化工学报 ›› 2022, Vol. 73 ›› Issue (1): 362-375.DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20211244
武鹏1,3( ),王芳2,3(
),王芳2,3( ),曾玺2,3,战洪仁1,岳君容3,王婷婷3,许光文1,3
),曾玺2,3,战洪仁1,岳君容3,王婷婷3,许光文1,3
收稿日期:2021-08-27
修回日期:2021-10-19
出版日期:2022-01-05
发布日期:2022-01-18
通讯作者:
王芳
作者简介:武鹏(1995—),男,硕士研究生,基金资助:
Peng WU1,3( ),Fang WANG2,3(
),Fang WANG2,3( ),Xi ZENG2,3,Hongren ZHAN1,Junrong YUE3,Tingting WANG3,Guangwen XU1,3
),Xi ZENG2,3,Hongren ZHAN1,Junrong YUE3,Tingting WANG3,Guangwen XU1,3
Received:2021-08-27
Revised:2021-10-19
Online:2022-01-05
Published:2022-01-18
Contact:
Fang WANG
摘要:
采用微型流化床反应分析仪(MFBRA)考察了不同温度(T,750~950℃)和水蒸气分压(SP,10%~30%)下生物质焦油水蒸气重整过程中的气体生成、气体产物中总碳转化和焦油转化等反应特性,求算反应动力学,并与焦油热裂解特性进行比较。在热裂解过程中,随温度增加,各气体(H2、CH4、CO、CO2)产率和气体产物中的总碳转化率增加,反应时间缩短。而在焦油水蒸气重整过程中,等温下的反应时间明显延长,且H2、CH4、CO产率和气体产物中的总碳转化率显著提升,而CO2产率在850℃时有最大值。在焦油水蒸气重整过程中,不仅有焦油裂解,还有裂解产物与水蒸气的反应,促进碳转化。在950℃、SP=30%条件下,气体产物中的总碳转化率达到92.34%。水蒸气作用下,气体组分的产率和气体产物中的总碳转化率增加,而等温条件下的反应速率下降。水蒸气分压对各气体组分的影响具有差异性。随分压增加,CO、CH4的生成速率和气体产物中的总碳转化的反应速率增加;H2生成速率逐渐下降,速率稳定段扩大;CO2生成速率在850℃时有最大值。采用均相模型求取焦油水蒸气重整反应过程中的活化能,气体产物的生成活化能(H2、CO、CO2和CH4)、气体产物中的总碳转化及焦油转化的活化能明显偏低,分别为90.10、42.01、58.56、64.92、61.44和63.26 kJ/mol,对应数值明显小于焦油热裂解,说明水蒸气对焦油重整反应的促进作用。最后,将焦油热裂解动力学数据与文献数据对比,验证了MFBRA对焦油水蒸气重整反应测试的可行性和分析结果的准确性。
中图分类号:
武鹏, 王芳, 曾玺, 战洪仁, 岳君容, 王婷婷, 许光文. 微型流化床中焦油热裂解和水蒸气重整的反应特性及动力学对比[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(1): 362-375.
Peng WU, Fang WANG, Xi ZENG, Hongren ZHAN, Junrong YUE, Tingting WANG, Guangwen XU. Comparison of reaction characteristics and kinetics between tar thermal cracking and steam reforming in a micro fluidized bed reaction analyzer[J]. CIESC Journal, 2022, 73(1): 362-375.
