化工学报 ›› 2022, Vol. 73 ›› Issue (10): 4648-4658.DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20220770
贺冲1( ), 白进2, 郭晶3, 孔令学2, 鲁浩2, 李怀柱2, 秦育红1, 李文2
), 白进2, 郭晶3, 孔令学2, 鲁浩2, 李怀柱2, 秦育红1, 李文2
收稿日期:2022-06-01
修回日期:2022-07-22
出版日期:2022-10-05
发布日期:2022-11-02
通讯作者:
贺冲
作者简介:贺冲(1989—),男,博士,讲师,hechong@tyut.edu.cn
基金资助:
Chong HE1( ), Jin BAI2, Jing GUO3, Lingxue KONG2, Hao LU2, Huaizhu LI2, Yuhong QIN1, Wen LI2
), Jin BAI2, Jing GUO3, Lingxue KONG2, Hao LU2, Huaizhu LI2, Yuhong QIN1, Wen LI2
Received:2022-06-01
Revised:2022-07-22
Online:2022-10-05
Published:2022-11-02
Contact:
Chong HE
摘要:
采用灰熔点仪、XRD和热力学模拟,研究气氛和化学组成对高铁煤灰熔融特性的影响机理。研究结果表明,灰熔融温度随铁含量、钙含量或硅铝比增加而降低。弱还原气氛下低钙或低硅铝比煤灰熔融存在明显的初始熔融阶段,熔融过程遵循“软化-熔融”机理,而空气气氛下高钙或高硅铝比煤灰熔融过程属于“熔融-溶解”机理。弱还原气氛下铁含量增加显著促进石英和钙长石熔融,空气气氛下钙含量增加促进刚玉和石英熔融或转化为钙基硅铝盐。弱还原气氛下液相含量随硅铝比或铁含量增加而增加,液相黏度随钙含量或铁含量增加而降低,促进熔融传质;空气气氛下低钙或低硅铝比煤灰中铁存在于含铁固溶体,导致液相黏度高或液相含量低,熔融传质受阻。
中图分类号:
贺冲, 白进, 郭晶, 孔令学, 鲁浩, 李怀柱, 秦育红, 李文. 气氛和化学组成对高铁煤灰熔融特性的影响机理[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(10): 4648-4658.
Chong HE, Jin BAI, Jing GUO, Lingxue KONG, Hao LU, Huaizhu LI, Yuhong QIN, Wen LI. Effects of atmosphere and chemical composition on fusion characteristics of high-iron coal ash[J]. CIESC Journal, 2022, 73(10): 4648-4658.
| 组成 | 含量/% |
|---|---|
| SiO2 | 35.17 |
| Al2O3 | 19.16 |
| Fe2O3 | 16.31 |
| CaO | 18.04 |
| MgO | 1.83 |
| Na2O | 0.51 |
| K2O | 0.31 |
| SO3 | 8.05 |
| TiO2 | 0.61 |
表1 兖州煤灰的化学组成
Table 1 Chemical composition of YZ coal ash
| 组成 | 含量/% |
|---|---|
| SiO2 | 35.17 |
| Al2O3 | 19.16 |
| Fe2O3 | 16.31 |
| CaO | 18.04 |
| MgO | 1.83 |
| Na2O | 0.51 |
| K2O | 0.31 |
| SO3 | 8.05 |
| TiO2 | 0.61 |
| 样品 | 含量/% | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SiO2 | Al2O3 | Fe2O3 | CaO | |
| YZ | 39.61 | 21.64 | 18.39 | 20.36 |
| 不同铁含量的煤灰 | ||||
| F5 | 46.11 | 25.19 | 5.00 | 23.70 |
| F10 | 43.68 | 23.86 | 10.00 | 22.45 |
| F15 | 41.26 | 22.54 | 15.00 | 21.21 |
