化工学报 ›› 2024, Vol. 75 ›› Issue (11): 4178-4187.DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20240559
收稿日期:2024-05-26
修回日期:2024-07-01
出版日期:2024-11-25
发布日期:2024-12-26
通讯作者:
马学虎
作者简介:阮达(1994—),男,博士研究生,ruanda1994@mail.dlut.edu.cn
基金资助:
Da RUAN( ), Jingjing HOU, Ziyi BO, Shuaishuai ZHANG, Xuehu MA(
), Jingjing HOU, Ziyi BO, Shuaishuai ZHANG, Xuehu MA( )
)
Received:2024-05-26
Revised:2024-07-01
Online:2024-11-25
Published:2024-12-26
Contact:
Xuehu MA
摘要:
微通道中环状流广泛应用于精细化学品合成等领域,而环状流中薄液膜的流动形态及厚度对反应过程的热质传递影响显著,因此实验利用激光诱导荧光法对薄液膜厚度进行精准在线测量。结果表明,随气相剪切力增大,液膜厚度降低,波动形态由低频高振幅波转变为高频低振幅波。二氯甲烷液相流量为3 ml/min、含气率为0.7时波动频率最高可达260 Hz。在相同含气率下,液膜形态由流体黏度和表面张力决定,液膜厚度随流体黏度增大而增大,液膜波动频率随表面张力增大而减小。通过薄液膜在微通道内受力分析,构建了不同流体的薄液膜厚度的预测模型,预测值与实验值偏差±15%。本研究明晰了微通道内不同物性液体及气速对液膜波动及厚度的影响,为薄液膜强化热质传递提供理论指导。
中图分类号:
阮达, 侯静静, 薄紫一, 张帅帅, 马学虎. 微通道内环状流薄液膜厚度及波动实验研究[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(11): 4178-4187.
Da RUAN, Jingjing HOU, Ziyi BO, Shuaishuai ZHANG, Xuehu MA. Study of thin liquid film thickness and fluctuation pattern of annular flow in microchannel[J]. CIESC Journal, 2024, 75(11): 4178-4187.
| 含气率(x) | 激光强度/% | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 水(Water) | 乙醇(EtOH) | 二氯甲烷(DCM) | |
| 0.1 | 35 | 35 | 36 |
| 0.2 | 35 | 35 | 38 |
| 0.3 | 38 | 37 | 40 |
| 0.4 | 38 | 38 | 39 |
| 0.5 | 40 | 40 | 41 |
| 0.6 | 41 | 40 | 43 |
| 0.7 | 41 | 42 | 44 |
表1 不同工况下的实验激光强度
Table 1 Experimental laser intensities under different operating conditions
| 含气率(x) | 激光强度/% | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 水(Water) | 乙醇(EtOH) | 二氯甲烷(DCM) | |
| 0.1 | 35 | 35 | 36 |
| 0.2 | 35 | 35 | 38 |
| 0.3 | 38 | 37 | 40 |
| 0.4 | 38 | 38 | 39 |
| 0.5 | 40 | 40 | 41 |
| 0.6 | 41 | 40 | 43 |
| 0.7 | 41 | 42 | 44 |
| 实验溶剂 | ρ/(kg/m3) | μ/(μPa·s) | σ/(mN/m) |
|---|---|---|---|
| EtOH | 785 | 1077 | 22.09 |
| DCM | 1326 | 413 | 28.16 |
| 水 | 997 | 912 | 72.18 |
| N2 | 1.165 | 17.48 | — |
表2 测试流体物性
Table 2 Experimental fluid properties
| 实验溶剂 | ρ/(kg/m3) | μ/(μPa·s) | σ/(mN/m) |
|---|---|---|---|
| EtOH | 785 | 1077 | 22.09 |
| DCM | 1326 | 413 | 28.16 |
| 水 | 997 | 912 | 72.18 |
| N2 | 1.165 | 17.48 | — |
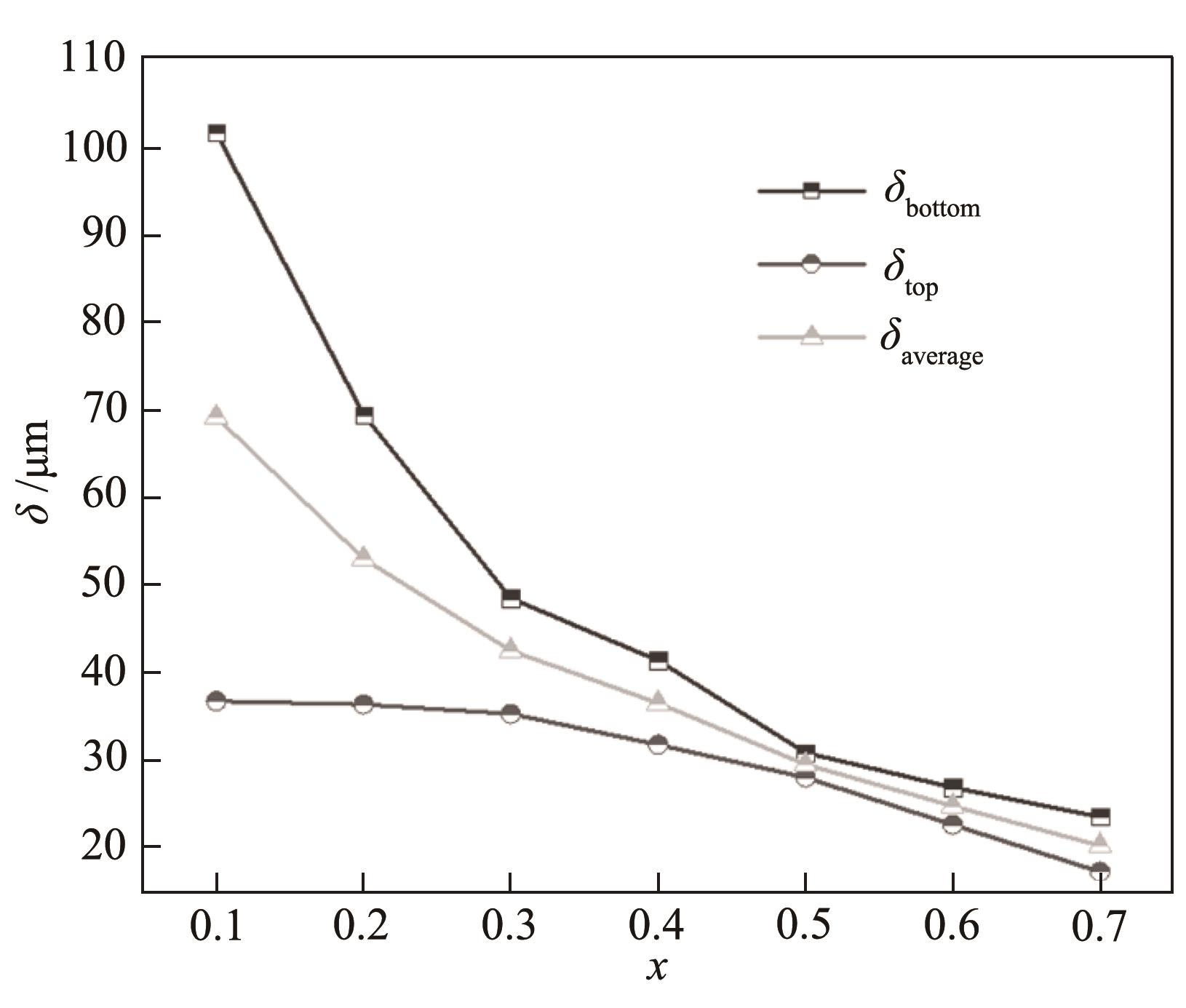
图6 通道顶部及底部的液膜厚度平均值随x的变化(QEtOH= 2 ml/min)
