化工学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 76 ›› Issue (2): 797-811.DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20240791
• 能源和环境工程 • 上一篇
张奇1( ), 张睿1, 郑涛1, 曹欣1, 刘植昌1, 刘海燕1, 徐春明1, 张荣2, 孟祥海1(
), 张睿1, 郑涛1, 曹欣1, 刘植昌1, 刘海燕1, 徐春明1, 张荣2, 孟祥海1( )
)
收稿日期:2024-07-13
修回日期:2024-08-17
出版日期:2025-03-25
发布日期:2025-03-10
通讯作者:
孟祥海
作者简介:张奇(1995—),男,博士研究生,zhangqicup@126.com
基金资助:
Qi ZHANG1( ), Rui ZHANG1, Tao ZHENG1, Xin CAO1, Zhichang LIU1, Haiyan LIU1, Chunming XU1, Rong ZHANG2, Xianghai MENG1(
), Rui ZHANG1, Tao ZHENG1, Xin CAO1, Zhichang LIU1, Haiyan LIU1, Chunming XU1, Rong ZHANG2, Xianghai MENG1( )
)
Received:2024-07-13
Revised:2024-08-17
Online:2025-03-25
Published:2025-03-10
Contact:
Xianghai MENG
摘要:
有机超强碱质子离子液体作为一种绿色溶剂,在CO2捕集领域展现出独特优势。选择由1,8-二氮杂双环[5.4.0]十一碳-7-烯(DBU)和N-叔丁基二乙醇胺(NtBuDEA)反应生成的有机超强碱双阳离子质子型离子液体[DBUH]2[NtBuDEA]为吸收剂,通过密度泛函理论和分子动力学模拟分析其与CO2之间的微观结构、作用机理及吸收过程。研究发现,阴离子[NtBuDEA]2-的烷基氧负离子在CO2吸收过程中发挥关键作用,与CO2发生化学键合作用,生成烷基碳酸盐[NtBuDEACOO]2-。CO2分子从气相扩散到吸收剂表面并在气/液界面处聚集,其吸收量在达到最大值后围绕平均值波动。温度和压力是影响CO2吸收的关键因素,降低吸收温度和提高CO2分压有利于CO2的捕集。水的存在虽降低了吸收剂与CO2的相互作用能,却提高了CO2的传输性能。
中图分类号:
张奇, 张睿, 郑涛, 曹欣, 刘植昌, 刘海燕, 徐春明, 张荣, 孟祥海. 基于分子模拟的新型双阳离子质子型离子液体捕集CO2研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(2): 797-811.
Qi ZHANG, Rui ZHANG, Tao ZHENG, Xin CAO, Zhichang LIU, Haiyan LIU, Chunming XU, Rong ZHANG, Xianghai MENG. Revealing CO2 capture by a novel dual-cation protic ionic liquid using molecular simulation[J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(2): 797-811.
| 计算项目/方法 | 计算参数 |
|---|---|
| functional | Perdew-Burke-Ernzerhof (PBE) |
| basis set | TZV2P-MOLOPT-PBE-GTH |
| dispersion correction | DFT-D3(BJ) |
| CUTOFF | 400 Ry |
| EPS_SCF | 1 × 10-7 Ha |
| MAX_DR | 0.003 Bohr |
| MAX_FORCE | 0.00045 Ha/Bohr |
| RMS_DR | 0.0015 Bohr |
| RMS_FORCE | 0.0003 Ha/Bohr |
表1 量化计算中的主要参数
Table 1 Main parameters in quantum calculations
| 计算项目/方法 | 计算参数 |
|---|---|
| functional | Perdew-Burke-Ernzerhof (PBE) |
| basis set | TZV2P-MOLOPT-PBE-GTH |
| dispersion correction | DFT-D3(BJ) |
| CUTOFF | 400 Ry |
| EPS_SCF | 1 × 10-7 Ha |
