化工学报 ›› 2023, Vol. 74 ›› Issue (5): 2000-2012.DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20230265
袁子涵( ), 王淑彦(
), 王淑彦( ), 邵宝力, 谢磊, 陈曦, 马一玫
), 邵宝力, 谢磊, 陈曦, 马一玫
收稿日期:2023-03-20
修回日期:2023-04-25
出版日期:2023-05-05
发布日期:2023-06-29
通讯作者:
王淑彦
作者简介:袁子涵(1995—),男,博士研究生,yuanzihan@stu.nepu.edu.cn
基金资助:
Zihan YUAN( ), Shuyan WANG(
), Shuyan WANG( ), Baoli SHAO, Lei XIE, Xi CHEN, Yimei MA
), Baoli SHAO, Lei XIE, Xi CHEN, Yimei MA
Received:2023-03-20
Revised:2023-04-25
Online:2023-05-05
Published:2023-06-29
Contact:
Shuyan WANG
摘要:
采用欧拉-欧拉双流体模型(TFM)结合颗粒动理学理论(KTGF)方法,对三维幂律流化床中的液固两相流动行为进行了模拟。基于幂律流体的流变方程以及压降方程,提出了两种幂律液固曳力模型,引入了考虑液膜效应的湿颗粒动态恢复系数模型,计算幂律流体与湿颗粒之间的作用力。将预测固含率分别与文献中测得的实验数据进行比较,结果表明结合动态恢复系数模型的相对误差介于0.45%~1.59%,与实验结果吻合较好。探究了稠度系数K以及流性指数n对颗粒流动特性的影响,结果表明随着流变参数的增大,床层内的颗粒平均浓度降低,湿颗粒表面液膜逐渐变厚,法向恢复系数降低;颗粒拟温度随n的升高先增大后减小,随K的上升而增大;曳力系数、颗粒压力以及颗粒黏度均随流变参数的增大而逐渐减小。颗粒在壁面处的浓度明显高于中心处附近的浓度,且颗粒在中心处向上运动,在壁面处附近回落,在流化床中形成环-核结构。
中图分类号:
袁子涵, 王淑彦, 邵宝力, 谢磊, 陈曦, 马一玫. 基于幂律液固曳力模型流化床内湿颗粒流动特性的研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(5): 2000-2012.
Zihan YUAN, Shuyan WANG, Baoli SHAO, Lei XIE, Xi CHEN, Yimei MA. Investigation on flow characteristics of wet particles with power-law liquid-solid drag models in fluidized bed[J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(5): 2000-2012.
| 符号 | 参数 | 文献[ | 本文模拟参数 | 文献[ | 本文模拟参数 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Din | 流化床直径/mm | 90 | 90 | 68 | 68 |
| H | 流化床高度/mm | 2000 | 1000 | 1100 | 1100 |
| h0 | 初始床高/mm | 120 | 120 | — | 200 |
| εs,max | 最大颗粒浓度 | — | 0.63 | — | 0.63 |
| ε0 | 初始颗粒浓度 | 0.578 | 0.578 | — | 0.6 |
| dp | 颗粒直径/mm | 4.6 | 4.6 | 3 | |
| ρs | 颗粒密度/(kg/m3) | 2258 | 2258 | 2500 | 2500 |
| ρl | 流体密度/(kg/m3) | 1001 | 1001 | 997 | 997 |
| K | 稠度系数/(Pa·s n ) | 0.013 | 0.013 | 0.0299 | 0.0299 |
| n | 流性指数 | 0.82 | 0.82 | 0.719 | 0.719 |
