化工学报 ›› 2021, Vol. 72 ›› Issue (S1): 453-460.DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20201517
收稿日期:2020-10-29
修回日期:2021-01-15
出版日期:2021-06-20
发布日期:2021-06-20
通讯作者:
林文胜
作者简介:何婷(1995—),女,博士研究生,Received:2020-10-29
Revised:2021-01-15
Online:2021-06-20
Published:2021-06-20
Contact:
LIN Wensheng
摘要:
沼气以及CO2驱采油的伴生气中都含有大量的CO2。为降低高含CO2天然气液化的能耗,提出了活化甲基二乙醇胺(MDEA)法脱除CO2的天然气液化系统,将液化厂中驱动压缩机的燃气轮机烟气余热用于吸收剂的再生过程,实现能耗的降低。采用HYSYS软件对系统进行了模拟研究并对脱碳过程的关键参数进行了分析。结果表明,CO2含量不超过10%时,脱碳再生的热耗可全部由烟气余热提供,CO2含量为30%时,烟气余热可提供接近50%的再生热耗;CO2含量为1%~30%时,系统的比功耗为0.577~0.611 kW·h/kg。
中图分类号:
何婷, 林文胜. 基于余热利用的活化MDEA法脱除CO2的天然气液化系统[J]. 化工学报, 2021, 72(S1): 453-460.
HE Ting, LIN Wensheng. Natural gas liquefaction system with activated MDEA method for CO2 removal based on waste heat utilization[J]. CIESC Journal, 2021, 72(S1): 453-460.
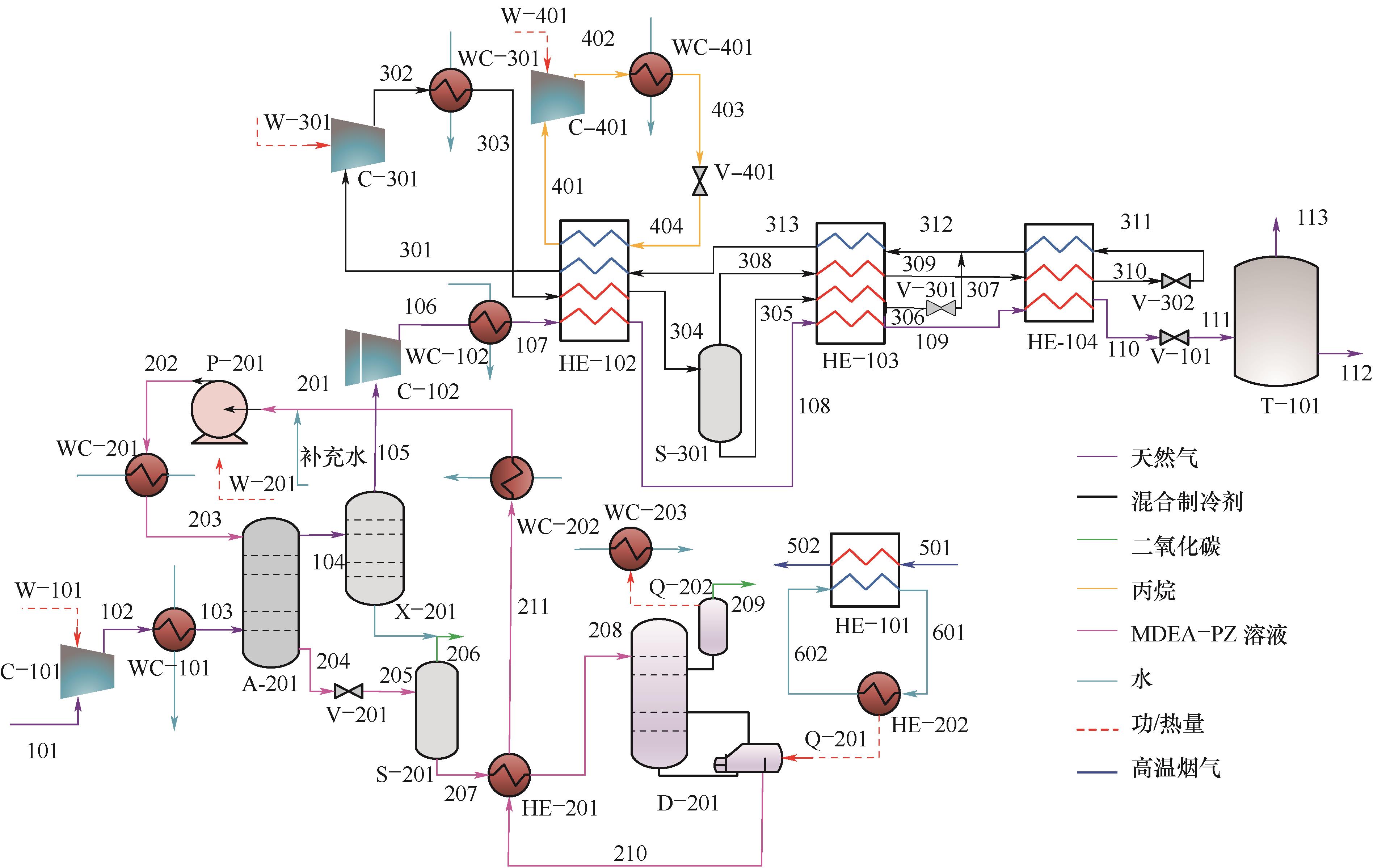
图1 基于余热利用的化学吸收法脱除CO2的天然气液化系统A—吸收塔;C—压缩机;D—再生塔;HE—换热器;P—泵;Q—热量;S—气液分离器;T—储罐;V—阀;W—功;WC—水冷器;X—组分分离器
Fig.1 Natural gas liquefaction system with chemical absorption method for CO2 removal based on waste heat utilization
| Parameters | Lower bound | Upper bound |
|---|---|---|
| N301-C1/(kmol/h) | 3000 | 4000 |
| N301-C2/(kmol/h) | 3000 | 4000 |
| N301-C3/(kmol/h) | 800 | 1200 |
| N301-C4/(kmol/h) | 200 | 600 |
| N301-N2/(kmol/h) | 300 | 800 |
| p302/kPa | 2000 | 3500 |
| T310/℃ | -150 | -130 |
| T306/℃ | -100 | -80 |
| T304/℃ | -45 | -20 |
| N401/(kmol/h) | 3000 | 7000 |
| p402/kPa | 1000 | 1800 |
表1 优化参数的上下限
Table 1 Upper and lower bounds of parameters to be optimized
| Parameters | Lower bound | Upper bound |
|---|---|---|
| N301-C1/(kmol/h) | 3000 | 4000 |
| N301-C2/(kmol/h) | 3000 | 4000 |
| N301-C3/(kmol/h) | 800 | 1200 |
| N301-C4/(kmol/h) | 200 | 600 |
| N301-N2/(kmol/h) | 300 | 800 |
| p302/kPa | 2000 | 3500 |
| T310/℃ | -150 | -130 |
| T306/℃ | -100 | -80 |
| T304/℃ | -45 | -20 |
| N401/(kmol/h) | 3000 | 7000 |
| p402/kPa | 1000 | 1800 |
| Flow | T/℃ | p/kPa | Molar flow/(kmol/h) | CO2 content/% | CH4 content/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 101 | 40 | 101 | 7200 | 10 | 90 |
| 103 | 40 | 1500 | 7200 | 10 | 90 |
| 104 | 40.03 | 1440 | 6473 | 0 | 99.56 |
| 201 | 40 | 150 | 16869 | 0.01 | 0 |
| 203 | 40 | 1440 | 16869 | 0.01 | 0 |
| 204 | 67.95 | 1500 | 17564 | 4.03 | 0.03 |
| 205 | 67.91 | 200 | 17564 | 4.03 | 0.03 |
| 208 | 85 | 200 | 17549 | 4.02 | 0 |
| 210 | 113.2 | 150 | 16790 | 0.01 | 0 |
| 211 | 89 | 150 | 16790 | 0.01 | 0 |
| 501 | 600 | 120 | 9410 | — | — |
| 502 | 176 | 120 | 9410 | — | — |
| 601 | 100 | 200 | 6000 | — | — |
| 602 | 120.2 | 200 | 6000 | — | — |
表2 净化段节点参数
