化工学报 ›› 2019, Vol. 70 ›› Issue (8): 3177-3187.DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20190001
收稿日期:2019-01-02
修回日期:2019-07-07
出版日期:2019-08-05
发布日期:2019-08-05
通讯作者:
袁金良
作者简介:赵加佩(1985—),男,博士,讲师,<email>jiapeizhao@126.com</email>
基金资助:
Jiapei ZHAO1( ),Chin Eng LOO2,Hao ZHOU3,Mingxi ZHOU3,Fu WANG1,Jinliang YUAN1(
),Chin Eng LOO2,Hao ZHOU3,Mingxi ZHOU3,Fu WANG1,Jinliang YUAN1( )
)
Received:2019-01-02
Revised:2019-07-07
Online:2019-08-05
Published:2019-08-05
Contact:
Jinliang YUAN
摘要:
通过中试规模烧结杯试验和综合烧结模型,将返矿平衡和非平衡条件相结合,研究了混合料特性(烧结碱度、焦炭和水分添加量)对火焰烽面特性和烧结性能的影响机理。模拟研究涉及多种烧结条件下的125个烧结杯工况。为揭示火焰烽面区域中熔体生成与凝固行为,使用FactSage软件进行化学热力学模拟并建立了更完善的熔化和凝固子模型。模拟与试验研究表明,随着碱度和焦炭添加量的变化,火焰烽面速度、成品率、焦比和利用系数会出现局部最大或最小值。在本文烧结条件下,最大利用系数工况为碱度2.0、水分7.7%、焦炭6.4%。最小焦比工况为碱度2.0、水分6.5%、焦炭6.4%。最小焦比和最大利用系数的条件并不相同,而最终烧结操作取决于每个烧结厂的控制目标。
中图分类号:
赵加佩, 周昊, 周明煕, 王甫, 袁金良. 铁矿石烧结中混合料特性对火焰烽面与烧结性能的影响机理研究[J]. 化工学报, 2019, 70(8): 3177-3187.
Jiapei ZHAO, Chin Eng LOO, Hao ZHOU, Mingxi ZHOU, Fu WANG, Jinliang YUAN. Effect of sinter mix properties on the flame front properties and iron ore sintering performance[J]. CIESC Journal, 2019, 70(8): 3177-3187.
| 成分 | 质量分数/% | |
|---|---|---|
| 基础碱度(碱度值1.8) | 高碱度(碱度值2.2) | |
| Fe2O3 | 83.36 | 81.40 |
| CaO | 8.78 | 10.74 |
| SiO2 | 4.88 | 4.88 |
| Al2O3 | 1.48 | 1.48 |
| MgO | 1.50 | 1.50 |
表1 基础碱度和高碱度混合料化学成分
Table 1 Sinter mix chemistry for BASE and HB cases
| 成分 | 质量分数/% | |
|---|---|---|
| 基础碱度(碱度值1.8) | 高碱度(碱度值2.2) | |
| Fe2O3 | 83.36 | 81.40 |
| CaO | 8.78 | 10.74 |
| SiO2 | 4.88 | 4.88 |
| Al2O3 | 1.48 | 1.48 |
| MgO | 1.50 | 1.50 |
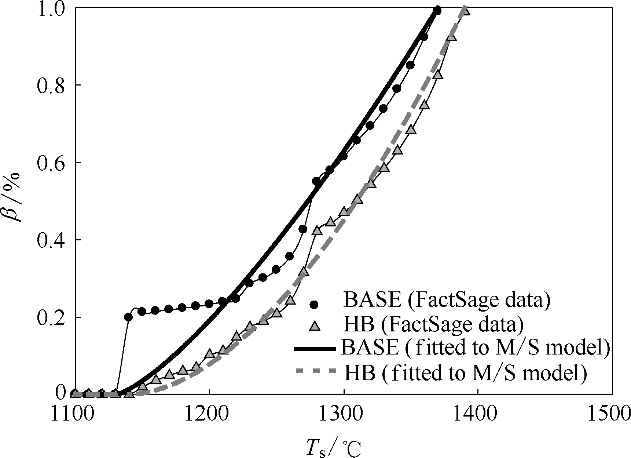
图1 FactSage模拟得出的两种碱度下熔体量β随温度T s的变化规律(基础碱度BASE和高碱度HB情况),图中两条曲线表示根据本文熔化和凝固模型[式(3)]所拟合得到的结果)
Fig.1 Variation of melt fraction β with temperature T s for the examples of two basicity levels (BASE and HB) predicted by thermochemical modelling with FactSage(The two lines indicate the results fitted to the melting and solidification model according to Eq. (3))
| 参数 | 数值 |
|---|---|
| 床高(含铺底料层)/mm | 550 |
| 铺底料层厚度/mm | 30 |
| 烧结杯截面积/m2 | 0.09 |
| 床点火温度/℃ | 1200 |
| 点火时间/s | 90 |
| 点火负压/kPa | 6 |
| 烧结负压/kPa | 16 |
| 落下强度试验(2m高)/次 | 4 |
