化工学报 ›› 2020, Vol. 71 ›› Issue (11): 5246-5255.DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20200285
张昕怡1,2( ),许蕊1,2,王钰棋1,2,张瑜1,2,王飞1,2,李迅1,2(
),许蕊1,2,王钰棋1,2,张瑜1,2,王飞1,2,李迅1,2( )
)
收稿日期:2020-03-18
修回日期:2020-07-07
出版日期:2020-11-05
发布日期:2020-11-05
通讯作者:
李迅
作者简介:张昕怡(1996—),女,硕士研究生,基金资助:
Xinyi ZHANG1,2( ),Rui XU1,2,Yuqi WANG1,2,Yu ZHANG1,2,Fei WANG1,2,Xun LI1,2(
),Rui XU1,2,Yuqi WANG1,2,Yu ZHANG1,2,Fei WANG1,2,Xun LI1,2( )
)
Received:2020-03-18
Revised:2020-07-07
Online:2020-11-05
Published:2020-11-05
Contact:
Xun LI
摘要:
将来源于解脂嗜热互营杆菌(Thermosyntropha lipolytica)的脂肪酶(TlLipA)基因tll1导入大肠杆菌BL21(DE3)中表达,通过热处理和镍柱亲和层析获得纯酶,并对其酶学性质进行研究。十二烷基硫酸钠-聚丙烯酰胺凝胶电泳(SDS-PAGE)显示TlLipA分子量为53×103,其最适反应温度为65℃,最适反应pH为8.0。在55~65℃范围内酶活较高且比较稳定;在pH7.0~11.0于室温保存1 h后,残留相对酶活仍达80%以上。1 mmol/L 金属离子Zn2+、Fe3+和试剂SDS,0.05%(质量分数)Tween 80,对酶活力具有强烈的抑制作用,残留相对酶活皆低于15%;1 mmol/L Mg2+、Mn2+对酶活力表现出轻微的激活作用。由底物专一性实验可得,该酶对辛酸对硝基苯酯(C8)和癸酸对硝基苯酯(C10)偏好明显。以棕榈酸对硝基苯酯(p-NPP)为底物,该酶动力学参数Km值为0.23 mmol/L,Vmax为33.50 mmol/(L·min),kcat为22.83 S-1。以重组脂肪酶为催化剂在无溶剂体系中制备生物柴油,含水率20%,酶加量200 U/g油,醇油比为4∶1的条件下,在55℃催化大豆油反应48 h,收率可达91.75%。
中图分类号:
张昕怡,许蕊,王钰棋,张瑜,王飞,李迅. 新型嗜热耐碱脂肪酶的纯化表征及应用[J]. 化工学报, 2020, 71(11): 5246-5255.
Xinyi ZHANG,Rui XU,Yuqi WANG,Yu ZHANG,Fei WANG,Xun LI. Purification and characterization of novel thermo-alkaline lipase and its application[J]. CIESC Journal, 2020, 71(11): 5246-5255.
