化工学报 ›› 2023, Vol. 74 ›› Issue (10): 4352-4366.DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20230915
• 过程安全 • 上一篇
江丙友1,3( ), 丁大伟1,3, 苏明清2(
), 丁大伟1,3, 苏明清2( ), 鲁昆仑1,3
), 鲁昆仑1,3
收稿日期:2023-09-01
修回日期:2023-09-24
出版日期:2023-10-25
发布日期:2023-12-22
通讯作者:
苏明清
作者简介:江丙友(1987—),男,博士,教授,cumtjiangby@163.com
基金资助:
Bingyou JIANG1,3( ), Dawei DING1,3, Mingqing SU2(
), Dawei DING1,3, Mingqing SU2( ), Kunlun LU1,3
), Kunlun LU1,3
Received:2023-09-01
Revised:2023-09-24
Online:2023-10-25
Published:2023-12-22
Contact:
Mingqing SU
摘要:
为了减小聚乙烯(PE)粉尘爆炸事故所带来的危害,使用20-L爆炸球以及自主搭建的粉尘爆燃火焰传播测试系统进行爆炸抑制实验,从爆炸压力行为和火焰传播行为探究了聚磷酸铵(APP)对PE粉尘的抑制特性。通过同步热分析仪分析了APP对PE粉尘热解特性的影响,采用Coats-Redfern方法计算了PE和APP-PE混合粉尘(I=1.0)在快速热解阶段的反应动力学参数,并结合爆炸产物探究了其抑制机理。结果表明:APP可有效降低PE粉尘的最大爆炸压力、最大爆炸压力上升速率以及火焰传播速度,当抑制比为1.0时,PE粉尘爆炸压力峰消失,标志着在该抑制比下被完全抑制。此外,通过分析热解动力学模型发现PE粉尘在快速热解阶段遵循A3模型,添加APP后遵循R2模型,其平均活化能分别为137.34 kJ/mol和228.52 kJ/mol,活化能的增加,说明APP的加入减缓了PE粉尘的氧化和热分解,表现出显著的抑制效果。研究结果可为防治PE粉尘爆炸提供理论依据和技术支撑。
中图分类号:
江丙友, 丁大伟, 苏明清, 鲁昆仑. 聚磷酸铵对聚乙烯粉尘爆炸特性及热解动力学影响研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(10): 4352-4366.
Bingyou JIANG, Dawei DING, Mingqing SU, Kunlun LU. Study on the effect of ammonium polyphosphate on the explosion characteristics and pyrolysis kinetics of polyethylene dusts[J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(10): 4352-4366.
| 样品 | 化学式 | 密度/ (g/cm³) | 熔点/ ℃ | 分子量 | D50/μm |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 聚乙烯(PE) | (C2H4) n | 0.962 | 85 | — | 25.369 |
| 聚磷酸铵(APP) | (NH4) n+2P n O3n+1 | 1.74 | — | 115 | 10.605 |
表1 PE和APP物理化学性质
Table 1 Physical and chemical properties of PE and APP
| 样品 | 化学式 | 密度/ (g/cm³) | 熔点/ ℃ | 分子量 | D50/μm |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 聚乙烯(PE) | (C2H4) n | 0.962 | 85 | — | 25.369 |
| 聚磷酸铵(APP) | (NH4) n+2P n O3n+1 | 1.74 | — | 115 | 10.605 |
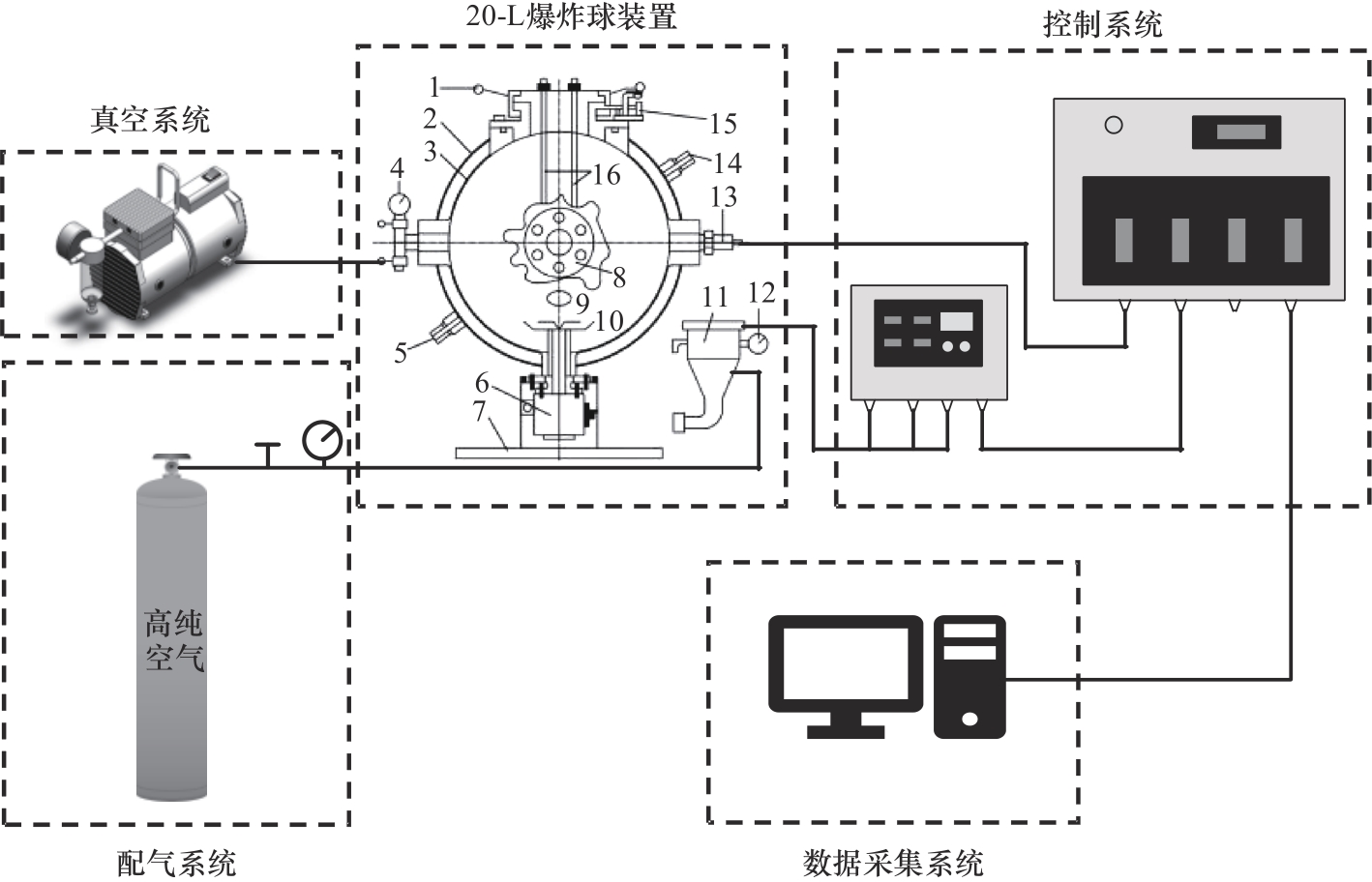
图4 20-L球形爆炸实验系统1—密封盖;2—夹层外套;3—夹层内套;4—真空表;5—循环水出口;6—气粉两相阀;7—底座;8—视窗;9—抽真空孔;10—分散阀;11—粉尘储存罐;12—压力表;13—压力传感器;14—循环水入口;15—安全限位开关;16—点火杆
Fig.4 20-L spherical explosion experimental system

图5 粉尘爆燃火焰传播测试系统1—高速摄像机;2—计算机;3—透明垂直石英玻璃管;4—点火电极;5—电磁阀;6—储气罐;7—阀门;8—压力表;9—气体管道;10—泄压阀;11—高压气瓶;12—控制系统
Fig.5 Dust deflagration flame propagation test system
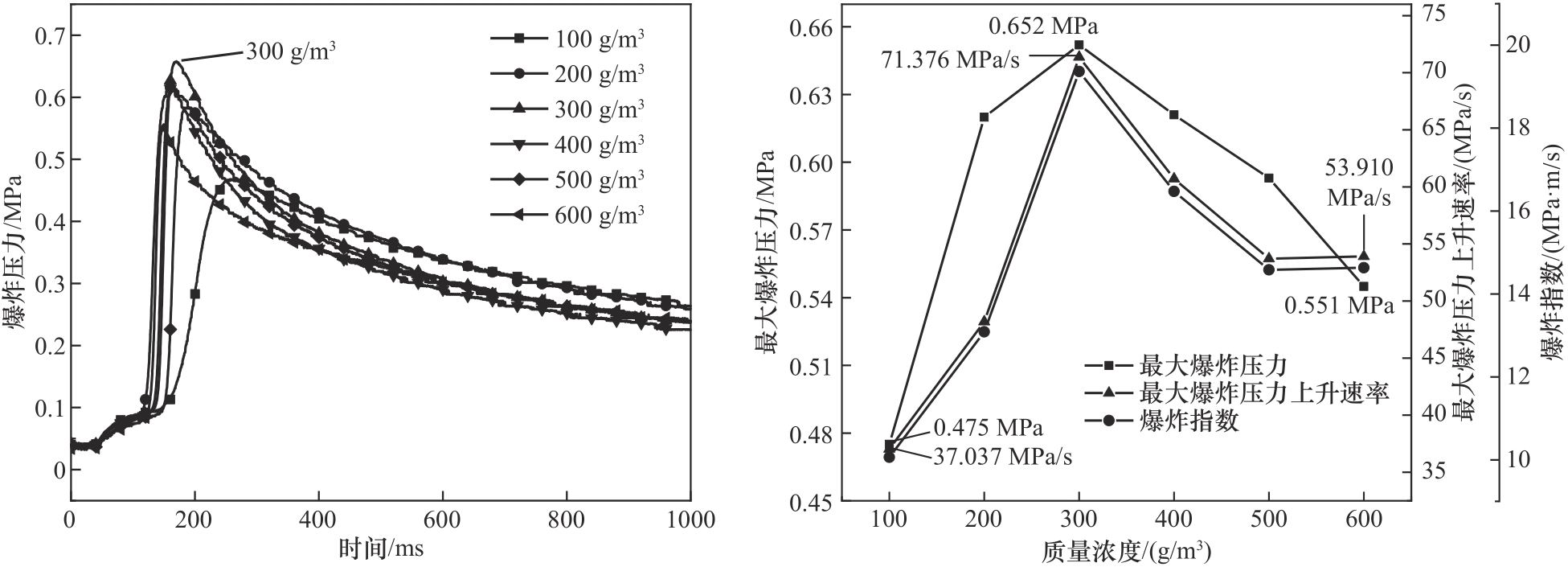
图6 不同浓度PE粉尘爆炸压力曲线和爆炸特性参数变化趋势
