化工学报 ›› 2022, Vol. 73 ›› Issue (7): 3212-3221.DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20220084
收稿日期:2022-01-14
修回日期:2022-03-27
出版日期:2022-07-05
发布日期:2022-08-01
通讯作者:
孟祥海
作者简介:欧阳萍(1992—),女,博士研究生,基金资助:
Ping OUYANG( ),Rui ZHANG,Jian ZHOU,Haiyan LIU,Zhichang LIU,Chunming XU,Xianghai MENG(
),Rui ZHANG,Jian ZHOU,Haiyan LIU,Zhichang LIU,Chunming XU,Xianghai MENG( )
)
Received:2022-01-14
Revised:2022-03-27
Online:2022-07-05
Published:2022-08-01
Contact:
Xianghai MENG
摘要:
铜铝双金属复合离子液体是新型碳四烷基化技术所用的绿色催化剂,电化学处理是回收工业应用过程外排复合离子液体中金属铜的有效途径之一,为此需要深入研究其电化学行为和电沉积铜机理。循环伏安研究发现,铜铝双金属复合离子液体在Pt盘电极、W盘电极和玻碳电极上的还原过程均包括铜的欠电势沉积、Cu(Ⅰ)的还原和铜的超电势沉积,氧化过程均包括Cu→Cu(Ⅰ)、Cu(Ⅰ)→Cu(Ⅱ)。计时安培研究表明,铜的成核方式为三维瞬时成核。长周期实验结果显示Cu(Ⅰ)的浓度随着时间下降的趋势变缓,表明电沉积铜速率逐步下降。电沉积电势对沉积产物的形貌影响较大,-2.60 V下的产物形貌更平整致密。XRD结果表明在-1.20~-2.60 V电势下阴极电沉积只生成金属铜。
中图分类号:
欧阳萍, 张睿, 周剑, 刘海燕, 刘植昌, 徐春明, 孟祥海. 铜铝双金属复合离子液体的电化学行为及电沉积铜机理[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(7): 3212-3221.
Ping OUYANG, Rui ZHANG, Jian ZHOU, Haiyan LIU, Zhichang LIU, Chunming XU, Xianghai MENG. Electrochemical behavior and copper electrodeposition mechanism of Cu-Al bimetallic composite ionic liquid[J]. CIESC Journal, 2022, 73(7): 3212-3221.
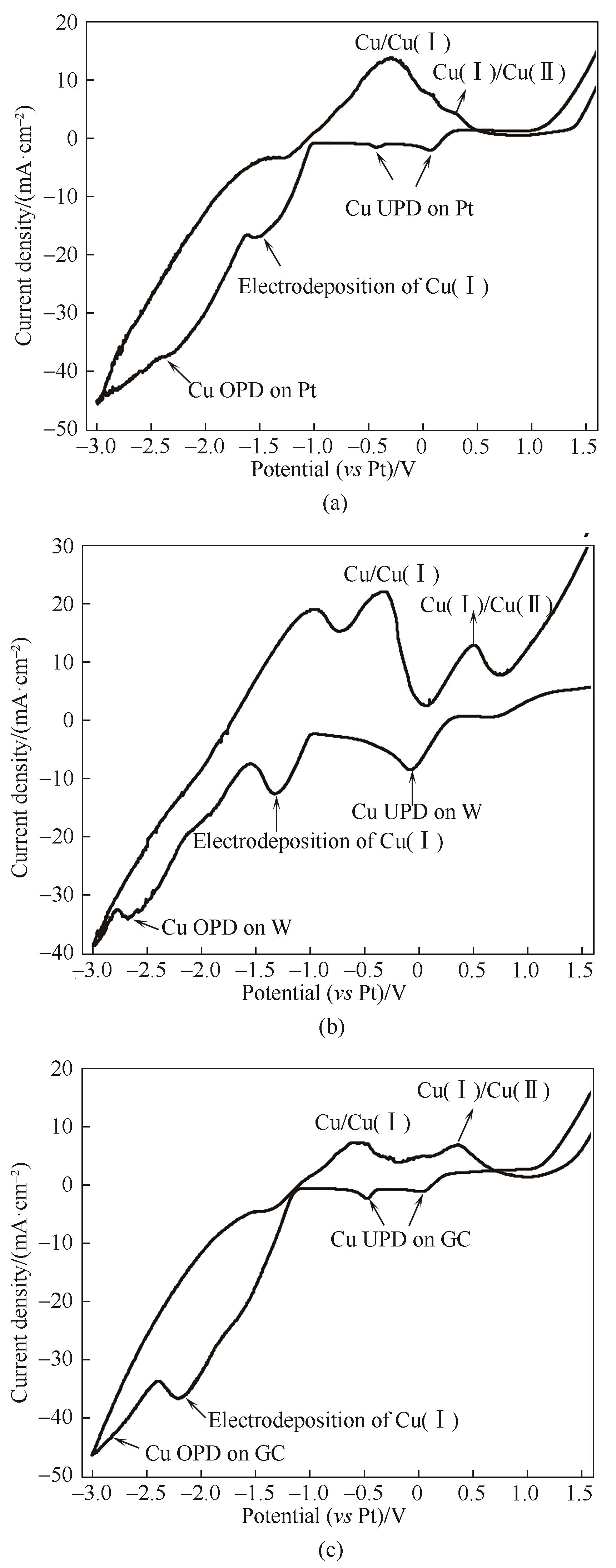
图1 铜铝双金属复合离子液体在Pt盘电极(a)、W盘电极(b)、玻碳电极(c)的循环伏安曲线(扫描速率为100 mV?s-1)
Fig.1 Cyclic voltammograms of Cu-Al bimetallic composite ionic liquid on Pt electrode (a), W electrode (b) and glass carbon electrode (c) with the scanning rate of 100 mV?s-1
| Electrode | Cu UPD/V | Electrodeposition of Cu(Ⅰ)/V | Cu→ Cu(Ⅰ)/V | Cu(Ⅰ)→Cu(Ⅱ)/V |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pt | 0.07,-0.43 | -1.55 | -0.30 | 0.29 |
| W | -0.08 | -1.32 | -0.31 | 0.54 |
| GC | 0.04,-0.47 | -2.21 | -0.52 | 0.36 |
表1 铜铝双金属复合离子液体在不同工作电极上CV曲线峰电位
Table 1 Cyclic voltametric data of Cu-Al bimetallic composite ionic liquid on different working electrodes
| Electrode | Cu UPD/V | Electrodeposition of Cu(Ⅰ)/V | Cu→ Cu(Ⅰ)/V | Cu(Ⅰ)→Cu(Ⅱ)/V |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pt | 0.07,-0.43 | -1.55 | -0.30 | 0.29 |
