化工学报 ›› 2024, Vol. 75 ›› Issue (S1): 259-266.DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20240382
收稿日期:2024-04-08
修回日期:2024-05-26
出版日期:2024-12-25
发布日期:2024-12-17
通讯作者:
张大骋
作者简介:赵振刚(1981—),男,博士,教授,zhaozhengang@kust.edu.cn
基金资助:
Zhengang ZHAO1,2( ), Mengyao ZHOU1, Dian JIN1, Dacheng ZHANG1,2(
), Mengyao ZHOU1, Dian JIN1, Dacheng ZHANG1,2( )
)
Received:2024-04-08
Revised:2024-05-26
Online:2024-12-25
Published:2024-12-17
Contact:
Dacheng ZHANG
摘要:
扩散层(DL)是直接甲醇燃料电池(DMFC)膜电极组件(MEA)的重要结构,为反应物从流场到催化层的传质提供通道,随着反应的进行,扩散层也为电子从催化层到流场的传输提供通道,因此,扩散层的导电率和表面形貌影响燃料电池的整体性能。泡沫碳(foam carbon,FC)材料具有优异的导电性能和三维网状结构,将其作为阴极扩散层(CDL),能够降低燃料电池膜电极与集流板间的接触电阻、电荷转移电阻和传质电阻。同时,泡沫碳的较高孔隙率和较小的表面接触角,可增加DMFC阴极催化层暴露在空气中的比例,提供更多的气液两相流道,是较好的催化剂载体。研究结果表明,与传统碳纸比较,泡沫碳作为阴极扩散层的燃料电池峰值功率密度从24.47 mW/cm2提升到39.24 mW/cm2,接触电阻由0.588 Ω降低至0.494 Ω,电荷转移电阻由2.784 Ω降低至1.816 Ω,传质阻抗由1.689 Ω降低至1.417 Ω。在100 mA/cm2的电流放电条件下,FC的放电时长为60 min,碳纸作为DL的放电时长为46 min,FC作为扩散层有更长的放电时间。研究结果说明在相同甲醇浓度以及体积下,新型结构有着比常规结构更高的能量效率。
中图分类号:
赵振刚, 周梦瑶, 金典, 张大骋. 基于泡沫碳扩散层的直接甲醇燃料电池改性研究[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(S1): 259-266.
Zhengang ZHAO, Mengyao ZHOU, Dian JIN, Dacheng ZHANG. Study on direct methanol fuel cell performance modification based on foam carbon diffusion layer[J]. CIESC Journal, 2024, 75(S1): 259-266.
材料 类型 | 厚度/ μm | 电阻率/ (Ω/cm) | 孔隙率/ % | 含碳量/ % |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| TGP-H-060 | 190 | 5.8 | 78 | 99.9 |
| foam carbon | 500 | 6.1×10-4 | 93 | 99.9 |
表1 CP与FC的具体参数
Table 1 Specific parameters of CP and FC
材料 类型 | 厚度/ μm | 电阻率/ (Ω/cm) | 孔隙率/ % | 含碳量/ % |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| TGP-H-060 | 190 | 5.8 | 78 | 99.9 |
| foam carbon | 500 | 6.1×10-4 | 93 | 99.9 |
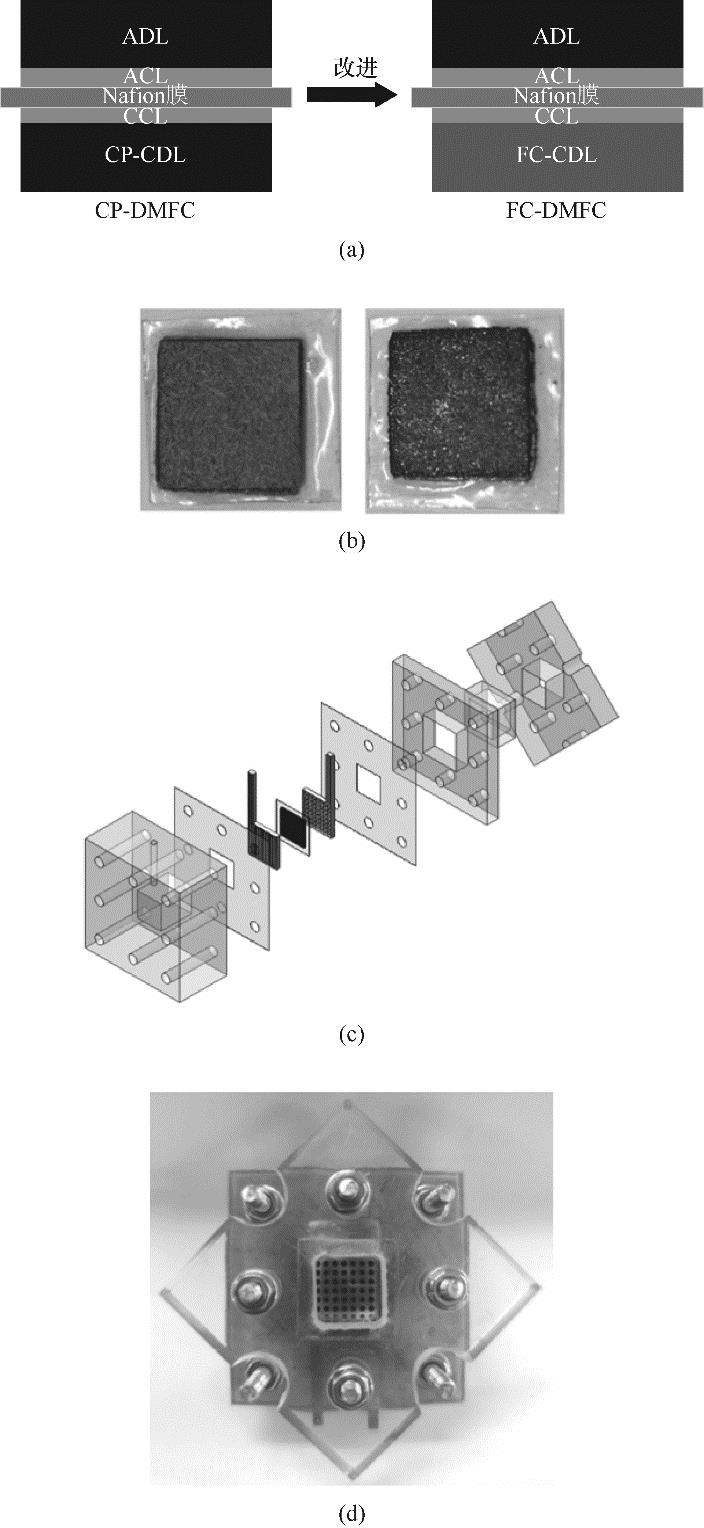
图3 MEA结构示意图(a);CP-MEA和FC-MEA (b);DMFC装配图(c);DMFC实物图(d)
Fig.3 Schematic diagram of MEA (a); CP-MEA, FC-MEA (b); Assembly structural diagram (c); Assembled DMFC (d)
| 甲醇浓度/ (mol/L) | CP-DMFC/(mW/cm2) | FC-DMFC/(mW/cm2) | 提升率/% |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0.5 | 18.48 | 36.00 | 94.81 |
| 1 | 24.47 | 39.24 | 60.36 |
| 2 | 20.65 | 28.71 | 39.03 |
| 3 | 15.06 | 15.58 | 3.45 |
表2 CP-DMFC和FC-DMFC在不同甲醇浓度下的最大功率密度
Table 2 Maximum power density of CP-DMFC and FC-DMFC under different methanol concentrations
| 甲醇浓度/ (mol/L) | CP-DMFC/(mW/cm2) | FC-DMFC/(mW/cm2) | 提升率/% |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0.5 | 18.48 | 36.00 | 94.81 |
| 1 | 24.47 | 39.24 | 60.36 |
