化工学报 ›› 2024, Vol. 75 ›› Issue (1): 255-267.DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20231148
赵碧丹1,2( ), 代伊杨1,3, 王军武1,2(
), 代伊杨1,3, 王军武1,2( ), 张永民3(
), 张永民3( )
)
收稿日期:2023-11-08
修回日期:2023-12-19
出版日期:2024-01-25
发布日期:2024-03-11
通讯作者:
王军武,张永民
作者简介:赵碧丹(1990—),女,博士,副研究员,bdzhao@ipe.ac.cn
基金资助:
Bidan ZHAO1,2( ), Yiyang DAI1,3, Junwu WANG1,2(
), Yiyang DAI1,3, Junwu WANG1,2( ), Yongmin ZHANG3(
), Yongmin ZHANG3( )
)
Received:2023-11-08
Revised:2023-12-19
Online:2024-01-25
Published:2024-03-11
Contact:
Junwu WANG, Yongmin ZHANG
摘要:
在密相床层内安装内构件可显著改善工业流化床的流化质量、强化气固传质和提高化学反应效率。由于长时间受气体和颗粒的挤压和冲击,流化床内构件可能会发生变形或断裂。为实现流化床内构件设计的科学性,确保其长周期可靠性,需要明确其受力机理与不同操作条件下受力特性。利用粗粒化CFD-DEM-IBM方法,实现了利用笛卡儿网格模拟流化床中倾斜挡板内构件受力特性的定量模拟,该方法拓展原有挡板应力统计方法,获得了不同倾斜角度对挡板所受应力的定量影响规律。模拟所得挡板受力随时间的演化曲线与实验报道较为一致,在流化床启动阶段会出现较大的峰值,同时成功复现在启动阶段的峰值受力总体与挡板在水平面上的投影面积成正比。模拟结果显示,在启动阶段,挡板受力中颗粒挤压作用力占主导,但在流化阶段,除颗粒作用力达到极大值外的大部分时间中挡板受到的气相压差力要大于颗粒作用力。当挡板倾斜角度较小时,挡板受力较大但抑制床内返混效果较好,因此在工业流化床内构件设计中应兼顾强化传递及长周期可靠性的需求,当挡板倾斜角度较小时应选择强度大的挡板材料。
中图分类号:
赵碧丹, 代伊杨, 王军武, 张永民. CFD-DEM-IBM方法探究流化床倾斜挡板内构件受力特性[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(1): 255-267.
Bidan ZHAO, Yiyang DAI, Junwu WANG, Yongmin ZHANG. CFD-DEM-IBM simulation on force characteristic on inclined-surface baffles in fluidized beds[J]. CIESC Journal, 2024, 75(1): 255-267.
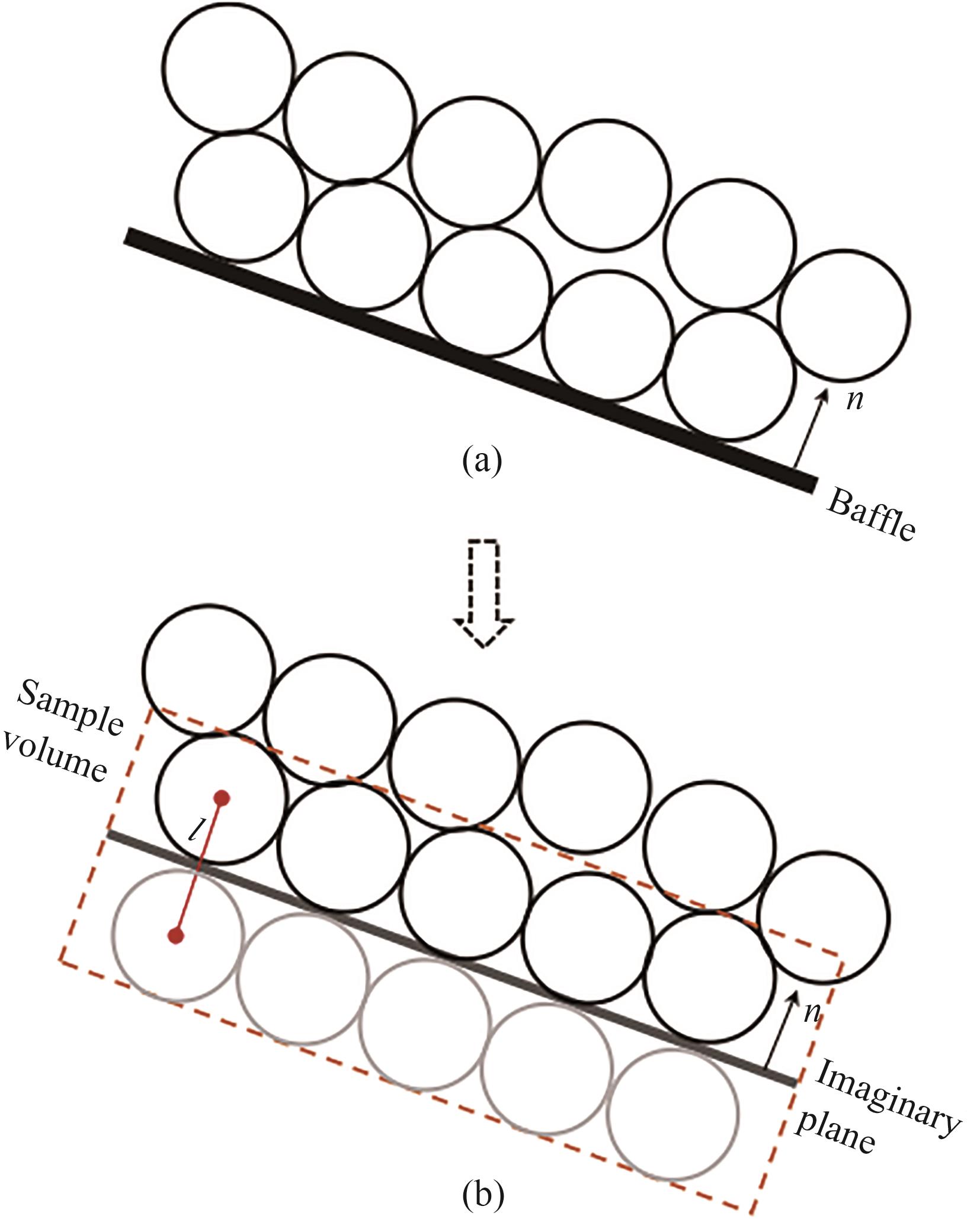
图3 (a)挡板与颗粒接触示意图;(b)使用“虚拟平面法”等效后的示意图[36]
Fig.3 (a) Schematic diagram of contact between baffle and particles; (b) Schematic diagram of contact between an imaginary plane and particles in dense bed[36]
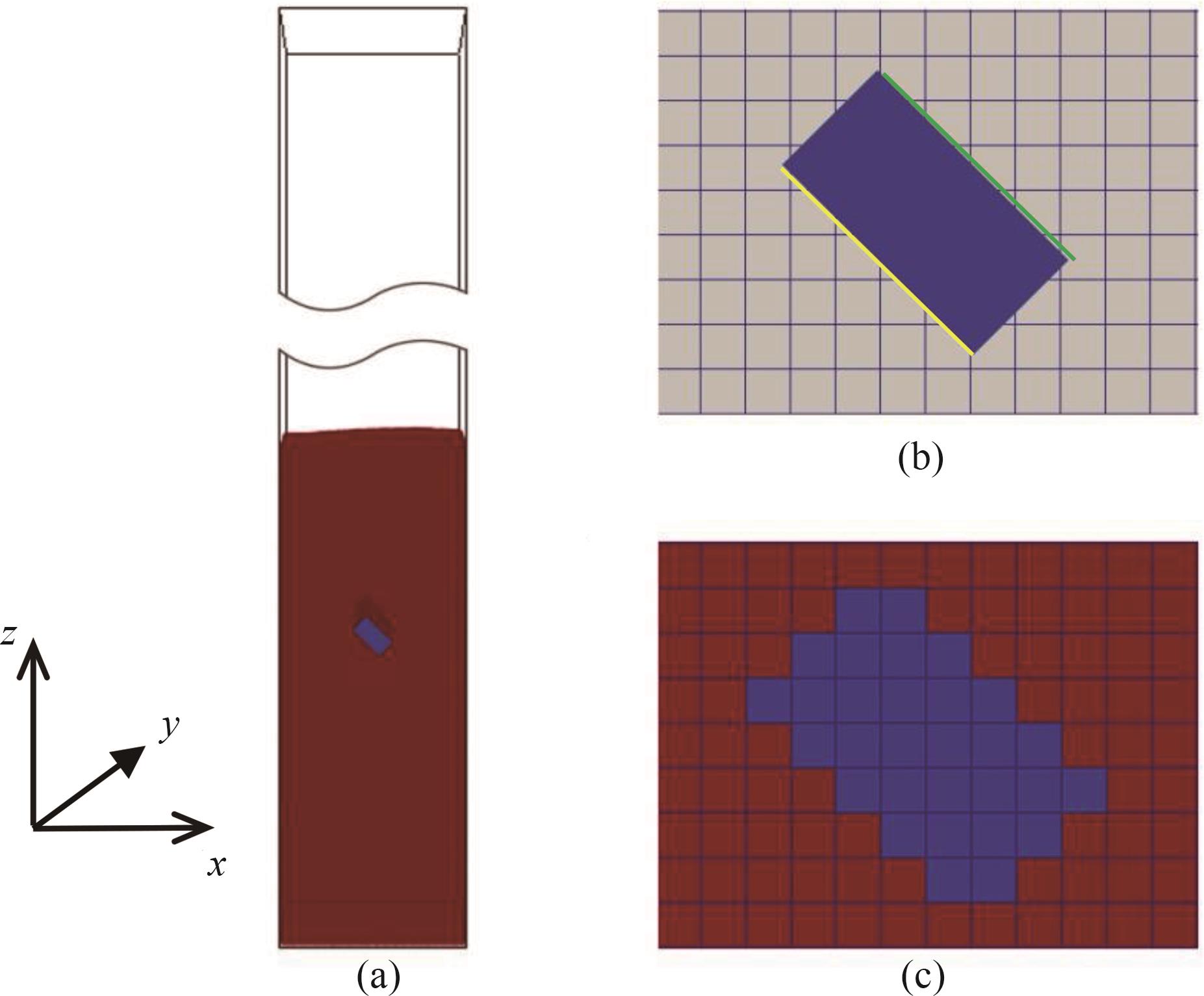
图4 (a)模拟中简化后的流化床几何结构(红色为颗粒相);(b)倾斜挡板与流体网格的关系(绿色表示挡板上表面,黄色表示挡板下表面); (c)IBM方法识别后的流体网格(红)和固体+IBM网格(蓝)
Fig.4 (a) The simplified geometric structure of the fluidized bed in the simulation with red indicating the particle phase; (b) The relationship between inclined baffles and fluid grids (The upper surface of the baffle is colored by green, and the lower surface is colored by yellow); (c) Fluid grid (red) and solid+IBM grid (blue) identified by IBM method