| 序号 | 反应方程式 | 反应类型 |
|---|---|---|
| R1 | tar | 热裂解反应 |
| R2 | CnHm + n H2O | 重整反应 |
| R3 | CnHx + CO2 | 干重整反应 |
| R4 | CO + H2O | 水煤气变换反应 |
| R5 | CnHx | 积炭反应 |
| R6 | C + H2O | 炭气化反应 |
| R7 | C + CO2 | 二氧化碳还原反应 |
| R8 | CH4 + H2O | 甲烷蒸气重整 |
表1 焦油水蒸气重整过程中涉及到的化学反应
Table 1 Reactions involved in the tar steam reforming process
| 序号 | 反应方程式 | 反应类型 |
|---|---|---|
| R1 | tar | 热裂解反应 |
| R2 | CnHm + n H2O | 重整反应 |
| R3 | CnHx + CO2 | 干重整反应 |
| R4 | CO + H2O | 水煤气变换反应 |
| R5 | CnHx | 积炭反应 |
| R6 | C + H2O | 炭气化反应 |
| R7 | C + CO2 | 二氧化碳还原反应 |
| R8 | CH4 + H2O | 甲烷蒸气重整 |
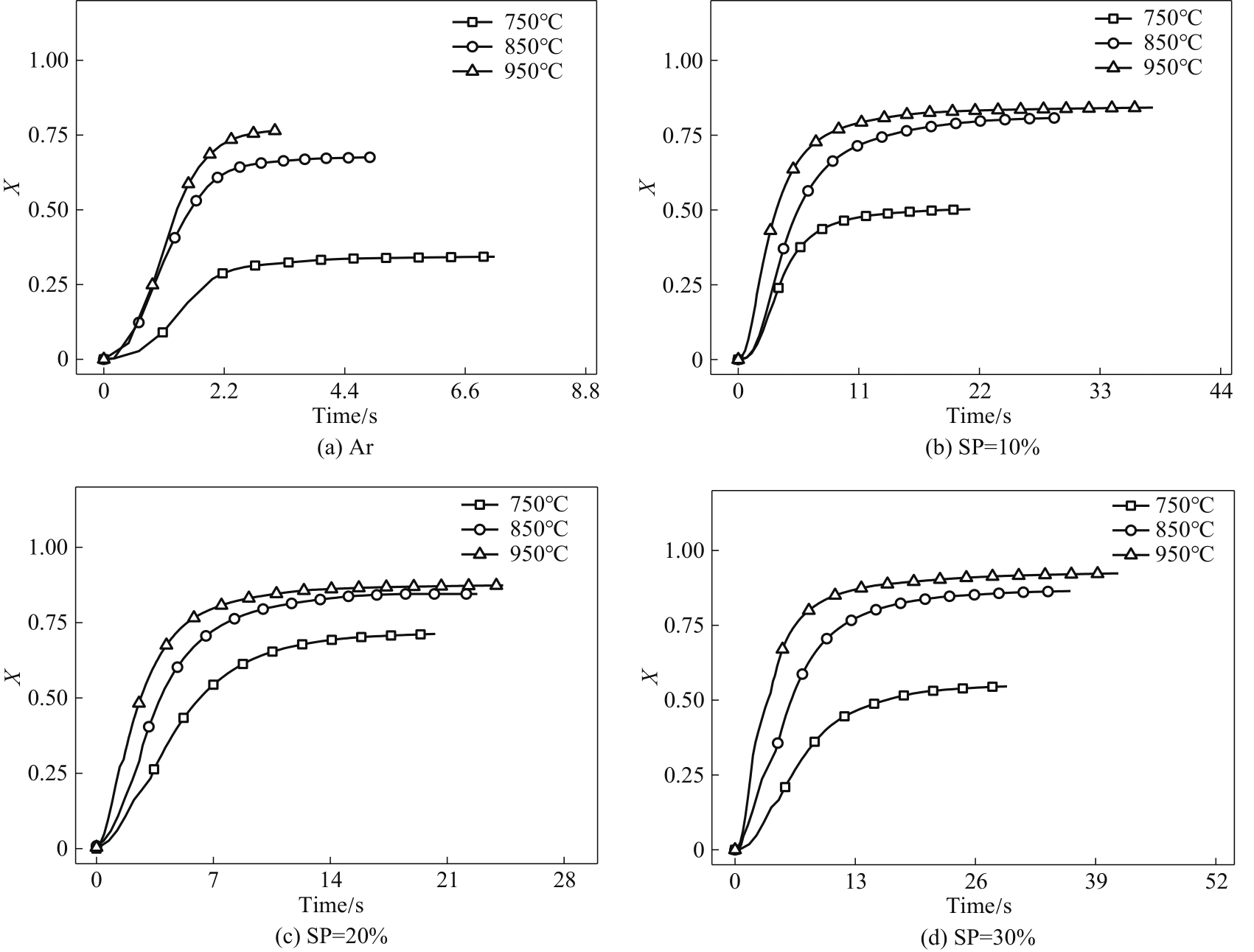
图8 焦油热裂解(a)和水蒸气重整[(b)~(d)]过程中气体产物中的总碳转化率变化
Fig.8 Variation of carbon conversion in the gaseous products during tar thermal cracking (a) and steam reforming [(b)—(d)]
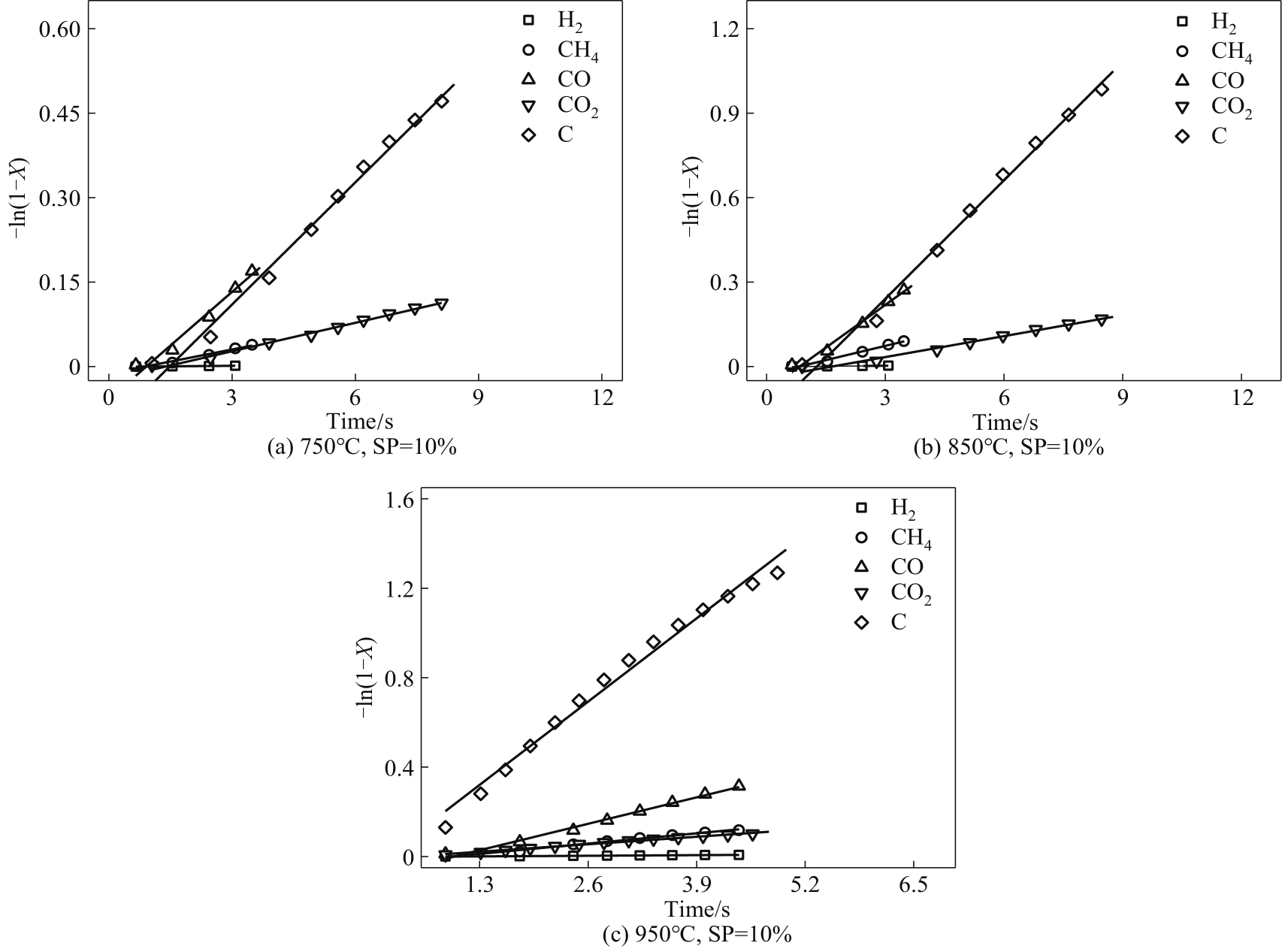
图11 不同温度下各气体和气体产物中总碳转化的均相模型数据拟合
Fig.11 Fitting of homogeneous model data of gas generation and total carbon conversion in gaseous products at different temperatures
| 气体 | 水蒸气分压 | Ea/(kJ/mol) | A/s-1 | R2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| H2 | Ar | 117.05 | 427.32 | 0.993 |
| SP=10% | 86.40 | 13.14 | 0.997 | |
| SP=20% | 89.40 | 17.44 | 0.996 | |
| SP=30% | 94.49 | 26.87 | 0.999 | |
| average (10%—30%) | 90.10 | 19.15 | 0.997 | |
| CO | Ar | 45.28 | 23.60 | 0.987 |
| SP=10% | 44.87 | 12.39 | 0.999 | |
| SP=20% | 39.67 | 6.25 | 0.989 | |
| SP=30% | 41.49 | 7.11 | 0.995 | |
| average (10%—30%) | 42.01 | 8.58 | 0.994 | |
| CO2 | Ar | 62.24 | 94.66 | 0.982 |
| SP=10% | 56.33 | 10.79 | 0.991 | |
| SP=20% | 59.45 | 17.79 | 0.999 | |
| SP=30% | 59.91 | 11.92 | 0.990 | |
| average (10%—30%) | 58.56 | 13.50 | 0.993 | |
| CH4 | Ar | 62.55 | 46.89 | 0.995 |
| SP=10% | 62.90 | 24.12 | 0987 | |
| SP=20% | 67.51 | 37.77 | 0.993 | |
| SP=30% | 64.36 | 26.36 | 0.999 | |
| average (10%—30%) | 64.92 | 29.42 | 0.993 | |
| C | Ar | 69.64 | 725.83 | 0.998 |
| SP=10% | 62.51 | 101.79 | 0.998 | |
| SP=20% | 60.55 | 125.24 | 0.989 | |
| SP=30% | 61.26 | 78.63 | 0.991 | |
| average (10%—30%) | 61.44 | 101.87 | 0.996 | |
| Total | Ar | 71.14 | 706.32 | 0.992 |
| SP=10% | 63.55 | 105.14 | 0.993 | |
| SP=20% | 62.81 | 163.92 | 0.988 | |
| SP=30% | 63.42 | 99.67 | 0.999 | |
| average (10%—30%) | 63.26 | 122.91 | 0.993 |
表2 焦油热裂解和水蒸气重整的反应动力学数据
