化工学报 ›› 2022, Vol. 73 ›› Issue (8): 3307-3325.DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20220583
收稿日期:2022-04-24
修回日期:2022-08-04
出版日期:2022-08-05
发布日期:2022-09-06
通讯作者:
陈鹏忠,彭孝军
作者简介:陈昊(1996—),男,博士研究生,chenhao2019@mail.dlut.edu.com
基金资助:
Hao CHEN1( ), Pengzhong CHEN1,2(
), Pengzhong CHEN1,2( ), Xiaojun PENG1,3(
), Xiaojun PENG1,3( )
)
Received:2022-04-24
Revised:2022-08-04
Online:2022-08-05
Published:2022-09-06
Contact:
Pengzhong CHEN, Xiaojun PENG
摘要:
由于具有光源波长短(13.5 nm)、图案化分辨率高等优点,极紫外(extreme ultraviolet, EUV)光刻技术被认为是突破5 nm甚至是3 nm半导体芯片制程节点的关键技术,与之相对应的EUV光刻胶研发广受关注。但传统的基于聚合物体系的化学放大光刻胶(chemical amplified resist, CAR)因尺寸过大、对EUV吸收低,限制了其在EUV光刻技术的应用进程。部分含有d轨道电子的金属元素具有高的EUV吸收截面,在光刻胶分子中引入这些金属元素可以有效提高对EUV的灵敏度。通过分子设计制备尺寸小、EUV吸收高的金属基光刻胶材料是解决EUV光刻胶服役性能问题的有效途径,已得到了广泛的研究。本文按金属氧簇(MOCs)、金属氧化物纳米粒子(NP)、金属-有机小分子(MORE)进行分类,对目前国内外的EUV光刻胶研究进展进行总结,并对EUV光刻胶未来所面临的机遇和挑战进行了展望。
中图分类号:
陈昊, 陈鹏忠, 彭孝军. 金属基极紫外光刻胶[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(8): 3307-3325.
Hao CHEN, Pengzhong CHEN, Xiaojun PENG. Metal-based extreme ultraviolet photoresist[J]. CIESC Journal, 2022, 73(8): 3307-3325.
| Environment | D0 × 1016 / (ph/cm2) | D100 × 1016 / (ph/cm2) | D0 /s | D100 /s | γ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| UHV | 1.4 | 2.7 | 550 | 1100 | 3.3 |
| 1.2 | 2.2 | 470 | 870 | 3.8 | |
| 2.1 | 4.0 | 850 | 1600 | 3.7 | |
| PMeOH = 1 mbar | 2.5 | 4.1 | 980 | 1700 | 4.4 |
| 2.0 | 3.4 | 810 | 1400 | 4.4 |
表1 五种环境下Keggin-NaSn13光刻胶的D0和D100值
Table1 D0 and D100 values of Keggin-NaSn13 photoresist in five environments
| Environment | D0 × 1016 / (ph/cm2) | D100 × 1016 / (ph/cm2) | D0 /s | D100 /s | γ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| UHV | 1.4 | 2.7 | 550 | 1100 | 3.3 |
| 1.2 | 2.2 | 470 | 870 | 3.8 | |
| 2.1 | 4.0 | 850 | 1600 | 3.7 | |
| PMeOH = 1 mbar | 2.5 | 4.1 | 980 | 1700 | 4.4 |
| 2.0 | 3.4 | 810 | 1400 | 4.4 |
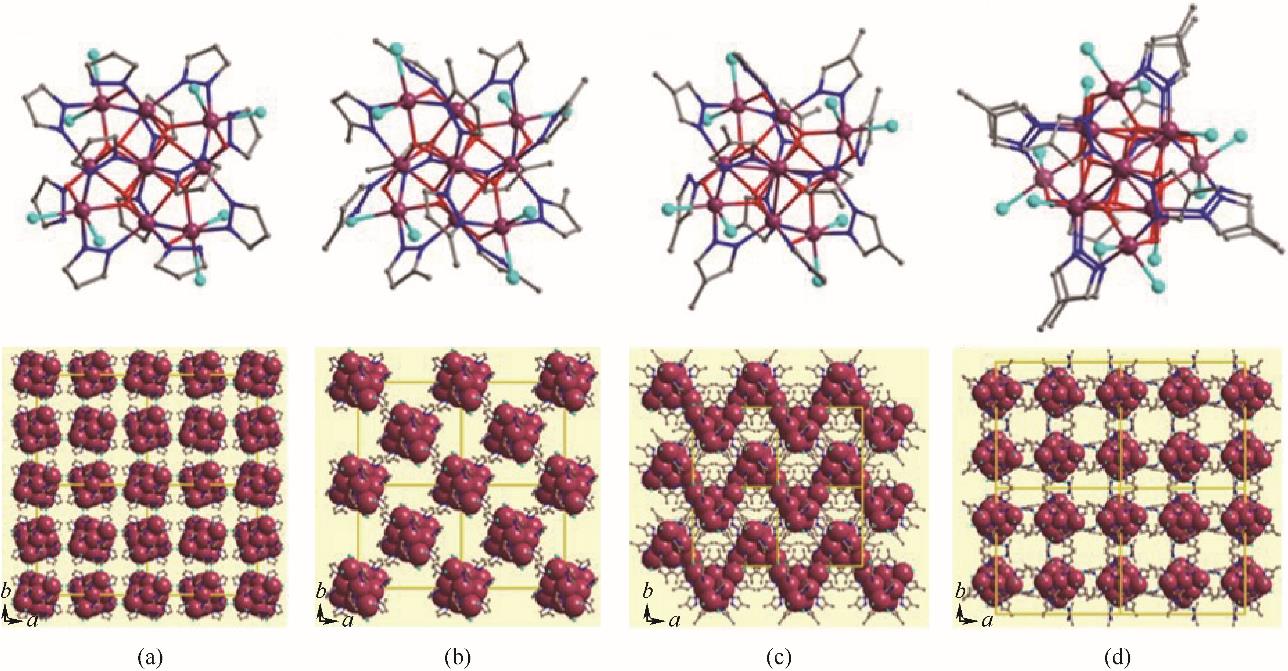
图14 TOC-22(a)、TOC-37(b)、TOC-38(c)、TOC-39(d)的结构示意图和堆积方式示意图[68]
Fig.14 Schematic illustration of the structure and packing models of TOC-22(a), TOC-37(b), TOC-38(c), TOC-39(d)[68]
| 45 | Fallica R, Haitjema J, Wu L J, et al. Absorption coefficient of metal-containing photoresists in the extreme ultraviolet[J]. Nanolithography, MEMS, and MOEMS, 2018, 17(2): 1. |
| 46 | Xu H, Sakai K, Kasahara K, et al. Metal–organic framework-inspired metal-containing clusters for high-resolution patterning[J]. Chemistry of Materials, 2018, 30(12): 4124-4133. |
| 47 | Zhang Y, Haitjema J, Baljozovic M, et al. Dual-tone application of a tin-oxo cage photoresist under E-beam and EUV exposure[J]. Journal of Photopolymer Science and Technology, 2018, 31(2): 249-255. |
| 48 | Bae W J, Trikeriotis M, Sha J, et al. High refractive index and high transparency HfO2 nanocomposites for next generation lithography[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry, 2010, 20(25): 5186. |
| 49 | Tiwale N, Subramanian A, Kisslinger K, et al. Advancing next generation nanolithography with infiltration synthesis of hybrid nanocomposite resists[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry C, 2019, 7(29): 8803-8812. |
