化工学报 ›› 2024, Vol. 75 ›› Issue (11): 4298-4308.DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20240535
收稿日期:2024-05-20
修回日期:2024-06-27
出版日期:2024-11-25
发布日期:2024-12-26
通讯作者:
肖永厚
作者简介:郭强(1998—),男,硕士研究生,guoqiang202103@163.com
基金资助:
Qiang GUO1( ), Qidong ZHAO2, Yonghou XIAO1,2,3(
), Qidong ZHAO2, Yonghou XIAO1,2,3( )
)
Received:2024-05-20
Revised:2024-06-27
Online:2024-11-25
Published:2024-12-26
Contact:
Yonghou XIAO
摘要:
双回流(DR)变压吸附(PSA)工艺具有不受压力比影响的优势,有望突破传统PSA的热力学限制同时获得两种高纯气体。基于两塔四步DR PSA工艺,分别考察了活性炭(AC)、13X和5A分子筛复合吸附剂以及Cu(Ⅰ)/AC单吸附剂的分离效果,实现了同时制备高纯H2和CO产品。利用Aspen Adsorption模拟平台开发了一个由质量、动量和能量平衡方程组成的非等温吸附模型,并通过固定床吸附实验验证了模型的可靠性。结果表明,AC、13X和5A分子筛复合吸附剂的DR PSA工艺分离效率欠佳,但表现出更强的CO解吸能力;而单独以Cu(Ⅰ)/AC为吸附剂,可以显著提升分离效率,即以CO/H2=0.5/0.5(体积比)合成气为原料,获得纯度>99.999%的H2产品,其中CO含量<0.20 ml/m3,收率达96.69%;同时CO产品纯度>97.00%,收率达99.16%。增大轻、重组分回流比可以进一步提高H2和CO产品气的纯度。
中图分类号:
郭强, 肇启东, 肖永厚. 双回流变压吸附高效分离CO/H2制备高纯H2和CO[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(11): 4298-4308.
Qiang GUO, Qidong ZHAO, Yonghou XIAO. Preparation of high-purity H2 and CO by efficient separation of CO/H2 using dual-reflux pressure swing adsorption process[J]. CIESC Journal, 2024, 75(11): 4298-4308.
| Parameters | AC/13X/5A | Cu(Ⅰ)/AC |
|---|---|---|
| height of adsorbent layer/m | 0.50/0.50/0.80 | 2.0 |
| diameter of adsorbent layer/m | 0.13 | 0.20 |
| thickness of bed wall | 0.0050 | 0.0020 |
| inter-particle voidage | 0.43/0.35/0.35 | 0.35 |
| intra-particle voidage | 0.61/0.65/0.65 | 0.33 |
| bulk solid density of adsorbent/ (kg/m3) | 708.00/851.29/715.70 | 625.00 |
| adsorbent particle radius/mm | 2.0 | 1.4 |
| feed gas pressure/bar | 5.0 | 5.0 |
| feed flow rate/(L/min) | 33.33 | 33.33 |
表1 吸附床的性质和操作条件
Table 1 Properties of the adsorption bed and operating conditions
| Parameters | AC/13X/5A | Cu(Ⅰ)/AC |
|---|---|---|