Table 2 Reaction kinetics data of tar thermal cracking and steam reforming
| 气体 | 水蒸气分压 | Ea/(kJ/mol) | A/s-1 | R2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| H2 | Ar | 117.05 | 427.32 | 0.993 |
| SP=10% | 86.40 | 13.14 | 0.997 | |
| SP=20% | 89.40 | 17.44 | 0.996 | |
| SP=30% | 94.49 | 26.87 | 0.999 | |
| average (10%—30%) | 90.10 | 19.15 | 0.997 | |
| CO | Ar | 45.28 | 23.60 | 0.987 |
| SP=10% | 44.87 | 12.39 | 0.999 | |
| SP=20% | 39.67 | 6.25 | 0.989 | |
| SP=30% | 41.49 | 7.11 | 0.995 | |
| average (10%—30%) | 42.01 | 8.58 | 0.994 | |
| CO2 | Ar | 62.24 | 94.66 | 0.982 |
| SP=10% | 56.33 | 10.79 | 0.991 | |
| SP=20% | 59.45 | 17.79 | 0.999 | |
| SP=30% | 59.91 | 11.92 | 0.990 | |
| average (10%—30%) | 58.56 | 13.50 | 0.993 | |
| CH4 | Ar | 62.55 | 46.89 | 0.995 |
| SP=10% | 62.90 | 24.12 | 0987 | |
| SP=20% | 67.51 | 37.77 | 0.993 | |
| SP=30% | 64.36 | 26.36 | 0.999 | |
| average (10%—30%) | 64.92 | 29.42 | 0.993 | |
| C | Ar | 69.64 | 725.83 | 0.998 |
| SP=10% | 62.51 | 101.79 | 0.998 | |
| SP=20% | 60.55 | 125.24 | 0.989 | |
| SP=30% | 61.26 | 78.63 | 0.991 | |
| average (10%—30%) | 61.44 | 101.87 | 0.996 | |
| Total | Ar | 71.14 | 706.32 | 0.992 |
| SP=10% | 63.55 | 105.14 | 0.993 | |
| SP=20% | 62.81 | 163.92 | 0.988 | |
| SP=30% | 63.42 | 99.67 | 0.999 | |
| average (10%—30%) | 63.26 | 122.91 | 0.993 |
| 产物 | 仪器 | 原料 | T/K | Ea/(kJ/mol) | 文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| total | MFB | biomass tar | 1023—1223 | 69.64 | this study |
| MFB | biomass tar | 1023—1223 | 78.2 | [ | |
| fixed bed | biomass tar | 773—1073 | 70.5 | [ | |
| TGA | biomass tar | 1223 | 79.6 | [ | |
| fixed bed | biomass tar | 773—1373 | 76.6 | [ | |
| H2 | MFB | biomass tar | 1023—1223 | 117.05 | this study |
| fixed bed | biomass tar | 773—1073 | 129 | [ | |
| CO | MFB | biomass tar | 1023—1223 | 45.28 | this study |
| MFB | model compound | 1023—1223 | 53.35 | [ | |
| CH4 | MFB | biomass tar | 1023—1223 | 62.55 | this study |
| MFB | biomass tar | 1023—1223 | 63.19 | [ |
表3 焦油热裂解活化能与文献数据对比
Table 3 Comparison of Ea between tar thermal cracking in this study and literatures
| 产物 | 仪器 | 原料 | T/K | Ea/(kJ/mol) | 文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| total | MFB | biomass tar | 1023—1223 | 69.64 | this study |
| MFB | biomass tar | 1023—1223 | 78.2 | [ | |