| u0 | 流体表观速度/(cm/s) | 5.35~8.96 | Same | 2.416~10.436 | Same |
| e | 法向恢复系数 | — | 0.98, ewet | — | 0.98, ewet |
| 网格数 | — | 10×100×10 | — | 10×100×10 |
表1 数值模拟参数及文献[15-16]实验值
Table 1 Parameters used in numerical simulations and experiments by Ref.[15-16]
| 符号 | 参数 | 文献[ | 本文模拟参数 | 文献[ | 本文模拟参数 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Din | 流化床直径/mm | 90 | 90 | 68 | 68 |
| H | 流化床高度/mm | 2000 | 1000 | 1100 | 1100 |
| h0 | 初始床高/mm | 120 | 120 | — | 200 |
| εs,max | 最大颗粒浓度 | — | 0.63 | — | 0.63 |
| ε0 | 初始颗粒浓度 | 0.578 | 0.578 | — | 0.6 |
| dp | 颗粒直径/mm | 4.6 | 4.6 | 3 | |
| ρs | 颗粒密度/(kg/m3) | 2258 | 2258 | 2500 | 2500 |
| ρl | 流体密度/(kg/m3) | 1001 | 1001 | 997 | 997 |
| K | 稠度系数/(Pa·s n ) | 0.013 | 0.013 | 0.0299 | 0.0299 |
| n | 流性指数 | 0.82 | 0.82 | 0.719 | 0.719 |
| u0 | 流体表观速度/(cm/s) | 5.35~8.96 | Same | 2.416~10.436 | Same |
| e | 法向恢复系数 | — | 0.98, ewet | — | 0.98, ewet |
| 网格数 | — | 10×100×10 | — | 10×100×10 |

图4 不同流变参数下颗粒浓度瞬时分布图(左:干颗粒;右:湿颗粒)
Fig.4 Instantaneous concentration of particles with different flow behavior indexes and consistency coefficients at 50 s (left: dry particles; right: wet particles)
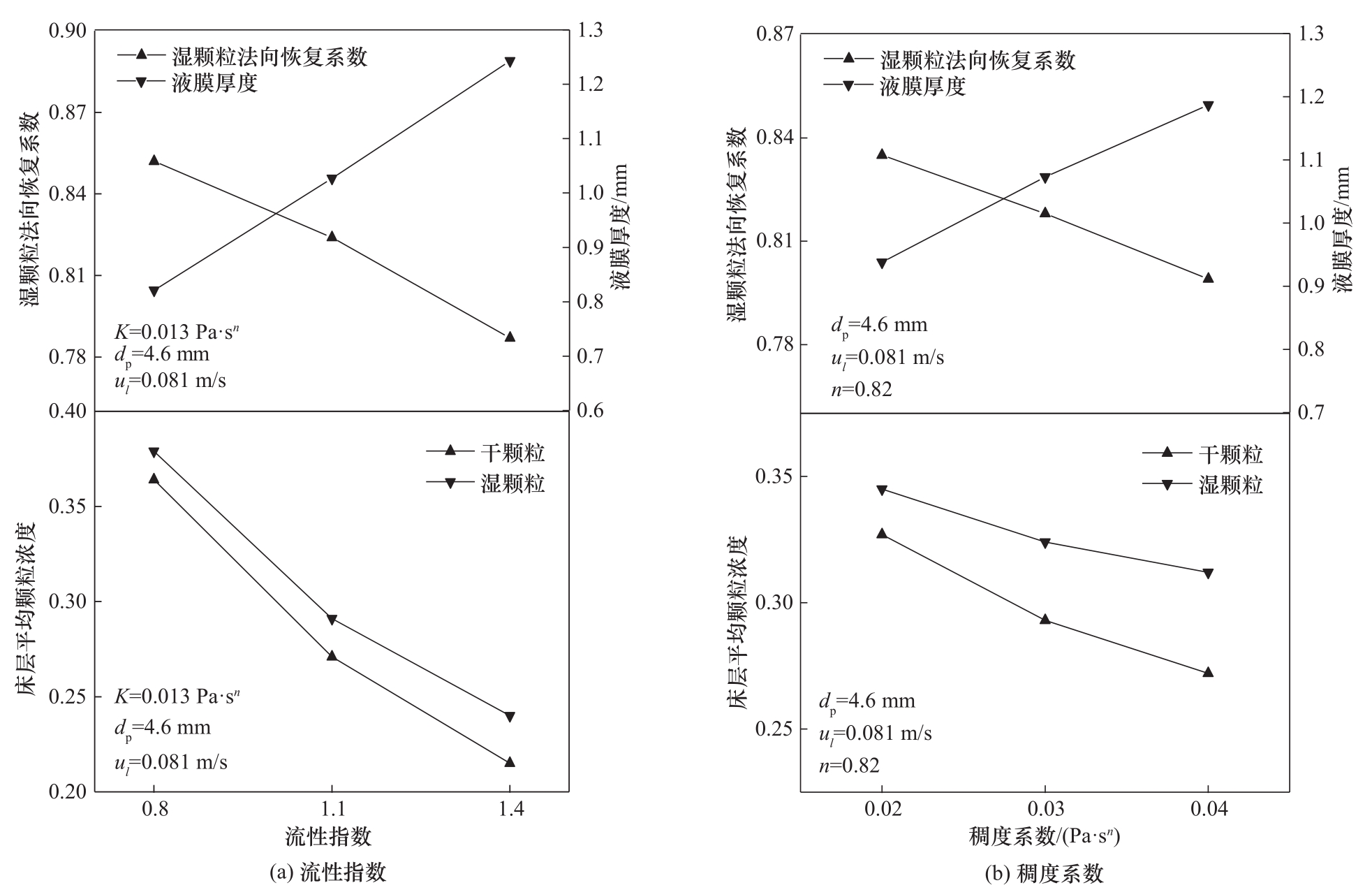
图5 不同流性指数和稠度系数下的床层平均颗粒浓度、湿颗粒法向恢复系数以及液膜厚度
Fig.5 Time-averaged concentration of particles, normal restitution coefficient and liquid film thickness with different flow behavior indexes and consistency coefficients

图6 不同流性指数和稠度系数下同一高度处时均颗粒体积分数的径向分布
Fig.6 Radial distributions of the time-averaged particles concentration with different flow behavior indexes and consistency coefficients at the same height
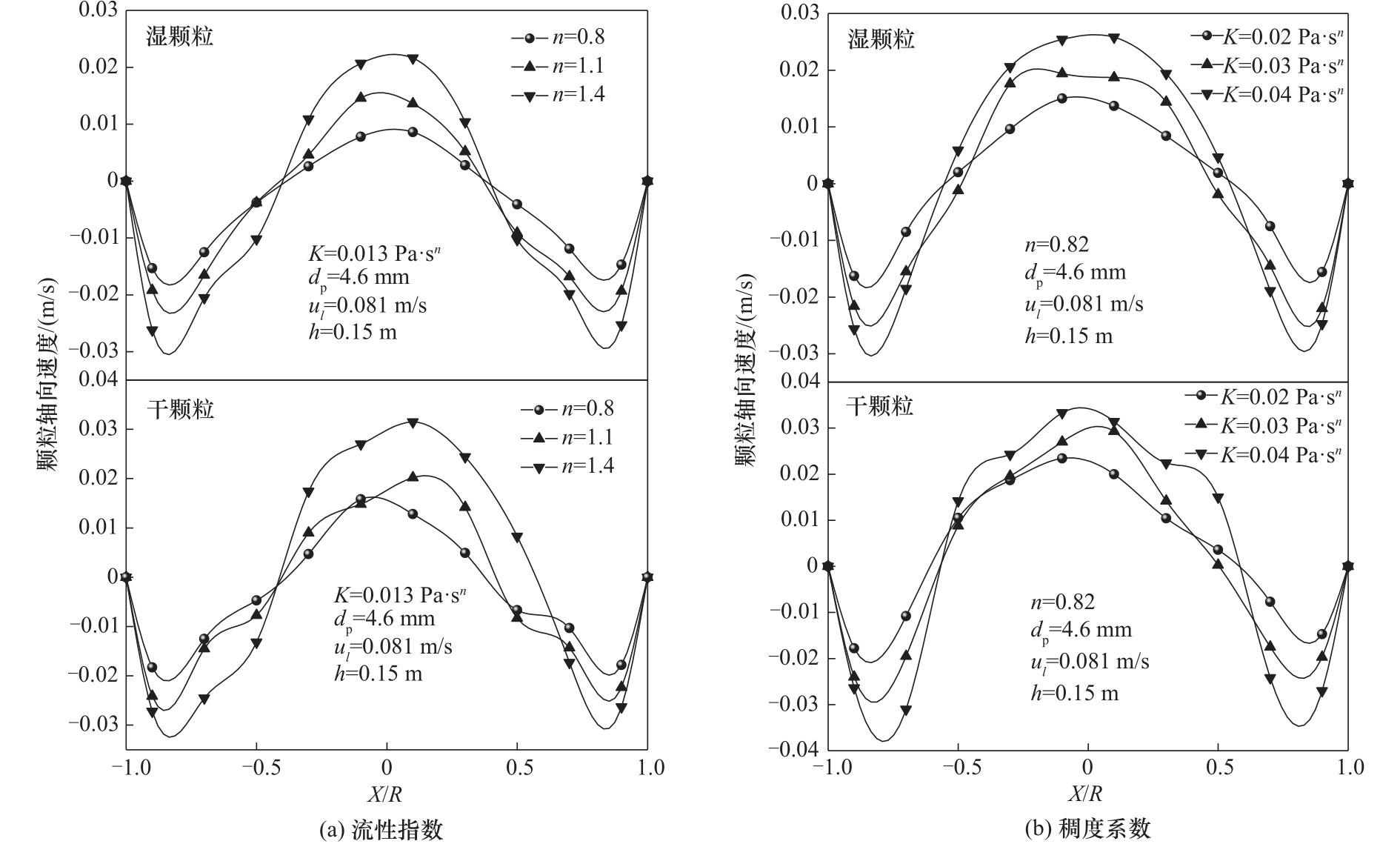
图7 不同流性指数和稠度系数下同一高度处时均颗粒轴向速度的径向分布
Fig.7 Radial distributions of the time-averaged axial velocity of particles with different flow behavior indexes and consistency coefficients at the same height