Fig.6 Trends in explosion pressure curves and explosion characteristic parameters for different concentrations of PE dusts

图9 不同APP添加量下PE粉尘爆燃火焰传播前锋位置和火焰传播速度
Fig.9 PE dust deflagration flame propagation front position and flame propagation velocity under different amount of APP
| 火焰传播时间/ms | 灰度均值 | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 未添加APP | 0.1 g APP | 0.2 g APP | |
| 60 | 4.2217 | 4.8477 | 1.4867 |
| 70 | 5.5303 | 5.2869 | 1.8246 |
| 80 | 7.6907 | 6.1680 | 2.0551 |
| 90 | 10.6845 | 7.7607 | 2.1089 |
| 95 | 11.9554 | 6.9204 | 2.1988 |
| 100 | 14.2547 | 10.9432 | 2.5561 |
| 115 | 22.0191 | 15.3787 | 3.9400 |
| 130 | 23.9056 | 16.3275 | 5.7265 |
| 140 | 29.0628 | 17.5043 | 9.0453 |
| 200 | 19.0878 | 15.9452 | 16.1389 |
| 250 | 9.6807 | 7.4677 | 8.7830 |
| 280 | 5.2990 | 5.6537 | 7.1399 |
表2 PE火焰灰度频数分布平均值
Table 2 Average of PE flame grey scale frequency distributions
| 火焰传播时间/ms | 灰度均值 | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 未添加APP | 0.1 g APP | 0.2 g APP | |
| 60 | 4.2217 | 4.8477 | 1.4867 |
| 70 | 5.5303 | 5.2869 | 1.8246 |
| 80 | 7.6907 | 6.1680 | 2.0551 |
| 90 | 10.6845 | 7.7607 | 2.1089 |
| 95 | 11.9554 | 6.9204 | 2.1988 |
| 100 | 14.2547 | 10.9432 | 2.5561 |
| 115 | 22.0191 | 15.3787 | 3.9400 |
| 130 | 23.9056 | 16.3275 | 5.7265 |
| 140 | 29.0628 | 17.5043 | 9.0453 |
| 200 | 19.0878 | 15.9452 | 16.1389 |
| 250 | 9.6807 | 7.4677 | 8.7830 |
| 280 | 5.2990 | 5.6537 | 7.1399 |
| 样品 | 升温速率/ (K/min) | 活化能/ (kJ/mol) | 指前因子/min-1 | 机理函数 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PE | 5 | 94.81 | 5.36×105 | A3模型 |
| 10 | 159.17 | 3.95×1010 | A3模型 | |
| 20 | 158.04 | 3.31×1010 | A3模型 | |
| 平均值 | 137.34 | 2.42×1010 | ||
| APP-PE | 5 | 224.93 | 6.93×1014 | R2模型 |
| 10 | 228.05 | 1.09×1015 | R2模型 | |
| 20 | 232.59 | 2.60×1015 | R2模型 | |
| 平均值 | 228.52 | 1.46×1015 |
表3 PE与APP-PE混合粉尘(I=1.0)在不同升温速率下的动力学参数
Table 3 Kinetic parameters of PE and APP-PE mixture (I=1.0) at different heating rates
| 样品 | 升温速率/ (K/min) | 活化能/ (kJ/mol) | 指前因子/min-1 | 机理函数 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PE | 5 | 94.81 | 5.36×105 | A3模型 |
| 10 | 159.17 | 3.95×1010 | A3模型 | |
| 20 | 158.04 | 3.31×1010 | A3模型 | |
| 平均值 | 137.34 | 2.42×1010 | ||
| APP-PE | 5 | 224.93 | 6.93×1014 | R2模型 |
| 10 | 228.05 | 1.09×1015 | R2模型 | |