| F20 | 38.83 | 21.21 | 20.00 | 19.96 |
| F25 | 36.40 | 19.89 | 25.00 | 18.71 |
| 不同钙含量的高铁煤灰 | ||||
| Ca5 | 49.54 | 27.07 | 18.39 | 5.00 |
| Ca15 | 43.08 | 23.53 | 18.39 | 15.00 |
| Ca25 | 36.61 | 20.00 | 18.39 | 25.00 |
| Ca35 | 30.14 | 16.47 | 18.39 | 35.00 |
| 不同硅铝比的高铁煤灰 | ||||
| SA1 | 30.63 | 30.63 | 18.39 | 20.36 |
| SA2 | 40.83 | 20.42 | 18.39 | 20.36 |
| SA3 | 45.94 | 15.31 | 18.39 | 20.36 |
| SA4 | 49.00 | 12.25 | 18.39 | 20.36 |
表2 高铁模拟灰的化学组成
Table 2 Chemical composition of high-iron synthetic ash
| 样品 | 含量/% | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SiO2 | Al2O3 | Fe2O3 | CaO | |
| YZ | 39.61 | 21.64 | 18.39 | 20.36 |
| 不同铁含量的煤灰 | ||||
| F5 | 46.11 | 25.19 | 5.00 | 23.70 |
| F10 | 43.68 | 23.86 | 10.00 | 22.45 |
| F15 | 41.26 | 22.54 | 15.00 | 21.21 |
| F20 | 38.83 | 21.21 | 20.00 | 19.96 |
| F25 | 36.40 | 19.89 | 25.00 | 18.71 |
| 不同钙含量的高铁煤灰 | ||||
| Ca5 | 49.54 | 27.07 | 18.39 | 5.00 |
| Ca15 | 43.08 | 23.53 | 18.39 | 15.00 |
| Ca25 | 36.61 | 20.00 | 18.39 | 25.00 |
| Ca35 | 30.14 | 16.47 | 18.39 | 35.00 |
| 不同硅铝比的高铁煤灰 | ||||
| SA1 | 30.63 | 30.63 | 18.39 | 20.36 |
| SA2 | 40.83 | 20.42 | 18.39 | 20.36 |
| SA3 | 45.94 | 15.31 | 18.39 | 20.36 |
| SA4 | 49.00 | 12.25 | 18.39 | 20.36 |
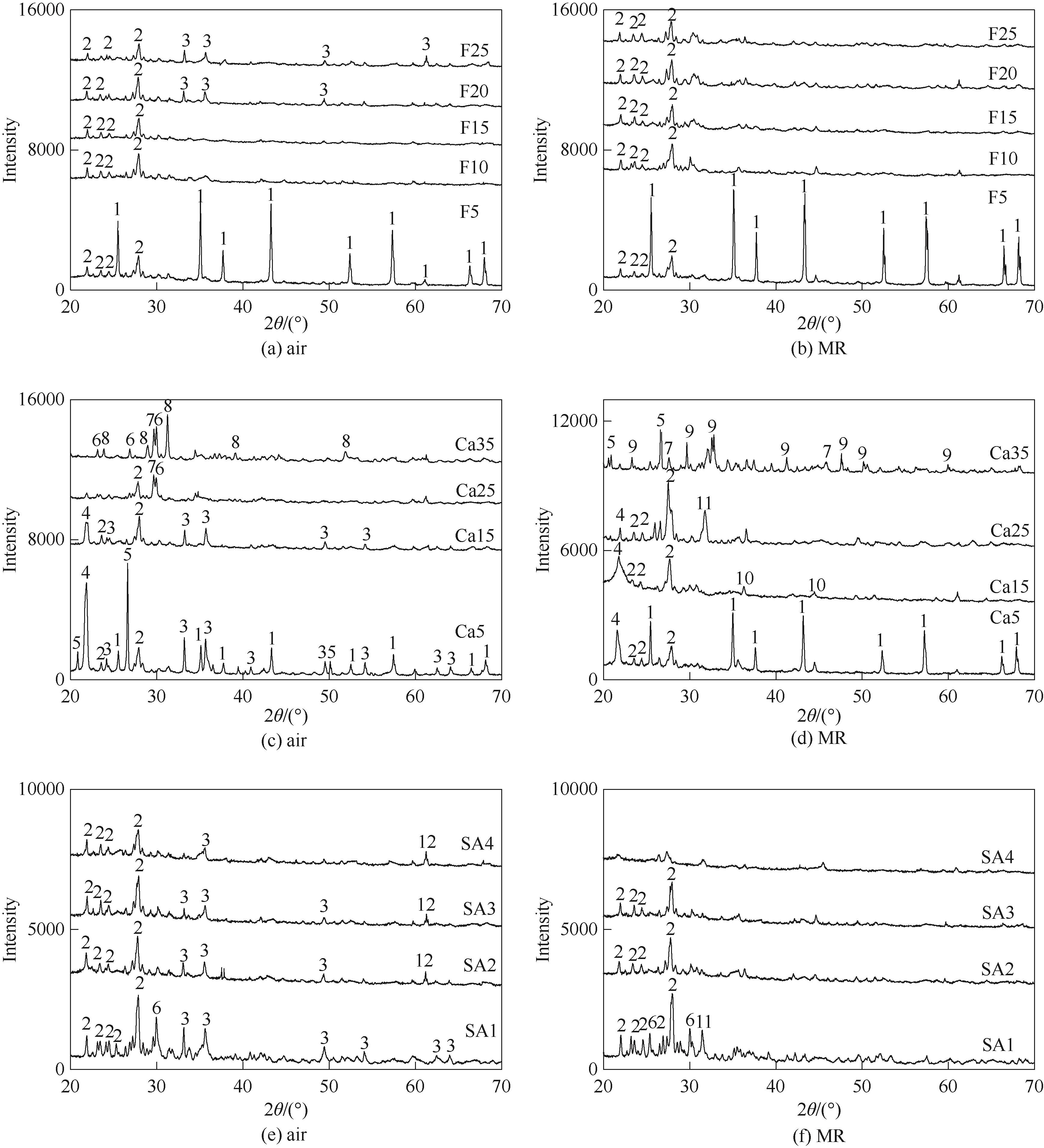
图3 灰样在1200℃的XRD谱图1—刚玉(Al2O3); 2—钙长石(CaAl2Si2O8); 3—赤铁矿(Fe2O3); 4—方石英(SiO2); 5—石英(SiO2); 6—硅灰石(CaSiO3); 7—假硅灰石(Ca3Si3O9);8—黄长石(Ca2Al2SiO7); 9—硅酸二钙(Ca2SiO4); 10—橄榄石(Fe2SiO4); 11—斜硅钙石(Ca2SiO4); 12—硅酸铁(Fe2SiO4)
Fig.3 XRD patterns of ash at 1200℃1—corundum (Al2O3);2—anorthite (CaAl2Si2O8);3—hematite (Fe2O3); 4—cristobalite (SiO2); 5—quartz (SiO2); 6—wollastonite (CaSiO3); 7—pseudowollastonite (Ca3Si3O9); 8—gehlenite (Ca2Al2SiO7); 9—calcium silicate (Ca2SiO4); 10—fayalite (Fe2SiO4); 11—larnite (Ca2SiO4);12—iron silicate (Fe2SiO4)
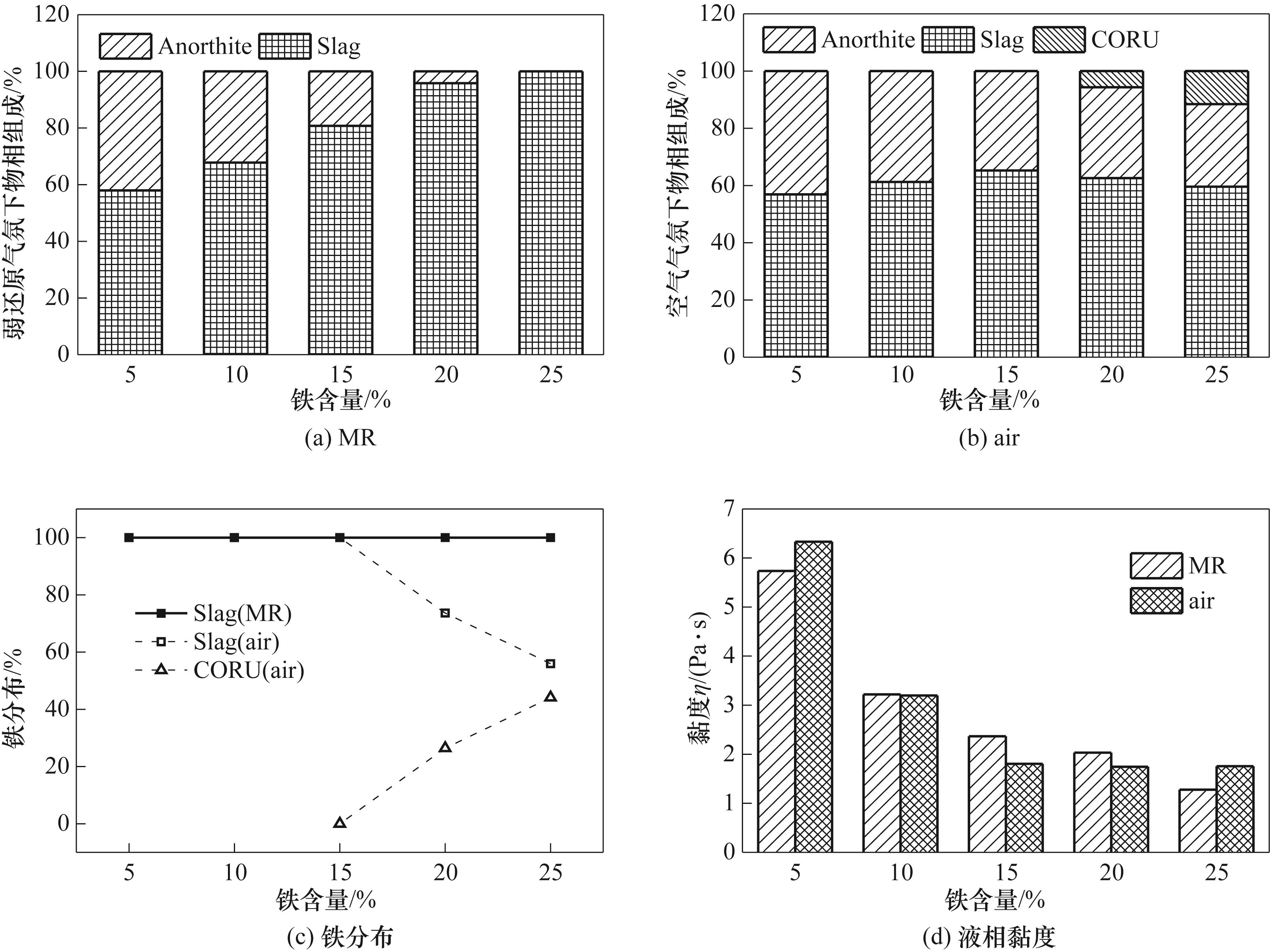
图4 1350℃铁含量对高温灰渣物相组成、铁分布及液相黏度的影响