| height of adsorbent layer/m | 0.50/0.50/0.80 | 2.0 |
| diameter of adsorbent layer/m | 0.13 | 0.20 |
| thickness of bed wall | 0.0050 | 0.0020 |
| inter-particle voidage | 0.43/0.35/0.35 | 0.35 |
| intra-particle voidage | 0.61/0.65/0.65 | 0.33 |
| bulk solid density of adsorbent/ (kg/m3) | 708.00/851.29/715.70 | 625.00 |
| adsorbent particle radius/mm | 2.0 | 1.4 |
| feed gas pressure/bar | 5.0 | 5.0 |
| feed flow rate/(L/min) | 33.33 | 33.33 |
| Model equation | Expression | Equation |
|---|---|---|
| mass balance | (1) | |
| energy balance | gas phase | (2) |
| solid phase | (3) | |
| bed wall | (4) | |
| (5) | ||
| (6) | ||
| (7) | ||
| momentum balance | (8) | |
| LDF | (9) | |
| (10) | ||
| ideal gas law | (11) |
表2 DR PSA模型中使用的方程
Table 2 The equations used in DR PSA model
| Model equation | Expression | Equation |
|---|---|---|
| mass balance | (1) | |
| energy balance | gas phase | (2) |
| solid phase | (3) | |
| bed wall | (4) | |
| (5) | ||
| (6) | ||
| (7) | ||
| momentum balance | (8) | |
| LDF | (9) | |
| (10) | ||
| ideal gas law | (11) |
| Adsorbent | Parameters | H2 | Ar | CO |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AC | Qm/(mmol/g) | 10.68 | 7.00 | 6.82 |
| b0/bar-1 | 2.16×10-5 | 1.76×10-4 | 9.05×10-6 | |
| ΔH/(kJ/mol) | -12.84 | -13.53 | -22.58 | |
| 13X | Qm/(mmol/g) | 6.50 | 4.41 | 3.18 |
| b0/bar-1 | 1.33×10-4 | 2.92×10-4 | 8.49×10-5 | |
| ΔH/(kJ/mol) | -8.00 | -11.00 | -21.00 | |
| 5A | Qm/(mmol/g) | 1.15 | 4.24 | 2.24 |
| b0/bar-1 | 2.82×10-4 | 1.67×10-4 | 6.14×10-6 | |
| ΔH/(kJ/mol) | -9.23 | -13.30 | -29.77 |
表3 AC、13X和5A的扩展型Langmuir吸附模型拟合参数
Table 3 Fitting parameters of extended Langmuir adsorption models for AC, 13X and 5A
| Adsorbent | Parameters | H2 | Ar | CO |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AC | Qm/(mmol/g) | 10.68 | 7.00 | 6.82 |
