化工学报 ›› 2020, Vol. 71 ›› Issue (11): 5159-5168.DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20200252
收稿日期:2020-03-12
修回日期:2020-06-08
出版日期:2020-11-05
发布日期:2020-11-05
通讯作者:
周虎
作者简介:刘万强(1971—),男,博士,副教授,基金资助:
Wanqiang LIU( ),Fan YANG(
),Fan YANG( ),Hua YUAN,Yuanda ZHANG,Pinggui YI,Hu ZHOU(
),Hua YUAN,Yuanda ZHANG,Pinggui YI,Hu ZHOU( )
)
Received:2020-03-12
Revised:2020-06-08
Online:2020-11-05
Published:2020-11-05
Contact:
Hu ZHOU
摘要:
传热是化工生产的基本问题之一,热导率是化工产品生产工艺设计中一类重要的热力学数据。通过非平衡分子动力学方法模拟了8种液态醇类有机物在不同温度下的导热过程。热导率计算值与实验值的平均相对偏差为3.77%。通过对热流的分解发现,分子动能、分子间库仑相互作用和分子内的二面角对醇类有机物的热传导影响较大。同时随着分子链增长,通过分子内相互作用进行的热传导逐渐占主导作用,表明醇类有机物的热能传输机理与分子结构有显著关系。此外,随着温度的升高,通过分子的动能、分子间库仑作用和分子内键角、键伸缩作用项传输的热流增大,表明温度对液态醇类有机物的热传导也有一定影响。本工作从微观分子间和分子内作用分析了液态醇类有机物结构和温度对热导率的影响,为液态有机物的热传导研究提供了微观依据。
中图分类号:
刘万强,杨帆,袁华,张远达,易平贵,周虎. 醇类有机物热传导的分子动力学模拟及微观机理研究[J]. 化工学报, 2020, 71(11): 5159-5168.
Wanqiang LIU,Fan YANG,Hua YUAN,Yuanda ZHANG,Pinggui YI,Hu ZHOU. Molecular dynamics simulation and mechanism study on thermal conductivity of alcohols[J]. CIESC Journal, 2020, 71(11): 5159-5168.
| Method | Compound | Deviation/% | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|
| NEMD | alcohols | 18—30 | [ |
| BD-NEMD | methanol and ethanol | 5 | [ |
| Green-Kubo | ethanol | 10 | [ |
| Green-Kubo | ethylene glycol | 20—30 | [ |
表1 部分醇类有机物的分子动力学模拟研究结果
Table 1 Results of some MD simulation for calculating thermal conductivity of alcohols
| Method | Compound | Deviation/% | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|
| NEMD | alcohols | 18—30 | [ |
| BD-NEMD | methanol and ethanol | 5 | [ |
| Green-Kubo | ethanol | 10 | [ |
| Green-Kubo | ethylene glycol | 20—30 | [ |
| Compound | λ273K/(W·m-1·K-1) | λ288K/(W·m-1·K-1) | λ298K/(W·m-1·K-1) | λ323K/(W·m-1·K-1) | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cal. | Exp. | RD/% | Cal. | Exp. | RD/% | Cal. | Exp. | RD/% | Cal. | Exp. | RD/% | |
| ethanol | 0.172 | 0.175 | -1.71 | 0.169 | 0.171 | -1.17 | 0.170 | 0.168 | 1.19 | 0.167 | 0.162 | 3.09 |
| propanol | 0.163 | 0.162 | 0.62 | 0.159 | 0.158 | 0.63 | 0.163 | 0.156 | 4.49 | 0.150 | 0.151 | -0.66 |
| butanol | 0.160 | 0.158 | 1.27 | 0.157 | 0.155 | 1.29 | 0.150 | 0.153 | -1.96 | 0.149 | 0.148 | 0.67 |
| pentanol | 0.155 | 0.157 | -1.27 | 0.152 | 0.154 | -1.30 | 0.156 | 0.153 | 1.96 | 0.152 | 0.149 | 2.01 |
| hexanol | 0.164 | 0.159 | 3.14 | 0.151 | 0.156 | -3.21 | 0.154 | 0.154 | 0.00 | 0.146 | 0.148 | -1.35 |
| heptanol | 0.165 | 0.162 | 1.85 | 0.158 | 0.159 | -0.63 | 0.150 | 0.157 | -4.46 | 0.148 | 0.151 | -1.99 |
| octanol | 0.166 | 0.166 | 0.00 | 0.170 | 0.162 | 4.94 | 0.159 | 0.160 | -0.63 | 0.155 | 0.154 | 0.65 |
| nonanol | 0.160 | 0.166 | -3.61 | 0.161 | 0.163 | -1.23 | 0.161 | 0.161 | 0.00 | 0.155 | 0.155 | 0.00 |
表2 NEMD模拟计算得到的热导率与实验值[1]比较
Table 2 Comparison of thermal conductivity of experimental values and simulated values of alcohols obtained by NEMD simulation
