化工学报 ›› 2019, Vol. 70 ›› Issue (3): 791-800.DOI: 10.11949/j.issn.0438-1157.20181067
曾少娟1( ),尚大伟1,余敏1,2,陈昊3,董海峰1,张香平1(
),尚大伟1,余敏1,2,陈昊3,董海峰1,张香平1( )
)
收稿日期:2018-09-25
修回日期:2018-12-07
出版日期:2019-03-05
发布日期:2019-03-05
通讯作者:
张香平
作者简介:<named-content content-type="corresp-name">曾少娟</named-content>(1982—),女,博士,副研究员,<email>sjzeng@ipe.ac.cn</email>|张香平(1969—),女,博士,研究员,<email>xpzhang@ipe.ac.cn</email>
基金资助:
Shaojuan ZENG1( ),Dawei SHANG1,Min YU1,2,Hao CHEN3,Haifeng DONG1,Xiangping ZHANG1(
),Dawei SHANG1,Min YU1,2,Hao CHEN3,Haifeng DONG1,Xiangping ZHANG1( )
)
Received:2018-09-25
Revised:2018-12-07
Online:2019-03-05
Published:2019-03-05
Contact:
Xiangping ZHANG
摘要:
氨(NH3)是典型有毒有害工业气态污染物,也是形成PM2.5中二次颗粒物的根本原因之一,大量含氨气体的排放严重威胁人类的生活环境和健康。采用传统的酸法或水法,通常存在腐蚀性强、污染重、能耗高等问题,且难以回收利用氨资源。离子液体因其极低的挥发性、较好的化学/热稳定性、酸碱可调及高的氨溶解度等特点,为高效低能耗NH3分离提供了新途径。综述了近年来国内外离子液体在NH3分离中的研究进展,重点总结了常规离子液体、功能离子液体及离子液体溶剂/材料对NH3的吸收/吸附性能,阐明了阴阳离子、功能基团对NH3吸收性能的影响规律及其吸收机理,并探讨了该方向的研究和发展趋势。
中图分类号:
曾少娟, 尚大伟, 余敏, 陈昊, 董海峰, 张香平. 离子液体在氨气分离回收中的应用及展望[J]. 化工学报, 2019, 70(3): 791-800.
Shaojuan ZENG, Dawei SHANG, Min YU, Hao CHEN, Haifeng DONG, Xiangping ZHANG. Applications and perspectives of NH3 separation and recovery with ionic liquids[J]. CIESC Journal, 2019, 70(3): 791-800.

图3 [Emim][NTf2]阴阳离子与NH3相互作用及径向分布[16]
Fig.3 Interactions and molecular dynamics simulations between NH3 and [Emim][NTf2][16](copyright 2009 John Wiley and Sons)
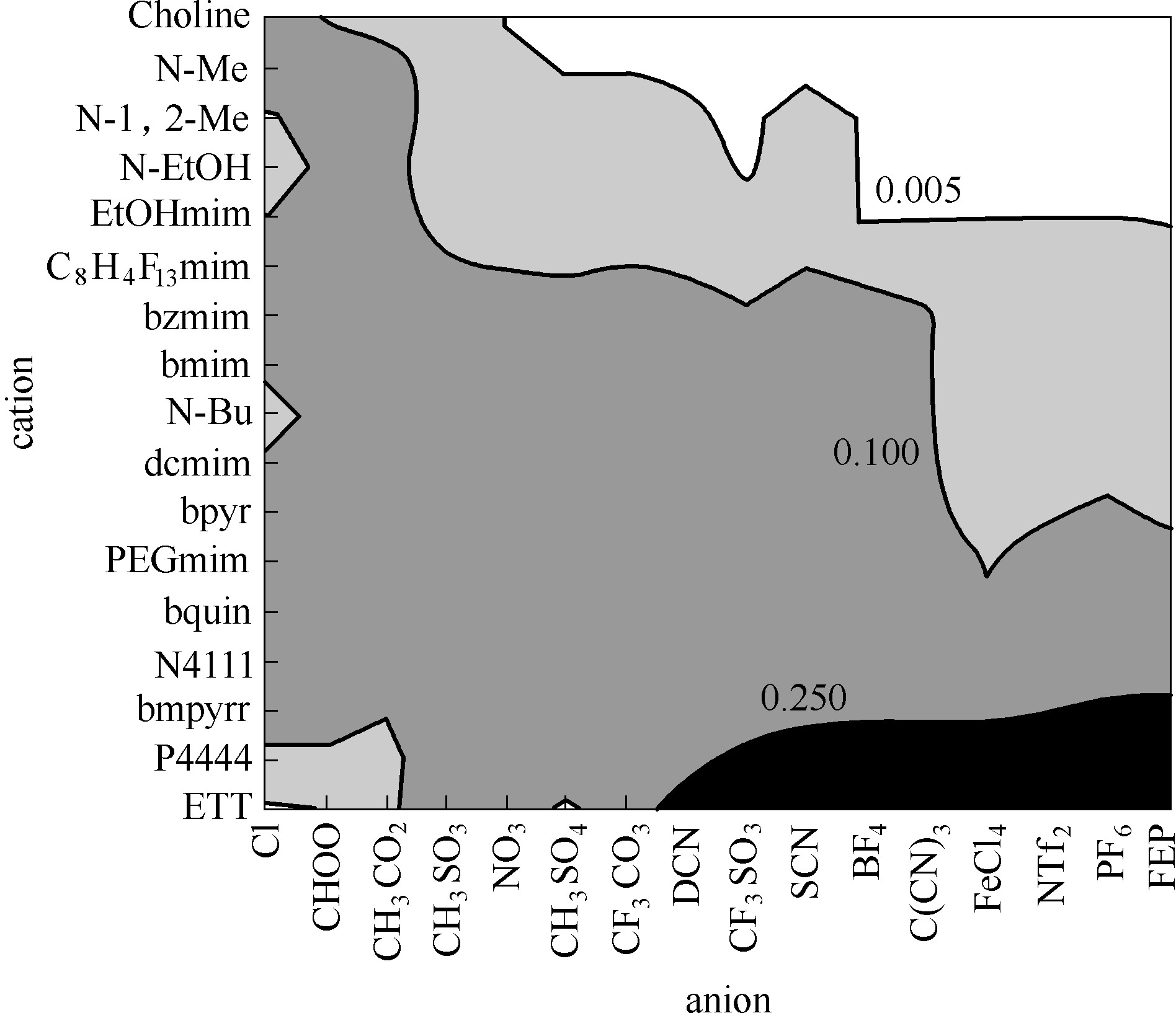
图4 采用COSMO-RS 预测的25℃时NH3在272种离子液体的Henry常数[31]
Fig.4 Predicted Henry’s law constants (MPa) of NH3 in 272 ILs at 25℃ calculated by COSMO-RS[31] (copyright 2011 Elservier)
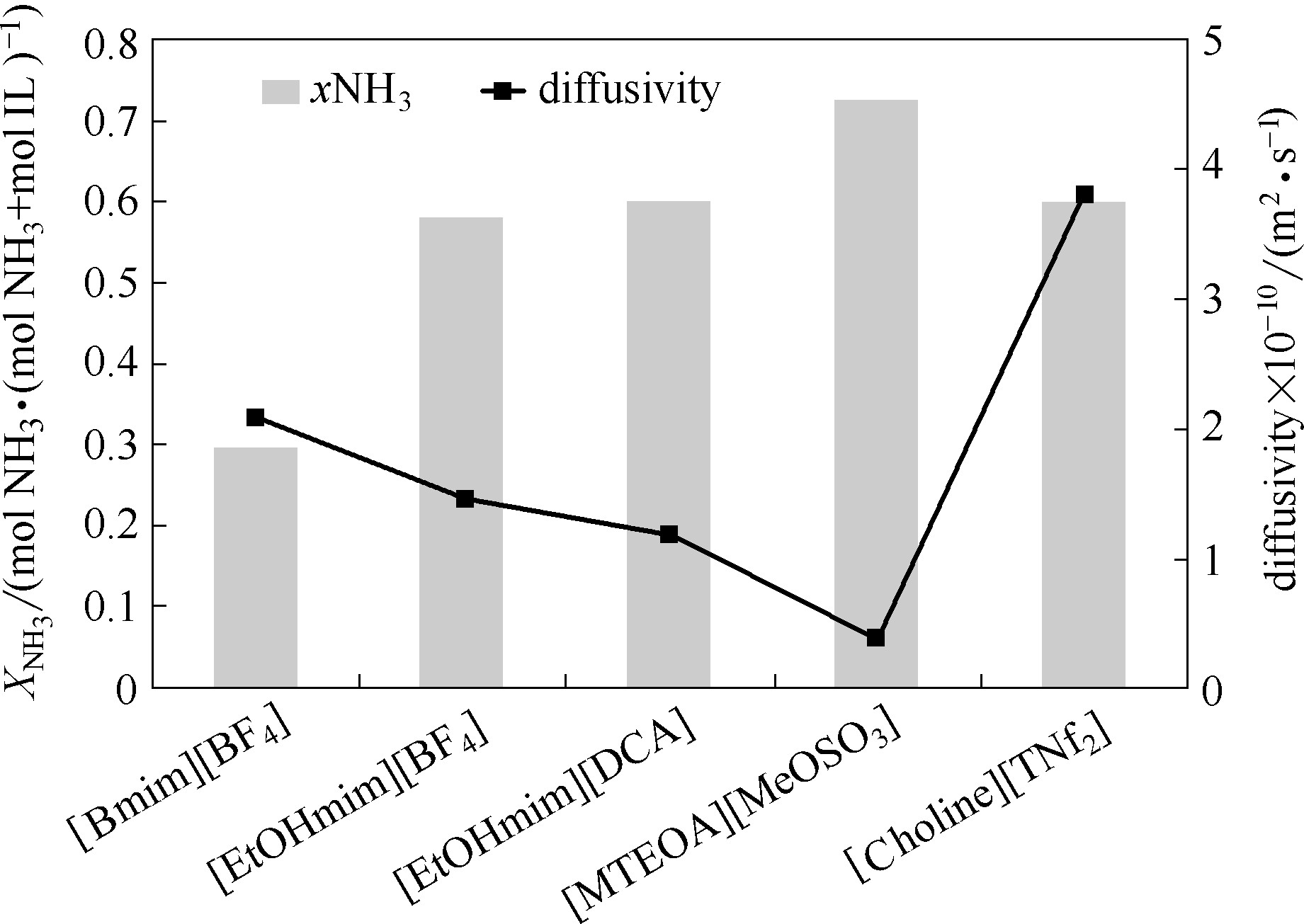
图5 20℃和常压下羟基离子液体对NH3吸收量和表观扩散系数[33]
Fig.5 NH3 solubility and apparent diffusion coefficients in hydroxyl ILs at 20℃ and atmospheric pressure[33] (copyright 2012 Elservier)
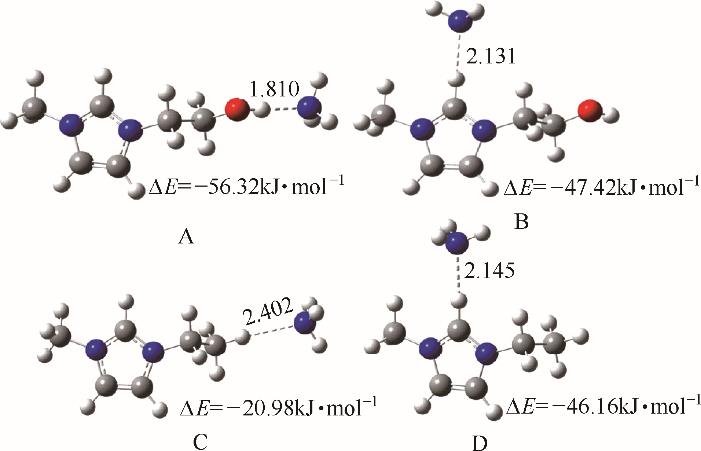
图6 [EOHmim]+-NH3(A和B)和[Emim]+-NH3(C和D)间的结构优化和相互作用[38](O:红色;N:蓝色;H:白色;C:灰色)
Fig.6 Optimized structures and interaction energies for [EOHmim]+-NH3 (A and B) and [Emim]+ -NH 3 (C and D) systems[38] (O, red; N, blue; H, white; C, gray) (copyright 2015 Royal Society of Chemistry)

图8 30℃和常压下[Cnmim]2[Co(NCS)4] 和 [Cnmim][SCN]对NH3的吸收[44]
Fig.8 NH3 absorption in [Cnmim]2[Co(NCS)4] and [Cnmim][SCN] at 30℃ and 101 kPa[44] (copyright 2015 Royal Society of Chemistry)
| 离子液体种类 | 吸收温度/℃ | 压力/kPa | NH3吸收量 | 参考文献 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| /(mol NH3?(mol absorbent)-1) | /(g NH3?(g absorbent)-1) | ||||
| [Emim][BF4] | 20 | 140 | 0.274 | 0.024 | [ |