| 焦炭添加量/%(dob②) | 6.00, 6.25①, 6.50 |
| 碱度(CaO/SiO2) | 1.5, 1.8①, 2.1 |
| 混合料水分含量/%(tmb③) | 6.7, 7.2①, 7.6 |
表2 返矿平衡烧结杯试验条件[10,11]
Table 2 Summary of conditions for return fines balanced sinter pot tests[10,11]
| 参数 | 数值 |
|---|---|
| 床高(含铺底料层)/mm | 550 |
| 铺底料层厚度/mm | 30 |
| 烧结杯截面积/m2 | 0.09 |
| 床点火温度/℃ | 1200 |
| 点火时间/s | 90 |
| 点火负压/kPa | 6 |
| 烧结负压/kPa | 16 |
| 落下强度试验(2m高)/次 | 4 |
| 焦炭添加量/%(dob②) | 6.00, 6.25①, 6.50 |
| 碱度(CaO/SiO2) | 1.5, 1.8①, 2.1 |
| 混合料水分含量/%(tmb③) | 6.7, 7.2①, 7.6 |
| 参数 | 数值 |
|---|---|
| 床高(含铺底料层)/mm | 600 |
| 铺底料层厚度/mm | 30 |
| 烧结杯截面积/m2 | 0.088 |
| 床点火温度/℃ | 1200 |
| 点火时间/s | 90 |
| 点火负压/kPa | 6 |
| 烧结负压/kPa | 16 |
| 落下强度试验(2m高)/次 | 4 |
| 返矿用量/%(dob②) | 32.4 |
| 焦炭添加量/%(dob②) | 5.9, 6.15, 6.4①, 6.65, 6.9 |
| 碱度(CaO/SiO2) | 0.8, 1.4, 2.0①, 2.6, 3.2 |
| 混合料水分含量/%(tmb③) | 6.5, 6.8, 7.1①, 7.4, 7.7 |
表3 返矿不平衡的模拟工况条件
Table 3 Summary of conditions for simulation cases with constant return fines level
| 参数 | 数值 |
|---|---|
| 床高(含铺底料层)/mm | 600 |
| 铺底料层厚度/mm | 30 |
| 烧结杯截面积/m2 | 0.088 |
| 床点火温度/℃ | 1200 |
| 点火时间/s | 90 |
| 点火负压/kPa | 6 |
| 烧结负压/kPa | 16 |
| 落下强度试验(2m高)/次 | 4 |
| 返矿用量/%(dob②) | 32.4 |
| 焦炭添加量/%(dob②) | 5.9, 6.15, 6.4①, 6.65, 6.9 |
| 碱度(CaO/SiO2) | 0.8, 1.4, 2.0①, 2.6, 3.2 |
| 混合料水分含量/%(tmb③) | 6.5, 6.8, 7.1①, 7.4, 7.7 |

图2 返矿平衡条件下烧结杯试验的返矿量、成品率、火焰烽面速度、利用系数和焦比随碱度变化结果(模型预测结果也示于图中)
Fig.2 Sinter pot test results of return fines level, yield, FFS, productivity and coke rate at increasing basicity levels(MT, β mean, yield, FFS, productivity and coke rate predicted by the model are also shown)

图3 返矿平衡条件下烧结杯试验的返矿量、成品率、火焰烽面速度、利用系数和焦比随焦炭添加量的变化结果(模型预测结果也示于图中)
Fig.3 Sinter pot test results of return fines level, yield, FFS, productivity and coke rate at increasing coke addition levels(MT, β mean, yield, FFS, productivity and coke rate predicted by the model are also shown)
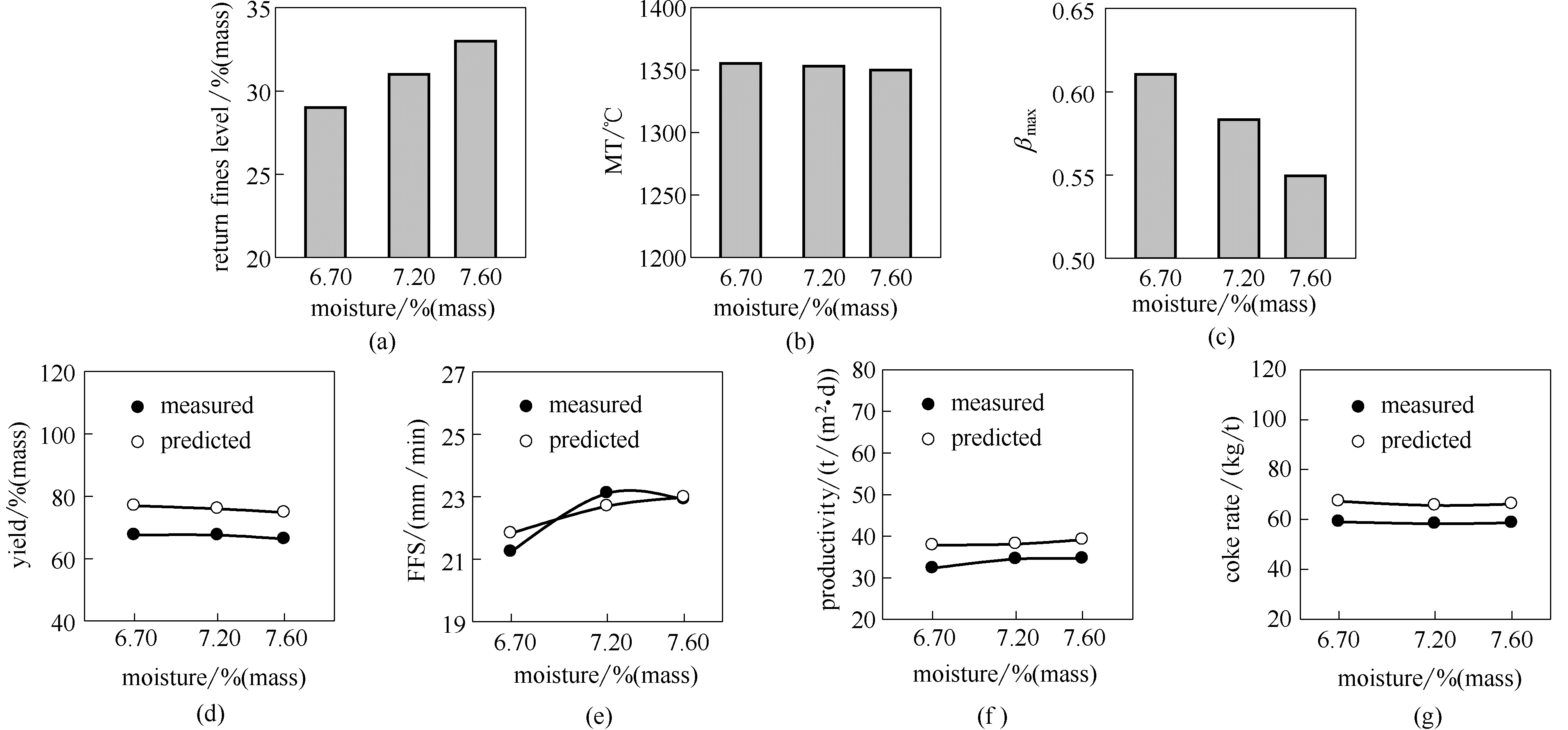
图4 返矿平衡条件下烧结杯试验的返矿量、成品率、火焰烽面速度、利用系数和焦比随水分添加量的变化结果(模型预测结果也示于图中)
Fig.4 Sinter pot test results of return fines level, yield, FFS, productivity and coke rate at increasing mix moisture levels(MT, β mean, yield, FFS, productivity and coke rate predicted by the model are also shown)
