CIESC Journal ›› 2024, Vol. 75 ›› Issue (3): 1019-1027.DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20240071
• Material science and engineering, nanotechnology • Previous Articles Next Articles
Jihao WU( ), Tao CHEN, Siyu LIU, Mengke LIU, Juan YANG(
), Tao CHEN, Siyu LIU, Mengke LIU, Juan YANG( )
)
Received:2024-01-05
Revised:2024-02-22
Online:2024-05-11
Published:2024-03-25
Contact:
Juan YANG
通讯作者:
杨卷
作者简介:吴吉昊(2000—),男,硕士研究生,w0608hao@163.com
基金资助:CLC Number:
Jihao WU, Tao CHEN, Siyu LIU, Mengke LIU, Juan YANG. Preparation of pitch-based hard carbon by bi-functional activation strategy for sodium-ion batteries[J]. CIESC Journal, 2024, 75(3): 1019-1027.
吴吉昊, 陈涛, 刘思宇, 刘梦柯, 杨卷. 双功能活化制备沥青基硬炭用于钠离子电池负极[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(3): 1019-1027.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
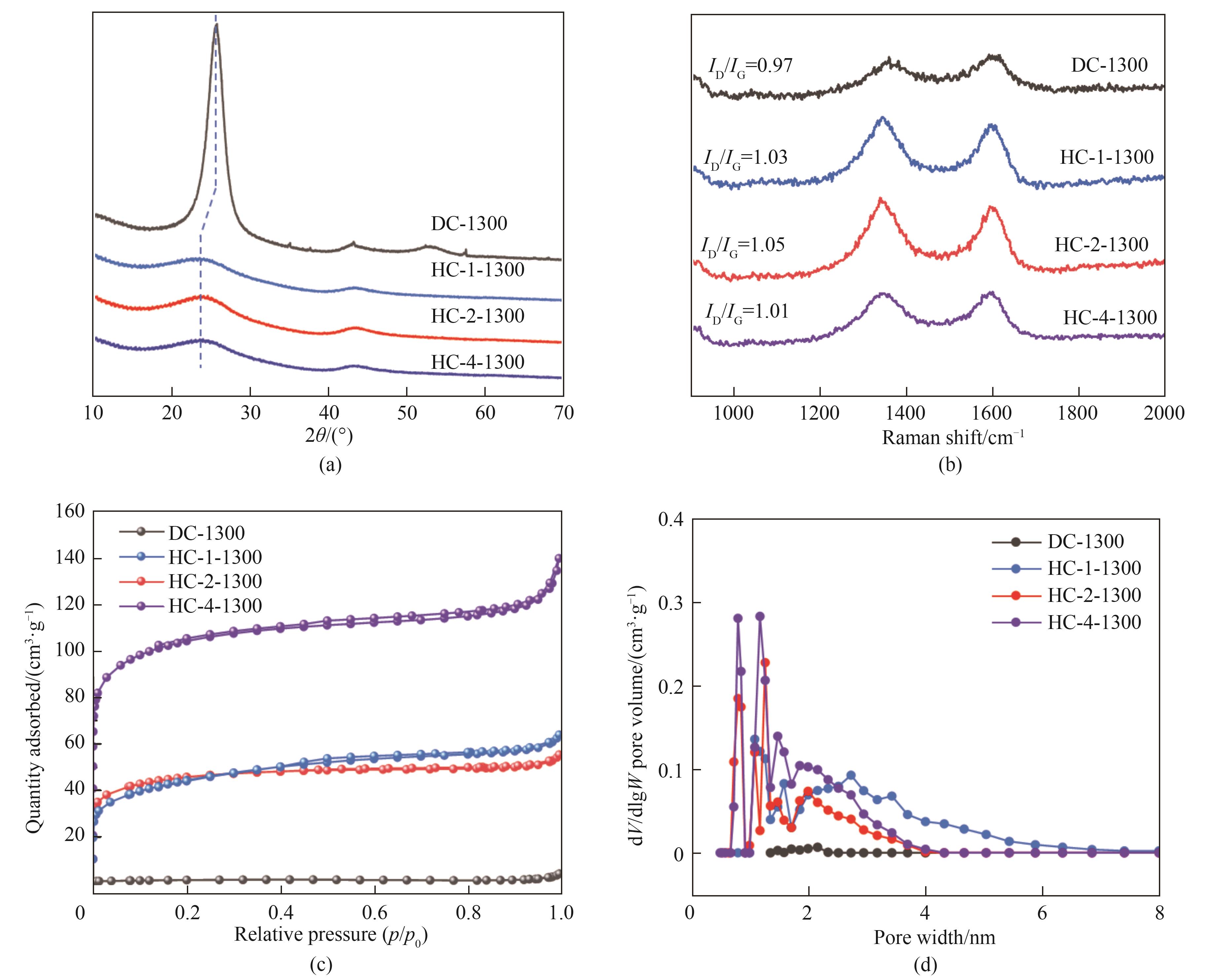
Fig.2 XRD patterns (a), Raman spectra (b), N2 adsorption/desorption curves (c) and pore size distribution (d) of DC-1300,HC-1-1300,HC-2-1300 and HC-4-1300
| 样品 | d002/nm | BET表面积/ (m2·g-1) | 孔体积/ (cm3·g-1) | 库仑 效率/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DC-1300 | 0.345 | 3.3 | 0.005 | 75.6 |
| HC-1-1300 | 0.376 | 155.5 | 0.098 | 82.2 |
| HC-2-1300 | 0.372 | 164.8 | 0.084 | 81.5 |
| HC-4-1300 | 0.370 | 378.9 | 0.214 | 79.4 |
Table 1 Structural and electrochemical parameters of different samples
| 样品 | d002/nm | BET表面积/ (m2·g-1) | 孔体积/ (cm3·g-1) | 库仑 效率/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DC-1300 | 0.345 | 3.3 | 0.005 | 75.6 |
| HC-1-1300 | 0.376 | 155.5 | 0.098 | 82.2 |
| HC-2-1300 | 0.372 | 164.8 | 0.084 | 81.5 |
| HC-4-1300 | 0.370 | 378.9 | 0.214 | 79.4 |
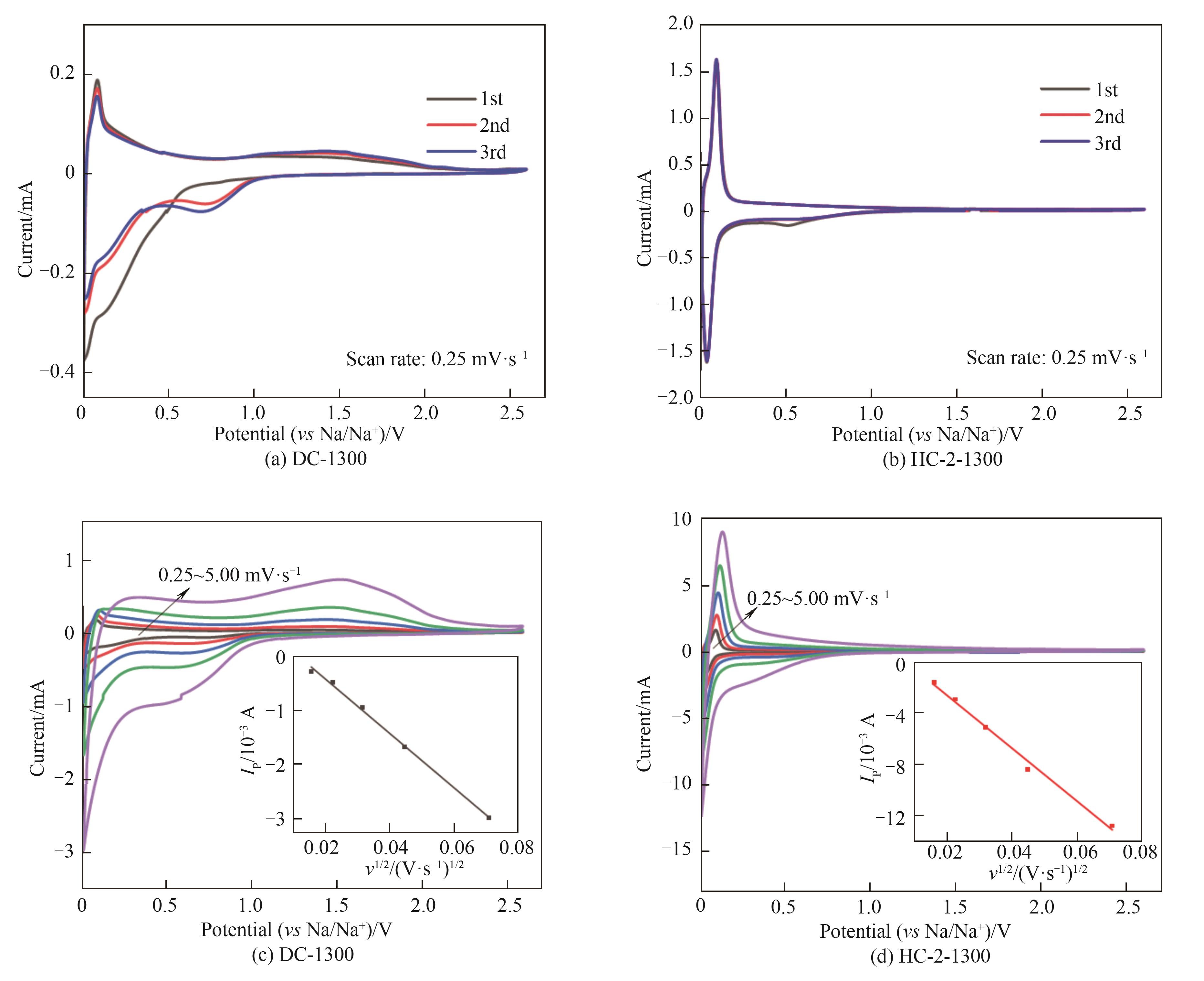
Fig.3 CV curves of DC-1300 (a) and HC-2-1300 (b) at the scan rate of 0.25 mV·s-1; CV curves at different scan rates from 0.25 to 5.00 mV·s-1 and linear relationship between Ipand v1/2 of DC-1300 (c) and HC-2-1300 (d)
