CIESC Journal ›› 2021, Vol. 72 ›› Issue (11): 5738-5750.DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20210668
• Energy and environmental engineering • Previous Articles Next Articles
Boyang WANG( ),Jili XIA,Xiaoling DONG,Hang GUO,Wencui LI(
),Jili XIA,Xiaoling DONG,Hang GUO,Wencui LI( )
)
Received:2021-05-17
Revised:2021-07-30
Online:2021-11-12
Published:2021-11-05
Contact:
Wencui LI
通讯作者:
李文翠
作者简介:王博阳(1996—),男,硕士研究生,基金资助:CLC Number:
Boyang WANG, Jili XIA, Xiaoling DONG, Hang GUO, Wencui LI. Study on sodium storage behavior of hard carbons derived from coal with different grades of metamorphism[J]. CIESC Journal, 2021, 72(11): 5738-5750.
王博阳, 夏吉利, 董晓玲, 郭行, 李文翠. 不同变质程度煤衍生硬炭的储钠行为研究[J]. 化工学报, 2021, 72(11): 5738-5750.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
| 煤种 | 原煤工业分析/%(质量) | 脱灰样工业分析/%(质量) | 脱灰样元素分析/%(质量) | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mad | Ad | Vdaf | Mad | Ad | Vdaf | C | N | H | S | O | |
| 无烟煤(WYM) | 0.11 | 10.37 | 10.23 | 1.50 | 1.00 | 9.70 | 88.91 | 0.42 | 4.04 | 0.66 | 5.97 |
| 烟煤(YM) | 2.32 | 3.78 | 30.72 | 3.20 | 0.41 | 28.01 | 76.01 | 0.83 | 4.62 | 0.60 | 17.90 |
| 次烟煤(CYM) | 5.21 | 4.80 | 47.51 | 4.56 | 0.31 | 42.62 | 71.64 | 0.85 | 6.01 | 0.42 | 21.08 |
| 褐煤(HM) | 8.45 | 15.27 | 49.96 | 6.71 | 0.75 | 44.01 | 67.83 | 1.33 | 5.10 | 1.10 | 24.55 |
Table 1 Industrial analysis before and after deashing of different coals and elemental analysis results of coals after deashing
| 煤种 | 原煤工业分析/%(质量) | 脱灰样工业分析/%(质量) | 脱灰样元素分析/%(质量) | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mad | Ad | Vdaf | Mad | Ad | Vdaf | C | N | H | S | O | |
| 无烟煤(WYM) | 0.11 | 10.37 | 10.23 | 1.50 | 1.00 | 9.70 | 88.91 | 0.42 | 4.04 | 0.66 | 5.97 |
| 烟煤(YM) | 2.32 | 3.78 | 30.72 | 3.20 | 0.41 | 28.01 | 76.01 | 0.83 | 4.62 | 0.60 | 17.90 |
| 次烟煤(CYM) | 5.21 | 4.80 | 47.51 | 4.56 | 0.31 | 42.62 | 71.64 | 0.85 | 6.01 | 0.42 | 21.08 |
| 褐煤(HM) | 8.45 | 15.27 | 49.96 | 6.71 | 0.75 | 44.01 | 67.83 | 1.33 | 5.10 | 1.10 | 24.55 |
| 组分 | 原煤XRF分析/%(质量) | 脱灰样XRF分析/%(质量) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| WYM | YM | CYM | HM | WYM | YM | CYM | HM | |
| SiO2 | 4.240 | 0.320 | 0.360 | 7.560 | 0.180 | 0.093 | 0.000 | 0.011 |
| Al2O3 | 3.790 | 0.300 | 0.410 | 2.440 | 0.680 | 0.130 | 0.000 | 0.096 |
| Fe2O3 | 0.410 | 1.210 | 0.785 | 0.779 | 0.040 | 0.166 | 0.561 | 0.221 |
| CaO | 0.520 | 2.690 | 2.150 | 0.973 | 0.060 | 0.050 | 0.110 | 0.010 |