| 2 | 20.65 | 28.71 | 39.03 |
| 3 | 15.06 | 15.58 | 3.45 |
| 项目 | CP-DMFC | FC-DMFC | 提升率 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Rm/Ω | 0.588 | 0.494 | -16.0% |
| Ri/Ω | 1.421 | 1.437 | 1.1% |
| Rct/Ω | 2.784 | 1.816 | -34.8% |
| Rmt/Ω | 1.689 | 1.417 | -16.1% |
表3 ECM参数识别结果
Table 3 Parameter identification results
| 项目 | CP-DMFC | FC-DMFC | 提升率 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Rm/Ω | 0.588 | 0.494 | -16.0% |
| Ri/Ω | 1.421 | 1.437 | 1.1% |
| Rct/Ω | 2.784 | 1.816 | -34.8% |
| Rmt/Ω | 1.689 | 1.417 | -16.1% |
| 1 | 郭仕权, 孙亚昕, 李从举. 直接甲醇燃料电池(DMFC)阳极过渡金属基催化剂的研究进展[J]. 工程科学学报, 2022, 44(4): 625-640. |
| Guo S Q, Sun Y X, Li C J. Research progress in anode transition metal-based catalysts for direct methanol fuel cell[J]. Chinese Journal of Engineering, 2022, 44(4): 625-640. | |
| 2 | Chen X Y, Li T C, Shen J N, et al. From structures, packaging to application: a system-level review for micro direct methanol fuel cell[J]. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 2017, 80: 669-678. |
| 3 | 严文锐, 张劲, 王海宁, 等. 重整甲醇高温聚合物电解质膜燃料电池研究进展与展望[J]. 化工进展, 2021, 40(6): 2980-2992. |
| Yan W R, Zhang J, Wang H N, et al. Advancement toward reforming methanol high temperature polymer electrolyte membrane fuel cells[J]. Chemical Industry and Engineering Progress, 2021, 40(6): 2980-2992. | |
| 4 | Su S J, Liang J S, Luo Y, et al. A new water management system for air-breathing direct methanol fuel cell using superhydrophilic capillary network and evaporation wings[J]. Energy Conversion and Management, 2021, 246: 114665. |
| 5 | Abraham B G, Chetty R. Design and fabrication of a quick-fit architecture air breathing direct methanol fuel cell[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2021, 46(9): 6845-6856. |
| 6 | Alias M S, Kamarudin S K, Zainoodin A M, et al. Active direct methanol fuel cell: an overview[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2020, 45(38): 19620-19641. |
| 7 | Wang L W, Yin L, Yang W L, et al. Evaluation of structural aspects and operation environments on the performance of passive micro direct methanol fuel cell[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2021, 46(2): 2594-2605. |
| 8 | Xing L, Shi W D, Su H N, et al. Membrane electrode assemblies for PEM fuel cells: a review of functional graded design and optimization[J]. Energy, 2019, 177: 445-464. |
| 9 | 马小杰, 方卫民. 质子交换膜燃料电池双极板研究进展[J]. 材料导报, 2006, 20(1): 26-30. |