| [Emim][BF4] | 25 | 110 | 0.173 | 0.015 | [ |
| [Bmim][BF4] | 25 | 220 | 0.465 | 0.035 | [ |
| [Hmim][BF4] | 25 | 220 | 0.581 | 0.039 | [ |
| [Omim][BF4] | 25 | 120 | 0.387 | 0.025 | [ |
| [Bmim][PF6] | 25 | 174 | 0.538 | 0.032 | [ |
| [Bmim][BF4] | 25.4 | 101 | 0.112 | 0.008 | [ |
| [Emim][NTf2] | 26.4 | 101 | 0.122 | 0.005 | [ |
| [Hmim][Cl] | 24.8 | 101 | 0.252 | 0.021 | [ |
| [Emim][Ac] | 25.3 | 101 | 0.348 | 0.035 | [ |
| [Emim][EtOSO3] | 24.6 | 101 | 0.342 | 0.025 | [ |
| [Emim][SCN] | 25 | 101 | 0.188 | 0.019 | [ |
| [DMEA][Ac] | 25 | 163 | 0.905 | 0.103 | [ |
| [Bmim][BF4] | 20 | 101 | 0.449 | 0.034 | [ |
| [EOHmim][BF4] | 20 | 101 | 1.703 | 0.135 | [ |
| [Choline][NTf2] | 20 | 101 | 1.857 | 0.064 | [ |
| [MTEOA][MeOSO3] | 20 | 101 | 3.545 | 0.219 | [ |
| [MTEOA][MeOSO3] | 40 | 101 | 1.381 | 0.085 | [ |
| [EtOHmim][DCA] | 20 | 101 | 2.125 | 0.190 | [ |
| [EtOHmim][DCA] | 40 | 100 | 0.887 | 0.079 | [ |
| [EtOHmim][NTf2] | 25 | 105.5 | 0.976 | 0.041 | [ |
| [EtOHmim][PF6] | 25 | 106.8 | 0.980 | 0.062 | [ |
| [EtOHmim][BF4] | 25 | 98.9 | 0.825 | 0.066 | [ |
| [EtOHmim][SCN] | 25 | 95.3 | 0.538 | 0.050 | [ |
| [EtOHmim][DCA] | 25 | 108.5 | 0.600 | 0.054 | [ |
| [EtOHmim][NO3] | 25 | 106.6 | 0.522 | 0.047 | [ |
| [Eim][NTf2] | 40 | 105.12 | 2.73 | 0.123 | [ |
| [Mim][NTf2] | 40 | 102.71 | 2.68 | 0.128 | [ |
| [Mmim][NTf2] | 40 | 98.63 | 2.40 | 0.108 | [ |
| [Bmmim][NTf2] | 30 | 119.43 | 0.25 | 0.010 | [ |
| [Bmmim][NTf2] | 40 | 100.49 | 0.20 | 0.008 | [ |
| [Bmmim][NTf2] | 60 | 114.60 | 0.19 | 0.008 | [ |
| [Bim][SCN] | 30 | 98.82 | 2.18 | 0.202 | [ |
| [Bim][SCN] | 40 | 96.59 | 1.96 | 0.182 | [ |
| [Bim][SCN] | 60 | 102.56 | 1.56 | 0.145 | [ |
| [Bmim][SCN] | 40 | 82.92 | 0.15 | 0.013 | [ |
| [Bmim][SCN] | 60 | 79.87 | 0.09 | 0.008 | [ |
| [Bim][NO3] | 30 | 100.09 | 1.50 | 0.136 | [ |
| [Bim][NO3] | 40 | 141.53 | 1.72 | 0.156 | [ |
| [Bim][NO3] | 60 | 122.40 | 1.14 | 0.104 | [ |
| [Bmim][DCA] | 30 | 114.28 | 0.30 | 0.025 | [ |
| [Bmim][DCA] | 40 | 128.32 | 0.22 | 0.018 | [ |
| [Bmim][DCA] | 60 | 104.86 | 0.13 | 0.011 | [ |
| [Bmmim][DCA] | 30 | 115.38 | 0.25 | 0.020 | [ |
| [Bmmim][DCA] | 40 | 103.42 | 0.12 | 0.009 | [ |
| [Bmmim][DCA] | 60 | 126.48 | 0.14 | 0.011 | [ |
| [Bim][NTf2] | 40 | 101 | 2.69 | 0.113 | [ |
| [Bmim][NTf2] | 40 | 101 | 0.28 | 0.011 | [ |
| [HOOC(CH2)3mim][NTf2] | 40 | 101 | 1.54 | 0.059 | [ |
| [Bmim][Zn2Cl5] | 50 | 103.5 | 8.025 | 0.305 | [ |
| [Emim]2[Co(NCS)4] | 30 | 101 | 5.99 | 0.198 | [ |