| MgO | 0.000 | 0.360 | 0.000 | 0.240 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 |
| Cr2O3 | 0.024 | 0.033 | 0.000 | 0.033 | 0.004 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 |
| Na2O | 0.110 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.280 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 |
| CuO | 0.009 | 0.000 | 0.011 | 0.013 | 0.001 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.006 |
Table 2 X-Ray fluorescence spectrum analysis results for the raw coals and demineralized coals
| 组分 | 原煤XRF分析/%(质量) | 脱灰样XRF分析/%(质量) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| WYM | YM | CYM | HM | WYM | YM | CYM | HM | |
| SiO2 | 4.240 | 0.320 | 0.360 | 7.560 | 0.180 | 0.093 | 0.000 | 0.011 |
| Al2O3 | 3.790 | 0.300 | 0.410 | 2.440 | 0.680 | 0.130 | 0.000 | 0.096 |
| Fe2O3 | 0.410 | 1.210 | 0.785 | 0.779 | 0.040 | 0.166 | 0.561 | 0.221 |
| CaO | 0.520 | 2.690 | 2.150 | 0.973 | 0.060 | 0.050 | 0.110 | 0.010 |
| MgO | 0.000 | 0.360 | 0.000 | 0.240 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 |
| Cr2O3 | 0.024 | 0.033 | 0.000 | 0.033 | 0.004 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 |
| Na2O | 0.110 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.280 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 |
| CuO | 0.009 | 0.000 | 0.011 | 0.013 | 0.001 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.006 |
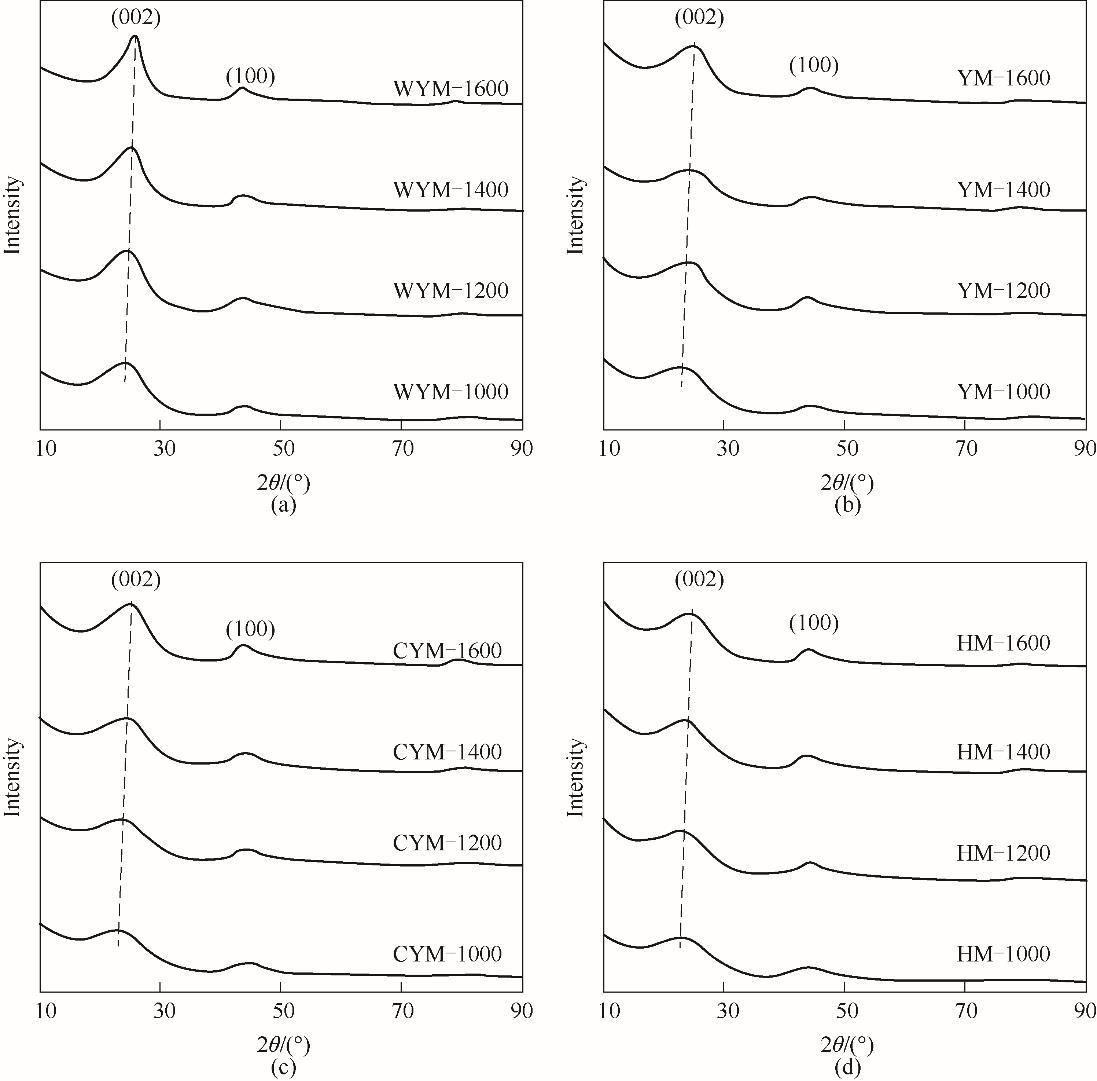
Fig.3 XRD patterns of the samples prepared at different carbonization temperatures(a) WYM-based carbons; (b) YM-based carbons; (c) CYM-based carbons; (d) HM coal-based carbons
| Sample | d002/nm | Lc/nm | La/nm | AG/AD | SBET/(m2·g-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| WYM-1000 | 0.364 | 2.43 | 1.86 | 0.36 | 3.66 |
| WYM-1200 | 0.362 | 2.59 | 1.94 | 0.40 | 8.06 |
| WYM-1400 | 0.358 | 3.10 | 2.03 | 0.48 | 3.00 |
| WYM-1600 | 0.349 | 4.03 | 2.43 | 0.51 | 4.32 |
| YM-1000 | 0.381 | 2.13 | 1.75 | 0.27 | 4.53 |
| YM-1200 | 0.374 | 2.32 | 1.83 | 0.29 | 3.95 |
| YM-1400 | 0.370 | 2.46 | 2.06 | 0.44 | 2.63 |
| YM-1600 | 0.364 | 2.60 | 2.13 | 0.49 | 1.96 |
| CYM-1000 | 0.380 | 2.13 | 1.77 | 0.26 | 5.53 |
| CYM-1200 | 0.377 | 2.25 | 1.80 | 0.30 | 9.94 |
| CYM-1400 | 0.372 | 2.32 | 2.09 | 0.38 | 2.28 |
| CYM-1600 | 0.365 | 2.56 | 2.18 | 0.44 | 2.20 |
| HM-1000 | 0.384 | 2.11 | 1.80 | 0.21 | 4.13 |
| HM-1200 | 0.381 | 2.20 | 1.82 | 0.24 | 4.24 |
| HM-1400 | 0.376 | 2.33 | 1.98 | 0.28 | 3.42 |