Fig.6 Mean value of liquid film thickness at the top and bottom of the channel as a function of x (QEtOH = 2 ml/min)
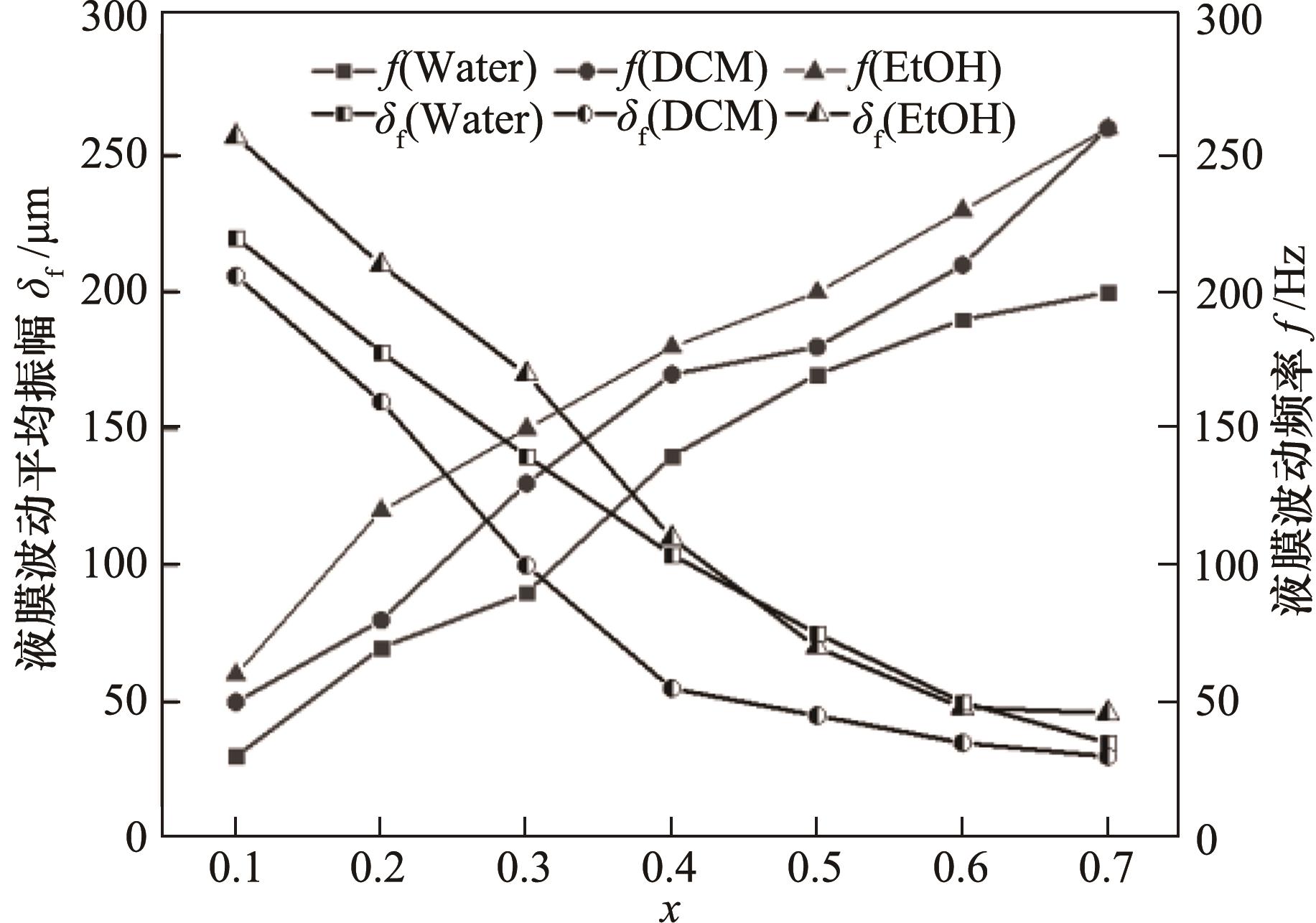
图9 不同流体(水、EtOH、DCM)的液膜波动平均振幅及频率随x的变化
Fig.9 Average amplitude and frequency of liquid film fluctuations of different fluids (water, EtOH, DCM) as a function of x
| 1 | Dong G H, Chen B, Liu B, et al. Advanced oxidation processes in microreactors for water and wastewater treatment: development, challenges, and opportunities[J]. Water Research, 2022, 211: 118047. |
| 2 | Feng H, Zhang Y, Liu J, et al. Towards heterogeneous catalysis: a review on recent advances of depositing nanocatalysts in continuous-flow microreactors[J]. Molecules, 2022, 27(22): 8052. |
| 3 | Battat S, Weitz D A, Whitesides G M. An outlook on microfluidics: the promise and the challenge[J]. Lab on a Chip, 2022, 22(3): 530-536. |
| 4 | Yan Z F, Tian J X, Du C C, et al. Reaction kinetics determination based on microfluidic technology[J]. Chinese Journal of Chemical Engineering, 2022, 41: 49-72. |
| 5 | Ran J F, Wang X X, Liu Y H, et al. Microreactor-based micro/nanomaterials: fabrication, advances, and outlook[J]. Materials Horizons, 2023, 10(7): 2343-2372. |
| 6 | 张经纬, 周弋惟, 陈卓, 等. 微反应器内的有机合成前沿进展[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(8): 3472-3482. |
| Zhang J W, Zhou Y W, Chen Z, et al. Advances in frontiers of organic synthesis in microreactor[J]. CIESC Journal, 2022, 73(8): 3472-3482. | |
| 7 | Firuzi S, Sadeghi R. Simulation of carbon dioxide absorption process by aqueous monoethanolamine in a microchannel in annular flow pattern[J]. Microfluidics and Nanofluidics, 2018, 22(10): 109. |
| 8 | Ye X, Cheng Y Q, Chen Y S, et al. Microcavity-enabled local oscillation of Taylor bubbles in a microchannel[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2021, 60(2): 1055-1066. |
| 9 | 尧超群, 乐军, 赵玉潮, 等. 微通道内气-液弹状流动及传质特性研究进展[J]. 化工学报, 2015, 66(8): 2759-2766. |
| Yao C Q, Yue J, Zhao Y C, et al. Review on flow and mass transfer characteristics of gas-liquid slug flow in microchannels[J]. CIESC Journal, 2015, 66(8): 2759-2766. | |