| fixed bed | biomass tar | 773—1073 | 70.5 | [ | |
| TGA | biomass tar | 1223 | 79.6 | [ | |
| fixed bed | biomass tar | 773—1373 | 76.6 | [ | |
| H2 | MFB | biomass tar | 1023—1223 | 117.05 | this study |
| fixed bed | biomass tar | 773—1073 | 129 | [ | |
| CO | MFB | biomass tar | 1023—1223 | 45.28 | this study |
| MFB | model compound | 1023—1223 | 53.35 | [ | |
| CH4 | MFB | biomass tar | 1023—1223 | 62.55 | this study |
| MFB | biomass tar | 1023—1223 | 63.19 | [ |
| 1 | Bridgwater A V. The technical and economic feasibility of biomass gasification for power generation[J]. Fuel, 1995, 74(5): 631-653. |
| 2 | 常圣强, 李望良, 张晓宇, 等. 生物质气化发电技术研究进展[J]. 化工学报, 2018, 69(8): 3318-3330. |
| Chang S Q, Li W L, Zhang X Y, et al. Progress in biomass gasification power generation technology[J]. CIESC Journal, 2018, 69(8): 3318-3330. | |
| 3 | 王辅臣.煤气化技术在中国: 回顾与展望[J]. 洁净煤技术, 2021, 27(1): 1-33. |
| Wang F C. Coal gasification technologies in China: review and prospect[J]. Clean Coal Technology, 2021, 27(1): 1-33. | |
| 4 | 房倚天, 王志青, 李俊国, 等. 多段分级转化流化床煤气化技术研究开发进展[J]. 煤炭转化, 2018, 41(3): 1-11. |
| Fang Y T, Wang Z Q, Li J G, et al. Research and development progress in multi-stage conversion fluidized bed coal gasification technology[J]. Coal Conversion, 2018, 41(3): 1-11. | |
| 5 | Li C S, Resources Suzuki K., properties and utilization of tar[J]. Resources, Conservation and Recycling, 2010, 54(11): 905-915. |
| 6 | 赵善辉, 罗永浩, 苏毅, 等. 部分氧化对焦油模型化合物苯酚转化的机理[J]. 化工学报, 2013, 64(10): 3790-3796. |
| Zhao S H, Luo Y H, Su Y, et al. Reaction mechanism for partial oxidation of biomass tar[J]. CIESC Journal, 2013, 64(10): 3790-3796. | |
| 7 | Nakamura S, Kitano S, Yoshikawa K. Biomass gasification process with the tar removal technologies utilizing bio-oil scrubber and char bed[J]. Applied Energy, 2016, 170: 186-192. |
| 8 | 王芳, 曾玺, 孙延林, 等. 两段流化床中半焦催化脱除焦油特性[J]. 化工学报, 2017, 68(10): 3762-3769. |
| Wang F, Zeng X, Sun Y L, et al. Characteristics of char catalytic reforming of tar in two-stage fluidized bed[J]. CIESC Journal, 2017, 68(10): 3762-3769. | |
| 9 | 蒋剑春, 金淳, 张进平, 等. 生物质催化气化工业应用技术研究[J]. 林产化学与工业, 2001, 21(4): 21-26. |
| Jiang J C, Jin C, Zhang J P, et al. Study on industrial applied technology for biomass catalytic gasification[J]. Chemistry and Industry of Forest Products, 2001, 21(4): 21-26. | |