图8 不同流性指数和稠度系数下时均曳力系数随颗粒体积分数的变化
Fig.8 Time-averaged drag coefficient as a function of particles concentration under different flow behavior indexes and consistency coefficients
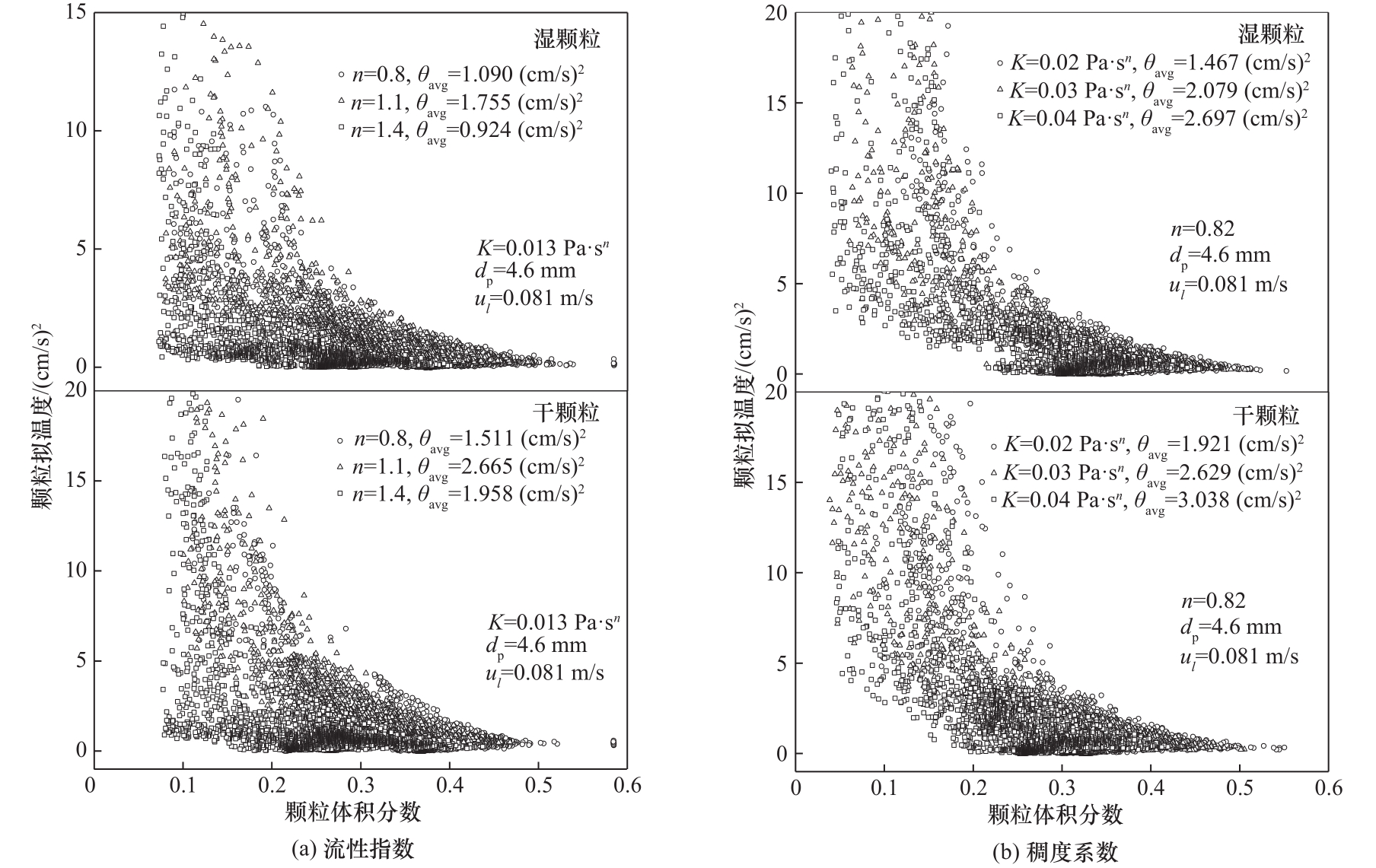
图9 不同流性指数和稠度系数下时均颗粒拟温度随颗粒体积分数的变化
Fig.9 Time-averaged granular temperature as a function of particles concentration under different flow behavior indexes and consistency coefficients

图10 不同流性系数和稠度系数下时均颗粒压力随颗粒体积分数的变化
Fig.10 Time-averaged granular pressure as a function of particles concentration under different flow behavior indexes and consistency coefficients

图11 不同流性指数和稠度系数下时均颗粒黏度随颗粒体积分数的变化
Fig.11 Time-averaged granular viscosity as a function of particles concentration under different flow behavior indexes and consistency coefficients
| 1 | Cheng Y, Zhu J X. CFD modelling and simulation of hydrodynamics in liquid-solid circulating fluidized beds[J]. The Canadian Journal of Chemical Engineering, 2005, 83(2): 177-185. |
| 2 | 郭慕孙,李洪钟.流态化手册[M].北京:石油工业出版社,1994. |
| Kwauk M S, Li H Z. Handbook of Fluidization[M]. Beijing: Petroleum Industry Press, 1994. | |
| 3 | Lu H L, Gidaspow D. Hydrodynamics of binary fluidization in a riser: CFD simulation using two granular temperatures[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2003, 58(16): 3777-3792. |
| 4 | Yang L, Du K. A comprehensive review on the natural, forced, and mixed convection of non-Newtonian fluids (nanofluids) inside different cavities[J]. Journal of Thermal Analysis and Calorimetry, 2020, 140(5): 2033-2054. |
| 5 | Shende T, Niasar V J, Babaei M. Effective viscosity and Reynolds number of non-Newtonian fluids using Meter model[J]. Rheologica Acta, 2021, 60(1): 11-21. |
| 6 | Qi Z, Kuang S B, Yu A B. Lattice Boltzmann investigation of non-Newtonian fluid flow through a packed bed of uniform spheres[J]. Powder Technology, 2019, 343: 225-236. |