| Compound | λ273K/(W·m-1·K-1) | λ288K/(W·m-1·K-1) | λ298K/(W·m-1·K-1) | λ323K/(W·m-1·K-1) | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cal. | Exp. | RD/% | Cal. | Exp. | RD/% | Cal. | Exp. | RD/% | Cal. | Exp. | RD/% | |
| ethanol | 0.172 | 0.175 | -1.71 | 0.169 | 0.171 | -1.17 | 0.170 | 0.168 | 1.19 | 0.167 | 0.162 | 3.09 |
| propanol | 0.163 | 0.162 | 0.62 | 0.159 | 0.158 | 0.63 | 0.163 | 0.156 | 4.49 | 0.150 | 0.151 | -0.66 |
| butanol | 0.160 | 0.158 | 1.27 | 0.157 | 0.155 | 1.29 | 0.150 | 0.153 | -1.96 | 0.149 | 0.148 | 0.67 |
| pentanol | 0.155 | 0.157 | -1.27 | 0.152 | 0.154 | -1.30 | 0.156 | 0.153 | 1.96 | 0.152 | 0.149 | 2.01 |
| hexanol | 0.164 | 0.159 | 3.14 | 0.151 | 0.156 | -3.21 | 0.154 | 0.154 | 0.00 | 0.146 | 0.148 | -1.35 |
| heptanol | 0.165 | 0.162 | 1.85 | 0.158 | 0.159 | -0.63 | 0.150 | 0.157 | -4.46 | 0.148 | 0.151 | -1.99 |
| octanol | 0.166 | 0.166 | 0.00 | 0.170 | 0.162 | 4.94 | 0.159 | 0.160 | -0.63 | 0.155 | 0.154 | 0.65 |
| nonanol | 0.160 | 0.166 | -3.61 | 0.161 | 0.163 | -1.23 | 0.161 | 0.161 | 0.00 | 0.155 | 0.155 | 0.00 |
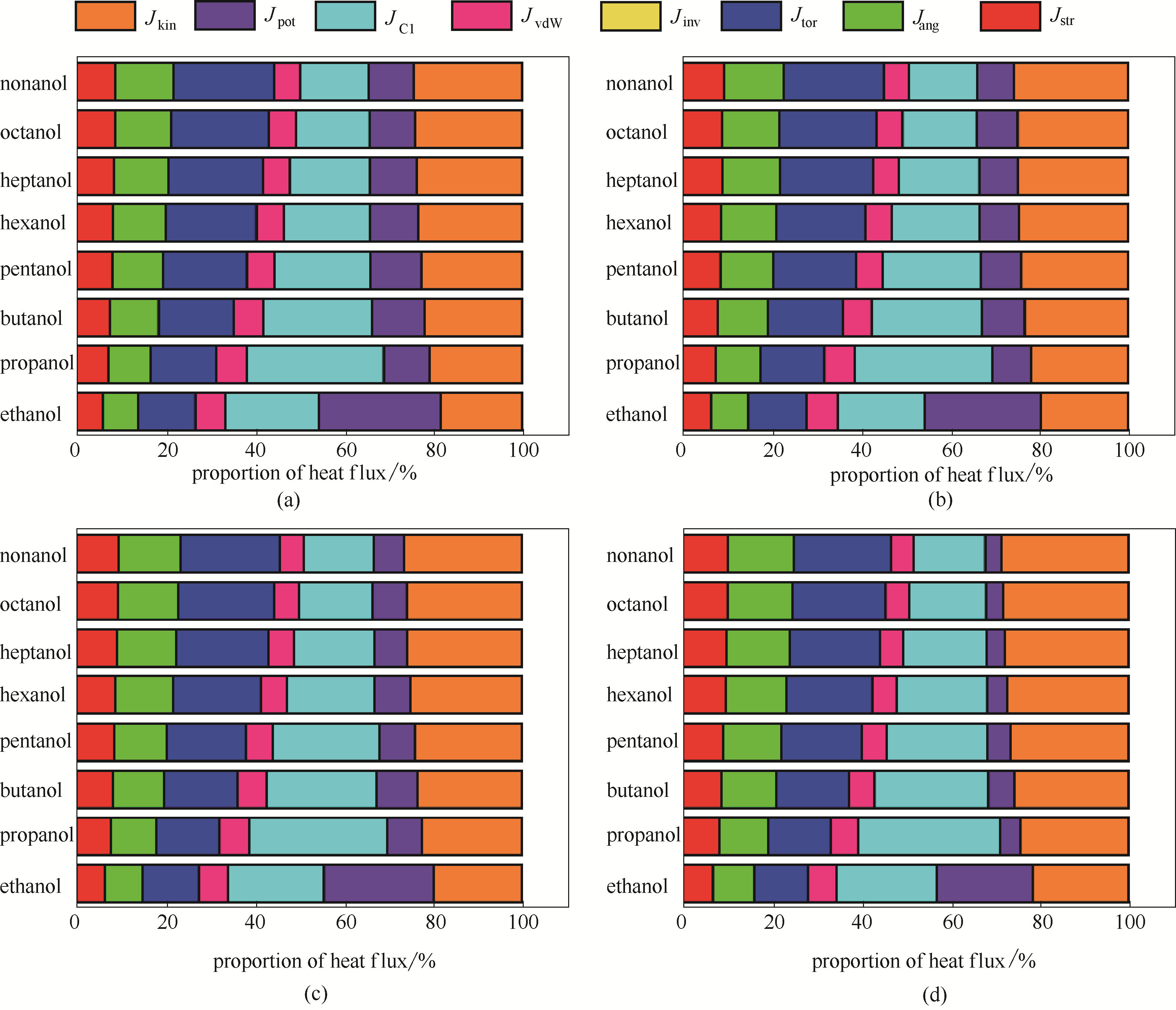
图2 273 K(a)、288 K(b)、298 K(c)和323 K(d) 8种醇的不同作用类型相互作用热通量相对大小
Fig.2 The proportion of heat flux of alcohols at 273 K (a), 288 K (b), 298 K (c) and 323 K (d) respectively
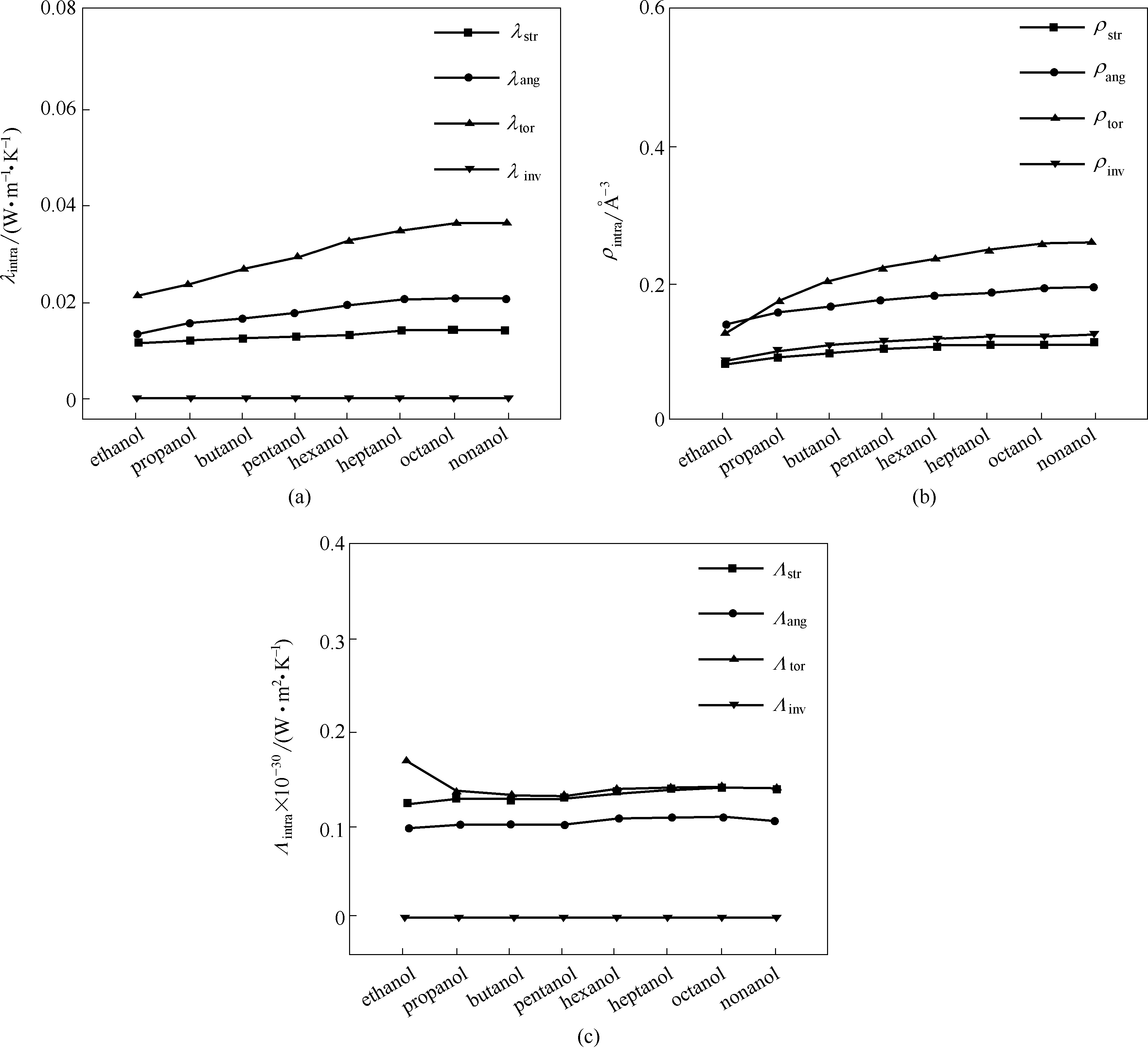
图4 醇类有机物在273 K下各分子内相互作用项的部分热导率λintra(a),密度ρintra(b)和传热效率Λintra(c)
Fig.4 The partial thermal conductivity λintra(a), the density ρintra(b), and the efficiency Λintra(c) of intramolecular interaction paths for alcohols at 273 K, respectively
| Compound | ρ273K/(g?cm-3) | ρ288K/(g?cm-3) | ρ298K/(g?cm-3) | ρ323K/(g?cm-3) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Exp. | Cal. | Exp. | Cal. | Exp. | Cal. | Exp. | Cal. | |
| ethanol | 0.808 | 0.751 | 0.795 | 0.741 | 0.786 | 0.722 | 0.763 | 0.706 |
| propanol | 0.822 | 0.755 | 0.809 | 0.744 | 0.800 | 0.736 | 0.778 | 0.709 |
| butanol | 0.826 | 0.763 | 0.814 | 0.745 | 0.806 | 0.747 | 0.785 | 0.713 |
| pentanol | 0.831 | 0.768 | 0.820 | 0.757 | 0.812 | 0.747 | 0.792 | 0.724 |
| hexanol | 0.834 | 0.772 | 0.823 | 0.757 | 0.816 | 0.749 | 0.798 | 0.727 |
| heptanol | 0.838 | 0.772 | 0.827 | 0.759 | 0.820 | 0.746 | 0.801 | 0.726 |
| octanol | 0.841 | 0.770 | 0.830 | 0.762 | 0.823 | 0.752 | 0.804 | 0.734 |
| nonanol | 0.841 | 0.769 | 0.831 | 0.762 | 0.825 | 0.751 | 0.808 | 0.738 |
表A1 不同温度下模拟体系质量密度的实验值与计算值
Table A1 Experimental and calculated values of mass density of simulated systems at different temperatures
| Compound | ρ273K/(g?cm-3) | ρ288K/(g?cm-3) | ρ298K/(g?cm-3) | ρ323K/(g?cm-3) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Exp. | Cal. | Exp. | Cal. | Exp. | Cal. | Exp. | Cal. | |
| ethanol | 0.808 | 0.751 | 0.795 | 0.741 | 0.786 | 0.722 | 0.763 | 0.706 |
| propanol | 0.822 | 0.755 | 0.809 | 0.744 | 0.800 | 0.736 | 0.778 | 0.709 |