| [Bmim]2[Co(NCS)4] | 30 | 101 | 6.03 | 0.180 | [ |
| [Hmim]2[Co(NCS)4] | 30 | 101 | 6.09 | 0.166 | [ |
| [Emim][SCN] | 30 | 101 | 0.18 | 0.018 | [ |
| [Bmim][SCN] | 30 | 101 | 0.19 | 0.016 | [ |
| [Hmim][SCN] | 30 | 101 | 0.20 | 0.015 | [ |
| [Bmim][MeSO3]/urea(1∶1) | 30 | 123.6 | — | 0.015 | [ |
| ChCl/Res/Gly (1∶3∶5) | 40 | 101 | — | 0.130 | [ |
表1 文献报道的不同离子液体对NH3的吸收量
Table 1 NH3 capacities of different ionic liquids reported in literatures
| 离子液体种类 | 吸收温度/℃ | 压力/kPa | NH3吸收量 | 参考文献 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| /(mol NH3?(mol absorbent)-1) | /(g NH3?(g absorbent)-1) | ||||
| [Emim][BF4] | 20 | 140 | 0.274 | 0.024 | [ |
| [Emim][BF4] | 25 | 110 | 0.173 | 0.015 | [ |
| [Bmim][BF4] | 25 | 220 | 0.465 | 0.035 | [ |
| [Hmim][BF4] | 25 | 220 | 0.581 | 0.039 | [ |
| [Omim][BF4] | 25 | 120 | 0.387 | 0.025 | [ |
| [Bmim][PF6] | 25 | 174 | 0.538 | 0.032 | [ |
| [Bmim][BF4] | 25.4 | 101 | 0.112 | 0.008 | [ |
| [Emim][NTf2] | 26.4 | 101 | 0.122 | 0.005 | [ |
| [Hmim][Cl] | 24.8 | 101 | 0.252 | 0.021 | [ |
| [Emim][Ac] | 25.3 | 101 | 0.348 | 0.035 | [ |
| [Emim][EtOSO3] | 24.6 | 101 | 0.342 | 0.025 | [ |
| [Emim][SCN] | 25 | 101 | 0.188 | 0.019 | [ |
| [DMEA][Ac] | 25 | 163 | 0.905 | 0.103 | [ |
| [Bmim][BF4] | 20 | 101 | 0.449 | 0.034 | [ |
| [EOHmim][BF4] | 20 | 101 | 1.703 | 0.135 | [ |
| [Choline][NTf2] | 20 | 101 | 1.857 | 0.064 | [ |
| [MTEOA][MeOSO3] | 20 | 101 | 3.545 | 0.219 | [ |
| [MTEOA][MeOSO3] | 40 | 101 | 1.381 | 0.085 | [ |
| [EtOHmim][DCA] | 20 | 101 | 2.125 | 0.190 | [ |
| [EtOHmim][DCA] | 40 | 100 | 0.887 | 0.079 | [ |
| [EtOHmim][NTf2] | 25 | 105.5 | 0.976 | 0.041 | [ |
| [EtOHmim][PF6] | 25 | 106.8 | 0.980 | 0.062 | [ |
| [EtOHmim][BF4] | 25 | 98.9 | 0.825 | 0.066 | [ |
| [EtOHmim][SCN] | 25 | 95.3 | 0.538 | 0.050 | [ |
| [EtOHmim][DCA] | 25 | 108.5 | 0.600 | 0.054 | [ |
| [EtOHmim][NO3] | 25 | 106.6 | 0.522 | 0.047 | [ |
| [Eim][NTf2] | 40 | 105.12 | 2.73 | 0.123 | [ |
| [Mim][NTf2] | 40 | 102.71 | 2.68 | 0.128 | [ |
| [Mmim][NTf2] | 40 | 98.63 | 2.40 | 0.108 | [ |
| [Bmmim][NTf2] | 30 | 119.43 | 0.25 | 0.010 | [ |
| [Bmmim][NTf2] | 40 | 100.49 | 0.20 | 0.008 | [ |
| [Bmmim][NTf2] | 60 | 114.60 | 0.19 | 0.008 | [ |
| [Bim][SCN] | 30 | 98.82 | 2.18 | 0.202 | [ |
| [Bim][SCN] | 40 | 96.59 | 1.96 | 0.182 | [ |
| [Bim][SCN] | 60 | 102.56 | 1.56 | 0.145 | [ |
| [Bmim][SCN] | 40 | 82.92 | 0.15 | 0.013 | [ |
| [Bmim][SCN] | 60 | 79.87 | 0.09 | 0.008 | [ |
| [Bim][NO3] | 30 | 100.09 | 1.50 | 0.136 | [ |
| [Bim][NO3] | 40 | 141.53 | 1.72 | 0.156 | [ |