Fig.4 Effect of Fe2O3 content on phase composition [(a) MR; (b) air], iron distribution (c), and slag viscosity (d) at 1350℃

图5 1350℃钙含量对高温灰渣物相组成、铁分布及液相黏度的影响
Fig.5 Effect of CaO content on phase composition [(a) MR; (b) air], iron distribution (c), and slag viscosity (d) at 1350℃
| 1 | Xie K C. Reviews of clean coal conversion technology in China: situations & challenges[J]. Chinese Journal of Chemical Engineering, 2021, 35: 62-69. |
| 2 | 王辅臣. 煤气化技术在中国:回顾与展望[J]. 洁净煤技术, 2021, 27(1): 1-33. |
| Wang F C. Coal gasification technologies in China: review and prospect[J]. Clean Coal Technology, 2021, 27(1): 1-33. | |
| 3 | Song W J, Tang L H, Zhu Z B, et al. Rheological evolution and crystallization response of molten coal ash slag at high temperatures[J]. AIChE Journal, 2013, 59(8): 2726-2742. |
| 4 | 李文, 白进. 煤的灰化学[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2013: 74. |
| Li W, Bai J. Chemistry of Ash from Coal[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2013: 74. | |
| 5 | 刘洁妤, 龚岩, 吴晓翔, 等. 多喷嘴对置式气化炉内颗粒挥发分火焰可视化研究[J]. 化工学报, 2021, 72(3): 1275-1282. |
| Liu J Y, Gong Y, Wu X X, et al. Visualization study on particle volatile flame opposed multi-burner impinging entrained-flow gasifier[J]. CIESC Journal, 2021, 72(3): 1275-1282. | |
| 6 | 苗苗, 孔皓, 张缦, 等. 多元煤灰灰熔点及晶体组成特性研究[J]. 化工学报, 2019, 70(8): 2909-2918. |
| Miao M, Kong H, Zhang M, et al. Ash fusion temperature and crystal composition of multi-component coal ash[J]. CIESC Journal, 2019, 70(8): 2909-2918. | |
| 7 | 杨砚. 气化炉堵渣问题浅析[J]. 大氮肥, 2020, 43(3): 160-163. |
| Yang Y. A study on slag block in gasifier[J]. Large Scale Nitrogenous Fertilizer Industry, 2020, 43(3): 160-163. | |
| 8 | He C, Bai J, Ilyushechkin A, et al. Effect of chemical composition on the fusion behaviour of synthetic high-iron coal ash[J]. Fuel, 2019, 253: 1465-1472. |
| 9 | 胡晓飞, 郭庆华, 刘霞, 等. 高钙高铁煤灰熔融及黏温特性研究[J]. 燃料化学学报, 2016, 44(7): 769-776. |