| W | -0.08 | -1.32 | -0.31 | 0.54 |
| GC | 0.04,-0.47 | -2.21 | -0.52 | 0.36 |
| v/(mV?s-1) | E | E | Ia1/(mA?cm-2) | E | E | Ia2/(mA?cm-2) | ∣Ic2/Ia2∣ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 100 | 0.50 | 0.33 | 12.81 | -0.31 | -0.54 | 21.98 | 0.57 |
| 200 | 0.53 | 0.39 | 14.95 | -0.23 | -0.49 | 26.50 | 0.58 |
| 300 | 0.58 | 0.44 | 17.51 | -0.12 | -0.42 | 31.68 | 0.64 |
| 400 | 0.67 | 0.52 | 19.52 | -0.09 | -0.37 | 34.68 | 0.65 |
| 500 | 0.70 | 0.54 | 21.54 | -0.02 | -0.35 | 38.25 | 0.66 |
| 600 | 0.80 | 0.62 | 23.91 | 0.05 | -0.32 | 41.72 | 0.69 |
| average | — | — | — | — | — | — | 0.63 |
表2 铜铝双金属复合离子液体在W盘工作电极上不同扫描速率下的CV曲线的氧化峰数据
Table 2 Data of oxidation peaks of CV curves of Cu-Al bimetallic composite ionic liquid on W electrode under different scanning rates
| v/(mV?s-1) | E | E | Ia1/(mA?cm-2) | E | E | Ia2/(mA?cm-2) | ∣Ic2/Ia2∣ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 100 | 0.50 | 0.33 | 12.81 | -0.31 | -0.54 | 21.98 | 0.57 |
| 200 | 0.53 | 0.39 | 14.95 | -0.23 | -0.49 | 26.50 | 0.58 |
| 300 | 0.58 | 0.44 | 17.51 | -0.12 | -0.42 | 31.68 | 0.64 |
| 400 | 0.67 | 0.52 | 19.52 | -0.09 | -0.37 | 34.68 | 0.65 |
| 500 | 0.70 | 0.54 | 21.54 | -0.02 | -0.35 | 38.25 | 0.66 |
| 600 | 0.80 | 0.62 | 23.91 | 0.05 | -0.32 | 41.72 | 0.69 |
| average | — | — | — | — | — | — | 0.63 |
| v/(mV?s-1) | E | E | Ic1/(mA?cm-2) | E | E | Ic2/(mA?cm-2) | αc2 | D0/(10-6cm2?s-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 100 | -0.08 | 0.11 | -8.53 | -1.32 | -1.17 | -12.44 | 0.31 | 2.41 |
| 200 | -0.17 | 0.05 | -13.32 | -1.37 | -1.24 | -15.44 | 0.37 | 1.86 |
| 300 | -0.33 | -0.08 | -19.21 | -1.44 | -1.29 | -20.17 | 0.33 | 2.11 |
| 400 | -0.41 | -0.12 | -21.74 | -1.50 | -1.34 | -22.42 | 0.30 | 1.96 |
| 500 | -0.43 | -0.14 | -24.85 | -1.55 | -1.38 | -25.41 | 0.28 | 2.01 |
| 600 | -0.47 | -0.17 | -27.20 | -1.63 | -1.42 | -28.60 | 0.23 | 2.12 |
| average | — | — | — | — | — | — | 0.30 | 2.08 |
表3 铜铝双金属复合离子液体在W盘工作电极上不同扫描速率下的CV曲线的还原峰数据