| 50 | Grzeskowiak S, Narasimhan A, Murphy M, et al. Reactivity of metal-oxalate EUV resists as a function of the central metal[C]//SPIE Advanced Lithography. Proc SPIE 10146, Advances in Patterning Materials and Processes XXXIV, San Jose, California, USA. 2017, 10146: 14-24 |
| 51 | Fallica R, Watts B, Rösner B, et al. Changes in the near edge X-ray absorption fine structure of hybrid organic–inorganic resists upon exposure[J]. Nanotechnology, 2018, 29(36): 36LT03. |
| 52 | Sadegh N, van der Geest M, Haitjema J, et al. XUV induced bleaching of a tin oxo cage photoresist studied by high harmonic absorption spectroscopy[J]. Journal of Photopolymer Science and Technology, 2020, 33(2): 145-151. |
| 53 | Frederick R T, Saha S, Diulus J T, et al. Thermal and radiation chemistry of butyltin oxo hydroxo: a model inorganic photoresist[J]. Microelectronic Engineering, 2019, 205: 26-31. |
| 54 | Haitjema J, Wu L J, Giuliani A, et al. Photo-induced fragmentation of a tin-oxo cage compound[J]. Journal of Photopolymer Science and Technology, 2018, 31(2): 243-247. |
| 55 | van Lokeren L, Willem R, van der Beek D, et al. Probing the anions mediated associative behavior of tin-12 oxo-macrocations by pulsed field gradient NMR spectroscopy[J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2010, 114(39): 16087-16091. |
| 56 | Ribot F, Escax V, Martins J C, et al. Probing ionic association on metal oxide clusters by pulsed field gradient NMR spectroscopy: the example of Sn12-oxo clusters[J]. Chemistry - A European Journal, 2004, 10(7): 1747-1751. |
| 57 | Closser K D, Ogletree D F, Naulleau P, et al. The importance of inner-shell electronic structure for enhancing the EUV absorption of photoresist materials[J]. The Journal of Chemical Physics, 2017, 146(16): 164106. |
| 58 | Li G Y, Fu M C, Zheng Y, et al. TiO2 microring resonators with high Q and compact footprint fabricated by a bottom-up method[J]. Optics Letters, 2020, 45(18): 5012-5015. |
| 59 | Woo J C, Joo Y H, Kim C I. Surface etching of TiO2Thin films using high density Cl2/Ar plasma[J]. Transactions on Electrical and Electronic Materials, 2015, 16(6): 346-350. |
| 60 | Shkondin E, Takayama O, Lindhard J M, et al. Fabrication of high aspect ratio TiO2 and Al2O3 nanogratings by atomic layer deposition[J]. Journal of Vacuum Science & Technology A: Vacuum, Surfaces, and Films, 2016, 34(3): 031605. |
| 61 | Cardineau B, Del Re R, Marnell M, et al. Photolithographic properties of tin-oxo clusters using extreme ultraviolet light (13.5 nm)[J]. Microelectronic Engineering, 2014, 127: 44-50. |
| 62 | Haitjema J, Zhang Y, Vockenhuber M, et al. Extreme ultraviolet patterning of tin-oxo cages[J]. Nanolithography, MEMS, and MOEMS, 2017, 16(3): 1. |
| 63 | Sharps M C, Marsh D A, Zakharov L N, et al. Implications of crystal structure on organotin carboxylate photoresists[J]. Crystal Research and Technology, 2017, 52(10): 1700081. |
| 64 | Frederick R T, Diulus J T, Hutchison D C, et al. Effect of oxygen on thermal and radiation-induced chemistries in a model organotin photoresist[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2019, 11(4): 4514-4522. |
| 65 | Diulus J T, Frederick R T, Hutchison D C, et al. Effect of ambient conditions on radiation-induced chemistries of a nanocluster organotin photoresist for next-generation EUV nanolithography[J]. ACS Applied Nano Materials, 2020, 3(3): 2266-2277. |