| b0/bar-1 | 2.16×10-5 | 1.76×10-4 | 9.05×10-6 | |
| ΔH/(kJ/mol) | -12.84 | -13.53 | -22.58 | |
| 13X | Qm/(mmol/g) | 6.50 | 4.41 | 3.18 |
| b0/bar-1 | 1.33×10-4 | 2.92×10-4 | 8.49×10-5 | |
| ΔH/(kJ/mol) | -8.00 | -11.00 | -21.00 | |
| 5A | Qm/(mmol/g) | 1.15 | 4.24 | 2.24 |
| b0/bar-1 | 2.82×10-4 | 1.67×10-4 | 6.14×10-6 | |
| ΔH/(kJ/mol) | -9.23 | -13.30 | -29.77 |
| Parameters | H2 | Ar | CO | CH4 | N2 | CO2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Qm/(mmol/g) | 38.87 | 6.56 | 2.00 | 3.23 | 7.18 | 5.38 |
| b0/bar-1 | 1.0×10-5 | 1.8×10-4 | 1.0×10-5 | 5.0×10-5 | 1.9×10-5 | 7.5×10-6 |
| ΔH/(kJ/mol) | -8.50 | -13.74 | -31.45 | -20.60 | -15.87 | -26.83 |
表4 Cu(Ⅰ)/AC的扩展型Langmuir吸附模型拟合参数
Table 4 Fitting parameters of extended Langmuir adsorption model for Cu(Ⅰ)/AC
| Parameters | H2 | Ar | CO | CH4 | N2 | CO2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Qm/(mmol/g) | 38.87 | 6.56 | 2.00 | 3.23 | 7.18 | 5.38 |
| b0/bar-1 | 1.0×10-5 | 1.8×10-4 | 1.0×10-5 | 5.0×10-5 | 1.9×10-5 | 7.5×10-6 |
| ΔH/(kJ/mol) | -8.50 | -13.74 | -31.45 | -20.60 | -15.87 | -26.83 |
| Bed | Duration/s | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 100 | 20 | 100 | 20 | |
| 1 | AD | VU | PU | PR |
| 2 | PU | PR | AD | VU |
表5 DR PSA工艺循环时间
Table 5 Cycle time of DR PSA process
| Bed | Duration/s | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 100 | 20 | 100 | 20 | |
| 1 | AD | VU | PU | PR |
| 2 | PU | PR | AD | VU |
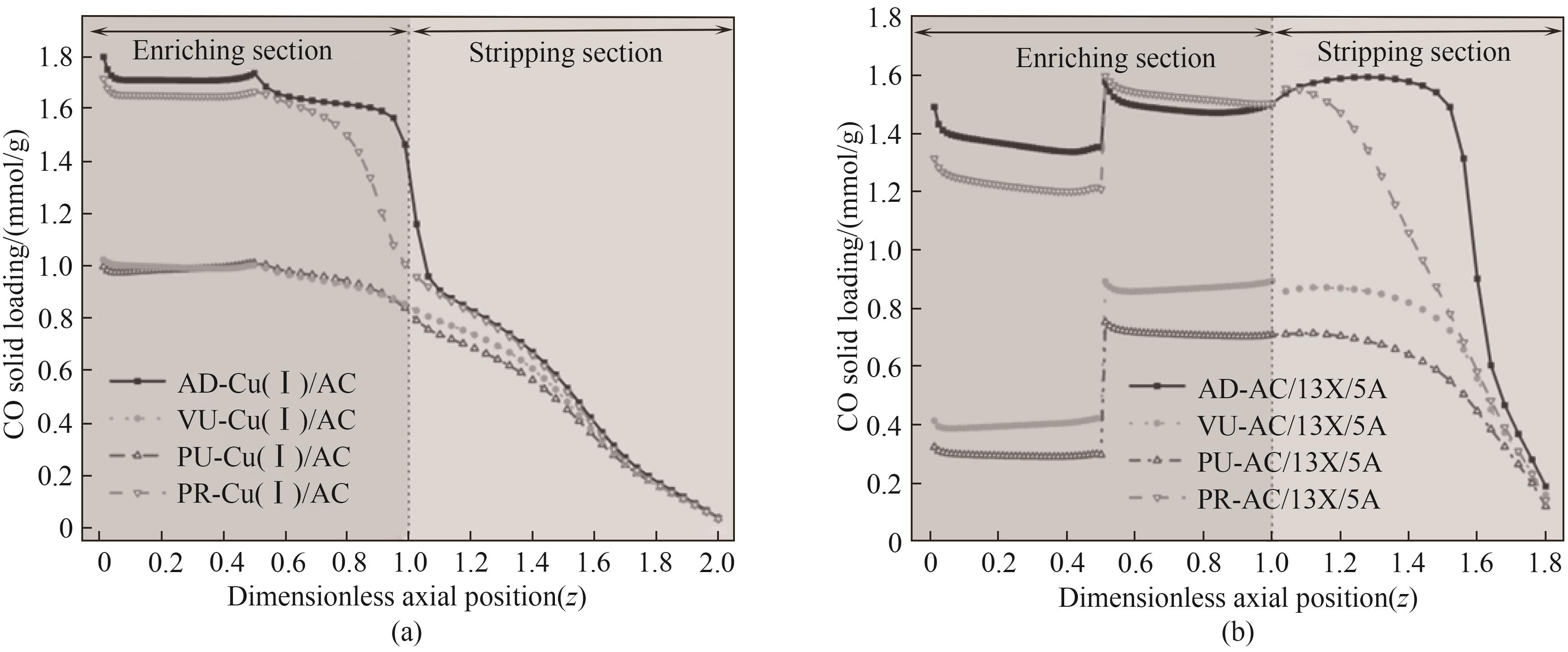
图7 一个循环周期内各步骤结束后AC、13X和5A复合吸附剂和Cu(Ⅰ)/AC吸附床内CO轴向浓度分布
Fig.7 Axial concentration distribution of CO in AC, 13X and 5A composite adsorbent and Cu(Ⅰ)/AC adsorption beds after each step within a cycle
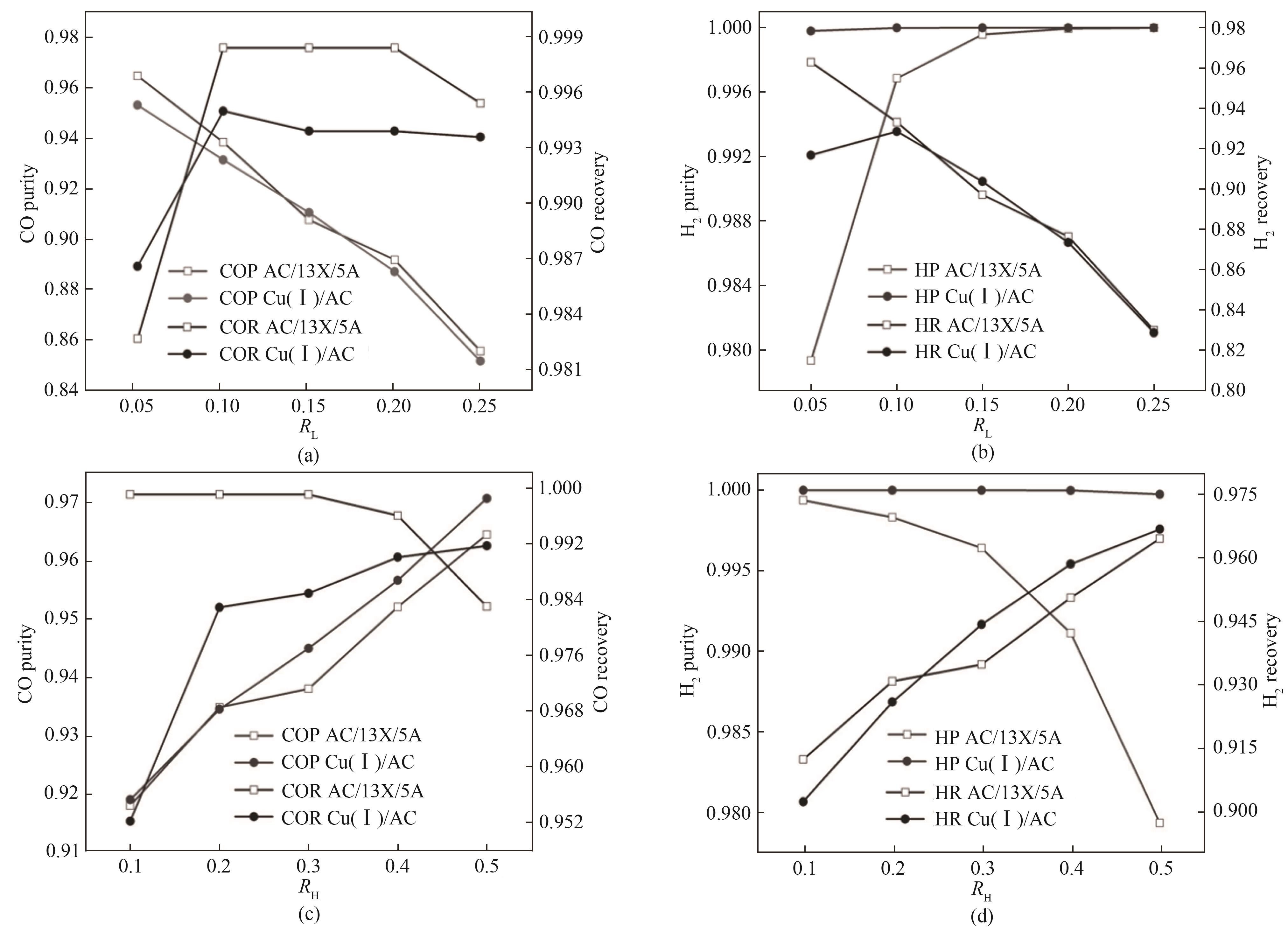
图8 不同轻重回流比对产品气纯度的影响(AC、13X和5A分子筛复合吸附剂和Cu(Ⅰ)/AC单吸附剂床)