| 10 | Cheng L X, Xia G D. Flow patterns and flow pattern maps for adiabatic and diabatic gas liquid two phase flow in microchannels: fundamentals, mechanisms and applications[J]. Experimental Thermal and Fluid Science, 2023, 148: 110988. |
| 11 | Shao N, Gavriilidis A, Angeli P. Flow regimes for adiabatic gas-liquid flow in microchannels[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2009, 64(11): 2749-2761. |
| 12 | Sattari-Najafabadi M, Nasr Esfahany M, Wu Z, et al. Mass transfer between phases in microchannels: a review[J]. Chemical Engineering and Processing - Process Intensification, 2018, 127: 213-237. |
| 13 | Jose N A, Zeng H C, Lapkin A A. Hydrodynamic assembly of two-dimensional layered double hydroxide nanostructures[J]. Nature Communications, 2018, 9(1): 4913. |
| 14 | Sobieszuk P, Napieralska K. Investigations of mass transfer in annular gas-liquid flow in a microreactor[J]. Chemical and Process Engineering, 2016, 37(1): 55-64. |
| 15 | Jose N A, Zeng H C, Lapkin A A. Scalable and precise synthesis of two-dimensional metal organic framework nanosheets in a high shear annular microreactor[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2020, 388: 124133. |
| 16 | Etminan A, Muzychka Y S, Pope K. Liquid film thickness of two-phase slug flows in capillary microchannels: a review paper[J]. The Canadian Journal of Chemical Engineering, 2022, 100(2): 325-348. |
| 17 | Patel R S, Weibel J A, Garimella S V. Characterization of liquid film thickness in slug-regime microchannel flows[J]. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 2017, 115: 1137-1143. |
| 18 | Donniacuo A, Charnay R, Mastrullo R, et al. Film thickness measurements for annular flow in minichannels: description of the optical technique and experimental results[J]. Experimental Thermal and Fluid Science, 2015, 69: 73-85. |
| 19 | 张鹏, 姜玉雁, 王涛. 方管两相流中微液膜的测量与分析[J]. 工程热物理学报, 2022, 43(7): 1911-1915. |
| Zhang P, Jiang Y Y, Wang T. Measurement and analysis of square microchannel liquid film in two-phase flow[J]. Journal of Engineering Thermophysics, 2022, 43(7): 1911-1915. | |
| 20 | Sun Y H, Guo C H, Jiang Y Y, et al. Transient film thickness and microscale heat transfer during flow boiling in microchannels[J]. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 2018, 116: 458-470. |