Table 3 Data of reduction peaks of CV curves of Cu-Al bimetallic composite ionic liquid on W electrode under different scanning rates
| v/(mV?s-1) | E | E | Ic1/(mA?cm-2) | E | E | Ic2/(mA?cm-2) | αc2 | D0/(10-6cm2?s-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 100 | -0.08 | 0.11 | -8.53 | -1.32 | -1.17 | -12.44 | 0.31 | 2.41 |
| 200 | -0.17 | 0.05 | -13.32 | -1.37 | -1.24 | -15.44 | 0.37 | 1.86 |
| 300 | -0.33 | -0.08 | -19.21 | -1.44 | -1.29 | -20.17 | 0.33 | 2.11 |
| 400 | -0.41 | -0.12 | -21.74 | -1.50 | -1.34 | -22.42 | 0.30 | 1.96 |
| 500 | -0.43 | -0.14 | -24.85 | -1.55 | -1.38 | -25.41 | 0.28 | 2.01 |
| 600 | -0.47 | -0.17 | -27.20 | -1.63 | -1.42 | -28.60 | 0.23 | 2.12 |
| average | — | — | — | — | — | — | 0.30 | 2.08 |
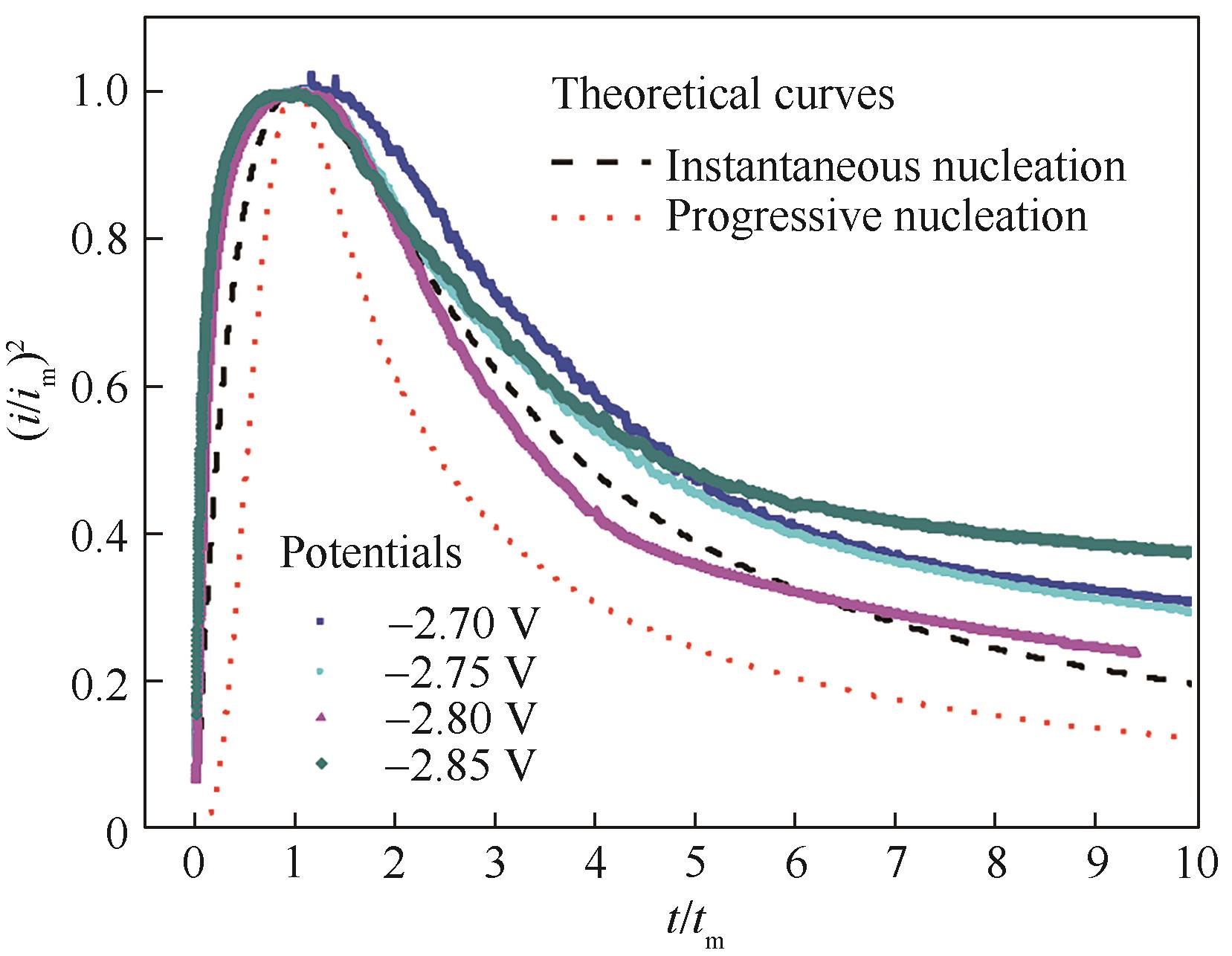
图5 铜铝双金属复合离子液体不同电压下电流-时间暂态无量纲曲线实验与理论对比
Fig.5 Comparison of the dimensionless experimental current-time transient of Cu-Al bimetallic composite ionic liquid with the theoretical curves for instantaneous nucleation and progressive nucleation
| Potential/V | Time/h | Charge/C |
|---|---|---|
| -2.60 | 0.5 | 40.1 |
| -2.60 | 1.0 | 39.1 |
| -2.60 | 1.5 | 37.7 |
| -2.60 | 2.0 | 38.4 |
| -2.60 | 2.5 | 37.0 |
| -2.60 | 3.0 | 37.4 |
| -2.60 | 3.5 | 34.1 |
| -2.60 | 4.0 | 33.9 |
| -2.60 | 4.5 | 34.1 |
| -2.60 | 5.0 | 33.7 |
| -2.60 | 5.5 | 33.9 |
| -2.60 | 6.0 | 32.7 |
| -2.60 | 6.5 | 32.0 |
| -2.60 | 7.0 | 32.5 |
| -2.60 | 7.5 | 32.4 |
| -2.60 | 8.0 | 31.7 |
表4 铜铝双金属复合离子液体长周期电沉积过程不同时间通过的电量
Table 4 Charge for different time during long-term electrodeposition of Cu-Al bimetallic composite ionic liquid
| Potential/V | Time/h | Charge/C |
|---|---|---|
| -2.60 | 0.5 | 40.1 |
| -2.60 | 1.0 | 39.1 |
| -2.60 | 1.5 | 37.7 |
| -2.60 | 2.0 | 38.4 |
| -2.60 | 2.5 | 37.0 |
| -2.60 | 3.0 | 37.4 |
| -2.60 | 3.5 | 34.1 |
| -2.60 | 4.0 | 33.9 |
| -2.60 | 4.5 | 34.1 |
| -2.60 | 5.0 | 33.7 |
| -2.60 | 5.5 | 33.9 |
| -2.60 | 6.0 | 32.7 |
| -2.60 | 6.5 | 32.0 |
| -2.60 | 7.0 | 32.5 |
| -2.60 | 7.5 | 32.4 |
| -2.60 | 8.0 | 31.7 |
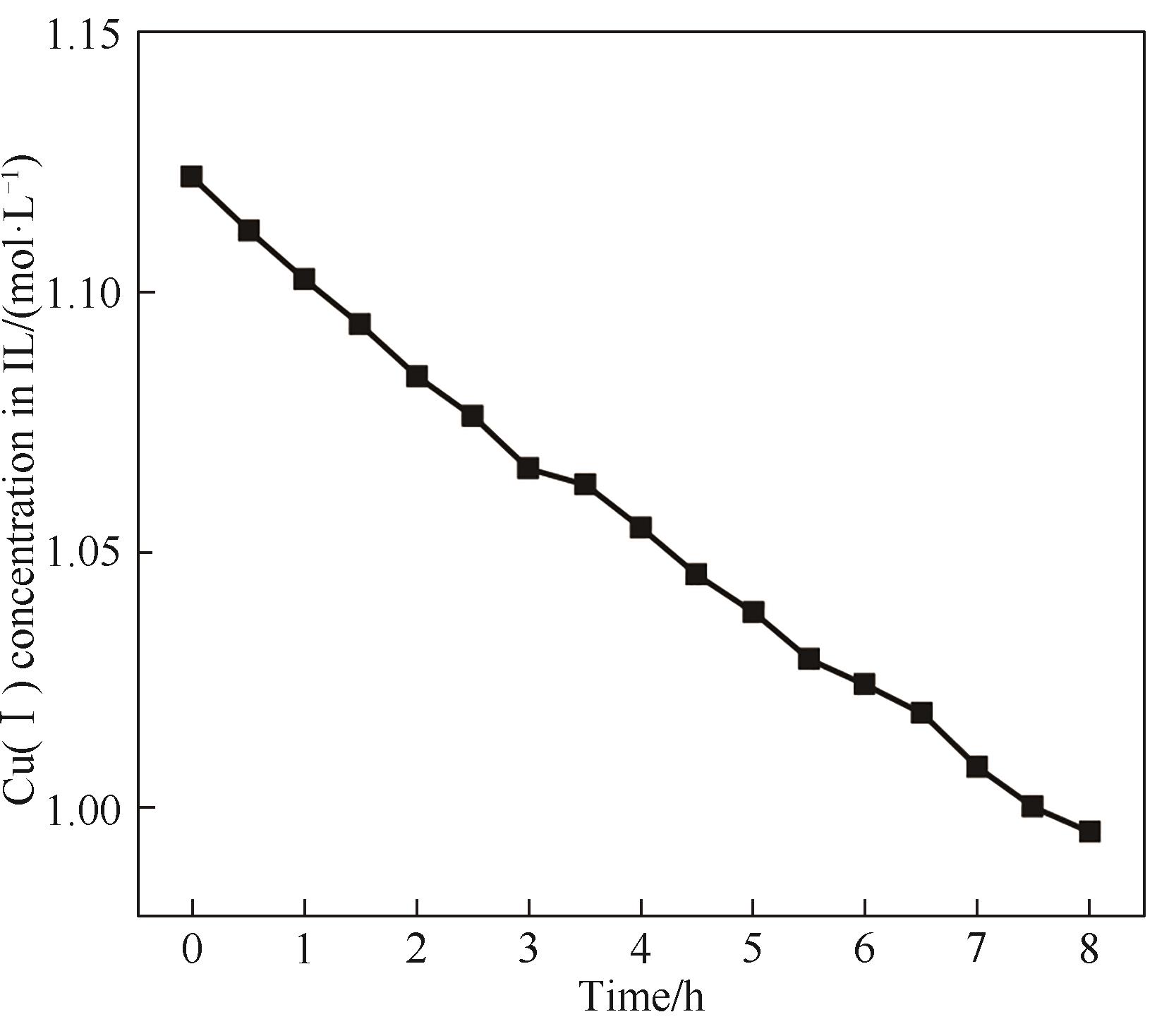