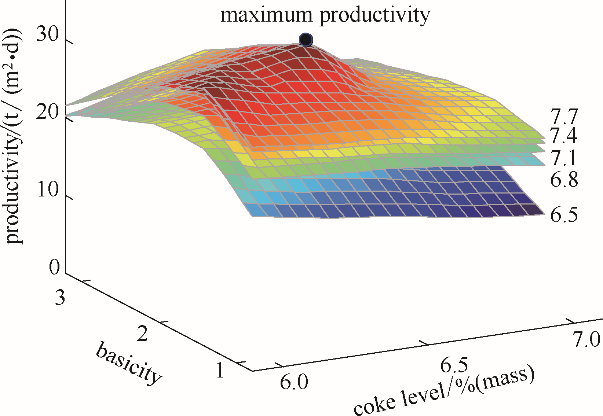
图10 模型计算所得利用系数随碱度、焦炭和水分添加量的变化规律(图中黑点位置为最大利用系数参数位置)
Fig.10 Variation of productivity with basicity, coke and mix moisture levels for five moisture levels (6.5%—7.7%)
| 1 | Zhao J , Loo C E , Ellis B G . Improving energy efficiency in iron ore sintering through segregation: a theoretical investigation [J]. ISIJ Int., 2016, 56(7): 1148-1156. |
| 2 | Zhou H , Zhao J P , Loo C E , et al . Model predictions of important bed and gas properties during iron ore sintering [J]. ISIJ Int., 2012, 52(12): 2168-2176. |
| 3 | Zhao J , Loo C E , Zhou H , et al . Modelling and analysis of the combustion behaviour of granulated fuel particles in iron ore sintering [J]. Combust. Flame, 2018, 189: 257-274. |
| 4 | Loo C E , Hutchens M F . Quantifying the resistance to airflow during iron ore sintering [J]. ISIJ Int., 2003, 43(5): 630-636. |
| 5 | Loo C E , Matthews L T . Assimilation of large ore and flux particles in iron ore sintering [J]. Trans. Inst. Min. Metall.(Sect. C: Miner Process. Extr. Metall),1992,101: C105-C117. |
| 6 | Lu L , Adam M , Kilburn M , et al . Substitution of charcoal for coke breeze in iron ore sintering [J]. ISIJ Int., 2013, 53(9): 1607-1616. |
| 7 | Zhao J , Loo C E . Dependence of flame front speed on iron ore sintering conditions [J]. Miner. Process. Extr. Metall. (TIMM C), 2016, 125(3): 165-171. |
| 8 | Bhagat R P . Factors affecting return sinter fines regimed and strand productivity in iron ore sintering [J]. ISIJ Int., 1999, 39(9): 889-895. |
| 9 | Umadevi T , Sah R , Mahapatra P C . Influence of sinter basicity (CaO/SiO2) on low and high alumina iron ore sinter quality [J]. Mineral Processing and Extractive Metallurgy, 2014, 123(2): 75-85. |
| 10 | Loo C E , Wong D J . Fundamental insights into the sintering behaviour of goethitic ore blends [J]. ISIJ Int., 2005, 45(4): 459-468. |
| 11 | Loo C E , Wong D J . Fundamental factors determining laboratory sintering results [J]. ISIJ Int., 2005, 45(4): 449-458. |
| 12 | Zhao J P , Loo C E , Dukino R D . Modelling fuel combustion in iron ore sintering [J]. Combust. Flame, 2015, 162(4): 1019-1034. |
