化工学报 ›› 2022, Vol. 73 ›› Issue (7): 3057-3067.DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20220329
朱江伟1( ),马鹏飞1(
),马鹏飞1( ),杜晓1,杨言言2,郝晓刚1(
),杜晓1,杨言言2,郝晓刚1( ),罗善霞3
),罗善霞3
收稿日期:2022-03-03
修回日期:2022-05-19
出版日期:2022-07-05
发布日期:2022-08-01
通讯作者:
马鹏飞,郝晓刚
作者简介:朱江伟(1997—),男,硕士研究生,基金资助:
Jiangwei ZHU1( ),Pengfei MA1(
),Pengfei MA1( ),Xiao DU1,Yanyan YANG2,Xiaogang HAO1(
),Xiao DU1,Yanyan YANG2,Xiaogang HAO1( ),Shanxia LUO3
),Shanxia LUO3
Received:2022-03-03
Revised:2022-05-19
Online:2022-07-05
Published:2022-08-01
Contact:
Pengfei MA,Xiaogang HAO
摘要:
磷是一种不可再生资源。为解决现有磷污染以及磷资源流失等问题,通过油浴与热化学还原相结合的方法,成功制备出一种NiFe-LDH/rGO电活性杂化膜材料。使用电化学方法,在氧化还原电位的控制下,Ni、Fe(Ⅱ/Ⅲ)双金属发生核外电子的跃迁,高价态的Ni、Fe(Ⅲ)与
中图分类号:
朱江伟, 马鹏飞, 杜晓, 杨言言, 郝晓刚, 罗善霞. 基于可变价NiFe-LDH/rGO对磷酸根离子的特异性电控分离[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(7): 3057-3067.
Jiangwei ZHU, Pengfei MA, Xiao DU, Yanyan YANG, Xiaogang HAO, Shanxia LUO. Specific electronically controlled separation of phosphate anions based on variable valence NiFe-LDH/rGO[J]. CIESC Journal, 2022, 73(7): 3057-3067.
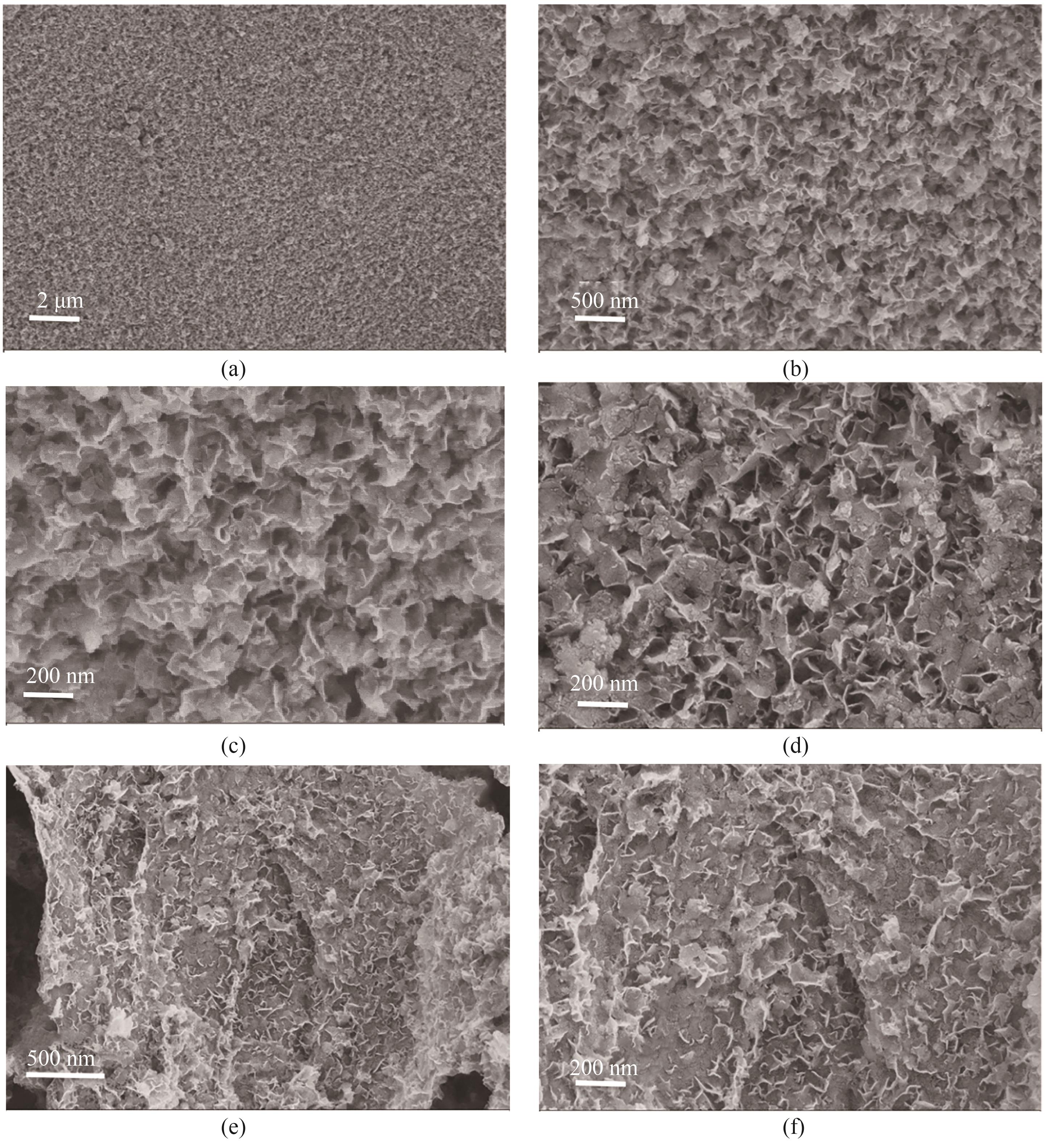
图1 (a)~(c) 不同放大倍数下LDH的SEM图; (d) LDH/GO杂化材料的SEM图; (e)、(f)不同放大倍数下LDH/rGO杂化材料的SEM图
Fig.1 (a)—(c) SEM images of LDH at different magnification; (d) SEM image of LDH/GO hybrid matrials;(e), (f) SEM images of LDH/rGO hybrid matrials at different magnification
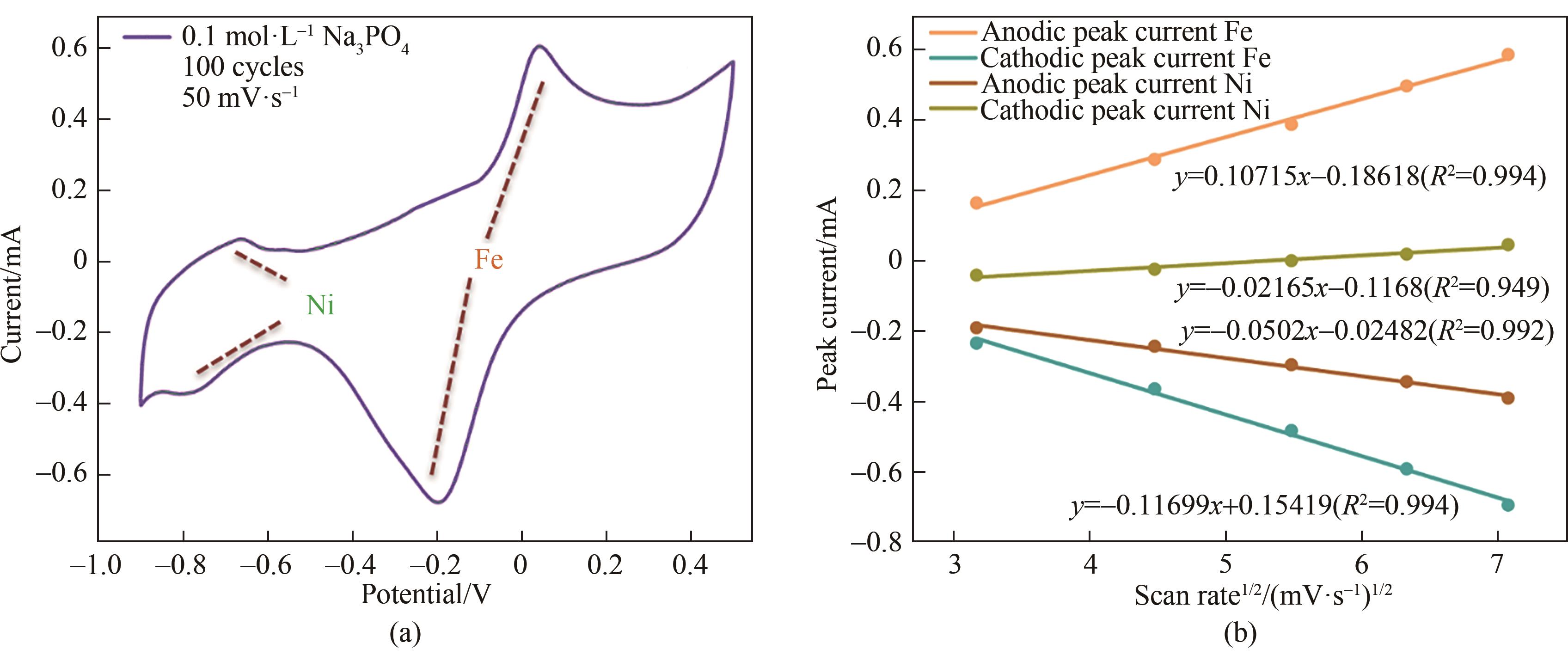
图3 (a) 0.1 mol·L-1 Na3PO4溶液中NiFe-LDH/rGO杂化膜在50 mV·s-1扫速下的CV曲线; (b) 0.1 mol·L-1 Na3PO4溶液中NiFe-LDH/rGO杂化膜阳极和阴极峰值电流随扫速平方根的变化规律
Fig.3 (a) CV curves of NiFe-LDH/rGO hybrid films in 0.1 mol·L-1 Na3PO4 solution at 50 mV·s-1; (b) The variation of anode and cathode peak current of the NiFe-LDH /rGO hybrid film with the square root of scanning speed in 0.1 mol·L-1 Na3PO4 solution
| I/mA | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ni(阳极) | Ni(阴极) | Fe(阳极) | Fe(阴极) | ||
| 10 | 3.162 | 0.167 | -0.232 | -0.038 | -0.188 |
| 20 | 4.472 | 0.291 | -0.362 | -0.021 | -0.241 |