| MAX_DR | 0.003 Bohr |
| MAX_FORCE | 0.00045 Ha/Bohr |
| RMS_DR | 0.0015 Bohr |
| RMS_FORCE | 0.0003 Ha/Bohr |
| 种类 | ΔH/(kJ·mol-1) | ΔG/(kJ·mol-1) |
|---|---|---|
| [NtBuDEA]2- - CO2 | -98.67 | -54.77 |
| [3-MethylPyr]- - CO2 | -75.41 | -30.02 |
| [4-MethylPyr]- - CO2 | -74.98 | -30.53 |
| [Pyr]- - CO2 | -72.29 | -29.50 |
| [4-BromoPyr]- - CO2 | -53.58 | -13.54 |
| [3-PhenylPyr]- - CO2 | -52.03 | -11.72 |
表2 不同阴离子-CO2系统的热力学参数对比
Table 2 Thermochemical parameters comparison of different anions-CO2 systems
| 种类 | ΔH/(kJ·mol-1) | ΔG/(kJ·mol-1) |
|---|---|---|
| [NtBuDEA]2- - CO2 | -98.67 | -54.77 |
| [3-MethylPyr]- - CO2 | -75.41 | -30.02 |
| [4-MethylPyr]- - CO2 | -74.98 | -30.53 |
| [Pyr]- - CO2 | -72.29 | -29.50 |
| [4-BromoPyr]- - CO2 | -53.58 | -13.54 |
| [3-PhenylPyr]- - CO2 | -52.03 | -11.72 |
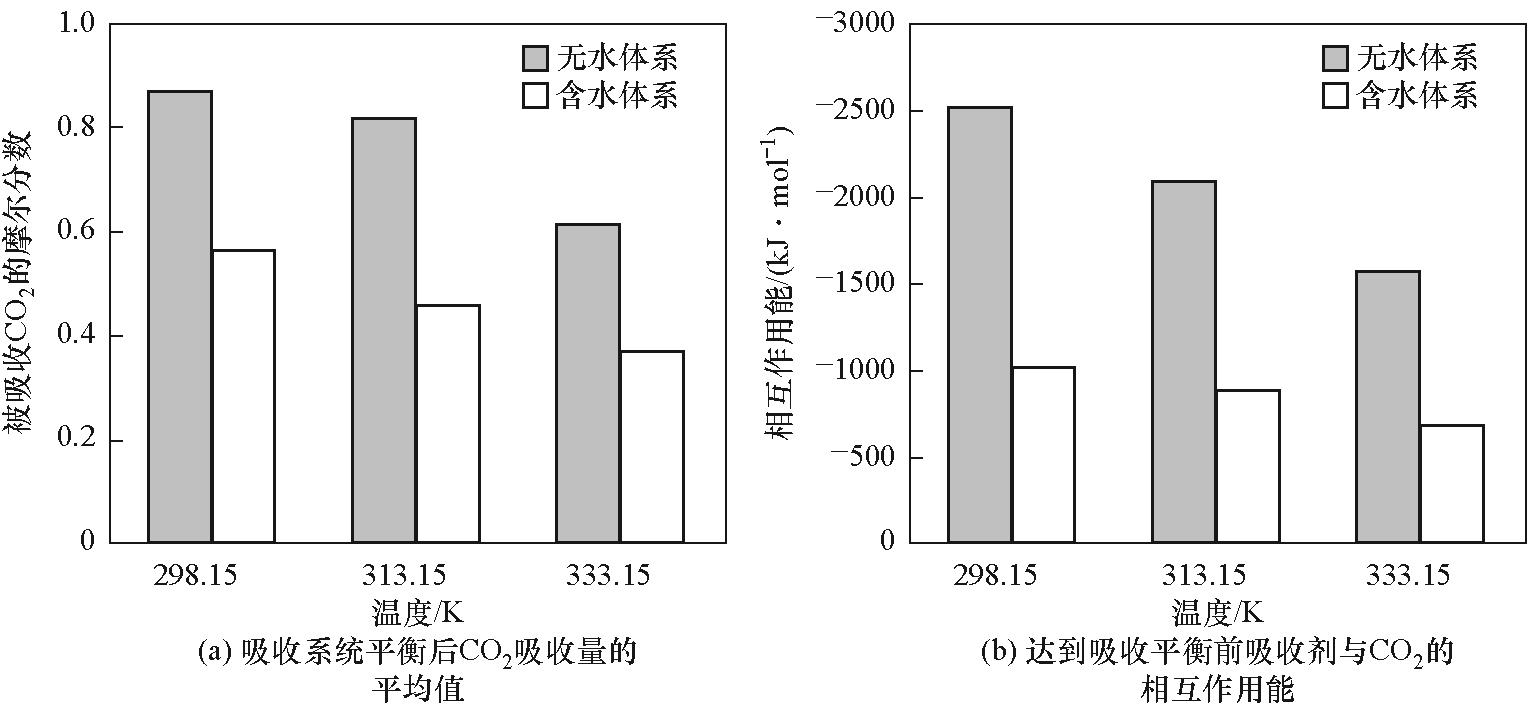
图8 吸收平衡后的CO2吸收量和平衡前吸收剂与CO2的相互作用能
Fig.8 The CO2 amount after absorption equilibrium and the interaction energy between the absorbent and CO2 prior to equilibrium
| 初始气相压力/atm | CO2在气相的分子数 |
|---|---|
| 1.5 | 186 |
| 2 | 248 |
| 2.5 | 310 |
| 3 | 372 |
| 3.5 | 434 |
| 4 | 496 |
| 5 | 620 |
| 6 | 744 |
| 8 | 992 |
| 10 | 1240 |
表3 298.15 K时不同压力条件下吸收系统气相中CO2分子的初始数量
Table 3 Initial number of CO2 molecules in gas phase for the absorption systems at various pressures conditions and at 298.15 K
| 初始气相压力/atm | CO2在气相的分子数 |
|---|---|
| 1.5 | 186 |
| 2 | 248 |
| 2.5 | 310 |
| 3 | 372 |
| 3.5 | 434 |
| 4 | 496 |
| 5 | 620 |
| 6 | 744 |
| 8 | 992 |
| 10 | 1240 |
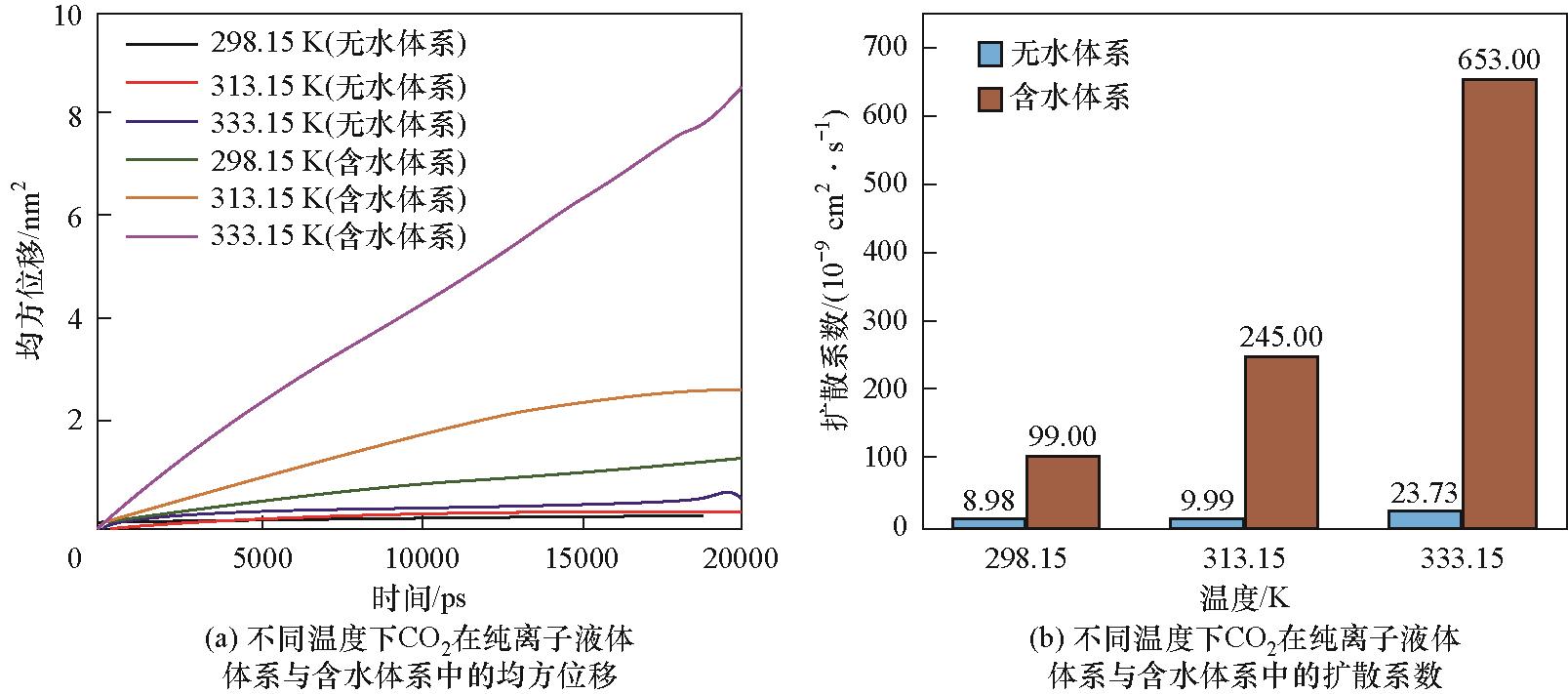
图12 CO2在纯离子液体与含30%(质量分数)水的离子液体体系中均方位移与扩散系数的比较
Fig.12 Comparison of mean square displacement and diffusion coefficient of CO2 in pure ionic liquid and 30%(mass) water-containing systems
| 1 | Bai Y G, Wang K X, Wang L L, et al. Experimental investigation on post-combustion CO2 capture for [Bpy][NO3] and MEA aqueous blends with lower regeneration energy[J]. Separation and Purification Technology, 2023, 327: 124846. |
| 2 | 唐政, 郑涛, 刘晗, 等. 双金属卤化物络合萃取分离直馏石脑油中的芳烃[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(12): 4926-4933. |