| Hu X F, Guo Q H, Liu X, et al. Ash fusion and viscosity behavior of coal ash with high content of Fe and Ca[J]. Journal of Fuel Chemistry and Technology, 2016, 44(7): 769-776. | |
| 10 | He C, Bai J, Kong L, et al. Effect of iron valence distribution on ash fusion behavior under Ar atmosphere by a metallic iron addition in the synthetic coal ash[J]. Fuel, 2022, 310: 122340. |
| 11 | He C, Bai J, Kong L X, et al. The precipitation of metallic iron from coal ash slag in the entrained flow coal gasifier: by thermodynamic calculation[J]. Fuel Processing Technology, 2017, 162: 98-104. |
| 12 | Wei Y J, Li H X, Yamada N, et al. A microscopic study of the precipitation of metallic iron in slag from iron-rich coal during high temperature gasification[J]. Fuel, 2013, 103: 101-110. |
| 13 | Vassilev S V, Kitano K, Takeda S, et al. Influence of mineral and chemical composition of coal ashes on their fusibility[J]. Fuel Processing Technology, 1995, 45(1): 27-51. |
| 14 | 陈晓东, 孔令学, 白进, 等. 高温气化条件下Na2O对煤灰中矿物质演化行为的影响[J]. 燃料化学学报, 2016, 44(3): 263-272. |
| Chen X D, Kong L X, Bai J, et al. Effect of Na2O on mineral transformation of coal ash under high temperature gasification condition[J]. Journal of Fuel Chemistry and Technology, 2016, 44(3): 263-272. | |
| 15 | Liu B, He Q H, Jiang Z H, et al. Relationship between coal ash composition and ash fusion temperatures[J]. Fuel, 2013, 105: 293-300. |
| 16 | 陈胜, 于敦喜, 吴建群, 等. 新疆高钙煤混烧对灰中含钙矿物熔融特性影响[J]. 化工学报, 2020, 71(9): 4260-4269. |
| Chen S, Yu D X, Wu J Q, et al. Effects of Xinjiang high calcium coal co-firing on melting characteristics of Ca-bearing minerals in ash [J]. CIESC Journal, 2020, 71(9): 4260-4269. | |
| 17 | Bell D A, Towler B F, Fan M. Coal Gasification and Its Applications[M]. Oxford: William Andrew, 2011: 83. |
| 18 | Song W J, Tang L H, Zhu X D, et al. Prediction of Chinese coal ash fusion temperatures in Ar and H2 atmospheres[J]. Energy & Fuels, 2009, 23(4): 1990-1997. |