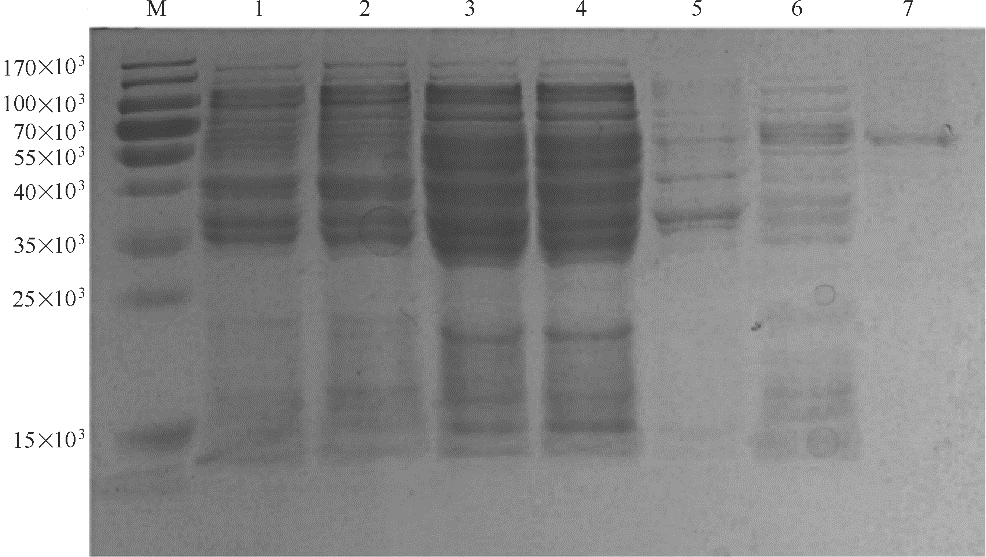
图1 重组脂肪酶 TlLipA 的SDS-PAGE 分析M—蛋白质标准分子量;1—质粒pET28a转化BL21(DE3) 重组菌的全细胞液;2—质粒pET28a转化BL21(DE3) 重组菌的上清液;3—质粒pET28a-TLL1转化BL21(DE3) 重组菌的全细胞液;4—质粒pET28a-TLL1转化BL21(DE3) 重组菌的上清液;5—质粒pET28a-TLL1转化BL21(DE3) 重组菌的沉淀;6—质粒pET28a-TLL1转化BL21(DE3)重组菌热处理后的上清液;7—质粒pET28a-TLL1转化BL21(DE3)重组菌的Ni2+亲和柱纯化后的酶液
Fig.1 SDS-PAGE analysis of the recombinant lipase TlLipA
| 纯化步骤 | 总体积/ml | 总酶活/U | 比酶活/ (U/mg) | 回收率/% | 纯化倍数 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 粗酶液 | 10 | 469.96 | 1.99 | 100 | 1 |
| 热处理 | 10 | 340.35 | 6.48 | 72.42 | 3.26 |
| 镍柱亲和层析 | 4 | 114.64 | 22.11 | 24.39 | 11.11 |
表1 重组脂肪酶 TlLipA 的纯化
Table 1 The purification of recombinant lipase TlLipA
| 纯化步骤 | 总体积/ml | 总酶活/U | 比酶活/ (U/mg) | 回收率/% | 纯化倍数 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 粗酶液 | 10 | 469.96 | 1.99 | 100 | 1 |
| 热处理 | 10 | 340.35 | 6.48 | 72.42 | 3.26 |
| 镍柱亲和层析 | 4 | 114.64 | 22.11 | 24.39 | 11.11 |
| 金属离子和化学试剂 | 相对酶活/% |
|---|---|
control Fe3+ Co2+ Zn2+ Mn2+ Ca2+ K+ Mg2+ Na+ Ni2+ Cu2+ PMSF LAS Tween 80 AEO-7 EDTA SDS Triton X-100 | 100±3.15 11.71±2.49 90.84±1.72 9.73±1.34 113.24±3.04 81.24±7.04 90.27±4.60 108.55±7.11 88.76±5.46 87.63±3.68 69.31±6.50 86.39±3.46 72.62±4.37 8.19±2.16 16.36±2.73 15.90±2.61 2.28±1.44 61.15±1.07 |
表2 金属离子和化学试剂对酶活性的影响
Table 2 Effects of ions and reagents on the activity of the lipase
| 金属离子和化学试剂 | 相对酶活/% |
|---|---|
control Fe3+ Co2+ Zn2+ Mn2+ Ca2+ K+ Mg2+ Na+ Ni2+ Cu2+ PMSF LAS Tween 80 AEO-7 EDTA SDS Triton X-100 | 100±3.15 11.71±2.49 90.84±1.72 9.73±1.34 113.24±3.04 81.24±7.04 90.27±4.60 108.55±7.11 88.76±5.46 87.63±3.68 69.31±6.50 86.39±3.46 72.62±4.37 8.19±2.16 16.36±2.73 15.90±2.61 2.28±1.44 61.15±1.07 |
| 脂肪酶来源 | 最适温度/℃ | 最适pH | Km/(mmol/L) | Vmax/(mmol/(L·min)) | 文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T. lipolytica(TlLipA) | 65 | 8 | 0.23 | 33.50 | 本文 |
| G. thermodenitrificans AV-5 | 65 | 9 | 0.44 | 0.556 | [ |
| T. Anoxybacillus flavithermus HBB 134 | 50 | 9 | 0.084 | 1.29 | [ |
| Staphylococcus aureus | 40 | 8 | 1.57 | 3.25 | [ |
| Thermotoga maritima | 70 | 7.5 | 8 | 2.50 | [ |
| Geobacillus sp. | 65 | 8.5 | 14 | 17.86 | [ |
| Streptomyces thermocarboxydus ME168 | 50 | 8 | 0.28 | 16.54 | [ |
表3 各嗜热耐碱脂肪酶动力学参数比较
Table 3 Comparison of kinetic parameters of various thermo-alkaline lipases
| 脂肪酶来源 | 最适温度/℃ | 最适pH | Km/(mmol/L) | Vmax/(mmol/(L·min)) | 文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T. lipolytica(TlLipA) | 65 | 8 | 0.23 | 33.50 | 本文 |
| G. thermodenitrificans AV-5 | 65 | 9 | 0.44 | 0.556 | [ |
| T. Anoxybacillus flavithermus HBB 134 | 50 | 9 | 0.084 | 1.29 | [ |
| Staphylococcus aureus | 40 | 8 | 1.57 | 3.25 | [ |
| Thermotoga maritima | 70 | 7.5 | 8 | 2.50 | [ |
| Geobacillus sp. | 65 | 8.5 | 14 | 17.86 | [ |