| 20 | 232.59 | 2.60×1015 | R2模型 | |
| 平均值 | 228.52 | 1.46×1015 |
| 1 | Cheng Y C, Chang S C, Shu C M. Effects of volatile organic compounds on the explosion characteristics of polyethylene dust[J]. Process Safety and Environmental Protection, 2022, 168: 114-122. |
| 2 | Gan B, Gao W, Jiang H, et al. Flame propagation behaviors and temperature characteristics in polyethylene dust explosions[J]. Powder Technology, 2018, 328: 345-357. |
| 3 | Han O S, Lee J S. Pyrolysis characteristic and ignition energy of high-density polyethylene powder[J]. Journal of the Korean Institute of Gas, 2014, 18(3): 31-37. |
| 4 | Yan X Q, Yu J L. Dust explosion incidents in China[J]. Process Safety Progress, 2012, 31(2): 187-189. |
| 5 | 张延松, 李南, 郭瑞, 等. 月桂酸与硬脂酸粉尘爆炸过程热解动力学与火焰传播特性关系[J]. 爆炸与冲击, 2022, 42(7): 159-170. |
| Zhang Y S, Li N, Guo R, et al. Relationship between pyrolysis kinetics and flame propagation characteristics of lauric acid and stearic acid dust explosion[J]. Explosion and Shock, 2022, 42(7): 159-170. | |
| 6 | Yuan Z, Khakzad N, Khan F, et al. Dust explosions: a threat to the process industries[J]. Process Safety and Environmental Protection, 2015, 98: 57-71. |
| 7 | 纪文涛. 气粉两相混合体系爆炸及泄放特性研究[D]. 大连: 大连理工大学, 2018. |
| Ji W T. Study on explosion and discharge characteristics of gas-powder two-phase mixed system[D]. Dalian: Dalian University of Technology, 2018. | |
| 8 | 林晨迪. 不同抑爆粉体对聚乙烯粉尘爆炸的抑制作用研究[D]. 焦作: 河南理工大学, 2020. |
| Lin C D. Study on the inhibitory effect of different explosion suppression powders on polyethylene dust explosion[D]. Jiaozuo: Henan Polytechnic University, 2020. | |
| 9 | Lin S, Liu Z T, Qian J F, et al. Inertant effects and mechanism of Al(OH)3 powder on polyethylene dust explosions based on flame propagation behavior and thermal analysis[J]. Fire Safety Journal, 2021, 124: 103392. |
| 10 | Bu Y J, Ma Z P, Li C, et al. Effect of admixed solid inertants on dispersibility of combustible dust clouds in a modified Hartmann tube[J]. Process Safety and Environmental Protection, 2020, 135: 1-11. |
| 11 | 庞磊, 赵钰, 杨凯, 等. 低密度聚乙烯粉尘云爆炸敏感性实验[J]. 消防科学与技术, 2019, 38(9): 1211-1215. |
| Pang L, Zhao Y, Yang K, et al. Experiment of explosion sensitivity on LDPE dust clouds[J]. Fire Science and Technology, 2019, 38(9): 1211-1215. | |