| HM-1600 | 0.368 | 2.46 | 2.07 | 0.40 | 4.42 |
Table 3 Structural parameters of coal-based hard carbons prepared at different carbonization temperatures
| Sample | d002/nm | Lc/nm | La/nm | AG/AD | SBET/(m2·g-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| WYM-1000 | 0.364 | 2.43 | 1.86 | 0.36 | 3.66 |
| WYM-1200 | 0.362 | 2.59 | 1.94 | 0.40 | 8.06 |
| WYM-1400 | 0.358 | 3.10 | 2.03 | 0.48 | 3.00 |
| WYM-1600 | 0.349 | 4.03 | 2.43 | 0.51 | 4.32 |
| YM-1000 | 0.381 | 2.13 | 1.75 | 0.27 | 4.53 |
| YM-1200 | 0.374 | 2.32 | 1.83 | 0.29 | 3.95 |
| YM-1400 | 0.370 | 2.46 | 2.06 | 0.44 | 2.63 |
| YM-1600 | 0.364 | 2.60 | 2.13 | 0.49 | 1.96 |
| CYM-1000 | 0.380 | 2.13 | 1.77 | 0.26 | 5.53 |
| CYM-1200 | 0.377 | 2.25 | 1.80 | 0.30 | 9.94 |
| CYM-1400 | 0.372 | 2.32 | 2.09 | 0.38 | 2.28 |
| CYM-1600 | 0.365 | 2.56 | 2.18 | 0.44 | 2.20 |
| HM-1000 | 0.384 | 2.11 | 1.80 | 0.21 | 4.13 |
| HM-1200 | 0.381 | 2.20 | 1.82 | 0.24 | 4.24 |
| HM-1400 | 0.376 | 2.33 | 1.98 | 0.28 | 3.42 |
| HM-1600 | 0.368 | 2.46 | 2.07 | 0.40 | 4.42 |
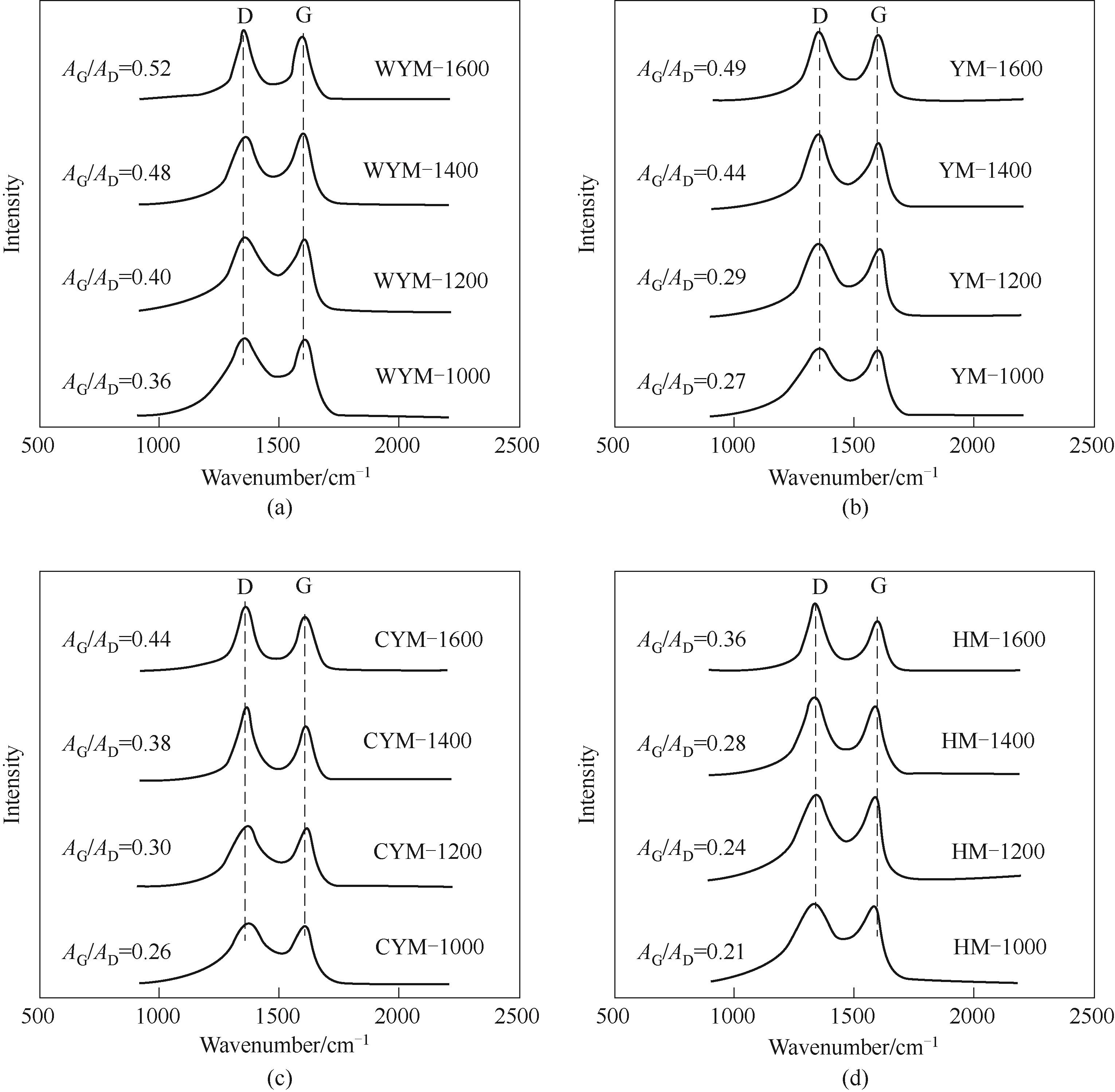
Fig.4 Raman spectra of the samples prepared at different carbonization temperatures(a) WYM-based carbons; (b) YM-based carbons; (c) CYM-based carbons; (d) HM-based carbons
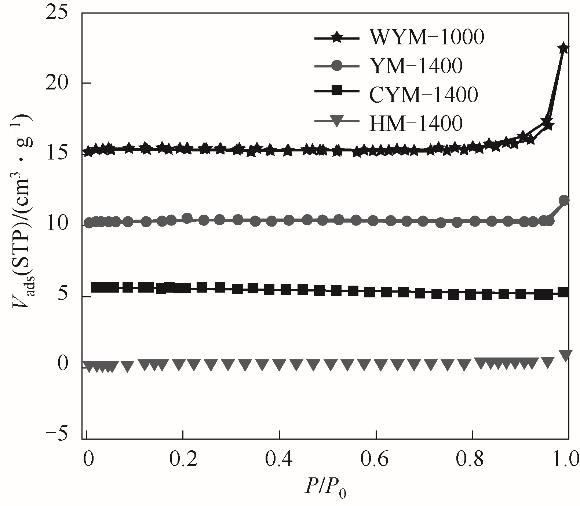
Fig.5 Nitrogen sorption isotherms of WYM-1000, YM-1400, CYM-1400 and HM-1400(The isotherm of WYM-1000, YM-1400 and CYM-1400 are vertically offset by 15, 10 and 5 cm3·g-1, respectively)
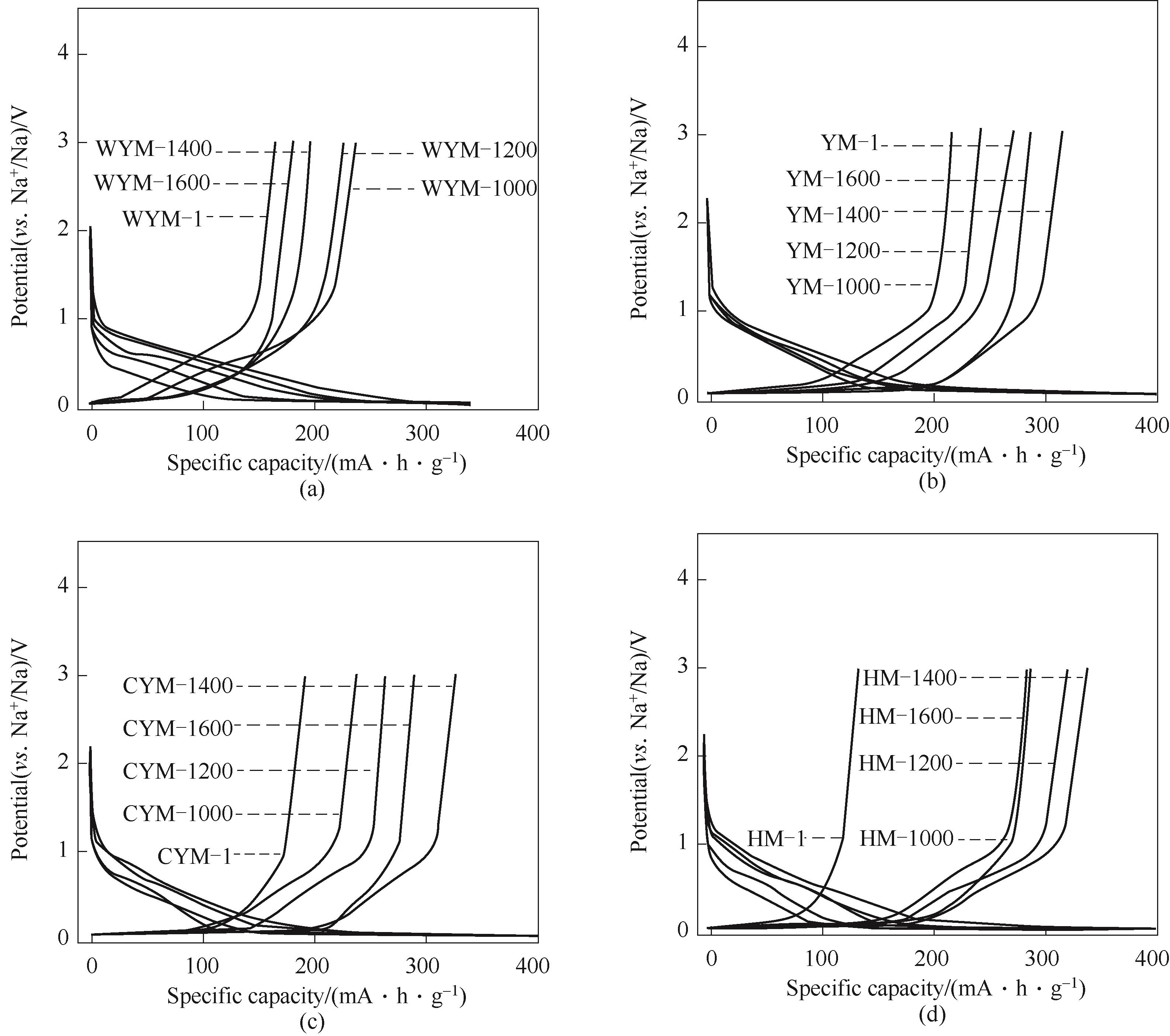
Fig.7 The first galvanostatic charge/discharge profiles at 0.02 A·g-1 of each coal-based carbons as anode materials of sodium-ion batteries(a) WYM-based carbons; (b) YM-based carbons; (c) CYM-based carbons; (d) HM coal-based carbons
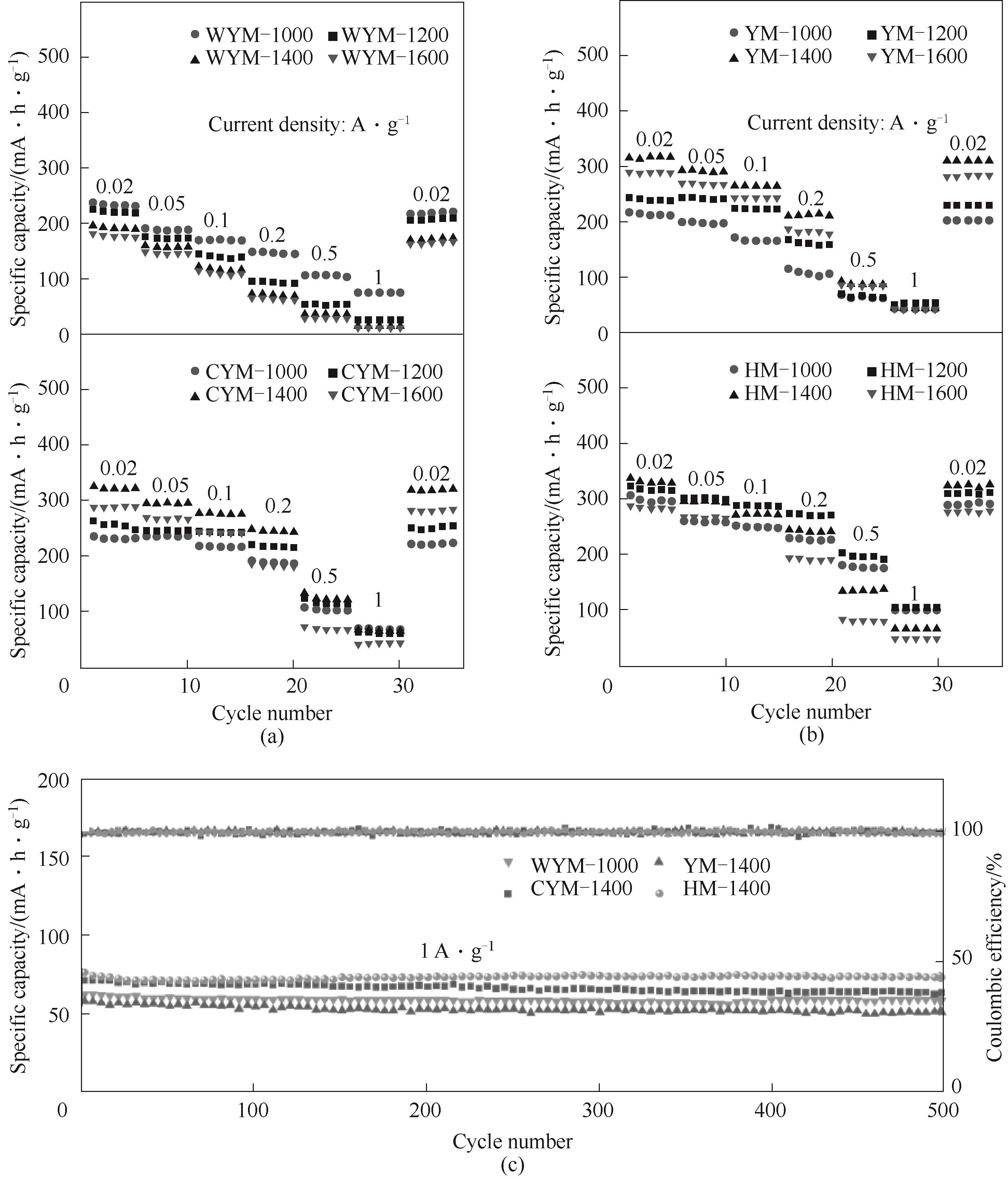
Fig.8 Rate performance of the samples under the current density ranging from 0.02—1 A·g-1: (a) WYM and CYM-based hard carbons; (b) YM and HM-based hard carbons; (c) Cycle performance of the hard carbons at a current density of 1 A·g-1
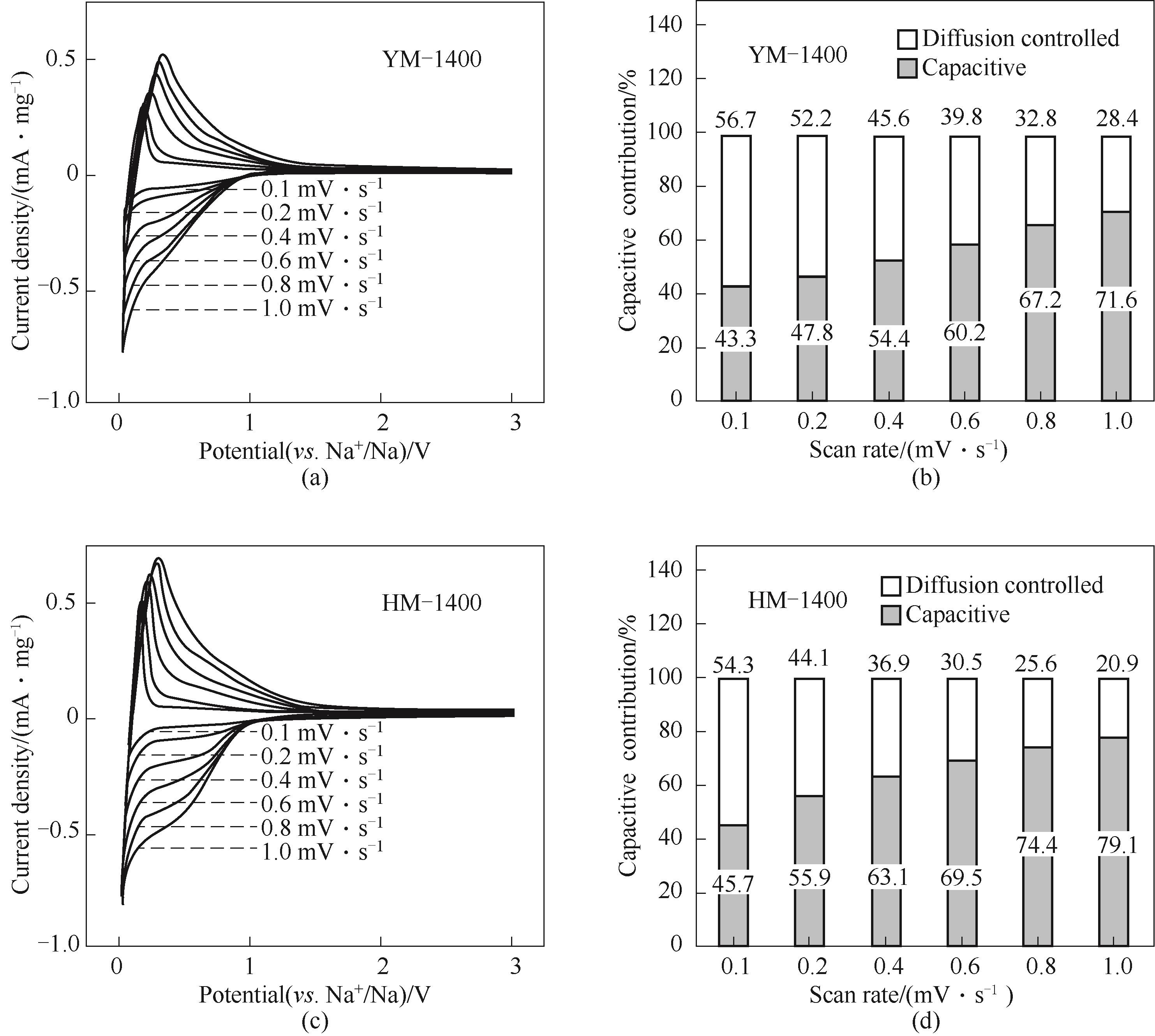
Fig.9 CV curves of YM-1400 (a) and HM-1400 (c) at different scan rates from 0.1—1 mV·s-1; Normalized contribution ratio of capacitive capacities of YM-1400 (b) and HM-1400 (d) at different scan rates
| 样品编号 | 元素分析/%(质量) | XPS分峰C 1s/% | XPS分峰O 1s/% | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | C | H | O | sp2C | sp3C | C—O | —OH | C O O | |