| Ma X J, Fang W M. Research and progress of bipolar plate for proton-exchange membrane fuel cell[J]. Materials Review, 2006, 20(1): 26-30. | |
| 10 | 张立昌, 蔡超, 谭金婷, 等. 质子交换膜燃料电池微孔层在反极过程中的耐久性研究[J]. 材料导报, 2022, 36(14): 67-73. |
| Zhang L C, Cai C, Tan J T, et al. Study on the durability of the microporous layer of proton exchange membrane fuel cell during the voltage reversal process[J]. Materials Reports, 2022, 36(14): 67-73. | |
| 11 | Ali Abdelkareem M, Sayed E T, Nakagawa N. Significance of diffusion layers on the performance of liquid and vapor feed passive direct methanol fuel cells[J]. Energy, 2020, 209: 118492. |
| 12 | Zhao Z G, Wang Z T, Li K, et al. Cathode diffusion layer and current collector with slotted foam stainless steel for a micro direct methanol fuel cell[J]. RSC Advances, 2022, 12(44): 28738-28745. |
| 13 | Rambabu G, Bhat S D, Figueiredo F M L. Carbon nanocomposite membrane electrolytes for direct methanol fuel cells—a concise review[J]. Nanomaterials, 2019, 9(9): 1292. |
| 14 | 高帷韬, 雷一杰, 张勋, 等. 质子交换膜燃料电池研究进展[J]. 化工进展, 2022, 41(3): 1539-1555. |
| Gao W T, Lei Y J, Zhang X, et al. An overview of proton exchange membrane fuel cell[J]. Chemical Industry and Engineering Progress, 2022, 41(3): 1539-1555. | |
| 15 | Ali Abdelkareem M, Sayed E T, Mohamed H O, et al. Nonprecious anodic catalysts for low-molecular-hydrocarbon fuel cells: theoretical consideration and current progress[J]. Progress in Energy and Combustion Science, 2020, 77: 100805. |
| 16 | Tan W C, Saw L H, Thiam H S, et al. Overview of porous media/metal foam application in fuel cells and solar power systems[J]. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 2018, 96: 181-197. |
| 17 | Yuan W, Tang Y, Yang X J, et al. Porous metal materials for polymer electrolyte membrane fuel cells—a review[J]. Applied Energy, 2012, 94: 309-329. |
| 18 | Zhao Z G, Zhang F, Zhang Y H, et al. Performance optimization of μDMFC with foamed stainless steel cathode current collector[J]. Energies, 2021, 14(20): 6608. |
| 19 | Braz B A, Moreira C S, Oliveira V B, et al. Effect of the current collector design on the performance of a passive direct methanol fuel cell[J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2019, 300: 306-315. |
| 20 | Braz B A, Oliveira V B, Pinto A M F R. Experimental studies of the effect of cathode diffusion layer properties on a passive direct methanol fuel cell power output[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2019, 44(35): 19334-19343. |
