化工学报 ›› 2020, Vol. 71 ›› Issue (3): 997-1008.DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20190630
李庭樑1,2,3,4,岑继文1,2,3,黄文博1,2,3,曹文炅1,2,3,蒋方明1,2,3( )
)
收稿日期:2019-06-10
修回日期:2019-10-29
出版日期:2020-03-05
发布日期:2020-03-05
通讯作者:
蒋方明
基金资助:
Tingliang LI1,2,3,4,Jiwen CEN1,2,3,Wenbo HUANG1,2,3,Wenjiong CAO1,2,3,Fangming JIANG1,2,3( )
)
Received:2019-06-10
Revised:2019-10-29
Online:2020-03-05
Published:2020-03-05
Contact:
Fangming JIANG
摘要:
用于干热岩热能开采的增强型地热系统存在投资高、风险大、工质漏损、设备腐蚀、地面沉降等问题,利用超长重力热管进行地热开采可以有效规避这些问题。搭建了超长重力热管实验平台,实验研究了超长重力热管的适宜充液量、运行的稳定性和不同冷却水流量下的传热性能并分析了其可能的原因;研究表明在恒定加热功率下,热管的合适充液量为蒸发容积的40%左右,在运行期间,与传统短热管相比,超长热管展现出了强烈的振荡性,振荡频率与加热功率和充液量息息相关;在恒定加热功率下,随着冷却水流量的增加,热管采出功率先增加后逐渐趋于平缓。此外,特别探讨了热管在极端充液量下的传热性能,研究表明在极端充液量下,热管底部形成一定高度的气柱,由于气柱的持续存在导致热量无法传递到热管顶端。实验结果初步证实了超长重力热管在开采干热岩热能上的可行性,为下一步的实际应用提供了基础支持。
中图分类号:
李庭樑, 岑继文, 黄文博, 曹文炅, 蒋方明. 超长重力热管传热性能实验研究[J]. 化工学报, 2020, 71(3): 997-1008.
Tingliang LI, Jiwen CEN, Wenbo HUANG, Wenjiong CAO, Fangming JIANG. Experimental study on heat transfer performance of super long gravity heat pipe[J]. CIESC Journal, 2020, 71(3): 997-1008.
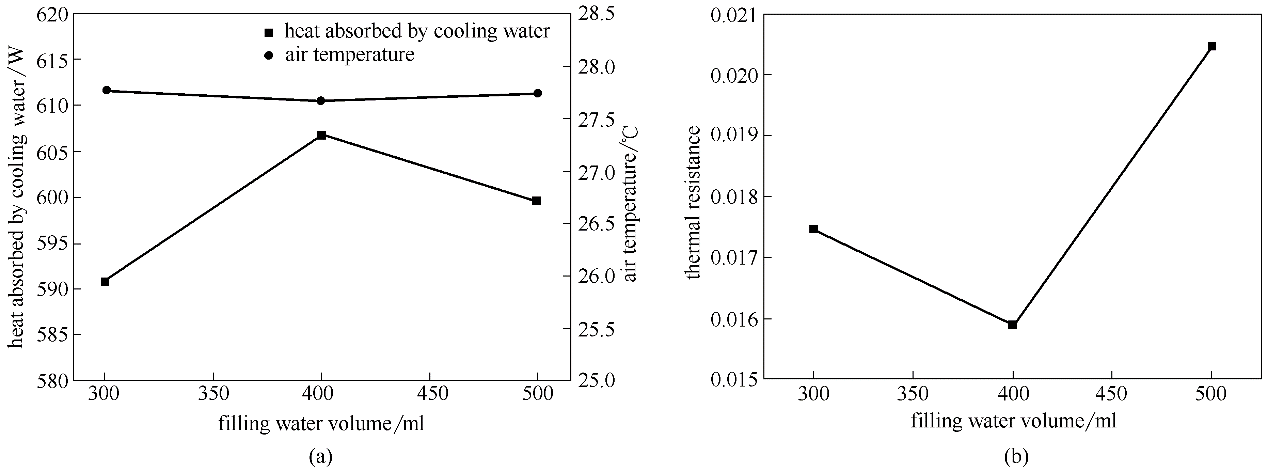
图4 不同充液量下热管的采热性能(加热功率为800 W,冷却水流量为6.0 ml/s)
Fig.4 Heat transfer performance of heat pipes under different liquid filling (heat power is 800 W, cooling water flow rate is 6.0 ml/s )
| 充液量/ml | 积液深度/cm | 采出功率/W |
|---|---|---|
| 200 | 88.2 | 460.4 |
| 300 | 132.2 | 474.8 |
| 400 | 176.4 | 499.8 |
| 600 | 264.5 | 451.9 |
| 800 | 352.6 | 446.6 |
| 1000 | 440.9 | 445.5 |
| 1300 | 573.0 | 434.9 |
| 1600 | 705.3 | 418.6 |
| 2500 | 1102.0 | 286.2 |
| 5000 | 2204.0 | 0 |
表1 不同充液量下积液深度和采出功率(加热功率为600 W,冷却水流量为5.5 ml/s)