| 19 | Yu D X, Zhao L, Zhang Z Y, et al. Iron transformation and ash fusibility during coal combustion in air and O2/CO2 medium[J]. Energy & Fuels, 2012, 26(6): 3150-3155. |
| 20 | 吕俊复, 史航, 吴玉新, 等. 烟气气氛对准东煤灰熔融特性影响的显微观察[J]. 煤炭学报, 2021, 46(1): 263-273. |
| Lyu J F, Shi H, Wu Y X, et al. Influence of flue gas atmosphere on Zhundong coal ash melting characteristics through microscopic observation[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2021, 46(1): 263-273. | |
| 21 | 殷志源, 项群扬, 竺浩炜. 不同气氛下煤灰中铁含量对灰熔融特性影响研究[J]. 煤质技术, 2019, 34(3): 36-38, 42. |
| Yin Z Y, Xiang Q Y, Zhu H W. Influence research of iron content on coal ash fusion behavior under different atmospheres[J]. Coal Quality Technology, 2019, 34(3): 36-38, 42. | |
| 22 | 魏博, 谭厚章, 王学斌, 等. 煤燃烧过程中复杂气氛下的灰熔融特性[J]. 燃烧科学与技术, 2017, 23(4): 320-324. |
| Wei B, Tan H Z, Wang X B, et al. Ash fusion characteristics under complex atmosphere in coal combustion process[J]. Journal of Combustion Science and Technology, 2017, 23(4): 320-324. | |
| 23 | Huffman G P, Huggins F E, Dunmyre G R. Investigation of the high-temperature behaviour of coal ash in reducing and oxidizing atmospheres[J]. Fuel, 1981, 60(7): 585-597. |
| 24 | 张鹏启, 杨琪琪, 屠卡滨, 等. 晋城粉煤煤灰不均匀熔融规律研究[J]. 燃料化学学报, 2018, 46(1): 8-14. |
| Zhang P Q, Yang Q Q, Tu K B, et al. Research on the uneven ash melting behavior of pulverized Jincheng coal[J]. Journal of Fuel Chemistry and Technology, 2018, 46(1): 8-14. | |
| 25 | 代鑫, 白进, 李东涛, 等. Al2O3-SiO2-CaO-FeO四元体系煤灰结构及流动性关系的实验和理论研究[J]. 燃料化学学报, 2019, 47(6): 641-648. |
| Dai X, Bai J, Li D T, et al. Experimental and theoretical investigation on relationship between structures of coal ash and its fusibility for Al2O3-SiO2-CaO-FeO system[J]. Journal of Fuel Chemistry and Technology, 2019, 47(6): 641-648. | |
| 26 | Yuan Z S, Wang J, Kong L X, et al. Comparison study of fusibility between coal ash and synthetic ash[J]. Fuel Processing Technology, 2021, 211: 106593. |