| 66 | Sharps M, Frederick R T, Javitz M L, et al. Organotin carboxylate reagents for nanopatterning: chemical transformations during direct-write electron beam processes[J]. Chemistry of Materials, 2019, 31(13): 4840-4850. |
| 67 | Kenane N, Keszler D A. High-resolution lithographic patterning with organotin films: role of CO2 in differential dissolution rates[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2021, 13(16): 18974-18983. |
| 68 | Wang D, Yi X F, Zhang L. Non-alkyl tin-oxo clusters as new-type patterning materials for nanolithography[J]. Science China Chemistry, 2022, 65(1): 114-119. |
| 69 | Rösner B, Fallica R, Johnson M, et al. Nanolithographic top-down patterning of polyoxovanadate-based nanostructures with switchable electrical resistivity[J]. ChemNanoMat, 2020, 6(11): 1620-1624. |
| 70 | Sharma S K, Kumar R, Chauhan M, et al. All-new nickel-based metal core organic cluster (MCOC) resist for N7 + node patterning[C]//SPIE Advanced Lithography. Proc SPIE 11326, Advances in Patterning Materials and Processes ⅩⅩⅩⅦ. San Jose, California, USA. 2020, 11326: 1132604. |
| 71 | Rathore A, Pollentier I, Cipriani M, et al. Extreme ultraviolet-printability and mechanistic studies of engineered hydrogen silsesquioxane photoresist systems[J]. ACS Applied Polymer Materials, 2021, 3(4): 1964-1972. |
| 72 | Pollentier I, Vesters Y, Jiang J, et al. Unraveling the role of secondary electrons upon their interaction with photoresist during EUV exposure[C]//SPIE Photomask Technology and EUV Lithography. Proc SPIE 10450, International Conference on Extreme Ultraviolet Lithography 2017, Monterey, California, USA. 2017, 10450: 65-71. |
| 73 | Wu L J, Hilbers M F, Lugier O, et al. Fluorescent labeling to investigate nanopatterning processes in extreme ultraviolet lithography[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2021, 13(43): 51790-51798. |
| 74 | Thakur N, Vockenhuber M, Ekinci Y, et al. Fluorine-rich zinc oxoclusters as extreme ultraviolet photoresists: chemical reactions and lithography performance[J]. ACS Materials Au, 2022, 2(3): 343-355. |
| 75 | Rohdenburg M, Thakur N, Cartaya R, et al. Role of low-energy electrons in the solubility switch of Zn-based oxocluster photoresist for extreme ultraviolet lithography[J]. Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics: PCCP, 2021, 23(31): 16646-16657. |
| 76 | Wu L J, Tiekink M, Giuliani A, et al. Tuning photoionization mechanisms of molecular hybrid materials for EUV lithography applications[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry C, 2019, 7(1): 33-37. |
| 77 | Frederick R T, Amador J M, Goberna-Ferrón S, et al. Mechanistic study of HafSOx extreme ultraviolet inorganic resists[J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2018, 122(28): 16100-16112. |
| 78 | Kosma V, Kasahara K, Xu H, et al. Elucidating the patterning mechanism of zirconium-based hybrid photoresists[J]. Journal of Micro/Nanolithography, MEMS, and MOEMS, 2017, 16: 041007. |
| 79 | Trikeriotis M, Bae W J, Schwartz E, et al. Development of an inorganic photoresist for DUV, EUV, and electron beam imaging[C]//SPIE Advanced Lithography. Proc SPIE 7639, Advances in Resist Materials and Processing Technology ⅩⅩⅦ, San Jose, California, USA. 2010, 7639: 120-129. |