Table 1 Depth of filling water and production power at different liquid fillings (heating power is 600 W, cooling water flow rate is 5.5 ml/s)
| 充液量/ml | 积液深度/cm | 采出功率/W |
|---|---|---|
| 200 | 88.2 | 460.4 |
| 300 | 132.2 | 474.8 |
| 400 | 176.4 | 499.8 |
| 600 | 264.5 | 451.9 |
| 800 | 352.6 | 446.6 |
| 1000 | 440.9 | 445.5 |
| 1300 | 573.0 | 434.9 |
| 1600 | 705.3 | 418.6 |
| 2500 | 1102.0 | 286.2 |
| 5000 | 2204.0 | 0 |

图5 不同充液量下积液深度和采出功率(加热功率为600 W,冷却水流量为5.5 ml/s)
Fig.5 Depth of filling water and production power under different liquid fillings (heating power is 600 W, cooling water flow rate is 5.5 ml/s)
| 充液量/ml | 积液深度/cm | 静水压/kPa | 绝热段温度/℃ | 绝热段饱和蒸汽压力/kPa | 蒸发段总压力/kPa | 理论蒸发温度/℃ | 热管实际蒸发温度/℃ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 200 | 88.2 | 8.8 | 53.2 | 14.5 | 23.3 | 63.4 | 68.2 |
| 300 | 132.2 | 13.2 | 50.8 | 12.9 | 26.1 | 65.9 | 66.8 |
| 400 | 176.4 | 17.6 | 51.4 | 13.2 | 30.9 | 69.8 | 71.8 |
| 600 | 264.5 | 26.5 | 50.9 | 12.9 | 39.3 | 75.5 | 74.7 |
| 800 | 352.6 | 35.3 | 51.3 | 13.2 | 48.5 | 80.5 | 81.5 |
| 1000 | 440.9 | 44.1 | 61.2 | 21.1 | 65.2 | 88.1 | 90.1 |
| 1300 | 573.0 | 57.3 | 50.4 | 12.6 | 69.9 | 89.9 | 90.8 |
| 1600 | 705.3 | 70.5 | 48.2 | 11.3 | 81.8 | 94.1 | 95.3 |
| 2500 | 1102 | 110.2 | 46.0 | 10.1 | 120.3 | 104.8 | 102.5 |
表2 理论蒸发温度与实际蒸发温度(加热功率为600 W,循环流量为5.5 ml/s)
Table 2 Theoretical and actual evaporation temperature (heating power is 600 W, circulating flow rate is 5.5 ml/s)
| 充液量/ml | 积液深度/cm | 静水压/kPa | 绝热段温度/℃ | 绝热段饱和蒸汽压力/kPa | 蒸发段总压力/kPa | 理论蒸发温度/℃ | 热管实际蒸发温度/℃ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 200 | 88.2 | 8.8 | 53.2 | 14.5 | 23.3 | 63.4 | 68.2 |
| 300 | 132.2 | 13.2 | 50.8 | 12.9 | 26.1 | 65.9 | 66.8 |