Fig.8 The influence of different light to heavy reflux ratios on the purity of product gas on AC, 13X and 5A composite and Cu(Ⅰ)/AC adsorbents
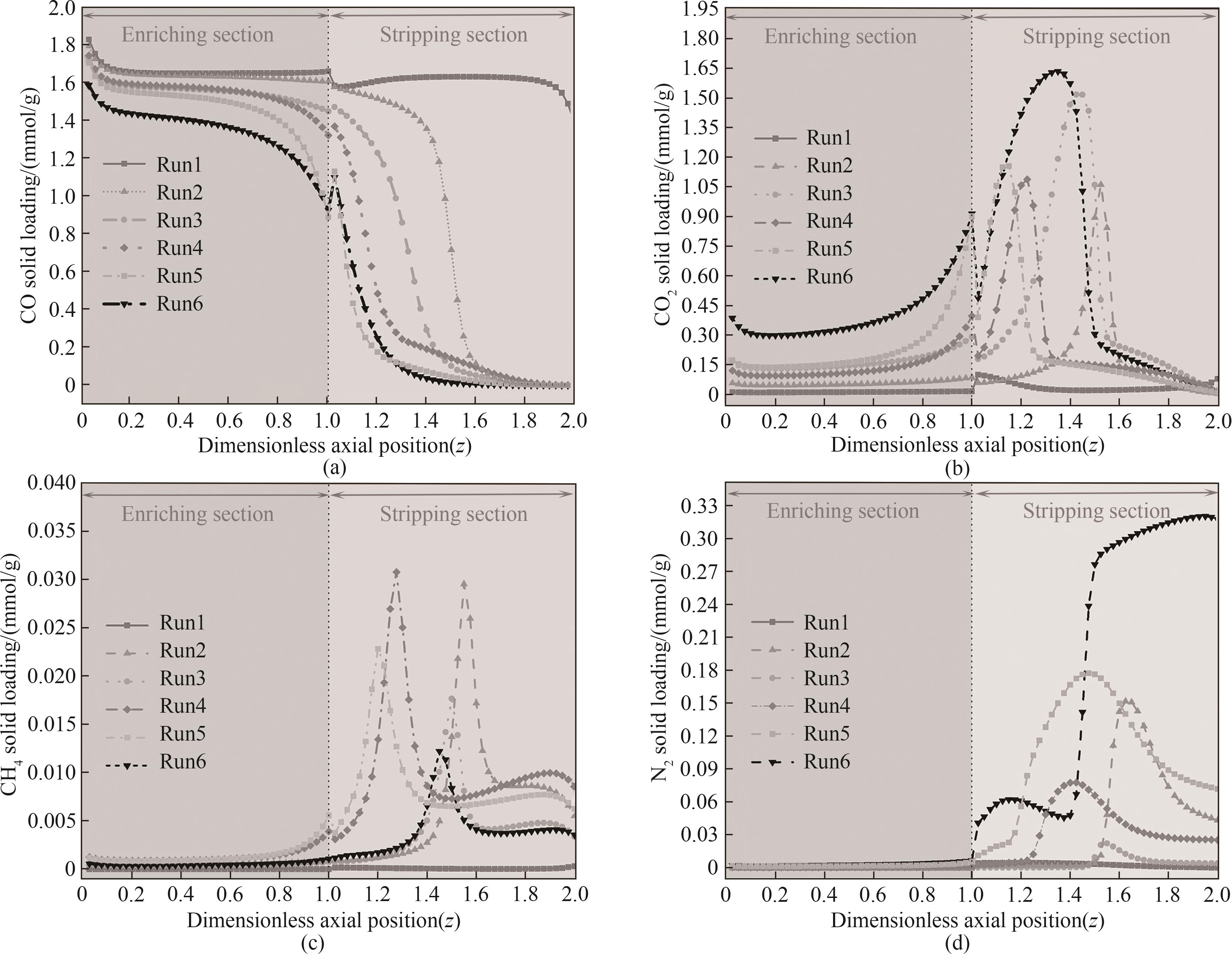
图11 多组分竞争吸附条件下H2/CO/CO2/CH4/N2合成气各循环步骤结束时的固相浓度分布
Fig.11 Solid phase concentration distribution at the end of each cycle of H2/CO/CO2/CH4/N2 synthesis gas under multi-component competitive adsorption conditions
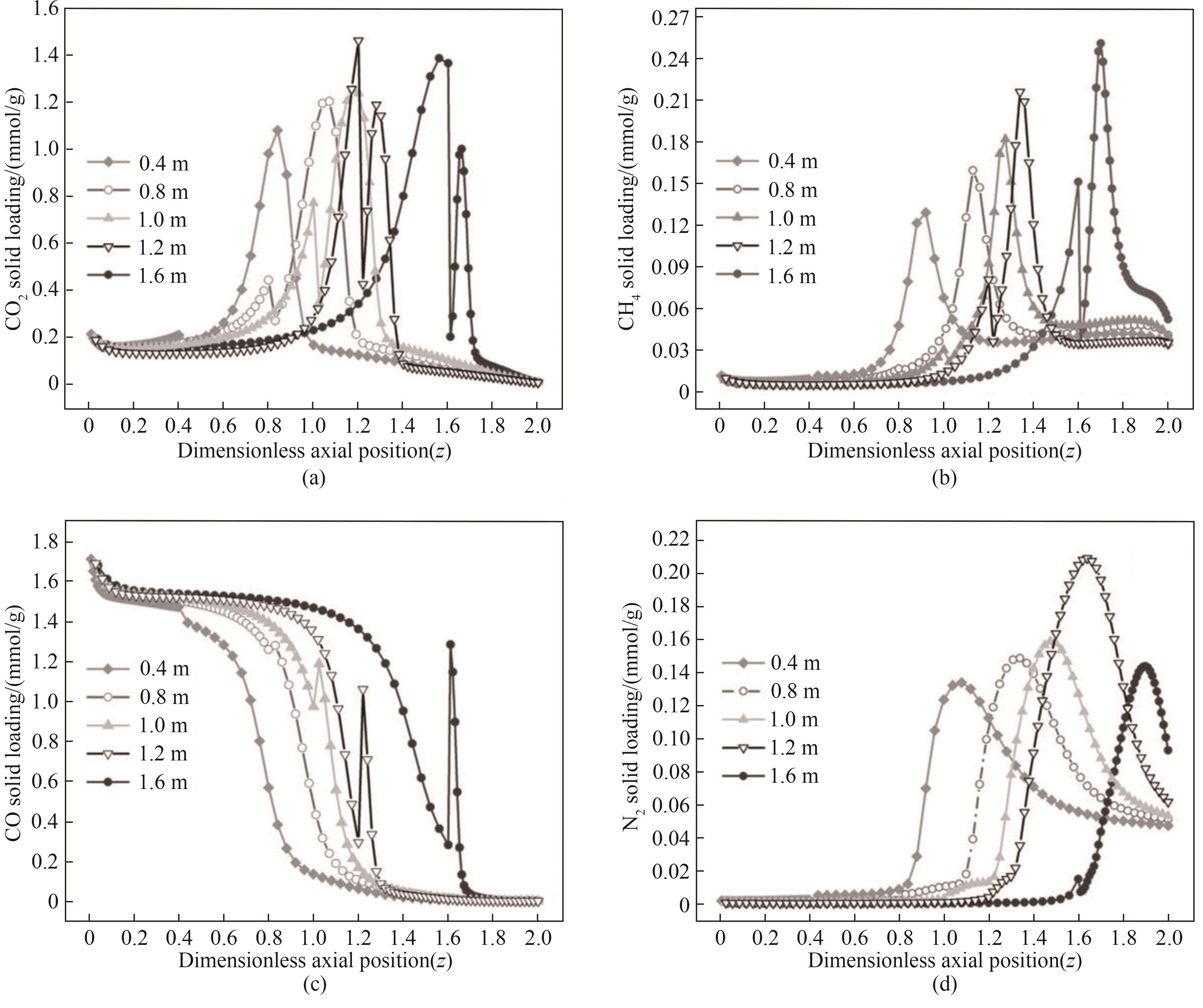
图12 不同进料位置对AD步骤结束后各组分固相浓度分布的影响
Fig.12 Effects of different feed positions on the solid phase concentration distribution of each component after AD step
| 1 | Chen Y, Lin J, Li L, et al. Local structure of Pt species dictates remarkable performance on Pt/Al2O3 for preferential oxidation of CO in H2 [J]. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 2021, 282: 119588. |
| 2 | 陈健, 姬存民, 卜令兵. 碳中和背景下工业副产气制氢技术研究与应用[J]. 化工进展, 2022, 41(3): 1479-1486. |
| Chen J, Ji C M, Bu L B. Research and application of hydrogen production technology from industrial by-product gas under the background of carbon neutrality[J]. Chemical Industry and Engineering Progress, 2022, 41(3): 1479-1486. | |
| 3 | Yang S H, Xiao Y H, Zhang W Y, et al. Facile preparation of Cu(Ⅰ)/5A via one-step impregnation with highly dispersed CuCl in ethanol single solvent toward selective adsorption of CO from H2 stream[J]. ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering, 2022, 10(48): 15958-15967. |
| 4 | Kim A R, Yoon T U, Kim S I, et al. Creating high CO/CO2 selectivity and large CO working capacity through facile loading of Cu(Ⅰ) species into an iron-based mesoporous metal-organic framework[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2018, 348: 135-142. |
| 5 | Yin Y, Wen Z H, Shi L, et al. Cuprous/vanadium sites on MIL-101 for selective CO adsorption from gas mixtures with superior stability[J]. ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering, 2019, 7(13): 11284-11292. |