| Streptomyces thermocarboxydus ME168 | 50 | 8 | 0.28 | 16.54 | [ |
| 脂肪酶来源 | 反应 温度/℃ | 反应 时间/h | 醇油比 | 原料油 | 生物柴油 收率/% | 文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T. lipolytica(TlLipA) | 55 | 48 | 4∶1 | 大豆油 | 91.75 | 本文 |
| G. thermodenitrificans AV-5 | 65 | 48 | 3∶1 | 废餐饮油 | 76 | [ |
| G.thermodenitrificans AV-5 | 65 | 48 | 3∶1 | 椰子油 | 45.5 | [ |
| Bacillus sp. | 55 | 40 | 3∶1 | Oedogonium sp. oil. | 76 | [ |
| Idiomarina sp. W33 | 60 | 60 | 4∶1 | 麻风树油 | 84 | [ |
表4 各嗜热耐碱脂肪酶制备生物柴油比较
Table 4 Comparison of preparation of biodiesel using various thermo-alkaline lipases
| 脂肪酶来源 | 反应 温度/℃ | 反应 时间/h | 醇油比 | 原料油 | 生物柴油 收率/% | 文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T. lipolytica(TlLipA) | 55 | 48 | 4∶1 | 大豆油 | 91.75 | 本文 |
| G. thermodenitrificans AV-5 | 65 | 48 | 3∶1 | 废餐饮油 | 76 | [ |
| G.thermodenitrificans AV-5 | 65 | 48 | 3∶1 | 椰子油 | 45.5 | [ |
| Bacillus sp. | 55 | 40 | 3∶1 | Oedogonium sp. oil. | 76 | [ |
| Idiomarina sp. W33 | 60 | 60 | 4∶1 | 麻风树油 | 84 | [ |
| 1 | Jaeger K E, Eggert T. Lipases for biotechnology[J]. Current Opinion Biotechnology, 2002, 13(4): 390-397. |
| 2 | Joseph B, Ramteke P W, Thomas G. Cold active microbial lipases: some hot issues and recent developments[J]. Biotechnology Advances, 2008, 26(5): 457-470. |
| 3 | Gupta R, Gupta N, Rathi P. Bacterial lipases: an overview of production, purification and biochemical properties[J]. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2004, 64(6): 763-781. |
| 4 | 武海棠, 许康力, 杨芳霞, 等. 萃取-酯交换耦合法制备生物柴油过程催化剂应用研究进展[J]. 林业工程学报, 2017, 2(2): 95-100. |
| Wu H T, Xu K L, Yang F X, et al. Recent development in application of catalyst to biodiesel production by coupling extraction and transesterification[J]. Journal of Forestry Engineering, 2017, 2(2): 95-100. | |
| 5 | 黄璜, 李宗军, 王远亮, 等. 各类微生物脂肪酶酶学性质及应用的研究进展[J]. 粮油食品科技, 2014, 22(1): 109-118. |
| Huang H, Li Z J, Wang Y L, et al. Progress in enzymatic properties of microbial lipase and applications[J]. Science and Technology of Cereals, Oils and Foods, 2014, 22(1): 109-118. | |
| 6 | 魏涛, 杨昆鹏, 郏未未, 等. Thermoanaerobacter sp.X514嗜热脂肪酶LipTX的异源表达与酶学性质研究[J]. 现代食品科技, 2016, 32(11): 91-97. |
| Wei T, Yang K P, Jia W W, et al. Heterologous expression and enzymatic properties of lipase LipTX from thermophilic bacterium Thermoanaerobacter sp. strain X514[J]. Modern Food Science and Technology, 2016, 32(11): 91-97. | |
| 7 | 刘弘忍, 王亮亮, 何琦阳, 等. 南极嗜冷杆菌脂肪酶的原核可溶性表达优化及酶学性能表征[J].林业工程学报, 2016, 1(5): 71-77. |
| Liu H R, Wang L L, He Q Y, et al. Optimized soluble expression and characterization of a cold-adapted lipase from psychrotrophic bacterium in Escherichia coli[J]. Journal of Forestry Engineering, 2016, 1(5): 71-77. | |
| 8 | 王柏婧, 冯雁, 王师钰, 等. 嗜热酶的特性及其应用[J]. 微生物学报, 2002, 2(2): 259-262. |