| 12 | 刘义, 赵东风, 路帅, 等. 聚乙烯粉体粒径对静电放电点火的影响[J]. 河北大学学报(自然科学版), 2007, 27(6): 625-629. |
| Liu Y, Zhao D F, Lu S, et al. Effects of polyethylene size on ignition of electrostatics discharge[J]. Journal of Hebei University (Natural Science Edition), 2007, 27(6): 625-629. | |
| 13 | 刘义, 赵东风, 路帅, 等. 聚乙烯粉体输送系统安全可接受程度分析方法[J]. 石油化工高等学校学报, 2010, 23(2): 72-75. |
| Liu Y, Zhao D F, Lu S, et al. Analysis method of acceptable safety degree on polyethylene dust conveying system[J]. Journal of Petrochemical Universities, 2010, 23(2): 72-75. | |
| 14 | 刘义, 赵东风, 路帅, 等. 可燃性气体对PE粉体静电放电点火的影响[J]. 合成树脂及塑料, 2008, 25(1): 20-22, 26. |
| Liu Y, Zhao D F, Lu S, et al. Effect of combustible gas on ignition of PE dust electrostatics discharge[J]. China Synthetic Resin and Plastics, 2008, 25(1): 20-22, 26. | |
| 15 | Gan B, Li B, Jiang H, et al. Ethylene/polyethylene hybrid explosions(Ⅰ): Effects of ethylene concentrations on flame propagations[J]. Journal of Loss Prevention in the Process Industries, 2018, 54: 93-102. |
| 16 | 刘路. 聚乙烯粉尘燃爆特性研究[D]. 东营: 中国石油大学(华东), 2019. |
| Liu L. Study on explosion characteristics of polyethylene dust[D]. Dongying: China University of Petroleum, 2019. | |
| 17 | 喻健良, 侯玉洁, 闫兴清, 等. 密闭空间内聚乙烯粉尘爆炸火焰传播特性的实验研究[J]. 化工学报, 2019, 70(3): 1227-1235. |
| Yu J L, Hou Y J, Yan X Q, et al. Experimental study on flame propagation characteristic of polyethylene dust explosion under confined chamber[J]. CIESC Journal, 2019, 70(3): 1227-1235. | |
| 18 | 喻健良, 纪文涛, 孙会利, 等. 乙烯/聚乙烯两相体系爆炸特性[J]. 化工学报, 2017, 68(12): 4841-4847. |
| Yu J L, Ji W T, Sun H L, et al. Explosibility of hybrid mixtures of ethylene and polyethylene dust[J]. CIESC Journal, 2017, 68(12): 4841-4847. | |
| 19 | 甘波. 乙烯/聚乙烯混合爆炸火焰传播机理研究[D]. 大连: 大连理工大学, 2020. |
| Gan B. Study on flame propagation mechanism of ethylene/polyethylene mixed explosion[D]. Dalian: Dalian University of Technology, 2020. | |
| 20 | 梁一鸣, 贺锋, 张鏖, 等. 含磷酸盐对聚乙烯粉尘爆燃的抑制影响实验研究[J]. 中国安全生产科学技术, 2023, 19(4): 135-141. |
| Liang Y M, He F, Zhang A, et al. Experimental study on inhibitory effect of phosphates on polyethylene dust deflagration[J]. Journal of Safety Science and Technology, 2023, 19(4): 135-141. | |
| 21 | 王燕, 何佳, 杨晶晶, 等. 草酸盐和碳酸氢盐抑制聚乙烯粉尘爆炸特性[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(9): 4207-4216. |