| 30 | 5.477 | 0.390 | -0.481 | 0.002 | -0.294 |
| 40 | 6.324 | 0.500 | -0.590 | 0.020 | -0.342 |
| 50 | 7.071 | 0.589 | -0.693 | 0.047 | -0.389 |
表1 0.1 mol·L-1 Na3PO4溶液中不同扫速对应的阴、阳极峰值电流
Table 1 Cathodic and anodic peak currents corresponding to different scanning rates in 0.1 mol·L-1 Na3PO4 solution
| I/mA | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ni(阳极) | Ni(阴极) | Fe(阳极) | Fe(阴极) | ||
| 10 | 3.162 | 0.167 | -0.232 | -0.038 | -0.188 |
| 20 | 4.472 | 0.291 | -0.362 | -0.021 | -0.241 |
| 30 | 5.477 | 0.390 | -0.481 | 0.002 | -0.294 |
| 40 | 6.324 | 0.500 | -0.590 | 0.020 | -0.342 |
| 50 | 7.071 | 0.589 | -0.693 | 0.047 | -0.389 |
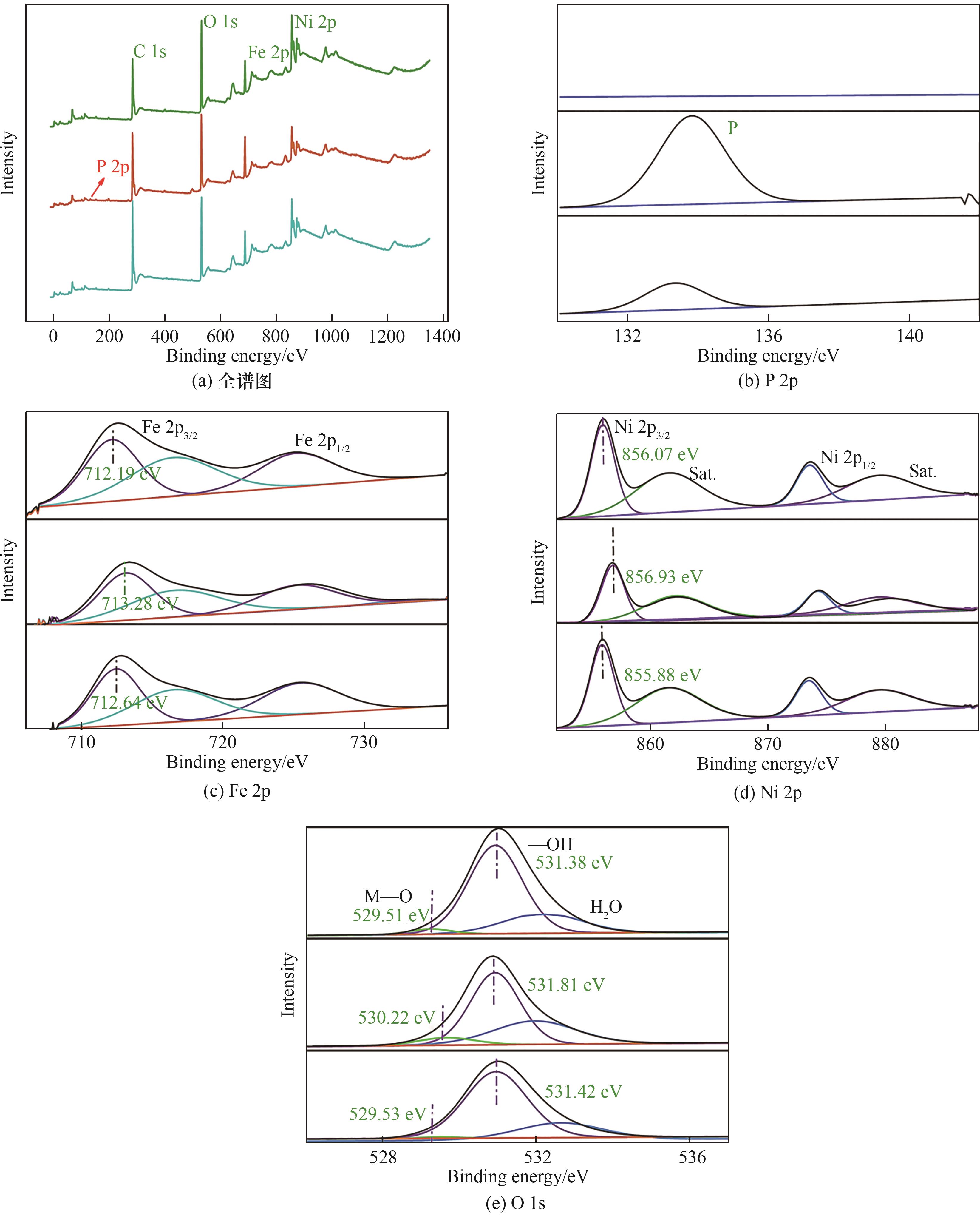
图4 0.1 mol·L-1 Na3PO4溶液中NiFe-LDH/rGO杂化膜在初始(上)、氧化(中)与还原(下)状态时的XPS谱图
Fig.4 XPS spectra of NiFe-LDH/rGO hybrid film in 0.1 mol·L-1 Na3PO4 solution at initial (top), oxidation (middle) and reduction (bottom) states
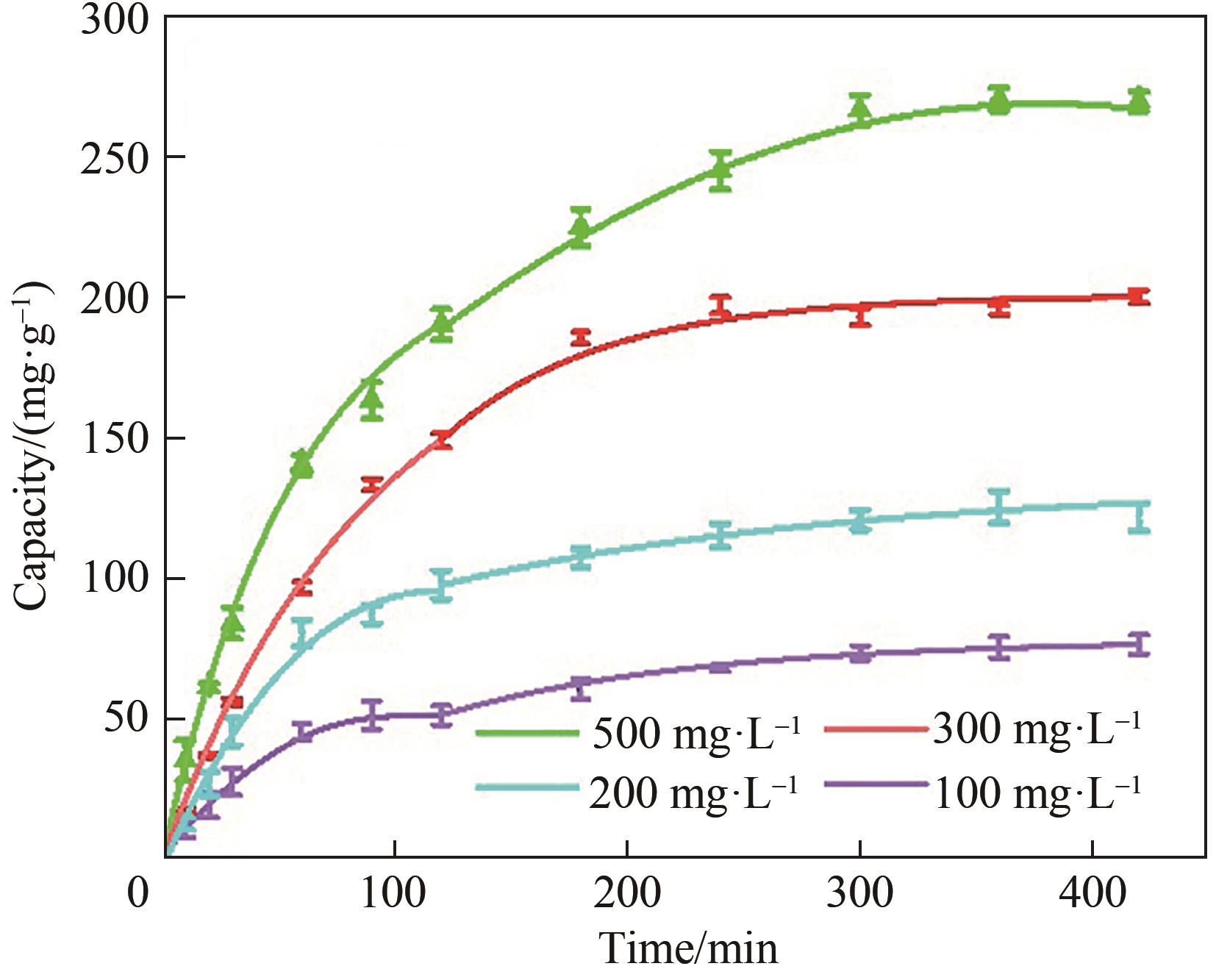
图5 不同初始浓度下NiFe-LDH/rGO杂化膜对PO43-的吸附容量
Fig.5 The adsorption capacity of NiFe-LDH/rGO hybrid films for phosphate anionsat different initial concentrations
| C0/(mg·L-1) | qe(exp)/( mg·g-1) | Pseudo-first-order | Pseudo-second-order | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| k1/min-1 | qe(cal)/( mg·g-1) | R2 | k2/min-1 | qe(cal)/(mg·g-1) | R2 | ||
| 101.58 | 76.35 | 0.011 | 60.138 | 0.948 | 1.55×10-4 | 90.090 | 0.997 |
| 192.72 | 121.74 | 0.017 | 105.047 | 0.866 | 8.87×10-5 | 149.477 | 0.986 |
| 301.93 | 200.18 | 0.018 | 174.493 | 0.971 | 4.38×10-5 | 236.967 | 0.996 |
| 512.36 | 269.68 | 0.012 | 265.219 | 0.966 | 4.57×10-5 | 282.486 | 0.996 |
表2 不同浓度下NiFe-LDH/rGO杂化膜对PO43-的动力学模型参数和相关因子
Table 2 Kinetic model parameters and related factors of phosphate anions induced by NiFe-LDH/rGO hybrid film at different concentrations
| C0/(mg·L-1) | qe(exp)/( mg·g-1) | Pseudo-first-order | Pseudo-second-order | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| k1/min-1 | qe(cal)/( mg·g-1) | R2 | k2/min-1 | qe(cal)/(mg·g-1) | R2 | ||