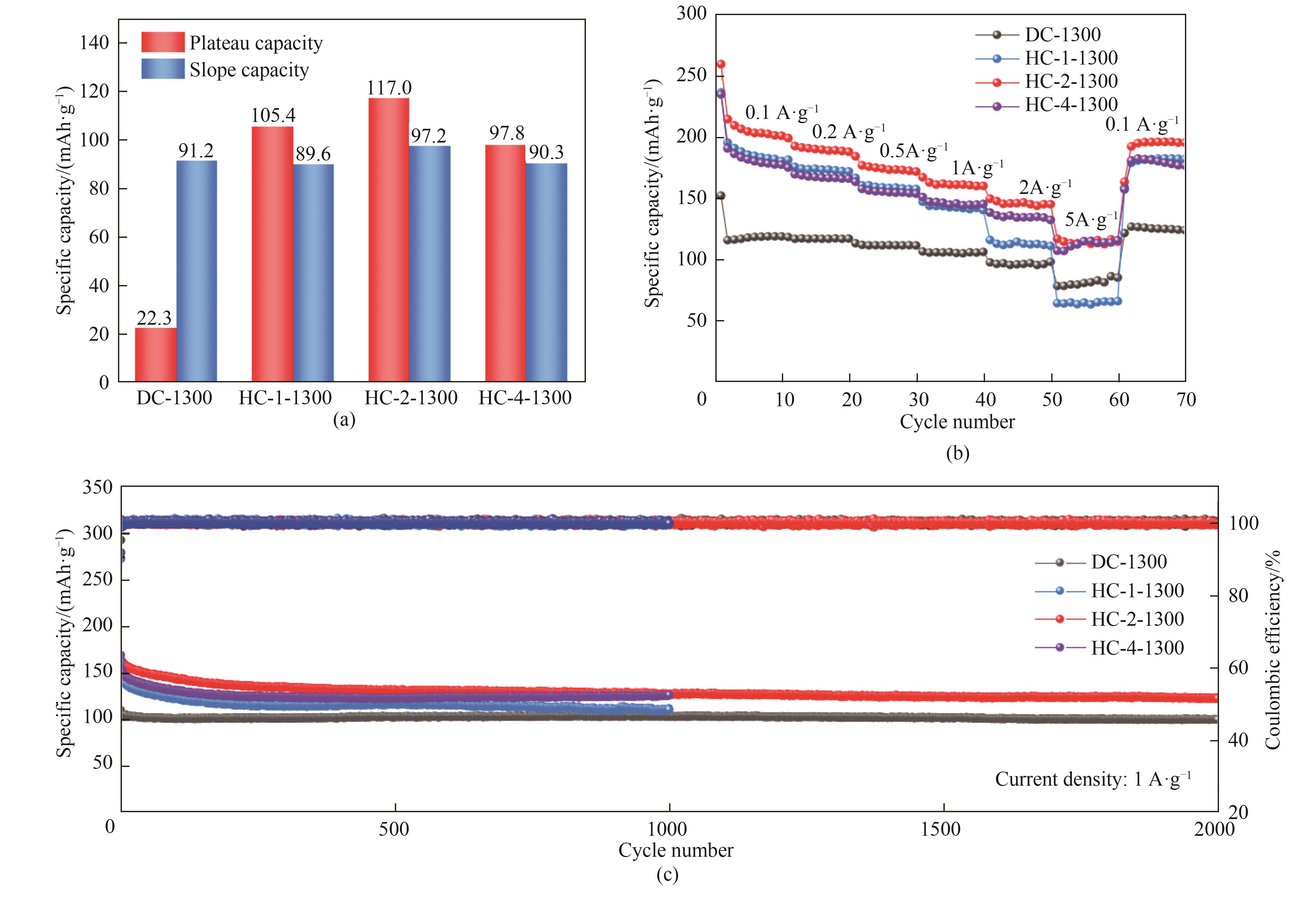
Fig.5 The capacity contribution (a), rate capability (b) at current density of 0.1 A·g-1 and cyclic performance at 1 A·g-1 (c) of DC-1300, HC-1100, HC-1300 and HC-1500
| 1 | Delmas C. Sodium and sodium-ion batteries: 50 years of research[J]. Advanced Energy Materials, 2018, 8(17): 1703137. |
| 2 | 车晓刚, 靳皎, 张艺潇, 等. 煤基富氧多孔炭纳米片的制备及其超级电容器性能[J]. 新型炭材料, 2023, 38(6): 1050-1058. |
| Che X G, Jin J, Zhang Y X, et al. Fabrication of coal-based oxygen-rich porous carbon nanosheets for high-performance supercapacitors[J]. New Carbon Materials, 2023, 38(6): 1050-1058. | |
| 3 | Vaalma C, Buchholz D, Weil M, et al. A cost and resource analysis of sodium-ion batteries[J]. Nature Reviews Materials, 2018, 3(4): 18013. |
| 4 | Luo W, Shen F, Bommier C, et al. Na-ion battery anodes: materials and electrochemistry[J]. Accounts of Chemical Research, 2016, 49(2): 231-240. |
| 5 | Zu C X, Li H. Thermodynamic analysis on energy densities of batteries[J]. Energy & Environmental Science, 2011, 4(8): 2614-2624. |
| 6 | Stevens D A, Dahn J R. The mechanisms of lithium and sodium insertion in carbon materials[J]. Journal of the Electrochemical Society, 2001, 148(8): A803. |
| 7 | Alvin S, Cahyadi H S, Hwang J, et al. Revealing the intercalation mechanisms of lithium, sodium, and potassium in hard carbon[J]. Advanced Energy Materials, 2020, 10(20): 2000283. |
| 8 | Liu Y Y, Merinov B V, Goddard W A. Origin of low sodium capacity in graphite and generally weak substrate binding of Na and Mg among alkali and alkaline earth metals[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2016, 113(14): 3735-3739. |
| 9 | 杨涵, 张一波, 李琦, 等. 面向实用化的钠离子电池碳负极:进展及挑战[J]. 化工进展, 2023, 42(8): 4029-4042. |