| 21 | Anastasiou A D, Makatsoris C, Gavriilidis A, et al. Application of μ-PIV for investigating liquid film characteristics in an open inclined microchannel[J]. Experimental Thermal and Fluid Science, 2013, 44: 90-99. |
| 22 | Mishra D K, Mohanty D, Gupta R, et al. Effect of bend on film thickness in slug, slug-annular, and annular flow regimes in gas-liquid flow in a microchannel[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2022, 61(37): 14081-14092. |
| 23 | Bartkus G V, Kuznetsov V V. Experimental study of wavy-annular flow in a rectangular microchannel using LIF method[J]. Journal of Physics: Conference Series, 2021, 2119(1): 012061. |
| 24 | Yoshinaga Y, Dang C, Hihara E. Experimental study on two-phase flow pattern and liquid film thickness in microchannels[C]//15th International Refrigeration and Air Conditioning Conference at Purdue. America: School of Mechanical Engineering, 2014: 2594. |
| 25 | Han Y, Kanno H, Ahn Y J, et al. Measurement of liquid film thickness in micro tube annular flow[J]. International Journal of Multiphase Flow, 2015, 73: 264-274. |
| 26 | Patel R S, Garimella S V. Technique for quantitative mapping of three-dimensional liquid-gas phase boundaries in microchannel flows[J]. International Journal of Multiphase Flow, 2014, 62: 45-51. |
| 27 | Zhao Z Y, Wang B H, Wang J, et al. Liquid film characteristics measurement based on NIR in gas-liquid vertical annular upward flow[J]. Measurement Science and Technology, 2022, 33(6): 065014. |
| 28 | Xu Z, Jiang Y D, Wang B L, et al. Void fraction measurement of gas-liquid two-phase flow with a 12-electrode contactless resistivity array sensor under different excitation patterns[J]. Measurement Science and Technology, 2020, 31(11): 115103. |
| 29 | Zhang P, Wang T, Jiang Y Y, et al. Experimental study of initial liquid film thickness in square microchannel two-phase flow[J]. Heat Transfer Research, 2022, 53(10): 51-69. |
| 30 | Wang M, Bai Y X, Liu J G, et al. Experimental and modeling study on liquid film thickness of horizontal gas-liquid annular flow using ultrasonic method[J]. Flow Measurement and Instrumentation, 2024, 96: 102538. |