| 项目 | 参数 | 数值 |
|---|---|---|
| 床内网格数 | Lx ×Ly ×Lz | 300×300×2200 |
| 挡板网格数 | lx ×ly ×lz | 60×300×30 |
| 颗粒 | Sauter平均颗粒直径/μm | 595 |
| 密度/(kg/m3) | 2906 | |
| 最小流态化时空隙率 | 0.47 | |
| 最小流化速度/(m/s) | 0.33 | |
| 球形度 | 0.86 | |
| 颗粒粗粒化率 | 5 | |
| 粗粒化后床内颗粒总数 | 3439103 | |
| 非弹性碰撞恢复系数 | 0.9 | |
| 滑动摩擦系数 | 0.3 | |
| 滚动摩擦系数 | 0.01 | |
| 特征速度/(m/s) | 0.5 | |
| 杨氏模量/Pa | 1×108 | |
| 泊松比 | 0.3 | |
| 时间步长/s | 1×10-5 | |
| 静止堆积床高/m | 1 | |
| 气体 | 密度/(kg/m3) | 1.2 |
| 黏度/(Pa·s) | 1.8×10-5 | |
| 表观气速/(m/s) | 0.6 | |
| 出口压力/Pa | 101325 | |
| CFD网格大小/mm | 10×10×10 | |
| 时间步长/s | 1×10-4 |
表1 流化床中的参数设置
Table 1 Parameter settings in fluidized beds
| 项目 | 参数 | 数值 |
|---|---|---|
| 床内网格数 | Lx ×Ly ×Lz | 300×300×2200 |
| 挡板网格数 | lx ×ly ×lz | 60×300×30 |
| 颗粒 | Sauter平均颗粒直径/μm | 595 |
| 密度/(kg/m3) | 2906 | |
| 最小流态化时空隙率 | 0.47 | |
| 最小流化速度/(m/s) | 0.33 | |
| 球形度 | 0.86 | |
| 颗粒粗粒化率 | 5 | |
| 粗粒化后床内颗粒总数 | 3439103 | |
| 非弹性碰撞恢复系数 | 0.9 | |
| 滑动摩擦系数 | 0.3 | |
| 滚动摩擦系数 | 0.01 | |
| 特征速度/(m/s) | 0.5 | |
| 杨氏模量/Pa | 1×108 | |
| 泊松比 | 0.3 | |
| 时间步长/s | 1×10-5 | |
| 静止堆积床高/m | 1 | |
| 气体 | 密度/(kg/m3) | 1.2 |
| 黏度/(Pa·s) | 1.8×10-5 | |
| 表观气速/(m/s) | 0.6 | |
| 出口压力/Pa | 101325 | |
| CFD网格大小/mm | 10×10×10 | |
| 时间步长/s | 1×10-4 |
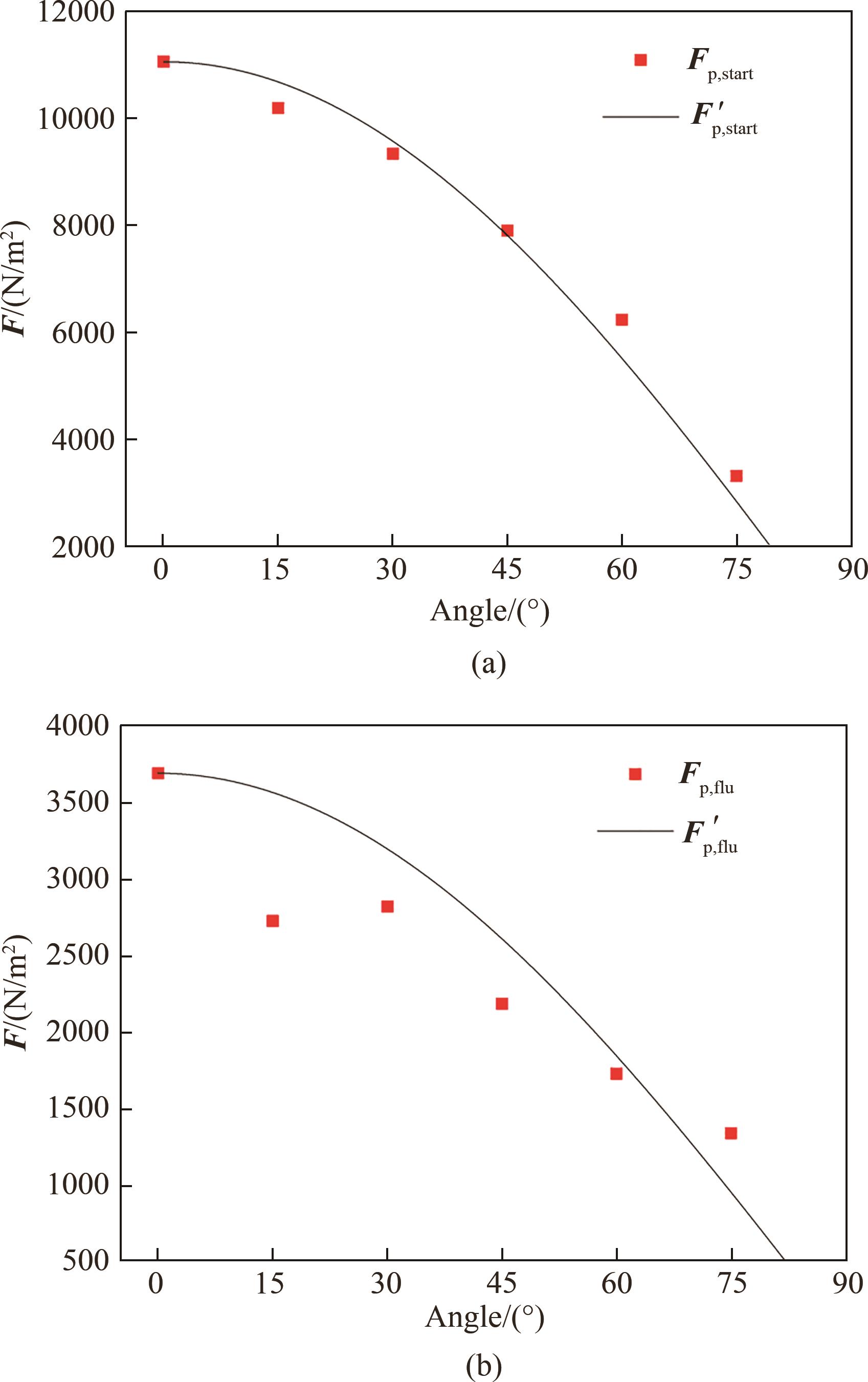
图11 启动阶段(a)和流化阶段(b)挡板受颗粒作用力随倾斜角度的变化情况
Fig.11 The variation of the force by particles on the baffle at the start-up stage (a) and the fluidization stage (b) with the inclination angle
| 1 | 郭慕孙,李洪钟.流态化手册[M].北京:化学工业出版社,2008: 150. |
| Kwauk M, Li H Z. Fluidization Manual [M]. Beijing:Chemical Industry Press, 2008: 150. | |
| 2 | John R G, Knowlton T M, Avidan A A. Circulating Fluidized Beds[M]. Springer Science & Business Media, 2012: 5. |