| 101.58 | 76.35 | 0.011 | 60.138 | 0.948 | 1.55×10-4 | 90.090 | 0.997 |
| 192.72 | 121.74 | 0.017 | 105.047 | 0.866 | 8.87×10-5 | 149.477 | 0.986 |
| 301.93 | 200.18 | 0.018 | 174.493 | 0.971 | 4.38×10-5 | 236.967 | 0.996 |
| 512.36 | 269.68 | 0.012 | 265.219 | 0.966 | 4.57×10-5 | 282.486 | 0.996 |

图6 ESIX (rGO)、 IX (NiFe-LDH/rGO)、 ESIX (NiFe-LDH)和ESIX (NiFe-LDH/rGO)对磷酸盐阴离子的吸附容量曲线
Fig.6 Phosphate anions uptake capacity curves of ESIX (rGO), IX (NiFe-LDH/rGO), ESIX (NiFe-LDH) and ESIX (NiFe-LDH/rGO)

图7 (a)NiFe-LDH/rGO杂化膜在初始浓度均为300 mg·L-1下对PO43-、 SO42-、 NO3-和Cl-的竞争性吸附; (b) 0.30 mol·L-1 NaNO3, 0.30 mol·L-1 NaCl, 0.15 mol·L-1 Na2SO4和0.10 mol·L-1 Na3PO4电解液中NiFe-LDH/rGO复合膜的CV曲线
Fig.7 (a) Competitive adsorption of PO43-, SO42-, NO3-, and Cl- for NiFe-LDH/rGO hybrid films at an initial concentration of 300 mg·L-1; (b) CV curves of NiFe-LDH/rGO hybrid film in 0.30 mol·L-1 NaNO3, 0.30 mol·L-1 NaCl, 0.15 mol·L-1 Na2SO4, and 0.10 mol·L-1 Na3PO4 electrolytic solutions
| Anion | Adsorption capacity/(mg·g-1) | Separation coefficient (KD) | Relative separation factor (α) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 178.012 | 0.865 | 1 | |
| 70.871 | 0.274 | 3.163 | |
| 50.336 | 0.185 | 4.678 | |
| Cl- | 45.248 | 0.156 | 5.551 |
表3 NiFe-LDH/rGO杂化膜在初始浓度均为300 mg·L-1下对PO43-、SO42-、NO3-和Cl-的分离系数和相对分离因子
Table 3 Separation coefficients and relative separation factors of PO43-, SO42-, NO3-, and Cl- of the NiFe-LDH/rGO hybrid film at the initial concentration of 300 mg·L-1
| Anion | Adsorption capacity/(mg·g-1) | Separation coefficient (KD) | Relative separation factor (α) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 178.012 | 0.865 | 1 | |
| 70.871 | 0.274 | 3.163 | |
| 50.336 | 0.185 | 4.678 | |
| Cl- | 45.248 | 0.156 | 5.551 |
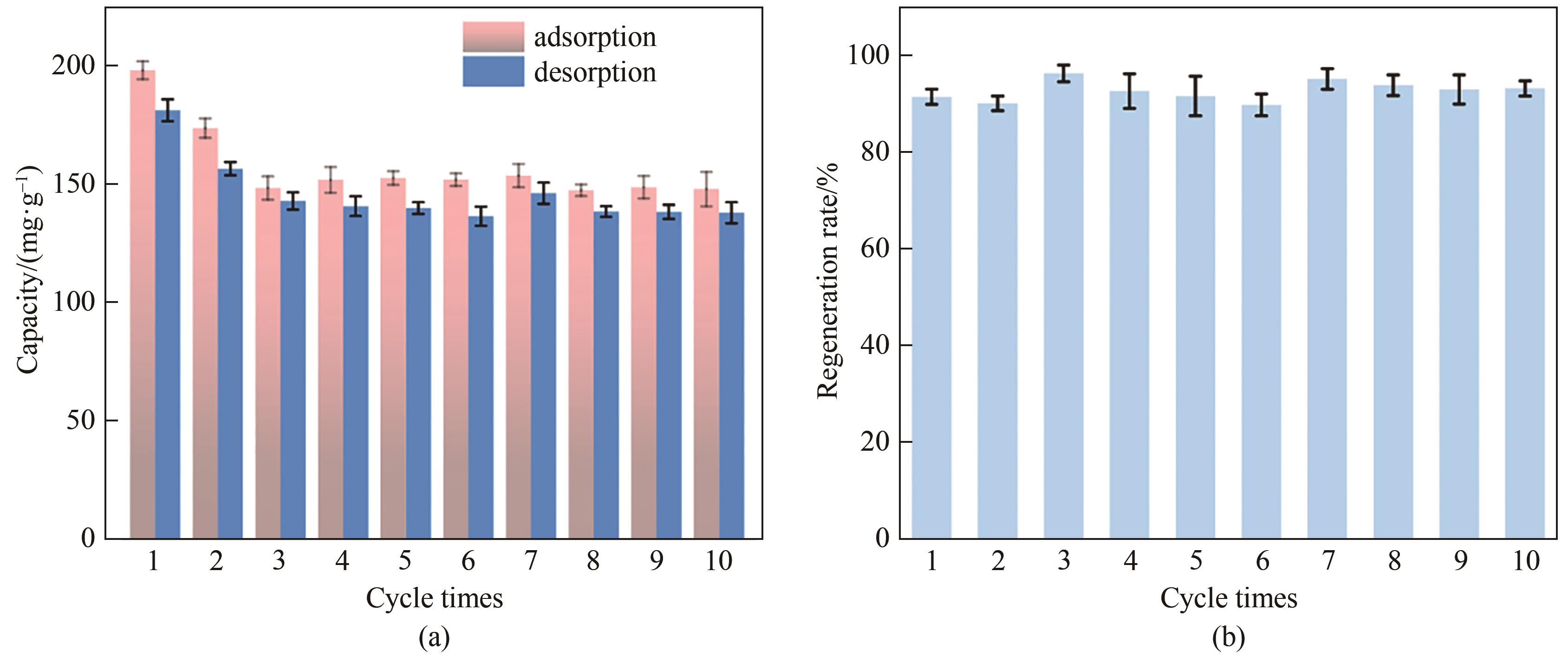
图8 NiFe-LDH/rGO杂化膜在300 mg·L-1的磷酸钠 (吸附) 和硝酸钠 (脱附) 溶液中对PO43-的吸脱附容量(a)和再生效率(b)