| 13 | Litster J , Waters A . Influence of the material properties of iron ore sinter feed on granulation effectiveness [J]. Powder Technol., 1988, 55(2): 141-151. |
| 14 | Litster J , Waters A , Nicol S . A model for predicting the size distribution of product from a granulating drum [J]. Trans. ISIJ, 1986, 26(12): 1036-1044. |
| 15 | Hinkley J , Waters A G , Litster J D . An investigation of pre-ignition air flow in ferrous sintering [J]. Int. J. Miner. Process, 1994, 42(1/2): 37-52. |
| 16 | Zhou H , Zhao J P , Loo C E , et al . Numerical modeling of the iron ore sintering process [J]. ISIJ Int., 2012, 52(9): 1550–1558. |
| 17 | Zhao J , Loo C E , Yuan J , et al . A fundamental study of the cocombustion of coke and charcoal during iron ore sintering [J]. Energy & Fuels, 2018, 32(8): 8743-8759. |
| 18 | Ni M , Xiao H , Chi Y , et al . Combustion and inorganic bromine emission of waste printed circuit boards in a high temperature furnace [J]. Waste Management, 2012, 32(3): 568-574. |
| 19 | Xiao H , Zhou Z , Zhou H , et al . Conversion of HBr to Br2 in the flue gas from the combustion of waste printed circuit boards in post-combustion area [J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2017, 161: 239-244. |
| 20 | Xiao H , Chi Y , Buekens A . Combustion characteristics of waste printed circuit boards in thermogravimetric analyzers [J]. Environmental Progress & Sustainable Energy, 2015, 33(4): 1105-1110. |
| 21 | Kawaguchi T , Sato S , Takata K . Development and application of an integrated simulation model for iron ore sintering[C]// Ironmaking Conf. Proc. ISS, 1987: 99-106. |
| 22 | Nakano M , Okazaki J . Ideal behavior of sinter block densification and relation thereof to yield and strength in iron ore sintering [J]. ISIJ Int., 2011, 51(9): 1418-1424. |
| 23 | Yang W , Choi A , Choi E S , et al . Combustion characteristics in an iron ore sintering bed — evaluation of fuel substitution [J]. Combust. Flame, 2006, 145(3): 447-463. |
| 24 | Cheng Z , Yang J , Zhou L , et al . Sinter strength evaluation using process parameters under different conditions in iron ore sintering process [J]. Appl. Therm. Eng., 2016, 105: 894-904. |