| 7 | Kandasamy S, Venkatachalam S. Prediction of bed voidage in multi-phase fluidized bed using air/Newtonian and non-Newtonian liquid systems[J]. Desalination and Water Treatment, 2021, 211: 92-98. |
| 8 | Pang B X, Wang S Y, Lu H L. A modified drag model for power-law fluid-particle flow used in computational fluid dynamics simulation[J]. Advanced Powder Technology, 2021, 32(4): 1207-1218. |
| 9 | Shah S N, El Fadili Y, Chhabra R P. New model for single spherical particle settling velocity in power law (visco-inelastic) fluids[J]. International Journal of Multiphase Flow, 2007, 33(1): 51-66. |
| 10 | Marinack M C, Musgrave R E, C F Ⅲ Higgs. Experimental investigations on the coefficient of restitution of single particles[J]. Tribology Transactions, 2013, 56(4): 572-580. |
| 11 | Crüger B, Salikov V, Heinrich S, et al. Coefficient of restitution for particles impacting on wet surfaces: an improved experimental approach[J]. Particuology, 2016, 25: 1-9. |
| 12 | Liu G D, Yu F, Lu H L, et al. CFD-DEM simulation of liquid-solid fluidized bed with dynamic restitution coefficient[J]. Powder Technology, 2016, 304: 186-197. |
| 13 | Gao Z Y, Liu G D, Guo X Y, et al. A dynamic coefficient of restitution applied to two-fluid model in liquid-solid fluidized bed[J]. Powder Technology, 2022, 402: 117335. |
| 14 | Zhong H B, Zhang Y N, Xiong Q G, et al. Two-fluid modeling of a wet spouted fluidized bed with wet restitution coefficient model[J]. Powder Technology, 2020, 364: 363-372. |
| 15 | Broniarz-Press L, Agacinski P, Rozanski J. Shear-thinning fluids flow in fixed and fluidised beds[J]. International Journal of Multiphase Flow, 2007, 33(6): 675-689. |
| 16 | Miura H, Takahashi T, Ichikawa J, et al. Bed expansion in liquid-solid two-phase fluidized beds with Newtonian and non-Newtonian fluids over the wide range of Reynolds numbers[J]. Powder Technology, 2001, 117(3): 239-246. |