Fig.8 The adsorption and desorption capacity (a) and regeneration rate (b) of NiFe-LDH /rGO hybrid film for phosphate ions in 300 mg·L-1 sodium phosphate and sodium nitrate solutions, respectively
| 1 | 袁伟皓, 王华, 曾一川, 等. 大型通江湖泊藻类增殖驱动要素的时空分异特征[J]. 环境工程, 2021, 39(10): 64-71, 128. |
| Yuan W H, Wang H, Zeng Y C, et al. Spatiotemporal variation of driving factors of algal proliferation in a large river-connected lake[J]. Environmental Engineering, 2021, 39(10): 64-71, 128. | |
| 2 | Wildemeersch M, Tang S H, Ermolieva T, et al. Containing the risk of phosphorus pollution in agricultural watersheds[J]. Sustainability, 2022, 14(3): 1717. |
| 3 | Garnache C, Swinton S, Herriges J, et al. Solving the phosphorus pollution puzzle: synthesis and directions for future research[J]. American Journal of Agricultural Economics, 2016, 98: 1334-1359. |
| 4 | 秦伯强. 浅水湖泊湖沼学与太湖富营养化控制研究[J]. 湖泊科学, 2020, 32(5): 1229-1243. |
| Qin B Q. Shallow lake limnology and control of eutrophication in Lake Taihu[J]. Journal of Lake Sciences, 2020, 32(5): 1229-1243. | |
| 5 | Sun Y, Feng X L, Zheng W S. Nanoscale lanthanum carbonate hybridized with polyacrylic resin for enhanced phosphate removal from secondary effluent[J]. Journal of Chemical & Engineering Data, 2020, 65(9): 4512-4522. |
| 6 | Wu B L, Lo I M C. Surface functional group engineering of CeO2 particles for enhanced phosphate adsorption[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2020, 54(7): 4601-4608. |
| 7 | Prashantha Kumar T K M, Mandlimath T R, Sangeetha P, et al. Nanoscale materials as sorbents for nitrate and phosphate removal from water[J]. Environmental Chemistry Letters, 2018, 16(2): 389-400. |
| 8 | Morimoto K, Anraku S, Hoshino J, et al. Surface complexation reactions of inorganic anions on hydrotalcite-like compounds[J]. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 2012, 384: 99-104. |
| 9 | Li N, Tian Y, Zhao J H, et al. Ultrafast selective capture of phosphorus from sewage by 3D Fe3O4@ZnO via weak magnetic field enhanced adsorption[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2018, 341: 289-297. |