Table 2 Node parameters of purification section
| Flow | T/℃ | p/kPa | Molar flow/(kmol/h) | CO2 content/% | CH4 content/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 101 | 40 | 101 | 7200 | 10 | 90 |
| 103 | 40 | 1500 | 7200 | 10 | 90 |
| 104 | 40.03 | 1440 | 6473 | 0 | 99.56 |
| 201 | 40 | 150 | 16869 | 0.01 | 0 |
| 203 | 40 | 1440 | 16869 | 0.01 | 0 |
| 204 | 67.95 | 1500 | 17564 | 4.03 | 0.03 |
| 205 | 67.91 | 200 | 17564 | 4.03 | 0.03 |
| 208 | 85 | 200 | 17549 | 4.02 | 0 |
| 210 | 113.2 | 150 | 16790 | 0.01 | 0 |
| 211 | 89 | 150 | 16790 | 0.01 | 0 |
| 501 | 600 | 120 | 9410 | — | — |
| 502 | 176 | 120 | 9410 | — | — |
| 601 | 100 | 200 | 6000 | — | — |
| 602 | 120.2 | 200 | 6000 | — | — |
| Flow | T/℃ | p/kPa | Molar flow/(kmol/h) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 105 | 40 | 1400 | 6473 |
| 107 | 40 | 5000 | 6473 |
| 108 | -35 | 5000 | 6473 |
| 109 | -112 | 5000 | 6473 |
| 110 | -162.5 | 5000 | 6473 |
| 111 | -160.7 | 110 | 6473 |
| 301 | 37 | 120 | 8682 |
| 303 | 40 | 3000 | 8682 |
| 304 | -34 | 3000 | 8682 |
| 306 | -94 | 3000 | 5416 |
| 307 | -114.3 | 120 | 5416 |
| 310 | -145 | 3000 | 3266 |
| 311 | -165.6 | 120 | 3266 |
| 401 | 35.19 | 120 | 5289 |
| 403 | 40 | 1380 | 5289 |
| 404 | -38.25 | 120 | 5289 |
表3 液化段节点参数
Table 3 Node parameters of liquefaction section
| Flow | T/℃ | p/kPa | Molar flow/(kmol/h) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 105 | 40 | 1400 | 6473 |
| 107 | 40 | 5000 | 6473 |
| 108 | -35 | 5000 | 6473 |
| 109 | -112 | 5000 | 6473 |
| 110 | -162.5 | 5000 | 6473 |
| 111 | -160.7 | 110 | 6473 |
| 301 | 37 | 120 | 8682 |
| 303 | 40 | 3000 | 8682 |
| 304 | -34 | 3000 | 8682 |
| 306 | -94 | 3000 | 5416 |
| 307 | -114.3 | 120 | 5416 |
| 310 | -145 | 3000 | 3266 |
| 311 | -165.6 | 120 | 3266 |
| 401 | 35.19 | 120 | 5289 |
| 403 | 40 | 1380 | 5289 |
| 404 | -38.25 | 120 | 5289 |
| CO2 content/% | Regeneration heat load /(kJ/m3) | Net regeneration heat load/(kJ/m3) | Purification power consumption/(kW·h/m3) | w/(kW·h/kg) | α/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 140.19 | 0 | 0.096 | 0.577 | 25.1 |
| 10 | 828.99 | 0 | 0.087 | 0.584 | 84.9 |
| 30 | 2116.19 | 1092.5 | 0.099 | 0.611 | 92.0 |
表4 系统的能量消耗
Table 4 Energy consumption of system
| CO2 content/% | Regeneration heat load /(kJ/m3) | Net regeneration heat load/(kJ/m3) | Purification power consumption/(kW·h/m3) | w/(kW·h/kg) | α/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 140.19 | 0 | 0.096 | 0.577 | 25.1 |
| 10 | 828.99 | 0 | 0.087 | 0.584 | 84.9 |
| 30 | 2116.19 | 1092.5 | 0.099 | 0.611 | 92.0 |