| 17 | Gidaspow D. Multiphase Flow and Fluidization: Continuum and Kinetic Theory Descriptions[M]. Boston: Academic Press, 1994. |
| 18 | Carman P C. Fluid flow through granular beds[J]. Chemical Engineering Research and Design, 1997, 75: S32-S48. |
| 19 | Sheffield R E, Metzner A B. Flows of nonlinear fluids through porous media[J]. AIChE Journal, 1976, 22(4): 736-744. |
| 20 | 田兴旺, 王平, 徐士鸣. 颗粒堆积多孔介质内幂律流体的流动阻力特性[J]. 哈尔滨工业大学学报, 2017, 49(1):126-132. |
| Tian X W, Wang P, Xu S M. Flow resistance characteristics of power law fluid flow through granular porous medium[J]. Journal of Harbin Institute of Technology, 2017, 49(1):126-132. | |
| 21 | Ergun S. Fluid flow through packed columns[J]. Chemical Engineering Progress, 1952, 48(2): 89-94. |
| 22 | Kemblowski Z, Michniewicz M. A new look at the laminar flow of power law fluids through granular beds[J]. Rheologica Acta, 1979, 18(6): 730-739. |
| 30 | Shenoy A V. Darcy-Forchheimer natural, forced and mixed convection heat transfer in non-Newtonian power-law fluid-saturated porous media[J]. Transport in Porous Media, 1993, 11(3): 219-241. |
| 31 | Richardson J F, Zaki W N. The sedimentation of a suspension of uniform spheres under conditions of viscous flow[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 1954, 3(2): 65-73. |
| 32 | Gollwitzer F, Rehberg I, Kruelle C A, et al. Coefficient of restitution for wet particles[J]. Physical Review. E, Statistical, Nonlinear, and Soft Matter Physics, 2012, 86(1 Pt 1): 011303. |
| 33 | Åkesjö A, Vamling L, Sasic S, et al. On the measuring of film thickness profiles and local heat transfer coefficients in falling films[J]. Experimental Thermal and Fluid Science, 2018, 99: 287-296. |