| YM-1000 | 1.65 | 94.47 | 0.42 | 3.46 | 57.43 | 18.02 | 5.76 | 43.82 | 50.42 |
| YM-1200 | 1.06 | 96.23 | 0.21 | 2.5 | 64.04 | 18.20 | 5.17 | 45.60 | 49.23 |
| YM-1400 | 0.3 | 98.06 | 0.10 | 1.54 | 70.62 | 10.76 | 4.31 | 54.13 | 41.56 |
| YM-1600 | 0.08 | 99.09 | 0.06 | 0.77 | 72.01 | 11.91 | 1.08 | 58.71 | 40.21 |
| HM-1000 | 1.09 | 91.42 | 0.48 | 7.01 | 61.74 | 22.12 | 30.67 | 31.21 | 38.13 |
| HM-1200 | 0.45 | 95.69 | 0.22 | 3.64 | 66.05 | 17.57 | 14.38 | 40.06 | 45.57 |
| HM-1400 | 0.30 | 97.74 | 0.10 | 1.86 | 66.54 | 16.97 | 10.24 | 46.86 | 42.68 |
| HM-1600 | 0.08 | 98.63 | 0.08 | 1.21 | 68.37 | 13.96 | 0.43 | 64.85 | 34.73 |
Table 4 Elemental and XPS analysis results of YM and HM coal-based hard carbons
| 样品编号 | 元素分析/%(质量) | XPS分峰C 1s/% | XPS分峰O 1s/% | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | C | H | O | sp2C | sp3C | C—O | —OH | C O O | |
| YM-1000 | 1.65 | 94.47 | 0.42 | 3.46 | 57.43 | 18.02 | 5.76 | 43.82 | 50.42 |
| YM-1200 | 1.06 | 96.23 | 0.21 | 2.5 | 64.04 | 18.20 | 5.17 | 45.60 | 49.23 |
| YM-1400 | 0.3 | 98.06 | 0.10 | 1.54 | 70.62 | 10.76 | 4.31 | 54.13 | 41.56 |
| YM-1600 | 0.08 | 99.09 | 0.06 | 0.77 | 72.01 | 11.91 | 1.08 | 58.71 | 40.21 |
| HM-1000 | 1.09 | 91.42 | 0.48 | 7.01 | 61.74 | 22.12 | 30.67 | 31.21 | 38.13 |
| HM-1200 | 0.45 | 95.69 | 0.22 | 3.64 | 66.05 | 17.57 | 14.38 | 40.06 | 45.57 |
| HM-1400 | 0.30 | 97.74 | 0.10 | 1.86 | 66.54 | 16.97 | 10.24 | 46.86 | 42.68 |
| HM-1600 | 0.08 | 98.63 | 0.08 | 1.21 | 68.37 | 13.96 | 0.43 | 64.85 | 34.73 |
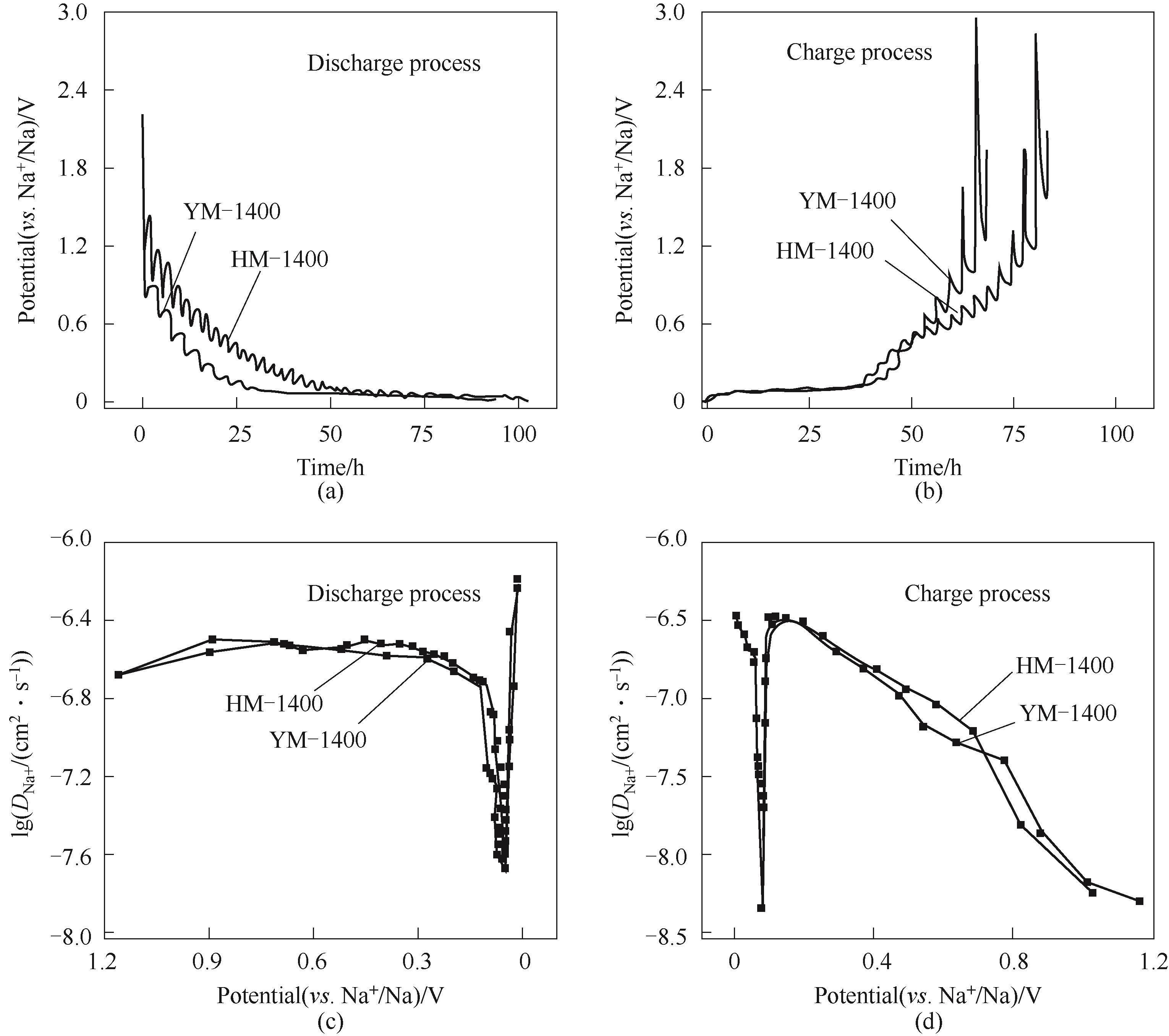
Fig.11 GITT measurements of YM-1400和HM-1400[(a), (b)]; Sodium-ion apparent diffusion coefficients calculated from the GITT potential profiles of the HM-1400 and YM-1400 electrodes during discharge and charge process[(c), (d)]
| 1 | Yabuuchi N, Kubota K, Dahbi M, et al. Research development on sodium-ion batteries[J]. Chemical Reviews, 2014, 114(23): 11636-11682. |
| 2 | Zhao C L, Wang Q D, Yao Z P, et al. Rational design of layered oxide materials for sodium-ion batteries[J]. Science, 2020, 370(6517): 708-711. |
| 3 | Pu X J, Wang H M, Zhao D, et al. Recent progress in rechargeable sodium-ion batteries: toward high-power applications[J]. Small, 2019, 15(32): 1805427. |
| 4 | He Y Z, Xu P, Zhang B, et al. Ultrasmall MnO nanoparticles supported on nitrogen-doped carbon nanotubes as efficient anode materials for sodium ion batteries[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2017, 9(44): 38401-38408. |