| Yang H, Zhang Y B, Li Q, et al. Practical carbon anodes for sodium-ion batteries: progress and challenge[J]. Chemical Industry and Engineering Progress, 2023, 42(8):4029-4042. | |
| 10 | Meng Q S, Lu Y X, Ding F X, et al. Tuning the closed pore structure of hard carbons with the highest Na storage capacity[J]. ACS Energy Letters, 2019, 4(11): 2608-2612. |
| 11 | Xu T Y, Qiu X, Zhang X, et al. Regulation of surface oxygen functional groups and pore structure of bamboo-derived hard carbon for enhanced sodium storage performance[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2023, 452: 139514. |
| 12 | Kubota K, Shimadzu S, Yabuuchi N, et al. Structural analysis of sucrose-derived hard carbon and correlation with the electrochemical properties for lithium, sodium, and potassium insertion[J]. Chemistry of Materials, 2020, 32(7): 2961-2977. |
| 13 | Choi J, Lee Y, Chae Y, et al. Unveiling the transformation of liquid crystalline domains into carbon crystallites during carbonization of mesophase pitch-derived fibers[J]. Carbon, 2022, 199: 288-299. |
| 14 | Liu S Y, Shao W L, Zhang W S, et al. Regulating microstructures of soft carbon anodes by terminations of Ti3C2T MXene toward fast and stable sodium storage[J]. Nano Energy, 2021, 87: 106097. |
| 15 | Lu Y X, Zhao C L, Qi X G, et al. Pre-oxidation-tuned microstructures of carbon anodes derived from pitch for enhancing Na storage performance[J]. Advanced Energy Materials, 2018, 8(27): 1800108. |
| 16 | Xu R, Yi Z L, Song M X, et al. Boosting sodium storage performance of hard carbons by regulating oxygen functionalities of the cross-linked asphalt precursor[J]. Carbon, 2023, 206: 94-104. |
| 17 | Chen H, Sun N, Wang Y X, et al. One stone two birds: pitch assisted microcrystalline regulation and defect engineering in coal-based carbon anodes for sodium-ion batteries[J]. Energy Storage Materials, 2023, 56(69): 532-541. |