| 3 | Nelson M J, Nakhla G, Zhu J. Fluidized-bed bioreactor applications for biological wastewater treatment: a review of research and developments[J]. Engineering, 2017, 3(3): 330-342. |
| 4 | Li J, Kwauk M. Particle-Fluid Two-Phase Flow: The Energy-Minimization Multi-Scale Method[M]. Beijing:Metallurgical Industry Press, 1994: 122-125. |
| 5 | Li J, Ge W, Wang W, et al. Focusing on mesoscales: from the energy-minimization multiscale model to mesoscience[J]. Current Opinion in Chemical Engineering, 2016, 13: 10-23. |
| 6 | 卢天雄. 流化床反应器[M]. 北京:化学工业出版社, 1986: 74-82. |
| Lu T X. Fluidized Bed Reactor [M]. Beijing:Chemical Industry Press, 1986: 74-82. | |
| 7 | 周遊, 鲁维民, 郑冲,等. 多孔挡板导流筒型流化床内构件研究[J]. 过程工程学报, 1995(2): 143-150. |
| Zhou Y, Lu W M, Zheng C, et al. Investigations on the draft tube internal in gas-solid fluidized beds[J]. The Chinese Journal of Process Engineering, 1995(2): 143-150. | |
| 8 | 黄学静, 徐文青, 魏耀东, 等. 半干法循环流化床脱硫反应器内构件研究进展[J]. 化工进展, 2014, 33(10): 2540-2545. |
| Huang X J, Xu W Q, Wei Y D, et al. Studies on internal components in semi-dry circulating fluidized bed desulfurization reactor[J]. Chemical Industry and Engineering Progress, 2014, 33(10): 2540-2545. | |
| 9 | 杨帅. 内构件鼓泡流化床中流动结构及其计算机模拟研究[D]. 北京: 中国科学院大学, 2016. |
| Yang S. Study on flow structure and computer simulation in a bubbling fluidized bed with internal components[D]. Beijing: University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2016. | |
| 10 | 董群, 贾昭, 王丽, 等. 催化裂化流化床内构件的研究进展[J]. 化工进展, 2010, 29(9): 1609-1614. |
| Dong Q, Jia Z, Wang L, et al. An outline for inner-loop studies in FCC fluidized bed[J]. Chemical Industry and Engineering Progress, 2010, 29(9): 1609-1614. | |
| 11 | Rall R R. Apparatus for contacting of gases and solids in fluidized beds: US6224833[P]. 2001-05-01. |
| 12 | 金涌, 俞芷青, 张礼, 等. 流化床反应器塔形内构件的研究[J]. 化工学报, 1980, 31(2): 117-128. |