| 10 | Phuphuakrat T, Namioka T, Yoshikawa K. Absorptive removal of biomass tar using water and oily materials[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2011, 102(2): 543-549. |
| 11 | 孙云娟, 蒋剑春. 生物质气化过程中焦油的去除方法综述[J]. 生物质化学工程, 2006, 40(2): 31-35. |
| Sun Y J, Jiang J C. A review of measures for tar elimination in biomass gasification processes[J]. Biomass Chemical Engineering, 2006, 40(2): 31-35. | |
| 12 | 杨秀山, 赵军, 骆海鹏, 等. 微生物降解生物质气化洗焦废水和焦油的研究[J]. 中国环境科学, 2001, 21(2): 109-111. |
| Yang X S, Zhao J, Luo H P, et al. Study on microbial degradation of tar-wash wastewater and tar in biomass gasification by microorganisms[J]. China Environmental Science, 2001, 21(2): 109-111. | |
| 13 | Zeng X, Ueki Y, Yoshiie R, et al. Recent progress in tar removal by char and the applications: a comprehensive analysis[J]. Carbon Resources Conversion, 2020, 3:1-18. |
| 14 | 颜蓓蓓, 王建, 刘彬, 等. 生物油金属水热原位加氢提质技术研究进展[J]. 化工学报, 2021, 72(4): 1783-1795. |
| Yan B B, Wang J, Liu B, et al. Research progress of bio-oil metal hydrothermal in-situ hydrogenation technology[J]. CIESC Journal, 2021, 72(4): 1783-1795. | |
| 15 | Jess A. Mechanisms and kinetics of thermal reactions of aromatic hydrocarbons from pyrolysis of solid fuels[J]. Fuel, 1996, 75(12): 1441-1448. |
| 16 | Li C S, Suzuki K. Tar property, analysis, reforming mechanism and model for biomass gasification—an overview[J]. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 2009, 13(3): 594-604. |
| 17 | 刘阳, 刘捷成, 俞海淼, 等. 新型镍基镁渣催化重整松木热解挥发分焦油析出特性研究[J]. 化工学报, 2019, 70(8): 2991-2999. |
| Liu Y, Liu J C, Yu H M, et al. Characteristics of tar formation during catalytic reforming of pyrolysis volatile from pine saw dust over novel Ni-based magnesium slag catalyst[J]. CIESC Journal, 2019, 70(8): 2991-2999. | |
| 18 | Udomsirichakorn J, Salam P A. Review of hydrogen-enriched gas production from steam gasification of biomass: the prospect of CaO-based chemical looping gasification[J]. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 2014, 30: 565-579. |
| 19 | Shen Y F, Yoshikawa K. Recent progresses in catalytic tar elimination during biomass gasification or pyrolysis—a review[J]. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 2013, 21: 371-392. |