| 400 | 176.4 | 17.6 | 51.4 | 13.2 | 30.9 | 69.8 | 71.8 |
| 600 | 264.5 | 26.5 | 50.9 | 12.9 | 39.3 | 75.5 | 74.7 |
| 800 | 352.6 | 35.3 | 51.3 | 13.2 | 48.5 | 80.5 | 81.5 |
| 1000 | 440.9 | 44.1 | 61.2 | 21.1 | 65.2 | 88.1 | 90.1 |
| 1300 | 573.0 | 57.3 | 50.4 | 12.6 | 69.9 | 89.9 | 90.8 |
| 1600 | 705.3 | 70.5 | 48.2 | 11.3 | 81.8 | 94.1 | 95.3 |
| 2500 | 1102 | 110.2 | 46.0 | 10.1 | 120.3 | 104.8 | 102.5 |

图6 理论蒸发温度与实际蒸发温度对比(加热功率为600 W,冷却水流量为5.5 ml/s)
Fig.6 Comparison of theoretical and actual evaporation temperature (heating power is 600 W, circulating flow rate is 5.5 ml/s)

图7 不同充液量下各点温度随时间变化曲线(冷却水流量为5.5 ml/s)
Fig.7 Temperaturevs time curve of each measuring point under different liquid fillings (cooling water flow rate is 5.5 ml/s)

图8 不同加热功率下热管各测点温度变化情况(充液量为5000 ml,冷却水流量为5.5 ml/s)
Fig.8 Temperature variation curve of heat pipe under different heating powers (filling water volume is 5000 ml, cooling water flow rate is 5.5 ml/s)
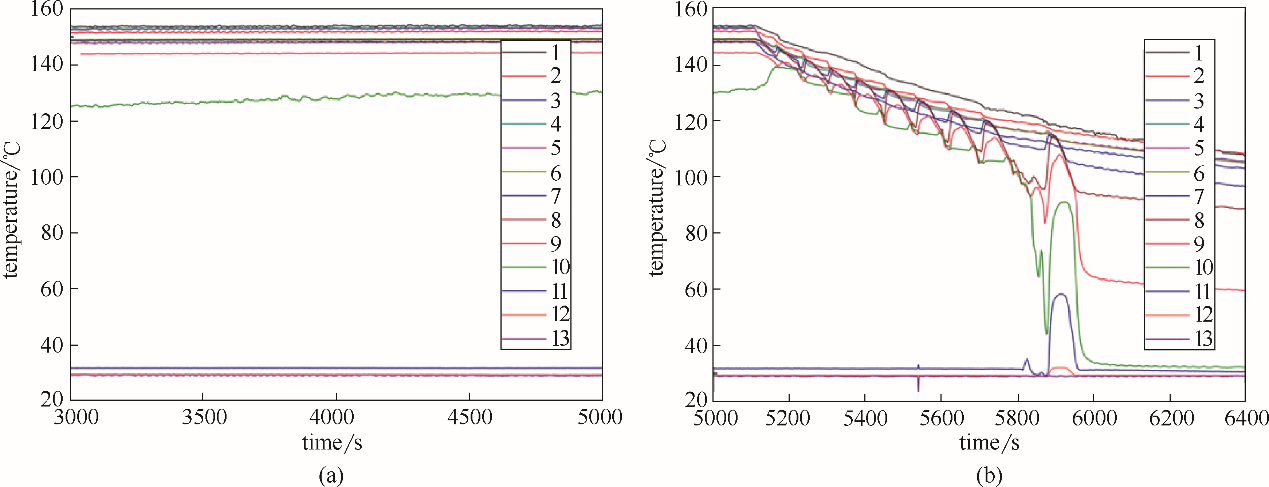
图9 加热功率为600 W(a)和停止加热(b)后热管各点温度随时间变化情况(充液量为5000 ml,冷却水流量为5.5 ml/s)
Fig.9 Temperature of heat pipe changes with time when the heating power is 600 W (a) and heating power is stopped (b) (filling water volume is 5000 ml, cooling water flow rate is 5.5 ml/s)
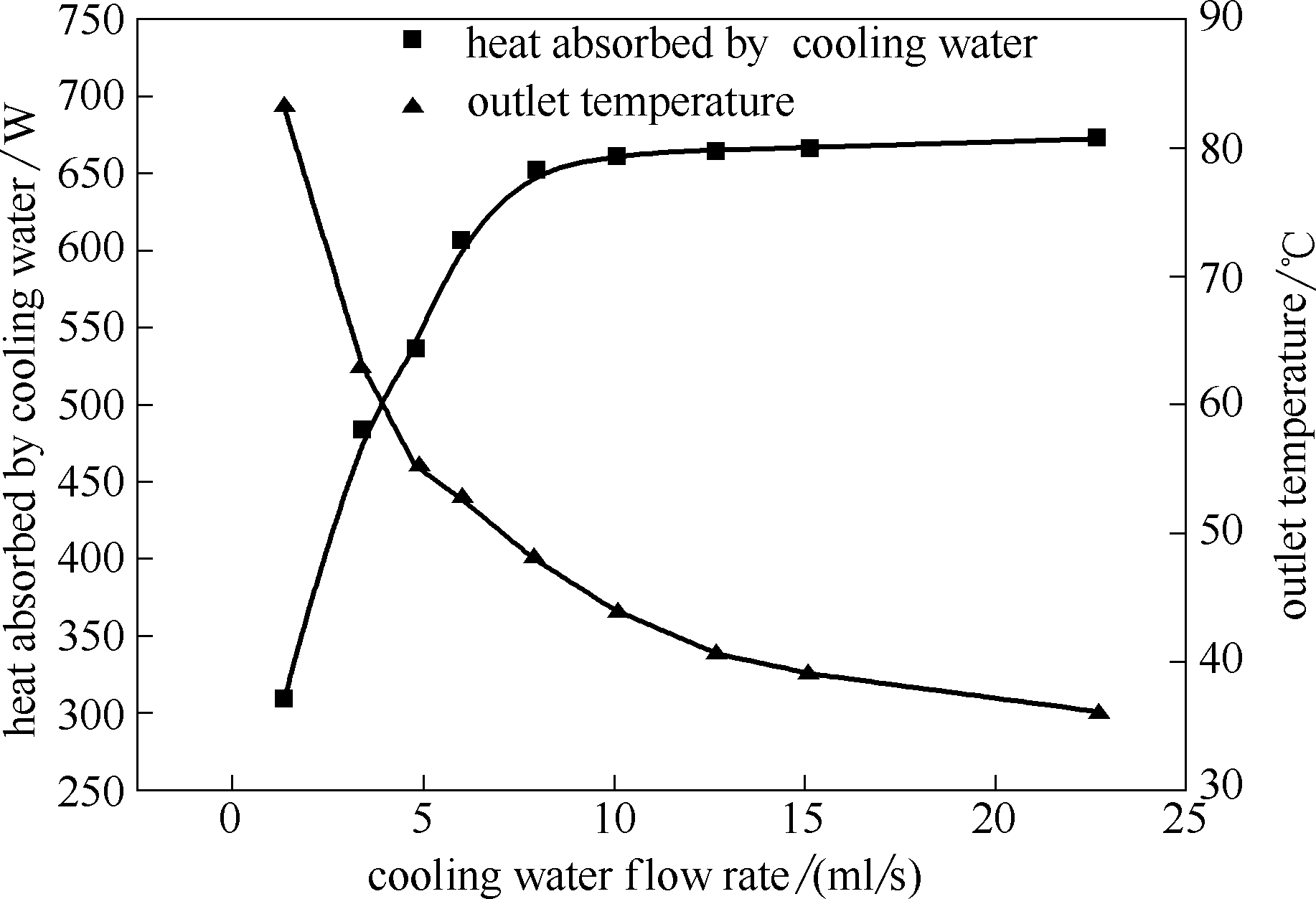
图10 不同冷却水流量下热管的采热性能(充液量为400 ml,加热功率为800 W)
Fig.10 Heat transfer performance of heat pipes under different cooling water flow rates (filling water volume is 400 ml, heating power is 800 W)

图11 蒸发段温度与绝热段温度随循环流量变化(充液量为400 ml,加热功率为800 W)
Fig.11 Evaporation section temperature and adiabatic section temperature evolution with increasing cooling water flow rate (filling water volume is 400 ml, heating power is 800 W)