| 18 | Lu P, Sun Y, Xiang H F, et al. 3D amorphous carbon with controlled porous and disordered structures as a high-rate anode material for sodium-ion batteries[J]. Advanced Energy Materials, 2018, 8(8): 1702434. |
| 19 | Wang T, Peng L N, Deng B, et al. Cellulose degradation of cottonseed meal derived porous carbon for supercapacitor[J]. Fuel, 2024, 357: 129653. |
| 20 | Zheng J J, Yan B, Feng L, et al. Potassium citrate assisted synthesis of hierarchical porous carbon materials for high performance supercapacitors[J]. Diamond and Related Materials, 2022, 128: 109247. |
| 21 | Ge P, Hou H S, Cao X Y, et al. Multidimensional evolution of carbon structures underpinned by temperature-induced intermediate of chloride for sodium-ion batteries[J]. Advanced Science, 2018, 5(6): 1800080. |
| 22 | Damodar D, Ghosh S, Usha Rani M, et al. Hard carbon derived from sepals of Palmyra palm fruit calyx as an anode for sodium-ion batteries[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2019, 438: 227008. |
| 23 | Lu H Y, Ai F X, Jia Y L, et al. Exploring sodium-ion storage mechanism in hard carbons with different microstructure prepared by ball-milling method[J]. Small, 2018, 14(39): e1802694. |
| 24 | 陈涛, 吴吉昊, 车晓刚, 等. 改性沥青基硬碳材料的可控制备及其储钠性能[J]. 洁净煤技术, 2023, 29(2): 92-98. |
| Chen T, Wu J H, Che X G, et al. Fabrication of modified pitch-based hard carbon materials for high-performance sodium-ion storage[J]. Clean Coal Technology, 2023, 29(2): 92-98. | |
| 25 | Han H X, Chen X Y, Qian J F, et al. Hollow carbon nanofibers as high-performance anode materials for sodium-ion batteries[J]. Nanoscale, 2019, 11(45): 21999-22005. |
| 26 | Wang K F, Sun F, Wang H, et al. Altering thermal transformation pathway to create closed pores in coal-derived hard carbon and boosting of Na+ plateau storage for high-performance sodium-ion battery and sodium-ion capacitor[J]. Advanced Functional Materials, 2022, 32(34): 2203725. |