| Upgrading technologies | CH4 purity (vol)/% | Energy consumption (kW·h/m3 of raw biogas) | H2S/water pre-upgrading | Additional heat |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| water scrubbing + regeneration | 97 (93—99) | 0.3 (0.2—0.46) | necessary | not necessary |
| physical absorption | 97 (95—99) | 0.25 (0.2—0.3) | necessary | necessary |
| chemical absorption | 98 (97—99) | 0.4 (0.3—0.8) | not necessary | necessary |
| pressure swing absorption | 97 (95—99) | 0.25 (0.2—0.3) | necessary | not necessary |
| membrane technology | 95 (80—99) | 0.3 (0.15—0.43) | not necessary | not necessary |
表5 不同沼气净化技术的特点[29]
Table 5 Characteristics of different biogas upgrading technologies[29]
| Upgrading technologies | CH4 purity (vol)/% | Energy consumption (kW·h/m3 of raw biogas) | H2S/water pre-upgrading | Additional heat |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| water scrubbing + regeneration | 97 (93—99) | 0.3 (0.2—0.46) | necessary | not necessary |
| physical absorption | 97 (95—99) | 0.25 (0.2—0.3) | necessary | necessary |
| chemical absorption | 98 (97—99) | 0.4 (0.3—0.8) | not necessary | necessary |
| pressure swing absorption | 97 (95—99) | 0.25 (0.2—0.3) | necessary | not necessary |
| membrane technology | 95 (80—99) | 0.3 (0.15—0.43) | not necessary | not necessary |
| CO2 content/% | Circulation amine /(kmol/h) | η/% | Replenish solvent water /(kmol/h) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 4035 | 0.03 | 46 |
| 10 | 16870 | 0.11 | 56 |
| 30 | 45682 | 0.28 | 70 |
表6 系统的物质消耗
Table 6 Material consumption of the system
| CO2 content/% | Circulation amine /(kmol/h) | η/% | Replenish solvent water /(kmol/h) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 4035 | 0.03 | 46 |
| 10 | 16870 | 0.11 | 56 |
| 30 | 45682 | 0.28 | 70 |
| 1 | 程序, 崔宗均, 朱万斌. 论另类非常规天然气: 生物天然气的开发[J]. 天然气工业, 2013, 33(1): 137-144. |
| Cheng X, Cui Z J, Zhu W B. A discussion on the exploitation of biogas: another kind of unconventional natural gas resources [J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2013, 33(1): 137-144. | |
| 2 | Kárászová M, Sedláková Z, Izák P. Gas permeation processes in biogas upgrading: a short review [J]. Chemical Papers, 2015, 69(10): 1277-1283. |
| 3 | 赵洪坤. CO2驱采油技术研究与应用现状[J]. 中国石油和化工标准与质量, 2016, 36(16): 99, 102. |
| Zhao H K. Research and application status of CO2 flooding oil recovery technology [J]. China Petroleum and Chemical Standard and Quality, 2016, 36(16): 99, 102. | |
| 4 | 陈小华. 浅述二氧化碳驱油技术应用现状[J]. 中国石油和化工标准与质量, 2019, 39(12): 43-44, 46. |
| Chen X H. Brief introduction to the application status of carbon dioxide flooding technology [J]. China Petroleum and Chemical Standard and Quality, 2019, 39(12): 43-44, 46. | |