| 10 | Wu B, Wan J, Zhang Y, et al. Selective phosphate removal from water and wastewater using sorption: process fundamentals and removal mechanisms[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2020, 54: 50-66. |
| 11 | Niu J J, Yan W, Du J, et al. An electrically switched ion exchange film with molecular coupling synergistically-driven ability for recovery of Ag+ ions from wastewater[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2020, 389: 12449-12457. |
| 12 | 郝晓刚, 郭金霞, 张忠林, 等. 电沉积铁氰化镍薄膜的电控离子交换性能[J]. 化工学报, 2005, 56(12): 2380-2386. |
| Hao X G, Guo J X, Zhang Z L, et al. Electrochemically switched ion exchange properties of electrodeposited nickel hexacyanoferrate thin films[J]. Journal of Chemical Industry and Engineering (China), 2005, 56 (12): 2380-2386. | |
| 13 | 马旭莉, 张权, 杜晓, 等. α-ZrP/PANI电控离子交换膜对Pb2+的选择性分离[J]. 稀有金属材料与工程, 2016, 45(8): 2139-2145. |
| Ma X L, Zhang Q, Du X, et al. Selective separation to Pb2+ of electrochemically switched ion exchange film of α-ZrP/PANI[J]. Rare Metal Materials and Engineering, 2016, 45(8): 2139-2145. | |
| 14 | Du X, Guan G Q, Li X M, et al. A novel electroactive λ-MnO2/PPy/PSS core-shell nanorod coated electrode for selective recovery of lithium ions at low concentration[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2016, 4(36): 13989-13996. |
| 15 | Hong S P, Yoon H, Lee J, et al. Selective phosphate removal using layered double hydroxide/reduced graphene oxide (LDH/rGO) composite electrode in capacitive deionization[J]. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 2020, 564: 1-7. |
| 16 | Rahman S, Navarathna C M, Krishna Das N, et al. High capacity aqueous phosphate reclamation using Fe/Mg-layered double hydroxide (LDH) dispersed on biochar[J]. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 2021, 597: 182-195. |