| Jin Y, Yu Z Q, Zhang L, et al. Study on tower internals of fluidized bed reactor[J]. Journal of Chemical Industry and Engineering(China), 1980, 31(2): 117-128. | |
| 13 | 金涌, 俞芷青, 张礼, 等. 流化床脊形内构件[J]. 石油化工, 1986, 15(5): 269-277. |
| Jin Y, Yu Z Q, Zhang L, et al. Fluidized bed ridge internals[J]. Petrochemical Technology, 1986, 15(5): 269-277. | |
| 14 | 张永民, 王红梅, 卢春喜, 等. 导向挡板对催化裂化颗粒湍动流化床流动特性的影响[J]. 中国石油大学学报(自然科学版), 2008(4): 118-122. |
| Zhang Y M, Wang H M, Lu C X, et al. Effects of louvre baffles on hydrodynamic properties of turbulent fluidized beds of FCC particles[J]. Journal of China University of Petroleum (Edition of National Science),2008(4): 118-122. | |
| 15 | Yang Z, Zhang Y, Zhang H. CPFD simulation on effects of louver baffles in a two-dimensional fluidized bed of Geldart A particles[J]. Advanced Powder Technology, 2019, 30(11): 2712-2725. |
| 16 | 曲悦, 潘腾, 杨越林, 等. 三维单旋导向挡板鼓泡流化床内气固流动的CPFD模拟[J]. 高校化学工程学报, 2021, 35(4): 657-664. |
| Qu Y, Pan T, Yang Y L, et al. CPFD simulation of gas-solid flow in a three-dimensional bubbling fluidized bed with louver baffles[J]. Journal of Chemical Engineering of Chinese Universities, 2021, 35(4): 657-664. | |
| 17 | 时瑶, 王德武, 赵斌, 等. 旋流筛板式气固挡板流化床内压力脉动特性[J]. 过程工程学报, 2019, 19(1): 91-101. |
| Shi Y, Wang D W, Zhao B, et al. Pressure fluctuations in a gas-solid fluidized bed with rotating sieve tray type baffles[J]. The Chinese Journal of Process Engineering, 2019, 19(1): 91-101. | |
| 18 | 张英, 王强. CROSSER格栅在催化裂化装置中的应用[J]. 中外能源, 2010, 15(4): 69-71. |
| Zhang Y, Wang Q. The application of CROSSER grid in fluid catalytic cracking unit[J]. Sino-Global Energy, 2010, 15(4): 69-71. | |
| 19 | 魏飞, 杨艳辉, 金涌. 内构件对高密度提升管内气体混合行为的影响[J]. 化工学报, 2001, 52(9): 766-770. |
| Wei F, Yang Y H, Jin Y. Effect of internals on gas dispersion in high density riser[J]. Journal of Chemical Industry and Engineering(China), 2001, 52(9): 766-770. | |