| butanol | 0.826 | 0.763 | 0.814 | 0.745 | 0.806 | 0.747 | 0.785 | 0.713 |
| pentanol | 0.831 | 0.768 | 0.820 | 0.757 | 0.812 | 0.747 | 0.792 | 0.724 |
| hexanol | 0.834 | 0.772 | 0.823 | 0.757 | 0.816 | 0.749 | 0.798 | 0.727 |
| heptanol | 0.838 | 0.772 | 0.827 | 0.759 | 0.820 | 0.746 | 0.801 | 0.726 |
| octanol | 0.841 | 0.770 | 0.830 | 0.762 | 0.823 | 0.752 | 0.804 | 0.734 |
| nonanol | 0.841 | 0.769 | 0.831 | 0.762 | 0.825 | 0.751 | 0.808 | 0.738 |
| Compound | Jstr/ (MW·m-2) | Jang/ (MW·m-2) | Jtor/ (MW·m-2) | Jinv/ (MW·m-2) | JvdW/ (MW·m-2) | JCl/ (MW·m-2) | Jpot/ (MW·m-2) | Jkin/ (MW·m-2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 273 K | ||||||||
| ethanol | 82.35061 | 105.5749 | 173.2012 | 1.166184 | 93.33839 | 286.4405 | 371.678 | 248.0089 |
| propanol | 95.427 | 130.7635 | 196.4533 | 0.585375 | 93.64934 | 412.9896 | 140.9174 | 280.7405 |
| butanol | 102.2969 | 144.5943 | 230.6405 | 0.25144 | 90.01795 | 331.163 | 160.8052 | 295.7485 |
| pentanol | 107.868 | 154.3851 | 253.6832 | 0.000517 | 87.71279 | 291.5588 | 152.6921 | 307.3169 |
| hexanol | 111.1385 | 161.5822 | 272.2318 | 0.192211 | 85.97666 | 262.5442 | 149.1838 | 314.8754 |
| heptanol | 114.1706 | 166.809 | 285.5701 | 0.332879 | 83.79046 | 238.7217 | 143.6668 | 320.7745 |
| octanol | 116.1588 | 170.8392 | 295.6281 | 0.456438 | 81.58639 | 220.2334 | 138.452 | 324.2486 |
| nonanol | 118.2226 | 174.2786 | 304.655 | 0.546975 | 80.09264 | 204.8891 | 135.421 | 328.5367 |
| 288 K | ||||||||
| ethanol | 88.59901 | 113.6205 | 174.6725 | 1.23144 | 93.83133 | 267.6399 | 356.5573 | 267.6399 |
| propanol | 99.90495 | 136.3767 | 194.1579 | 0.605893 | 91.07394 | 417.0604 | 118.3188 | 294.1697 |
| butanol | 107.0843 | 150.4192 | 226.3646 | 0.262161 | 85.5488 | 333.7362 | 133.8917 | 309.7504 |
| pentanol | 113.2669 | 161.7038 | 250.8701 | 0.006098 | 83.09045 | 296.5954 | 125.7172 | 322.7532 |
| hexanol | 116.3273 | 168.5521 | 268.0233 | 0.19607 | 81.54108 | 265.5234 | 122.2882 | 329.8472 |
| heptanol | 119.7637 | 174.7064 | 281.0965 | 0.356169 | 79.75569 | 241.4785 | 116.8366 | 336.7934 |
| octanol | 118.6948 | 174.2466 | 293.9069 | 0.474525 | 80.82509 | 221.6068 | 128.2734 | 331.6131 |
| nonanol | 123.9406 | 182.1128 | 301.084 | 0.569318 | 77.058 | 207.7246 | 111.1315 | 344.7189 |
| 298 K | ||||||||
| ethanol | 87.98672 | 112.9572 | 168.2807 | 1.206443 | 88.32364 | 293.7441 | 331.1771 | 266.7173 |
| propanol | 102.5047 | 139.5892 | 192.5958 | 0.615713 | 89.51541 | 419.0179 | 105.4844 | 301.6295 |
| butanol | 110.7437 | 155.6268 | 226.0706 | 0.264945 | 86.09783 | 338.6185 | 121.7853 | 320.4123 |
| pentanol | 112.9239 | 160.9453 | 241.8836 | 0.004015 | 79.95448 | 323.2599 | 109.6565 | 323.2599 |
| hexanol | 119.3759 | 172.3581 | 265.5312 | 0.207462 | 79.42465 | 267.028 | 107.6302 | 338.3892 |
| heptanol | 122.6607 | 177.7654 | 278.0849 | 0.36209 | 76.12581 | 243.1349 | 100.1216 | 344.334 |