| 5 | Li Z, Zhang C Z, Han F, et al. Improving the cycle stability of FeCl3-graphite intercalation compounds by polar Fe2O3 trapping in lithium-ion batteries[J]. Nano Research, 2019, 12(8): 1836-1844. |
| 6 | Li Z, Zhang C Z, Han F, et al. Towards high-volumetric performance of Na/Li-ion batteries: a better anode material with molybdenum pentachloride-graphite intercalation compounds (MoCl5-GICs)[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2020, 8(5): 2430-2438. |
| 7 | Deng W W, Qian J F, Cao Y L, et al. Graphene-wrapped Na2C12H6O4 nanoflowers as high performance anodes for sodium-ion batteries[J]. Small, 2016, 12(5): 583-587. |
| 8 | Fu S D, Ni J F, Xu Y, et al. Hydrogenation driven conductive Na2Ti3O7 nanoarrays as robust binder-free anodes for sodium-ion batteries[J]. Nano Letters, 2016, 16(7): 4544-4551. |
| 9 | Sun N, Guan Z R X, Liu Y W, et al. Extended “adsorption-insertion” model: a new insight into the sodium storage mechanism of hard carbons[J]. Advanced Energy Materials, 2019, 9(32): 1901351. |
| 10 | Qu W H, Guo Y B, Shen W Z, et al. Using asphaltene supermolecules derived from coal for the preparation of efficient carbon electrodes for supercapacitors[J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2016, 120(28): 15105-15113. |
| 11 | Qi Y R, Lu Y X, Liu L L, et al. Retarding graphitization of soft carbon precursor: from fusion-state to solid-state carbonization[J]. Energy Storage Materials, 2020, 26: 577-584. |
| 12 | 陆倩, 徐园园, 木沙江, 等. 不粘煤基活性炭作超级电容器电极材料: 硼、氮掺杂对其电化学性能的影响[J]. 新型炭材料, 2017, 32(5): 442-450. |
| Lu Q, Xu Y Y, Mu S J, et al. The effect of nitrogen and/or boron doping on the electrochemical performance of non-caking coal-derived activated carbons for use as supercapacitor electrodes[J]. New Carbon Materials, 2017, 32(5): 442-450. | |
| 13 | Li Y M, Hu Y S, Qi X G, et al. Advanced sodium-ion batteries using superior low cost pyrolyzed anthracite anode: towards practical applications[J]. Energy Storage Materials, 2016, 5: 191-197. |
| 14 | Lu H Y, Sun S F, Xiao L F, et al. High-capacity hard carbon pyrolyzed from subbituminous coal as anode for sodium-ion batteries[J]. ACS Applied Energy Materials, 2019, 2(1): 729-735. |
| 15 | Liu X F, Song D Z, He X Q, et al. Insight into the macromolecular structural differences between hard coal and deformed soft coal[J]. Fuel, 2019, 245: 188-197. |