| 80 | Trikeriotis M, Krysak M, Chung Y S, et al. A new inorganic EUV resist with high-etch resistance[C]//SPIE Proceedings, Extreme Ultraviolet (EUV) Lithography Ⅲ. San Jose, California. 2012: 83220U. |
| 81 | Li L, Chakrabarty S, Spyrou K, et al. Studying the mechanism of hybrid nanoparticle photoresists: effect of particle size on photopatterning[J]. Chemistry of Materials, 2015, 27(14): 5027-5031. |
| 82 | Mattson E C, Cabrera Y, Rupich S M, et al. Chemical modification mechanisms in hybrid hafnium oxo-methacrylate nanocluster photoresists for extreme ultraviolet patterning[J]. Chemistry of Materials, 2018, 30(17): 6192-6206. |
| 83 | Yang K, Xu H, Sakai K, et al. Radical sensitive zinc-based nanoparticle EUV photoresists[C]//SPIE Advanced Lithography. Proc SPIE 10960, Advances in Patterning Materials and Processes ⅩⅩⅩⅥ, San Jose, California, USA. 2019, 10960: 205-211. |
| 84 | 李冰, 马洁, 刁翠梅, 等. 光刻胶材料发展状况及下一代光刻技术对图形化材料的挑战[J]. 新材料产业, 2018(12): 43-47. |
| Li B, Ma J, Diao C M, et al. The development of photoresist materials and the challenge of next generation lithography technology to patterned materials [J]. Advanced Materials Industry, 2018(12): 43-47. | |
| 85 | Belmonte G K, Cendron S W, Guruprasad Reddy P, et al. Mechanistic insights of Sn-based non-chemically-amplified resists under EUV irradiation[J]. Applied Surface Science, 2020, 533: 146553. |
| 86 | Peter J, Moinuddin M G, Ghosh S, et al. Organotin in nonchemically amplified polymeric hybrid resist imparts better resolution with sensitivity for next-generation lithography[J]. ACS Applied Polymer Materials, 2020, 2(5): 1790-1799. |
| 87 | Enomoto S, Yoshino T, Machida K, et al. Effects of an organotin compound on radiation-induced reactions of extreme-ultraviolet resists utilizing polarity change and radical crosslinking[J]. Japanese Journal of Applied Physics, 2019, 58(1): 016504. |
| 88 | Passarelli J, Murphy M, del Re R, et al. High-sensitivity molecular organometallic resist for EUV (MORE)[C]//Advances in Patterning Materials and Processes ⅩⅩⅫ, SPIE Proceedings. San Jose, California, USA. 2015: 94250T. |
| 89 | Hasan S, Murphy M, Weires M, et al. Oligomers of MORE: molecular organometallic resists for EUV[C]//SPIE Advanced Lithography. Proc SPIE 10960, Advances in Patterning Materials and Processes ⅩⅩⅩⅥ, San Jose, California, USA. 2019, 10960: 205-213. |
| 90 | Murphy M, Sitterly J, Grzeskowiak S, et al. Mechanisms of photodecomposition of metal-containing EUV photoresists: isotopic labelling studies[C]//SPIE Advanced Lithography. Proc SPIE 10586, Advances in Patterning Materials and Processes ⅩⅩⅩⅤ, San Jose, California, USA. 2018, 10586: 16-25. |
| 91 | Yin L, Wang H C, Reagan B A, et al. 6.7-nm emission from Gd and Tb plasmas over a broad range of irradiation parameters using a single laser[J]. Physical Review Applied, 2016, 6(3): 034009. |
| 92 | Uzoma P C, Shabbir S, Hu H, et al. Multilayer reflective coatings for BEUV lithography: a review[J]. Nanomaterials (Basel, Switzerland), 2021, 11(11): 2782. |
| 93 | Hong S, Kim J S, Lee J U, et al. Evaluation of metal absorber materials for beyond extreme ultraviolet lithography[J]. Journal of Nanoscience and Nanotechnology, 2015, 15(11): 8652-8655. |