| 5 | 马鹏飞, 韩波, 张亮, 等. 油田CO2驱产出气处置方案及CO2捕集回注工艺[J]. 化工进展, 2017, 36(S1): 533-539. |
| Ma P F, Han B, Zhang L, et al. Disposal scheme of produced gas and CO2 capture for re-injection in CO2 EOR [J]. Chemical Industry and Engineering Progress, 2017, 36(S1): 533-539. | |
| 6 | 周淑霞. 沼气液化制取生物质LNG关键技术研究[D]. 济南: 山东大学, 2012. |
| Zhou S X. Research on key technologies on liquefied production of biomass LNG from biogas [D]. Jinan: Shandong University, 2012. | |
| 7 | 袁青, 刘音, 毕研霞, 等. 油气田开发中CO2腐蚀机理及防腐方法研究进展[J]. 天然气与石油, 2015, 33(2): 78-81, 13. |
| Yuan Q, Liu Y, Bi Y X, et al. Research on CO2 corrosion and corrosion control method in oil and gas field development [J]. Natural Gas and Oil, 2015, 33(2): 78-81, 13. | |
| 8 | 王玉柱, 蒋洪, 赵建彬, 等. 天然气回收乙烷中二氧化碳固体形成的防控措施[J]. 天然气化工(C1化学与化工), 2020, 45(2): 106-112. |
| Wang Y Z, Jiang H, Zhao J B, et al. Prevention and control measures of carbon dioxide solid formation in ethane recovery from natural gas [J]. Natural Gas Chemical Industry, 2020, 45(2): 106-112. | |
| 9 | 常学煜, 李玉星, 张盈盈, 等. 天然气脱酸工艺参数优化及节能研究[J]. 天然气化工(C1化学与化工), 2017, 42(3): 67-72, 92. |
| Chang X Y, Li Y X, Zhang Y Y, et al. Optimization of process parameters and energy-saving research for natural gas deacidification process [J]. Natural Gas Chemical Industry, 2017, 42(3): 67-72, 92. | |
| 10 | 李超伟, 仵浩, 范良忠. 两种物理吸收法在沼气脱碳中的模拟对比研究[J]. 可再生能源, 2012, 30(9): 75-79. |
| Li C W, Wu H, Fan L Z. Comparative study of two physical absorption method in the simulation of biogas decarbonization [J]. Renewable Energy Resources, 2012, 30(9): 75-79. | |
| 11 | Liu Z, Green W H. Experimental investigation of sorbent for warm CO2 capture by pressure swing adsorption [J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2013, 52(28): 9665-9673. |
| 12 | Awad A, Aljundi I H. Layer-by-layer assembly of carbide derived carbon-polyamide membrane for CO2 separation from natural gas [J]. Energy, 2018, 157: 188-199. |
| 13 | Berstad D, Nekså P, Anantharaman R. Low-temperature CO2 removal from natural gas [J]. Energy Procedia, 2012, 26: 41-48. |
| 14 | 万宇飞, 邓骁伟, 程涛, 等. 不同含碳量天然气脱碳方案选择[J]. 油气田环境保护, 2013, 23(3): 56-58, 75. |
| Wan Y F, Deng X W, Cheng T, et al. Decarbonization scheme selection for natural gas with different carbon content [J]. Environmental Protection of Oil & Gas Fields, 2013, 23(3): 56-58, 75. | |
| 15 | Yang H Q, Xu Z H, Fan M H, et al. Progress in carbon dioxide separation and capture: a review [J]. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 2008, 20(1): 14-27. |