| 16 | Xie X, Zhao Y, Qiu P H, et al. Investigation of the relationship between infrared structure and pyrolysis reactivity of coals with different ranks[J]. Fuel, 2018, 216: 521-530. |
| 17 | Steel K M, Patrick J W. The production of ultra clean coal by sequential leaching with HF followed by HNO3[J]. Fuel, 2003, 82(15/16/17): 1917-1920. |
| 18 | Mathews J P, Chaffee A L. The molecular representations of coal—a review[J]. Fuel, 2012, 96: 1-14. |
| 19 | Wang B Y, Xia J L, Dong X L, et al. Highly purified carbon derived from deashed anthracite for sodium-ion storage with enhanced capacity and rate performance[J]. Energy & Fuels, 2020, 34(12): 16831-16837. |
| 20 | Li Q, Wang Z H, He Y, et al. Pyrolysis characteristics and evolution of char structure during pulverized coal pyrolysis in drop tube furnace: influence of temperature[J]. Energy & Fuels, 2017, 31(5): 4799-4807. |
| 21 | Wang D C, Jin L J, Wei B Y, et al. Oxidative catalytic cracking and reforming of coal pyrolysis volatiles over NiO[J]. Energy & Fuels, 2020, 34(6): 6928-6937. |
| 22 | He X Q, Liu X F, Nie B S, et al. FTIR and Raman spectroscopy characterization of functional groups in various rank coals[J]. Fuel, 2017, 206: 555-563. |
| 23 | Zhang S X, Li C R, Huang R, et al. Thermogravimetric study of the kinetics and characteristics of the pyrolysis of pulverized coal[J]. Materials Research Express, 2020, 7(8): 085604. |
| 24 | Wang C Y, Xing Y W, Xia Y C, et al. Investigation of interactions between oxygen-containing groups and water molecules on coal surfaces using density functional theory[J]. Fuel, 2021, 287: 119556. |
| 25 | Miura K. Mild conversion of coal for producing valuable chemicals[J]. Fuel Processing Technology, 2000, 62(2/3): 119-135. |
| 26 | Lu Y X, Zhao C L, Qi X G, et al. Pre-oxidation-tuned microstructures of carbon anodes derived from pitch for enhancing Na storage performance[J]. Advanced Energy Materials, 2018, 8(27): 1800108. |
| 27 | Sun D, Luo B, Wang H Y, et al. Engineering the trap effect of residual oxygen atoms and defects in hard carbon anode towards high initial Coulombic efficiency[J]. Nano Energy, 2019, 64: 103937. |
| 28 | Sadezky A, Muckenhuber H, Grothe H, et al. Raman microspectroscopy of soot and related carbonaceous materials: spectral analysis and structural information[J]. Carbon, 2005, 43(8): 1731-1742. |
| 29 | Li Y M, Mu L Q, Hu Y S, et al. Pitch-derived amorphous carbon as high performance anode for sodium-ion batteries[J]. Energy Storage Materials, 2016, 2: 139-145. |