| [Bim][NO3] | 60 | 122.40 | 1.14 | 0.104 | [ |
| [Bmim][DCA] | 30 | 114.28 | 0.30 | 0.025 | [ |
| [Bmim][DCA] | 40 | 128.32 | 0.22 | 0.018 | [ |
| [Bmim][DCA] | 60 | 104.86 | 0.13 | 0.011 | [ |
| [Bmmim][DCA] | 30 | 115.38 | 0.25 | 0.020 | [ |
| [Bmmim][DCA] | 40 | 103.42 | 0.12 | 0.009 | [ |
| [Bmmim][DCA] | 60 | 126.48 | 0.14 | 0.011 | [ |
| [Bim][NTf2] | 40 | 101 | 2.69 | 0.113 | [ |
| [Bmim][NTf2] | 40 | 101 | 0.28 | 0.011 | [ |
| [HOOC(CH2)3mim][NTf2] | 40 | 101 | 1.54 | 0.059 | [ |
| [Bmim][Zn2Cl5] | 50 | 103.5 | 8.025 | 0.305 | [ |
| [Emim]2[Co(NCS)4] | 30 | 101 | 5.99 | 0.198 | [ |
| [Bmim]2[Co(NCS)4] | 30 | 101 | 6.03 | 0.180 | [ |
| [Hmim]2[Co(NCS)4] | 30 | 101 | 6.09 | 0.166 | [ |
| [Emim][SCN] | 30 | 101 | 0.18 | 0.018 | [ |
| [Bmim][SCN] | 30 | 101 | 0.19 | 0.016 | [ |
| [Hmim][SCN] | 30 | 101 | 0.20 | 0.015 | [ |
| [Bmim][MeSO3]/urea(1∶1) | 30 | 123.6 | — | 0.015 | [ |
| ChCl/Res/Gly (1∶3∶5) | 40 | 101 | — | 0.130 | [ |
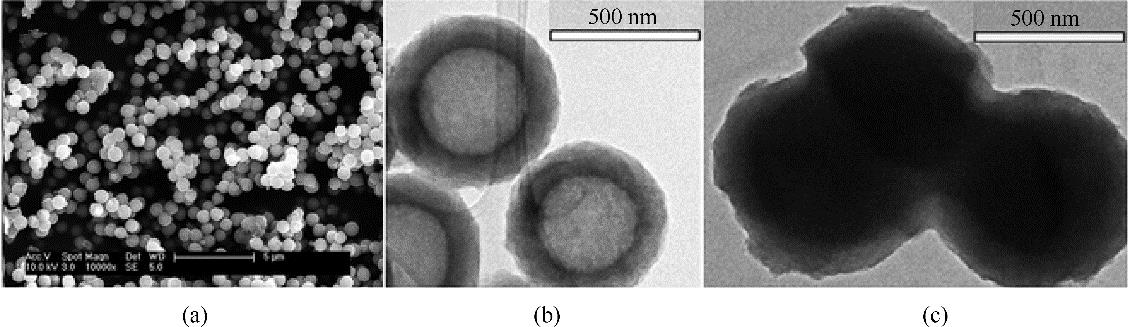
图9 碳微球SEM照片(a)及碳微球(b)和胶囊离子液体材料(c)TEM照片[49]
Fig.9 SEM images of carbon submicrocapsules (a), TEM images of carbon submicrocapsules (b) and [EtOHmim][BF4]-based ENILs (c) [49] (copyright 2016 Royal Society of Chemistry)
| 1 | WarnerJ X, DickersonR R, WeiZ, et al. Increased atmospheric ammonia over the world s major agricultural areas detected from space[J]. Geophys. Res. Lett., 2017, 44(6): 2875-2884. |
| 2 | ErismanJ W, BleekerA, GallowayJ, et al. Reduced nitrogen in ecology and the environment[J]. Environ. Pollut., 2007, 150(1): 140-149. |
| 3 | SuttonM A, ErismanJ W, DentenerF, et al. Ammonia in the environment: from ancient times to the present[J]. Environ. Pollut., 2008, 156(3): 583-604. |
| 4 | SchaferD, XiaJ Z, VogtM, et al. Experimental investigation of the solubility of ammonia in methanol[J].J. Chem. Eng. Data, 2007, 52(5): 1653-1659. |
| 5 | WangL, HuangX, YuY, et al. Eliminating ammonia emissions during rare earth separation through control of equilibrium acidity in a HEH(EHP)-Cl system[J]. Green Chem., 2013, 15(7): 1889-1894. |
| 6 | 王芬, 周敏. 焦炉煤气中氨的回收[J]. 洁净煤技术, 2009, (4): 108-111. |
| WangF, ZhouM. Recovery of ammonia from coking product[J]. Clean Coal Technol., 2009,( 4): 108-111. | |
| 7 | 李强. 氨回收系统存在问题及改进措施[J]. 大氮肥, 2011, (6): 418-419. |
| LiQ. Problems in ammonia recovery system and improvement measures[J]. Large Scale Nitrogenous Fertilizer Industry, 2011, (6): 418-419. | |
| 8 | 林璐璐. 氨回收工艺方案的选择[J]. 广东化工, 2016, 43(334): 239-243. |
