Storage, 2021, 38: 102501. |
| 80 | Wu S K, Zhou C, Doroodchi E, et al. A review on high-temperature thermochemical energy storage based on metal oxides redox cycle[J]. Energy Conversion and Management, 2018, 168: 421-453. |
| 81 | Mastronardo E, Qian X, Coronado J M, et al. The favourable thermodynamic properties of Fe-doped CaMnO3 for thermochemical heat storage[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2020, 8(17): 8503-8517. |
| 82 | Mishra A, Li T Y, Li F X, et al. Oxygen vacancy creation energy in Mn-containing perovskites: an effective indicator for chemical looping with oxygen uncoupling[J]. Chemistry of Materials, 2018, 31(3):689-98. |
| 83 | Galinsky N, Mishra A, Zhang J, et al. Ca1-xAxMnO3 (A = Sr and Ba) perovskite based oxygen carriers for chemical looping with oxygen uncoupling (CLOU)[J]. Applied Energy, 2015, 157: 358-367. |
| 84 | Maiti D, Hare B J, Daza Y A, et al. Earth abundant perovskite oxides for low temperature CO2 conversion[J]. Energy & Environmental Science, 2018, 11(3): 648-659. |
| 85 | Ezbiri M, Allen K M, Gàlvez M E, et al. Design principles of perovskites for thermochemical oxygen separation[J]. ChemSusChem, 2015, 8(11): 1966-1971. |
| [1] | 范孝雄, 郝丽芳, 范垂钢, 李松庚. LaMnO3/生物炭催化剂低温NH3-SCR催化脱硝性能研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(9): 3821-3830. |
| [2] | 傅予, 刘兴翀, 王瀚雨, 李海敏, 倪亚飞, 邹文静, 雷月, 彭永姗. F3EACl修饰层对钙钛矿太阳能电池性能提升的研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(8): 3554-3563. |
| [3] | 李盼, 马俊洋, 陈志豪, 王丽, 郭耘. Ru/α-MnO2催化剂形貌对NH3-SCO反应性能的影响[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(7): 2908-2918. |
| [4] | 周小文, 杜杰, 张战国, 许光文. 基于甲烷脉冲法的Fe2O3-Al2O3载氧体还原特性研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(6): 2611-2623. |
| [5] | 孙永尧, 高秋英, 曾文广, 王佳铭, 陈艺飞, 周永哲, 贺高红, 阮雪华. 面向含氮油田伴生气提质利用的膜耦合分离工艺设计优化[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(5): 2034-2045. |
| [6] | 刘倩, 曹禹, 周琦, 穆景山, 历伟. 孔道结构修饰的Ziegler-Natta催化剂设计与高抗冲低缠结UHMWPE的制备[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(3): 1092-1101. |
| [7] | 陈号, 田仪娟, 全学军, 蒋子文, 李纲. 铬铁矿在HCl-HF体系中的分解行为[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(3): 1161-1174. |
| [8] | 王锋, 陈钰, 裴鸿艳, 刘东东, 张静, 张立新. 1,2,4-𫫇二唑类衍生物的设计、合成及抗菌活性[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(3): 1390-1398. |
| [9] | 孙嘉辰, 裴春雷, 陈赛, 赵志坚, 何盛宝, 巩金龙. 化学链低碳烷烃氧化脱氢技术进展[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(1): 205-223. |
| [10] | 张婉晨, 陈晓阳, 吕秋秋, 钟秦, 朱腾龙. Co掺杂SrTi0.3Fe0.7O3-δ 阳极SOFC在化工副产气燃料下的性能及稳定性[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(9): 4079-4086. |
| [11] | 袁妮妮, 郭拓, 白红存, 何育荣, 袁永宁, 马晶晶, 郭庆杰. 化学链燃烧过程Fe2O3/Al2O3载氧体表面CH4反应:ReaxFF-MD模拟[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(9): 4054-4061. |
| [12] | 侯跃辉, 刘璇, 廉应江, 韩梅, 尧超群, 陈光文. 超声微反应器内三硝基间苯三酚合成工艺研究[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(8): 3597-3607. |
| [13] | 艾承燚, 乔金硕, 王振华, 孙旺, 孙克宁. 原位析出纳米合金的PrBaFe2O6-δ 基阳极构筑及其在固体碳燃料电池中的应用研究[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(8): 3708-3719. |
| [14] | 徐珂, 史国强, 薛冬峰. 无机杂化钙钛矿团簇材料:介尺度钙钛矿材料发光性质研究[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(6): 2748-2756. |
| [15] | 刘梦溪, 范怡平, 闫子涵, 姚秀颖, 卢春喜. 提升管进料区内气体射流流动行为的调控及工业应用[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(6): 2496-2513. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备 11010102001995号
京公网安备 11010102001995号