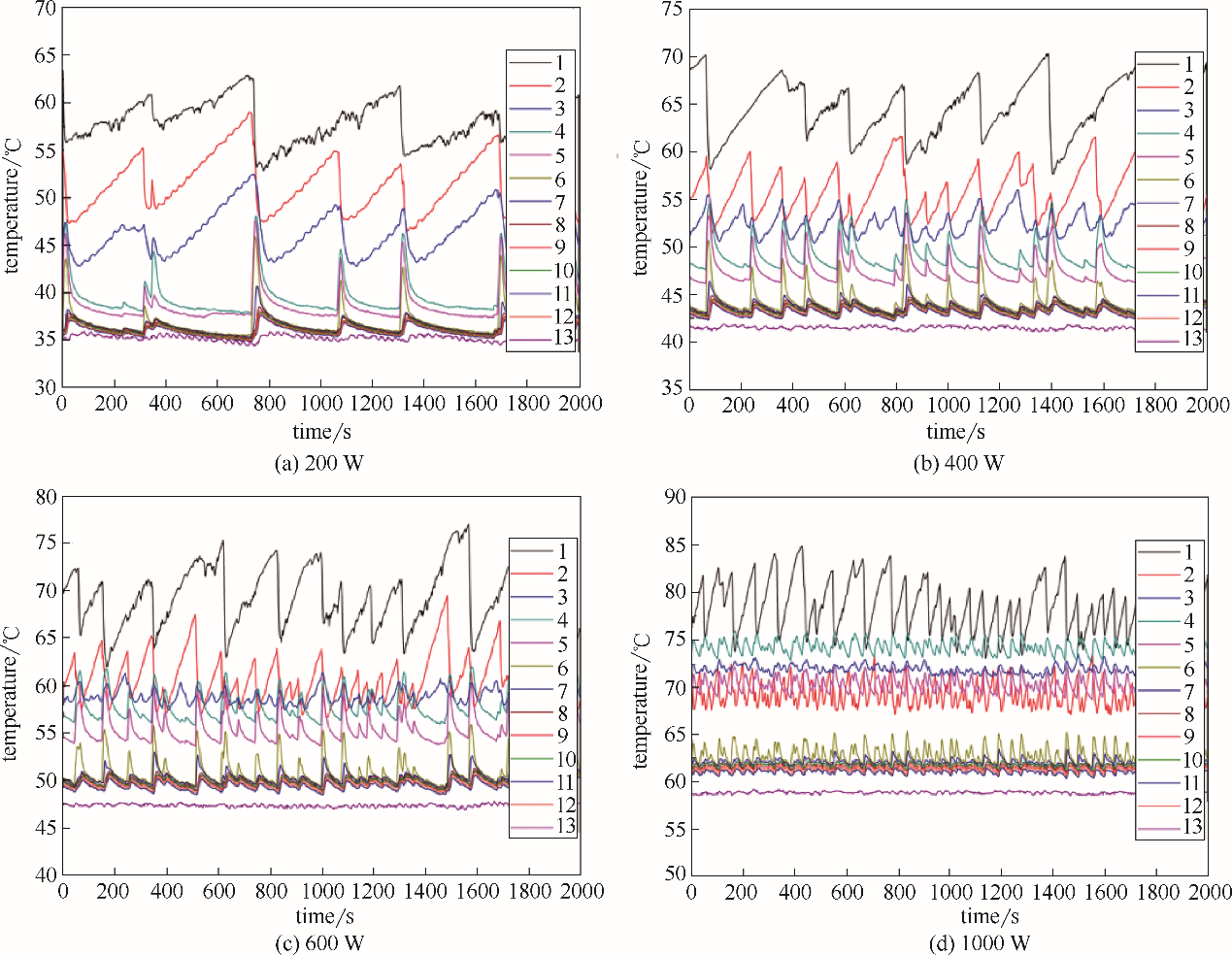
图12 不同加热功率下热管的振荡频率(充液量为400 ml,冷却水流量为6.0 ml/s)
Fig.12 Oscillation frequency of heat pipe under different heating powers(filling water volume is 400 ml, cooling water flow rate is 6.0 ml/s)

图13 不同加热功率下热管的振荡频率(充液量为1000 ml,循环流量为6.0 ml/s)
Fig.13 Oscillation frequency of heat pipe under different heating powers(filling water volume is 1000 ml, cooling water flow rate is 6.0 ml/s)
| 1 | 汪集旸,胡圣标,庞忠和,等.中国大陆干热岩地热资源潜力评估[J].科技导报,2012,30(32):25-31. |
| Wang J Y,Hu S B,Pang Z H,et al.Estimate of geothermal resources potential for hot dry rock in the continental area of China[J].Science & Technology Review,2012,30(32):25-31. | |
| 2 | 郭剑,陈继良,曹文炅,等.增强型地热系统研究综述[J].电力建设,2014,35(4):10-24. |
| Guo J,Chen J L,Cao W J,et al.Research review on enhanced geothermal system[J].Electric Power Construction,2014,35(4):10-24. | |
| 3 | 许天福,张延军,曾昭发,等.增强型地热系统(干热岩)开发技术进展[J].科技导报,2012,30(32):42-45. |
| Xu T F,Zhang Y J,Zeng S F,et al.Technology progress in an enhanced geothermal system(hot dry rock)[J].Science & Technology Review,2012,30(32):42-45. | |
| 4 | 蔺文静,刘志明,马峰,等.我国陆区干热岩资源潜力估算[J].地球学报,2012,33(5):807-811. |
| Lin W J,Liu Z M,Ma F,et al.An estimation of HDR resources in China’s mainland[J].Acta Geoscientica Sinica,2012,33(5):807-811. | |
| 5 | Norbeck J,Mcclure M,Horne R.Analysis of hydromechanical reservoir response during fluid circulation at the Fenton Hill Enhanced Geothermal System test site[C]//Proceedings of 38th New Zealand Geothermal Workshop.Auckland, New Zealand,2016. |
| 6 | Tester J W,And erson B J,Batchelor A S,et al.The Future of Geothermal Energy-Impact of Enhanced Geothermal Systems (EGS) on the United States in the 21st Century[M].Cambridge MA:Massachusetts Institute of Technology,2006. |