| 20 | 刘会娥, 杨艳辉, 魏飞, 等. 内构件对于提升管中颗粒混合行为的影响[J]. 化学反应工程与工艺, 2002, 18(2): 109-114. |
| Liu H E, Yang Y H, Wei F, et al. Solids mixing behavior in riser with internals[J]. Chemical Reaction Engineering and Technology, 2002, 18(2): 109-114. | |
| 21 | Zhao G, Shi X, Wu Y, et al. 3D CFD simulation of gas-solids hydrodynamics and bubbles behaviors in empty and packed bubbling fluidized beds[J]. Powder Technology, 2019, 351: 1-15. |
| 22 | 王丽军, 王丽雅, 张煜, 等. 带阻尼内构件鼓泡塔的研究(Ⅱ):内构件对气液传质速率的影响[J]. 化学反应工程与工艺, 2007(2): 109-113. |
| Wang L J, Wang L Y, Zhang Y, et al. Study on the bubble column equipped with resistance internals(Ⅱ):Effects of the internals on gas-liquid mass transfer[J]. Chemical Reaction Engineering and Technology, 2007(2): 109-113. | |
| 23 | Youssef A A, Hamed M E, Grimes J T, et al. Hydrodynamics of pilot-scale bubble columns: effect of internals[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2013, 52(1): 43-55. |
| 24 | Baskakov A P, Michkovskii B A. Vertical forces acting on horizontal disks in a fluidized bed[J]. Journal of Engineering Physics, 1974, 27(6): 1464-1466. |
| 25 | Nguyen T H, Grace J R. Forces on objects immersed in fluidized beds[J]. Powder Technology, 1978, 19(2): 255-264. |
| 26 | Donovan J E. A study of forces on simulated heat exchange tubes immersed in a cold fluidized bed[D]. America: Oergon State University,1979. |
| 27 | Kennedy T C, Donovan J E, Trigas A. Forces on immersed tubes in fluidized beds[J]. AIChE Journal, 1981, 27(3): 351-357. |
| 28 | Nagahashi Y, Yamamoto D, Asako Y. Forces on horizontal tubes of non-circular cross-section in fluidized beds[C]//The 14th International Engineering Conference on Fluidization: From Fundamentals to Products. Netherlands, 2013: 1-8. |
| 29 | 王若艺, 刘对平, 李智, 等. 细颗粒气固流化床内斜片挡板受力特性的实验研究[J]. 过程工程学报, 2015, 15(3): 375-380. |