| 27 | Ilyushechkin A Y, Hla S S. Viscosity of high-iron slags from Australian coals[J]. Energy & Fuels, 2013, 27(7): 3736-3742. |
| 28 | 赵超越, 李风海, 马名杰. 硅酸盐熔体结构对煤灰黏温特性调控研究进展[J]. 应用化工, 2021, 50(7): 1938-1941. |
| Zhao C Y, Li F H, Ma M J. Review on the regulation of viscosity-temperature characteristics from silicate melt structure variation[J]. Applied Chemical Industry, 2021, 50(7): 1938-1946. | |
| 29 | Song W J, Tang L H, Zhu X D, et al. Effect of coal ash composition on ash fusion temperatures[J]. Energy & Fuels, 2010, 24(1): 182-189. |
| 30 | Wang J J, Guo Q H, Wei J T, et al. Understanding the influence of iron on fluidity and crystallization characteristics of synthetic coal slags[J]. Fuel Processing Technology, 2020, 209: 106532. |
| 31 | Kondratiev A, Jak E. Predicting coal ash slag flow characteristics (viscosity model for the Al2O3-CaO-‘FeO’-SiO2 system)[J]. Fuel, 2001, 80(14): 1989-2000. |
| 32 | Zhou H, Xing Y J, Zhou M X. Effects of modified kaolin adsorbents on sodium adsorption efficiency and ash fusion characteristics during Zhundong coal combustion[J]. Journal of the Energy Institute, 2021, 97: 203-212. |
| 33 | Yan T G, Kong L X, Bai J, et al. Thermomechanical analysis of coal ash fusion behavior[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2016, 147: 74-82. |
| 34 | Zhang W W, Huang S, Wu S Y, et al. Ash fusion characteristics and gasification activity during biomasses co-gasification process[J]. Renewable Energy, 2020, 147: 1584-1594. |
| 35 | Wang Z G, Kong L X, Bai J, et al. Effect of vanadium and nickel on iron-rich ash fusion characteristics[J]. Fuel, 2019, 246: 491-499. |
| 36 | Wei B, Wang X B, Tan H Z, et al. Effect of silicon-aluminum additives on ash fusion and ash mineral conversion of Xinjiang high-sodium coal[J]. Fuel, 2016, 181: 1224-1229. |