| 6 | Guo Q, Qiao Y, Xiao Y H, et al. Synthesis of hydrophobic CuCl/LaA modified by butyltrichlorosilane towards enhanced CO adsorption under humid environment[J]. Applied Surface Science, 2024, 659: 159882. |
| 7 | Ahmad W, Chan F L, Chaffee A L, et al. Dimethoxymethane production via catalytic hydrogenation of carbon monoxide in methanol media[J]. ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering, 2020, 8(4): 2081-2092. |
| 8 | Xue C L, Hao W M, Cheng W P, et al. Effects of pore size distribution of activated carbon (AC) on CuCl dispersion and CO adsorption for CuCl/AC adsorbent[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2019, 375: 122049. |
| 9 | Ahad N, de Klerk A. Fischer-Tropsch acid water processing by Kolbe electrolysis[J]. Fuel, 2018, 211: 415-419. |
| 10 | Zhang J, Wang L, Wu Z Y, et al. Mesoporous Co-Al oxide nanosheets as highly efficient catalysts for CO oxidation[J]. AIChE Journal, 2020, 66(5): e16923. |
| 11 | Rubaiee S. High sour natural gas dehydration treatment through low temperature technique: process simulation, modeling and optimization[J]. Chemosphere, 2023, 320: 138076. |
| 12 | Cheng X, Liao Y, Lei Z, et al. Multi-scale design of MOF-based membrane separation for CO2/CH4 mixture via integration of molecular simulation, machine learning and process modeling and simulation[J]. Journal of Membrane Science, 2023, 672: 121430. |
| 13 | Feyzbar-Khalkhali-Nejad F, Hassani E, Rashti A, et al. Adsorption-based CO removal: principles and materials[J]. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 2021, 9(4): 105317. |
| 14 | 肖永厚, 肖红岩, 李本源, 等. 基于Aspen Adsorption的氦气/甲烷吸附分离过程模拟优化[J]. 化工学报, 2019, 70(7): 2556-2563. |
| Xiao Y H, Xiao H Y, Li B Y, et al. Optimization of helium/methane adsorption separation process based on Aspen Adsorption simulation[J]. CIESC Journal, 2019, 70(7): 2556-2563. | |