| octanol | 125.058 | 182.0887 | 289.8456 | 0.483914 | 75.27087 | 224.3338 | 99.52106 | 348.9841 |
| nonanol | 126.9109 | 186.5117 | 297.3773 | 0.587973 | 73.19684 | 208.9527 | 93.39459 | 354.1787 |
| 323 K | ||||||||
| ethanol | 94.44256 | 121.7495 | 164.777 | 1.270205 | 86.1226 | 304.3557 | 294.614 | 289.2095 |
| propanol | 109.4977 | 148.8176 | 187.5502 | 0.645945 | 83.78129 | 425.1214 | 64.5793 | 323.3033 |
| butanol | 117.2486 | 164.5488 | 218.7043 | 0.269378 | 78.09459 | 343.464 | 76.82576 | 340.5539 |
| pentanol | 123.3485 | 175.3366 | 242.1652 | 0.007284 | 75.84128 | 303.4792 | 71.65321 | 353.422 |
| hexanol | 128.1472 | 183.9092 | 258.5265 | 0.214408 | 72.87701 | 272.8254 | 63.01978 | 363.5166 |
| heptanol | 131.455 | 190.117 | 270.929 | 0.387389 | 69.7516 | 248.777 | 55.96572 | 370.4024 |
| octanol | 134.7473 | 195.9925 | 282.6226 | 0.526943 | 69.26389 | 230.4936 | 53.36009 | 377.35 |
| nonanol | 136.9088 | 199.7251 | 291.0947 | 0.631816 | 67.9927 | 214.095 | 51.09756 | 381.8325 |
表A2 通过对热流分解分别得到在不同温度下醇类有机物各类热通量所占比例
Table A2 Proportions of each type of heat flux of alcohol organics at different temperatures obtained by heat flux decomposition, respectively
| Compound | Jstr/ (MW·m-2) | Jang/ (MW·m-2) | Jtor/ (MW·m-2) | Jinv/ (MW·m-2) | JvdW/ (MW·m-2) | JCl/ (MW·m-2) | Jpot/ (MW·m-2) | Jkin/ (MW·m-2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 273 K | ||||||||
| ethanol | 82.35061 | 105.5749 | 173.2012 | 1.166184 | 93.33839 | 286.4405 | 371.678 | 248.0089 |
| propanol | 95.427 | 130.7635 | 196.4533 | 0.585375 | 93.64934 | 412.9896 | 140.9174 | 280.7405 |
| butanol | 102.2969 | 144.5943 | 230.6405 | 0.25144 | 90.01795 | 331.163 | 160.8052 | 295.7485 |
| pentanol | 107.868 | 154.3851 | 253.6832 | 0.000517 | 87.71279 | 291.5588 | 152.6921 | 307.3169 |
| hexanol | 111.1385 | 161.5822 | 272.2318 | 0.192211 | 85.97666 | 262.5442 | 149.1838 | 314.8754 |
| heptanol | 114.1706 | 166.809 | 285.5701 | 0.332879 | 83.79046 | 238.7217 | 143.6668 | 320.7745 |
| octanol | 116.1588 | 170.8392 | 295.6281 | 0.456438 | 81.58639 | 220.2334 | 138.452 | 324.2486 |
| nonanol | 118.2226 | 174.2786 | 304.655 | 0.546975 | 80.09264 | 204.8891 | 135.421 | 328.5367 |
| 288 K | ||||||||
| ethanol | 88.59901 | 113.6205 | 174.6725 | 1.23144 | 93.83133 | 267.6399 | 356.5573 | 267.6399 |
| propanol | 99.90495 | 136.3767 | 194.1579 | 0.605893 | 91.07394 | 417.0604 | 118.3188 | 294.1697 |
| butanol | 107.0843 | 150.4192 | 226.3646 | 0.262161 | 85.5488 | 333.7362 | 133.8917 | 309.7504 |
| pentanol | 113.2669 | 161.7038 | 250.8701 | 0.006098 | 83.09045 | 296.5954 | 125.7172 | 322.7532 |
| hexanol | 116.3273 | 168.5521 | 268.0233 | 0.19607 | 81.54108 | 265.5234 | 122.2882 | 329.8472 |
| heptanol | 119.7637 | 174.7064 | 281.0965 | 0.356169 | 79.75569 | 241.4785 | 116.8366 | 336.7934 |