| 20 | Jönsson O. Thermal cracking of tars and hydrocarbons by addition of steam and oxygen in the cracking zone[M]//Fundamentals of Thermochemical Biomass Conversion. Dordrecht: Springer Netherlands, 1985: 733-746. |
| 21 | Garcia X A, Hüttinger K J. Steam gasification of naphthalene as a model reaction of homogeneous gas/gas reactions during coal gasification[J]. Fuel, 1989, 68(10): 1300-1310. |
| 22 | Li Q, Wang Q, Kayamori A, et al. Experimental study and modeling of heavy tar steam reforming[J]. Fuel Processing Technology, 2018, 178: 180-188. |
| 23 | Zhu F S, Zhang H, Yang H P, et al. Plasma reforming of tar model compound in a rotating gliding arc reactor: understanding the effects of CO2 and H2O addition[J]. Fuel, 2020, 259: 116271. |
| 24 | Warsita A, Al-attab K A, Zainal Z A. Effect of water addition in a microwave assisted thermal cracking of biomass tar models[J]. Applied Thermal Engineering, 2017, 113: 722-730. |
| 25 | 张玉明, 纪德馨, 朱翰文, 等. 微型流化床中萘裂解生成小分子气体的反应动力学研究[J]. 化工学报, 2021, 72(5): 2604-2615. |
| Zhang Y M, Ji D X, Zhu H W, et al. Reaction kinetics of naphthalene cracking into small molecule gas in a micro fluidized bed[J]. CIESC Journal, 2021, 72(5): 2604-2615. | |
| 26 | Yang J X, Kaewpanha M, Karnjanakom S, et al. Steam reforming of biomass tar over calcined egg shell supported catalysts for hydrogen production[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2016, 41(16): 6699-6705. |
| 27 | Sun H L, Feng D D, Zhao Y J, et al. Mechanism of catalytic tar reforming over biochar: description of volatile-H2O-char interaction[J]. Fuel, 2020, 275: 117954. |
| 28 | Quan C, Xu S P, Zhou C C. Steam reforming of bio-oil from coconut shell pyrolysis over Fe/olivine catalyst[J]. Energy Conversion and Management, 2017, 141: 40-47. |
| 29 | Wei B Y, Yang H, Hu H Q, et al. Enhanced production of light tar from integrated process of in situ catalytic upgrading lignite tar and methane dry reforming over Ni/mesoporous Y[J]. Fuel, 2020, 279: 118533. |
| 30 | 武荣成, 张纯, 许光文. 内构件移动床碎煤热解中试产物分布特性[J]. 煤炭转化, 2019, 42(2): 13-17. |
| Wu R C, Zhang C, Xu G W. Characteristics of coal pyrolysis product distribution in moving-bed reactor with internals[J]. Coal Conversion, 2019, 42(2): 13-17. | |
| 31 | 胡二峰, 张纯, 武荣成, 等. 内构件固定床反应器中不同水分煤的热解特性[J]. 化工学报, 2015, 66(7): 2656-2663. |