| 15 | Hu G P, May E F, Li K G. We commercialized a methane capture technology in ten years—Here's how[J]. Nature, 2022, 604: 242-245. |
| 16 | 尚华, 白洪灏, 刘佳奇, 等. CH4-N2在自支撑颗粒型Silicalite-1上的吸附分离及PSA模拟[J]. 化工学报, 2020, 71(5): 2088-2098. |
| Shang H, Bai H H, Liu J Q, et al. PSA simulation and adsorption separation of CH4-N2 by self-supporting pellets Silicalite-1[J]. CIESC Journal, 2020, 71(5): 2088-2098. | |
| 17 | Li Y X, Jin M M, Shi S, et al. Adjusting accommodation microenvironment for Cu+ to enhance oxidation inhibition for thiophene capture[J]. AIChE Journal, 2021, 67(10): e17368. |
| 18 | Du S J, Wang X J, Huang J W, et al. Ultramicroporous carbons featuring sub-Ångstrom tunable apertures for the selective separation of light hydrocarbon[J]. AIChE Journal, 2021, 67(9): e17285. |
| 19 | Li C L, Wang J, Wang Z F, et al. Understanding the vacuum autoreduction behavior of Cu species in CuCl/NaY adsorbent for CO/N2 separation[J]. Microporous and Mesoporous Materials, 2024, 365: 112904. |
| 20 | Zhang N N, Xiao J S, Bénard P, et al. Single- and double-bed pressure swing adsorption processes for H2/CO syngas separation[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2019, 44(48): 26405-26418. |
| 21 | Oh H, Lee S, Beum H T, et al. CO recovery from blast furnace gas by vacuum pressure swing adsorption process: experimental and simulation approach[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2022, 346: 131062. |
| 22 | Zhou Y, Shen Y H, Fu Q, et al. CO enrichment from low-concentration syngas by a layered-bed VPSA process[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2017, 56(23): 6741-6754. |