| 30 | Cao Y L, Xiao L F, Sushko M L, et al. Sodium ion insertion in hollow carbon nanowires for battery applications[J]. Nano Letters, 2012, 12(7): 3783-3787. |
| 31 | Qi Y R, Lu Y X, Ding F X, et al. Slope-dominated carbon anode with high specific capacity and superior rate capability for high safety Na-ion batteries[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2019, 58(13): 4361-4365. |
| 32 | Alvin S, Yoon D, Chandra C, et al. Revealing sodium ion storage mechanism in hard carbon[J]. Carbon, 2019, 145: 67-81. |
| 33 | Jiang B, Zhang Y, Yan D, et al. Ultrafast sodium storage through capacitive behaviors in carbon nanosheets with enhanced ion transport[J]. ChemElectroChem, 2019, 6(12): 3043-3048. |
| 34 | Xia J L, Yan D, Guo L P, et al. Hard carbon nanosheets with uniform ultramicropores and accessible functional groups showing high realistic capacity and superior rate performance for sodium-ion storage[J]. Advanced Materials, 2020, 32(21): 2000447. |
| [1] | Yepin CHENG, Daqing HU, Yisha XU, Huayan LIU, Hanfeng LU, Guokai CUI. Application of ionic liquid-based deep eutectic solvents for CO2 conversion [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(9): 3640-3653. |
| [2] | Lei WU, Jiao LIU, Changcong LI, Jun ZHOU, Gan YE, Tiantian LIU, Ruiyu ZHU, Qiuli ZHANG, Yonghui SONG. Catalytic microwave pyrolysis of low-rank pulverized coal for preparation of high value-added modified bluecoke powders containing carbon nanotubes [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(9): 3956-3967. |
| [3] | Yali HU, Junyong HU, Suxia MA, Yukun SUN, Xueyi TAN, Jiaxin HUANG, Fengyuan YANG. Development of novel working fluid and study on electrochemical characteristics of reverse electrodialysis heat engine [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(8): 3513-3521. |
| [4] | Mengmeng ZHANG, Dong YAN, Yongfeng SHEN, Wencui LI. Effect of electrolyte types on the storage behaviors of anions and cations for dual-ion batteries [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(7): 3116-3126. |
| [5] | Wentao WU, Liangyong CHU, Lingjie ZHANG, Weimin TAN, Liming SHEN, Ningzhong BAO. High-efficient preparation of cardanol-based self-healing microcapsules [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(7): 3103-3115. |