| 17 | 来天艺, 王纪康, 李天, 等. 光电解水产活性氢/氧耦合加氢/氧化过程用水滑石基纳米材料[J]. 化工学报, 2020, 71(10): 4327-4349. |
| Lai T Y, Wang J K, Li T, et al. Photoelectrochemical water splitting into active hydrogen/oxygen species coupling with hydrogenation/oxidation process using layered double hydroxides-based nanocatalysts[J]. CIESC Journal, 2020, 71(10): 4327-4349. | |
| 18 | Liu C, Zhang M Y, Pan G, et al. Phosphate capture by ultrathin MgAl layered double hydroxide nanoparticles[J]. Applied Clay Science, 2019, 177: 82-90. |
| 19 | Tian M, Liu C F, Neale Z G, et al. Chemically bonding NiFe-LDH nanosheets on rGO for superior lithium-ion capacitors[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2019, 11(39): 35977-35986. |
| 20 | Son Y R, Park S J. Influence of carboxymethyl cellulose content on structures and electrochemical behaviors of reduced graphene oxide films[J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2020, 330: 135219. |
| 21 | Shinde D B, Vlassiouk I V, Talipov M R, et al. Exclusively proton conductive membranes based on reduced graphene oxide polymer composites[J]. ACS Nano, 2019, 13(11): 13136-13143. |
| 22 | 杨言言, 李永国, 祝小雯, 等. 电活性镍钴双金属氧化物高选择性去除/回收水中磷酸盐离子[J]. 无机材料学报, 2021, 36(3): 292-298. |
| Yang Y Y, Li Y G, Zhu X W, et al. Potential induced reversible removal/recovery of phosphate anions with high selectivity using an electroactive NiCo-layered double oxide film[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(3): 292-298. | |
| 23 | Forticaux A, Dang L N, Liang H F, et al. Controlled synthesis of layered double hydroxide nanoplates driven by screw dislocations[J]. Nano Letters, 2015, 15(5): 3403-3409. |
| 24 | Ghani M, Ghoreishi S M, Azamati M. Magnesium-aluminum-layered double hydroxide-graphene oxide composite mixed-matrix membrane for the thin-film microextraction of diclofenac in biological fluids[J]. Journal of Chromatography A, 2018, 1575: 11-17. |