| octanol | 118.6948 | 174.2466 | 293.9069 | 0.474525 | 80.82509 | 221.6068 | 128.2734 | 331.6131 |
| nonanol | 123.9406 | 182.1128 | 301.084 | 0.569318 | 77.058 | 207.7246 | 111.1315 | 344.7189 |
| 298 K | ||||||||
| ethanol | 87.98672 | 112.9572 | 168.2807 | 1.206443 | 88.32364 | 293.7441 | 331.1771 | 266.7173 |
| propanol | 102.5047 | 139.5892 | 192.5958 | 0.615713 | 89.51541 | 419.0179 | 105.4844 | 301.6295 |
| butanol | 110.7437 | 155.6268 | 226.0706 | 0.264945 | 86.09783 | 338.6185 | 121.7853 | 320.4123 |
| pentanol | 112.9239 | 160.9453 | 241.8836 | 0.004015 | 79.95448 | 323.2599 | 109.6565 | 323.2599 |
| hexanol | 119.3759 | 172.3581 | 265.5312 | 0.207462 | 79.42465 | 267.028 | 107.6302 | 338.3892 |
| heptanol | 122.6607 | 177.7654 | 278.0849 | 0.36209 | 76.12581 | 243.1349 | 100.1216 | 344.334 |
| octanol | 125.058 | 182.0887 | 289.8456 | 0.483914 | 75.27087 | 224.3338 | 99.52106 | 348.9841 |
| nonanol | 126.9109 | 186.5117 | 297.3773 | 0.587973 | 73.19684 | 208.9527 | 93.39459 | 354.1787 |
| 323 K | ||||||||
| ethanol | 94.44256 | 121.7495 | 164.777 | 1.270205 | 86.1226 | 304.3557 | 294.614 | 289.2095 |
| propanol | 109.4977 | 148.8176 | 187.5502 | 0.645945 | 83.78129 | 425.1214 | 64.5793 | 323.3033 |
| butanol | 117.2486 | 164.5488 | 218.7043 | 0.269378 | 78.09459 | 343.464 | 76.82576 | 340.5539 |
| pentanol | 123.3485 | 175.3366 | 242.1652 | 0.007284 | 75.84128 | 303.4792 | 71.65321 | 353.422 |
| hexanol | 128.1472 | 183.9092 | 258.5265 | 0.214408 | 72.87701 | 272.8254 | 63.01978 | 363.5166 |
| heptanol | 131.455 | 190.117 | 270.929 | 0.387389 | 69.7516 | 248.777 | 55.96572 | 370.4024 |
| octanol | 134.7473 | 195.9925 | 282.6226 | 0.526943 | 69.26389 | 230.4936 | 53.36009 | 377.35 |
| nonanol | 136.9088 | 199.7251 | 291.0947 | 0.631816 | 67.9927 | 214.095 | 51.09756 | 381.8325 |
| 1 | Vargaftik N B. Handbook of Thermal Conductivity of Liquids and Gases[M]. Boca Raton FL: CRC press, 1994. |
| 2 | Algaer E A, Müller-Plathe F. Molecular dynamics calculations of the thermal conductivity of molecular liquids, polymers, and carbon nanotubes[J]. Soft Materials, 2012, 10(1/2/3): 42-80. |
| 3 | Bao H, Chen J, Gu X, et al. A review of simulation methods in micro/nanoscale heat conduction[J]. ES Energy & Environment, 2018, 1: 16-55. |
| 4 | Assael M J, Antoniadis K D, Wakeham W A. Historical evolution of the transient hot-wire technique[J]. International Journal of Thermophysics, 2010, 31(6): 1051-1072. |
| 5 | Nagvekar M, Daubert T E. A group contribution method for liquid thermal conductivity[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 1987, 26(7): 1362-1365. |
| 6 | Rodenbush C M, Viswanath D S, Hsieh F. A group contribution method for the prediction of thermal conductivity of liquids and its application to the prandtl number for vegetable oils[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 1999, 38(11): 4513-4519. |