| Wang Y, He J, Yang J J, et al. Inhibition of polyethylene dust explosion by oxalate and bicarbonate[J]. CIESC Journal, 2022, 73(9): 4207-4216. | |
| 22 | Wei L J, Su M Q, Wang K, et al. Suppression effects of ABC powder on explosion characteristics of hybrid C2H4/polyethylene dust[J]. Fuel, 2022, 310: 122159. |
| 23 | Zhang Y S, Pan Z C, Yang J J, et al. Study on the suppression mechanism of (NH4)2CO3 and SiC for polyethylene deflagration based on flame propagation and experimental analysis[J]. Powder Technology, 2022, 399: 117193. |
| 24 | Yuan B H, Sun Y R, Chen X F, et al. Poorly-/well-dispersed graphene: abnormal influence on flammability and fire behavior of intumescent flame retardant[J]. Composites Part A: Applied Science and Manufacturing, 2018, 109: 345-354. |
| 25 | 纪文涛, 李璐, 李忠, 等. 聚磷酸铵抑制PMMA粉尘爆炸特性研究[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(1): 461-469. |
| Ji W T, Li L, Li Z, et al. Study on suppression of PMMA dust explosion by ammonium polyphosphate[J]. CIESC Journal, 2022, 73(1): 461-469. | |
| 26 | Yang J, Yu Y, Li Y H, et al. Inerting effects of ammonium polyphosphate on explosion characteristics of polypropylene dust[J]. Process Safety and Environmental Protection, 2019, 130: 221-230. |
| 27 | Zhao Q, Li Y, Chen X F. Fire extinguishing and explosion suppression characteristics of explosion suppression system with N2/APP after methane/coal dust explosion[J]. Energy, 2022, 257: 124767. |
| 28 | Pang L, Cao J, Ma R, et al. Risk assessment method of polyethylene dust explosion based on explosion parameters[J]. Journal of Loss Prevention in the Process Industries, 2021, 69: 104397. |
| 29 | Yan X Q, Yu J L. Dust explosion venting of small vessels at the elevated static activation overpressure[J]. Powder Technology, 2014, 261: 250-256. |
| 30 | 鲁昆仑, 陈晓坤, 王媛媛, 等. 碳酸氢钠及其固态分解产物对玉米淀粉爆炸抑制实验研究[J]. 中国安全生产科学技术, 2021, 17(9): 126-131. |
| Lu K L, Chen X K, Wang Y Y, et al. Experimental study on inhibition of cornstarch dust explosion with sodium bicarbonate and its solid decomposition product[J]. Journal of Safety Science and Technology, 2021, 17(9): 126-131. | |
| 31 | Qiu D Y, Chen X F, Hao L J, et al. Partial suppression of acetaminophen dust explosion by synergistic multiphase inhibitors[J]. Process Safety and Environmental Protection, 2023, 172: 262-272. |