| [1] | 张双星, 刘舫辰, 张义飞, 杜文静. R-134a脉动热管相变蓄放热实验研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(S1): 165-171. |
| [2] | 江河, 袁俊飞, 王林, 邢谷雨. 均流腔结构对微细通道内相变流动特性影响的实验研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(S1): 235-244. |
| [3] | 吴延鹏, 刘乾隆, 田东民, 陈凤君. 相变材料与热管耦合的电子器件热管理研究进展[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(S1): 25-31. |
| [4] | 于宏鑫, 邵双全. 水结晶过程的分子动力学模拟分析[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(S1): 250-258. |
| [5] | 陈哲文, 魏俊杰, 张玉明. 超临界水煤气化耦合SOFC发电系统集成及其能量转化机制[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(9): 3888-3902. |
| [6] | 韩晨, 司徒友珉, 朱斌, 许建良, 郭晓镭, 刘海峰. 协同处理废液的多喷嘴粉煤气化炉内反应流动研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(8): 3266-3278. |
| [7] | 傅予, 刘兴翀, 王瀚雨, 李海敏, 倪亚飞, 邹文静, 雷月, 彭永姗. F3EACl修饰层对钙钛矿太阳能电池性能提升的研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(8): 3554-3563. |
| [8] | 张贲, 王松柏, 魏子亚, 郝婷婷, 马学虎, 温荣福. 超亲水多孔金属结构驱动的毛细液膜冷凝及传热强化[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(7): 2824-2835. |
| [9] | 史昊鹏, 钟达文, 廉学新, 张君峰. 朝下多尺度沟槽翅片结构表面沸腾换热实验研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(7): 2880-2888. |
| [10] | 史方哲, 甘云华. 超薄热管启动特性和传热性能数值模拟[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(7): 2814-2823. |
| [11] | 邢美波, 张中天, 景栋梁, 张洪发. 磁调控水基碳纳米管协同多孔材料强化相变储/释能特性[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(7): 3093-3102. |
| [12] | 李振, 张博, 王丽伟. PEG-EG固-固相变材料的制备和性能研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(6): 2680-2688. |
| [13] | 葛泽峰, 吴雨青, 曾名迅, 查振婷, 马宇娜, 侯增辉, 张会岩. 灰化学成分对生物质气化特性的影响规律[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(5): 2136-2146. |
| [14] | 黄磊, 孔令学, 白进, 李怀柱, 郭振兴, 白宗庆, 李平, 李文. 油页岩添加对准东高钠煤灰熔融行为影响的研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(5): 2123-2135. |
| [15] | 代佳琳, 毕唯东, 雍玉梅, 陈文强, 莫晗旸, 孙兵, 杨超. 热物性对混合型CPCMs固液相变特性影响模拟研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(5): 1914-1927. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备 11010102001995号
京公网安备 11010102001995号