| 7 | Tsotsas E, Schluender E U. Numerical calculation of the thermal conductivity of two regular bidispersed beds of spherical particles[J]. Computers & Chemical Engineering, 1990, 14(9): 1031-1038. |
| 8 | Liu W, Lu H, Cao C, et al. An improved quantitative structure property relationship model for predicting thermal conductivity of liquid aliphatic alcohols[J]. Journal of Chemical and Engineering Data, 2018, 63(12): 4735-4740. |
| 9 | Lu H, Yang F, Liu W, et al. A robust model for estimating thermal conductivity of liquid alkyl halides[J]. SAR and QSAR in Environmental Research, 2020, 31(2): 73-85. |
| 10 | Ohara T. Contribution of intermolecular energy transfer to heat conduction in a simple liquid[J]. Journal of Chemical Physics, 1999, 111(21): 9667-9672. |
| 11 | Ohara T. Intermolecular energy transfer in liquid water and its contribution to heat conduction: a molecular dynamics study[J]. Journal of Chemical Physics, 1999, 111(14): 6492-6500. |
| 12 | Zhang M, Lussetti E, de Souza L E S, et al. Thermal conductivities of molecular liquids by reverse nonequilibrium molecular dynamics[J]. Journal of Physical Chemistry B, 2005, 109(31): 15060-15067. |
| 13 | 李嘉辰, 俞斌, 王琦, 等. 分子模拟研究壳聚糖-氮化硼纳米管封装及输运阿霉素[J]. 化工学报, 2020, 71(1): 354-360. |
| Li J C, Yu B, Wang Q, et al. Molecular simulation on doxorubicin encapsulation and transport by chitosan-boron nitride nanotubes[J]. CIESC Journal, 2020, 71(1): 354-360. | |
| 14 | 王韬, 刘向阳, 何茂刚. 离子液体[bmim][Tf2N]的分子动力学模拟[J]. 化工学报, 2019, 70: 258-264. |
| Wang T, Liu X Y, He M G. Molecular dynamics simulation of ionic liquid [bmim][Tf2N][J]. CIESC Journal, 2019, 70: 258-264. | |
| 15 | 杨慧芳, 关海莲, 李平, 等. 煤颗粒燃烧过程氧化机理及有机氮转化的分子模拟: 以宁东红石湾煤为例[J]. 化工学报, 2020, 71(2): 799-810. |
| Yang H F, Guan H L, Li P, et al. Molecular modeling of oxidation mechanism and organic nitrogen conversion in coal particle combustion: a case study on HSW coal of Ningdong[J]. CIESC Journal, 2020, 71(2): 799-810. | |
| 16 | 张博, 何依然, 刘迎春, 等. 异喹啉类生物碱和G-四链体结合的分子动力学研究[J]. 化工学报, 2020, 71(1): 344-353. |
| Zhang B, He Y R, Liu Y C, et al. Molecular dynamics study of binding of isoquinoline alkaloids to G-quadruplex[J]. CIESC Journal, 2020, 71(1): 344-353. | |
| 17 | 邹瀚影, 冯妍卉, 邱琳, 等. 十八烷酸热传导机制的尺度效应研究[J]. 化工学报, 2019, 70: 155-160. |
| Zou H Y, Feng Y H, Qiu L, et al. Size effect of heat conduction mechanism on stearic acid[J]. CIESC Journal, 2019, 70: 155-160. | |
| 18 | Matsubara H, Kikugawa G, Bessho T, et al. Understanding the chain length dependence of thermal conductivity of liquid alcohols at 298 K on the basis of molecular-scale energy transfer[J]. Fluid Phase Equilibria, 2017, 441: 24-32. |
| 19 | Guevara-Carrion G, Nieto-Draghi C, Vrabec J, et al. Prediction of transport properties by molecular simulation: methanol and ethanol and their mixture[J]. Journal of Physical Chemistry B, 2008, 112(51): 16664-16674. |