| 94 | Xu Q, Tian H, Zhao Y P, et al. Effect of time delay on laser-triggered discharge plasma for a beyond EUV source[J]. Symmetry, 2019, 11(5): 658. |
| 95 | Yoshida K, Fujioka S, Higashiguchi T, et al. Beyond extreme ultra violet (BEUV) radiation from spherically symmetrical high-Z plasmas[J]. Journal of Physics: Conference Series, 2016, 688: 012046. |
| 96 | Kilbane D, O'Sullivan G. Extreme ultraviolet emission spectra of Gd and Tb ions[J]. Journal of Applied Physics, 2010, 108(10): 104905. |
| 1 | Pimpin A, Srituravanich W. Review on micro- and nanolithography techniques and their applications[J]. Engineering Journal, 2012, 16(1): 37-56. |
| 2 | Ghosh S, Pradeep C P, Sharma S K, et al. Recent advances in non-chemically amplified photoresists for next generation IC technology[J]. RSC Advances, 2016, 6(78): 74462-74481. |
| 3 | Reichmanis E, Thompson L F. Polymer materials for microlithography[J]. Annual Review of Materials Science, 1987, 17: 235-271. |
| 4 | Manouras T, Argitis P. High sensitivity resists for EUV lithography: a review of material design strategies and performance results[J]. Nanomaterials (Basel, Switzerland), 2020, 10(8): 1593. |
| 5 | Li L, Liu X, Pal S, et al. Extreme ultraviolet resist materials for sub-7 nm patterning[J]. Chemical Society Reviews, 2017, 46(16): 4855-4866. |
| 6 | Reichmanis E, Thompson L F. Polymer materials for microlithography[J]. Chemical Review, 1989, 89(6): 1273-1289. |
| 7 | 顾雪松, 李小欧, 刘亚栋, 等. g-线/i-线光刻胶研究进展[J]. 应用化学, 2021, 38(9): 1091-1104. |
| Gu X S, Li X O, Liu Y D, et al. Research progress on g-line and i-line photoresists[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Chemistry, 2021, 38(9): 1091-1104. | |
| 8 | Bratton D, Ayothi R, Deng H, et al. Diazonaphthoquinone molecular glass photoresists: patterning without chemical amplification[J]. Chemistry of Materials, 2007, 19(15): 3780-3786. |
| 9 | Khanna D N, Durham D L, Seyedi F, et al. Novolak resins with high thermal-stability, high-resolution, improved photospeed and etch characteristics for advanced photoresist applications[J]. Polymer Engineering & Science, 1992, 32(20): 1500-1508. |
| 10 | Ito H, Willson C G. Chemical amplification in the design of dry developing resist materials[J]. Polymer Engineering & Science, 1983, 23(18): 1012-1018. |
| 11 | Ito H. Chemical amplification resists: inception, implementation in device manufacture, and new developments[J]. Journal of Polymer Science Part A: Polymer Chemistry, 2003, 41(24): 3863-3870. |
| 12 | Reichmanis E, Houlihan F M, Nalamasu O, et al. Chemical amplification mechanisms for microlithography[J]. Chemistry of Materials, 1991, 3(3): 394-407. |
| 13 | Lee S M, Frechet J M J. Design of new positive-tone photoresists based on the acid-catalyzed hydrolysis of phenylmethanediol diesters[J]. Chemistry of Materials, 1994, 6(10): 1830-1837. |
| 14 | Ito H. Chemical amplification resists: history and development within IBM[J]. IBM Journal of Research and Development, 2000, 44(1.2): 119-130. |
| 15 | Allen R D, Sooriyakumaran R, Opitz J, et al. Progress in 193 nm positive resists[J]. Journal of Photopolymer Science and Technology, 1996, 9(3): 465-474. |