| Tang Z, Zheng T, Liu H, et al. Separation of aromatics from straight-run naphtha by complexation extraction using bimetallic halides[J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(12): 4926-4933. | |
| 3 | 孟祥海, 张睿, 刘海燕, 等. 复合离子液体碳四烷基化技术开发与应用[J]. 中国科学: 化学, 2018, 48(4): 387-396. |
| Meng X H, Zhang R, Liu H Y, et al. Development and application of composite ionic liquid catalyzed isobutane alkylation technology[J]. Scientia Sinica (Chimica), 2018, 48(4): 387-396. | |
| 4 | 欧阳萍, 张睿, 周剑, 等. 铜铝双金属复合离子液体的电化学行为及电沉积铜机理[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(7): 3212-3221. |
| Ouyang P, Zhang R, Zhou J, et al. Electrochemical behavior and copper electrodeposition mechanism of Cu-Al bimetallic composite ionic liquid[J]. CIESC Journal, 2022, 73(7): 3212-3221. | |
| 5 | Zeng S J, Zhang X P, Bai L, et al. Ionic-liquid-based CO2 capture systems: structure, interaction and process[J]. Chemical Reviews, 2017, 117(14): 9625-9673. |
| 6 | Sheridan Q R, Schneider W F, Maginn E J. Role of molecular modeling in the development of CO2-reactive ionic liquids[J]. Chemical Reviews, 2018, 118(10): 5242-5260. |
| 7 | Ruan J W, Ye X Z, Wang R Z, et al. Experimental and theoretical study on efficient CO2 absorption coordinated by molecules and ions of DBN and 1,2,4-triazole formed deep eutectic solvents[J]. Fuel, 2023, 334: 126709. |
| 8 | Xiong W J, Shi M Z, Peng L L, et al. Low viscosity superbase protic ionic liquids for the highly efficient simultaneous removal of H2S and CO2 from CH4 [J]. Separation and Purification Technology, 2021, 263: 118417. |
| 9 | Zhang Q, Bahamon D, Alkhatib I I I, et al. Molecular insights into the CO2 absorption mechanism by superbase protic ionic liquids by a combined density functional theory and molecular dynamics approach[J]. Journal of Molecular Liquids, 2024, 394: 123683. |
| 10 | Heldebrant D J, Yonker C R, Jessop P G, et al. Organic liquid CO2 capture agents with high gravimetric CO2 capacity[J]. Energy & Environmental Science, 2008, 1(4): 487-493. |