| 7 | Richards H,Parker R,Green A,Jones R,et al.The performance and characteristics of the experimental hot dry rock geothermal reservoir at Rosemanowes, Cornwall (1985—1988)[J].Geothermics,1994,23(2):73-109. |
| 8 | Parker R.The Rosemanowes HDR project 1983—1991[J].Geothermics,1999,28(4/5):603-615. |
| 9 | Genter A,Evans K,Cuenot N,Fritsch D,et al.Contribution of the exploration of deep crystalline fractured reservoir of Soultz to the knowledge of enhanced geothermal systems (EGS)[J].Comptes Rendus Geoscience,2010,342(7/8):502-516. |
| 10 | Karrech A.Non-equilibrium thermodynamics for fully coupled thermal hydraulic mechanical chemical processes[J].Journal of the Mechanics and Physics of Solids,2013,61(3):819-837. |
| 11 | Taron J,Elsworth D.Coupled mechanical and chemical processes in engineered geothermal reservoirs with dynamic permeability[J].International Journal of Rock Mechanics and Mining Sciences,2010,47(8):1339-1348. |
| 12 | Sanyal S K,Morrow J W,Butler S J,et al.Cost of electricity from enhanced geothermal systems[C]//Thirty-Second Workshop on Geothermal Reservoir Engineering.2007,32:1-11. |
| 13 | 陆川,王贵玲.干热岩研究现状与展望[J].科技导报,2015,33(19):13-21. |
| Lu C,Wang G L.Current status and prospect of hot dry rock research[J].Science & Technology Review,2015,33(19):13-21. | |
| 14 | Chen D,Wyborn D.Habanero field tests in the Cooper Basin, Australia: a proof-of-concept for EGS[J].Geothermal Resources Council Transactions,2009,33(1):159-164. |
| 15 | Johnston I W,Narsilio G A,Colls S.Emerging geothermal energy technologies[J].KSCE Journal of Civil Engineering,2011,15(4):643-653. |