| 25 | He H M, Kang H L, Ma S L, et al. High adsorption selectivity of ZnAl layered double hydroxides and the calcined materials toward phosphate[J]. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 2010, 343: 225-231. |
| 26 | Abo El-Reesh G Y, Farghali A A, Taha M, et al. Novel synthesis of Ni/Fe layered double hydroxides using urea and glycerol and their enhanced adsorption behavior for Cr(Ⅵ) removal[J]. Scientific Reports, 2020, 10: 587. |
| 27 | Chen J, Fan X L, Ji X, et al. Intercalation of Bi nanoparticles into graphite results in an ultra-fast and ultra-stable anode material for sodium-ion batteries[J]. Energy & Environmental Science, 2018, 11(5): 1218-1225. |
| 28 | Hao X G, Yan T, Wang Z D, et al. Unipolar pulse electrodeposition of nickel hexacyanoferrate thin films with controllable structure on platinum substrates[J]. Thin Solid Films, 2012, 520(7): 2438-2448. |
| 29 | Youmbi B S, Pélisson C H, Denicourt-Nowicki A, et al. Impact of the charge transfer process on the Fe2+/Fe3+ distribution at Fe3O4 magnetic surface induced by deposited Pd clusters[J]. Surface Science, 2021, 712: 121879. |
| 30 | Wan J, Wu B L, Lo I M C. Development of Fe0/Fe3O4 composites with tunable properties facilitated by Fe2+ for phosphate removal from river water[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2020, 388: 124242. |
| 31 | Ji W W, Niu J J, Zhang W, et al. An electroactive ion exchange hybrid film with collaboratively-driven ability for electrochemically-mediated selective extraction of chloride ions[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2022, 427: 130807. |
| 32 | Zhao G Q, Li C F, Wu X, et al. Reduced graphene oxide modified NiFe-calcinated layered double hydroxides for enhanced photocatalytic removal of methylene blue[J]. Applied Surface Science, 2018, 434: 251-259. |
| 33 | Xu W S, Zheng W J, Wang F J, et al. Using iron ion-loaded aminated polyacrylonitrile fiber to efficiently remove wastewater phosphate[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2021, 403: 126349. |