| 27 | Chu Y, Zhang J, Zhang Y B, et al. Reconfiguring hard carbons with emerging sodium-ion batteries: a perspective[J]. Advanced Materials, 2023, 35(31): e2212186. |
| 28 | 任博阳, 车晓刚, 刘思宇, 等. 熔融盐法制备煤基多孔碳纳米片用于钠离子电池负极[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(10): 4745-4753. |
| Ren B Y, Che X G, Liu S Y, et al. Preparation of coal-based porous carbon nanosheets by molten salt strategy as anodes for sodium-ion batteries[J]. CIESC Journal, 2022, 73(10): 4745-4753. | |
| 29 | Wang L, Xiao Q Z, Wu L J, et al. Spinel LiCrTiO4 fibers as an advanced anode material in high performance lithium ion batteries[J]. Solid State Ionics, 2013, 236: 43-47. |
| 30 | Zou H L, Liang X, Feng X Y, et al. Chromium-modified Li4Ti5O12 with a synergistic effect of bulk doping, surface coating, and size reducing[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2016, 8(33): 21407-21416. |
| 31 | Li Y Q, Lu Y X, Meng Q S, et al. Regulating pore structure of hierarchical porous waste cork-derived hard carbon anode for enhanced Na storage performance[J]. Advanced Energy Materials, 2019, 9(48): 1902852. |
| 32 | Stratford J M, Allan P K, Pecher O, et al. Mechanistic insights into sodium storage in hard carbon anodes using local structure probes[J]. Chemical Communications, 2016, 52(84): 12430-12433. |
| 33 | 殷秀平, 赵玉峰, 张久俊. 钠离子电池硬碳基负极材料的研究进展[J]. 电化学, 2023, 29(10): 2204301. |
| Yin X P, Zhao Y F, Zhang J J. Research progress and performance improvement strateqies of hard carbon anode materials for sodium-lon batteries[J]. Journal of Electrochemistry, 2023, 29(10): 2204301. | |
| 34 | He H N, He J, Yu H B, et al. Dual-interfering chemistry for soft-hard carbon translation toward fast and durable sodium storage[J]. Advanced Energy Materials, 2023, 13(16): 2300357. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||