| 16 | 刘明言.地热流体的腐蚀与结垢控制现状[J].新能源进展,2015,3(1):38-46. |
| Liu M Y.A review on controls of corrosion and scaling in geothermal fluids[J].Advances in New and Renewable Energy,2015,3(1):38-46. | |
| 17 | 尤伟静,刘延锋,郭明晶.地热资源开发利用过程中的主要环境问题 [J].安全与环境工程,2013,20(2):24-28. |
| You W J,Liu Y F,Guo M J.Environmental issues in the development and utilization of geothermal resources[J].Safety and Environmental Engineering,2013,20(2):24-28. | |
| 18 | 张劲草,辛公明,陈岩,等.蒸发段和冷凝段变化对重力热管性能的影响[J].化工学报,2017,68(4):1343-1348. |
| Zhang J C,Xin G M,Chen Y,et al.Influence of changing evaporator/condenser section on operation characteristics of gravity heat pipe[J].CIESC Journal,2017,68(4):1343-1348. | |
| 19 | Bachmann C E,Wiemer S,Woessner J,et al.Statistical analysis of the induced Basel 2006 earthquake sequence: introducing a probability-based monitoring approach for Enhanced Geothermal Systems[J].Geophysical Journal International,2011,186(2):793-807. |
| 20 | Giardini D.Geothermal quake risks must be faced[J].Nature,2009,462(7275):848. |
| 21 | Srimuang W,Amatachaya P.A review of the applications of heat pipe heat exchangers for heat recovery[J].Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews,2012,16(6):4303-4315. |
| 22 | Faghri A.Heat pipes: review, opportunities and challenges[J].Frontiers in Heat Pipes (FHP),2014,5(1):1-48. |
| 23 | Tien C,Sun K.Minimum meniscus radius of heat pipe wicking materials[J].International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer,1971,14(11):1853-1855. |
| 24 | 孙荟晶,孙世梅.热管技术在可再生能源利用中的研究与探索[J].现代化工,2007,27(S2):517-520. |