| LinL L. Process project selection for ammonia recovery[J]. Guangdong Chemical Industry, 2016, 43(334): 239-243. | |
| 9 | LeiZ G, DaiC N, ChenB H. Gas solubility in ionic liquids[J]. Chem. Rev., 2014, 114(2): 1289-1326. |
| 10 | ZengS J, ZhangX P, BaiL, et al. Ionic liquid-based CO2 capture systems: structure, interaction and process[J]. Chem. Rev., 2017, 117(14): 9625-9673. |
| 11 | ZhangX P, ZhangX C, DongH F, et al. Carbon capture with ionic liquids: overview and progress[J]. Energ. Environ. Sci., 2012, 5(5): 6668-6681. |
| 12 | 陈晏杰, 姚月华, 张香平, 等. 基于离子液体的合成氨驰放气中氨回收工艺模拟计算[J]. 过程工程学报, 2011, 11(4): 644-651. |
| ChenY J, YaoY H, ZhangX P, et al. Simulation and optimization of ammonia recovery with ionic liquid from purge gas in ammonia synthesis plant[J]. Chin. J. Process Eng., 2011, 11(4): 644-651. | |
| 13 | ZengS J, GaoH, ZhangX, et al. Efficient and reversible capture of SO2 by pyridinium-based ionic liquids[J]. Chem. Eng. J., 2014, 251: 248-256. |
| 14 | HuangK, CaiD N, ChenY, et al. Thermodynamic validation of 1-alkyl-3-methylimidazolium carboxylates as task-specific ionic liquids for H2S absorption[J]. AIChE J., 2013, 59(6): 2227-2235. |
| 15 | LuoX Y, GuoY, DingF, et al. Significant improvements in CO2 capture by pyridine-containing anion-functionalized ionic liquids through multiple-site cooperative interactions[J]. Angew Chem. Int. Edit., 2014, 53(27): 7053-7057. |
| 16 | ShiW, MaginnE J. Molecular simulation of ammonia absorption in the ionic liquid 1-ethyl-3-methylimidazolium bis(trifluoromethylsulfonyl)imide (EmimTf2N)[J]. AIChE J., 2009, 55(9): 2414-2421. |
| 17 | LiG H, ZhouQ, ZhangX P, et al. Solubilities of ammonia in basic imidazolium ionic liquids[J]. Fluid Phase Equilibr., 2010, 297(1): 34-39. |
| 18 | HuangW J, SunG M, ZhengD X, et al. Vapor-liquid equilibrium measurements of NH3 + H2O + ionic liquid (DmimCl, DmimBF4, and DmimDMP) systems[J].J. Chem. Eng. Data, 2013, 58(5): 1354-1360. |
| 19 | YokozekiA, ShiflettM B. Ammonia solubilities in room-temperature ionic liquids[J]. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res., 2007, 46(5): 1605-1610. |
| 20 | YokozekiA, ShiflettM B. Vapor-liquid equilibria of ammonia plus ionic liquid mixtures[J]. Appl. Energ., 2007, 84(12): 1258-1273. |
| 21 | AkiS, MelleinB R, SaurerE M, et al. High-pressure phase behavior of carbon dioxide with imidazolium-based ionic liquids[J]. J. Phys. Chem. B, 2004, 108(52): 20355-20365. |