| 25 | Zhao J , Loo C E . Dependence of flame front speed on iron ore sintering conditions[C]// Iron Ore Conference 2015. 2015: 83-90. |
| [1] | 宋嘉豪, 王文. 斯特林发动机与高温热管耦合运行特性研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(S1): 287-294. |
| [2] | 张思雨, 殷勇高, 贾鹏琦, 叶威. 双U型地埋管群跨季节蓄热特性研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(S1): 295-301. |
| [3] | 晁京伟, 许嘉兴, 李廷贤. 基于无管束蒸发换热强化策略的吸附热池的供热性能研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(S1): 302-310. |
| [4] | 程成, 段钟弟, 孙浩然, 胡海涛, 薛鸿祥. 表面微结构对析晶沉积特性影响的格子Boltzmann模拟[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(S1): 74-86. |
| [5] | 叶展羽, 山訸, 徐震原. 用于太阳能蒸发的折纸式蒸发器性能仿真[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(S1): 132-140. |
| [6] | 张双星, 刘舫辰, 张义飞, 杜文静. R-134a脉动热管相变蓄放热实验研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(S1): 165-171. |
| [7] | 张义飞, 刘舫辰, 张双星, 杜文静. 超临界二氧化碳用印刷电路板式换热器性能分析[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(S1): 183-190. |
| [8] | 陈爱强, 代艳奇, 刘悦, 刘斌, 吴翰铭. 基板温度对HFE7100液滴蒸发过程的影响研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(S1): 191-197. |
| [9] | 刘明栖, 吴延鹏. 导光管直径和长度对传热影响的模拟分析[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(S1): 206-212. |
| [10] | 王志国, 薛孟, 董芋双, 张田震, 秦晓凯, 韩强. 基于裂隙粗糙性表征方法的地热岩体热流耦合数值模拟与分析[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(S1): 223-234. |
| [11] | 齐聪, 丁子, 余杰, 汤茂清, 梁林. 基于选择吸收纳米薄膜的太阳能温差发电特性研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(9): 3921-3930. |
| [12] | 李艺彤, 郭航, 陈浩, 叶芳. 催化剂非均匀分布的质子交换膜燃料电池操作条件研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(9): 3831-3840. |
| [13] | 王玉兵, 李杰, 詹宏波, 朱光亚, 张大林. R134a在菱形离散肋微小通道内的流动沸腾换热实验研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(9): 3797-3806. |
| [14] | 李科, 文键, 忻碧平. 耦合蒸气冷却屏的真空多层绝热结构对液氢储罐自增压过程的影响机制研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(9): 3786-3796. |
| [15] | 何松, 刘乔迈, 谢广烁, 王斯民, 肖娟. 高浓度水煤浆管道气膜减阻两相流模拟及代理辅助优化[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(9): 3766-3774. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备 11010102001995号
京公网安备 11010102001995号