图6 铜铝双金属复合离子液体8 h长周期实验过程Cu(Ⅰ)浓度随时间的变化
Fig.6 Trend of Cu(Ⅰ) concentration for Cu-Al bimetallic composite ionic liquid during long-term electrodeposition
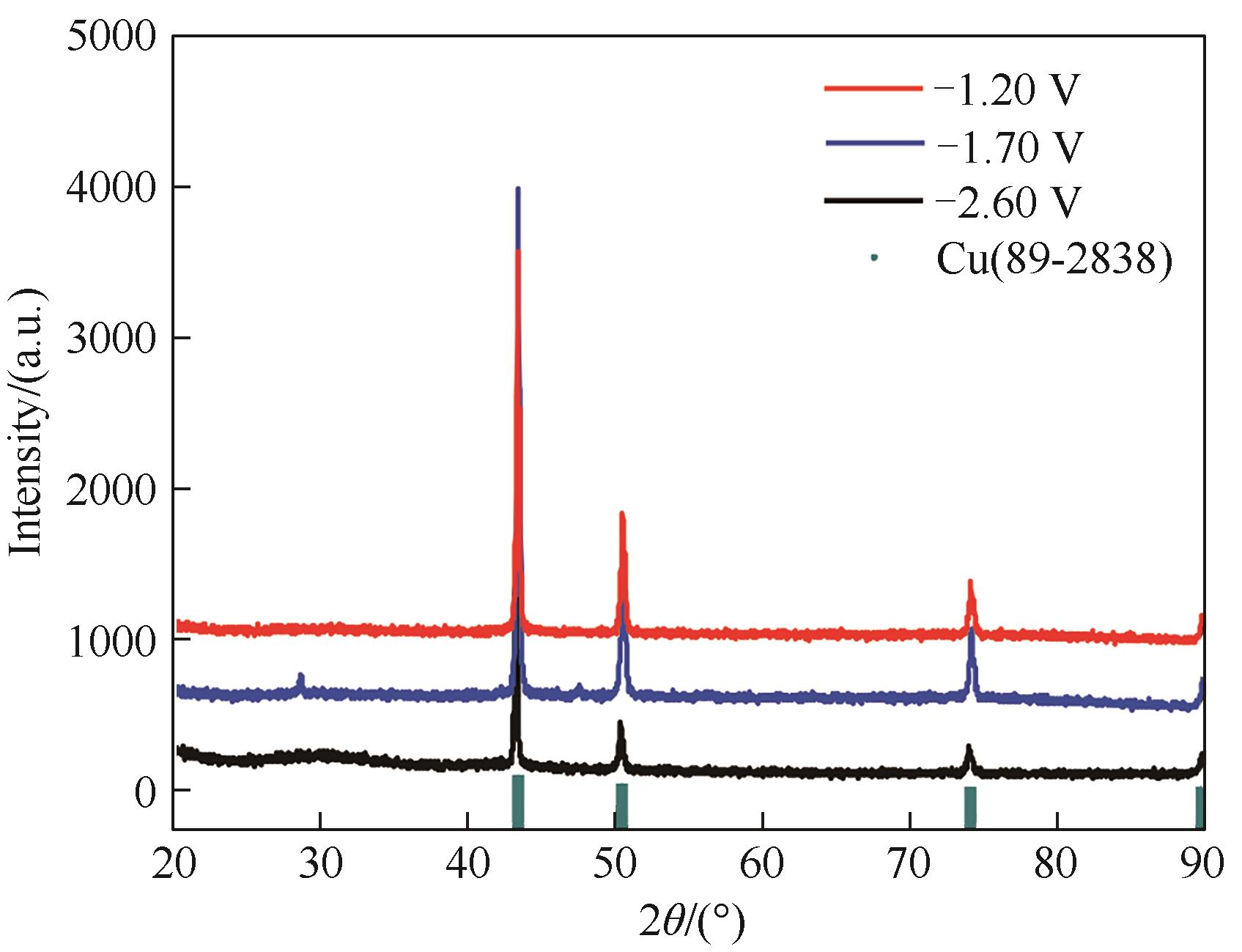
图9 铜铝双金属复合离子液体在不同电势(-1.20、-1.70、-2.60 V, vs Pt)下的电沉积产物的XRD谱图
Fig.9 XRD patterns of cathodic electrodeposits from Cu-Al bimetallic composite ionic liquid on the silver electrode at the potentials of -1.20, -1.70 and -2.60 V (vs. Pt)
| 1 | Andricacos P C, Uzoh C, Dukovic J O, et al. Damascene copper electroplating for chip interconnections[J]. IBM Journal of Research and Development, 1998, 42(5): 567-574. |
| 2 | Andricacos P C. Copper on-chip interconnections: a breakthrough in electrodeposition to make better chips[J]. The Electrochemical Society Interface, 1999, 8(1): 32-37. |
| 3 | 王鸿建. 电镀工艺学[M]. 哈尔滨:哈尔滨工业大学出版社, 1995: 96-110. |
| Wang H J. Electroplating Technology[M]. Harbin: Harbin Institute of Technology Press, 1995: 96-110. | |
| 4 | 陈范才. 现代电镀技术[M]. 北京:中国纺织出版社, 2009: 155-164. |
| Chen F C. Modern Electroplating Technology[M]. Beijing: China Textile & Apparel Press, 2009: 155-164. | |
| 5 | 余德超, 谈定生. 电镀铜技术在电子材料中的应用[J]. 电镀与涂饰, 2007, 26(2): 43-47. |
| Yu D C, Tan D S. Applications of copper plating technology to electronic materials[J]. Electroplating & Finishing, 2007, 26(2): 43-47. | |
| 6 | Welton T. Room-temperature ionic liquids: solvents for synthesis and catalysis[J]. Chemical Reviews, 1999, 99(8): 2071-2084. |
| 7 | Ispas A, Bund A. Electrodeposition in ionic liquids[J]. The Electrochemical Society Interface, 2014, 23(1): 47-51. |
| 8 | Nanjundiah C, Osteryoung R A. Electrochemical studies of Cu(Ⅰ) and Cu(Ⅱ) in an aluminum chloride‐N‐(n‐butyl)pyridinium chloride ionic liquid[J]. Journal of the Electrochemical Society, 1983, 130(6): 1312-1318. |
| 9 | Hussey C L, King L A, Carpio R A. The electrochemistry of copper in a room temperature acidic chloroaluminate melt[J]. Journal of the Electrochemical Society, 1979, 126(6): 1029-1034. |