| 20 | Petravic J. Thermal conductivity of ethanol[J]. Journal of Chemical Physics, 2005, 123: 174503. |
| 21 | Lin Y, Hsiao P, Chieng C. Constructing a force interaction model for thermal conductivity computation using molecular dynamics simulation: ethylene glycol as an example[J]. Journal of Chemical Physics, 2011, 134(15): 154509. |
| 22 | Fan Z, Pereira L F C, Wang H, et al. Force and heat current formulas for many-body potentials in molecular dynamics simulations with applications to thermal conductivity calculations[J]. Physical Review B, 2015, 92(9): 94301. |
| 23 | Torii D, Nakano T, Ohara T. Contribution of inter- and intramolecular energy transfers to heat conduction in liquids[J]. Journal of Chemical Physics, 2008, 128(4): 44504. |
| 24 | Matsubara H, Kikugawa G, Bessho T, et al. Effects of molecular structure on microscopic heat transport in chain polymer liquids[J]. Journal of Chemical Physics, 2015, 142(16): 164509. |
| 25 | Lv W, Henry A. Direct calculation of modal contributions to thermal conductivity via Green-Kubo modal analysis[J]. New Journal of Physics, 2016, 18(1): 13028. |
| 26 | Sun H, Mumby S J, Maple J R, et al. An ab initio CFF93 all-atom force field for polycarbonates[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 1994, 116(7): 2978-2987. |
| 27 | Zhu W, Wang X, Xiao J, et al. Molecular dynamics simulations of AP/HMX composite with a modified force field[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2009, 167(1): 810-816. |
| 28 | Sun Y, Chen L, Cui L, et al. Molecular dynamics simulation of cross-linked epoxy resin and its interaction energy with graphene under two typical force fields[J]. Computational Materials Science, 2018, 143: 240-247. |
| 29 | Ikeshoji T, Hafskjold B. Non-equilibrium molecular dynamics calculation of heat conduction in liquid and through liquid-gas interface[J]. Molecular Physics, 1994, 81(2): 251-261. |
| 30 | Jund P, Jullien R. Molecular-dynamics calculation of the thermal conductivity of vitreous silica[J]. Physical Review B, 1999, 59(21): 13707. |
| 31 | Brown W M, Yamada M. Implementing molecular dynamics on hybrid high performance computers—three-body potentials[J]. Computer Physics Communications, 2013, 184(12): 2785-2793. |
| 32 | Brown W M, Kohlmeyer A, Plimpton S J, et al. Implementing molecular dynamics on hybrid high performance computers—particle-particle particle-mesh[J]. Computer Physics Communications, 2012, 183(3): 449-459. |
| 33 | Brown W M, Wang P, Plimpton S J, et al. Implementing molecular dynamics on hybrid high performance computers—short range forces[J]. Computer Physics Communications, 2011, 182(4): 898-911. |
| 34 | Nguyen T D. GPU-accelerated Tersoff potentials for massively parallel molecular dynamics simulations[J]. Computer Physics Communications, 2017, 212: 113-122. |
| 35 | Nguyen T D, Plimpton S J. Accelerating dissipative particle dynamics simulations for soft matter systems[J]. Computational Materials Science, 2015, 100: 173-180. |