| 21 | Braz B A, Oliveira V B, Pinto A M F R. Optimization of a passive direct methanol fuel cell with different current collector materials[J]. Energy, 2020, 208: 118394. |
| 22 | Hao W B, Ma H Y, Sun G X, et al. Magnesia phosphate cement composite bipolar plates for passive type direct methanol fuel cells[J]. Energy, 2019, 168: 80-87. |
| 23 | Zhu Y L, Zhang X J, Li J Y, et al. Three-dimensional graphene as gas diffusion layer for micro direct methanol fuel cell[J]. International Journal of Modern Physics B, 2018, 32(12): 1850145. |
| 24 | Zhang X Y, Huang Y X, Zhou X L, et al. Characterizations of carbonized electrospun mats as diffusion layers for direct methanol fuel cells[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2020, 448: 227410. |
| 25 | Alrashidi A, Liu H T. Laser-perforated anode gas diffusion layers for direct methanol fuel cells[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2021, 46(34): 17886-17896. |
| 26 | 朱逸涵. 泡沫碳基柔性自支撑材料的制备及其电化学和微波吸收性能研究[D]. 镇江: 江苏大学, 2022. |
| Zhu Y H. Carbon foam-based flexible self-standing materials: synthesis, electrochemical and microwave absorbing properties[D]. Zhenjiang: Jiangsu University, 2022. | |
| 27 | 闫涛. 三维泡沫碳材料的制备、改性及其电化学性能研究[D]. 天津: 天津大学, 2020. |
| Yan T. Preparation, modification and electrochemical performance of threedimensional carbon foams[D]. Tianjin: Tianjin University, 2020. | |
| 28 | Zhu Y H, Wang D F, Yan X H, et al. Rational design for Mn3O4@carbon foam nanocomposite with 0D@3D structure for boosting electrochemical performance[J]. Energy & Fuels, 2020, 34(11): 14924-14933. |
| 29 | Zhu Y H, Wang D F, Yan X H, et al. Vertical, dense and uniform V2O5 nanoneedle arrays on carbon foam for boosting electrochemical performance[J]. Journal of Energy Storage, 2021, 37: 102492. |
| 30 | Okech G, Emam M, Mori S, et al. Enhancing the performance of direct methanol fuel cells using new cathode flow field designs: an experimental investigation[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2024, 57: 161-175. |
| 31 | Okech G, Emam M, Mori S, et al. Experimental study on the effect of new anode flow field designs on the performance of direct methanol fuel cells[J]. Energy Conversion and Management, 2024, 301: 117988. |
| 32 | Li Y, Zhang X L, Nie L, et al. Stainless steel fiber felt as cathode diffusion backing and current collector for a micro direct methanol fuel cell with low methanol crossover[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2014, 245: 520-528. |