| 10 | Chen P Y, Sun I W. Electrochemical study of copper in a basic 1-ethyl-3-methylimidazolium tetrafluoroborate room temperature molten salt[J]. Electrochimica Acta, 1999, 45(3): 441-450. |
| 11 | Shakeela K, Dithya A S, Rao C J, et al. Electrochemical behaviour of Cu(Ⅰ)/Cu(Ⅱ) redox couple in 1-hexyl-3-methylimidazolium chloride ionic liquid[J]. Journal of Chemical Sciences, 2015, 127(1): 133-140. |
| 12 | Kitada A, Yanase K, Ichii T, et al. Potentiostatic Cu-Zn alloying for polymer metallization using medium-low temperature ionic liquid baths[J]. Journal of The Electrochemical Society, 2013, 160(9): D417-D421. |
| 13 | 刘海, 徐存英, 唐杰, 等. ChCl-urea-ZnO-Cu2O低共熔溶剂电镀铜锌合金[J]. 化工学报, 2018, 69(10): 4402-4408. |
| Liu H, Xu C Y, Tang J, et al. Electroplating of Zn-Cu alloys in ChCl-urea-ZnO-Cu2O deep eutectic solvents[J]. CIESC Journal, 2018, 69(10): 4402-4408. | |
| 14 | Sun J, Ming T Y, Qian H X, et al. Electrochemical behaviors and electrodeposition of single-phase Cu-Sn alloy coating in[BMIM]Cl[J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2019, 297: 87-93. |
| 15 | Chen P Y, Deng M J, Zhuang D X. Electrochemical codeposition of copper and manganese from room-temperature n-butyl-n-methylpyrrolidinium bis(trifluoromethylsulfonyl)imide ionic liquid[J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2009, 54(27): 6935-6940. |
| 16 | Wang S H, Guo X, Yang H Y W, et al. Electrodeposition mechanism and characterization of Ni-Cu alloy coatings from a eutectic-based ionic liquid[J]. Applied Surface Science, 2014, 288: 530-536. |
| 17 | Tierney B J, Pitner W R, Mitchell J A, et al. Electrodeposition of copper and copper‐aluminum alloys from a room‐temperature chloroaluminate molten salt[J]. Journal of the Electrochemical Society, 1998, 145(9): 3110-3116. |
| 18 | Assaker I B, Dhahbi M. Electrochemical study and electrodeposition of copper in the hydrophobic tri-n-octylmethylammonium chloride ionic liquid media[J]. Journal of Molecular Liquids, 2011, 161(1): 13-18. |
| 19 | 孙杰, 明庭云, 钱慧璇, 等. BMIMPF6离子液体中铜沉积的电化学行为[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2018, 39(7): 1497-1502. |