| Wang B J, Feng Y, Wang S Y, et al. Characteristics and application of thermophilic enzymes[J]. Acta Microbiologica Sinica, 2002, 2(2): 259-262. | |
| 9 | Bora L, Gohain D, Das R. Recent advances in production and biotechnological applications of thermostable and alkaline bacterial lipases[J]. Journal of Chemical Technology & Biotechnology, 2013, 88(11): 1959-1970. |
| 10 | 何祯祥, 王伟. 中国能源林业研发现状与发展策略[J]. 林业科技开发, 2006, (4): 8-11. |
| He Z X, Wang W. Energy forest in China: progress and prospects[J].China Forestry Science and Technology, 2006, (4): 8-11. | |
| 11 | Robles-Medina A, González-Moreno P A, Esteban-Cerdán L, et al. Biocatalysis: towards ever greener biodiesel production[J]. Biotechnology Advances, 2009, 27(4): 398-408. |
| 12 | Christopher L P, Zambare V P, Zambare A, et al. A thermo-alkaline lipase from a new thermophile Geobacillus thermodenitrificans AV-5 with potential application in biodiesel production[J]. Journal of Chemical Technology & Biotechnology, 2015, 90(11): 2007-2016. |
| 13 | Sivaramakrishnan R, Muthukumar K. Isolation of thermo-stable and solvent-tolerant Bacillus sp. lipase for the production of biodiesel[J]. Applied Biochemistry & Biotechnology, 2012, 166(4): 1095-1111. |
| 14 | Green M R, Sambrook J. Molecular Cloning: a Laboratory Manual[M]. Cold Spring Harbor, NY: Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, 2012. |
| 15 | 王月皎, 夏乾竣, 周佩, 等. 解糖热纤维菌木糖苷酶的分离纯化及其酶学性质[J]. 化工进展, 2017, 36(3): 1041-1046. |
| Wang Y J, Xia Q J, Zhou P, et al. Purification and characterization of a thermostable β-xylosidase from Caldicellulosiruptor saccharolyticus[J]. Chemical Industry and Engineering Progress, 2017, 36(3): 1041-1046. | |
| 16 | Bradford M M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding[J]. Analytical Biochemistry, 1976, 72(1): 248-254. |
| 17 | Bakir Z B, Metin K. Purification and characterization of an alkali-thermostable lipase from thermophilic Anoxybacillus flavithermus HBB 134[J]. Journal of Microbiology Biotechnology, 2016, 26(6): 1087-1097. |
| 18 | Snellman E A, Sullivan E R, Colwell R R. Purification and properties of the extracellular lipase, LipA, of Acinetobacter sp. RAG-1[J]. European Journal of Biochemistry, 2002, 269(23): 5771-5779. |
| 19 | Kumar S, Kikon K, Upadhyay A, et al. Production, purification, and characterization of lipase from thermophilic and alkaliphilic Bacillus coagulans BTS-3[J]. Protein Expression & Purification, 2005, 41(1): 38-44. |
| 20 | Sifour M, Saeed H M, Zaghloul T I, et al. Purification and properties of a lipase from thermophilic Geobacillus stearothermophilus strain-5[J]. International Journal of Biological Chemistry, 2010, 4(4): 203-212. |
| 21 | McPhillips K, Waters D M, Parlet C, et al. Purification and characterisation of a β-1,4-xylanase from Remersoniathermophila CBS 540.69 and its application in bread making[J]. Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 2014, 172(4): 1747-1762. |