| Wang R Y, Liu D P, Li Z, et al. Experimental study on the acting forces on a single slant slat immersed in a gas and fine particles fluidized bed[J]. The Chinese Journal of Process Engineering, 2015, 15(3): 375-380. | |
| 30 | Liu D, Zhang S, Zhang Y, et al. Forces on an immersed horizontal slat during starting up a fluidized bed[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2017, 173: 402-410. |
| 31 | Liu D, Zhang S, Wang R, et al. Dynamic forces on a horizontal slat immersed in a fluidized bed of fine particles[J]. Chemical Engineering Research and Design, 2017, 117: 604-613. |
| 32 | 刘对平. 气固流化床挡板内构件受力特性的实验研究[D]. 北京:中国石油大学(北京), 2019. |
| Liu D P. Experimental study on stress characteristics of baffle inner members of gas-solid fluidized bed[D]. Beijing:China University of Petroleum, 2019. | |
| 33 | 李铁男, 赵碧丹, 赵鹏, 等. 气固流化床启动阶段挡板内构件受力特性的CFD-DEM模拟[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(6): 2649-2661. |
| Li T N, Zhao B D, Zhao P, et al. CFD-DEM simulation of the force acting on immersed baffles during the start-up stage of a gas-solid fluidized bed[J]. CIESC Journal, 2022, 73(6): 2649-2661. | |
| 34 | Tamarin A I, Livshits Y E, Galershtein D M, et al. Forces acting on a body in a nonuniform fluidized bed[J]. Journal of Engineering Physics, 1977, 32: 165-168. |
| 35 | Nagahashi Y, Asako Y, Lim K S, et al. Dynamic forces on a horizontal tube due to passing bubbles in fluidized beds[J]. Powder Technology, 1998, 98(2): 177-182. |
| 36 | Rong D, Mikami T, Horio M. Particle and bubble movements around tubes immersed in fluidized beds—a numerical study[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 1999, 54(23): 5737-5754. |
| 37 | Nagahashi Y, Takeuchi H, Grace J R, et al. Dynamic forces on an immersed cylindrical tube and analysis of particle interaction in 2D-gas fluidized beds[J]. Advanced Powder Technology, 2018, 29(12): 3552-3560. |