| Sun J, Ming T Y, Qian H X, et al. Electrochemical behavior of copper electrodeposition in BMIMPF6 ionic liquid[J]. Chemical Journal of Chinese Universities, 2018, 39(7): 1497-1502. | |
| 20 | Kore R, Berton P, Kelley S P, et al. Group IIIA halometallate ionic liquids: speciation and applications in catalysis[J]. ACS Catalysis, 2017, 7(10): 7014-7028. |
| 21 | Brown L C, Hogg J M, Swadźba-kwaśny M. Lewis acidic ionic liquids[J]. Topics in Current Chemistry (Cham), 2017, 375(5): 78. |
| 22 | 孟祥海, 张睿, 刘海燕, 等. 复合离子液体碳四烷基化技术开发与应用[J]. 中国科学: 化学, 2018, 48(4): 387-396. |
| Meng X H, Zhang R, Liu H Y, et al. Development and application of composite ionic liquid catalyzed isobutane alkylation technology[J]. Scientia Sinica(Chimica), 2018, 48(4): 387-396. | |
| 23 | 刘植昌, 张睿, 刘鹰, 等. 复合离子液体催化碳四烷基化反应性的研究[J]. 燃料化学学报, 2006, 34(3): 328-331. |
| Liu Z C, Zhang R, Liu Y, et al. Study on isobutane alkylation catalyzed by composite ionic liquid[J]. Journal of Fuel Chemistry and Technology, 2006, 34(3): 328-331. | |
| 24 | 韩晔华, 欧阳萍, 张艳芬, 等. 基于实时直接分析质谱技术的氯铝酸及其复合离子液体分析[J]. 中国科学: 化学, 2020, 50(6): 720-728. |
| Han Y H, Ouyang P, Zhang Y F, et al. Comprehensive analysis of chloroaluminate and composite ionic liquids using direct analysis in real time mass spectrometry[J]. Scientia Sinica(Chimica), 2020, 50(6): 720-728. | |
| 25 | Saravanan G, Mohan S. Nucleation of copper on mild steel in copper chloride (CuCl2·2H2O)-1-ethyl-3-methylimidazolium chloride [EMIM]Cl-ethylene glycol (EG) ionic liquid[J]. New Journal of Chemistry, 2013, 37(8): 2564-2567. |
| 26 | Wang S X, Pei Q F, Xu C Y, et al. Effects of cuprous ion on electrodeposition of aluminum from AlCl3-BMIC ionic liquid[J]. Journal of The Electrochemical Society, 2021, 168(1): 012502 |
| 27 | Chen P Y, Sun I W. Electrochemistry of copper in 1-methyl-3-ethylimidazolium tetrafluoroborate room temperature molten salts[J]. ECS Proceedings Volumes, 1998(1): 55-65. |