| 31 | Shri Vignesh K, Vasudevan C, Arunkumar S, et al. Laser induced fluorescence measurement of liquid film thickness and variation in Taylor flow[J]. European Journal of Mechanics-B, 2018, 70: 85-92. |
| [1] | 赵振刚, 周梦瑶, 金典, 张大骋. 基于泡沫碳扩散层的直接甲醇燃料电池改性研究[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(S1): 259-266. |
| [2] | 徐英宇, 杨国强, 彭璟, 孙海宁, 张志炳. 微界面高级氧化处理煤化工废水的研究[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(S1): 283-291. |
| [3] | 李雨霜, 王兴成, 温伯尧, 骆政园, 白博峰. 多孔介质中乳状液驱油的两相流动过程及其影响因素[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(S1): 56-66. |
| [4] | 刘律, 刘洁茹, 范亮亮, 赵亮. 基于层流效应的被动式颗粒分离微流控方法研究[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(S1): 67-75. |
| [5] | 杜得辉, 冯威, 张江辉, 项燕龙, 乔高攀, 李蔚. 微型翅片疏水复合强化管管内流动沸腾换热预测模型[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(S1): 95-107. |
| [6] | 祝赫, 张仪, 齐娜娜, 张锴. 欧拉-欧拉双流体模型中颗粒黏性对液固散式流态化的影响[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(9): 3103-3112. |
| [7] | 唐昊, 胡定华, 李强, 张轩畅, 韩俊杰. 抗加速度双切线弧流道内气泡动力学行为数值与可视化研究[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(9): 3074-3082. |
| [8] | 王皓宇, 杨杨, 荆文婕, 杨斌, 唐雨, 刘毅. 不同旋流器作用下气液螺旋环状流动特性研究[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(8): 2744-2755. |
| [9] | 赵亮, 李雨桥, 张德, 沈胜强. 螺旋喷嘴内外流场特性的实验研究[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(8): 2777-2786. |
| [10] | 罗正航, 李敬宇, 陈伟雄, 种道彤, 严俊杰. 摇摆运动下低流率蒸汽冷凝换热特性和气泡受力数值模拟[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(8): 2800-2811. |
| [11] | 曲玖哲, 杨鹏, 杨绪飞, 张伟, 宇波, 孙东亮, 王晓东. 硅基微柱簇阵列微通道流动沸腾实验研究[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(8): 2840-2851. |
| [12] | 李彦熹, 王晔春, 谢向东, 王进芝, 王江, 周煜, 潘盈秀, 丁文涛, 郭烈锦. 蜗壳式多通道气液旋流分离器结构优化及分离特性研究[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(8): 2875-2885. |
| [13] | 吕方明, 包志铭, 王博文, 焦魁. 气体扩散层侵入流道对燃料电池水管理影响研究[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(8): 2929-2938. |
| [14] | 余清杰, 杨洪海, 刘玉浩, 方海洲, 何伟琪, 王军, 卢心诚. 脉动热管温度信号的小波分析及流型识别[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(7): 2497-2504. |
| [15] | 周文轩, 刘珍, 张福建, 张忠强. 高通量-高截留率时间维度膜法水处理机理研究[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(7): 2583-2593. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备 11010102001995号
京公网安备 11010102001995号