| 32 | Huang C Y, Yuan B H, Zhang H M, et al. Investigation on thermokinetic suppression of ammonium polyphosphate on sucrose dust deflagration: based on flame propagation, thermal decomposition and residue analysis[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2021, 403: 123653. |
| 33 | Wang Y, Qi Y, Pei B, et al. Suppression of polyethylene dust explosion by sodium bicarbonate[J]. Powder Technology, 2020, 367: 206-212. |
| 34 | Alongi J, Han Z D, Bourbigot S. Intumescence: tradition versus novelty. A comprehensive review[J]. Progress in Polymer Science, 2015, 51: 28-73. |
| 35 | Wu Y, Meng X B, Zhang Y S, et al. Experimental study on the suppression of coal dust explosion by silica aerogel[J]. Energy, 2023, 267: 126372. |
| 36 | Guo R, Li N, Zhang X Y, et al. Suppression mechanism of micron/nano PMMA dust flame based on thermal analysis[J]. Advanced Powder Technology, 2022, 33(12): 103848. |
| 37 | Zhang G Y, Zhang Y S, Huang X W, et al. Effect of pyrolysis and oxidation characteristics on lauric acid and stearic acid dust explosion hazards[J]. Journal of Loss Prevention in the Process Industries, 2020, 63: 104039. |
| 38 | 王德明, 辛海会, 戚绪尧, 等. 煤自燃中的各种基元反应及相互关系: 煤氧化动力学理论及应用[J]. 煤炭学报, 2014, 39(8): 1667-1674. |
| Wang D M, Xin H H, Qi X Y, et al. Mechanism and relationships of elementary reactions in spontaneous combustionof coal: the coal oxidation kinetics theory and application[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2014, 39(8): 1667-1674. | |
| 39 | Zhang Y, Cao W, Rao G, et al. Experiment-based investigations on the variation laws of functional groups on ignition energy of coal dusts[J]. Combustion Science and Technology, 2018, 190(10): 1850-1860. |
| 40 | Sun Y R, Yuan B H, Chen X F, et al. Suppression of methane/air explosion by kaolinite-based multi-component inhibitor[J]. Powder Technology, 2019, 343: 279-286. |
| 41 | 杨克, 王辰升, 纪虹, 等. 聚多巴胺包覆混合粉体抑制甲烷爆炸的实验研究[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(9): 4245-4254. |
| Yang K, Wang C S, Ji H, et al. Experimental study on inhibition of methane explosion by polydopamine coated mixed powder[J]. CIESC Journal, 2022, 73(9): 4245-4254. | |
| 42 | 黄信达. 无卤环保新型APP阻燃剂制备与性能研究[D]. 昆明: 昆明理工大学, 2022. |