| 11 | Zhu X, Song M L, Xu Y J. DBU-based protic ionic liquids for CO2 capture[J]. ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering, 2017, 5(9): 8192-8198. |
| 12 | Zhang X M, Xiong W J, Peng L L, et al. Highly selective absorption separation of H2S and CO2 from CH4 by novel azole-based protic ionic liquids[J]. AIChE Journal, 2020, 66(6): e16936. |
| 13 | 朱先会, 王甫, 夏杰成, 等. 功能型离子液体协同吸收NH3和CO2的密度泛函理论研究[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(10): 4324-4334. |
| Zhu X H, Wang F, Xia J C, et al. Density functional theory investigation on the NH3 and CO2 absorption by functional ionic liquids[J]. CIESC Journal, 2022, 73(10): 4324-4334. | |
| 14 | Shaikh A R, Vidal-López A, Brotons-Rufes A, et al. Amino acid ionic liquids as efficient catalysts for CO2 capture: a combined static and dynamic approach[J]. Results in Surfaces and Interfaces, 2024, 14: 100175. |
| 15 | Wang B H, Zhu M X, Liu M Z, et al. Design of novel dual functional ionic liquids and DFT study on their CO2 absorption mechanism[J]. Journal of Molecular Liquids, 2022, 366: 120340. |
| 16 | Yoon B, Voth G A. Elucidating the molecular mechanism of CO2 capture by amino acid ionic liquids[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2023, 145(29): 15663-15667. |
| 17 | Frisch M, Trucks G W, Schlegel H B, et al. Gaussian 09[M]. Wallingford CT: Gaussian, Inc., 2013. |
| 18 | Lee C, Yang W T, Parr R G. Development of the Colle-Salvetti correlation-energy formula into a functional of the electron density[J]. Physical Review B, 1988, 37(2): 785-789. |
| 19 | Becke A D. Density‐functional thermochemistry (Ⅲ): The role of exact exchange[J]. Journal of Chemical Physics, 1993, 98(7): 5648-5652. |
| 20 | Gordon M S, Binkley J S, Pople J A, et al. Self-consistent molecular-orbital methods (22): small split-valence basis sets for second-row elements[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 1982, 104(10): 2797-2803. |
| 21 | Martínez L, Andrade R, Birgin E G, et al. PACKMOL: a package for building initial configurations for molecular dynamics simulations[J]. Journal of Computational Chemistry, 2009, 30(13): 2157-2164. |