| 23 | Li D D, Zhou Y, Shen Y H, et al. Experiment and simulation for separating CO2/N2 by dual-reflux pressure swing adsorption process[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2016, 297: 315-324. |
| 24 | Weh R, Xiao G K, Ashraful Islam M, et al. Upgrading sub-quality natural gas by dual reflux-pressure swing adsorption using activated carbon and ionic liquidic zeolite[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2020, 392: 123753. |
| 25 | Zhang Y C, Saleman T L H, Li G, et al. Non-isothermal numerical simulations of dual reflux pressure swing adsorption cycles for separating N2 +CH4 [J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2016, 292: 366-381. |
| 26 | Weh R, Xiao G K, Sadeghi Pouya E, et al. Helium recovery and purification by dual reflux pressure swing adsorption[J]. Separation and Purification Technology, 2022, 288: 120603. |
| 27 | 汪亚燕, 田彩霞, 丁兆阳, 等. 基于双回流变压吸附工艺的空气分离模拟及分析[J]. 化工学报, 2019, 70(10): 4002-4011. |
| Wang Y Y, Tian C X, Ding Z Y, et al. Simulation and analysis of dual-reflux pressure swing adsorption for air separation[J]. CIESC Journal, 2019, 70(10): 4002-4011. | |
| 28 | Zhang C, Shen Y H, Zhang D H, et al. Vacuum pressure swing adsorption for producing fuel cell grade hydrogen from IGCC[J]. Energy, 2022, 257: 124715. |
| 29 | Park Y, Ju Y, Park D, et al. Adsorption equilibria and kinetics of six pure gases on pelletized zeolite 13X up to 1.0 MPa: CO2, CO, N2, CH4, Ar and H2 [J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2016, 292: 348-365. |
| 30 | Golmakani A, Ali Nabavi S, Manović V. Production of negative-emission biomethane by twin double-bed pressure swing adsorption with tail gas sequestration[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2021, 408: 127312. |
| [1] | 任冠宇, 张义飞, 李新泽, 杜文静. 翼型印刷电路板式换热器流动传热特性数值研究[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(S1): 108-117. |