| 22 | Zheng H. Isolation, purification, and characterization of a thermostable xylanase from a novel strain, Paenibacillus campinasensis G1-1[J]. Journal of Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2012, 22(7): 930-938. |
| 23 | 唐庆芸, 王永华. 表面活性剂对T1脂肪酶活力的影响[J]. 现代食品科技, 2017, 33(3): 185-189. |
| Tang Q Y, Wang Y H.Effect of surfactants on T1 lipase activity[J]. Modern Food Science and Technology, 2017, 33(3): 185-189. | |
| 24 | Fojan P, Jonson P H, Petersen M T N, et al. What distinguishes an esterase from a lipase: a novel structural approach[J]. Biochimie, 2000, 82(11): 1033-1041. |
| 25 | Gaur R, Gupta A, Khare S K. Purification and characterization of lipase from solvent tolerant Pseudomonas aeruginosa PseA[J]. Process Biochemistry, 2008, 43(10): 1040-1046. |
| 26 | Lesuisse E, Schanck K, Colson C. Purification and preliminary characterization of the extracellular lipase of Bacillus subtilis 168, an extremely basic pH-tolerant enzyme[J]. European Journal of Biochemistry, 2010, 216(1): 155-160. |
| 27 | Sarkar P, Yamasaki S, Basak S, et al. Purification and characterization of a new alkali-thermostable lipase from Staphylococcus aureus isolated from Arachis hypogaea rhizosphere[J]. Process Biochemistry, 2012, 47(5): 858-866. |
| 28 | Tian R, Chen H Y, Ni Z, et al. Expression and characterization of a novel thermo-alkalistable lipase from hyperthermophilic bacterium Thermotoga maritima[J]. Applied Biochemistry & Biotechnology, 2015, 176(5): 1482-1497. |
| 29 | Akshita M, Rakesh K, Reena G. Isolation of lipase producing thermophilic bacteria: optimization of production and reaction conditions for lipase from Geobacillus sp.[J]. Acta Microbiologica Et Immunologica Hungarica, 2012, 59(4): 435-50. |
| 30 | Aran H K, Prasertsan P, Zimmermann W, et al. Sugar ester synthesis by thermostable lipase from Streptomyces thermocarboxydus ME168[J]. Applied Biochemistry & Biotechnology, 2012, 166(8): 1969-1982. |
| 31 | Chen H C, Ju H Y, Wu T T, et al. Research article continuous production of lipase-catalyzed biodiesel in a packed-bed reactor: optimization and enzyme reuse study[J]. Journal of Biomedicine & Biotechnology, 2011, 6(1): 137-143. |
| 32 | Azócar L, Navia R, Beroiz L, et al. Enzymatic biodiesel production kinetics using co-solvent and an anhydrous medium: a strategy to improve lipase performance in a semi-continuous reactor[J]. New Biotechnology, 2014, 31(5): 422-429. |
| 33 | Du W, Xu Y, Liu D, et al. Comparative study on lipase-catalyzed transformation of soybean oil for biodiesel production with different acyl acceptors[J]. Journal of Molecular Catalysis B Enzymatic, 2004, 30(3/4): 125-129. |