| 28 | Zhang Y N, Zhang R, Wu L, et al. Solubilities, structures, and speciations of bimetallic composite ionic liquids: X-ray absorption fine structure and density functional theory calculations[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2021, 60(20): 7535-7544. |
| 29 | Li Q B, Jiang J Y, Li G F, et al. The electrochemical stability of ionic liquids and deep eutectic solvents[J]. Science China Chemistry, 2016, 59(5): 571-577. |
| 30 | Endres F, Schweizer A. The electrodeposition of copper on Au(111) and on HOPG from the 66/34 mol% aluminium chloride/1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium chloride room temperature molten salt: an EC-STM study[J]. Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics, 2000, 2(23): 5455-5462. |
| 31 | Suneesh P V, Satheesh Babu T G, Ramachandran T. Electrodeposition of aluminium and aluminium-copper alloys from a room temperature ionic liquid electrolyte containing aluminium chloride and triethylamine hydrochloride[J]. International Journal of Minerals, Metallurgy, and Materials, 2013, 20(9): 909-916. |
| 32 | Sebastián P, Vallés E, Gómez E. Copper electrodeposition in a deep eutectic solvent. First stages analysis considering Cu(Ⅰ) stabilization in chloride media[J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2014, 123: 285-295. |
| 33 | Abbott A P, El Ttaib K, Frisch G, et al. Electrodeposition of copper composites from deep eutectic solvents based on choline chloride[J]. Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics, 2009, 11(21): 4269-4277. |
| 34 | Scharifker B, Hills G. Theoretical and experimental studies of multiple nucleation[J]. Electrochimica Acta, 1983, 28(7): 879-889. |
| 35 | Gunawardena G, Hills G, Montenegro I, et al. Electrochemical nucleation(I): General considerations[J]. Journal of Electroanalytical Chemistry and Interfacial Electrochemistry, 1982, 138(2): 225-239. |
| 36 | 陈国华, 王光信. 电化学方法应用[M]. 北京:化学工业出版社, 2003: 2-5. |
| Chen G H, Wang G X. Application of Electrochemical Methods[M]. Beijing:Chemical Industry Press, 2003: 2-5. |