| Hu E F, Zhang C, Wu R C, et al. Pyrolysis of coal with different moisture contents in fixed-bed reactor with internals[J]. CIESC Journal, 2015, 66(7): 2656-2663. | |
| 32 | 冯冬冬. 多活性位焦炭原位催化裂解生物质焦油的反应机理研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学, 2018. |
| Feng D D. Mechanism of in situ catalytic cracking of biomass tar over biochar with multiple active sites[D]. Harbin: Harbin Institute of Technology, 2018. | |
| 33 | Sun H L, Sun S Z, Feng D D, et al. Mechanism of coke formation and corresponding gas fraction characteristics in biochar-catalyzed tar reforming during corn straw pyrolysis[J]. Fuel Processing Technology, 2021, 221: 106903. |
| 34 | 王芳杰. 胜利褐煤温和气化焦油催化重整研究[D]. 北京: 中国矿业大学, 2014. |
| Wang F J. Catalytic reforming of tar derived from mild gasification of Shengli lignite[D]. Beijing: China University of Mining and Technology, 2014. | |
| 35 | 张静静. 生物质合成气甲烷化耦合焦油重整研究[D]. 大连: 大连理工大学, 2019. |
| Zhang J J. Simultaneous tar reforming and syngas methanation of biogenous syngas[D]. Dalian: Dalian University of Technology, 2019. | |
| 36 | Avni E, Coughlin R W, Solomon P R, et al. Mathematical modelling of lignin pyrolysis[J]. Fule, 1985, 64(11): 1495-1501. |
| 37 | Li Q, Wang Q, Tsuboi Y, et al. Steam reforming of tar studied in bench-scale experiments and pilot-scale tests with simulations[J]. Fuel, 2021, 290: 120028. |
| 38 | Hu D D, Zeng X, Wang F, et al. Comparison of tar thermal cracking and catalytic reforming by char in a micro fluidized bed reaction analyzer[J]. Fuel, 2021, 290: 120038. |
| 39 | 李旭, 由世俊, 张欢, 等. 生物质炭催化重整焦油的动力学模型研究[J]. 太阳能学报, 2014, 35(6): 949-954. |
| Li X, You S J, Zhang H, et al. Study on kinetic model of catalytic reforming reaction over biomass char[J]. Acta Energiae Solaris Sinica, 2014, 35(6): 949-954. | |
| 40 | Xu T T, Xu F, Hu Z Q, et al. Non-isothermal kinetics of biomass-pyrolysis-derived-tar (BPDT) thermal decomposition via thermogravimetric analysis[J]. Energy Conversion and Management, 2017, 138: 452-460. |
| 41 | Morf P, Hasler P, Nussbaumer T. Mechanisms and kinetics of homogeneous secondary reactions of tar from continuous pyrolysis of wood chips[J]. Fuel, 2002, 81(7): 843-853. |
| 42 | Boroson M L, Howard J B, Longwell J P, et al. Product yields and kinetics from the vapor phase cracking of wood pyrolysis tars[J]. AIChE Journal, 1989, 35(1):120-128. |