| 16 | Banat F, Younas O, Didarul I. Energy and exergical dissection of a natural gas sweetening plant using methyldiethanol amine (MDEA) solution [J]. Journal of Natural Gas Science and Engineering, 2014, 16: 1-7. |
| 17 | Moioli S, Giuffrida A, Romano M C, et al. Assessment of MDEA absorption process for sequential H2S removal and CO2 capture in air-blown IGCC plants [J]. Applied Energy, 2016, 183: 1452-1470. |
| 18 | 陈杰, 郭清, 花亦怀, 等. MDEA+MEA/DEA混合胺液脱碳性能试验研究[J]. 天然气工业, 2014, 34(5): 137-143. |
| Chen J, Guo Q, Hua Y H, et al. An experimental study of absorption and desorption of blended amine solutions MDEA+MEA/DEA for natural gas decarburization [J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2014, 34(5): 137-143. | |
| 19 | 陈颖, 赵越超, 梁宏宝, 等. 以MDEA为主体的混合胺溶液吸收CO2研究进展[J]. 应用化工, 2014, 43(3): 531-534, 538. |
| Chen Y, Zhao Y C, Liang H B, et al. Progress in CO2 absorption using active MDEA based aqueous solutions [J]. Applied Chemical Industry, 2014, 43(3): 531-534, 538. | |
| 20 | Privalova E, Rasi S, Mäki-Arvela P, et al. CO2 capture from biogas: absorbent selection [J]. RSC Advances, 2013, 3(9): 2979-2994. |
| 21 | 张磊, 蒋洪. 高含CO2天然气脱碳工艺中MDEA活化剂优选[J]. 石油与天然气化工, 2017, 46(4): 22-29. |
| Zhang L, Jiang H. MDEA activator optimization for decarbonization process of high CO2-containing natural gas [J]. Chemical Engineering of Oil & Gas, 2017, 46(4): 22-29. | |
| 22 | Hajji A, Chahartaghi M, Kahani M. Thermodynamic analysis of natural gas liquefaction process with propane pre-cooled mixed refrigerant process (C3MR) [J]. Cryogenics, 2019, 103: 102978. |
| 23 | IGU. IGU 2019 World LNG Report [R]. Barcelona: IGU, [2019-06-07]. https://igu.org/resources/igu-world-lng-report-2019/. |
| 24 | 李泽伟, 周明亮, 杨磊, 等. 余热利用技术在陆梁油田的应用[J]. 油气田环境保护, 2015, 25(5): 49-51, 92. |
| Li Z W, Zhou M L, Yang L, et al. Application of waste heat utilization technology in Luliang oilfield [J]. Environmental Protection of Oil & Gas Fields, 2015, 25(5): 49-51, 92. | |
| 25 | Franco A, Vaccaro M. A combined energetic and economic approach for the sustainable design of geothermal plants [J]. Energy Conversion and Management, 2014, 87: 735-745. |
| 26 | Varga Z, Csaba T. Techno-economic evaluation of waste heat recovery by organic Rankine cycle using pure light hydrocarbons and their mixtures as working fluid in a crude oil refinery [J]. Energy Conversion and Management, 2018, 174: 793-801. |
| 27 | Chan C W, Ling-Chin J, Roskilly A P. A review of chemical heat pumps, thermodynamic cycles and thermal energy storage technologies for low grade heat utilisation [J]. Applied Thermal Engineering, 2013, 50(1): 1257-1273. |