| 16 | Nozaki K. Material innovations for 193-nm resists[J]. Journal of Photopolymer Science and Technology, 2010, 23(6): 795-801. |
| 17 | Sanders D P. Advances in patterning materials for 193 nm immersion lithography[J]. Chemical Reviews, 2010, 110(1): 321-360. |
| 18 | López-Gejo J, Kunjappu J T, Zhou J, et al. Polycycloalkanes as potential third-generation immersion fluids for photolithography at 193 nm [J]. Chemistry of Materials, 2007, 19(15): 3641-3647. |
| 19 | Matsumoto K, Costner E A, Nishimura I, et al. High index resist for 193 nm immersion lithography[J]. Macromolecules, 2008, 41(15): 5674-5680. |
| 20 | Seisyan R P. Nanolithography in microelectronics: a review[J]. Technical Physics, 2011, 56(8): 1061-1073. |
| 21 | 朋小康, 黄兴文, 刘荣涛, 等. 光刻胶成膜剂:发展与未来[J]. 应用化学, 2021, 38(9): 1079-1090. |
| Peng X K, Huang X W, Liu R T, et al. Photoresist film-forming agent: development and future[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Chemistry, 2021, 38(9): 1079-1090. | |
| 22 | Fu N, Liu Y X, Ma X L, et al. EUV lithography: state-of-the-art review[J]. Journal of Microelectronic Manufacturing, 2019, 2(2): 1-6. |
| 23 | Singh V, Satyanarayana V S V, Sharma S K, et al. Towards novel non-chemically amplified (n-CARS) negative resists for electron beam lithography applications[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry C, 2014, 2(12): 2118. |
| 24 | Satyanarayana V S V, Kessler F, Singh V, et al. Radiation-sensitive novel polymeric resist materials: iterative synthesis and their EUV fragmentation studies[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2014, 6(6): 4223-4232. |
| 25 | Vieu C, Carcenac F, Pépin A, et al. Electron beam lithography: resolution limits and applications[J]. Applied Surface Science, 2000, 164(1/2/3/4): 111-117. |
| 26 | Irie S, Endo M, Sasago M, et al. Study of transmittance of polymers and influence of photoacid generator on resist transmittance at extreme ultraviolet wavelength[J]. Japanese Journal of Applied Physics, 2002, 41( 9): 5864-5867. |
| 27 | Kozawa T, Tagawa S. Radiation chemistry in chemically amplified resists[J]. Japanese Journal of Applied Physics, 2010, 49: 030001. |
| 28 | Rathore A, Pollentier I, Singh H, et al. Effect of molecular weight on the EUV-printability of main chain scission type polymers[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry C, 2020, 8(17): 5958-5966. |
| 29 | Reddy P G, Pal S P, Kumar P, et al. Polyarylenesulfonium salt as a novel and versatile nonchemically amplified negative tone photoresist for high-resolution extreme ultraviolet lithography applications[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2017, 9(1): 17-21. |
| 30 | Kostko O, Xu B, Ahmed M, et al. Fundamental understanding of chemical processes in extreme ultraviolet resist materials[J]. The Journal of Chemical Physics, 2018, 149(15): 154305. |
| 31 | Thakur N, Bliem R, Mochi I, et al. Mixed-ligand zinc-oxoclusters: efficient chemistry for high resolution nanolithography[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry C, 2020, 8(41): 14499-14506. |
| 32 | Nishikubo T, Kudo H. Recent development in molecular resists for extreme ultraviolet lithography[J]. Journal of Photopolymer Science and Technology, 2011, 24(1): 9-18. |