| 22 | HuangX, MargulisC J, LiY, et al. Why is the partial molar volume of CO2 so small when dissolved in a room temperature ionic liquid? Structure and dynamics of CO2 dissolved in [Bmim][PF6][J]. J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2005, 127(50): 17842-17851. |
| 23 | YunusN M, MutalibM I A, ManZ, et al. Solubility of CO2 in pyridinium based ionic liquids[J]. Chem. Eng. J., 2012, 189: 94-100. |
| 24 | KazarianS G, BriscoeB J, WeltonT. Combining ionic liquids and supercritical fluids: in situ ATR-IR study of CO2 dissolved in two ionic liquids at high pressures[J]. Chem. Commun., 2000, 20: 2047-2048. |
| 25 | DongK, ZhangS J, WangD X, et al. Hydrogen bonds in imidazolium ionic liquids[J]. J. Phys. Chem. A, 2006, 110(31): 9775-9782. |
| 26 | CrowhurstL, MawdsleyP R, Perez-ArlandisJ M, et al. Solvent-solute interactions in ionic liquids[J]. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2003, 5(13): 2790-2794. |
| 27 | CadenaC, AnthonyJ L, ShahJ K, et al. Why is CO2 so soluble in imidazolium-based ionic liquids?[J]. J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2004, 126(16): 5300-5308. |
| 28 | AnthonyJ L, AndersonJ L, MaginnE J, et al. Anion effects on gas solubility in ionic liquids[J]. J. Phys. Chem. B, 2005, 109(13): 6366-6374. |
| 29 | BhargavaB L, BalasubramanianS. Probing anion-carbon dioxide interactions in room temperature ionic liquids: gas phase cluster calculations[J]. Chem. Phys. Lett., 2007, 444(4/5/6): 242-246. |
| 30 | SekiT, GrunwaldtJ D, BaikerA. In situ attenuated total reflection infrared spectroscopy of imidazolium-based room-temperature ionic liquids under “supercritical” CO2[J]. J. Phys. Chem. B, 2009, 113(1): 114-122. |
| 31 | PalomarJ, Gonzalez-MiquelM, BediaJ, et al. Task-specific ionic liquids for efficient ammonia absorption[J]. Sep. Purif. Technol., 2011, 82: 43-52. |
| 32 | RuizE, FerroV R, de RivaJ, et al. Evaluation of ionic liquids as absorbents for ammonia absorption refrigeration cycles using COSMO-based process simulations[J]. Appl. Energ., 2014, 123: 281-291. |
| 33 | BediaJ, PalomarJ, Gonzalez-MiquelM, et al. Screening ionic liquids as suitable ammonia absorbents on the basis of thermodynamic and kinetic analysis[J]. Sep. Purif. Technol., 2012, 95: 188-195. |
| 34 | ZhangX, DongH F, HuangY, et al. Experimental study on gas holdup and bubble behavior in carbon capture systems with ionic liquid[J]. Chem. Eng. J., 2012, 209: 607-615. |
| 35 | HolbreyJ D, ReichertW M, SwatloskiR P, et al. Efficient, halide free synthesis of new, low cost ionic liquids: 1,3-dialkylimidazolium salts containing methyl- and ethyl-sulfate anions[J]. Green Chem., 2002, 4(5): 407-413. |