| Sun H J,Sun S M.Utilization and exploration of heat pipe technology for renewable energy source[J].Modern Chemical Industry,2007,27(S2):517-520. | |
| 25 | Seo J,Bang I C,Lee J Y.Length effect on entrainment limit of large-L/D vertical heat pipe[J].International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer,2016,97:751-759. |
| 26 | 张军,张辉,张红,等.地热热管融雪系统应用研究[J].太阳能学报,2011,32(12):1822-1826. |
| Zhang J,Zhang H,Zhang H,et al.Application study of geothermic heat pipe snow melting system [J].Acta Energiae Solaris Sinica,2011,32(12):1822-1826. | |
| 27 | 杨永平,魏庆朝,周顺华,等.热管技术及其在多年冻土工程中的应用研究[J].岩土工程学报,2005,27(6):698-706. |
| Yang Y P,Wei Q C,Zhou S H,et al.Thermosyphon technology and its application in permafrost[J].Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering,2005,27(6):698-706. | |
| 28 | 张玉丰,吴晓东,李伟超.重力热管井筒伴热方式可行性分析[J].石油勘探与开发,2007,34(4):483-487. |
| Zhang Y F,Wu X D,Li W C.Feasibility of two-phase closed thermosyphon heating method [J].Petroleum Exploration and Development,2007,34(4):483-487. | |
| 29 | Kusaba S,Suzuki H,Hirowatari K,et al.Extraction of geothermal energy and electric power generation using a large scale heat pipe[C]//Proceedings of World Geothermal Congress.2000:3489-3494. |
| 30 | 蒋方明,黄文博,曹文炅.干热岩热能的热管开采方案及其技术可行性研究[J].新能源进展,2017,5(6):426-434. |
| Jiang F M,Huang W B,Cao W J.Mining hot dry rock geothermal energy by heat pipe: conceptual design and technical feasibility study [J].Advances in New and Renewable Energy,2017,5(6):426-434. |
| [1] | 晁京伟, 许嘉兴, 李廷贤. 基于无管束蒸发换热强化策略的吸附热池的供热性能研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(S1): 302-310. |
| [2] | 程成, 段钟弟, 孙浩然, 胡海涛, 薛鸿祥. 表面微结构对析晶沉积特性影响的格子Boltzmann模拟[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(S1): 74-86. |