| Huang X D. Study on preparation and properties of halogen-free environmental protection new APP flame retardant[D]. Kunming: Kunming University of Science and Technology, 2022. | |
| 43 | Lin H J, Yan H, Liu B, et al. The influence of KH-550 on properties of ammonium polyphosphate and polypropylene flame retardant composites[J]. Polymer Degradation and Stability, 2011, 96(7): 1382-1388. |
| [1] | 毕丽森, 刘斌, 胡恒祥, 曾涛, 李卓睿, 宋健飞, 吴翰铭. 粗糙界面上纳米液滴蒸发模式的分子动力学研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(S1): 172-178. |
| [2] | 于宏鑫, 邵双全. 水结晶过程的分子动力学模拟分析[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(S1): 250-258. |
| [3] | 金正浩, 封立杰, 李舒宏. 氨水溶液交叉型再吸收式热泵的能量及 分析[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(S1): 53-63. 分析[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(S1): 53-63. |
| [4] | 程成, 段钟弟, 孙浩然, 胡海涛, 薛鸿祥. 表面微结构对析晶沉积特性影响的格子Boltzmann模拟[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(S1): 74-86. |
| [5] | 肖明堃, 杨光, 黄永华, 吴静怡. 浸没孔液氧气泡动力学数值研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(S1): 87-95. |
| [6] | 范孝雄, 郝丽芳, 范垂钢, 李松庚. LaMnO3/生物炭催化剂低温NH3-SCR催化脱硝性能研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(9): 3821-3830. |
| [7] | 郑佳丽, 李志会, 赵新强, 王延吉. 离子液体催化合成2-氰基呋喃反应动力学研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(9): 3708-3715. |
| [8] | 孟令玎, 崇汝青, 孙菲雪, 孟子晖, 刘文芳. 改性聚乙烯膜和氧化硅固定化碳酸酐酶[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(8): 3472-3484. |
| [9] | 汪林正, 陆俞冰, 张睿智, 罗永浩. 基于分子动力学模拟的VOCs热氧化特性分析[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(8): 3242-3255. |
| [10] | 杨克, 贾岳, 纪虹, 邢志祥, 蒋军成. 垃圾焚烧飞灰对瓦斯爆炸压力及火焰传播的抑制作用及机理研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(8): 3597-3607. |
| [11] | 杨越, 张丹, 郑巨淦, 涂茂萍, 杨庆忠. NaCl水溶液喷射闪蒸-掺混蒸发的实验研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(8): 3279-3291. |
| [12] | 李珍宝, 李超, 王虎, 王绍瑞, 黎泉. MPP抑制铝镁合金粉尘爆炸微观机理研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(8): 3608-3614. |
| [13] | 曾如宾, 沈中杰, 梁钦锋, 许建良, 代正华, 刘海峰. 基于分子动力学模拟的Fe2O3纳米颗粒烧结机制研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(8): 3353-3365. |
| [14] | 李锦潼, 邱顺, 孙文寿. 煤浆法烟气脱硫中草酸和紫外线强化煤砷浸出过程[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(8): 3522-3532. |
| [15] | 张蒙蒙, 颜冬, 沈永峰, 李文翠. 电解液类型对双离子电池阴阳离子储存行为的影响[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(7): 3116-3126. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备 11010102001995号
京公网安备 11010102001995号