| 22 | Lu T, Chen F W. Multiwfn: a multifunctional wavefunction analyzer[J]. Journal of Computational Chemistry, 2012, 33(5): 580-592. |
| 23 | Humphrey W, Dalke A, Schulten K. VMD: visual molecular dynamics[J]. Journal of Molecular Graphics, 1996, 14(1): 33-38. |
| 24 | Kühne T D, Iannuzzi M, Del Ben M, et al. CP2K: an electronic structure and molecular dynamics software package-quickstep: efficient and accurate electronic structure calculations[J]. The Journal of Chemical Physics, 2020, 152(19): 194103. |
| 25 | Bussi G, Donadio D, Parrinello M. Canonical sampling through velocity rescaling[J]. The Journal of Chemical Physics, 2007, 126(1): 014101. |
| 26 | van der Spoel D, Lindahl E, Hess B, et al. GROMACS: fast, flexible, and free[J]. Journal of Computational Chemistry, 2005, 26(16): 1701-1718. |
| 27 | Essmann U, Perera L, Berkowitz M L, et al. A smooth particle mesh Ewald method[J]. The Journal of Chemical Physics, 1995, 103(19): 8577-8593. |
| 28 | Berendsen H J C, Postma J P M, van Gunsteren W F, et al. Molecular dynamics with coupling to an external bath[J]. The Journal of Chemical Physics, 1984, 81(8): 3684-3690. |
| 29 | Wang J M, Wolf R M, Caldwell J W, et al. Development and testing of a general amber force field[J]. Journal of Computational Chemistry, 2004, 25(9): 1157-1174. |
| 30 | Grimme S, Bannwarth C, Shushkov P. A robust and accurate tight-binding quantum chemical method for structures, vibrational frequencies, and noncovalent interactions of large molecular systems parametrized for all spd-block elements (Z = 1-86)[J]. Journal of Chemical Theory and Computation, 2017, 13(5): 1989-2009. |
| 31 | Fu H, Wang X Y, Sang H N, et al. The study of bicyclic amidine-based ionic liquids as promising carbon dioxide capture agents[J]. Journal of Molecular Liquids, 2020, 304: 112805. |
| 32 | Zheng W Z, Cao P, Yuan Y, et al. Experimental and modeling study of isobutane alkylation with C4 olefin catalyzed by Brønsted acidic ionic liquid/sulfuric acid[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2019, 377: 119578. |