| 43 | Gai C, Dong Y P, Lv Z, et al. Pyrolysis behavior and kinetic study of phenol as tar model compound in micro fluidized bed reactor[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2015, 40(25): 7956-7964. |
| [1] | 郑佳丽, 李志会, 赵新强, 王延吉. 离子液体催化合成2-氰基呋喃反应动力学研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(9): 3708-3715. |
| [2] | 陈佳起, 赵万玉, 姚睿充, 侯道林, 董社英. 开心果壳基碳点的合成及其对Q235碳钢的缓蚀行为研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(8): 3446-3456. |
| [3] | 吴文涛, 褚良永, 张玲洁, 谭伟民, 沈丽明, 暴宁钟. 腰果酚生物基自愈合微胶囊的高效制备工艺研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(7): 3103-3115. |
| [4] | 董茂林, 陈李栋, 黄六莲, 吴伟兵, 戴红旗, 卞辉洋. 酸性助水溶剂制备木质纳米纤维素及功能应用研究进展[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(6): 2281-2295. |
| [5] | 杨峥豪, 何臻, 常玉龙, 靳紫恒, 江霞. 生物质快速热解下行式流化床反应器研究进展[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(6): 2249-2263. |
| [6] | 葛泽峰, 吴雨青, 曾名迅, 查振婷, 马宇娜, 侯增辉, 张会岩. 灰化学成分对生物质气化特性的影响规律[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(5): 2136-2146. |
| [7] | 祖凌鑫, 胡荣庭, 李鑫, 陈余道, 陈广林. 木质生物质化学组分的碳释放产物特征和反硝化利用程度[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(3): 1332-1342. |
| [8] | 刘海芹, 李博文, 凌喆, 刘亮, 俞娟, 范一民, 勇强. 羟基-炔点击化学改性半乳甘露聚糖薄膜的制备及性能研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(3): 1370-1378. |
| [9] | 郑杰元, 张先伟, 万金涛, 范宏. 丁香酚环氧有机硅树脂的制备及其固化动力学研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(2): 924-932. |
| [10] | 陈健鑫, 朱瑞杰, 盛楠, 朱春宇, 饶中浩. 纤维素基生物质多孔炭的制备及其超级电容器性能研究[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(9): 4194-4206. |
| [11] | 郝泽光, 张乾, 高增林, 张宏文, 彭泽宇, 杨凯, 梁丽彤, 黄伟. 生物质与催化裂化油浆共热解协同作用研究[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(9): 4070-4078. |
| [12] | 张东旺, 杨海瑞, 周托, 黄中, 李诗媛, 张缦. 生物质锅炉对流受热面积灰冷态模拟实验研究[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(8): 3731-3738. |
| [13] | 刘新华, 韩振南, 韩健, 梁斌, 张楠, 胡善伟, 白丁荣, 许光文. 基于热解与燃烧反应重构的低NO x 解耦燃烧原理与技术[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(8): 3355-3368. |
| [14] | 朱莲峰, 王超, 张梦娟, 刘方正, 贾鑫, 安萍, 许光文, 韩振南. 水蒸气/氧流化床两段煤气化制备低焦油合成气工艺实验[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(8): 3720-3730. |
| [15] | 王凯玥, 马永丽, 李琛, 刘明言. 气液固微型流化床的气液传质系数[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(8): 3529-3540. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备 11010102001995号
京公网安备 11010102001995号