| [1] | 胡超, 董玉明, 张伟, 张红玲, 周鹏, 徐红彬. 浓硫酸活化五氧化二钒制备高浓度全钒液流电池正极电解液[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(S1): 338-345. |
| [2] | 宋瑞涛, 王派, 王云鹏, 李敏霞, 党超镔, 陈振国, 童欢, 周佳琦. 二氧化碳直接蒸发冰场排管内流动沸腾换热数值模拟分析[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(S1): 96-103. |
| [3] | 张义飞, 刘舫辰, 张双星, 杜文静. 超临界二氧化碳用印刷电路板式换热器性能分析[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(S1): 183-190. |
| [4] | 范孝雄, 郝丽芳, 范垂钢, 李松庚. LaMnO3/生物炭催化剂低温NH3-SCR催化脱硝性能研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(9): 3821-3830. |
| [5] | 杨百玉, 寇悦, 姜峻韬, 詹亚力, 王庆宏, 陈春茂. 炼化碱渣湿式氧化预处理过程DOM的化学转化特征[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(9): 3912-3920. |
| [6] | 米泽豪, 花儿. 基于DFT和COSMO-RS理论研究多元胺型离子液体吸收SO2气体[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(9): 3681-3696. |
| [7] | 陈哲文, 魏俊杰, 张玉明. 超临界水煤气化耦合SOFC发电系统集成及其能量转化机制[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(9): 3888-3902. |
| [8] | 杨学金, 杨金涛, 宁平, 王访, 宋晓双, 贾丽娟, 冯嘉予. 剧毒气体PH3的干法净化技术研究进展[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(9): 3742-3755. |
| [9] | 陈美思, 陈威达, 李鑫垚, 李尚予, 吴有庭, 张锋, 张志炳. 硅基离子液体微颗粒强化气体捕集与转化的研究进展[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(9): 3628-3639. |
| [10] | 程业品, 胡达清, 徐奕莎, 刘华彦, 卢晗锋, 崔国凯. 离子液体基低共熔溶剂在转化CO2中的应用[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(9): 3640-3653. |
| [11] | 李锦潼, 邱顺, 孙文寿. 煤浆法烟气脱硫中草酸和紫外线强化煤砷浸出过程[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(8): 3522-3532. |
| [12] | 杨菲菲, 赵世熙, 周维, 倪中海. Sn掺杂的In2O3催化CO2选择性加氢制甲醇[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(8): 3366-3374. |
| [13] | 洪瑞, 袁宝强, 杜文静. 垂直上升管内超临界二氧化碳传热恶化机理分析[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(8): 3309-3319. |
| [14] | 李凯旋, 谭伟, 张曼玉, 徐志豪, 王旭裕, 纪红兵. 富含零价钴活性位点的钴氮碳/活性炭设计及甲醛催化氧化应用研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(8): 3342-3352. |
| [15] | 胡亚丽, 胡军勇, 马素霞, 孙禹坤, 谭学诣, 黄佳欣, 杨奉源. 逆电渗析热机新型工质开发及电化学特性研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(8): 3513-3521. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备 11010102001995号
京公网安备 11010102001995号