| 36 | Plimpton S. Fast parallel algorithms for short-range molecular dynamics[J]. Journal of Computational Physics, 1995, 117(1): 1-19. |
| 37 | Boone P, Babaei H, Wilmer C E. Heat flux for many-body interactions: corrections to LAMMPS[J]. Journal of Chemical Theory and Computation, 2019, 15(10): 5579-5587. |
| 38 | Wirnsberger P, Frenkel D, Dellago C. An enhanced version of the heat exchange algorithm with excellent energy conservation properties[J]. Journal of Chemical Physics, 2015, 143(12): 124104. |
| 39 | Hoover W G. Canonical dynamics: equilibrium phase-space distributions[J]. Physical Review A, 1985, 31(3): 1695-1697. |
| 40 | Ohara T, Chia Yuan T, Torii D, et al. Heat conduction in chain polymer liquids: molecular dynamics study on the contributions of inter- and intramolecular energy transfer[J]. Journal of Chemical Physics, 2011, 135(3): 34507. |
| [1] | 张双星, 刘舫辰, 张义飞, 杜文静. R-134a脉动热管相变蓄放热实验研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(S1): 165-171. |
| [2] | 张义飞, 刘舫辰, 张双星, 杜文静. 超临界二氧化碳用印刷电路板式换热器性能分析[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(S1): 183-190. |
| [3] | 陈爱强, 代艳奇, 刘悦, 刘斌, 吴翰铭. 基板温度对HFE7100液滴蒸发过程的影响研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(S1): 191-197. |
| [4] | 刘明栖, 吴延鹏. 导光管直径和长度对传热影响的模拟分析[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(S1): 206-212. |
| [5] | 王志国, 薛孟, 董芋双, 张田震, 秦晓凯, 韩强. 基于裂隙粗糙性表征方法的地热岩体热流耦合数值模拟与分析[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(S1): 223-234. |
| [6] | 晁京伟, 许嘉兴, 李廷贤. 基于无管束蒸发换热强化策略的吸附热池的供热性能研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(S1): 302-310. |
| [7] | 程成, 段钟弟, 孙浩然, 胡海涛, 薛鸿祥. 表面微结构对析晶沉积特性影响的格子Boltzmann模拟[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(S1): 74-86. |
| [8] | 李艺彤, 郭航, 陈浩, 叶芳. 催化剂非均匀分布的质子交换膜燃料电池操作条件研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(9): 3831-3840. |
| [9] | 王玉兵, 李杰, 詹宏波, 朱光亚, 张大林. R134a在菱形离散肋微小通道内的流动沸腾换热实验研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(9): 3797-3806. |
| [10] | 李科, 文键, 忻碧平. 耦合蒸气冷却屏的真空多层绝热结构对液氢储罐自增压过程的影响机制研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(9): 3786-3796. |
| [11] | 陈杰, 林永胜, 肖恺, 杨臣, 邱挺. 胆碱基碱性离子液体催化合成仲丁醇性能研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(9): 3716-3730. |
| [12] | 齐聪, 丁子, 余杰, 汤茂清, 梁林. 基于选择吸收纳米薄膜的太阳能温差发电特性研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(9): 3921-3930. |
| [13] | 杨越, 张丹, 郑巨淦, 涂茂萍, 杨庆忠. NaCl水溶液喷射闪蒸-掺混蒸发的实验研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(8): 3279-3291. |
| [14] | 曾如宾, 沈中杰, 梁钦锋, 许建良, 代正华, 刘海峰. 基于分子动力学模拟的Fe2O3纳米颗粒烧结机制研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(8): 3353-3365. |
| [15] | 杨菲菲, 赵世熙, 周维, 倪中海. Sn掺杂的In2O3催化CO2选择性加氢制甲醇[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(8): 3366-3374. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备 11010102001995号
京公网安备 11010102001995号