| 34 | Zheng Y, Quan J, Ning X, et al. Lipase-catalyzed transesterification of soybean oil for biodiesel production in tert-amyl alcohol[J]. World Journal of Microbiology & Biotechnology, 2009, 25(1): 41-46. |
| 35 | 李相, 刘涛, 杨江科. 响应面法优化洋葱伯克霍尔德菌固定化脂肪酶催化合成生物柴油工艺[J]. 北京化工大学学报(自然科学版), 2009, 36(5): 80-85. |
| Li X, Liu T, Yang J K. Optimization of the production of biodiesel catalyzed by immobilized lipase from Burkholderia cepacia using a response surface method[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Chemical Technology (Natural Science), 2009, 36(5): 80-85. | |
| 36 | Li X, Qian P, Wu S G, et al. Characterization of an organic solvent-tolerant lipase from Idiomarina sp. W33 and its application for biodiesel production using Jatropha oil[J]. Extremophiles, 2014, 18(1): 171-178. |
| [1] | 程业品, 胡达清, 徐奕莎, 刘华彦, 卢晗锋, 崔国凯. 离子液体基低共熔溶剂在转化CO2中的应用[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(9): 3640-3653. |
| [2] | 涂玉明, 邵高燕, 陈健杰, 刘凤, 田世超, 周智勇, 任钟旗. 钙基催化剂的设计合成及应用研究进展[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(7): 2717-2734. |
| [3] | 陈雅鑫, 袁航, 刘冠章, 毛磊, 杨纯, 张瑞芳, 张光亚. 蛋白质纳米笼介导的酶自固定化研究进展[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(7): 2773-2782. |
| [4] | 汤晓玲, 王嘉瑞, 朱玄烨, 郑仁朝. 基于Pickering乳液的卤醇脱卤酶催化合成手性环氧氯丙烷[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(7): 2926-2934. |
| [5] | 毛磊, 刘冠章, 袁航, 张光亚. 可捕集CO2的纳米碳酸酐酶粒子的高效制备及性能研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(6): 2589-2598. |
| [6] | 胡阳, 孙彦. 酶分子的自驱动及其介导的微纳马达[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(1): 116-132. |
| [7] | 谭卓涛, 齐思雨, 许梦蛟, 戴杰, 朱晨杰, 应汉杰. 辅酶自循环的氧化还原级联体系在生物催化过程中的应用:机遇与挑战[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(1): 45-59. |
| [8] | 刘昕, 戈钧, 李春. 光驱动微生物杂合系统提高生物制造水平[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(1): 330-341. |
| [9] | 安绍杰, 许洪峰, 李思, 许远航, 李佳锡. 利用分子机器的组装与分解构建pH敏感性谷胱甘肽过氧化物人工酶[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(8): 3669-3678. |
| [10] | 张劢, 田瑶, 郭之旗, 王叶, 窦广进, 宋浩. 光催化-生物杂合系统设计优化用于燃料和化学品绿色合成[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(7): 2774-2789. |
| [11] | 张军, 胡升, 顾菁, 袁浩然, 陈勇. 甲醇体系电镀污泥衍生磁性多金属材料催化糠醛加氢转化[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(7): 2996-3006. |
| [12] | 孙甲琛, 孙文涛, 孙慧, 吕波, 李春. 甘草黄酮合酶Ⅱ催化甘草素特异性合成7,4′-二羟基黄酮[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(7): 3202-3211. |
| [13] | 张红锐, 张田, 隆曦孜, 李先宁. 光催化与微生物燃料电池耦合对Cu-EDTA的降解特性[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(5): 2149-2157. |
| [14] | 张家仁, 刘海超. 大豆油与甲醇酯交换反应体系的相平衡研究[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(5): 1920-1929. |
| [15] | 王淋, 付乾, 肖帅, 李卓, 李俊, 张亮, 朱恂, 廖强. 高效可见光响应微生物/光电化学耦合人工光合作用系统[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(2): 887-893. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备 11010102001995号
京公网安备 11010102001995号