| [6] | Zhilong WANG, Ye YANG, Zhenzhen ZHAO, Tao TIAN, Tong ZHAO, Yahui CUI. Influence of mixing time and sequence on the dispersion properties of the cathode slurry of lithium-ion battery [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(7): 3127-3138. |
| [7] | Jiali GE, Tuxiang GUAN, Xinmin QIU, Jian WU, Liming SHEN, Ningzhong BAO. Synthesis of FeF3 nanoparticles covered by vertical porous carbon for high performance Li-ion battery cathode [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(7): 3058-3067. |
| [8] | Yuanhao QU, Wenyi DENG, Xiaodan XIE, Yaxin SU. Study on electro-osmotic dewatering of sludge assisted by activated carbon/graphite [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(7): 3038-3050. |
| [9] | Tan ZHANG, Guang LIU, Jinping LI, Yuhan SUN. Performance regulation strategies of Ru-based nitrogen reduction electrocatalysts [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(6): 2264-2280. |
| [10] | Zhenghao YANG, Zhen HE, Yulong CHANG, Ziheng JIN, Xia JIANG. Research progress in downer fluidized bed reactor for biomass fast pyrolysis [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(6): 2249-2263. |
| [11] | Feng ZHU, Kailin CHEN, Xiaofeng HUANG, Yinzhu BAO, Wenbin LI, Jiaxin LIU, Weiqiang WU, Wangwei GAO. Performance study of KOH modified carbide slag for removal of carbonyl sulfide [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(6): 2668-2679. |
| [12] | Jing LI, Conghao SHEN, Daliang GUO, Jing LI, Lizheng SHA, Xin TONG. Research progress in the application of lignin-based carbon fiber composite materials in energy storage components [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(6): 2322-2334. |
| [13] | Ruikang LI, Yingying HE, Weipeng LU, Yuanyuan WANG, Haodong DING, Yongming LUO. Study on the electrochemical enhanced cobalt-based cathode to activate peroxymonosulfate [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(5): 2207-2216. |
| [14] | Chengze WANG, Kaili GU, Jinhua ZHANG, Jianxuan SHI, Yiwei LIU, Jinxiang LI. Sulfidation couples with aging to enhance the reactivity of zerovalent iron toward Cr(Ⅵ) in water [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(5): 2197-2206. |
| [15] | Xu GUO, Yongzheng ZHANG, Houbing XIA, Na YANG, Zhenzhen ZHU, Jingyao QI. Research progress in the removal of water pollutants by carbon-based materials via electrooxidation [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(5): 1862-1874. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||