| 28 | Singh B K, Shrivastava N. Exhaust gas heat recovery for C. I. engine — a review [J]. IJESRT Journal, 2014, 4(5): 14-19. |
| 29 | Baccioli A, Antonelli M, Frigo S, et al. Small scale bio-LNG plant: comparison of different biogas upgrading techniques [J]. Applied Energy, 2018, 217: 328-335. |
| 30 | Lawal A O, Idem R O. Kinetics of the oxidative degradation of CO2 loaded and concentrated aqueous MEA-MDEA blends during CO2 absorption from flue gas streams [J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2006, 45(8): 2601-2607. |
| [1] | 杨天阳, 邹慧明, 周晖, 王春磊, 田长青. -30℃电动汽车补气式CO2热泵制热性能实验研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(S1): 272-279. |
| [2] | 代宝民, 王启龙, 刘圣春, 张佳宁, 李鑫海, 宗凡迪. 非共沸工质辅助过冷CO2冷热联供系统的热力学性能分析[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(S1): 64-73. |
| [3] | 陈美思, 陈威达, 李鑫垚, 李尚予, 吴有庭, 张锋, 张志炳. 硅基离子液体微颗粒强化气体捕集与转化的研究进展[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(9): 3628-3639. |
| [4] | 张瑞航, 曹潘, 杨锋, 李昆, 肖朋, 邓春, 刘蓓, 孙长宇, 陈光进. ZIF-8纳米流体天然气乙烷回收工艺的产品纯度关键影响因素分析[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(8): 3386-3393. |
| [5] | 牛超, 沈胜强, 杨艳, 潘泊年, 李熠桥. 甲烷BOG喷射器流动过程计算与性能分析[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(7): 2858-2868. |
| [6] | 李贵贤, 曹阿波, 孟文亮, 王东亮, 杨勇, 周怀荣. 耦合固体氧化物电解槽的CO2制甲醇过程设计与评价研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(7): 2999-3009. |
| [7] | 孙永尧, 高秋英, 曾文广, 王佳铭, 陈艺飞, 周永哲, 贺高红, 阮雪华. 面向含氮油田伴生气提质利用的膜耦合分离工艺设计优化[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(5): 2034-2045. |
| [8] | 李明川, 樊栓狮, 徐赋海, 卢惠东, 李晓军. 水合物热分解Stefan相变模型解的存在性及Laplace变换求解[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(4): 1746-1754. |
| [9] | 杨灿, 孙雪琦, 尚明华, 张建, 张香平, 曾少娟. 相变离子液体体系吸收分离CO2的研究现状及展望[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(4): 1419-1432. |
| [10] | 陈俊先, 姬忠礼, 赵瑜, 张倩, 周岩, 刘猛, 刘震. 基于微波技术的天然气管道内颗粒物在线检测方法研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(3): 1042-1053. |
| [11] | 何万媛, 陈一宇, 朱春英, 付涛涛, 高习群, 马友光. 阵列凸起微通道内气液两相传质特性研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(2): 690-697. |
| [12] | 王峰, 张顺鑫, 余方博, 刘亚, 郭烈锦. 光催化CO2还原制碳氢燃料系统优化策略研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(1): 29-44. |
| [13] | 党迎喜, 谈朋, 刘晓勤, 孙林兵. 辐射冷却和太阳能加热驱动的CO2变温捕获[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(1): 469-478. |
| [14] | 杨克, 王辰升, 纪虹, 郑凯, 邢志祥, 毕海普, 蒋军成. 聚多巴胺包覆混合粉体抑制甲烷爆炸的实验研究[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(9): 4245-4254. |
| [15] | 裴仁花, 王永洪, 张新儒, 李晋平. 碳纳米管/环糊精金属有机骨架协同强化混合基质膜的CO2分离[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(9): 3904-3914. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备 11010102001995号
京公网安备 11010102001995号