| 38 | Ge W, Guo L, Liu X, et al. Mesoscience-based virtual process engineering[J]. Computers & Chemical Engineering, 2019, 126: 68-82. |
| 39 | Bian W, Chen X, Wang J. A critical comparison of two-fluid model, discrete particle method and direct numerical simulation for modeling dense gas-solid flow of rough spheres[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2019, 210: 115233. |
| 40 | Hua L, Zhao H, Li J, et al. Eulerian-Eulerian simulation of irregular particles in dense gas-solid fluidized beds[J]. Powder Technology, 2015, 284: 299-311. |
| 41 | Lan B, Xu J, Zhao P, et al. Scale-up effect of residence time distribution of polydisperse particles in continuously operated multiple-chamber fluidized beds[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2021, 244: 116809. |
| 42 | Tsuji Y, Kawaguchi T, Tanaka T. Discrete particle simulation of two-dimensional fluidized bed[J]. Powder Technology, 1993, 77(1): 79-87. |
| 43 | Peng Z, Doroodchi E, Luo C, et al. Influence of void fraction calculation on fidelity of CFD-DEM simulation of gas-solid bubbling fluidized beds[J]. AIChE Journal, 2014, 60(6): 2000-2018. |
| 44 | Zhao P, Xu J, Ge W, et al. A CFD-DEM-IBM method for Cartesian grid simulation of gas-solid flow in complex geometries[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2020, 389: 124343. |
| 45 | Zhao P, Xu J, Liu X, et al. A computational fluid dynamics-discrete element-immersed boundary method for Cartesian grid simulation of heat transfer in compressible gas-solid flow with complex geometries[J]. Physics of Fluids, 2020, 32(10): 103306. |
| 46 | He M, Zhao B, Wang J. Particle pressures in gas-fluidized beds: a computational fluid dynamics-discrete element method study[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2022, 61(26): 9489-9497. |