| 33 | 李洋. 金属基微型直接甲醇燃料电池关键技术研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学, 2019. |
| Li Y. Research on the key technologies of metal based micro direct methanol fuel cell[D]. Harbin: Harbin Institute of Technology, 2019. | |
| 34 | Yuan T, Zou Z Q, Chen M, et al. New anodic diffusive layer for passive micro-direct methanol fuel cell[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2009, 192(2): 423-428. |
| [1] | 陈森洋, 靳蒲航, 谭志明, 谢公南. 质子交换膜燃料电池中蛇形流道液滴运动数值仿真研究[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(S1): 183-194. |
| [2] | 徐英宇, 杨国强, 彭璟, 孙海宁, 张志炳. 微界面高级氧化处理煤化工废水的研究[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(S1): 283-291. |
| [3] | 李雨霜, 王兴成, 温伯尧, 骆政园, 白博峰. 多孔介质中乳状液驱油的两相流动过程及其影响因素[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(S1): 56-66. |
| [4] | 刘律, 刘洁茹, 范亮亮, 赵亮. 基于层流效应的被动式颗粒分离微流控方法研究[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(S1): 67-75. |
| [5] | 杜得辉, 冯威, 张江辉, 项燕龙, 乔高攀, 李蔚. 微型翅片疏水复合强化管管内流动沸腾换热预测模型[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(S1): 95-107. |
| [6] | 祝赫, 张仪, 齐娜娜, 张锴. 欧拉-欧拉双流体模型中颗粒黏性对液固散式流态化的影响[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(9): 3103-3112. |
| [7] | 唐昊, 胡定华, 李强, 张轩畅, 韩俊杰. 抗加速度双切线弧流道内气泡动力学行为数值与可视化研究[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(9): 3074-3082. |
| [8] | 王皓宇, 杨杨, 荆文婕, 杨斌, 唐雨, 刘毅. 不同旋流器作用下气液螺旋环状流动特性研究[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(8): 2744-2755. |
| [9] | 赵亮, 李雨桥, 张德, 沈胜强. 螺旋喷嘴内外流场特性的实验研究[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(8): 2777-2786. |
| [10] | 罗正航, 李敬宇, 陈伟雄, 种道彤, 严俊杰. 摇摆运动下低流率蒸汽冷凝换热特性和气泡受力数值模拟[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(8): 2800-2811. |
| [11] | 王倩倩, 李冰, 郑伟波, 崔国民, 赵兵涛, 明平文. 氢燃料电池局部动态特征三维模型[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(8): 2812-2820. |
| [12] | 曲玖哲, 杨鹏, 杨绪飞, 张伟, 宇波, 孙东亮, 王晓东. 硅基微柱簇阵列微通道流动沸腾实验研究[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(8): 2840-2851. |
| [13] | 李彦熹, 王晔春, 谢向东, 王进芝, 王江, 周煜, 潘盈秀, 丁文涛, 郭烈锦. 蜗壳式多通道气液旋流分离器结构优化及分离特性研究[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(8): 2875-2885. |
| [14] | 吕方明, 包志铭, 王博文, 焦魁. 气体扩散层侵入流道对燃料电池水管理影响研究[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(8): 2929-2938. |
| [15] | 朱楼, 宋杨凡, 王猛, 施睿鹏, 厉彦民, 陈鸿伟, 刘卓, 魏翔. 中心脉冲气-液-固循环流化床微生物燃料电池产电特性[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(8): 2991-3001. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备 11010102001995号
京公网安备 11010102001995号