| [1] | 江河, 袁俊飞, 王林, 邢谷雨. 均流腔结构对微细通道内相变流动特性影响的实验研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(S1): 235-244. |
| [2] | 范孝雄, 郝丽芳, 范垂钢, 李松庚. LaMnO3/生物炭催化剂低温NH3-SCR催化脱硝性能研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(9): 3821-3830. |
| [3] | 程业品, 胡达清, 徐奕莎, 刘华彦, 卢晗锋, 崔国凯. 离子液体基低共熔溶剂在转化CO2中的应用[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(9): 3640-3653. |
| [4] | 郑玉圆, 葛志伟, 韩翔宇, 王亮, 陈海生. 中高温钙基材料热化学储热的研究进展与展望[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(8): 3171-3192. |
| [5] | 胡亚丽, 胡军勇, 马素霞, 孙禹坤, 谭学诣, 黄佳欣, 杨奉源. 逆电渗析热机新型工质开发及电化学特性研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(8): 3513-3521. |
| [6] | 孟令玎, 崇汝青, 孙菲雪, 孟子晖, 刘文芳. 改性聚乙烯膜和氧化硅固定化碳酸酐酶[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(8): 3472-3484. |
| [7] | 张蒙蒙, 颜冬, 沈永峰, 李文翠. 电解液类型对双离子电池阴阳离子储存行为的影响[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(7): 3116-3126. |
| [8] | 葛加丽, 管图祥, 邱新民, 吴健, 沈丽明, 暴宁钟. 垂直多孔碳包覆的FeF3正极的构筑及储锂性能研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(7): 3058-3067. |
| [9] | 屈园浩, 邓文义, 谢晓丹, 苏亚欣. 活性炭/石墨辅助污泥电渗脱水研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(7): 3038-3050. |
| [10] | 李盼, 马俊洋, 陈志豪, 王丽, 郭耘. Ru/α-MnO2催化剂形貌对NH3-SCO反应性能的影响[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(7): 2908-2918. |
| [11] | 张琦钰, 高利军, 苏宇航, 马晓博, 王翊丞, 张亚婷, 胡超. 碳基催化材料在电化学还原二氧化碳中的研究进展[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(7): 2753-2772. |
| [12] | 张谭, 刘光, 李晋平, 孙予罕. Ru基氮还原电催化剂性能调控策略[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(6): 2264-2280. |
| [13] | 蔡斌, 张效林, 罗倩, 党江涛, 左栗源, 刘欣梅. 导电薄膜材料的研究进展[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(6): 2308-2321. |
| [14] | 朱兴驰, 郭志远, 纪志永, 汪婧, 张盼盼, 刘杰, 赵颖颖, 袁俊生. 选择性电渗析镁锂分离过程模拟优化[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(6): 2477-2485. |
| [15] | 毛磊, 刘冠章, 袁航, 张光亚. 可捕集CO2的纳米碳酸酐酶粒子的高效制备及性能研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(6): 2589-2598. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备 11010102001995号
京公网安备 11010102001995号