| 34 | 陆慧林. 稠密颗粒流体两相流的颗粒动理学[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2017. |
| Lu H L. Particle Dynamics of Dense Granular Fluid Two-Phase Flow[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2017. | |
| 35 | Jiang Z C, Hagemeier T, Bück A, et al. Experimental measurements of particle collision dynamics in a pseudo-2D gas-solid fluidized bed[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2017, 167: 297-316. |
| 23 | Christopher R H, Middleman S. Power-law flow through a packed tube[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Fundamentals, 1965, 4(4): 422-426. |
| 24 | Denn M M. Continuous drawing of liquids to form fibers[J]. Annual Review of Fluid Mechanics, 1980, 12: 365-387. |
| 25 | Foscolo P U, Gibilaro L G, Waldram S P. A unified model for particulate expansion of fluidised beds and flow in fixed porous media[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 1983, 38(8): 1251-1260. |
| 26 | Dharmadhikari R V, Kale D D. Flow of non-Newtonian fluids through porous media[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 1985, 40(3): 527-529. |
| 27 | Agarwal P K, O’Neill B K. Transport phenomena in multi-particle systems(Ⅰ): Pressure drop and friction factors: unifying the hydraulic-radius and submerged-object approaches[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 1988, 43(9): 2487-2499. |
| 28 | Chhabra R P, Comiti J, Machač I. Flow of non-Newtonian fluids in fixed and fluidised beds[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2001, 56(1): 1-27. |
| 29 | Poggie J, Smits A J. Wavelet analysis of wall-pressure fluctuations in a supersonic blunt-fin flow[J]. AIAA Journal, 1997, 35(10): 1597-1603. |
| [1] | 宋嘉豪, 王文. 斯特林发动机与高温热管耦合运行特性研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(S1): 287-294. |