| [3] | 张化福, 童莉葛, 张振涛, 杨俊玲, 王立, 张俊浩. 机械蒸汽压缩蒸发技术研究现状与发展趋势[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(S1): 8-24. |
| [4] | 吴馨, 龚建英, 靳龙, 王宇涛, 黄睿宁. 超声波激励下铝板表面液滴群输运特性的研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(S1): 104-112. |
| [5] | 叶展羽, 山訸, 徐震原. 用于太阳能蒸发的折纸式蒸发器性能仿真[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(S1): 132-140. |
| [6] | 张双星, 刘舫辰, 张义飞, 杜文静. R-134a脉动热管相变蓄放热实验研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(S1): 165-171. |
| [7] | 毕丽森, 刘斌, 胡恒祥, 曾涛, 李卓睿, 宋健飞, 吴翰铭. 粗糙界面上纳米液滴蒸发模式的分子动力学研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(S1): 172-178. |
| [8] | 张义飞, 刘舫辰, 张双星, 杜文静. 超临界二氧化碳用印刷电路板式换热器性能分析[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(S1): 183-190. |
| [9] | 陈爱强, 代艳奇, 刘悦, 刘斌, 吴翰铭. 基板温度对HFE7100液滴蒸发过程的影响研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(S1): 191-197. |
| [10] | 刘明栖, 吴延鹏. 导光管直径和长度对传热影响的模拟分析[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(S1): 206-212. |
| [11] | 王志国, 薛孟, 董芋双, 张田震, 秦晓凯, 韩强. 基于裂隙粗糙性表征方法的地热岩体热流耦合数值模拟与分析[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(S1): 223-234. |
| [12] | 齐聪, 丁子, 余杰, 汤茂清, 梁林. 基于选择吸收纳米薄膜的太阳能温差发电特性研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(9): 3921-3930. |
| [13] | 李艺彤, 郭航, 陈浩, 叶芳. 催化剂非均匀分布的质子交换膜燃料电池操作条件研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(9): 3831-3840. |
| [14] | 王玉兵, 李杰, 詹宏波, 朱光亚, 张大林. R134a在菱形离散肋微小通道内的流动沸腾换热实验研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(9): 3797-3806. |
| [15] | 李科, 文键, 忻碧平. 耦合蒸气冷却屏的真空多层绝热结构对液氢储罐自增压过程的影响机制研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(9): 3786-3796. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备 11010102001995号
京公网安备 11010102001995号