| [2] | 杨勇, 祖子轩, 李煜坤, 王东亮, 范宗良, 周怀荣. T型圆柱形微通道内CO2碱液吸收数值模拟[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(S1): 135-142. |
| [3] | 黄俊豪, 庞克亮, 孙方远, 刘福军, 谷致远, 韩龙, 段衍泉, 冯妍卉. 干熄炉料钟结构对焦炭布料粒径均匀度影响的模拟研究[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(S1): 158-169. |
| [4] | 董新宇, 边龙飞, 杨怡怡, 张宇轩, 刘璐, 王腾. 冷却条件下倾斜上升管S-CO2流动与传热特性研究[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(S1): 195-205. |
| [5] | 郭骐瑞, 任丽媛, 陈康, 黄翔宇, 马卫华, 肖乐勤, 周伟良. 用于HTPB推进剂浆料的静态混合管数值模拟[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(S1): 206-216. |
| [6] | 李匡奚, 于佩潜, 王江云, 魏浩然, 郑志刚, 冯留海. 微气泡旋流气浮装置内流动分析与结构优化[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(S1): 223-234. |
| [7] | 汪张洲, 唐天琪, 夏嘉俊, 何玉荣. 基于复合相变材料的电池热管理性能模拟[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(S1): 329-338. |
| [8] | 胡俭, 姜静华, 范生军, 刘建浩, 邹海江, 蔡皖龙, 王沣浩. 中深层U型地埋管换热器取热特性研究[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(S1): 76-84. |
| [9] | 李舒月, 王欢, 周少强, 毛志宏, 张永民, 王军武, 吴秀花. 基于CPFD方法的U3O8氢还原流化床反应器数值模拟[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(9): 3133-3151. |
| [10] | 陈巨辉, 苏潼, 李丹, 陈立伟, 吕文生, 孟凡奇. 翅形扰流片作用下的微通道换热特性[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(9): 3122-3132. |
| [11] | 豆少军, 郝亮. PEMFC催化层耦合气体电荷传输过程的介观模拟[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(8): 3002-3010. |
| [12] | 钱啸宇, 阮璇, 李水清. 外加电场下电介质颗粒层结构重构与悬浮[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(8): 2756-2762. |
| [13] | 朱子良, 王爽, 姜宇昂, 林梅, 王秋旺. 欧拉-拉格朗日迭代固-液相变算法[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(8): 2763-2776. |
| [14] | 邓爱明, 何玉荣, 唐天琪, 胡彦伟. 导流板对喷雾流化床内颗粒生长过程影响的模拟[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(8): 2787-2799. |
| [15] | 金虎, 杨帆, 戴梦瑶. 基于格子Boltzmann方法的液滴在圆柱壁面上运动过程研究[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(8): 2897-2908. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备 11010102001995号
京公网安备 11010102001995号