| 33 | Bhattarai S, Neureuther A R, Naulleau P P. Study of shot noise in photoresists for extreme ultraviolet lithography through comparative analysis of line edge roughness in electron beam and extreme ultraviolet lithography[J]. Journal of Vacuum Science & Technology B, Nanotechnology and Microelectronics: Materials, Processing, Measurement, and Phenomena, 2017, 35(6): 061602. |
| 34 | Wood Ii O R. EUVL: challenges to manufacturing insertion[J]. Journal of Photopolymer Science and Technology, 2017, 30(5): 599-604. |
| 35 | Sanchez M I, Wallraff G M, Megiddo N, et al. An analysis of EUV resist stochastic printing failures[C]//SPIE Photomask Technology + EUV Lithography. Proc SPIE 11147, International Conference on Extreme Ultraviolet Lithography 2019, Monterey, California, USA. 2019, 11147: 125-140. |
| 36 | Bespalov I, Zhang Y, Haitjema J, et al. Key role of very low energy electrons in tin-based molecular resists for extreme ultraviolet nanolithography[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2020, 12(8): 9881-9889. |
| 37 | Luo C Y, Xu C C, Lv L, et al. Review of recent advances in inorganic photoresists[J]. RSC Advances, 2020, 10(14): 8385-8395. |
| 97 | Churilov S S, Kildiyarova R R, Ryabtsev A N, et al. EUV spectra of Gd and Tb ions excited in laser-produced and vacuum spark plasmas[J]. Physica Scripta, 2009, 80(4): 045303. |
| 98 | Wang J W, Wang X B, Zuo D L, et al. Characteristics of discharge and beyond extreme ultraviolet spectra of laser induced discharge gadolinium plasma[J]. Optics & Laser Technology, 2021, 138: 106904. |
| 99 | Alnaimi R, Wang H X, Zhang Z, et al. Design calculations and characterization of C/Cr multilayer mirrors in the 6 nm BEUV[J]. Optik, 2016, 127(2): 588-592. |
| 100 | Makhotkin I A, Zoethout E, Louis E, et al. Wavelength selection for multilayer coatings for the lithography generation beyond EUVL[C]//SPIE Advanced Lithography. Proc SPIE 8322, Extreme Ultraviolet (EUV) Lithography Ⅲ, San Jose, California, USA. 2012, 8322: 337-341. |
| 101 | Oyama T G, Oshima A, Washio M, et al. Method of predicting resist sensitivity for 6.x nm extreme ultraviolet lithography[J]. Journal of Vacuum Science & Technology B, Nanotechnology and Microelectronics: Materials, Processing, Measurement, and Phenomena, 2013, 31(4): 041604. |
| 102 | Oyama T G, Oshima A, Washio M, et al. Evaluation of resist sensitivity in extreme ultraviolet/soft X-ray region for next-generation lithography[J]. AIP Advances, 2011, 1(4): 042153. |
| 103 | Anderson C, Ashworth D, Baclea-An L M, et al. The SEMATECH Berkeley MET: demonstration of 15-nm half-pitch in chemically amplified EUV resist and sensitivity of EUV resists at 6.x-nm[C]//SPIE Advanced Lithography. Proc SPIE 8322, Extreme Ultraviolet (EUV) Lithography Ⅲ, San Jose, California, USA. 2012, 8322: 330-336 |
| 104 | Mojarad N, Vockenhuber M, Wang L, et al. Patterning at 6.5 nm wavelength using interference lithography[C]//Extreme Ultraviolet (EUV) Lithography Ⅳ, SPIE Proceedings. San Jose, California, USA. 2013: 867924. |
| 38 | Wang C W, Chang C Y, Ku Y. Photobase generator and photo decomposable quencher for high-resolution photoresist applications[C] //SPIE Advanced Lithography. Proc SPIE 7639, Advances in Resist Materials and Processing Technology ⅩⅩⅦ. San Jose, California, USA. 2010, 7639: 279-293. |