| [1] | 杨晋宁, 王卫凡, 徐冬, 刘毅, 翁小涵, 原野, 王志. 工业烟道气碳捕集膜技术放大研究进展[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(2): 504-518. |
| [2] | 姚佳逸, 张东辉, 唐忠利, 李文彬. 基于二级双回流的变压吸附捕碳工艺研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(2): 744-754. |
| [3] | 崔家馨, 殷梦凡, 郑涛, 刘晗, 张睿, 刘植昌, 刘海燕, 徐春明, 孟祥海. 铝铜双金属离子液体在1-己烯/正己烷分离中的应用[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(2): 686-694. |
| [4] | 冯海军, 章冰璇, 周健. 图神经网络模型预测和解释离子液体毒性的研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(1): 93-106. |
| [5] | 杨勇, 祖子轩, 李煜坤, 王东亮, 范宗良, 周怀荣. T型圆柱形微通道内CO2碱液吸收数值模拟[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(S1): 135-142. |
| [6] | 邱知, 谭明. 聚离子液体膜的制备及其在低钠高钾健康酱油中的应用[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(S1): 244-250. |
| [7] | 杜海燕, 朱凯, 游峰, 王金凤, 赵一帆, 张楠, 李英. 用于应变传感器的自愈合抗冻离子水凝胶[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(7): 2709-2722. |
| [8] | 张广宇, 付然飞, 孙冰, 袁俊聪, 冯翔, 杨朝合, 徐伟. CO2-环氧丙烷合成碳酸丙烯酯:氢键供体效应研究[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(6): 2243-2251. |
| [9] | 丁禹, 杨昌泽, 李军, 孙会东, 商辉. 原子尺度钼系加氢脱硫催化剂的研究进展与展望[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(5): 1735-1749. |
| [10] | 马旭, 滕亚栋, 刘杰, 王宇璐, 张鹏, 张莲海, 姚万龙, 展静, 吴青柏. 喷雾法水合物法捕集分离烟道气中CO2[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(5): 2001-2016. |
| [11] | 武颖韬, 费立涵, 孔祥东, 王帜, 汤成龙, 黄佐华. 咪唑二氰胺离子液体掺混糠醇的自燃及推进性能[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(5): 2017-2025. |
| [12] | 蒋方涛, 钱刚, 周兴贵, 段学志, 张晶. 基于[bmim][BF4]相转移催化的氟代碳酸乙烯酯高效合成[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(4): 1543-1551. |
| [13] | 王瑞瑞, 金颖, 刘玉梅, 李梦悦, 朱胜文, 闫瑞一, 刘瑞霞. 聚合离子液体设计及催化环己烷选择性氧化性能研究[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(4): 1552-1564. |
| [14] | 肖拥君, 时兆翀, 万仁, 宋璠, 彭昌军, 刘洪来. 反向传播神经网络用于预测离子液体的自扩散系数[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(2): 429-438. |
| [15] | 张欣, 薛宇, 马懿星, 王学谦, 王郎郎, 谢妮霏, 陈怡, 周晓霞. 电晕放电与介质阻挡放电净化氰化氢的机理[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(2): 675-684. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备 11010102001995号
京公网安备 11010102001995号