| [1] | 周尧, 杨小平, 倪一程, 刘继平, 魏进家, 严俊杰. 应用于新型环路热管的两相引射器数值模拟[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(1): 268-278. |
| [2] | 王义江, 孙莉, 刘梦涵, 杨金宏, 王国元. 基于响应面法的矿用翅片管空冷器参数优化[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(1): 279-291. |
| [3] | 王俊男, 何呈祥, 王忠东, 朱春英, 马友光, 付涛涛. T型微混合器内均相混合的数值模拟[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(1): 242-254. |
| [4] | 崔怡洲, 李成祥, 翟霖晓, 刘束玉, 石孝刚, 高金森, 蓝兴英. 亚毫米气泡和常规尺寸气泡气液两相流流动与传质特性对比[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(1): 197-210. |
| [5] | 宋嘉豪, 王文. 斯特林发动机与高温热管耦合运行特性研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(S1): 287-294. |
| [6] | 张思雨, 殷勇高, 贾鹏琦, 叶威. 双U型地埋管群跨季节蓄热特性研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(S1): 295-301. |
| [7] | 肖明堃, 杨光, 黄永华, 吴静怡. 浸没孔液氧气泡动力学数值研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(S1): 87-95. |
| [8] | 叶展羽, 山訸, 徐震原. 用于太阳能蒸发的折纸式蒸发器性能仿真[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(S1): 132-140. |
| [9] | 邵苛苛, 宋孟杰, 江正勇, 张旋, 张龙, 高润淼, 甄泽康. 水平方向上冰中受陷气泡形成和分布实验研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(S1): 161-164. |
| [10] | 张义飞, 刘舫辰, 张双星, 杜文静. 超临界二氧化碳用印刷电路板式换热器性能分析[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(S1): 183-190. |
| [11] | 王志国, 薛孟, 董芋双, 张田震, 秦晓凯, 韩强. 基于裂隙粗糙性表征方法的地热岩体热流耦合数值模拟与分析[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(S1): 223-234. |
| [12] | 袁佳琦, 刘政, 黄锐, 张乐福, 贺登辉. 泡状入流条件下旋流泵能量转换特性研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(9): 3807-3820. |
| [13] | 何松, 刘乔迈, 谢广烁, 王斯民, 肖娟. 高浓度水煤浆管道气膜减阻两相流模拟及代理辅助优化[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(9): 3766-3774. |
| [14] | 邢雷, 苗春雨, 蒋明虎, 赵立新, 李新亚. 井下微型气液旋流分离器优化设计与性能分析[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(8): 3394-3406. |
| [15] | 韩晨, 司徒友珉, 朱斌, 许建良, 郭晓镭, 刘海峰. 协同处理废液的多喷嘴粉煤气化炉内反应流动研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(8): 3266-3278. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备 11010102001995号
京公网安备 11010102001995号