| 39 | Yildirim O, Buitrago E, Hoefnagels R, et al. Improvements in resist performance towards EUV HVM[C]//SPIE Proceedings, Extreme Ultraviolet (EUV) Lithography Ⅷ. San Jose, California, USA. 2017: 101430Q. |
| 40 | Peng X M, Wang Y F, Xu J, et al. Molecular Glass photoresists with high resolution, low ler, and high sensitivity for EUV lithography[J]. Macromolecular Materials and Engineering, 2018, 303(6): 1700654. |
| 41 | Chen J P, Hao Q S, Wang S Q, et al. Molecular glass resists based on 9, 9'-spirobifluorene derivatives: pendant effect and comprehensive evaluation in extreme ultraviolet lithography[J]. ACS Applied Polymer Materials, 2019, 1(3): 526-534. |
| 42 | de Simone D, Vesters Y, Vandenberghe G. Photoresists in extreme ultraviolet lithography (EUVL)[J]. Advanced Optical Technologies, 2017, 6(3/4): 163-172. |
| 43 | Wu B Q, Kumar A. Extreme ultraviolet lithography: a review[J]. Journal of Vacuum Science & Technology B: Microelectronics and Nanometer Structures, 2007, 25(6): 1743. |
| 44 | Solak H H, He D, Li W, et al. Exposure of 38 nm period grating patterns with extreme ultraviolet interferometric lithography[J]. Applied Physics Letters, 1999, 75(15): 2328-2330. |
| [1] | 于源, 刘克润, 李兴帅, 刘家祥, 焦志伟. 涡流空气分级流场中颗粒运动及分布规律研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, (): 1-13. |
| [2] | 麻蓉, 张桥. PSA-低温甲醇洗-膜分离耦合的氢气分离系统建立与模拟[J]. 化工学报, 2023, (): 1-8. |
| [3] | 党青梅, 李强, 丁晖殿, 贾胜坤, 钱行, 苑杨, 黄克谨, 陈海胜. 基于动态模式分解的精馏吸收状态变量非设计条件下的重构与预测[J]. 化工学报, 2023, (): 1-13. |
| [4] | 胡建波, 刘洪超, 胡齐, 黄美英, 宋先雨, 赵双良. 有机笼跨细胞膜易位行为的分子动力学模拟研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(9): 3756-3765. |
| [5] | 赵亚欣, 张雪芹, 王荣柱, 孙国, 姚善泾, 林东强. 流穿模式离子交换层析去除单抗聚集体[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(9): 3879-3887. |
| [6] | 陈美思, 陈威达, 李鑫垚, 李尚予, 吴有庭, 张锋, 张志炳. 硅基离子液体微颗粒强化气体捕集与转化的研究进展[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(9): 3628-3639. |
| [7] | 傅予, 刘兴翀, 王瀚雨, 李海敏, 倪亚飞, 邹文静, 雷月, 彭永姗. F3EACl修饰层对钙钛矿太阳能电池性能提升的研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(8): 3554-3563. |
| [8] | 张瑞航, 曹潘, 杨锋, 李昆, 肖朋, 邓春, 刘蓓, 孙长宇, 陈光进. ZIF-8纳米流体天然气乙烷回收工艺的产品纯度关键影响因素分析[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(8): 3386-3393. |
| [9] | 朱娇, 栾丽萍, 从深震, 刘新磊. 氢气分离有机膜[J]. 化工学报, 2023, (): 1-22. |
| [10] | 张缘良, 栾昕奇, 苏伟格, 李畅浩, 赵钟兴, 周利琴, 陈健民, 黄艳, 赵祯霞. 离子液体复合萃取剂选择性萃取尼古丁的研究及DFT计算[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(7): 2947-2956. |
| [11] | 陈朝光, 贾玉香, 汪锰. 以低浓度废酸驱动中和渗析脱盐的模拟与验证[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(6): 2486-2494. |
| [12] | 韩奎奎, 谭湘龙, 李金芝, 杨婷, 张春, 张永汾, 刘洪全, 于中伟, 顾学红. 四通道中空纤维MFI分子筛膜用于二甲苯异构体分离[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(6): 2468-2476. |
| [13] | 贾晓宇, 杨剑, 王博, 林梅, 王秋旺. 金属丝网毛细特性的孔隙尺度数值分析[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(5): 1928-1938. |
| [14] | 李木金, 胡松, 施德磐, 赵鹏, 高瑞, 李进龙. 环氧丁烷尾气溶剂吸收及精制工艺[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(4): 1607-1618. |
| [15] | 王荣, 王永洪, 张新儒, 李晋平. 6FDA型聚酰亚胺炭分子筛气体分离膜的构筑及其应用[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(4): 1433-1445. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备 11010102001995号
京公网安备 11010102001995号