| [2] | 张思雨, 殷勇高, 贾鹏琦, 叶威. 双U型地埋管群跨季节蓄热特性研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(S1): 295-301. |
| [3] | 肖明堃, 杨光, 黄永华, 吴静怡. 浸没孔液氧气泡动力学数值研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(S1): 87-95. |
| [4] | 周绍华, 詹飞龙, 丁国良, 张浩, 邵艳坡, 刘艳涛, 郜哲明. 短管节流阀内流动噪声的实验研究及降噪措施[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(S1): 113-121. |
| [5] | 叶展羽, 山訸, 徐震原. 用于太阳能蒸发的折纸式蒸发器性能仿真[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(S1): 132-140. |
| [6] | 张义飞, 刘舫辰, 张双星, 杜文静. 超临界二氧化碳用印刷电路板式换热器性能分析[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(S1): 183-190. |
| [7] | 王志国, 薛孟, 董芋双, 张田震, 秦晓凯, 韩强. 基于裂隙粗糙性表征方法的地热岩体热流耦合数值模拟与分析[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(S1): 223-234. |
| [8] | 江河, 袁俊飞, 王林, 邢谷雨. 均流腔结构对微细通道内相变流动特性影响的实验研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(S1): 235-244. |
| [9] | 温凯杰, 郭力, 夏诏杰, 陈建华. 一种耦合CFD与深度学习的气固快速模拟方法[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(9): 3775-3785. |
| [10] | 王玉兵, 李杰, 詹宏波, 朱光亚, 张大林. R134a在菱形离散肋微小通道内的流动沸腾换热实验研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(9): 3797-3806. |
| [11] | 何松, 刘乔迈, 谢广烁, 王斯民, 肖娟. 高浓度水煤浆管道气膜减阻两相流模拟及代理辅助优化[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(9): 3766-3774. |
| [12] | 袁佳琦, 刘政, 黄锐, 张乐福, 贺登辉. 泡状入流条件下旋流泵能量转换特性研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(9): 3807-3820. |
| [13] | 韩晨, 司徒友珉, 朱斌, 许建良, 郭晓镭, 刘海峰. 协同处理废液的多喷嘴粉煤气化炉内反应流动研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(8): 3266-3278. |
| [14] | 程小松, 殷勇高, 车春文. 不同工质在溶液除湿真空再生系统中的性能对比[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(8): 3494-3501. |
| [15] | 刘文竹, 云和明, 王宝雪, 胡明哲, 仲崇龙. 基于场协同和 耗散的微通道拓扑优化研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(8): 3329-3341. 耗散的微通道拓扑优化研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(8): 3329-3341. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备 11010102001995号
京公网安备 11010102001995号