| 36 | YokozekiA, ShiflettM B. Vapor-liquid equilibria of ammonia + ionic liquid mixtures[J]. Appl. Energ., 2007, 84(12): 1258-1273. |
| 37 | IarikovD D, HacarliogluP, OyamaS T. Supported room temperature ionic liquid membranes for CO2/CH4 separation[J]. Chem. Eng. J., 2011, 166(1): 401-406. |
| 38 | LiZ J, ZhangX P, DongH F, et al. Efficient absorption of ammonia with hydroxyl-functionalized ionic liquids[J]. RSC Adv., 2015, 5(99): 81362-81370. |
| 39 | ShangD W, BaiL, ZengS J, et al. Enhanced NH3 capture by imidazolium-based protic ionic liquids with different anions and cation substituents[J]. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol., 2018, 93(5): 1228-1236. |
| 40 | ShangD W, ZhangX P, ZengS J, et al. Protic ionic liquid BimNTf2 with strong hydrogen bond donating ability for highly efficient ammonia absorption[J]. Green Chem., 2017, 19(4): 937-945. |
| 41 | SherwoodT K. Solubilities of sulfur dioxide and ammonia in water [J]. Industrial and Engineering Chemistry, 1925, 17: 745-747. |
| 42 | ChenW, LiangS Q, GuoY X, et al. Investigation on vapor-liquid equilibria for binary systems of metal ion-containing ionic liquid bmim Zn2Cl5/NH3 by experiment and modified UNIFAC model[J]. Fluid Phase Equilibr., 2013, 360: 1-6. |
| 43 | KohlerF, PoppS, KleferH, et al. Supported ionic liquid phase (SILP) materials for removal of hazardous gas compounds - efficient and irreversible NH3 adsorption[J]. Green Chem., 2014, 16(7): 3560-3568. |
| 44 | ZengS J, LiuL, ShangD W, et al. Efficient and reversible absorption of ammonia by cobalt ionic liquids through Lewis acid-base and cooperative hydrogen bond interactions[J]. Green Chem., 2018, 20(9): 2075-2083. |
| 45 | WangJ L, ZengS J, HuoF, et al. Metal chloride anion-based ionic liquids for efficient separation of NH3[J]. J. Clean Prod., 2019, 206: 661-669. |
| 46 | CaoX Z, SongT Y, WangX Q. Inorganic Chemistry[M]. 2nd ed. Beijing: Higher Education Press, 1994: 898-899. |
| 47 | AkhmetshinaA I, PetukhovA N, MecherguiA, et al. Evaluation of methanesulfonate-based deep eutectic solvent for ammonia sorption[J]. J. Chem. Eng. Data, 2018, 63(6): 1896-1904. |
| 48 | LiY H, AliM C, YangQ W, et al. Hybrid deep eutectic solvents with flexible hydrogen-bonded supramolecular networks for highly efficient uptake of NH3[J]. ChemSusChem, 2017, 10(17): 3368-3377. |
| 49 | LemusJ, BediaJ, MoyaC, et al. Ammonia capture from the gas phase by encapsulated ionic liquids (ENILs)[J]. RSC Adv., 2016, 6(66): 61650-61660. |
| 50 | PalomarJ, LemusJ, Alonso-MoralesN, et al. Encapsulated ionic liquids (ENILs): from continuous to discrete liquid phase[J]. Chem. Comm., 2012, 48(80): 10046-10048. |
| 51 | RuckartK N, ZhangY C, ReichertW M, et al. Sorption of ammonia in mesoporous-silica ionic liquid composites[J]. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res., 2016, 55(47): 12191-12204. |
| [1] | 王琪, 张斌, 张晓昕, 武虎建, 战海涛, 王涛. 氯铝酸-三乙胺离子液体/P2O5催化合成伊索克酸和2-乙基蒽醌[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(S1): 245-249. |
| [2] | 黄琮琪, 吴一梅, 陈建业, 邵双全. 碱性电解水制氢装置热管理系统仿真研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(S1): 320-328. |
| [3] | 金正浩, 封立杰, 李舒宏. 氨水溶液交叉型再吸收式热泵的能量及 分析[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(S1): 53-63. 分析[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(S1): 53-63. |
| [4] | 米泽豪, 花儿. 基于DFT和COSMO-RS理论研究多元胺型离子液体吸收SO2气体[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(9): 3681-3696. |
| [5] | 陈美思, 陈威达, 李鑫垚, 李尚予, 吴有庭, 张锋, 张志炳. 硅基离子液体微颗粒强化气体捕集与转化的研究进展[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(9): 3628-3639. |
| [6] | 程业品, 胡达清, 徐奕莎, 刘华彦, 卢晗锋, 崔国凯. 离子液体基低共熔溶剂在转化CO2中的应用[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(9): 3640-3653. |
| [7] | 王俐智, 杭钱程, 郑叶玲, 丁延, 陈家继, 叶青, 李进龙. 离子液体萃取剂萃取精馏分离丙酸甲酯+甲醇共沸物[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(9): 3731-3741. |
| [8] | 陈杰, 林永胜, 肖恺, 杨臣, 邱挺. 胆碱基碱性离子液体催化合成仲丁醇性能研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(9): 3716-3730. |
| [9] | 陆俊凤, 孙怀宇, 王艳磊, 何宏艳. 离子液体界面极化及其调控氢键性质的分子机理[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(9): 3665-3680. |
| [10] | 郑佳丽, 李志会, 赵新强, 王延吉. 离子液体催化合成2-氰基呋喃反应动力学研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(9): 3708-3715. |
| [11] | 车睿敏, 郑文秋, 王小宇, 李鑫, 许凤. 基于离子液体的纤维素均相加工研究进展[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(9): 3615-3627. |
| [12] | 赵亚欣, 张雪芹, 王荣柱, 孙国, 姚善泾, 林东强. 流穿模式离子交换层析去除单抗聚集体[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(9): 3879-3887. |
| [13] | 宋明昊, 赵霏, 刘淑晴, 李国选, 杨声, 雷志刚. 离子液体脱除模拟油中挥发酚的多尺度模拟与研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(9): 3654-3664. |
| [14] | 杨绍旗, 赵淑蘅, 陈伦刚, 王晨光, 胡建军, 周清, 马隆龙. Raney镍-质子型离子液体体系催化木质素平台分子加氢脱氧制备烷烃[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(9): 3697-3707. |
| [15] | 刘爽, 张霖宙, 许志明, 赵锁奇. 渣油及其组分黏度的分子层次组成关联研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(8): 3226-3241. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备 11010102001995号
京公网安备 11010102001995号